An Update on Current Therapeutic Options in IgA Nephropathy
Abstract
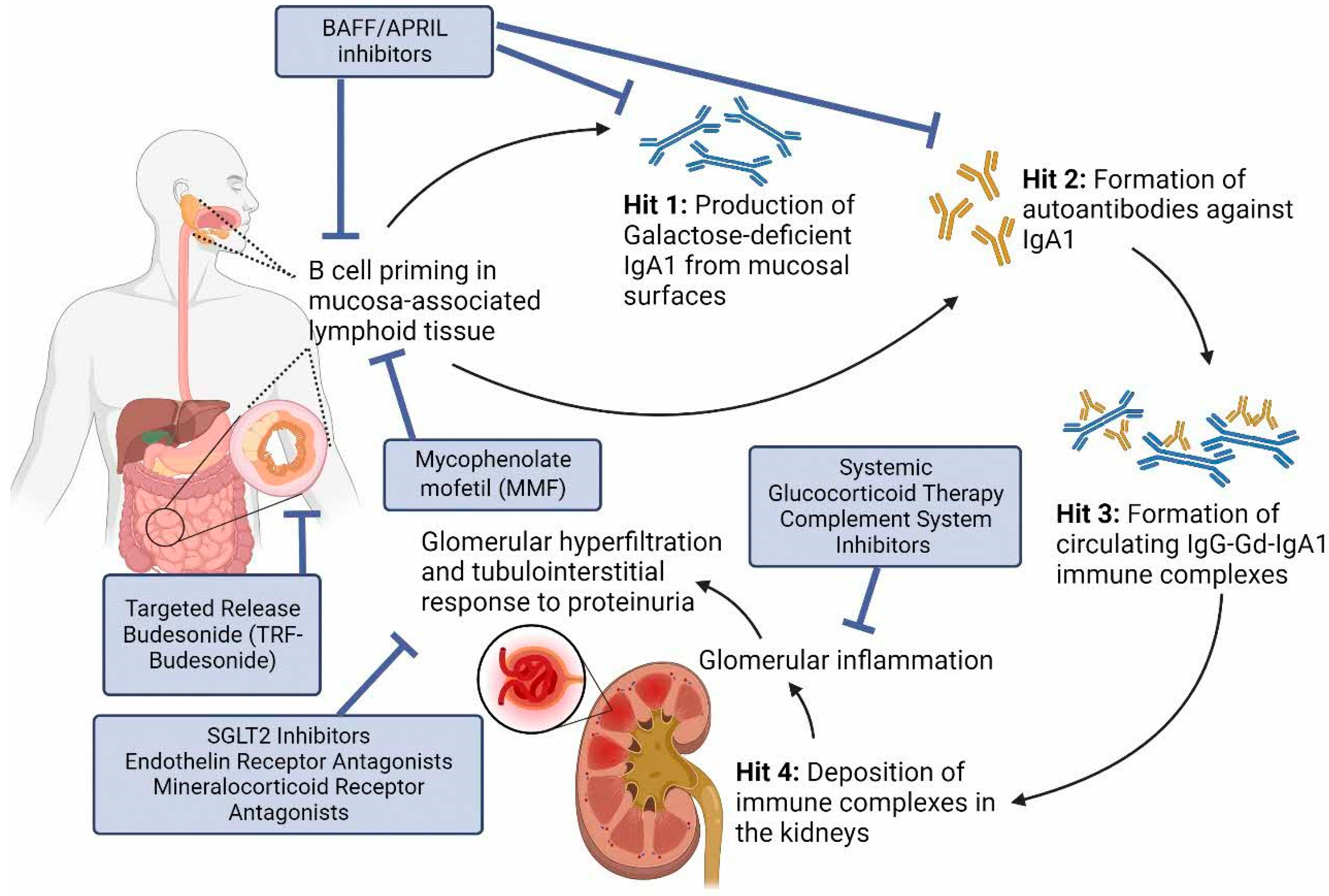
:1. Introduction
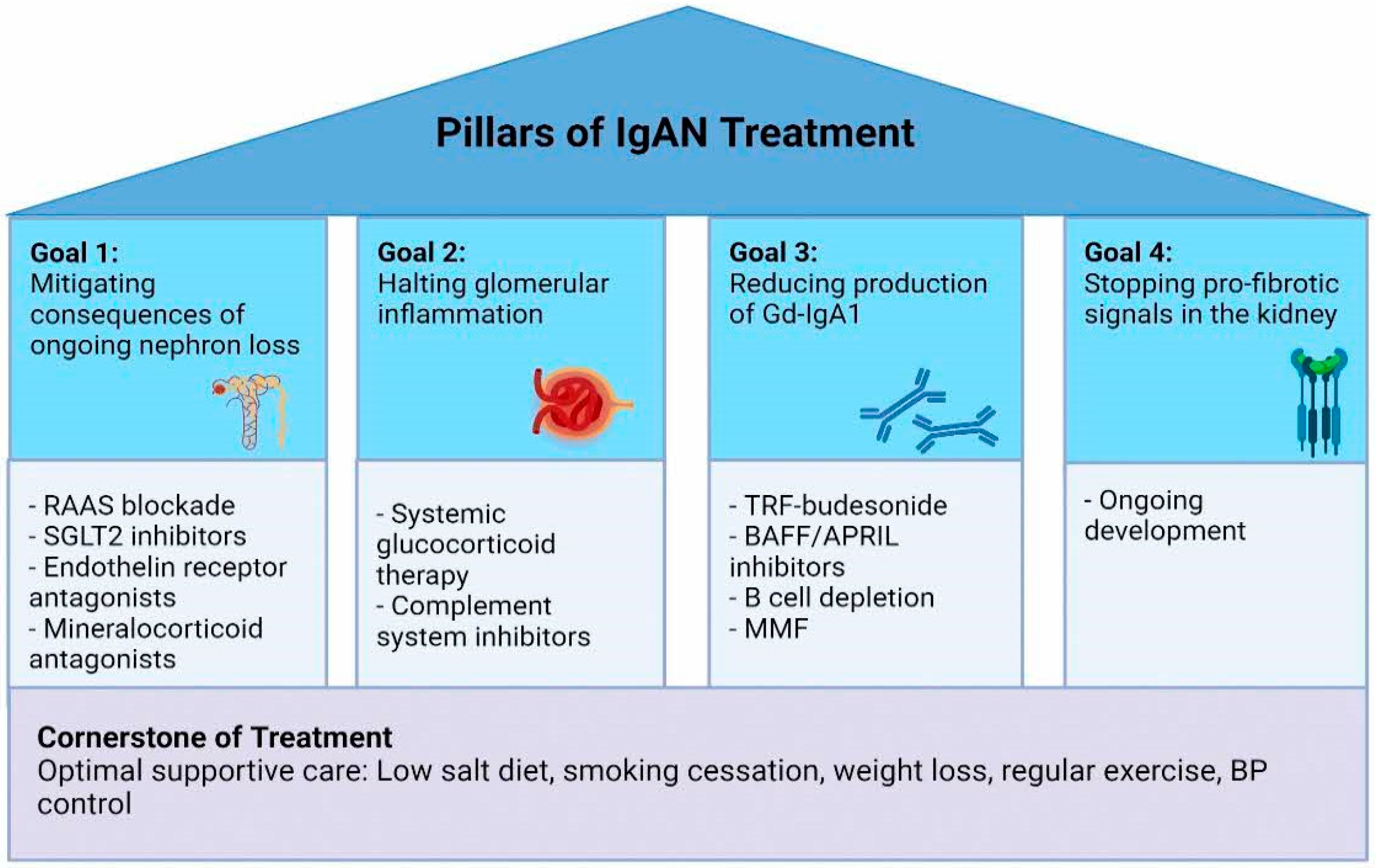
2. Cornerstone of Treatment: Optimal Supportive Care
3. Further Mitigation of Ongoing Nephron Loss
3.1. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 (SGLT2) Inhibitors
3.2. Endothelin Receptor Antagonists
3.3. Mineralocorticoid Receptor Antagonists (MRA)
4. Halting Glomerular Inflammation
4.1. The Role of Systemic Glucocorticoid Therapy
4.2. The Complement System and IgAN
4.2.1. Lectin Pathway Inhibition as an Anti-Inflammatory Approach in IgAN
4.2.2. Alternative Pathway Inhibition as an Anti-Inflammatory Approach in IgAN
4.2.3. Terminal Complement Pathway Inhibitors
5. Reducing Production of Pathogenic IgA
5.1. Targeted Release Formulation of Budesonide (TRF-Budesonide)
5.2. Targeting B-Cell Dysregulation through BAFF/APRIL Inhibition
5.3. B Cell Depleting Agents
5.4. Inhibiting Lymphocyte Proliferation with Mycophenolate Mofetil (MMF)
6. Stopping Pro-Fibrotic Signals in the Kidney
7. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rajasekaran, A.; Julian, B.A.; Rizk, D.V. IgA nephropathy: An interesting autoimmune kidney disease. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 361, 176–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.C.; Goh, S.M.; Barratt, J. Is immunoglobulin A nephropathy different in different ethnic populations? Nephrology 2019, 24, 885–895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibels, L.S.; Gyory, A.Z. IgA nephropathy: Analysis of the natural history, important factors in the progression of renal disease, and a review of the literature. Medicine 1994, 73, 79–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, M.G., Jr.; Donadio, J.V., Jr.; Bergstralh, E.J.; Grande, J.P. Predicting renal outcome in IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 1997, 8, 199–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donadio, J.V.; Grande, J.P. IgA nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 738–748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuels, J.A.; Strippoli, G.F.; Craig, J.C.; Schena, F.P.; Molony, D.A. Immunosuppressive treatments for immunoglobulin A nephropathy: A meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Nephrology 2004, 9, 177–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pitcher, D.; Braddon, F.; Hendry, B.; Mercer, A.; Osmaston, K.; Saleem, M.A.; Steenkamp, R.; Wong, K.; Turner, A.N.; Wang, K.; et al. Long-Term Outcomes in IgA Nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thompson, A.; Carroll, K.; Inker, L.A.; Floege, J.; Perkovic, V.; Boyer-Suavet, S.; Major, R.W.; Schimpf, J.I.; Barratt, J.; Cattran, D.C.; et al. Proteinuria Reduction as a Surrogate End Point in Trials of IgA Nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2019, 14, 469–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reich, H.N.; Troyanov, S.; Scholey, J.W.; Cattran, D.C. Remission of proteinuria improves prognosis in IgA nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2007, 18, 3177–3183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rauen, T.; Eitner, F.; Fitzner, C.; Sommerer, C.; Zeier, M.; Otte, B.; Panzer, U.; Peters, H.; Benck, U.; Mertens, P.R.; et al. Intensive Supportive Care plus Immunosuppression in IgA Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2225–2236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerular Diseases Work Group. KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Glomerular Diseases. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, S1–S276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- SPRINT Research Group; Wright, J.T., Jr.; Williamson, J.D.; Whelton, P.K.; Snyder, J.K.; Sink, K.M.; Rocco, M.V.; Reboussin, D.M.; Rahman, M.; Oparil, S.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Intensive versus Standard Blood-Pressure Control. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2103–2116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauen, T.; Wied, S.; Fitzner, C.; Eitner, F.; Sommerer, C.; Zeier, M.; Otte, B.; Panzer, U.; Budde, K.; Benck, U.; et al. After ten years of follow-up, no difference between supportive care plus immunosuppression and supportive care alone in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2020, 98, 1044–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; Mann, J.F.; McMurray, J.J.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, D.C.; Toto, R.D.; Stefansson, B.V.; Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.F.; McMurray, J.J.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Correa-Rotter, R.; et al. A pre-specified analysis of the DAPA-CKD trial demonstrates the effects of dapagliflozin on major adverse kidney events in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2021, 100, 215–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 117–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuffield Department of Population Health Renal Studies Group; SGLT2 Inhibitor Meta-Analysis Cardio-Renal Trialists’ Consortium. Consortium, Impact of diabetes on the effects of sodium glucose co-transporter-2 inhibitors on kidney outcomes: Collaborative meta-analysis of large placebo-controlled trials. Lancet 2022, 400, 1788–1801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Miguel, C.; Speed, J.S.; Kasztan, M.; Gohar, E.Y.; Pollock, D.M. Endothelin-1 and the kidney: New perspectives and recent findings. Curr. Opin. Nephrol. Hypertens. 2016, 25, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachtman, H.; Nelson, P.; Adler, S.; Campbell, K.N.; Chaudhuri, A.; Derebail, V.K.; Gambaro, G.; Gesualdo, L.; Gipson, D.S.; Hogan, J.; et al. DUET: A Phase 2 Study Evaluating the Efficacy and Safety of Sparsentan in Patients with FSGS. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 2745–2754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Alpers, C.E.; Barratt, J.; Bieler, S.; Diva, U.; Inrig, J.; Komers, R.; Mercer, A.; Noronha, I.L.; et al. Sparsentan in patients with IgA nephropathy: A prespecified interim analysis from a randomised, double-blind, active-controlled clinical trial. Lancet 2023, 401, 1584–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rovin, B.H.; Barratt, H.J.L.; Heerspink, C.E.; Alpers, S.; Bieler, D.W.; Chae, U.A.; Diva, J.; Floege, L.; Gesualdo, J.K.; Inrig, D.E.; et al. Efficacy and safety of sparsentan versus irbesartan in patients with IgA nephropathy (PROTECT): 2-year results from a randomised, active-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 2077–2090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novartis. Novartis Investigational Atrasentan Phase III Study Demonstrates Clinically Meaningful and Highly Statistically Significant Proteinuria Reduction in Patients with IgA Nephropathy (IgAN). 2023. Available online: https://www.novartis.com/news/media-releases/novartis-investigational-atrasentan-phase-iii-study-demonstrates-clinically-meaningful-and-highly-statistically-significant-proteinuria-reduction-patients-iga-nephropathy-igan (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Cosimato, C.; Agoritsas, T.; Mavrakanas, T.A. Mineralocorticoid receptor antagonists in patients with chronic kidney disease. Pharmacol. Ther. 2021, 219, 107701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolignano, D.; Palmer, S.C.; Navaneethan, S.D.; Strippoli, G.F. Aldosterone antagonists for preventing the progression of chronic kidney disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2014, CD007004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakris, G.L.; Agarwal, R.; Anker, S.D.; Pitt, B.; Ruilope, L.M.; Rossing, P.; Kolkhof, P.; Nowack, C.; Schloemer, P.; Joseph, A.; et al. Effect of Finerenone on Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2219–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Fujii, K.; Hiki, Y.; Tateno, S. Steroid therapy in IgA nephropathy: A prospective pilot study in moderate proteinuric cases. Q. J. Med. 1986, 61, 935–943. [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi, Y.; Hiki, Y.; Kokubo, T.; Horii, A.; Tateno, S. Steroid therapy during the early stage of progressive IgA nephropathy. A 10-year follow-up study. Nephron 1996, 72, 237–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, C.; Andrulli, S.; Del Vecchio, L.; Melis, P.; Fogazzi, G.B.; Altieri, P.; Ponticelli, C.; Locatelli, F. Corticosteroid effectiveness in IgA nephropathy: Long-term results of a randomized, controlled trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2004, 15, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, C.; Bolasco, P.G.; Fogazzi, G.B.; Andrulli, S.; Altieri, P.; Ponticelli, C.; Locatelli, F. Corticosteroids in IgA nephropathy: A randomised controlled trial. Lancet 1999, 353, 883–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Jiang, L.; Singh, A.K.; Wang, H. Combination therapy of prednisone and ACE inhibitor versus ACE-inhibitor therapy alone in patients with IgA nephropathy: A randomized controlled trial. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2009, 53, 26–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manno, C.; Torres, D.D.; Rossini, M.; Pesce, F.; Schena, F.P. Randomized controlled clinical trial of corticosteroids plus ACE-inhibitors with long-term follow-up in proteinuric IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2009, 24, 3694–3701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Zhang, H.; Wong, M.G.; Jardine, M.J.; Hladunewich, M.; Jha, V.; Monaghan, H.; Zhao, M.; Barbour, S.; Reich, H.; et al. Effect of Oral Methylprednisolone on Clinical Outcomes in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. JAMA 2017, 318, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Wong, M.G.; Hladunewich, M.A.; Jha, V.; Hooi, L.S.; Monaghan, H.; Zhao, M.; Barbour, S.; Jardine, M.J.; Reich, H.N.; et al. Effect of Oral Methylprednisolone on Decline in Kidney Function or Kidney Failure in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. JAMA 2022, 327, 1888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuire, M. Selecting Treatment for IgA Nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023, 18, 1109–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCoy, R.C.; Abramowsky, C.R.; Tisher, C.C. IgA nephropathy. Am. J. Pathol. 1974, 76, 123–144. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Bene, M.C.; Faure, G.C. Composition of mesangial deposits in IgA nephropathy: Complement factors. Nephron 1987, 46, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maillard, N.; Wyatt, R.J.; Julian, B.A.; Kiryluk, K.; Gharavi, A.; Fremeaux-Bacchi, V.; Novak, J. Current Understanding of the Role of Complement in IgA Nephropathy. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2015, 26, 1503–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rauterberg, E.W.; Lieberknecht, H.M.; Wingen, A.M.; Ritz, E. Complement membrane attack (MAC) in idiopathic IgA-glomerulonephritis. Kidney Int. 1987, 31, 820–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roos, A.; Rastaldi, M.P.; Calvaresi, N.; Oortwijn, B.D.; Schlagwein, N.; van Gijlswijk-Janssen, D.J.; Stahl, G.L.; Matsushita, M.; Fujita, T.; van Kooten, C.; et al. Glomerular activation of the lectin pathway of complement in IgA nephropathy is associated with more severe renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2006, 17, 1724–1734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiryluk, K.; Li, Y.; Scolari, F.; Sanna-Cherchi, S.; Choi, M.; Verbitsky, M.; Fasel, D.; Lata, S.; Prakash, S.; Shapiro, S.; et al. Discovery of new risk loci for IgA nephropathy implicates genes involved in immunity against intestinal pathogens. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafayette, R.A.; Rovin, B.H.; Reich, H.N.; Tumlin, J.A.; Floege, J.; Barratt, J. Safety, Tolerability and Efficacy of Narsoplimab, a Novel MASP-2 Inhibitor for the Treatment of IgA Nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2020, 5, 2032–2041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omeros Corporation. Omeros Corporation Provides Update on Interim Analysis of ARTEMIS-IGAN Phase 3 Trial of Narsoplimab in IgA Nephropathy. 2023. Available online: https://investor.omeros.com/news-releases/news-release-details/omeros-corporation-provides-update-interim-analysis-artemis-igan (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Zhang, H.; Rizk, D.V.; Perkovic, V.; Maes, B.; Kashihara, N.; Rovin, B.; Trimarchi, H.; Sprangers, B.; Meier, M.; Kollins, D.; et al. Results of a randomized double-blind placebo-controlled Phase 2 study propose iptacopan as an alternative complement pathway inhibitor for IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2023, 105, 189–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pharmaceuticals, A. Arrowhead Announces Interim Results from Ongoing Phase 1/2 Study of ARO-C3 for Treatment of Complement Mediated Diseases. 2023. Available online: https://ir.arrowheadpharma.com/news-releases/news-release-details/arrowhead-announces-interim-results-ongoing-phase-12-study-aro (accessed on 16 December 2023).
- Jayne, D.R.W.; Bruchfeld, A.N.; Harper, L.; Schaier, M.; Venning, M.C.; Hamilton, P.; Burst, V.; Grundmann, F.; Jadoul, M.; Szombati, I.; et al. Randomized Trial of C5a Receptor Inhibitor Avacopan in ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 2756–2767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayne, D.R.W.; Merkel, P.A.; Schall, T.J.; Bekker, P.; Advocate Study Group. Avacopan for the Treatment of ANCA-Associated Vasculitis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruchfeld, A.; Magin, H.; Nachman, P.; Parikh, S.; Lafayette, R.; Potarca, A.; Miao, S.; Bekker, P. C5a receptor inhibitor avacopan in immunoglobulin A nephropathy—An open-label pilot study. Clin. Kidney J. 2022, 15, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, S.C.; Cheung, C.K.; Barratt, J. New insights into the pathogenesis of IgA nephropathy. Pediatr. Nephrol. 2018, 33, 763–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wimbury, D.; Muto, M.; Bhachu, J.S.; Scionti, K.; Brown, J.; Molyneux, K.; Seikrit, C.; Maixnerová, D.; Pérez-Alós, L.; Garred, P.; et al. Targeted-release budesonide modifies key pathogenic biomarkers in immunoglobulin A nephropathy: Insights from the NEFIGAN trial. Kidney Int. 2023, 105, 381–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Lafayette, R.; Kristensen, J.; Stone, A.; Cattran, D.; Floege, J.; Tesar, V.; Trimarchi, H.; Zhang, H.; Eren, N.; et al. Results from part A of the multi-center, double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled NefIgArd trial, which evaluated targeted-release formulation of budesonide for the treatment of primary immunoglobulin A nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2023, 103, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafayette, R.; Kristensen, J.; Stone, A.; Floege, J.; Tesař, V.; Trimarchi, H.; Zhang, H.; Eren, N.; Paliege, A.; Reich, H.N.; et al. Efficacy and safety of a targeted-release formulation of budesonide in patients with primary IgA nephropathy (NefIgArd): 2-year results from a randomised phase 3 trial. Lancet 2023, 402, 859–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheung, C.K.; Barratt, J.; Carroll, K.; Lafayette, R.A.; Liew, A.; Suzuki, Y.; Tesar, V.; Trimarchi, H.; Wong, M.G.; Zhang, H.; et al. Targeting APRIL in the Treatment of IgA Nephropathy. Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2023. epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moldoveanu, Z.; Wyatt, R.J.; Lee, J.Y.; Tomana, M.; Julian, B.A.; Mestecky, J.; Huang, W.Q.; Anreddy, S.R.; Hall, S.; Hastings, M.C.; et al. Patients with IgA nephropathy have increased serum galactose-deficient IgA1 levels. Kidney Int. 2007, 71, 1148–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, N.; Hou, P.; Lv, J.; Moldoveanu, Z.; Li, Y.; Kiryluk, K.; Gharavi, A.G.; Novak, J.; Zhang, H. The level of galactose-deficient IgA1 in the sera of patients with IgA nephropathy is associated with disease progression. Kidney Int. 2012, 82, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McCarthy, D.D.; Kujawa, J.; Wilson, C.; Papandile, A.; Poreci, U.; Porfilio, E.A.; Ward, L.; Lawson, M.A.; Macpherson, A.J.; McCoy, K.D.; et al. Mice overexpressing BAFF develop a commensal flora-dependent, IgA-associated nephropathy. J. Clin. Investig. 2011, 121, 3991–4002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhai, Y.L.; Zhu, L.; Shi, S.F.; Liu, L.J.; Lv, J.C.; Zhang, H. Increased APRIL Expression Induces IgA1 Aberrant Glycosylation in IgA Nephropathy. Medicine 2016, 95, e3099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.Q.; Li, M.; Zhang, H.; Low, H.Q.; Wei, X.; Wang, J.Q.; Sun, L.D.; Sim, K.S.; Li, Y.; Foo, J.N.; et al. A genome-wide association study in Han Chinese identifies multiple susceptibility loci for IgA nephropathy. Nat. Genet. 2011, 44, 178–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiryluk, K.; Sanchez-Rodriguez, E.; Zhou, X.J.; Zanoni, F.; Liu, L.; Mladkova, N.; Khan, A.; Marasa, M.; Zhang, J.Y.; Balderes, O.; et al. Genome-wide association analyses define pathogenic signaling pathways and prioritize drug targets for IgA nephropathy. Nat. Genet. 2023, 55, 1091–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathur, M.; Barratt, J.; Chacko, B.; Chan, T.M.; Kooienga, L.; Oh, K.H.; Sahay, M.; Suzuki, Y.; Wong, M.G.; Yarbrough, J.; et al. A Phase 2 Trial of Sibeprenlimab in Patients with IgA Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 390, 20–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Hour, B.; Kooienga, L.; Roy, S.; Schwartz, B.; Siddiqui, A.; Tolentino, J.; Iyer, S.P.; Stromatt, C.; Endsley, A.; et al. POS-109 Interim results of phase 1 and 2 trials to investigate the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics, and clinical activity of BION-1301 in patients with IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, S46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barratt, J.; Tumlin, J.; Suzuki, Y.; Kao, A.; Aydemir, A.; Pudota, K.; Jin, H.; Gühring, H.; Appel, G. Randomized Phase II JANUS Study of Atacicept in Patients with IgA Nephropathy and Persistent Proteinuria. Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 7, 1831–1841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafayette, R.; Maes, B.; Lin, C.; Barbour, S.; Phoon, R.; Kim, S.G.; Tesar, V.; Floege, J.; Jha, V.; Barratt, J. #3848 Origin trial: 24-wk primary analysis of a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled PH2B study of atacicept in patients with igan. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2023, 38 (Suppl. S1), gfad063a_3848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, J.; Liu, L.; Hao, C.; Li, G.; Fu, P.; Xing, G.; Zheng, H.; Chen, N.; Wang, C.; Luo, P.; et al. Randomized Phase 2 Trial of Telitacicept in Patients with IgA Nephropathy with Persistent Proteinuria. Kidney Int. Rep. 2023, 8, 499–506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lafayette, R.A.; Canetta, P.A.; Rovin, B.H.; Appel, G.B.; Novak, J.; Nath, K.A.; Sethi, S.; Tumlin, J.A.; Mehta, K.; Hogan, M.; et al. A Randomized, Controlled Trial of Rituximab in IgA Nephropathy with Proteinuria and Renal Dysfunction. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2017, 28, 1306–1313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schrezenmeier, E.; Jayne, D.; Dorner, T. Targeting B Cells and Plasma Cells in Glomerular Diseases: Translational Perspectives. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 741–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maixnerova, D.; El Mehdi, D.; Rizk, D.V.; Zhang, H.; Tesar, V. New Treatment Strategies for IgA Nephropathy: Targeting Plasma Cells as the Main Source of Pathogenic Antibodies. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartono, C.; Chung, M.; Perlman, A.S.; Chevalier, J.M.; Serur, D.; Seshan, S.V.; Muthukumar, T. Bortezomib for Reduction of Proteinuria in IgA Nephropathy. Kidney Int. Rep. 2018, 3, 861–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frisch, G.; Lin, J.; Rosenstock, J.; Markowitz, G.; D’Agati, V.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Preddie, D.; Crew, J.; Valeri, A.; Appel, G. Mycophenolate mofetil (MMF) vs placebo in patients with moderately advanced IgA nephropathy: A double-blind randomized controlled trial. Nephrol. Dial. Transpl. 2005, 20, 2139–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maes, B.D.; Oyen, R.; Claes, K.; Evenepoel, P.; Kuypers, D.; Vanwalleghem, J.; Van Damme, B.; Vanrenterghem, Y.F. Mycophenolate mofetil in IgA nephropathy: Results of a 3-year prospective placebo-controlled randomized study. Kidney Int. 2004, 65, 1842–1849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogg, R.J.; Bay, R.C.; Jennette, J.C.; Sibley, R.; Kumar, S.; Fervenza, F.C.; Appel, G.; Cattran, D.; Fischer, D.; Hurley, R.M.; et al. Randomized controlled trial of mycophenolate mofetil in children, adolescents, and adults with IgA nephropathy. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2015, 66, 783–791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, S.; Leung, J.C.K.; Chan, L.Y.Y.; Lui, Y.H.; Tang, C.S.O.; Kan, C.H.; Ho, Y.W.; Lai, K.N. Mycophenolate mofetil alleviates persistent proteinuria in IgA nephropathy. Kidney Int. 2005, 68, 802–812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, F.F.; Xie, D.; Wang, J.; Xu, X.; Yang, X.; Ai, J.; Nie, S.; Liang, M.; Wang, G.; Jia, N.; et al. Effectiveness of Mycophenolate Mofetil Among Patients with Progressive IgA Nephropathy: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, e2254054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.; Liu, J.W.; Zhang, Y.T.; Wu, G. The Role of Renal Macrophage, AIM, and TGF-beta1 Expression in Renal Fibrosis Progression in IgAN Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 646650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leung, J.C.; Chan, L.Y.; Tsang, A.W.; Liu, E.W.; Lam, M.F.; Tang, S.C.; Lai, K.N. Anti-macrophage migration inhibitory factor reduces transforming growth factor-beta 1 expression in experimental IgA nephropathy. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2004, 19, 1976–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brezzi, B.; Del Prete, D.; Lupo, A.; Magistroni, R.; Gomez-Lira, M.; Bernich, P.; Anglani, F.; Mezzabotta, F.; Turco, A.; Furci, L.; et al. Primary IgA nephropathy is more severe in TGF-beta1 high secretor patients. J. Nephrol. 2009, 22, 747–759. [Google Scholar]
- Dahly-Vernon, A.J.; Sharma, M.; McCarthy, E.T.; Savin, V.J.; Ledbetter, S.R.; Roman, R.J. Transforming growth factor-beta, 20-HETE interaction, and glomerular injury in Dahl salt-sensitive rats. Hypertension 2005, 45, 643–648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz-Ortega, M.; Lamas, S.; Ortiz, A. Antifibrotic Agents for the Management of CKD: A Review. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2022, 80, 251–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Therapy | Mechanism of Action | Clinical Trial | Primary and Key Secondary Endpoints | Main Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Mitigating the Consequences of Ongoing Nephron Loss | ||||
| Sparsentan | Dual endothelin A and angiotensin II inhibitor | PROTECT * NCT03762850—completed Phase III randomized double-blind, active-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 36 weeks Change in eGFR at 110 weeks | Reduction of proteinuria greater in the sparsentan group (−49.8%) than the irbesartan group (−15.1%) eGFR chronic 2-year slope (weeks 6–110) was −2.7 mL/min per 1.73 m2 per year versus −3.8 mL/min per 1.73 m2 per year (difference 1.1 mL/min per 1.73 m2 per year, 95% CI 0.1 to 2.1; p = 0.037); eGFR total 2-year slope (day 1-week 110) was −2.9 mL/min per 1.73 m2 per year versus −3.9 mL/min per 1.73 m2 per year (difference 1.0 mL/min per 1.73 m2 per year, 95% CI −0.03 to 1.94; p = 0.058). |
| Atrasentan | Selective endothelin A receptor inhibitor | ALIGN * NCT04573478—ongoing Phase III randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 24 weeks Change in eGFR at 2.6 years | Awaited |
| 2. Halting Glomerular Inflammation | ||||
| Narsoplimab (OMS721) | Blocks lectin pathway activation by inhibiting MASP-2 | * NCT02682407—completed Staged phase II study | Change in proteinuria at 12 weeks | Reductions of proteinuria ranges from 54% to 95%, compared to baseline |
| ARTERMIS-IgAN * NCT03608033—terminated early Phase III randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 36 weeks Change in eGFR up to 144 weeks | Trial terminated due to lack of efficacy | ||
| Iptacopan (LNP023) | Blocks alternative pathway activation by inhibiting Factor B | * NCT03373461—completed Phase II randomized double-blind trial | Change in proteinuria at 3 months | Reduction of proteinuria of 23% achieved with iptacopan (200 mg twice daily arm), compared to placebo |
| APPLAUSE-IgAN * NCT04578834—ongoing Phase III randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 9 months Change in eGFR at 9 and 24 months | Awaited | ||
| IONIS-FB-LRx | Blocks alternative pathway activation by inhibiting Factor B | * NCT04014335—completed Phase II open-label study | Change in proteinuria at 29 weeks | Eight of 10 patients had a reduction in proteinuria at week 29 |
| IMAGINATION * NCT05797610—ongoing Phase III randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 37 weeks Change in eGFR at 105 weeks | Awaited | ||
| Pegcetacoplan (APL-2) | Blocks terminal pathway activation by inhibiting C3 | * NCT03453619—active, not recruiting Phase II single-arm open-label trial | Change in proteinuria at 48 weeks | Awaited |
| ARO-C3 | Blocks terminal pathway activation by inhibiting C3 | * NCT05083364—ongoing Phase I/II placebo-controlled study | Change in C3 at 169 days | Awaited |
| Avacopan (CCX168) | C5a receptor inhibitor | * NCT02384317—completed Pilot phase II open-label trial | Change in proteinuria at 12 weeks | Six of seven patients had improvement in the UPCR during the treatment period, three of whom had a improvement of 50%, compared to baseline |
| Cemdisiran (ALN-CC5) | Blocks terminal pathway activation by inhibiting C5 | * NCT03841448—completed Phase II randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 32 weeks | Reduction (placebo-adjusted) of proteinuria of 37.4% |
| Raviluzumab | Blocks terminal pathway activation by inhibiting C5 | * NCT04564339—ongoing Phase II randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 26 weeks | Reduction (placebo-adjusted) of proteinuria of 33.1% |
| Vemircopan (ALXN2050) | Blocks alternative pathway activation by inhibiting Factor D | * NCT05097989—ongoing Phase II randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 26 weeks | Awaited |
| 3. Reducing Production of Pathogenic IgA | ||||
| Nefecon (TRF-Budesonide) | Modulates mucosal B cells and plasma cells in the gut associated lymphoid tissue of the small intestine | NEFIGAN * NCT01738035—completed Phase IIB randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 9 months | Reduction of proteinuria of 24.4% (27.3% in 16 mg treatment group; 21.5% in 8 mg treatment group), compared to placebo |
| NefigArd * NCT03643965—completed Phase III randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 9 months Change in eGFR at 9 and 12 months | Reduction of proteinuria of 27%, compared to placebo; Improvement of eGFR decline by 5.05 mL/min per 1.73 m2, compared to placebo | ||
| Mycophenolate Mofetil (MMF) | Inhibits lymphocyte proliferation | MAIN * NCT01854814—completed Randomized open-label trial | Composite of doubling of serum creatinine, kidney failure, or death due to kidney disease Progression of chronic kidney disease | 77% risk reduction of composite end points (doubling of serum creatinine, kidney failure, or death due to kidney disease) |
| Sibeprenlimab (VIS639) | Inhibits APRIL | ENVISION * NCT04287985–completed Phase II randomized controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 12 months | Reduction of proteinuria between 47.2–62.0% in treatment arm compared to 20.0% in placebo arm |
| VISIONARY * NCT05248646—ongoing Phase III randomized controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 9 months Change in eGFR at 24 months | Awaited | ||
| Zigakibart (BION-1301) | Inhibits APRIL | * NCT03945318—interim analysis, awaiting final results Phase I and phase II open-label extension | Change in proteinuria at 3 months | Reduction of proteinuria of 30.4% at 12 weeks, compared to baseline; reduction of proteinuria of 66.9% at 52 weeks, compared to baseline |
| BEYOND * NCT05852938—ongoing Phase III randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 40 weeks Change in eGFR at 104 weeks | Awaited | ||
| Atacicept | Recombinant fusion protein that binds BAFF and APRIL | JANUS * NCT02808429—completed Phase II randomized controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 24, 48 and 72 weeks | Reduction of proteinuria of 24% at 12 weeks, 38% at 48 weeks and 50% at 72 weeks with atacicept 25 mg, compared to baseline |
| ORIGIN3 (Phase 2b) * NCT04716231—completed Phase IIb randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 24 weeks Change in eGFR at 24 weeks | Reduction of proteinuria of 33%, compared to placebo group | ||
| ORIGIN3 (Phase 3) * NCT04716231-ongoing Phase III randomized controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 36 weeks Change in eGFR at 104 weeks | Awaited | ||
| Telitacicept | Inhibits BAFF and APRIL | * NCT04291781—completed Phase II randomized placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 24 weeks | Reduction of proteinuria of 25–49%, compared to baseline |
| * NCT05799287—ongoing Phase III randomized double-blind, placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria at 104 weeks Change in eGFR at 3 years | Awaited | ||
| Povetacicept (ALPN-303) | Inhibits BAFF and APRIL | * NCT05732402—ongoing Phase I/II open-label trial | Change in proteinuria | Awaited |
| Borteozomib (Velcade) | Plasma cell depletion | * NCT01103778—completed Pilot open-label trial | Change in proteinuria at 1 year Change in eGFR at 1 year | Three of eight patients had full remission defined as proteinuria of less than 300 mg per day |
| Felzartamab | Plasma cell depletion | NCT05065970—ongoing Phase II randomized placebo-controlled trial | Change in proteinuria | Awaited |
| Mezagitamab | Plasma cell depletion | * NCT05174221—ongoing Phase IB open-label study | Change in proteinuria at 36 weeks | Awaited |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lim, R.S.; Yeo, S.C.; Barratt, J.; Rizk, D.V. An Update on Current Therapeutic Options in IgA Nephropathy. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13040947
Lim RS, Yeo SC, Barratt J, Rizk DV. An Update on Current Therapeutic Options in IgA Nephropathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(4):947. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13040947
Chicago/Turabian StyleLim, Regina Shaoying, See Cheng Yeo, Jonathan Barratt, and Dana V. Rizk. 2024. "An Update on Current Therapeutic Options in IgA Nephropathy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 4: 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13040947
APA StyleLim, R. S., Yeo, S. C., Barratt, J., & Rizk, D. V. (2024). An Update on Current Therapeutic Options in IgA Nephropathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(4), 947. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13040947





