Diagnostic Impact of Subcutaneous Edema in Gouty Feet Detected by Dual-Energy Computed Tomography and Ultrasound
Abstract
1. Introduction
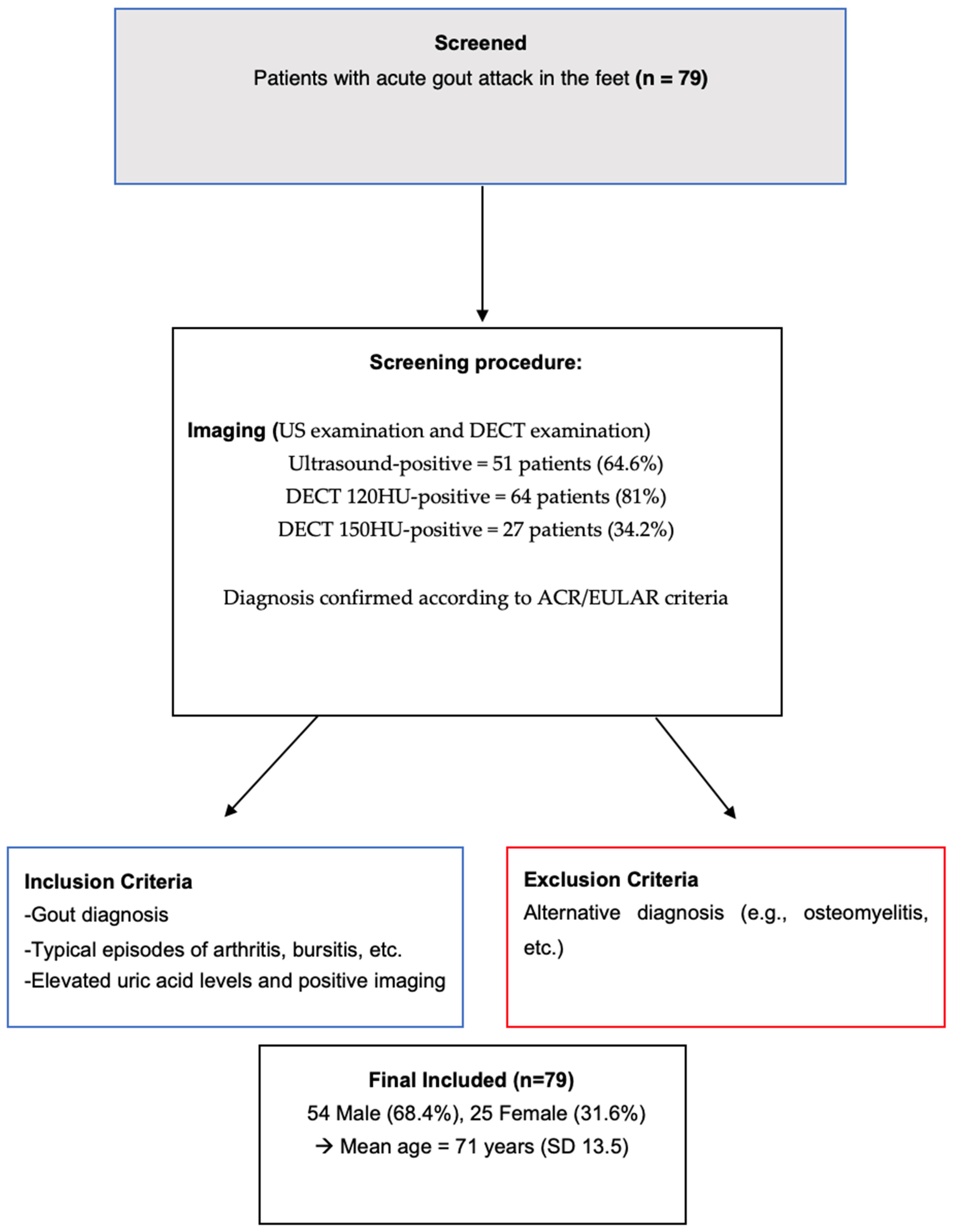
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.1.1. Inclusion Criteria
2.1.2. Exclusion Criteria
2.2. Image Analysis
2.2.1. Ultrasound Analysis
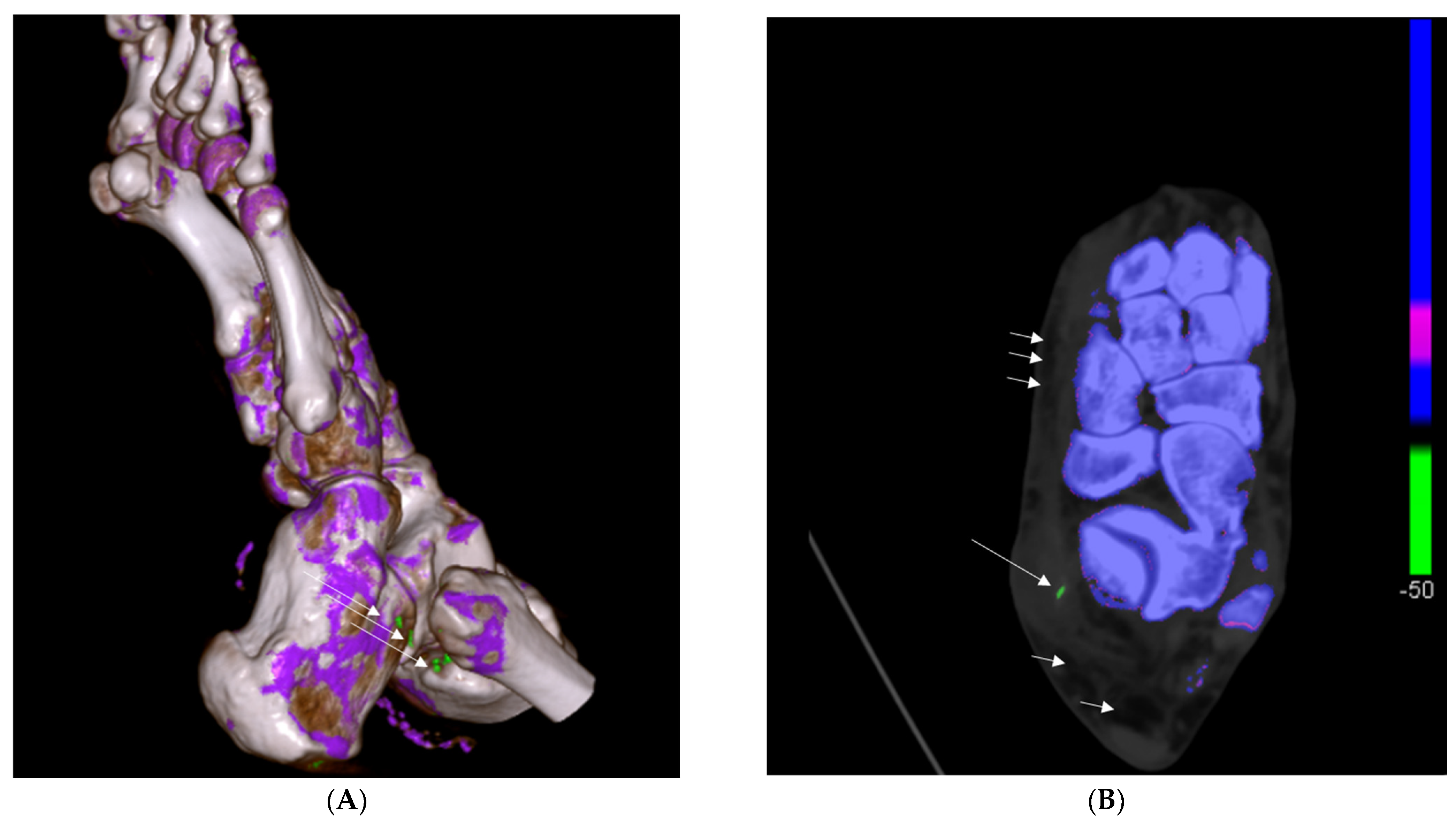
2.2.2. DECT Analysis
2.3. Imaging Examination
2.3.1. DECT Examination
2.3.2. Ultrasound Examination
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Demographic and Clinical Characteristics
3.2. Imaging Results and Associations with Lymphedema
3.2.1. Ultrasound Findings
3.2.2. DECT Findings
3.3. Binary Logistic Regression Analysis
3.4. Clinical Significance of Statistical Findings
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Girish, G.; Melville, D.M.; Kaeley, G.S.; Brandon, C.J.; Goyal, J.R.; Jacobson, J.A.; Jamadar, D.A. Imaging appearances in gout. Arthritis 2013, 2013, 673401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McQueen, F.M.; Chhana, A.; Dalbeth, N. Mechanisms of joint damage in gout: Evidence from cellular and imaging studies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2012, 8, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buckley, T.J. Radiologic features of gout. Am. Fam. Physician 1996, 54, 1232–1238. [Google Scholar]
- Dalbeth, N. Management of gout in primary care: Challenges and potential solutions. Rheumatology 2013, 52, 1549–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Glazebrook, K.N.; Guimarães, L.S.; Murthy, N.S.; Black, D.F.; Bongartz, T.; Manek, N.J.; Leng, S.; Fletcher, J.G.; McCollough, C.H. Identification of intraarticular and periarticular uric acid crystals with dual-energy CT: Initial evaluation. Radiology 2011, 261, 516–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bongartz, T.; Glazebrook, K.N.; Kavros, S.J.; Murthy, N.S.; Merry, S.P.; Franz, W.B., 3rd; Michet, C.J.; Veetil, B.M.A.; Davis, J.M.; Mason, T.G.; et al. Dual-energy CT for the diagnosis of gout: An accuracy and diagnostic yield study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1072–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Sun, Y.; Chen, H.; Kong, X.; Zhou, J.; Zhou, Y.; Ma, L.; Jiang, L. New urate depositions on dual-energy computed tomography in gouty arthritis during urate-lowering therapy. Rheumatol. Int. 2017, 37, 1365–1372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkenstaedt, T.; Manoliou, A.; Toniolo, M.; Higashigaito, K.; Andreisek, G.; Guggenberger, R.; Michel, B.; Alkadhi, H. Gouty arthritis: The diagnostic and therapeutic impact of dual-energy CT. Eur. Radiol. 2016, 26, 3989–3999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klauser, A.S.; Halpern, E.J.; Strobl, S.; Ellah, M.M.H.A.; Gruber, J.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Auer, T.; Feuchtner, G.; Jaschke, W. Gout of hand and wrist: The value of US as compared with DECT. Eur. Radiol. 2018, 28, 4174–4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peiteado, D.; De Miguel, E.; Villalba, A.; Ordóñez, M.C.; Castillo, C.; Martín-Mola, E. Value of a short four-joint ultrasound test for gout diagnosis: A pilot study. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2012, 30, 830–837. [Google Scholar]
- Gerster, J.C.; Landry, M.; Rappoport, G.; Rivier, G.; Duvoisin, B.; Schnyder, P. Enthesopathy and tendinopathy in gout: Computed tomographic assessment. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 1996, 55, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weniger, F.G.; Davison, S.P.; Risin, M.; Salyapongse, A.; Manders, E.K. Gouty flexor tenosynovitis of the digits: Report of three cases 1. J. Hand Surg. 2003, 28, 669–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Primm, D.D.; Allen, J.R. Gouty involvement of a flexor tendon in the hand. J. Hand Surg. 1983, 8, 863–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, E.D.; Sandim, G.B.; Mitraud, S.A.V.; Kubota, E.S.; Ferrari, A.J.L.; Fernandes, A.R.C. Sonographic description and classification of tendinous involvement in relation to tophi in chronic tophaceous gout. Insights Imaging 2010, 1, 143–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dalbeth, N.; Kalluru, R.; Aati, O.; Horne, A.; Doyle, A.J.; McQueen, F.M. Tendon involvement in the feet of patients with gout: A dual-energy CT study. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 72, 1545–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauser, A.S.; Strobl, S.; Schwabl, C.; Kremser, C.; Klotz, W.; Nikodinovska, V.V.; Stofferin, H.; Scharll, Y.; Halpern, E. Impact of Dual-Energy Computed Tomography (DECT) Postprocessing Protocols on Detection of Monosodium Urate (MSU) Deposits in Foot Tendons of Cadavers. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 2208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwabl, C.; Taljanovic, M.; Widmann, G.; Teh, J.; Klauser, A.S. Ultrasonography and dual-energy computed tomography: Impact for the detection of gouty deposits. Ultrasonography 2021, 40, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shupper, P.; Stitik, T.P. Tibialis Posterior Tenosynovitis: A Unique Musculoskeletal Manifestation of Gout. Am. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2018, 97, 143–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scirocco, C.; Rutigliano, I.M.; Finucci, A.; Iagnocco, A. Musculoskeletal ultrasonography in gout. Med. Ultrason. 2015, 17, 535–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullocks, J.M.; Downey, C.R.; Gibler, D.P.G.; Netscher, D.T. Crystal Deposition disease masquerading as proliferative tenosynovitis and its associated sequelae. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2009, 62, 128–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matcuk, G.R.; Katal, S.; Gholamrezanezhad, A.; Spinnato, P.; Waldman, L.E.; Fields, B.K.K.; Patel, D.B.; Skalski, M.R. Imaging of lower extremity infections: Predisposing conditions, atypical infections, mimics, and differentiating features. Skelet. Radiol. 2024, 53, 2099–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vulder, N.; Chen, M.; Huysse, W.; Herregods, N.; Verstraete, K.; Jans, L. Case Series: Dual-Energy CT in Extra-Articular Manifestations of Gout: Main Teaching Point: Dual-energy CT is a valuable asset in the detection of extra-articular manifestations of gout. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2020, 104, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ly, C.L.; Kataru, R.P.; Mehrara, B.J. Inflammatory Manifestations of Lymphedema. International journal of molecular sciences. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moffatt, C.J.; Gaskin, R.; Sykorova, M.; Dring, E.; Aubeeluck, A.; Franks, P.J.; Windrum, P.; Mercier, G.; Pinnington, L.; Quéré, I. Prevalence and Risk Factors for Chronic Edema in U.K. Community Nursing Services. Lymphat. Res. Biol. 2019, 17, 147–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neogi, T.; Jansen, T.L.T.A.; Dalbeth, N.; Fransen, J.; Schumacher, H.R.; Berendsen, D.; Brown, M.; Choi, H.; Edwards, N.L.; Janssens, H.J.E.M.; et al. 2015 Gout classification criteria: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 74, 1789–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suehiro, K.; Morikage, N.; Murakami, M.; Yamashita, O.; Ueda, K.; Samura, M.; Nakamura, K.; Hamano, K. Subcutaneous tissue ultrasonography in legs with dependent edema and secondary lymphedema. Ann. Vasc. Dis. 2014, 7, 21–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.K.; Jung, J.-Y.; Jee, W.-H.; Lee, J.J.; Park, S.-H. Combining non-contrast and dual-energy CT improves diagnosis of early gout. Eur. Radiol. 2019, 29, 1267–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, M.; Schmidt, W.A.; Thiele, R.G.; Keen, H.I.; Kaeley, G.S.; Naredo, E.; Iagnocco, A.; Bruyn, G.A.; Balint, P.V.; Filippucci, E.; et al. International Consensus for ultrasound lesions in gout: Results of Delphi process and web-reliability exercise. Rheumatology 2015, 54, 1797–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strobl, S.; Kremser, C.; Taljanovic, M.; Gruber, J.; Stofferin, H.; Bellmann-Weiler, R.; Klauser, A.S. Impact of Dual-Energy CT Postprocessing Protocol for the Detection of Gouty Arthritis and Quantification of Tophi in Patients Presenting with Podagra: Comparison with Ultrasound. Am. J. Roentgenol. 2019, 213, 1315–1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klauser, A.S.; Strobl, S.; Schwabl, C.; Klotz, W.; Feuchtner, G.; Moriggl, B.; Held, J.; Taljanovic, M.; Weaver, J.S.; Reijnierse, M.; et al. Prevalence of Monosodium Urate (MSU) Deposits in Cadavers Detected by Dual-Energy Computed Tomography (DECT). Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palazzi, C.; Olivieri, I.; D’amico, E.; Pace-Palitti, V.; Petricca, A. Symmetrical pitting edema resembling RS3PE in gout. Clin. Rheumatol. 2003, 22, 506–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, C.; Hsiao, Y.; Hsu, H.; Ko, Y.; Lin, T.; Chen, L.; Hsieh, S.; Li, K. Can ultrasound differentiate acute erosive arthritis associated with osteomyelitis, rheumatoid arthritis, or gouty arthritis? Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2019, 22, 1972–1977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Terslev, L.; Gutierrez, M.; Christensen, R.; Balint, P.V.; Bruyn, G.A.; Sedie, A.D.; Filippucci, E.; Garrido, J.; Hammer, H.B.; Iagnocco, A.; et al. Assessing Elementary Lesions in Gout by Ultrasound: Results of an OMERACT Patient-based Agreement and Reliability Exercise. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 42, 2149–2154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Demographics | |
|---|---|
| Gout diagnosis, n (%) | 79 (100) |
| Age years, mean (SD) | 71 (13.5) |
| Gender (female), n (%) | 25 (31.6) |
| Lymphedema, n (%) | 46 (58.2) |
| Ultrasound positive, n (%) | 51 (64.6) |
| 120 HU DECT positive, n (%) | 64 (81) |
| 150 HU DECT positive, n (%) | 27 (34.2) |
| Extra-articular MSU deposits, n (%) | 62 (78.5) |
| Intra-articular MSU deposits, n (%) | 24 (30.4) |
| Only extra-articular MSU deposits, n (%) | 40 (50.6) |
| Only intra-articular MSU deposits, n (%) | 2 (2.5) |
| Findings | Lymphedema | No Lymphedema | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ultrasound positive, n (%) | 51 (64.6) | 28 (35.4) | <0.001 |
| Extra-articular MSU Deposits, n (%) | 62 (78.5) | 17 (21.5) | <0.001 |
| Intra-articular MSU Deposits, n (%) | 24 (30.4) | 55 (69.6) | 0.96 |
| Age, years mean (SD) | 75.5 (13.3) | 64.7 (11.3) | <0.001 |
| Binary Logistic Regression | ||
|---|---|---|
| Odds Ratio | p-Value | |
| Age | 1.07 | 0.001 |
| Gender | 0.67 | 0.409 |
| Ultrasound positive | 9.75 | <0.001 |
| 120 HU DECT positive | 33.16 | <0.001 |
| 150 HU DECT positive | 2.19 | 0.118 |
| Extra-articular MSU deposits | 42.35 | <0.001 |
| Intra-articular MSU deposits | 1.0 | 0.990 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Held, J.; Strolz, C.; Reijnierse, M.; Taljanovic, M.; Lacaita, P.G.; Ouaret, M.; Gizewski, E.R.; Weiss, G.; Klauser, A.S. Diagnostic Impact of Subcutaneous Edema in Gouty Feet Detected by Dual-Energy Computed Tomography and Ultrasound. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247620
Held J, Strolz C, Reijnierse M, Taljanovic M, Lacaita PG, Ouaret M, Gizewski ER, Weiss G, Klauser AS. Diagnostic Impact of Subcutaneous Edema in Gouty Feet Detected by Dual-Energy Computed Tomography and Ultrasound. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(24):7620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247620
Chicago/Turabian StyleHeld, Julia, Christoph Strolz, Monique Reijnierse, Mihra Taljanovic, Pietro G. Lacaita, Miar Ouaret, Elke R. Gizewski, Günter Weiss, and Andrea S. Klauser. 2024. "Diagnostic Impact of Subcutaneous Edema in Gouty Feet Detected by Dual-Energy Computed Tomography and Ultrasound" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 24: 7620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247620
APA StyleHeld, J., Strolz, C., Reijnierse, M., Taljanovic, M., Lacaita, P. G., Ouaret, M., Gizewski, E. R., Weiss, G., & Klauser, A. S. (2024). Diagnostic Impact of Subcutaneous Edema in Gouty Feet Detected by Dual-Energy Computed Tomography and Ultrasound. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(24), 7620. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13247620






