Association Between Transient Hemodialysis and Risk of Bleeding During Peritoneal Dialysis Catheterization
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Data Collection and Assessment
2.3. Catheter Type and Placement
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical Characteristics of the Patients
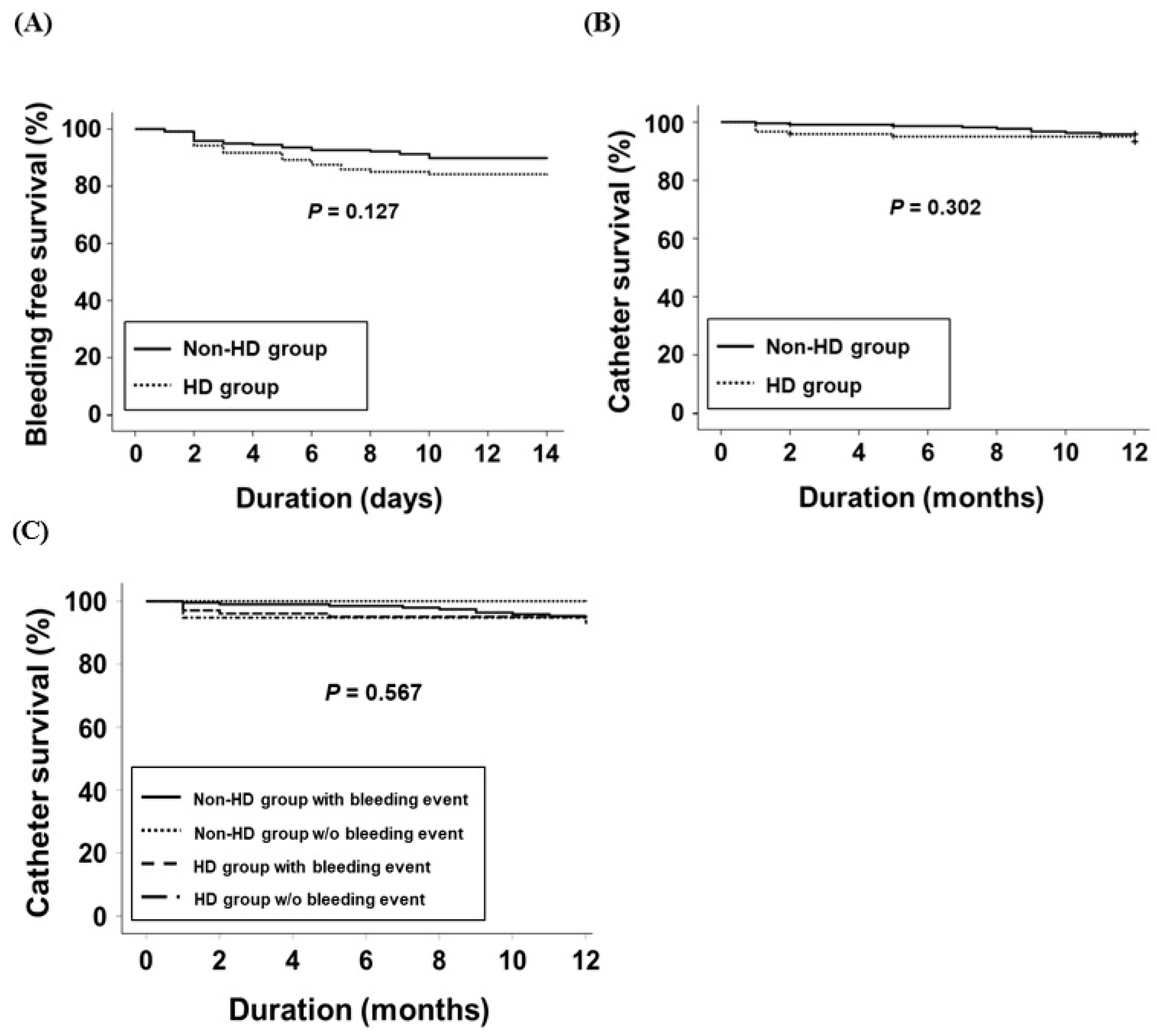
3.2. Complications Following PDC Insertion
3.3. Catheter Survival
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sohal, A.S.; Ganji, A.S.; Crowther, M.A.; Treleaven, D. Uremic bleeding: Pathophysiology and clinical risk factors. Thromb. Res. 2006, 118, 417–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.; Lin, T.; Huang, N.; Xia, X.; Li, J.; Qiu, Y.; Yang, X.; Mao, H.; Huang, F. Plasma fibrinogen and mortality in patients undergoing peritoneal dialysis: A prospective cohort study. BMC Nephrol. 2020, 17, 349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlieper, G.; Hess, K.; Floege, J.; Marx, N. The vulnerable patient with chronic kidney disease. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2016, 31, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mital, S.; Frie, L.F.; Piraino, B. Bleeding complications associated with peritoneal dialysis catheter. Perit. Dial. Int. 2004, 24, 478–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peppelenbosch, A.; van Kuijk, W.H.; Bouvy, N.D.; van der Sande, F.M.; Tordoir, J.H. Peritoneal dialysis catheter placement technique and complications. NTD Plus 2008, 1, iv23–iv28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.R.; Chen, C.H.; Chiu, K.Y.; Yang, C.R.; Cheng, C.L.; Ou, Y.C.; Ko, J.L.; Ho, H.C. Management of pericannular bleeding after peritoneal dialysis catheter placement. Perit. Dial. Int. 2012, 32, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, L.W.; Li, Q.C.; Yu, Z.L.; Zhang, L.L.; Liu, Q.; Li, Y.; Ou, S.T. Abdominal hemorrhage after peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion: A rare cause of luteal rupture: A case report. World J. Clin. Cases 2021, 9, 6510–6514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, S.J.; Dehoney, S.B.; Hooper, J.S.; Amanzadeh, J.; Busti, A.J. Evidence-based treatment recommendations for uremic bleeding. Nat. Clin. Pract. Nephrol. 2007, 3, 138–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weigert, A.L.; Schafer, A.I. Uremic bleeding: Pathogenesis and therapy. Am. J. Med. Sci. 1998, 316, 94–104. [Google Scholar]
- Palevsky, P.M. Perioperative management of patients with chronic kidney disease or ESRD. Best. Pract. Res. Clin. Anaesthesiol. 2004, 18, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnar, A.O.; Hiremath, S.; Brown, P.A.; Akbari, A. Risk factors for unplanned and crash dialysis starts: A protocol for a systematic review and meta-analysis. Syst. Rev. 2016, 5, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Shamy, O. Does temporary hemodialysis before peritoneal dialysis initiation affect patient outcomes? Kidney Int. Rep. 2022, 11, 1734–1736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frenkel, W.J.; Jongerius, E.J.; Mandjes-van Uitert, M.J.; van Munster, B.C.; de Rooij, S.E. Validation of the Charlson Comorbidity Index in acutely hospitalized elderly adults: A prospective cohort study. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2014, 62, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chow, K.M.; Li, P.K.; Cho, Y.; Abu-Alfa, A.; Bavanandan, S.; Brown, E.A.; Cullis, B.; Edwards, D.; Ethier, I.; Hurst, H.; et al. ISPD catheter-related Infection Recommendations; 2023 Update. Perit. Dial. Int. 2023, 43, 201–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang, S.H.; Park, J.W.; Cho, K.H.; Do, J.Y. Comparison of peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion techniques by nephrologists: Surgical vs blind methods. Semin. Dial. 2021, 34, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remuzzi, G. Bleeding in renal failure. Lancet 1988, 1, 1205–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Figueiredo, A.; Goh, B.L.; Jenkins, S.; Johnson, D.W.; Mactier, R.; Ramalakshmi, S.; Shrestha, B.; Struijk, D.; Wilkie, M. Clinical practice guidelines for peritoneal access. Perit. Dial. Int. 2010, 30, 424–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crabtree, J.H.; Chow, K.M. Peritoneal dialysis catheter insertion. Semin. Nephrol. 2017, 37, 17–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, R.V.; Mehta, R.H.; Al Badr, W.; Cooper, J.V.; Eva, K.J.; Kim, A.E. Influence of concurrent renal dysfunction on outcomes of patients with acute coronary syndromes and implication of the use of glycoprotein Iib/IIIa inhibitors. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2003, 41, 718–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Segal, J.B.; McNamara, R.L.; Miller, M.R.; Kim, N.; Goodman, S.N.; Powe, N.R.; Robinson, K.A.; Bass, E.B. Prevention of thromboembolism in atria1 fibrillation. A meta-analysis of trials of anticoagulants and antiplatelet drugs. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2000, 15, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rabiner, S.F. The effect of dialysis on platelet function of patients with renal failure. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 1972, 201, 234–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindsay, R.M.; Friesen, M.; Aronstam, A.; Andrus, F.; Clar, W.F.; Linton, A.L. Improvement of platelet function by increased frequency of hemodialysis. Clin. Nephrol. 1978, 10, 67–70. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, I.; Majeed, I.; Powell, R. Heparin induced thrombocytopenia: Diagnosis and management update. Postgrad. Med. J. 2007, 83, 575–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palmer, R.L. Laboratory diagnosis of bleeding disorders. Basic screening tests. Postgrad. Med. 1984, 76, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thachil, J.; Gatt, A.; Martlew, V. Management of surgical patients receiving anticoagulation and antiplatelet agents. Br. J. Surg. 2008, 95, 1437–1448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, P.; Peterson, L.B.; Binko, T.S.; Perterson, J.P.; Fornitz, G.G. Slightly elevated international normalized ratio predicts bleeding episodes in patients treated with direct oral anticoagulants. J. Int. Med. Res. 2020, 48, 0300060519894439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiner, R.W.; Coggins, C.; Carvalho, A.C. Bleeding time in uremia: A useful test to assess clinical bleeding. Am. J. Hematol. 1979, 7, 107–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Non-HD (n = 216) | HD (n = 120) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 57.5 ± 12.6 | 52.4 ± 14.0 | <0.001 |
| Sex (male) | 125 (57.9%) | 87 (72.5%) | 0.008 |
| CCI score | 5.1 ± 1.9 | 4.7 ± 2.0 | 0.028 |
| Diabetes | 131 (60.6%) | 70 (58.3%) | 0.678 |
| Hypertension | 180 (83.3%) | 93 (77.5%) | 0.189 |
| Use of AP or AC agents | 70 (32.4%) | 36 (30%) | 0.649 |
| Blood urea nitrogen (mg/dL) | 81.7 ± 24.7 | 97.2 ± 32.6 | <0.001 |
| Serum creatinine (mg/dL) | 7.5 ± 2.4 | 10.3 ± 4.2 | <0.001 |
| Platelet (K/μL) | 206 ± 74 | 215 ± 77 | 0.275 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 9.3 ± 1.3 | 8.9 ± 1.5 | 0.008 |
| INR | 1.0 ± 0.1 | 1.0 ± 0.3 | 0.241 |
| Operation method | 0.592 | ||
| Blind method | 136 (63%) | 72 (60%) | |
| Surgical method | 80 (37%) | 48 (40%) |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| HD group (ref: non-HD group) | 1.60 (0.87–2.95) | 0.134 | 1.81 (0.93–3.52) | 0.082 |
| Age (increase by 1 year) | 1.01 (0.98–1.03) | 0.583 | — | |
| Sex (ref: male) | 0.79 (0.41–1.53) | 0.488 | — | |
| CCI score (increase 1 score) | 1.09 (0.93–1.26) | 0.285 | — | |
| Use of AP or AC agents | 1.39 (0.74–2.60) | 0.308 | — | |
| BUN (increase by 1 mg/dL) | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.479 | — | |
| Serum Cr (increase by 1 mg/dL) | 0.95 (0.86–1.05) | 0.297 | 0.90 (0.80–1.00) | 0.051 |
| Platelet (K/μL) | 1.00 (0.99–1.00) | 0.077 | 0.99 (0.99–1.00) | 0.052 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 0.83 (0.66–1.05) | 0.114 | 0.79 (0.61–1.00) | 0.054 |
| INR | 2.17 (1.28–3.68) | 0.004 | 2.17 (1.20–3.92) | 0.010 |
| Univariate | ||
|---|---|---|
| HR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
| HD group (ref: non-HD group) | 1.64 (0.63–4.25) | 0.308 |
| Age (increase by 1 year) | 0.99 (0.96–1.04) | 0.905 |
| Sex (ref: male) | 0.35 (0.10–1.23) | 0.103 |
| CCI score (increase 1 score) | 1.04 (0.82–1.33) | 0.734 |
| Use of AP or AC agents | 1.51 (0.57–3.96) | 0.405 |
| BUN (increase by 1 mg/dL) | 1.01 (0.99–1.02) | 0.364 |
| Platelet (K/μL) | 1.00 (0.99–1.01) | 0.431 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 1.13 (0.81–1.60) | 0.471 |
| INR | 1.18 (0.23–6.19) | 0.842 |
| Operation method (ref: blind) | 0.88 (0.33–2.38) | 0.803 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kim, A.Y.; Cho, K.H.; Park, J.W.; Do, J.Y.; Kang, S.H. Association Between Transient Hemodialysis and Risk of Bleeding During Peritoneal Dialysis Catheterization. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13237188
Kim AY, Cho KH, Park JW, Do JY, Kang SH. Association Between Transient Hemodialysis and Risk of Bleeding During Peritoneal Dialysis Catheterization. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(23):7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13237188
Chicago/Turabian StyleKim, A Young, Kyu Hyang Cho, Jong Won Park, Jun Young Do, and Seok Hui Kang. 2024. "Association Between Transient Hemodialysis and Risk of Bleeding During Peritoneal Dialysis Catheterization" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 23: 7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13237188
APA StyleKim, A. Y., Cho, K. H., Park, J. W., Do, J. Y., & Kang, S. H. (2024). Association Between Transient Hemodialysis and Risk of Bleeding During Peritoneal Dialysis Catheterization. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(23), 7188. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13237188





