One Year Follow-Up Assessment of Impact of Rigorous Diet Regimen and Adequate C-PAP Therapy on Obese Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Subjects
2.2. Study Design
2.3. Body Mass Index
2.4. Polysomnography
2.5. Epworth Sleepiness Scale Questionnaire
2.6. Diet Regimen
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Age and Sex Distribution
3.2. Body Mass Index (BMI)
3.3. Apnea–Hypopnea Index (AHI)
3.4. Time Spent with Oxygen Saturation Below 90% (TST90)
3.5. Epworth Sleepiness Scale (ESS)
3.6. Within-Group Comparisons
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sateia, M.J. International classification of sleep disorders-third edition: Highlights and modifications. Chest 2014, 146, 1387–1394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.G.; Ramar, K.; Olson, E.J. Updates on definition, consequences and management of obstructive sleep apnea. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2011, 86, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.R. Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Ann. Intern. Med. 2019, 171, ITC81–ITC96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mannarino, M.R.; Di Filippo, F.; Pirro, M. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2012, 23, 586–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carratù, P.; Di Ciaula, A.; Dragonieri, S.; Ranieri, T.; Ciccone, M.M.; Portincasa, P.; Resta, O. Relationships between Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome and Cardiovascular risk in a naïve population of Southern Italy. Int. J. Clin. Pract. Dec. 2021, 75, e14952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasai, T.; Floras, J.S.; Bradley, T.D. Sleep apnea and cardiovascular disease: A bidirectional relationship. Circulation 2012, 126, 1495–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castaneda, A.; Jauregui-Maldonado, E.; Ratnani, I.; Varon, J.; Surani, S. Correlation between metabolic syndrome and sleep apnea. World J. Diabetes 2018, 9, 66–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ota, H.; Fujita, Y.; Yamauchi, M.; Muro, S.; Kimura, H.; Takasawa, S. Relationship Between Intermittent Hypoxia and Type 2 Diabetes in Sleep Apnea Syndrome. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkataraman, S.; Vungarala, S.; Covassin, N.; Somers, V.K. Sleep Apnea, Hypertension and the Sympathetic Nervous System in the Adult Population. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foldvary-Schaefer, N.R.; Waters, T.E. Sleep-Disordered Breathing. Continuum (MinneapMinn). Sleep Neurol. 2017, 4, 1093–1116. [Google Scholar]
- Franklin, K.A.; Lindberg, E. Obstructive sleep apnea is a common disorder in the population—A review on the epidemiology of sleep apnea. J. Thorac. Dis. 2015, 7, 1311–1322. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Punjabi, N.M. The epidemiology of adult obstructive sleep apnea. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 136–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Fan, J.; Guo, Y.; Zhou, J.; Chen, F.; Jin, Z.; Li, Y. Association between obstructive sleep apnoea syndrome and the risk of cardiovascular diseases: An updated systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2020, 71, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNellis, R.J.; Thomas, S. Screening for Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Adults. Am. Fam. Physician 2017, 96, 123–124. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Young, T.; Skatrud, J.; Peppard, P.E. Risk factors for obstructive sleep apnea in adults. JAMA 2004, 291, 2013–2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, A.R.; Patil, S.P.; Laffan, A.M.; Polotsky, V.; Schneider, H.; Smith, P.L. Obesity and obstructive sleep apnea: Pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic approaches. Proc. Am. Thorac. Soc. 2008, 5, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laratta, C.R.; Ayas, N.T.; Povitz, M.; Pendharkar, S.R. Diagnosis and treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. CMAJ 2017, 189, E1481–E1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, M.F.; Zito, A.; Carratù, P.; Falcone, V.A.; Bega, E.; Scicchitano, P.; Ciccone, M.; Resta, O. Obstructive Sleep Apnea, Hypertension, and Their Additive Effects on Atherosclerosis. Biochem. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 984193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero-Corral, A.; Caples, S.M.; Lopez-Jimenez, F.; Somers, V.K. Interactions between obesity and obstructive sleep apnea: Implications for treatment. Chest 2010, 137, 711–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gangitano, E.; Martinez-Sanchez, N.; Bellini, M.I.; Urciuoli, I.; Monterisi, S.; Mariani, S.; Ray, D.; Gnessi, L. Weight Loss and Sleep, Current Evidence in Animal Models and Humans. Nutrients 2023, 15, 3431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muscogiuri, G.; Barrea, L.; Annunziata, G.; Di Somma, C.; Laudisio, D.; Colao, A.; Savastano, S. Obesity and sleep disturbance: The chicken or the egg? Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019, 59, 2158–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araghi, M.H.; Chen, Y.F.; Jagielski, A.; Choudhury, S.; Banerjee, D.; Hussain, S.; Thomas, G.N.; Taheri, S. Effectiveness of lifestyle interventions on obstructive sleep apnea (OSA): Systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep 2013, 36, 1553–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davies, R.J.; Harrington, K.J.; Ormerod, O.J.; Stradling, J.R. Nasal continuous positive airway pressure in chronic heart failure with sleep-disordered breathing. Am. Rev. Respir. Dis. 1993, 147, 630–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakker, J.P.; Weaver, T.E.; Parthasarathy, S.; Aloia, M.S. Adherence to CPAP: What Should We Be Aiming For, and How Can We Get There? Chest 2019, 155, 1272–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawyer, A.M.; Gooneratne, N.S.; Marcus, C.L.; Ofer, D.; Richards, K.C.; Weaver, T.E. A systematic review of CPAP adherence across age groups: Clinical and empiric insights for developing CPAP adherence interventions. Sleep Med. Rev. 2011, 15, 343–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, Y.; Cui, X.; Zhu, X.; Guo, H.; Zhou, Q.; Yuan, P.; Cheng, H.; Wu, W. Effect of Weight Loss on the Apnea Hypopnea Index is Related to Waist Circumference in Chinese Adults with Overweight and Obesity. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. 2024, 17, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshaer, H.; Ryan, C.; Fernie, G.R.; Bradley, T.D. Reproducibility and predictors of the apnea hypopnea index across multiple nights. Sleep Sci. 2018, 11, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iber, C.; Ancoli-Israel, S.; Chesson, A.; Quan, S. The AASM Manual for the Scoring of Sleep and Associated Events: Rules, Terminology and Technical Specifications; American Academy of Sleep Medicine: Westchester, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Johns, M.W. A New Method for Measuring Daytime Sleepiness: The Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 1991, 14, 540–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johns, M.W. Reliability and Factor Analysis of the Epworth Sleepiness Scale. Sleep 1992, 15, 376–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damiani, M.F.; Quaranta, V.N.; Falcone, V.A.; Gadaleta, F.; Maiellari, M.; Ranieri, T.; Fanfulla, F.; Carratù, P.; Resta, O. The Epworth Sleepiness Scale: Conventional self vs physician administration. Chest 2013, 143, 1569–1575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumesnil, J.G.; Turgeon, J.; Tremblay, A.; Poirier, P.; Gilbert, M.; Gagnon, L.; St-Pierre, S.; Garneau, C.; Lemieux, I.; Pascot, A.; et al. Effect of a low-glycaemic index–low-fat–high protein diet on the atherogenic metabolic risk profile of abdominally obese men. Br. J. Nutr. 2001, 86, 557–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, G.; Zhuge, P.; Zhang, Z.; Ma, J. The impact of continuous positive airway pressure therapy on cardiovascular events in patients with obstructive sleep apnoea: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Breath 2024. [CrossRef]
- Igelström, H.; Emtner, M.; Lindberg, E.; Åsenlöf, P. Tailored behavioral medicine intervention for enhanced physical activity and healthy eating in patients with obstructive sleep apnea syndrome and overweight. Sleep Breath 2014, 18, 655–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobrosielski, D.A.; Papandreou, C.; Susheel, P.P.; Salas-Salvadó, J. Diet and exercise in the management of obstructive sleep apnoea and cardiovascular disease risk. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2017, 26, 160110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudgel, D.W.; Patel, S.R.; Ahasic, A.M.; Bartlett, S.J.; Bessesen, D.H.; Coaker, M.A.; Grunstein, R.R.; Gurubhagavatula, I.; Kapur, V.; Lettieri, C.J.; et al. The Role of Weight Management in the Treatment of Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea. An Official American Thoracic Society Clinical Practice Guideline. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 70–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epstein, L.J.; Kristo, D.; Strollo, P.J.; Friedman, N.; Malhotra, A.; Patil, S.P.; Ramar, K.; Rogers, R.; Schwab, R.J.; Weaver, E.M.; et al. Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. J. Clin. Sleep Med. 2009, 5, 263–276. [Google Scholar]
- Chirinos, J.A.; Gurubhagavatula, I.; Teff, K.; Rader, D.J.; Wadden, T.A.; Townsend, R.; Foster, G.D.; Maislin, G.; Saif, H.; Broderick, P.; et al. CPAP, weight loss, or both for obstructive sleep apnea. N. Engl. J. Med. 2014, 370, 2265–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malhotra, A.; Heilmann, C.R.; Banerjee, K.K.; Dunn, J.P.; Bunck, M.C.; Bednarik, J. Weight reduction and the impact on apnea-hypopnea index: A systematic meta-analysis. Sleep Med. 2024, 121, 26–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| 60 Individuals Obese, with OSA | |
|---|---|
| AGE m ± sd | 56.75 ± 14.90 |
| SEX f n (%) | 20 (33.3) |
| BMI m ± sd | 38.10 ± 3.52 |
| AHI m ± sd | 46.20 ± 13.13 |
| ODI m ± sd | 45.04 ± 14.10 |
| TST90 m ± sd | 25.45 ± 8.34 |
| ESS m ± sd | 14.35 ± 2.79 |
| Group 1 Perfect Diet and CPAP Adherence Compliance N = 20 | Group 2 Moderate Diet and CPAP Adherence Compliance N = 20 | Group 3 Insufficient Diet and CPAP Adherence Compliance N = 20 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| AGE m ± SD | 54.22 ± 16.88 | 59.66 ± 13.25 | 56.37 ± 14.60 | 0.515 |
| SEX n (%) | 4 (20) | 9 (45) | 7 (35) | 0.241 |
| T0_BMI m ± SD | 39.75 ± 3.99 | 36.45 ± 2.23 | 38.10 ± 3.44 | 0.010 |
| T0_AHI m ± SD | 53.81 ± 13.99 | 37.76 ± 5.72 | 47.02 ± 13.06 | 0.000 |
| T0_ODI m ± SD | 50.84 ± 15.70 | 41.19 ± 12.29 | 43.08 ± 12.83 | 0.070 |
| T0_TST90 m ± SD | 28.20 ± 9.12 | 20.55 ± 5.16 | 27.60 ± 8.24 | 0.004 |
| T0_ESS m ± SD | 14.85 ± 3.39 | 13.95 ± 1.93 | 14.25 ± 2.91 | 0.591 |
| T1_BMI m ± SD | 32.70 ± 3.35 | 31.00 ± 2.44 | 36.40 ± 3.21 | 0.000 |
| T1_AHI m ± SD | 37.68 ± 11.88 | 27.80 ± 5.59 | 42.98 ± 11.88 | 0.000 |
| T1_ODI m ± SD | 37.77 ± 9.96 | 33.49 ± 10.27 | 39.50 ± 11.81 | 0.198 |
| T1_TST90 m ± SD | 18.20 ± 5.82 | 14.20 ± 4.03 | 24.95 ± 7.51 | 0.000 |
| T1_ESS m ± SD | 10.55 ± 2.08 | 10.15 ± 1.95 | 12.80 ± 2.66 | 0.000 |
| Perfect Diet and C-PAP Adherence N = 20 | Insufficient Diet and C-PAP Adherence N = 20 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| AGE m ± SD | 54.22 ± 16.88 | 56.37 ± 14.60 | 0.668 |
| SEX n (%) | 4 (20) | 7 (35) | 0.378 |
| T0_BMI m ± SD | 39.75 ± 3.99 | 38.10 ± 3.44 | 0.170 |
| T0_AHI m ± SD | 53.81 ± 13.99 | 47.02 ± 13.06 | 0.121 |
| T0_ODI m ± SD | 50.84 ± 15.70 | 43.08 ± 12.83 | 0.095 |
| T0_TST90 m ± SD | 28.20 ± 9.12 | 27.60 ± 8.24 | 0.828 |
| T0_ESS m ± SD | 14.85 ± 3.39 | 14.25 ± 2.91 | 0.552 |
| T1_BMI m ± SD | 32.70 ± 3.35 | 36.40 ± 3.21 | 0.001 |
| T1_AHI m ± SD | 37.68 ± 11.88 | 42.98 ± 11.88 | 0.166 |
| T1_ODI m ± SD | 37.77 ± 9.96 | 39.50 ± 11.81 | 0.620 |
| T1_TST90 m ± SD | 18.20 ± 5.82 | 24.95 ± 7.51 | 0.004 |
| DeltaTST90 | −10.00 ± 4.71 | −2.65 ± 0.93 | 0.000 |
| %ReductionTST90 | 34.56 ± 9.35 | 10.05 ± 3.59 | 0.000 |
| T1_ESS m ± SD | 10.55 ± 2.08 | 12.80 ± 2.66 | 0.005 |
| Group 1 Perfect Diet and C-PAP Adherence Compliance N = 20 | Group 2 Moderate Diet and C-PAP Adherence N = 20 | Group 3 Insufficient Diet and C-PAP Adherence Compliance N = 20 | p Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DeltaTST90 | −10.00 ± 4.71 | −6.35 ± 2.43 | −2.65 ± 0.93 | 0.000 |
| °, %ReductionTST90 | 34.56 ± 9.35 | 30.63 ± 9.78 | 10.05 ± 3.59 | 0.000 |
| °, Delta ESS | −4.30 ± 2.05 | −3.80 ± 1.47 | −1.45 ± 0.75 | 0.000 |
| %ReductionESS | 27.70 ± 11.28 | 27.17 ± 9.76 | 10.04 ± 4.87 | 0.000 |
| *,,° DeltaAHI m ± SD | −16.13 ± 5.18 | −9.96 ± 1.78 | −4.04 ± 1.62 | 0.000 |
| °, %ReductionAHI | 30.56 ± 7.07 | 26.80 ± 5.64 | 8.58 ± 2.27 | 0.000 |
| *,,° DeltaBMI m ± SD | −7.05 ± 1.57 | −5.54 ± 1.23 | −1.70 ± 0.47 | 0.000 |
| °, %ReductionBMI | 17.70 ± 3.37 | 14.98 ± 3.44 | 4.43 ± 1.12 | 0.000 |
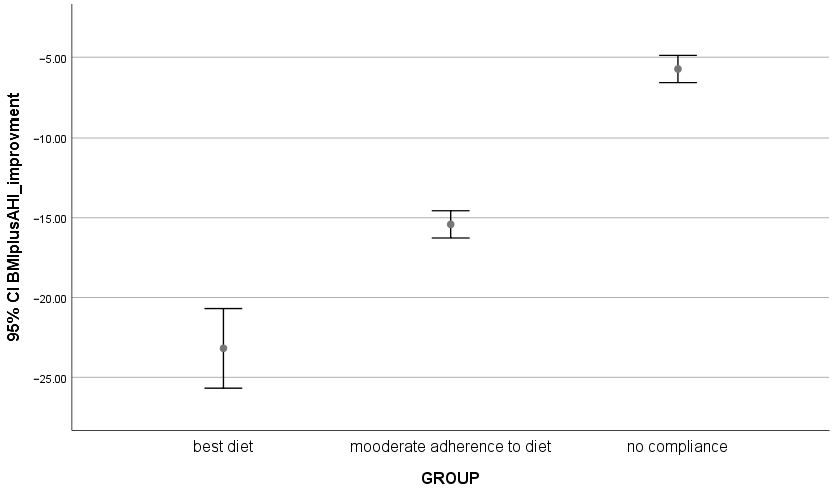
| *,,° BMI + AHI improvement ± SD | −23.18 ± 1.18 | −15.41 ± 1.82 | −5.74 ± 1.82 | 0.000 |
| Group 1 Perfect Diet and CPAP Adherence Compliance N = 20 | Group 2 Moderate Diet and CPAP Adherence Compliance N = 20 | Group 3 Insufficient Diet and CPAP Adherence Compliance N = 20 | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Parameters | T0 | T1 | p | T0 | T1 | p | T0 | T1 | p |
| BMI m ± SD | 39.75 ± 3.99 | 32.70 ± 3.35 | 0.000 | 36.45 ± 2.23 | 31.00 ± 2.44 | 0.000 | 38.10 ± 3.44 | 36.40 ± 3.21 | 0.003 |
| AHI m ± SD | 53.81 ± 13.99 | 37.68 ± 11.88 | 0.000 | 37.76 ± 5.72 | 27.80 ± 5.59 | 0.000 | 47.02 ± 13.06 | 42.98 ± 11.88 | 0.010 |
| ODI m ± SD | 50.84 ± 15.70 | 37.77 ± 9.96 | 0.000 | 41.19 ± 12.29 | 33.49 ± 10.27 | 0.000 | 43.08 ± 12.83 | 39.50 ± 11.81 | 0.003 |
| TST 90 m ± SD | 28.20 ± 9.12 | 18.20 ± 5.82 | 0.000 | 20.55 ± 5.16 | 14.20 ± 4.03 | 0.000 | 27.60 ± 8.24 | 24.95 ± 7.51 | 0.020 |
| ESS m ± SD | 14.85 ± 3.39 | 10.55 ± 2.08 | 0.000 | 13.95 ± 1.93 | 10.15 ± 1.95 | 0.000 | 14.25 ± 2.91 | 12.80 ± 2.66 | 0.020 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Carratù, P.; Dragonieri, S.; Quaranta, V.N.; Resta, O.; Portincasa, P.; Palmieri, V.O.; Carpagnano, G.E. One Year Follow-Up Assessment of Impact of Rigorous Diet Regimen and Adequate C-PAP Therapy on Obese Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13216360
Carratù P, Dragonieri S, Quaranta VN, Resta O, Portincasa P, Palmieri VO, Carpagnano GE. One Year Follow-Up Assessment of Impact of Rigorous Diet Regimen and Adequate C-PAP Therapy on Obese Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(21):6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13216360
Chicago/Turabian StyleCarratù, Pierluigi, Silvano Dragonieri, Vitaliano Nicola Quaranta, Onofrio Resta, Piero Portincasa, Vincenzo Ostilio Palmieri, and Giovanna Elisiana Carpagnano. 2024. "One Year Follow-Up Assessment of Impact of Rigorous Diet Regimen and Adequate C-PAP Therapy on Obese Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Retrospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 21: 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13216360
APA StyleCarratù, P., Dragonieri, S., Quaranta, V. N., Resta, O., Portincasa, P., Palmieri, V. O., & Carpagnano, G. E. (2024). One Year Follow-Up Assessment of Impact of Rigorous Diet Regimen and Adequate C-PAP Therapy on Obese Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea Syndrome: A Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(21), 6360. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13216360










