Safety and Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein 2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Transplant Recipients: Synthesis of Evidence
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Eligibility Criteria
2.3. Literature Search
2.4. Study Selection
2.5. Data Collection
2.6. Risk of Bias Assessment
2.7. Statistical Analysis
2.8. Certainty of Evidence
3. Results
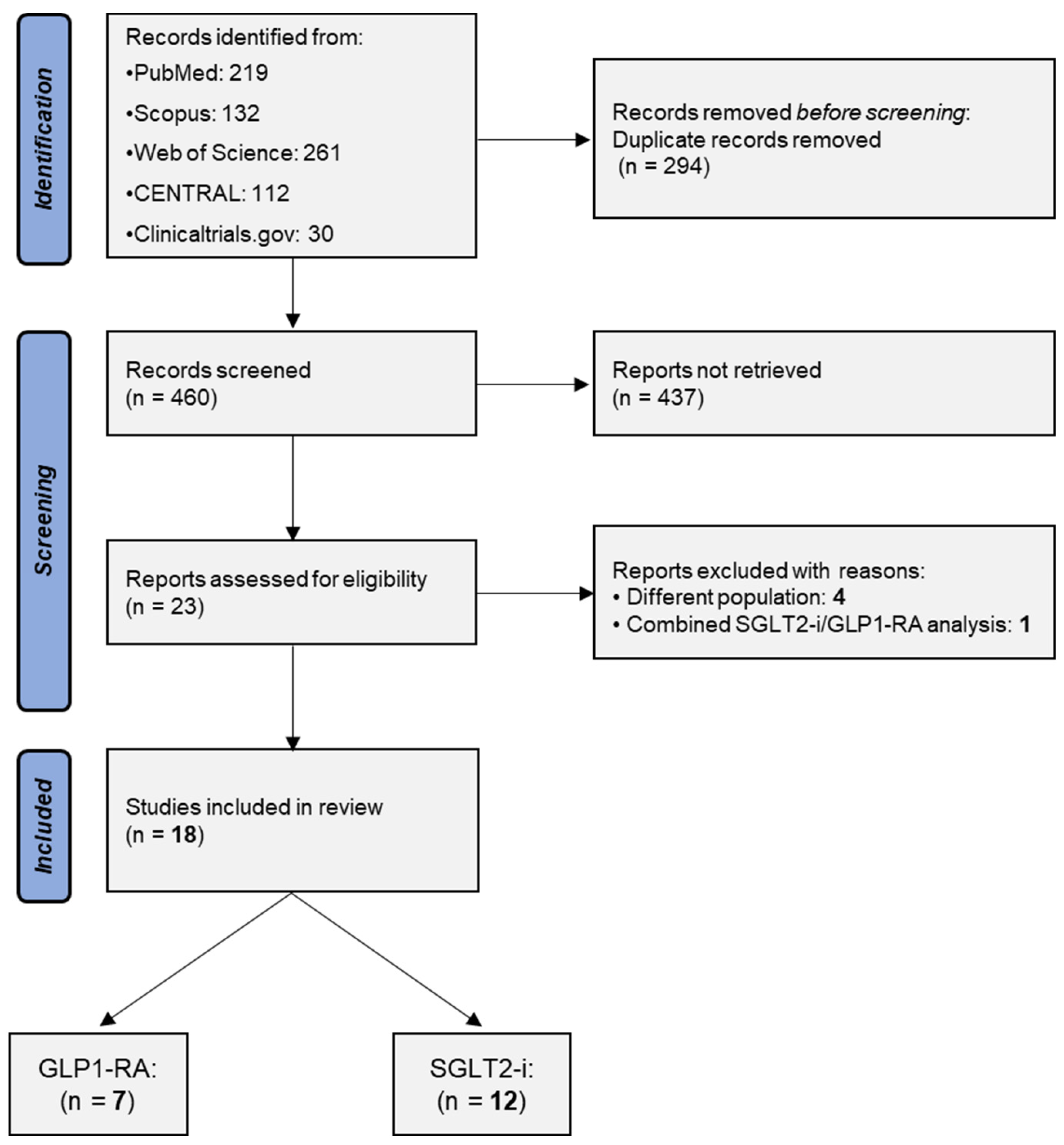
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Included Studies
3.3. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists
3.3.1. HbA1c
3.3.2. Body Weight
| Covariate | HbA1c | Weight | eGFR | Systolic Blood Pressure |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GLP1-RA | ||||
| Study location | 0.634 | 0.368 | 0.701 | NA |
| Study design | NA | NA | NA | NA |
| Follow-up | 0.008 | 0.126 | 0.265 | NA |
| Risk of bias | 0.945 | 0.511 | 0.605 | NA |
| SGLT2-i | ||||
| Study location | 0.423 | 0.807 | 0.247 | 0.035 |
| Study design | 0.273 | 0.823 | 0.666 | 0.969 |
| Follow-up | 0.050 | 0.572 | 0.868 | 0.518 |
| Risk of bias | 0.080 | 0.909 | 0.494 | 0.035 |
3.3.3. eGFR
3.3.4. Systolic Blood Pressure
3.3.5. Urinary Protein Excretion
3.3.6. Safety
3.4. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitors
3.4.1. HbA1c
3.4.2. Body Weight
3.4.3. eGFR
3.4.4. Systolic Blood Pressure
3.4.5. Urinary Protein Excretion
3.4.6. Patient and Graft Survival
3.4.7. Cardiovascular Events
3.4.8. Safety
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ojo, A.O.; Hanson, J.A.; Wolfe, R.A.; Leichtman, A.B.; Agodoa, L.Y.; Port, F.K. Long-Term Survival in Renal Transplant Recipients with Graft Function. Kidney Int. 2000, 57, 307–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangaswami, J.; Mathew, R.O.; Parasuraman, R.; Tantisattamo, E.; Lubetzky, M.; Rao, S.; Yaqub, M.S.; Birdwell, K.A.; Bennett, W.; Dalal, P.; et al. Cardiovascular Disease in the Kidney Transplant Recipient: Epidemiology, Diagnosis and Management Strategies. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 760–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aziz, F.; Jorgenson, M.; Garg, N.; Parajuli, S.; Mohamed, M.; Raza, F.; Mandelbrot, D.; Djamali, A.; Dhingra, R. New Approaches to Cardiovascular Disease and Its Management in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2022, 106, 1143–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Podestà, M.A.; Cucchiari, D.; Ciceri, P.; Messa, P.; Torregrosa, J.V.; Cozzolino, M. Cardiovascular Calcifications in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2022, 37, 2063–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chukwu, C.A.; Rao, A.; Middleton, R.; Kalra, P.A. Post-Transplant Cardiovascular Disease in Kidney Transplant Recipients: Incidence, Risk Factors, and Outcomes in the Era of Modern Immunosuppression. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Jardine, M.J.; Neal, B.; Bompoint, S.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Charytan, D.M.; Edwards, R.; Agarwal, R.; Bakris, G.; Bull, S.; et al. Canagliflozin and Renal Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes and Nephropathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 2295–2306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Stefánsson, B.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Chertow, G.M.; Greene, T.; Hou, F.-F.; Mann, J.F.E.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Lindberg, M.; Rossing, P.; et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1436–1446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The EMPA-KIDNEY Collaborative Group; Herrington, W.G.; Staplin, N.; Wanner, C.; Green, J.B.; Hauske, S.J.; Emberson, J.R.; Preiss, D.; Judge, P.; Mayne, K.J.; et al. Empagliflozin in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staplin, N.; Haynes, R.; Judge, P.K.; Wanner, C.; Green, J.B.; Emberson, J.; Preiss, D.; Mayne, K.J.; Ng, S.Y.A.; Sammons, E.; et al. Effects of Empagliflozin on Progression of Chronic Kidney Disease: A Prespecified Secondary Analysis from the Empa-Kidney Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2024, 12, 39–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, N.; Lee, M.M.Y.; Kristensen, S.L.; Branch, K.R.H.; Del Prato, S.; Khurmi, N.S.; Lam, C.S.P.; Lopes, R.D.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Pratley, R.E.; et al. Cardiovascular, Mortality, and Kidney Outcomes with GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomised Trials. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaman, A.M.; Bain, S.C.; Bakris, G.L.; Buse, J.B.; Idorn, T.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.E.; Nauck, M.A.; Rasmussen, S.; Rossing, P.; et al. Effect of the Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Semaglutide and Liraglutide on Kidney Outcomes in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: Pooled Analysis of SUSTAIN 6 and LEADER. Circulation 2022, 145, 575–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkovic, V.; Tuttle, K.R.; Rossing, P.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Mann, J.F.E.; Bakris, G.; Baeres, F.M.M.; Idorn, T.; Bosch-Traberg, H.; Lausvig, N.L.; et al. Effects of Semaglutide on Chronic Kidney Disease in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2024, 391, 109–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 Statement: An Updated Guideline for Reporting Systematic Reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Savović, J.; Page, M.J.; Elbers, R.G.; Blencowe, N.S.; Boutron, I.; Cates, C.J.; Cheng, H.-Y.; Corbett, M.S.; Eldridge, S.M.; et al. RoB 2: A Revised Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Randomised Trials. BMJ 2019, 366, l4898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.; Hernán, M.A.; Reeves, B.C.; Savović, J.; Berkman, N.D.; Viswanathan, M.; Henry, D.; Altman, D.G.; Ansari, M.T.; Boutron, I.; et al. ROBINS-I: A Tool for Assessing Risk of Bias in Non-Randomised Studies of Interventions. BMJ 2016, 355, i4919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papadimitropoulou, K.; Riley, R.D.; Dekkers, O.M.; Stijnen, T.; le Cessie, S. MA-Cont:Pre/Post Effect Size: An Interactive Tool for the Meta-Analysis of Continuous Outcomes Using R Shiny. Res. Synth. Methods 2022, 13, 649–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, L.; Xu, C. Arcsine-Based Transformations for Meta-Analysis of Proportions: Pros, Cons, and Alternatives. Health Sci. Rep. 2020, 3, e178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying Heterogeneity in a Meta-Analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and Fill: A Simple Funnel-Plot-Based Method of Testing and Adjusting for Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ioannidis, J.P.A.; Trikalinos, T.A. The Appropriateness of Asymmetry Tests for Publication Bias in Meta-Analyses: A Large Survey. Can. Med. Assoc. J. 2007, 176, 1091–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guyatt, G.; Oxman, A.D.; Akl, E.A.; Kunz, R.; Vist, G.; Brozek, J.; Norris, S.; Falck-Ytter, Y.; Glasziou, P.; deBeer, H.; et al. GRADE Guidelines: 1. Introduction—GRADE Evidence Profiles and Summary of Findings Tables. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2011, 64, 383–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dotan, I.; Rudman, Y.; Turjeman, A.; Akirov, A.; Steinmetz, T.; Calvarysky, B.; Cohen, T.D. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients with Diabetes Mellitus. Transplantation 2024, 108, e121–e128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Pesavento, T.E.; Washburn, K.; Walsh, D.; Meng, S. Largest Single-Centre Experience of Dulaglutide for Management of Diabetes Mellitus in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2019, 21, 1061–1065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thangavelu, T.; Lyden, E.; Shivaswamy, V. A Retrospective Study of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists for the Management of Diabetes After Transplantation. Diabetes Ther. 2020, 11, 987–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweiss, H.; Hall, R.; Zeilmann, D.; Escamilla, J.; Bhayana, S.; Patel, R.; Long, C. Single-Center Evaluation of Safety & Efficacy of Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Solid Organ Transplantation. Prog. Transplant. 2022, 32, 357–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yugueros González, A.; Kanter, J.; Sancho, A.; Gavela, E.; Solá, E.; Ávila, A.; Pallardó, L.M. Institutional Experience with New Antidiabetic Drugs in Kidney Transplant. Transplant. Proc. 2021, 53, 2678–2680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schork, A.; Eberbach, M.-L.; Artunc, F.; Bohnert, B.N.; Eisinger, F.; Heister, D.J.; Vosseler, D.; Nadalin, S.; Birkenfeld, A.L.; Heyne, N.; et al. SGLT2 Inhibitors Correct Fluid Overload in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients-A Prospective Observational Study. Transpl. Int. 2024, 37, 12879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Kwon, S.; Seo, Y.J.; Kim, Y.H.; Kwon, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.L.; Kim, C.D.; Park, S.H.; et al. Cardioprotective Effect of SGLT2 Inhibitor in Diabetic Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Multicenter Propensity Score Matched Study. Kidney Int. Rep. 2024, 9, 2474–2483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.S.; Lee, J.; Jung, C.H.; Park, J.Y.; Lee, W.J. Dulaglutide as an Effective Replacement for Prandial Insulin in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Review. Diabetes Metab. J. 2021, 45, 948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahzari, M.M.; Alluhayyan, O.B.; Almutairi, M.H.; Bayounis, M.A.; Alrayani, Y.H.; Omair, A.A.; Alshahrani, A.S. Safety and Efficacy of Semaglutide in Post Kidney Transplant Patients with Type 2 Diabetes or Post-Transplant Diabetes. J. Clin. Transl. Endocrinol. 2024, 36, 100343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kukla, A.; Hill, J.; Merzkani, M.; Bentall, A.; Lorenz, E.C.; Park, W.D.; D’costa, M.; Kudva, Y.C.; Stegall, M.D.; Shah, P. The Use of GLP1R Agonists for the Treatment of Type 2 Diabetes in Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplant. Direct 2020, 6, E524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vigara, L.A.; Villanego, F.; Orellana, C.; Naranjo, J.; Torrado, J.; Garcia, T.; Mazuecos, A. Effectiveness and Safety of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist in a Cohort of Kidney Transplant Recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 36, e14633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sato, T.; Azuma, Y.; Ozone, C.; Okazaki, M.; Takeda, A.; Okada, M.; Futamura, K.; Hiramitsu, T.; Goto, N.; Narumi, S.; et al. Possible Advantage of Glucagon-Like Peptide 1 Receptor Agonists for Kidney Transplant Recipients with Type 2 Diabetes. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2023, 108, 2597–2603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallik, R.; Ali, O.; Casabar, M.; Mukuba, D.; Byrne, C.; McCafferty, K.; Yaqoob, M.M.; Chowdhury, T.A. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Analogues in Renal Transplant Recipients with Diabetes: Medium Term Follow of Patients from a Single UK Centre. Diabet. Med. 2023, 40, e15057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, M.E.; Özler, T.E.; Merhametsiz, Ö.; Sözener, U.; Uyar, M.; Ercan, Z.; Bardak Demir, S.; Sezer, S.; Türkmen Sarıyıldız, G. The Results of SGLT-2 Inhibitors Use in Kidney Transplantation: 1-Year Experiences from Two Centers. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2023, 55, 2989–2999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez Fructuoso, A.I.; Raba, A.B.; Deras, E.B.; Vigara Sánchez, L.A.; Cecilio, R.V.S.; Esteve, A.F.; Vega, L.C.; Martínez, E.G.; González Garcia, M.E.; Coronado, P.S.; et al. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Therapy in Kidney Transplant Patients with Type 2 or Post-Transplant Diabetes: An Observational Multicentre Study. Clin. Kidney J. 2023, 16, 1022–1034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strøm Halden, T.A.; Kvitne, K.E.; Midtvedt, K.; Rajakumar, L.; Robertsen, I.; Brox, J.; Bollerslev, J.; Hartmann, A.; Asberg, A.; Jenssen, T. Efficacy and Safety of Empagliflozin in Renal Transplant Recipients with Posttransplant Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care 2019, 42, 1067–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisadome, Y.; Mei, T.; Noguchi, H.; Ohkuma, T.; Sato, Y.; Kaku, K.; Okabe, Y.; Nakamura, M. Safety and Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Pretransplant Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective, Single-Center, Inverse Probability of Treatment Weighting Analysis of 85 Transplant Patients. Transplant. Direct 2021, 7, E772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemke, A.; Brokmeier, H.M.; Leung, S.B.; Mara, K.C.; Mour, G.K.; Wadei, H.M.; Hill, J.M.; Stegall, M.; Kudva, Y.C.; Shah, P.; et al. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors for Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus after Kidney Transplantation. Clin. Transplant. 2022, 36, e14718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.H.; Kwon, S.; Jeon, Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Kwon, H.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, H.; Kim, Y.L.; Kim, C.D.; Park, S.H.; et al. The Efficacy and Safety of SGLT2 Inhibitor in Diabetic Kidney Transplant Recipients. Transplantation 2022, 106, E404–E412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahling, M.; Schork, A.; Nadalin, S.; Fritsche, A.; Heyne, N.; Guthoff, M. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) Inhibition in Kidney Transplant Recipients with Diabetes Mellitus. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 2019, 44, 984–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, T.; Yagan, J.; Hasan, A.; Gheith, O.A.; Mostafa, M.; Rida, S.; El-Serwi, N.; Shaker, M.; Khalid, M. Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter 2 Inhibitors & Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists, Efficacy & Safety in Diabetic Kidney Transplant Recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2023, 37, e15144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, C.C.; Brown, A.; Winstead, R.; Yakubu, I.; Demehin, M.; Kumar, D.; Gupta, G. Early Initiation of Sodium-Glucose Linked Transporter Inhibitors (SGLT-2i) and Associated Metabolic and Electrolyte Outcomes in Diabetic Kidney Transplant Recipients. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. 2020, 4, e00185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeggalam, A.; Liebich, J.A.; Yu, K.; Shrestha, E.; Nadella, S.; Ahir, V.; Newman, J.; Lentine, K.L.; Caliskan, Y.; Abu Al Rub, F.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Co-Transporter-2 Inhibitors in Patients with Kidney Transplantation and Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2023, 25, 1777–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilding, J.P.H.; Batterham, R.L.; Calanna, S.; Davies, M.; Van Gaal, L.F.; Lingvay, I.; McGowan, B.M.; Rosenstock, J.; Tran, M.T.D.; Wadden, T.A.; et al. Once-Weekly Semaglutide in Adults with Overweight or Obesity. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 989–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lincoff, A.M.; Brown-Frandsen, K.; Colhoun, H.M.; Deanfield, J.; Emerson, S.S.; Esbjerg, S.; Hardt-Lindberg, S.; Hovingh, G.K.; Kahn, S.E.; Kushner, R.F.; et al. Semaglutide and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Obesity without Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 389, 2221–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caruso, I.; Giorgino, F. Renal Effects of GLP-1 Receptor Agonists and Tirzepatide in Individuals with Type 2 Diabetes: Seeds of a Promising Future. Endocrine 2024, 84, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodera, R.; Shikata, K.; Kataoka, H.U.; Takatsuka, T.; Miyamoto, S.; Sasaki, M.; Kajitani, N.; Nishishita, S.; Sarai, K.; Hirota, D.; et al. Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonist Ameliorates Renal Injury through Its Anti-Inflammatory Action without Lowering Blood Glucose Level in a Rat Model of Type 1 Diabetes. Diabetologia 2011, 54, 965–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Nasr, M.; Usuelli, V.; Dellepiane, S.; Seelam, A.J.; Fiorentino, T.V.; D’Addio, F.; Fiorina, E.; Xu, C.; Xie, Y.; Balasubramanian, H.B.; et al. Glucagon-like Peptide 1 Receptor Is a T Cell-Negative Costimulatory Molecule. Cell Metab. 2024, 36, 1302–1319.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.C.; Chen, J.Y.; Chen, H.Y.; Yeh, F.Y.; Sun, C.Y.; Huang, T.T.M.; Wu, V.C. GLP-1 Receptor Agonists’ Impact on Cardio-Renal Outcomes and Mortality in T2D with Acute Kidney Disease. Nat. Commun. 2024, 15, 5912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sodhi, M.; Rezaeianzadeh, R.; Kezouh, A.; Etminan, M. Risk of Gastrointestinal Adverse Events Associated with Glucagon-Like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists for Weight Loss. JAMA 2023, 330, 1795–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Htike, Z.Z.; Zaccardi, F.; Papamargaritis, D.; Webb, D.R.; Khunti, K.; Davies, M.J. Efficacy and Safety of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Type 2 Diabetes: A Systematic Review and Mixed-Treatment Comparison Analysis. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 2017, 19, 524–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heerspink, H.J.L.; Jongs, N.; Chertow, G.M.; Langkilde, A.M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Correa-Rotter, R.; Rossing, P.; Sjöström, C.D.; Stefansson, B.V.; Toto, R.D.; et al. Effect of Dapagliflozin on the Rate of Decline in Kidney Function in Patients with Chronic Kidney Disease with and without Type 2 Diabetes: A Prespecified Analysis from the DAPA-CKD Trial. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2021, 9, 743–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, C.; Heerspink, H.J.L.; Zinman, B.; Inzucchi, S.E.; Koitka-Weber, A.; Mattheus, M.; Hantel, S.; Woerle, H.J.; Broedl, U.C.; Von Eynatten, M.; et al. Empagliflozin and Kidney Function Decline in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Slope Analysis from the EMPA-REG OUTCOME Trial. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2018, 29, 2755–2769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-Correa, J.I.; Correa-Rotter, R. Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors Mechanisms of Action: A Review. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 777861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eleftheriadis, T.; Pissas, G.; Tsogka, K.; Nikolaou, E.; Liakopoulos, V.; Stefanidis, I. A Unifying Model of Glucotoxicity in Human Renal Proximal Tubular Epithelial Cells and the Effect of the SGLT2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin. Int. Urol. Nephrol. 2020, 52, 1179–1189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Bommel, E.J.M.; Muskiet, M.H.A.; van Baar, M.J.B.; Tonneijck, L.; Smits, M.M.; Emanuel, A.L.; Bozovic, A.; Danser, A.H.J.; Geurts, F.; Hoorn, E.J.; et al. The Renal Hemodynamic Effects of the SGLT2 Inhibitor Dapagliflozin Are Caused by Post-Glomerular Vasodilatation Rather than Pre-Glomerular Vasoconstriction in Metformin-Treated Patients with Type 2 Diabetes in the Randomized, Double-Blind RED Trial. Kidney Int. 2020, 97, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narasaki, Y.; Kovesdy, C.P.; You, A.S.; Sumida, K.; Mallisetty, Y.; Surbhi, S.; Thomas, F.; Amin, A.N.; Streja, E.; Kalantar-Zadeh, K.; et al. Safety of SGLT2 Inhibitors, DPP-4 Inhibitors, and GLP-1 Receptor Agonists in US Veterans with and without Chronic Kidney Disease: A Population-Based Study. Lancet Reg. Health–Am. 2024, 36, 100814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, K.E.; Dhaliwal, K.; Robertshaw, S.; Verdin, N.; Benterud, E.; Lamont, N.; Drall, K.M.; McBrien, K.; Donald, M.; Tsuyuki, R.T.; et al. Consensus Recommendations for Sick Day Medication Guidance for People with Diabetes, Kidney, or Cardiovascular Disease: A Modified Delphi Process. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2023, 81, 564–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, S.; Sun, C. Can Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists Cause Acute Kidney Injury? An Analytical Study Based on Post-Marketing Approval Pharmacovigilance Data. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13, 1032199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neal, B.; Perkovic, V.; Mahaffey, K.W.; de Zeeuw, D.; Fulcher, G.; Erondu, N.; Shaw, W.; Law, G.; Desai, M.; Matthews, D.R. Canagliflozin and Cardiovascular and Renal Events in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiviott, S.D.; Raz, I.; Bonaca, M.P.; Mosenzon, O.; Kato, E.T.; Cahn, A.; Silverman, M.G.; Zelniker, T.A.; Kuder, J.F.; Murphy, S.A.; et al. Dapagliflozin and Cardiovascular Outcomes in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinman, B.; Wanner, C.; Lachin, J.M.; Fitchett, D.; Bluhmki, E.; Hantel, S.; Mattheus, M.; Devins, T.; Johansen, O.E.; Woerle, H.J.; et al. Empagliflozin, Cardiovascular Outcomes, and Mortality in Type 2 Diabetes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 2117–2128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisanapan, P.; Suppadungsuk, S.; Sanpawithayakul, K.; Thongprayoon, C.; Pattharanitima, P.; Tangpanithandee, S.; Mao, M.A.; Miao, J.; Cheungpasitporn, W. Safety and Efficacy of Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists among Kidney Transplant Recipients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Clin. Kidney J. 2024, 17, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lentine, K.L.; Miyata, K.N.; Lam, N.N.; Joseph, C.; McAdams-DeMarco, M.; Bae, S.; Chen, Y.; Caliskan, Y.; Sarabu, N.; Dhindsa, S.; et al. Sociodemographic Disparities in Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter-2 Inhibitor Use among US Kidney Transplant Recipients: An Observational Study of Real-World Pharmacy Records. Clin. Transplant. 2024, 38, e15257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Study | Country | Sample Size | Design | Investigated Drugs | Maintenance Immunosuppression | Follow-Up (Months) | Male Sex (%) | Age (Years) | Weight (kg) | BMI (kg/m2) | Diabetes Mellitus (%) | eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2024; Mahzari [30] | Saudi Arabia | GLP1-RA: 39 | RC | Semaglutide | Mycophenolate (100%), tacrolimus (97.4%) cyclosporine (2.6%), steroids (97.4%) | 18 | 74 | 54 | 95.7 | NR | 100 PTDM: 46 | 73.5 |
| 2024; Lim [28] | South Korea | SGLT2-i: 129 Control: 127 | RC | Empagliflozin, dapagliflozin | Tacrolimus (87%), cyclosporine (14.2%) | 56.3 | 70.5 | 54.5 | NR | 25.3 | 100 PTDM: 16.9 | NR |
| 2024; Schork [27] | Germany | SGLT2-i: 22 | PC | Dapagliflozin | NR | 6 | 72.7 | 61 | 85.5 | 27.3 | 81.8 PTDM: 36.4 | 38.6 |
| 2023; Mahmoud [42] | Kuwait | SGLT2-i: 98 GLP1-RA: 41 Control: 70 | RC | Canagliflozin, dulaglutide | Tacrolimus (75.1%), cyclosporine (19.1%) | 12 | 62.2 | 55.7 | NR | 31.3 | 100 PTDM: 41.1 | 66.3 |
| 2023; Mallik [34] | U.K. | GLP1-RA: 23 | RC | Dulaglutide, liraglutide | NR | 24 | 65 | 56.5 | NR | NR | 100 | NR |
| 2023; Fructuoso [36] | Spain | SGLT-2: 323 | PC | Empagliflozin, dapagliflozin, canagliflozin, ertugliflozin | Mycophenolate (79.6%), tacrolimus (87.9%), cyclosporine (2.9%), everolimus (9.1%), sirolimus (9.4%), steroids (57.2%) | 6 | 73.7 | 61.6 | 81.5 | NR | 100 PTDM: 60.5 | 58.4 |
| 2023; Demir [35] | Turkey | SGLT2-i: 36 Control: 21 | RC | Empagliflozin, dapagliflozin | Mycophenolate, tacrolimus, steroids | 12 | 63.2 | 51.3 | 78.5 | 28.5 | 100 PTDM: 54.4 | 72.7 |
| 2023; Yeggalam [44] | USA | SGLT2-i: 44 Control: 70 | RC | NR | NR | 12 | 63.2 | 61.5 | 94.6 | 31.5 | 100 PTDM: 46.5 | 53.9 |
| 2022; Vigara [32] | Spain | GLP1-RA: 40 | RC | Semaglutide, liraglutide, dulaglutide | Mycopheolate (95%), tacrolimus (100%), everolimus (2.5%), steroids (95%) | 12 | 52.5 | 62.8 | 93 | 35.8 | 100 | 46.1 |
| 2022; Sato [33] | Japan | GLP1-RA: 73 Control: 73 | RC | Liraglutide, dulaglutide, exenatide, lixisenatide | Mycophenolate or everolimus, tacrolimus or cyclosporine, steroids | 60 | 68.1 | 57.4 | NR | 24.8 | 100 | 45.8 |
| 2022; Lemke [39] | USA | SGLT2-i: 39 | RC | Canagliflozin, dapagliflozin, empagliflozin | Mycophenolate or azathioprine, tacrolimus or cyclosporine or belatacpt ± steroids | 12 | 74 | 57 | 87 | 30 | 100 PTDM: 44 | 62.2 |
| 2022; Lim [40] | South Korea | SGLT-2i: 202 Control: 554 | RC | Empagliflozin, dapagliflozin | Tacrolimus (81.9%), cyclosporine (19.5%), steroids (97.9%) | 72 | 67.2 | 52.4 | NR | 23.9 | 100 PTDM: 32.8 | 68.2 |
| 2021; Hisadome [38] | Japan | SGLT2-i: 28 Control: 57 | RC | Canagliflozin, ipragliflozin, empagliflozin, dapagliflozin, tofogliflozin | Mycophenolate or everolimus, tacrolimus or cyclosporine, steroids | 4 | 30.6 | 54.8 | 71.6 | 23.6 | 100 | 49.8 |
| 2021; Kim [29] | South Korea | GLP1-RA: 37 | RC | Dulaglutide | Tacrolimus (78.4%), cyclosporine (21.6%), steroids (100%) | 6 | 48.6 | 54.8 | 72.1 | 25.7 | 100 | 71.7 |
| 2020; Kukla [31] | USA | GLP1-RA: 17 | RC | Liraglutide, dulaglutide, exenatide | Mycophenolate (88.2%), tacrolimus (94.1%), everolimus (5.9%), steroids (64.7%) | 12 | 65 | 51.8 | 101.7 | 34.1 | 100 PTDM: 65 | 53 |
| 2020; Song [43] | USA | SGLT2-i: 50 | RC | Empagliflozin, canagliflozin, dapagliflozin | Mycophenolate (94%), tacrolimus (90%), steroids (98%) | 6 | 66 | 57 | NR | NR | 100 PTDM: 20 | 66.7 |
| 2019; Halden [37] | Norway | SGLT2-i: 22 Control: 22 | RCT | Empagliflozin | Mycophenolate (90.9%), tacrolimus (79.5%), cyclosporine (13.6%), everolimus (4.5%), steroids (97.7%) | 6 | 77.3 | 61 | 88 | 28.2 | PTDM: 100 | 62.5 |
| 2019; Mahling [41] | Germany | SGLT2-i: 10 | PC | Empagliflozin | Mycophenolate (90%), tacrolimus (90%), steroids (20%) | 12 | 80 | 66 | 75 | NR | 100 PTDM: 40 | 57 |
| Endpoint | Studies No. | Mean Difference (95% CI) | 95% PI | I2 | Trim-Fill Estimate (95% CI) | GRADE Assessment | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Certainty of Evidence | Downgrading | ||||||
| GLP1-RA | |||||||
| HbA1c (%) | 6 | −0.61 (−0.99; −0.23) * | −1.37; 0.15 | 57.0% | −0.25 (−0.70; 0.19) | Low | Study limitations, inconsistency |
| Weight (Kg) | 5 | −3.32 (−5.04; −1.59) * | −5.51; −1.12 * | 10.0% | −3.03 (−4.45; −1.61) * | Moderate | Study limitations |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 4 | 2.01 (−1.18; 5.20) | −1.18; 5.20 | 0% | 2.01 (−1.18; 5.20) | Low | Study limitations, imprecision |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 2 | −6.31 (−13.80; 1.19) | −14.12; 1.51 | 4.1% | NA | Low | Study limitations, imprecision |
| SGLT2-i | |||||||
| HbA1c (%) | 9 | −0.40 (−0.57; −0.23) * | −0.65; −0.15 * | 12.2% | −0.35 (−0.52; −0.18) | Moderate | Study limitations |
| Weight (Kg) | 8 | −2.21 (−2.74; −1.67) * | −2.74; −1.67 * | 0% | −2.21 (−2.74; −1.67) * | Moderate | Study limitations |
| eGFR (mL/min/1.73 m2) | 8 | −1.25 (−2.83; 0.34) | −3.64; 1.15 | 13.9% | −2.04 (−3.01; −1.06) * | Low | Study limitations, publication bias |
| Systolic blood pressure (mmHg) | 5 | −0.91 (−5.47; 3.64) | −9.40; 7.58 | 55.2% | −0.91 (−5.47; 3.64) | Very low | Study limitations, inconsistency, imprecision |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bellos, I.; Lagiou, P.; Benetou, V.; Marinaki, S. Safety and Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein 2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Transplant Recipients: Synthesis of Evidence. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206181
Bellos I, Lagiou P, Benetou V, Marinaki S. Safety and Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein 2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Transplant Recipients: Synthesis of Evidence. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(20):6181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206181
Chicago/Turabian StyleBellos, Ioannis, Pagona Lagiou, Vassiliki Benetou, and Smaragdi Marinaki. 2024. "Safety and Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein 2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Transplant Recipients: Synthesis of Evidence" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 20: 6181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206181
APA StyleBellos, I., Lagiou, P., Benetou, V., & Marinaki, S. (2024). Safety and Efficacy of Sodium-Glucose Transport Protein 2 Inhibitors and Glucagon-like Peptide-1 Receptor Agonists in Diabetic Kidney Transplant Recipients: Synthesis of Evidence. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(20), 6181. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206181








