Artificial Intelligence in Aesthetic Dentistry: Is Treatment with Aligners Clinically Realistic?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Study Type and Design
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Ethical Considerations
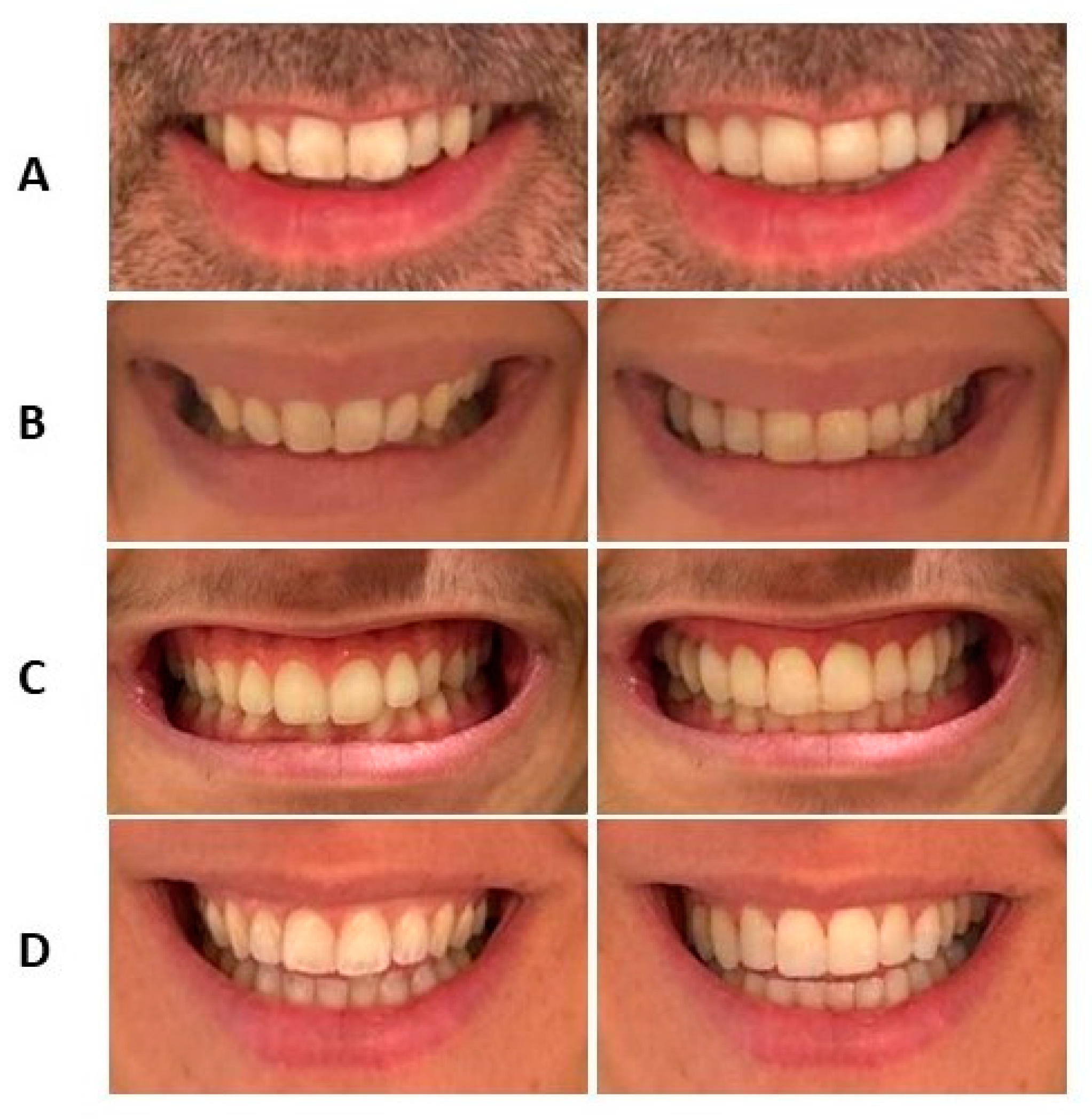
2.4. Procedure
2.5. Instruments and Measurements
2.6. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Method Error
3.2. Smile Width
3.3. Vertical Exposure of the Maxillary Central Incisor
3.4. Mesiodistal Width of the Maxillary Central Incisors
3.5. Mesiodistal Width of the Maxillary Lateral Incisor
3.6. Mesiodistal Proportion of Maxillary Central Incisor to Maxillary Lateral Incisor
3.7. Anterior Gingival Exposure
3.8. Upper and Lower Dental Midlines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- SV tends to generate simulations of broader smiles that, from an orthodontic perspective, are mostly achievable through aligner treatments.
- SV simulations show high predictability regarding the vertical movement of incisors that can be achieved with aligners.
- SV adjusts the mesiodistal size of the upper incisors in its simulations.
- The software modifies the mesiodistal proportion of the upper incisors, aiming for a “golden ratio” of 0.72, which implies alterations to dental dimensions.
- SV’s artificial intelligence does not make significant changes to gingival exposure, although a slight improvement in this aspect is observed.
- SV demonstrates the ability to identify and correct deviations in the dental midlines relative to the facial midline. However, there is a greater margin of error in the proposed corrections for the lower arch.
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tjan, A.H.; Miller, G.D.; The, J.G. Some esthetic factors in a smile. J. Prosthet. Dent. 1984, 51, 24–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nold, S.; Horvath, S.; Stampf, S.; Blatz, M. Analysis of select facial and dental esthetic parameters. Int. J. Periodontics Restor. Dent. 2014, 34, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Kazmi SM, R.; Khan, F.R.; Samejo, I. Analysis of different characteristics of smile. BDJ Open 2020, 6, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabri, R. The eight components of a balanced smile. J. Clin. Orthod. 2005, 39, 155–167; quiz 154. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sarver, D.M.; Ackerman, M.B. Dynamic smile visualization and quantification: Part 2. smile analysis and treatment strategies. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2003, 124, 116–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monnet-Corti, V.; Antezack, A.; Pignoly, M. Comment parfaire l’esthétique du sourire: Toujours en rose! L’ Orthod. Fr. 2018, 89, 71–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, R.M.; Assad Duarte, M.E.; Jardim da Motta, A.F.; Mucha, J.N.; Motta, A.T. Variations between maxillary central and lateral incisal edges and smile attractiveness. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 150, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dym, H.; Pierre, R., II. Diagnosis and treatment approaches to a “gummy smile”. Dent. Clin. N. Am. 2020, 64, 341–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabalan, R.M.; Tayyar, R.K.; Khattab, T.Z.; Hajeer, M.Y. Characteristics and dynamics of smile in patients with skeletal class II malocclusion versus class I malocclusion using still digital video captures: A three-group, cross-sectional, comparative study. Cureus 2022, 14, e30704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gill, D.S.; Naini, F.B.; Tredwin, C.J. Smile aesthetics. Dent. Update 2007, 34, 152–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, M.A.; Alghamdi, D.S.; Alghamdi, A.T. Visible portion of anterior teeth at rest and analysis of different smile characteristics in the Saudi population of the Jeddah region. Int. J. Dent. 2020, 2020, 8859376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smile Visualization. Invisalign.com. Available online: https://providerbio.invisalign.com/sv/dspokane (accessed on 2 August 2023).
- People News. Align Technology: SmileView. Available online: https://www.dentalreview.news/ (accessed on 12 April 2019).
- Ackerman, J.; Ackerman, M.; Brensinger, C.; Landis, J. A morphometric analysis of the posed smile. Clin. Orthod. Res. 1998, 1, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morales-Burruezo, I.; Gandía-Franco, J.L.; Cobo, J.; Vela-Hernández, A.; Bellot-Arcís, C. Arch expansion with the Invisalign system: Efficacy and predictability. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clements, K.M.; Bollen, A.M.; Huang, G.; King, G.; Hujoel, P.; Ma, T. Activation time and material stiffness of sequential removable orthodontic appliances. Part 2: Dental improvements. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2003, 124, 502–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Houle, J.P.; Piedade, L.; Todescan, R.; Pinheiro, F.H., Jr. The predictability of transverse changes with Invisalign. Angle Orthod. 2017, 87, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kravitz, N.D.; Kusnoto, B.; BeGole, E.; Obrez, A.; Agran, B. How well does Invisalign work? A prospective clinical study evaluating the efficacy of tooth movement with Invisalign. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2009, 135, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galan-Lopez, L.; Barcia-González, J.; Plasencia, E. A systematic review of the accuracy and efficiency of dental movements with Invisalign®. Daehan Ci’gwa Gyojeong Haghoeji/Korean J. Orthod. 2019, 49, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robertson, L.; Kaur, H.; Fagundes NC, F.; Romanyk, D.L.; Major, P.W.; Flores-Mir, C. Effectiveness of clear aligner therapy for orthodontic treatment: A systematic review. Orthod. Craniofacial Res. 2019, 23, 133–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, J.J.; Ledoux, P.M. Air-rotor stripping and proximal sealants. An SEM evaluation. J. Clin. Orthod. 1989, 23, 790–794. [Google Scholar]
- Levin, E.L. Dental esthetics and the golden proportion. J. Prosth. Dent. 1978, 40, 24–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzi, R.I.; Portes MI, P.; Ertty, E.; Meloti, F.; An, T.; De Almeida Cardoso, M. Aesthetic perception of smile in long face pattern patients who underwent maxillary impaction with miniplates or orthognathic surgery. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2022, 123, 498–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graber, L.W.; Vanarsdall, R.L.; Vig, K.W.L. Orthodontics—E-Book; Elsevier Health Sciences: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Parrini, S.; Rossini, G.; Castroflorio, T.; Fortini, A.; Deregibus, A.; Debernardi, C. Laypeople’s perceptions of frontal smile esthetics: A systematic review. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2016, 150, 740–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galluccio, G.; De Stefano, A.; Horodynski, M.; Impellizzeri, A.; Guarnieri, R.; Barbato, E.; Di Carlo, S.; De Angelis, F. Efficacy and Accuracy of Maxillary Arch Expansion with Clear Aligner Treatment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loberto, S.; Pavoni, C.; Fanelli, S.; Lugli, L.; Cozza, P.; Lione, R. Predictability of expansion movements performed by clear aligners in mixed dentition in both arches: A retrospective study on digital casts. BMC Oral Health 2024, 24, 694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahabuddin, N.; Kang, J.; Jeon, H.H. Predictability of the deep overbite correction using clear aligners. Am. J. Orthod. Dentofac. Orthop. 2023, 163, 793–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montalvo-Arias, D. Periodontal Considerations in Esthetic Dentistry; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 67–92. [Google Scholar]
- Pasciuti, E.; Coloccia, G.; Inchingolo, A.D.; Patano, A.; Ceci, S.; Bordea, I.R.; Cardarelli, F.; Di Venere, D.; Inchingolo, F.; Dipalma, G. Deep Bite Treatment with Aligners: A New Protocol. Appl. Sci. 2022, 12, 6709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aras, I.; Tuncer, A.V. Comparison of anterior and posterior mini-implant-assisted maxillary incisor intrusion: Root resorption and treatment efficiency. Angle Orthod. 2016, 86, 746–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathi, S.; Dhannawat, P.; Gilani, R.; Vishnani, R. A Multidisciplinary Aesthetic Treatment Approach for Peg Lateral of the Maxillary Incisors. Cureus 2022, 14, e29184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Melo, M.; Ata-Ali, J.; Ata-Ali, F.; Bulsei, M.; Grella, P.; Cobo, T.; Martínez-González, J.M. Evaluation of the maxillary midline, curve of the upper lip, smile line and tooth shape: A prospective study of 140 Caucasian patients. BMC Oral Health 2020, 20, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kantrong, N.; Traiveat, K.; Wongkhantee, S. Natural upper anterior teeth display an increasing proportion in mesio-distal direction. J. Clin. Exp. Dent. 2019, 11, e890–e897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Preston, J.D. The golden proportion revisited. J Esthet Dent. 1993, 5, 247–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Frequency | Percentage (%) | Cumulative Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enamel Reduction (Orthodontic) | 26 | 51.0 | 51.0 |
| Multidisciplinary Case | 11 | 21.6 | 72.5 |
| Excessive Enamel Reduction | 14 | 27.5 | 100.0 |
| Total | 51 | 100.0 |
| Frequency | Percentage (%) | Cumulative Percentage (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enamel Reduction (Orthodontic) | 16 | 31.4 | 31.4 |
| Multidisciplinary Case | 32 | 62.7 | 94.1 |
| Excessive Enamel Reduction | 3 | 5.9 | 100.0 |
| Total | 51 | 100.0 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mourgues, T.; González-Olmo, M.J.; Huanca Ghislanzoni, L.; Peñacoba, C.; Romero-Maroto, M. Artificial Intelligence in Aesthetic Dentistry: Is Treatment with Aligners Clinically Realistic? J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 6074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206074
Mourgues T, González-Olmo MJ, Huanca Ghislanzoni L, Peñacoba C, Romero-Maroto M. Artificial Intelligence in Aesthetic Dentistry: Is Treatment with Aligners Clinically Realistic? Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(20):6074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206074
Chicago/Turabian StyleMourgues, Thomas, María José González-Olmo, Luis Huanca Ghislanzoni, Cecilia Peñacoba, and Martín Romero-Maroto. 2024. "Artificial Intelligence in Aesthetic Dentistry: Is Treatment with Aligners Clinically Realistic?" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 20: 6074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206074
APA StyleMourgues, T., González-Olmo, M. J., Huanca Ghislanzoni, L., Peñacoba, C., & Romero-Maroto, M. (2024). Artificial Intelligence in Aesthetic Dentistry: Is Treatment with Aligners Clinically Realistic? Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(20), 6074. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13206074






