Prevention of Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema: An Up-to-Date Systematic Review of Different Surgical Approaches
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Literature Search
2.2. Data Extraction
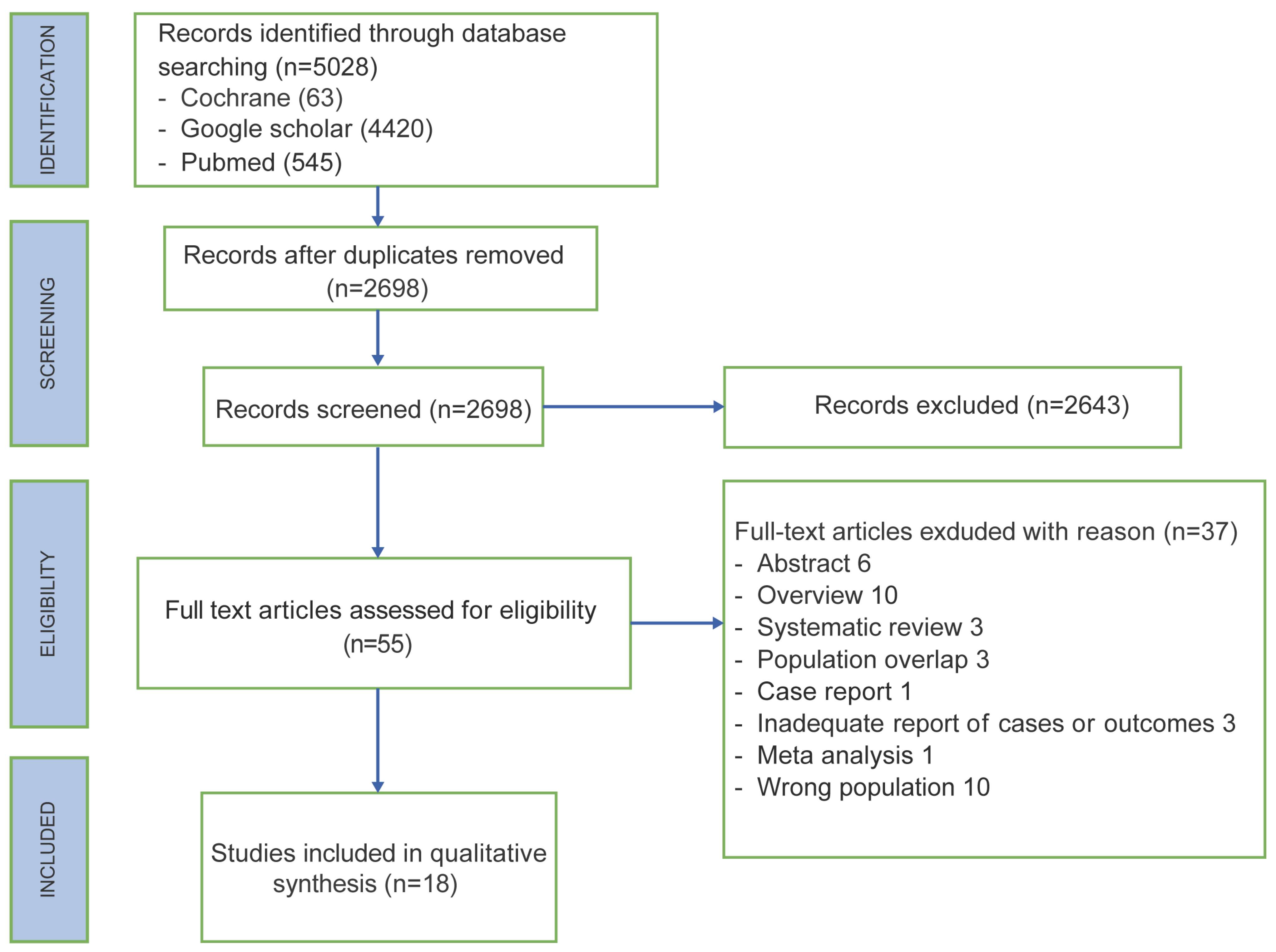
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristic
3.2. Patient Characteristics
| Article, Year of Publication and Number of Reference | Adjuvant Therapy | LVA Shunting Technique | LVA Feasibility | Follow-Up (Months) | Operating Time (min) | Method of Lymphedema Diagnosis | Cases with Lymphedema | Controls with Lymphedema | Cases with Lymphedema Who Received Adjuvant Radiotherapy | OCEBM and JADAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boccardo 2011 [16] | Cases: RT (11/23) Controls: RT (12/23) | Sleeve | 23/23 (100%) | 18 | 15–20 | V | 1/23 (4%) | 7/23 (30%) | 1/1 (100%) | 2 and 5 |
| Feldman 2015 [17] | Cases: RT (15/24), CT (23/24) Controls: RT (6/8), CT (7/8) | Sleeve | 24/32 (75%) | From 3 to 24 | 45 | V | 3/24 (13%) | 4/8 (50%) | 3/3 (100%) | 3 and 3 |
| Hahamoff 2019 [25] | Cases: RT (8/8), neoCT (5/8), adCT (4/8); Controls: RT (6/10), neoCT (4/10), adCT (4/10) | Sleeve | 8/8 (100%) | From 15 to 20 | From 32 to 95 | CA, BS | 0/8 (0%) | 4/10 (40%) | 0/0 | 3 and 3 |
| Herremans 2021 [18] | Cases: RT (67/76), CT (58/76), neoCT (36/76) Controls: RT (50/56), CT (42/56), neoCT (20/56) | Sleeve | 76/84 (90%) | 60 | nr | CA, BS, LQOLQ | 10/76 (13.2%) | 16/56 (28.6%) | Nr | 3 and 4 |
| Yoon 2021 [26] | Cases: RT (17/21), CT (16/21); Controls: RT (36/48), CT (38/48) | ETE LVA | 21/21 (100%) | 6 | From 30 to 60 | CA, BS | 0/21 (0%) | 9/48 (18.8%) | 0/0 | 2 and 5 |
| Ozmen 2022 [27] | Cases: RT (89/110); Controls: RT (68/84) | Sleeve | Nr | From 10 to 84 | nr | CA, BS | 18/110 (16%) | 57/84 (68%) | Nr | 3 and 4 |
| Weinstein 2022 [19] | Cases: RT (46/66), neoCT (56/66) adCT (26/66); Controls: RT (8/12), neoCT (8/12), adCT (8/12) | ETE or ETS LVA | Nr | 8 on average | nr | CA, BS | 4/66 (6%) | 1/12 (8%) | 3/4 (75%) | 3 and 4 |
| Article, Year of Publication and Number of Reference | Adjuvant Therapy | LVA Shunting Technique | LVA Feasibility | Follow-Up (Months) | Operating Time (min) | Method of Lymphedema Diagnosis | Cases with Lymphedema | Cases with Lymphedema Who Received Adjuvant Radiotherapy | OCEBM and JADAD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boccardo 2009 [20] | RT (7/18) | Sleeve | 18/19 (95%) | 12 | 15 | CA, LS | 0/18 (0%) | 0/0 | 4 and 3 |
| Casabona 2009 [21] | RT (8/8), CT (0/8) | Sleeve | 8/9 (89%) | 9 | 17 | CA | 0/8 (0%) | 0/0 | 4 and 3 |
| Boccardo 2015 [11] | RT (35/74) | Sleeve | 74/78 (95%) | 48 | 48 | V, LS | 3/74 (4%) | 3/3 | 4 and 3 |
| Johnson 2019 [14] | RT (26/32), CT (19/32) | Sleeve | nr | 12 | Nr | CA, BS | 1/32 (3.1%) | 1/32 | 4 and 4 |
| Scharwz 2019 [12] | RT (52/58), neoCT (43/58), adCT (10/58) | 37/58 ETE LVA, 21/58 sleeve | 58/60 (97%) | 29 | 95 | CA, BS | 2/43 (4.6%) | 2/2 | 4 and 3 |
| Cook 2021 [15] | RT (22/33), neoCT (24/33) | Sleeve | 33/33 (100%) | 12 | Nr | CA, LS | 3/33 (9%) | 3/3 | 4 and 4 |
| Shaffer 2020 [13] | RT (82/88), neoCT (61/88), adCT (20/88), neo + adCT (1/88) | ETE LVA or sleeve | 88/88 (100%) | 14.6 on average | From 161 to 253 | CA, BS | 5/88 (6%) | 4/5 | 4 and 4 |
| Han 2022 [22] | RT (3/3), neoCT (2/3) | Vascularized serratus anterior fascia flap | nr | 48 | Nr | CA | 0/3 (0%) | 0/0 | 4 and 3 |
| Lipman 2022 [23] | RT (16/19) | ETE or ETS LVA | nr | 10 on average | From 32 to 95 | CA, BS | 1/19 (5%) | nr | 4 and 3 |
| Pierazzi 2022 [24] | RT (5/5) | DLVA | 5/5 (100%) | 12 | Nr | CA | 0/5 (0%) | 0/0 | 4 and 3 |
| Yoshimatsu 2022 [28] | RT (2/4) | SCIP flap with DIEP | 4/4 (100%) | From 24 to 48 | Nr | V | 0/4 (0%) | 0/0 | 4 and 3 |
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Maclellan, R.A.; Greene, A.K. Lymphedema. Semin. Pediatr. Surg. 2014, 23, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taghian, N.R.; Miller, C.L.; Jammallo, L.S.; O’Toole, J.; Skolny, M.N. Lymphedema following breast cancer treatment and impact on quality of life: A review. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2014, 92, 227–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jørgensen, M.G.; Toyserkani, N.M.; Sørensen, J.A. The effect of prophylactic lymphovenous anastomosis and shunts for preventing cancer-related lymphedema: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microsurgery 2018, 38, 576–585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, A.R.; Kimball, S.; Epstein, S.; Recht, A.; Lin, S.J.; Lee, B.T.; James, T.A.; Singhal, D. Lymphedema Incidence After Axillary Lymph Node Dissection: Quantifying the Impact of Radiation and the Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventive Healing Approach. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2019, 82 (Suppl. S4), S234–S241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stuiver, M.M.; ten Tusscher, M.R.; Agasi-Idenburg, C.S.; Lucas, C.; Aaronson, N.K.; Bossuyt, P.M. Conservative interventions for preventing clinically detectable upper-limb lymphoedema in patients who are at risk of developing lymphoedema after breast cancer therapy. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2015, CD009765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badger, C.; Preston, N.; Seers, K.; Mortimer, P. Physical therapies for reducing and controlling lymphoedema of the limbs. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2004, CD003141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markkula, S.P.; Leung, N.; Allen, V.B.; Furniss, D. Surgical interventions for the prevention or treatment of lymphoedema after breast cancer treatment. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 2, CD011433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granzow, J.W.; Soderberg, J.M.; Kaji, A.H.; Dauphine, C. Review of current surgical treatments for lymphedema. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2014, 21, 1195–1201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kung, T.A.; Champaneria, M.C.; Maki, J.H.; Neligan, P.C. Current Concepts in the Surgical Management of Lymphedema. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 139, 1003e–1013e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campisi, C.C.; Ryan, M.; Boccardo, F.; Campisi, C. LyMPHA and the prevention of lymphatic injuries: A rationale for early microsurgical intervention. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2014, 30, 71–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccardo, F.; Casabona, F.; De Cian, F.; Friedman, D.; Murelli, F.; Puglisi, M.; Campisi, C.C.; Molinari, L.; Spinaci, S.; Dessalvi, S.; et al. Lymphatic microsurgical preventing healing approach (LYMPHA) for primary surgical prevention of breast cancer-related lymphedema: Over 4 years follow-up. Microsurgery 2015, 35, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwarz, G.S.; Grobmyer, S.R.; Djohan, R.S.; Cakmakoglu, C.; Bernard, S.L.; Radford, D.; Al-Hilli, Z.; Knackstedt, R.; Djohan, M.; Valente, S.A. Axillary reverse mapping and lymphaticovenous bypass: Lymphedema prevention through enhanced lymphatic visualization and restoration of flow. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019, 120, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shaffer, K.; Cakmakoglu, C.; Schwarz, G.S.; ElSherif, A.; Al-Hilli, Z.; Djohan, R.; Radford, D.M.; Grobmyer, S.; Bernard, S.; Moreira, A.; et al. Lymphedema Prevention Surgery: Improved Operating Efficiency over Time. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 4695–4701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.R.; Fleishman, A.; Granoff, M.D.; Shillue, K.D.; Houlihan, M.J.; Sharma, R.; Kansal, K.J.; Teller, P.; James, T.A.; Lee, B.T.M.; et al. Evaluating the Impact of Immediate Lymphatic Reconstruction for the Surgical Prevention of Lymphedema. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 147, 373e–381e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, J.A.; Sasor, S.E.; Loewenstein, S.N.; DeBrock, W.; Lester, M.; Socas, J.; Ludwig, K.K.; Fisher, C.S.; Hassanein, A.H. Immediate Lymphatic Reconstruction after Axillary Lymphadenectomy: A Single-Institution Early Experience. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 1381–1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccardo, F.M.; Casabona, F.; Friedman, D.; Puglisi, M.; De Cian, F.; Ansaldi, F.; Campisi, C. Surgical prevention of arm lymphedema after breast cancer treatment. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2011, 18, 2500–2505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feldman, S.; Bansil, H.; Ascherman, J.; Grant, R.; Borden, B.; Henderson, P.; Ojo, A.; Taback, B.; Chen, M.; Ananthakrishnan, P.; et al. Single Institution Experience with Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventive Healing Approach (LYMPHA) for the Primary Prevention of Lymphedema. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2015, 22, 3296–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herremans, K.M.; Cribbin, M.P.; Riner, A.N.; Neal, D.W.; Hollen, T.L.; Clevenger, P.; Munoz, D.; Blewett, S.; Giap, F.; Okunieff, P.G.; et al. Five-Year Breast Surgeon Experience in LYMPHA at Time of ALND for Treatment of Clinical T1-4N1-3M0 Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2021, 28, 5775–5787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, B.; Le, N.K.; Robertson, E.; Zimmerman, A.M.; Tavares, T.; Tran, T.; Laronga, C.; Panetta, N.J. Reverse Lymphatic Mapping and Immediate Microsurgical Lymphatic Reconstruction Reduces Early Risk of Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 149, 1061–1069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boccardo, F.; Casabona, F.; De Cian, F.; Friedman, D.; Villa, G.; Bogliolo, S.; Ferrero, S.; Murelli, F.; Campisi, C. Lymphedema microsurgical preventive healing approach: A new technique for primary prevention of arm lymphedema after mastectomy. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 703–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casabona, F.; Bogliolo, S.; Valenzano Menada, M.; Sala, P.; Villa, G.; Ferrero, S. Feasibility of axillary reverse mapping during sentinel lymph node biopsy in breast cancer patients. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2009, 16, 2459–2463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han Ang, C.; Wong, M. Incorporation of the Vascularized Serratus Fascia Flap during Latissimus Dorsi Flap Harvest to Minimize Morbidity after Axillary Clearance. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 1, 58–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lipman, K.; Luan, A.; Stone, K.; Wapnir, I.; Karin, M.; Nguyen, D. Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventive Healing Approach (LYMPHA) for Lymphedema Prevention after Axillary Lymph Node Dissection-A Single Institution Experience and Feasibility of Technique. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 11, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pierazzi, D.M.; Arleo, S.; Faini, G. Distally Prophylactic Lymphaticovenular Anastomoses after Axillary or Inguinal Complete Lymph Node Dissection Followed by Radiotherapy: A Case Series. Medicina 2022, 58, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hahamoff, M.; Gupta, N.; Munoz, D.; Lee, B.T.; Clevenger, P.; Shaw, C.; Spiguel, L.; Singhal, D. A Lymphedema Surveillance Program for Breast Cancer Patients Reveals the Promise of Surgical Prevention. J. Surg. Res. 2019, 244, 604–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, J.A.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, J.W.; Kim, J.H. Six-Month Follow-up for Investigating the Effect of Prophylactic Lymphovenous Anastomosis on the Prevention of Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema: A Preliminary Study in a Single Institution. Arch. Hand Microsurg. 2021, 26, 276–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozmen, T.; Layton, C.; Friedman-Eldar, O.; Melnikau, S.; Kesmodel, S.; Moller, M.G.; Avisar, E. Evaluation of Simplified Lymphatic Microsurgical Preventing Healing Approach (SLYMPHA) for the prevention of breast cancer-related lymphedema after axillary lymph node dissection using bioimpedance spectroscopy. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 48, 1713–1717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshimatsu, H.; Karakawa, R.; Fuse, Y.; Yano, T. Simultaneous Lymphatic Superficial Circumflex Iliac Artery Perforator Flap Transfer from the Zone 4 Region in Autologous Breast Reconstruction Using the Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Perforator Flap: A Proof-of-Concept Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casley-Smith, J.R. Measuring and representing peripheral oedema and its alterations. Lymphology 1994, 27, 56–70. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, M.; Korourian, S.; Henry-Tillman, R.; Adkins, L.; Mumford, S.; Westbrook, K.C.; Klimberg, V.S. Axillary reverse mapping (ARM): A new concept to identify and enhance lymphatic preservation. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 14, 1890–1895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nos, C.; Lesieur, B.; Clough, K.B.; Lecuru, F. Blue dye injection in the arm in order to conserve the lymphatic drainage of the arm in breast cancer patients requiring an axillary dissection. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2007, 14, 2490–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ochoa, D.; Korourian, S.; Boneti, C.; Adkins, L.; Badgwell, B.; Klimberg, V.S. Axillary reverse mapping: Five-year experience. Surgery 2014, 156, 1261–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tummel, E.; Ochoa, D.; Korourian, S.; Betzold, R.; Adkins, L.; McCarthy, M.; Hung, S.; Kalkwarf, K.; Gallagher, K.; Lee, J.Y.; et al. Does Axillary Reverse Mapping Prevent Lymphedema after Lymphadenectomy? Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 987–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yue, T.; Zhuang, D.; Zhou, P.; Zheng, L.; Fan, Z.; Zhu, J.; Hou, L.; Yu, F.; Dong, X.; Xiao, L.; et al. A Prospective Study to Assess the Feasibility of Axillary Reverse Mapping and Evaluate Its Effect on Preventing Lymphedema in Breast Cancer Patients. Clin. Breast Cancer 2015, 15, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boneti, C.; Korourian, S.; Bland, K.; Cox, K.; Adkins, L.L.; Henry-Tillman, R.S.; Klimberg, S.V. Axillary reverse mapping: Mapping and preserving arm lymphatics may be important in preventing lymphedema during sentinel lymph node biopsy. J. Am. Coll. Surg. 2008, 206, 1038–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shimotsuma, M.; Shields, J.W.; Simpson-Morgan, M.W.; Sakuyama, A.; Shirasu, M.; Hagiwara, A.; Takahashi, T. Morpho-physiological function and role of omental milky spots as omentum-associated lymphoid tissue (OALT) in the peritoneal cavity. Lymphology 1993, 26, 90–101. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, W.F. How to Get Started Performing Supermicrosurgical Lymphaticovenular Anastomosis to Treat Lymphedema. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2018, 81 (Suppl. S6), S15–S20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, A.R.; Asban, A.; Granoff, M.D.; Kang, C.O.; Lee, B.T.; Chatterjee, A.; Singhal, D. Is Immediate Lymphatic Reconstruction Cost-effective? Ann. Surg. 2021, 274, e581–e588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.R. Breast cancer-related lymphedema: Symptoms, diagnosis, risk reduction, and management. World J. Clin. Oncol. 2014, 5, 241–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiSipio, T.; Rye, S.; Newman, B.; Hayes, S. Incidence of unilateral arm lymphoedema after breast cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2013, 14, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basta, M.N.; Wu, L.C.; Kanchwala, S.K.; Serletti, J.M.; Tchou, J.C.; Kovach, S.J.; Fosnot, J.; Fischer, J.P. Reliable prediction of postmastectomy lymphedema: The Risk Assessment Tool Evaluating Lymphedema. Am. J. Surg. 2017, 213, 1125–1133.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, W.F.; Knackstedt, R. Delayed Distally Based Prophylactic Lymphaticovenular Anastomosis: Improved Functionality, Feasibility, and Oncologic Safety? J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2020, 36, e1–e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coriddi, M.; Dayan, J.; Bloomfield, E.; McGrath, L.N.; Diwan, R.; Monge, J.B.; Gutierrez, J.B.; Brown, S.; Boe, L.; Mehrara, B. Efficacy of Immediate Lymphatic Reconstruction to Decrease Incidence of Breast Cancer-related Lymphedema: Preliminary Results of Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Surg. 2023, 278, 630–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pagliara, D.; Grieco, F.; Rampazzo, S.; Pili, N.; Serra, P.L.; Cuomo, R.; Rubino, C. Prevention of Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema: An Up-to-Date Systematic Review of Different Surgical Approaches. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020555
Pagliara D, Grieco F, Rampazzo S, Pili N, Serra PL, Cuomo R, Rubino C. Prevention of Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema: An Up-to-Date Systematic Review of Different Surgical Approaches. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(2):555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020555
Chicago/Turabian StylePagliara, Domenico, Federica Grieco, Silvia Rampazzo, Nicola Pili, Pietro Luciano Serra, Roberto Cuomo, and Corrado Rubino. 2024. "Prevention of Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema: An Up-to-Date Systematic Review of Different Surgical Approaches" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 2: 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020555
APA StylePagliara, D., Grieco, F., Rampazzo, S., Pili, N., Serra, P. L., Cuomo, R., & Rubino, C. (2024). Prevention of Breast Cancer-Related Lymphedema: An Up-to-Date Systematic Review of Different Surgical Approaches. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(2), 555. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13020555






