Resistance Exercise Participation in Community-Dwelling Older Adults in Korea: Associated Factors and Sex Differences
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Participants
2.2. Resistance Exercise
2.3. Covariates
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Participant Characteristics
3.2. Factors Associated with Insufficient Participation in Resistance Exercise
3.3. Factors Associated with Insufficient Participation in Resistance Exercise by Sex
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hurst, C.; Robinson, S.M.; Witham, M.D.; Dodds, R.M.; Granic, A.; Buckland, C.; De Biase, S.; Finnegan, S.; Rochester, L.; Skelton, D.A.; et al. Resistance exercise as a treatment for sarcopenia: Prescription and delivery. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruiz, J.R.; Sui, X.; Lobelo, F.; Morrow, J.R., Jr.; Jackson, A.W.; Sjostrom, M.; Blair, S.N. Association between muscular strength and mortality in men: Prospective cohort study. BMJ 2008, 337, a439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stamatakis, E.; Lee, I.M.; Bennie, J.; Freeston, J.; Hamer, M.; O’Donovan, G.; Ding, D.; Bauman, A.; Mavros, Y. Does Strength-Promoting Exercise Confer Unique Health Benefits? A Pooled Analysis of Data on 11 Population Cohorts With All-Cause, Cancer, and Cardiovascular Mortality Endpoints. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2018, 187, 1102–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandolesi, L.; Polverino, A.; Montuori, S.; Foti, F.; Ferraioli, G.; Sorrentino, P.; Sorrentino, G. Effects of Physical Exercise on Cognitive Functioning and Wellbeing: Biological and Psychological Benefits. Front. Psychol. 2018, 9, 509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franco, M.R.; Tong, A.; Howard, K.; Sherrington, C.; Ferreira, P.H.; Pinto, R.Z.; Ferreira, M.L. Older people’s perspectives on participation in physical activity: A systematic review and thematic synthesis of qualitative literature. Br. J. Sports Med. 2015, 49, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenholm, S.; Tiainen, K.; Rantanen, T.; Sainio, P.; Heliovaara, M.; Impivaara, O.; Koskinen, S. Long-term determinants of muscle strength decline: Prospective evidence from the 22-year mini-Finland follow-up survey. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2012, 60, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, Y.A.; Lee, J.S.; Park, J.H.; Kim, Y.H. Patterns of physical activity and sedentary behavior and their associated factors among nondisabled stroke survivors. Maturitas 2022, 158, 10–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moran, M.; Van Cauwenberg, J.; Hercky-Linnewiel, R.; Cerin, E.; Deforche, B.; Plaut, P. Understanding the relationships between the physical environment and physical activity in older adults: A systematic review of qualitative studies. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2014, 11, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rhodes, R.E.; Lubans, D.R.; Karunamuni, N.; Kennedy, S.; Plotnikoff, R. Factors associated with participation in resistance training: A systematic review. Br. J. Sports Med. 2017, 51, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bopp, M.; Wilcox, S.; Oberrecht, L.; Kammermann, S.; McElmurray, C.T. Correlates of strength training in older rural African American and Caucasian women. Women Health 2004, 40, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.A.; Pedisic, Z.; van Uffelen, J.G.; Gale, J.; Banting, L.K.; Vergeer, I.; Stamatakis, E.; Bauman, A.E.; Biddle, S.J. The descriptive epidemiology of total physical activity, muscle-strengthening exercises and sedentary behaviour among Australian adults--results from the National Nutrition and Physical Activity Survey. BMC Public. Health 2016, 16, 73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuh, D.J.; Cooper, C. Physical activity at 36 years: Patterns and childhood predictors in a longitudinal study. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 1992, 46, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- An, K.Y.; Kang, D.W.; Morielli, A.R.; Friedenreich, C.M.; Reid, R.D.; McKenzie, D.C.; Gelmon, K.; Mackey, J.R.; Courneya, K.S. Patterns and predictors of exercise behavior during 24 months of follow-up after a supervised exercise program during breast cancer chemotherapy. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2020, 17, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coletta, A.M.; Marquez, G.; Thomas, P.; Thoman, W.; Bevers, T.; Brewster, A.M.; Hawk, E.; Basen-Engquist, K.; Gilchrist, S.C. Clinical factors associated with adherence to aerobic and resistance physical activity guidelines among cancer prevention patients and survivors. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0220814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nuzzo, J.L. Sex Difference in Participation in Muscle-Strengthening Activities. J. Lifestyle Med. 2020, 10, 110–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, K.; Kim, Y.; Kweon, S.; Kim, S.; Yun, S.; Park, S.; Lee, Y.K.; Kim, Y.; Park, O.; Jeong, E.K. Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 20th anniversary: Accomplishments and future directions. Epidemiol. Health 2021, 43, e2021025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kweon, S.; Kim, Y.; Jang, M.J.; Kim, Y.; Kim, K.; Choi, S.; Chun, C.; Khang, Y.H.; Oh, K. Data resource profile: The Korea National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (KNHANES). Int. J. Epidemiol. 2014, 43, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Global Recommendations on Physical Activity for Health. Available online: https://www.who.int/publications/i/item/9789241599979 (accessed on 2 December 2022).
- World Health Organization. Global Physical Activity Questionnaire (GPAQ) Analysis Guide. Available online: https://www.who.int/teams/noncommunicable-diseases/surveillance/systems-tools/physical-activity-surveillance (accessed on 19 June 2023).
- Lee, J.; Lee, C.; Min, J.; Kang, D.W.; Kim, J.Y.; Yang, H.I.; Park, J.; Lee, M.K.; Lee, M.Y.; Park, I.; et al. Development of the Korean Global Physical Activity Questionnaire: Reliability and validity study. Glob. Health Promot. 2020, 27, 44–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ku, P.W.; Steptoe, A.; Liao, Y.; Hsueh, M.C.; Chen, L.J. A cut-off of daily sedentary time and all-cause mortality in adults: A meta-regression analysis involving more than 1 million participants. BMC Med. 2018, 16, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. Regional Office for the Western Pacific. In The Asia-Pacific Perspective: Redefining Obesity and Its Treatment; Health Communications Australia: Sydney, Australia, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Hermoso, A.; López-Gil, J.F.; Ramírez-Vélez, R.; Alonso-Martínez, A.M.; Izquierdo, M.; Ezzatvar, Y. Adherence to aerobic and muscle-strengthening activities guidelines: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 3.3 million participants across 32 countries. Br. J. Sports Med. 2023, 57, 225–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.A.; Lee, D.C.; Khan, A.; Wiesner, G.H.; Bauman, A.E.; Stamatakis, E.; Biddle, S.J.H. Muscle-Strengthening Exercise Among 397,423 U.S. Adults: Prevalence, Correlates, and Associations With Health Conditions. Am. J. Prev. Med. 2018, 55, 864–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bennie, J.A.; De Cocker, K.; Smith, J.J.; Wiesner, G.H. The epidemiology of muscle-strengthening exercise in Europe: A 28-country comparison including 280,605 adults. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0242220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.A.; De Cocker, K.; Teychenne, M.J.; Brown, W.J.; Biddle, S.J.H. The epidemiology of aerobic physical activity and muscle-strengthening activity guideline adherence among 383,928 U.S. adults. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2019, 16, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennie, J.A.; Pedisic, Z.; van Uffelen, J.G.; Charity, M.J.; Harvey, J.T.; Banting, L.K.; Vergeer, I.; Biddle, S.J.; Eime, R.M. Pumping Iron in Australia: Prevalence, Trends and Sociodemographic Correlates of Muscle Strengthening Activity Participation from a National Sample of 195,926 Adults. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0153225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milanović, Z.; Pantelić, S.; Trajković, N.; Sporiš, G.; Kostić, R.; James, N. Age-related decrease in physical activity and functional fitness among elderly men and women. Clin. Interv. Aging 2013, 8, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, F.; Domingos, C.; Monteiro, D.; Morouço, P. A Review on Aging, Sarcopenia, Falls, and Resistance Training in Community-Dwelling Older Adults. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Depression and Other Common Mental Disorders: Global Health Estimates; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Bennie, J.A.; De Cocker, K.; Tittlbach, S. The epidemiology of muscle-strengthening and aerobic physical activity guideline adherence among 24,016 German adults. Scand. J. Med. Sci. Sports 2021, 31, 1096–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleg, J.L. Aerobic exercise in the elderly: A key to successful aging. Discov. Med. 2012, 13, 223–228. [Google Scholar]
- Konopka, A.R.; Harber, M.P. Skeletal muscle hypertrophy after aerobic exercise training. Exerc. Sport. Sci. Rev. 2014, 42, 53–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, M.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.H. Association of physical activity, smoking, and socioeconomic factors on health checkup participation in community-dwelling stroke survivors aged 50 years or older. BMC Public Health 2023, 23, 502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.W.; Tsai, T.I.; Yang, C.L.; Kuo, K.N. Gender differences in smoking behaviors in an Asian population. J Womens Health 2008, 17, 971–978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Linder, S.; Abu-Omar, K.; Geidl, W.; Messing, S.; Sarshar, M.; Reimers, A.K.; Ziemainz, H. Physical inactivity in healthy, obese, and diabetic adults in Germany: An analysis of related socio-demographic variables. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0246634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regensteiner, J.G.; Bauer, T.A.; Huebschmann, A.G.; Herlache, L.; Weinberger, H.D.; Wolfel, E.E.; Reusch, J.E. Sex differences in the effects of type 2 diabetes on exercise performance. Med. Sci. Sports Exerc. 2015, 47, 58–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bădescu, S.V.; Tătaru, C.; Kobylinska, L.; Georgescu, E.L.; Zahiu, D.M.; Zăgrean, A.M.; Zăgrean, L. The association between Diabetes mellitus and Depression. J. Med. Life 2016, 9, 120–125. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tian, Y.; Zhang, Y. The relationship between hypertension and physical activity in middle-aged and older adults controlling for demographic, chronic disease, and mental health variables. Medicine 2022, 101, e32092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayne, K.J.; Sullivan, M.K.; Lees, J.S. Sex and gender differences in the management of chronic kidney disease and hypertension. J. Hum. Hypertens. 2023, 37, 649–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donoghue, G.; Perchoux, C.; Mensah, K.; Lakerveld, J.; van der Ploeg, H.; Bernaards, C.; Chastin, S.F.; Simon, C.; O’Gorman, D.; Nazare, J.A. A systematic review of correlates of sedentary behaviour in adults aged 18–65 years: A socio-ecological approach. BMC Public Health 2016, 16, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chastin, S.F.; Buck, C.; Freiberger, E.; Murphy, M.; Brug, J.; Cardon, G.; O’Donoghue, G.; Pigeot, I.; Oppert, J.M. Systematic literature review of determinants of sedentary behaviour in older adults: A DEDIPAC study. Int. J. Behav. Nutr. Phys. Act. 2015, 12, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallmann-Sperlich, B.; Bucksch, J.; Hansen, S.; Schantz, P.; Froboese, I. Sitting time in Germany: An analysis of socio-demographic and environmental correlates. BMC Public Health 2013, 13, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
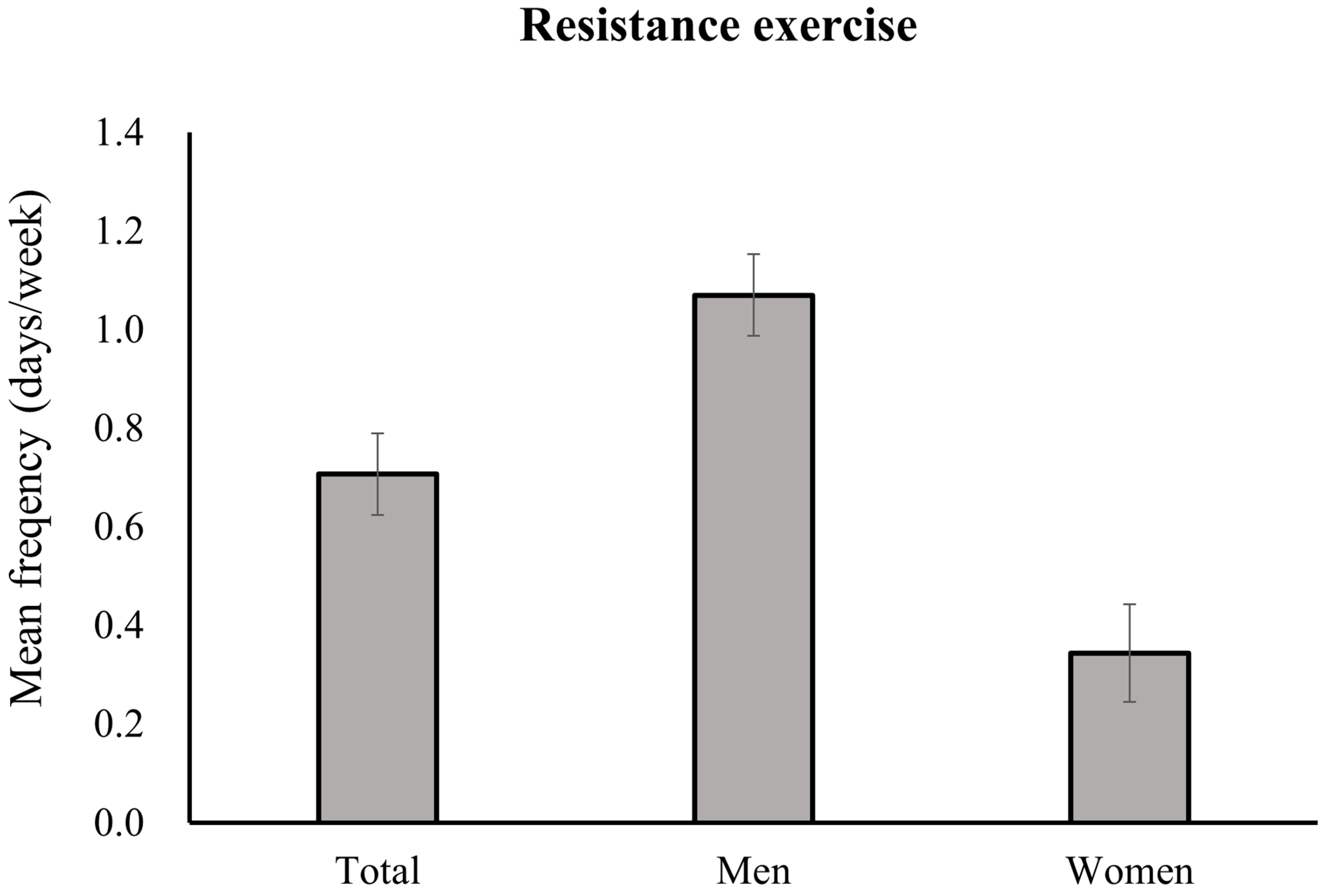
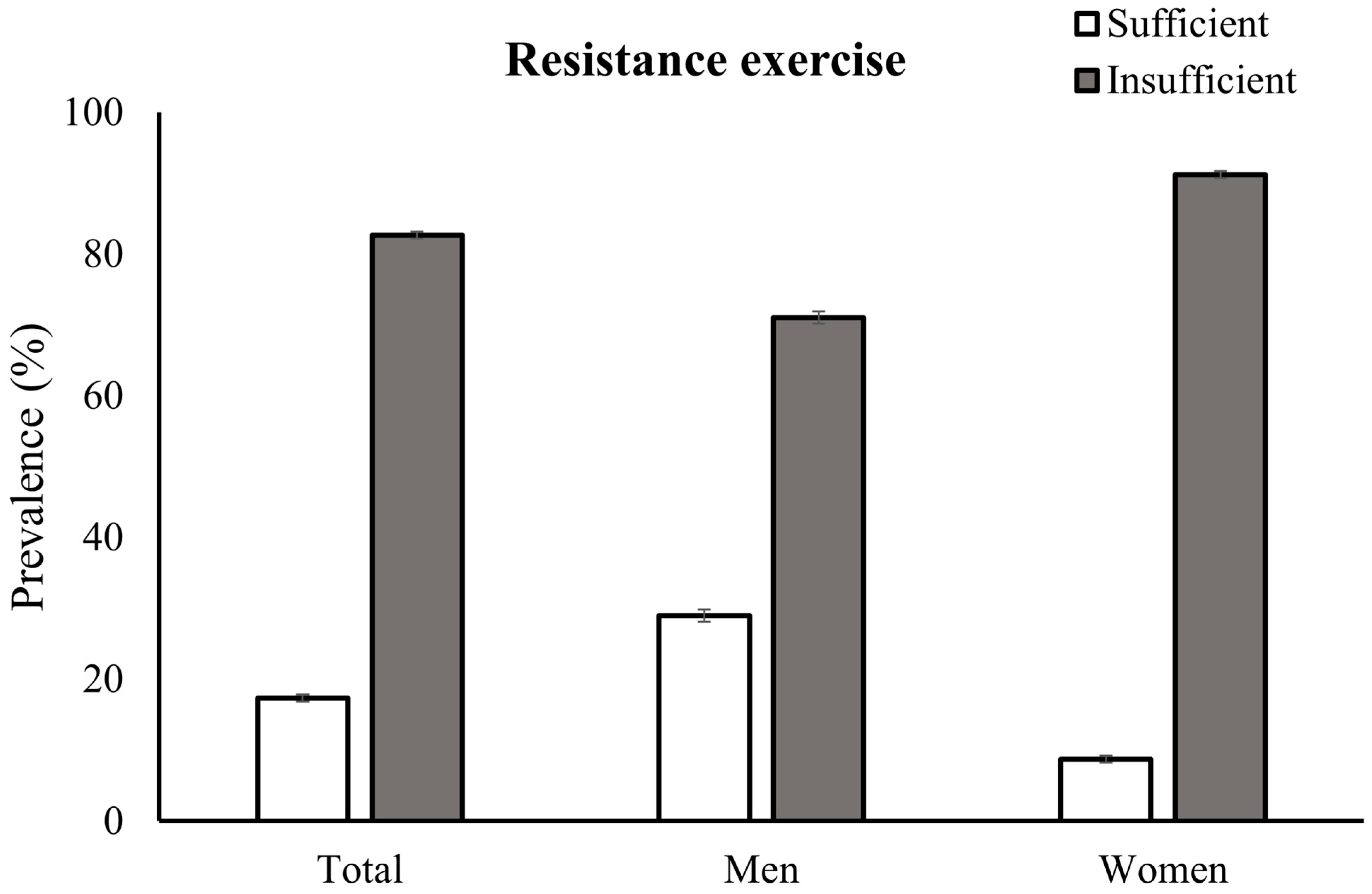
| Variable | Total Participants | Men | Women | p Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unweighted number (n) | 8671 | 3758 | 4913 | |
| Weighted number (n) | 6,323,508 | 2,689,087 | 3,634,421 | |
| Sociodemographic factors | ||||
| Age group (%) | <0.001 | |||
| 65–69 years | 33.20 (0.64) | 36.94 (0.96) | 30.44 (0.77) | |
| 70–74 years | 25.94 (0.54) | 27.59 (0.81) | 24.72 (0.70) | |
| 75–79 years | 24.16 (0.56) | 21.51 (0.73) | 26.12 (0.76) | |
| ≥80 years | 16.70 (0.53) | 13.97 (0.67) | 18.73 (0.71) | |
| Education (%) | <0.001 | |||
| ≥12 years | 26.92 (0.76) | 42.50 (1.06) | 15.38 (0.74) | |
| <12 years | 73.08 (0.76) | 57.50 (1.06) | 84.62 (0.74) | |
| Residence (%) | 0.488 | |||
| Urban | 75.74 (1.57) | 76.12 (1.71) | 75.45 (1.59) | |
| Rural | 24.26 (1.57) | 23.88 (1.71) | 24.55 (1.59) | |
| Household income (%) | <0.001 | |||
| High | 10.4 (0.6) | 12.7 (0.7) | 8.8 (0.6) | |
| Mid-high | 15.7 (0.6) | 17.6 (0.8) | 14.4 (0.7) | |
| Mid-low | 27.0 (0.7) | 30.1 (0.9) | 24.7 (0.7) | |
| Low | 46.8 (0.9) | 39.6 (1.0) | 52.2 (1.0) | |
| Cohabitants (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Yes | 79.7 (0.6) | 89.0 (0.6) | 72.8 (0.8) | |
| No | 20.3 (0.6) | 11.0 (0.6) | 27.2 (0.8) | |
| Behavioral factors | ||||
| Alcohol consumption (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Non-excessive | 93.83 (0.31) | 88.08 (0.63) | 98.12 (0.22) | |
| Excessive | 6.17 (0.31) | 11.92 (0.63) | 1.88 (0.22) | |
| Smoking (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Never | 62.65 (0.57) | 20.45 (0.76) | 94.11 (0.42) | |
| Past | 27.93 (0.52) | 60.73 (0.92) | 3.47 (0.30) | |
| Current | 9.42 (0.39) | 18.82 (0.76) | 2.42 (0.28) | |
| Aerobic exercise (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Sufficient | 32.94 (0.67) | 39.24 (0.96) | 28.24 (0.82) | |
| Insufficient | 67.06 (0.67) | 60.76 (0.96) | 71.76 (0.82) | |
| Sedentary time (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Low | 43.42 (0.76) | 47.08 (1.02) | 40.58 (0.92) | |
| High | 56.58 (0.76) | 52.92 (1.02) | 59.42 (0.92) | |
| Obesity status (%) | <0.001 | |||
| Underweight | 2.94 (0.21) | 3.61 (0.34) | 2.44 (0.26) | |
| Normal weight | 33.74 (0.62) | 35.94 (0.90) | 32.10 (0.82) | |
| Overweight | 26.44 (0.57) | 27.96 (0.88) | 25.31 (0.74) | |
| Obese | 36.88 (0.62) | 32.48 (0.93) | 40.15 (0.80) | |
| Presence of comorbidity (%) | ||||
| Hypertension | 63.31 (0.63) | 59.15 (0.93) | 66.38 (0.83) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes | 28.01 (0.57) | 28.83 (0.87) | 27.41 (0.74) | 0.207 |
| Cardiovascular disease | 13.51 (0.42) | 15.93 (0.66) | 11.72 (0.55) | <0.001 |
| Chronic lung disease | 30.19 (0.62) | 41.86 (0.95) | 21.56 (0.69) | <0.001 |
| Cancer | 9.96 (0.38) | 11.27 (0.58) | 8.99 (0.48) | 0.002 |
| Arthritis | 32.15 (0.58) | 13.45 (0.63) | 45.99 (0.82) | <0.001 |
| Depression | 6.36 (0.30) | 3.03 (0.34) | 8.82 (0.45) | <0.001 |
| Variable | Unadjusted | Adjusted * |
|---|---|---|
| Sociodemographic factors | ||
| Age groups | ||
| 65–69 years | Reference | Reference |
| 70–74 years | 1.22 (1.04–1.42) | 1.04 (0.87–1.24) |
| 75–79 years | 2.14 (1.80–2.55) | 1.53 (1.25–1.87) |
| ≥80 years | 3.69 (2.94–4.63) | 2.39 (1.86–3.07) |
| Sex | ||
| Men | Reference | Reference |
| Women | 4.26 (3.70–4.92) | 3.84 (3.02–4.88) |
| Education | ||
| ≥12 years | Reference | Reference |
| <12 years | 3.00 (2.62–3.45) | 1.56 (1.33–1.82) |
| Residence | ||
| Urban | Reference | Reference |
| Rural | 2.32 (1.85–2.92) | 1.89 (1.49–2.38) |
| Household income | ||
| High | Reference | Reference |
| Mid-high | 1.18 (0.93–1.49) | 1.02 (0.79–1.33) |
| Mid-low | 1.49 (1.20–1.86) | 1.10 (0.86–1.42) |
| Low | 2.84 (2.27–3.54) | 1.45 (1.13–1.88) |
| Cohabitants | ||
| Yes | Reference | Reference |
| No | 1.97 (1.67–2.33) | 1.01 (0.83–1.23) |
| Behavioral factors | ||
| Alcohol consumption | ||
| Non-excessive | Reference | Reference |
| Excessive | 0.61 (0.48–0.78) | 1.07 (0.82–1.39) |
| Smoking | ||
| Never | Reference | Reference |
| Past | 0.31 (0.27–0.35) | 0.91 (0.73–1.13) |
| Current | 0.63 (0.49–0.80) | 1.70 (1.26–2.29) |
| Aerobic exercise | ||
| Sufficient | Reference | Reference |
| Insufficient | 2.36 (2.07–2.68) | 1.68 (1.46–1.94) |
| Sedentary time | ||
| Low | Reference | Reference |
| High | 1.28 (1.11–1.48) | 1.04 (0.89–1.22) |
| Obesity status | ||
| Underweight | 1.66 (1.09–2.53) | 1.32 (0.85–2.05) |
| Normal weight | Reference | Reference |
| Overweight | 0.88 (0.74–1.03) | 0.92 (0.77–1.10) |
| Obese | 1.09 (0.92–1.28) | 1.00 (0.84–1.19) |
| Presence of comorbidity ** | ||
| Hypertension | 1.25 (1.09–1.44) | 0.96 (0.82–1.13) |
| Diabetes | 1.27 (1.10–1.47) | 1.28 (1.09–1.51) |
| Cardiovascular disease | 1.19 (0.98–1.43) | 1.19 (0.96–1.46) |
| Chronic lung disease | 0.67 (0.58–0.76) | 0.97 (0.83–1.13) |
| Cancer | 0.87 (0.71–1.07) | 1.00 (0.79–1.26) |
| Arthritis | 1.79 (1.54–2.07) | 0.93 (0.78–1.11) |
| Depression | 1.29 (0.96–1.73) | 0.84 (0.60–1.18) |
| Variable | Men | Women | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Unadjusted | Adjusted * | Unadjusted | Adjusted * | |
| Sociodemographic factors | ||||
| Age group (years) | ||||
| 65–69 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| 70–74 | 1.10 (0.91–1.34) | 0.98 (0.79–1.22) | 1.41 (1.09–1.84) | 1.18 (0.89–1.56) |
| 75–79 | 1.94 (1.55–2.42) | 1.57 (1.22–2.02) | 2.04 (1.49–2.79) | 1.42 (1.01–2.01) |
| ≥80 | 3.04 (2.30–4.01) | 2.38 (1.77–3.19) | 4.05 (2.64–6.21) | 2.24 (1.42–3.54) |
| Education (years) | ||||
| ≥12 | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| <12 | 1.96 (1.66–2.32) | 1.45 (1.20–1.75) | 2.46 (1.89–3.22) | 1.80 (1.32–2.44) |
| Residence | ||||
| Urban | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Rural | 2.64 (2.05–3.40) | 2.09 (1.60–2.74) | 2.01 (1.41–2.86) | 1.52 (1.05–2.21) |
| Household income | ||||
| High | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Mid-high | 1.11 (0.83–1.48) | 0.99 (0.73–1.35) | 1.17 (0.76–1.80) | 1.23 (0.80–1.90) |
| Mid-low | 1.46 (1.12–1.90) | 1.06 (0.79–1.43) | 1.44 (0.97–2.15) | 1.18 (0.77–1.81) |
| Low | 2.69 (2.05–3.53) | 1.60 (1.18–2.17) | 2.03 (1.38–2.99) | 1.07 (0.69–1.67) |
| Cohabitants | ||||
| Yes | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| No | 1.36 (1.06–1.76) | 0.99 (0.74–1.32) | 1.44 (1.11–1.87) | 1.06 (0.78–1.43) |
| Behavioral factors | ||||
| Alcohol | ||||
| Non-excessive | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Excessive | 1.05 (0.81–1.36) | 1.16 (0.88–1.54) | 0.83 (0.37–1.84) | 0.75 (0.34–1.65) |
| Smoking | ||||
| Never | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Past | 0.94 (0.77–1.16) | 0.97 (0.78–1.20) | 0.65 (0.36–1.19) | 0.61 (0.33–1.14) |
| Current | 1.81 (1.34–2.43) | 1.84 (1.35–2.52) | 1.46 (0.61–3.46) | 1.29 (0.52–3.22) |
| Aerobic exercise | ||||
| Sufficient | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Insufficient | 2.12 (1.80–2.50) | 1.70 (1.42–2.03) | 2.08 (1.62–2.66) | 1.67 (1.29–2.16) |
| Sedentary time | ||||
| Low | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| High | 1.08 (0.91–1.28) | 1.00 (0.82–1.21) | 1.44 (1.14–1.83) | 1.16 (0.90–1.49) |
| Obesity status | ||||
| Underweight | 1.92 (1.15–3.21) | 1.33 (0.79–2.23) | 1.64 (0.77–3.46) | 1.14 (0.54–2.40) |
| Normal weight | Reference | Reference | Reference | Reference |
| Overweight | 0.75 (0.61–0.92) | 0.83 (0.66–1.03) | 1.15 (0.85–1.55) | 1.18 (0.85–1.66) |
| Obese | 0.84 (0.68–1.02) | 0.97 (0.78–1.22) | 1.27 (0.98–1.65) | 1.08 (0.83–1.41) |
| Presence of comorbidity ** | ||||
| Hypertension | 0.91 (0.77–1.08) | 0.79 (0.65–0.97) | 1.74 (1.36–2.21) | 1.40 (1.09–1.79) |
| Diabetes | 1.23 (1.03–1.48) | 1.28 (1.05–1.56) | 1.56 (1.17–2.09) | 1.23 (0.90–1.68) |
| Cardiovascular disease | 1.36 (1.09–1.70) | 1.21 (0.95–1.55) | 1.39 (0.93–2.08) | 1.13 (0.74–1.74) |
| Chronic lung disease | 0.87 (0.73–1.03) | 0.96 (0.80–1.15) | 1.04 (0.79–1.36) | 1.00 (0.76–1.33 |
| Cancer | 1.15 (0.88–1.51) | 1.15 (0.87–1.54) | 0.64 (0.46–0.91) | 0.72 (0.50–1.03) |
| Arthritis | 1.12 (0.87–1.43) | 1.00 (0.76–1.30) | 0.96 (0.75–1.22) | 0.82 (0.64–1.06) |
| Depression | 1.33 (0.78–2.29) | 1.24 (0.72–2.12) | 0.69 (0.48–0.99) | 0.69 (0.46–1.02) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mun, S.Y.; Choi, B.-C.; Lee, J.S.; Kim, Y.H. Resistance Exercise Participation in Community-Dwelling Older Adults in Korea: Associated Factors and Sex Differences. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5900. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195900
Mun SY, Choi B-C, Lee JS, Kim YH. Resistance Exercise Participation in Community-Dwelling Older Adults in Korea: Associated Factors and Sex Differences. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(19):5900. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195900
Chicago/Turabian StyleMun, Seo Young, Byung-Chan Choi, Jung Soo Lee, and Yeo Hyung Kim. 2024. "Resistance Exercise Participation in Community-Dwelling Older Adults in Korea: Associated Factors and Sex Differences" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 19: 5900. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195900
APA StyleMun, S. Y., Choi, B.-C., Lee, J. S., & Kim, Y. H. (2024). Resistance Exercise Participation in Community-Dwelling Older Adults in Korea: Associated Factors and Sex Differences. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(19), 5900. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195900






