The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score Predicting Mortality Due to SARS-CoV-2 in Mexican Patients
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Participants
2.2. Data Collection
2.3. Outcome and Exposure Variable
2.4. Laboratory Biomarkers Reported for COVID-19
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Sample Overview
3.2. Assessment of the Hematologic and Biochemical Parameters for Predicting COVID-19 Mortality
3.3. Survival Analysis Using Kaplan–Meier Curves
3.4. MELD Score Is a Predictor of COVID-19 Mortality
3.5. Correlation Analysis between MELD Score and Inflammation-Related Parameters in Patients with COVID-19
3.6. Leukocyte Glucose Index Can Predict a MELD Score >9 in Patients with COVID-19
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Kumar, A.; Singh, R.; Kaur, J.; Pandey, S.; Sharma, V.; Thakur, L.; Sati, S.; Mani, S.; Asthana, S.; Sharma, T.K.; et al. Wuhan to World: The COVID-19 Pandemic. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 596201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, F.; Chen, W.; Chen, J.; Xu, D.; Xie, W.; Wang, X.; Xie, Y. Clinical features and risk factors of COVID-19-associated liver injury and function: A retrospective analysis of 830 cases. Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 21, 100267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, K.; Samuel, K.; Vandeputte, M.; Hayes, P.C.; Plevris, J.N. SARS-CoV-2 Infection and the Liver. Pathogens 2020, 9, 430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krishnan, A.; Prichett, L.; Tao, X.; Alqahtani, S.A.; Hamilton, J.P.; Mezey, E.; Strauss, A.T.; Kim, A.; Potter, J.J.; Chen, P.-H.; et al. Abnormal liver chemistries as a predictor of COVID-19 severity and clinical outcomes in hospitalized patients. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 570–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alva, N.V.; Méndez, O.R.; Gasca, J.C.; Salvador, I.; Hernández, N.; Valdez, M. Liver injury due to COVID-19 in critically ill adult patients. A retrospective study. Rev. Gastroenterol. Mex. (Engl. Ed.) 2024, 89, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Licata, A.; Minissale, M.G.; Distefano, M.; Montalto, G. Liver injury, SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19: What physicians should really know? GastroHep 2021, 3, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singal, A.K.; Kamath, P.S. Model for End-stage Liver Disease. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2013, 3, 50–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stawinski, P.M.; Dziadkowiec, K.N.; Al-Abbasi, B.; Suarez, L.; Simms, L.; Dewaswala, N.; Torres, P.; Al Rubaye, A.; Pino, J.; Marcus, A. Model of End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score as a Predictor of In-Hospital Mortality in Patients with COVID-19: A Novel Approach to a Classic Scoring System. Cureus 2021, 13, e15179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaya, Y.; Gülcü, O.; Aksakal, E.; Kalkan, K.; Aydın, Ş.; Kaya, A.; Bostan, S. A significant predictor of in-hospital and long-term mortality and progression in COVID-19 patients: The end-stage liver disease (MELD) score model. J. Med. Virol. 2023, 95, e28109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Samiee, M.; Shaldoum, M.; Abdelsameea, E.; Awad, S.M.; Omar, N.A. Impact of COVID-19 on Liver Functions Tests in Egyptian Patients with or without Chronic Liver Disease. Afro-Egypt J. Infect. Endem Dis. 2024, 14, 75–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; García-Hernández, O.; Martínez-Mier, G.; Osuna-Ramos, J.F.; De Jesús-González, L.A.; Farfan-Morales, C.N.; Palacios-Rápalo, S.N.; Cordero-Rivera, C.D.; Ordoñez-Rodríguez, T.; Ángel, R.M.d. The Role of Aspartate Aminotransferase-to-Lymphocyte Ratio Index (ALRI) in Predicting Mortality in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gemcioglu, E.; Davutoglu, M.; Catalbas, R.; Karabuga, B.; Kaptan, E.; Aypak, A.; Kalem, A.K.; Özdemir, M.; Yeşilova, N.Y.; A Kalkan, E.; et al. Predictive values of biochemical markers as early indicators for severe COVID-19 cases in admission. Future Virol. 2021, 16, 353–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, D.; Yang, H.; Yu, H.; Wang, T.; Chen, Z.; Yao, R.; Liang, Z. Diagnostic Value of Hematological and Biochemical Parameters Combinations for Predicting Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Suspected Patients. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2021, 362, 387–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, J.B.; Xu, C.; Zhang, R.B.; Wu, M.; Pan, C.K.; Li, X.J.; Wang, Q.; Zeng, F.; Zhu, S. Associations of procalcitonin, C-reaction protein and neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio with mortality in hospitalized COVID-19 patients in China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 15058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.P.; Liu, J.P.; Tao, W.Q.; Li, H.M. The diagnostic and predictive role of NLR, d-NLR and PLR in COVID-19 patients. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2020, 84, 106504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fois, A.G.; Paliogiannis, P.; Scano, V.; Cau, S.; Babudieri, S.; Perra, R.; Ruzzittu, G.; Zinellu, E.; Pirina, P.; Carru, C.; et al. The Systemic Inflammation Index on Admission Predicts In-Hospital Mortality in COVID-19 Patients. Molecules 2020, 25, 5725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos-Hernández, W.M.; Soto, L.F.; Del Rosario-Trinidad, M.; Farfan-Morales, C.N.; De Jesús-González, L.A.; Martínez-Mier, G.; Osuna-Ramos, J.F.; Bastida-González, F.; Bernal-Dolores, V.; del Ángel, R.M.; et al. Leukocyte glucose index as a novel biomarker for COVID-19 severity. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 14956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serin, I.; Sari, N.D.; Dogu, M.H.; Acikel, S.D.; Babur, G.; Ulusoy, A.; Onar, M.I.; Gokce, E.C.; Altunok, O.; Mert, F.Y.; et al. A new parameter in COVID-19 pandemic: Initial lactate dehydrogenase (LDH)/Lymphocyte ratio for diagnosis and mortality. J. Infect. Public Health 2020, 13, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ok, F.; Erdogan, O.; Durmus, E.; Carkci, S.; Canik, A. Predictive values of blood urea nitrogen/creatinine ratio and other routine blood parameters on disease severity and survival of COVID-19 patients. J. Med. Virol. 2021, 93, 786–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, H.A.M.; Thabet, A.A.; Wardany, A.A.; El-Adly, A.M.; Ali, M.; Hassan, M.E.A.; Abdeldayem, M.A.B.; Mohamed, A.-R.M.A.; Sobhy, A.; El-Mokhtar, M.A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 outbreak: Role of viral proteins and genomic diversity in virus infection and COVID-19 progression. Virol. J. 2024, 21, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dessie, Z.G.; Zewotir, T. Mortality-related risk factors of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis of 42 studies and 423,117 patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, K.; Zuo, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, M.; Xie, S.; Zhang, H.; Chen, X.; Liu, C. Early decrease in blood platelet count is associated with poor prognosis in COVID-19 patients—Indications for predictive, preventive, and personalized medical approach. EPMA J. 2020, 11, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citu, C.; Gorun, F.; Motoc, A.; Sas, I.; Gorun, O.M.; Burlea, B.; Tuta-Sas, I.; Tomescu, L.; Neamtu, R.; Malita, D.; et al. The Predictive Role of NLR, d-NLR, MLR, and SIRI in COVID-19 Mortality. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghobadi, H.; Mohammadshahi, J.; Javaheri, N.; Fouladi, N.; Mirzazadeh, Y.; Aslani, M.R. Role of leukocytes and systemic inflammation indexes (NLR, PLR, MLP, dNLR, NLPR, AISI, SIR-I, and SII) on admission predicts in-hospital mortality in non-elderly and elderly COVID-19 patients. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 916453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simon, P.; Le Borgne, P.; Lefevbre, F.; Cipolat, L.; Remillon, A.; Dib, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Gardeur, I.; Sabah, J.; Kepka, S.; et al. Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratio (PLR) Is Not a Predicting Marker of Severity but of Mortality in COVID-19 Patients Admitted to the Emergency Department: A Retrospective Multicenter Study. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslamijouybari, M.; Heydari, K.; Maleki, I.; Moosazadeh, M.; Hedayatizadeh-Omran, A.; Vahedi, L.; Ghasemian, R.; Sharifpour, A.; Alizadeh-Navaei, R. Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte and Platelet-to-Lymphocyte Ratios in COVID-19 Patients and Control Group and Relationship with Disease Prognosis. Casp. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 11 (Suppl. S1), 531–535. [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi, S.A.; Rad, S.; Rostami, T.; Rostami, M.; Mousavi, S.A.; Mirhoseini, S.A.; Kiumarsi, A. Hematologic predictors of mortality in hospitalized patients with COVID-19: A comparative study. Hematology 2020, 25, 383–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Kannan, S.; Khanna, P.; Singh, A.K. Role of platelet-to-lymphocyte count ratio (PLR), as a prognostic indicator in COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Med. Virol. 2022, 94, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanner, N.; Andrieux, G.; Badia-i-Mompel, P.; Edler, C.; Pfefferle, S.; Lindenmeyer, M.T.; Schmidt-Lauber, C.; Czogalla, J.; Wong, M.N.; Okabayashi, Y.; et al. Molecular consequences of SARS-CoV-2 liver tropism. Nat. Metab. 2022, 4, 310–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, Z.Y.; Li, G.X.; Chen, L.; Shu, C.; Song, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Q.; Jin, G.; Liu, T.; et al. Association of liver abnormalities with in-hospital mortality in patients with COVID-19. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 1295–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, A.; Sulkowski, M.; Barin, B.; Stablein, D.; Curry, M.; Nissen, N.; Dove, L.; Roland, M.; Florman, S.; Blumberg, E.; et al. MELD score is an important predictor of pretransplantation mortality in HIV-infected liver transplant candidates. Gastroenterology 2010, 138, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butt, A.A.; Ren, Y.; Lo Re, V.I.I.I.; Taddei, T.H.; Kaplan, D.E. Comparing Child-Pugh, MELD, and FIB-4 to Predict Clinical Outcomes in Hepatitis C Virus-Infected Persons: Results From ERCHIVES. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2017, 65, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, R.M.; Davern, T.; Munoz, S.; Han, S.-H.; McGuire, B.; Larson, A.M.; Hynan, L.; Lee, W.M.; Fontana, R.J.; U.S. Acute Liver Failure Study Group. Fulminant hepatitis A virus infection in the United States: Incidence, prognosis, and outcomes. Hepatology 2006, 44, 1589–1597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
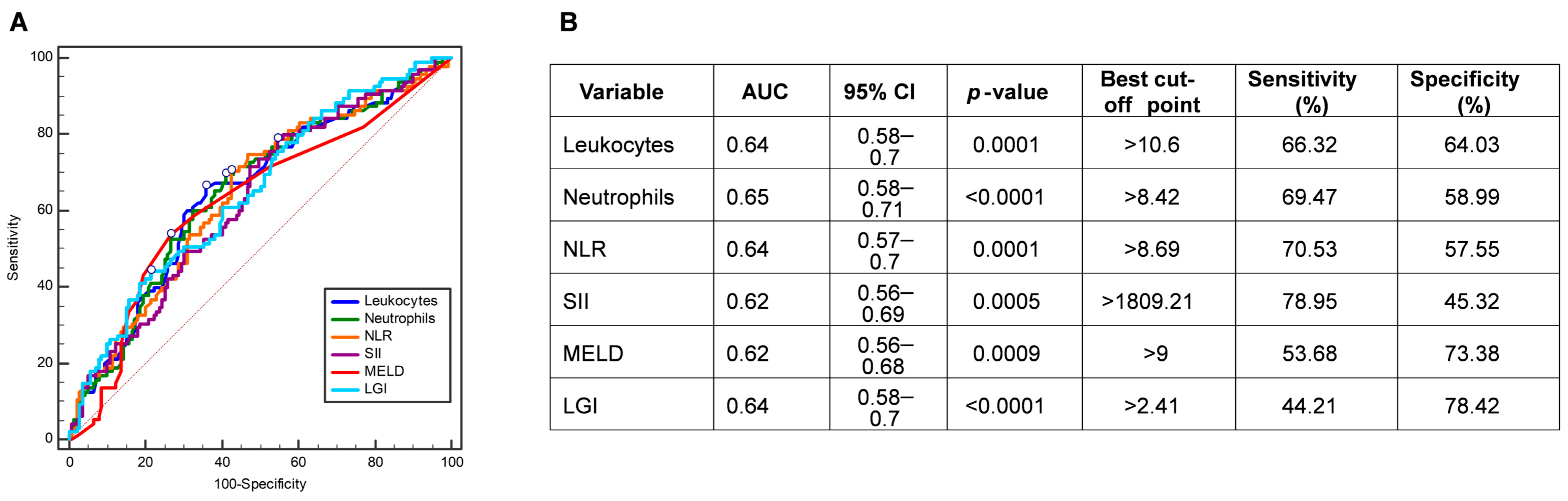
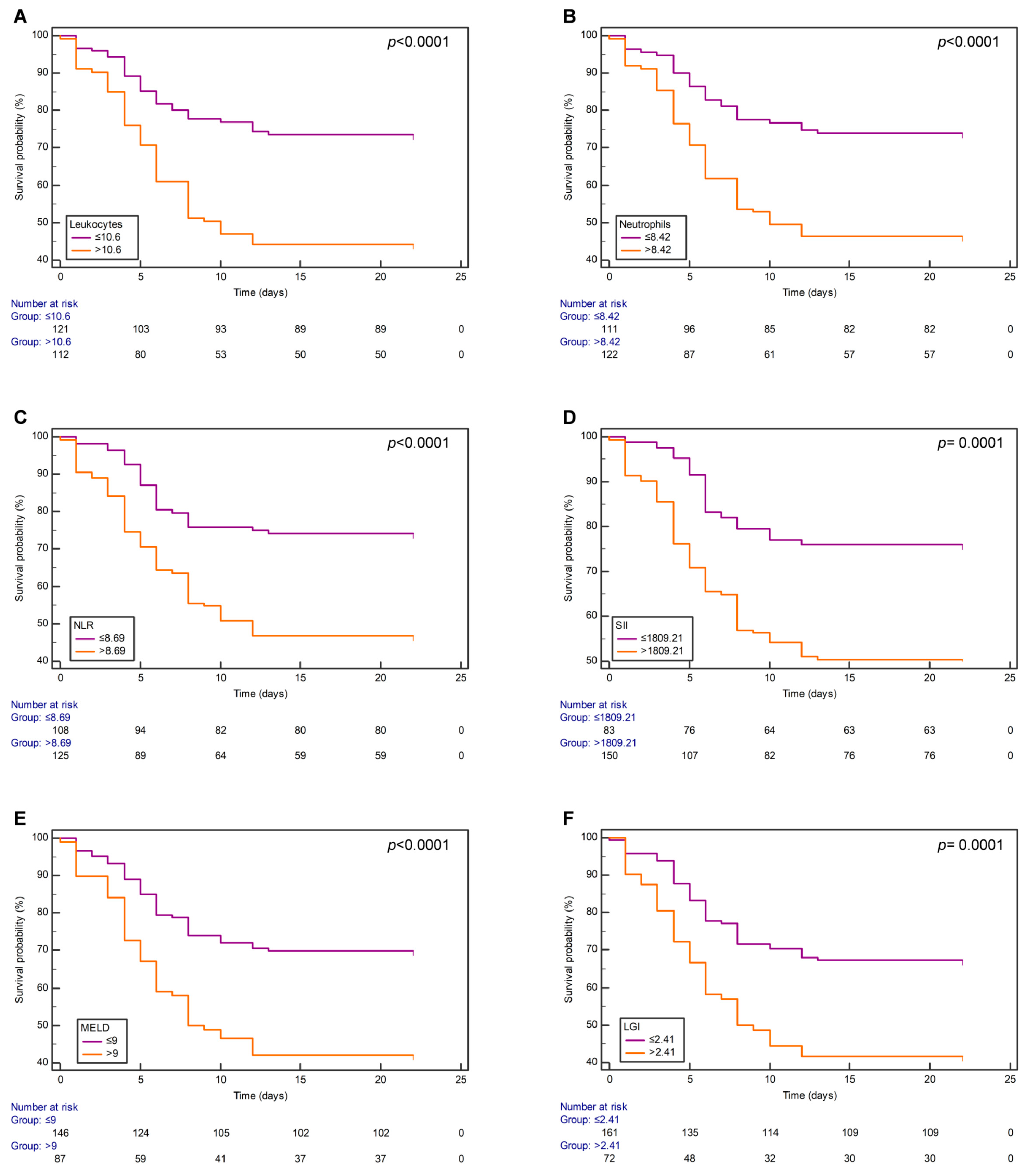

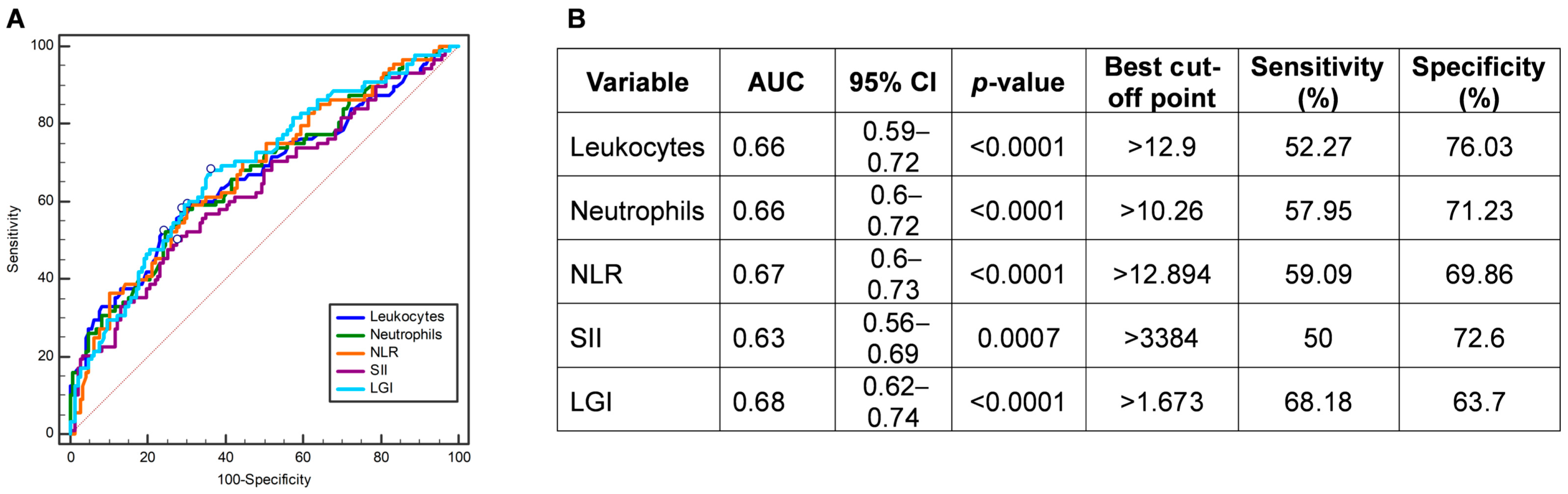
| Variable | Overall (n = 234) | Survival Group (n = 139) | Non-Survival Group (n = 95) | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, female | 71 (30.34%) | 41 (29.49%) | 30 (31.57%) | 0.734 | 1 |
| Age (years old) | 63.27 ± 12.91 | 62.74 ± 12.678 | 65.23 ± 13.86 | 0.005 | 0.190 |
| Height (m) | 1.6 ± 0.9 | 1.6 ± 0.09 | 1.59 ± 0.1 | 0.910 | 1 |
| Weight (kg) | 73.25 (22.5) | 74 (20.75) | 67 (21.25) | 0.220 | 1 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 28.07 (6.1) | 28.34 (5.57) | 27.4 (7) | 0.339 | 1 |
| Diabetes | 114 (48.71%) | 79 (56.83%) | 35 (36.84%) | 0.003 | 0.114 |
| Hypertension | 112 (47.86%) | 70 (50.35%) | 42 (44.21%) | 0.355 | 1 |
| FiO2 (%) | 50 (39) | 41 (31) | 60 (47) | 0.008 | 0.304 |
| SpO2 (%) | 64 (39) | 71 (38) | 58.5 (35) | 0.042 | 1 |
| Hemoglobin (g/dL) | 14.5 (2.7) | 14.5 (2.4) | 14.5 (3.2) | 0.373 | 1 |
| Hematocrit (%) | 44 (8) | 44 (7) | 44 (7) | 0.377 | 1 |
| MCV | 91 (6) | 91 (6) | 91 (5) | 0.152 | 1 |
| MCH | 30.2 (2.3) | 30.2 (2.3) | 30.2 (2.2) | 0.621 | 1 |
| Leukocytes (×109/L) | 10.45 (7) | 9.5 (6.7) | 12.6 (7.3) | 0.0001 | 0.003 |
| Neutrophils (×109/L) | 8.74 (6.8) | 7.72 (6.32) | 11.39 (7.52) | 0.0001 | 0.003 |
| Lymphocytes (×109/L) | 0.81 (0.7) | 0.86 (0.72) | 0.76 (0.65) | 0.122 | 1 |
| Platelets (×109/L) | 252 (135) | 246 (130) | 267 (128) | 0.355 | 1 |
| INR | 1.05 (0.17) | 1.03 (0.16) | 1.08 (0.18) | 0.048 | 1 |
| Glucose (mg/dL) | 143 (120) | 132.5 (105) | 158 (142) | 0.006 | 0.228 |
| Urea (mg/dL) | 45.8 (45.8) | 38.2 (38.6) | 57.1 (58.6) | 0.008 | 0.304 |
| Creatinine (mg/dL) | 0.9 (0.7) | 0.9 (0.5) | 1.1 (1.1) | 0.004 | 0.152 |
| LDH (U/L) | 850 (472) | 820 (462) | 916 (465) | 0.008 | 0.304 |
| BUN | 21.4 (20.8) | 17.75 (17.82) | 27 (27.5) | 0.002 | 0.076 |
| TB (mg/dL) | 0.6 (0.4) | 0.5 (0.4) | 0.6 (0.37) | 0.275 | 1 |
| DB (mg/dL) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.2 (0.2) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.004 | 0.152 |
| IB (mg/dL) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.3 (0.15) | 0.3 (0.2) | 0.186 | 1 |
| AST (IU/L) | 46 (44) | 42.5 (47) | 49 (40) | 0.331 | 1 |
| ALT (IU/L) | 37 (38) | 41.5 (45) | 32 (30) | 0.175 | 1 |
| ALRI | 60 (75.13) | 53.31 (69.67) | 65.04 (74.87) | 0.241 | 1 |
| APRI | 0.48 (0.61) | 0.49 (0.63) | 0.46 (0.52) | 0.785 | 1 |
| ANRI | 4.59 (7.07) | 5.14 (8.18) | 4.41 (5.85) | 0.178 | 1 |
| NLR | 9.44 (12.15) | 8.06 (11.02) | 14.57 (15.19) | 0.0001 | 0.003 |
| PLR | 284.67 (267.33) | 265.83 (238.26) | 329.78 (302.1) | 0.058 | 1 |
| SII | 2525.03 (3503.23) | 2149.52 (2759.38) | 3017.84 (3976.29) | 0.001 | 0.038 |
| MELD | 8 (5) | 8 (3) | 10 (7) | 0.001 | 0.038 |
| LGI | 1.61 (1.61) | 1.36 (1.4) | 1.88 (2) | 0.0001 | 0.003 |
| LDH/LR | 1038.27 (1091.26) | 933.76 (955.81) | 1193.15 (1237.85) | 0.014 | 0.504 |
| BUN/Cr | 20.4 (12.79) | 20.69 (13.19) | 20 (14.63) | 0.438 | 1 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | HR | 95% CI | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value |
| Leukocytes | 2.53 | 1.66–3.87 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 | 1.55 | 0.62–3.86 | 0.342 | 1 |
| Neutrophils | 2.45 | 1.59–3.79 | <0.0001 | 0.0003 | 0.96 | 0.36–2.51 | 0.939 | 1 |
| NLR | 2.46 | 1.58–3.82 | <0.0001 | 0.0003 | 1.34 | 0.73–2.45 | 0.340 | 1 |
| SII | 2.49 | 1.52–4 | 0.0002 | 0.001 | 1.46 | 0.75–2.83 | 0.255 | 1 |
| MELD | 2.34 | 1.56–3.5 | <0.0001 | 0.0001 | 1.83 | 1.2–2.8 | 0.005 | 0.030 |
| LGI | 2.17 | 1.45–3.25 | 0.0001 | 0.0006 | 1.2 | 0.74.1.95 | 0.444 | 1 |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Variable | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value | OR | 95% CI | p-Value | Adjusted p-Value |
| Leukocytes | 3.47 | 1.97–6.11 | <0.0001 | 0.0005 | 1.64 | 0.49–5.46 | 0.415 | 1 |
| Neutrophils | 3.41 | 1.96–5.94 | <0.0001 | 0.0005 | 0.89 | 0.25–3.11 | 0.864 | 1 |
| NLR | 3.34 | 1.92–5.82 | <0.0001 | 0.0005 | 2.25 | 1.1–5.13 | 0.052 | 0.260 |
| SII | 2.65 | 1.52–4.6 | 0.001 | 0.005 | 0.98 | 0.43–2.21 | 0.965 | 1 |
| LGI | 3.76 | 2.14–6.59 | <0.0001 | 0.0002 | 2.42 | 1.21–4.83 | 0.009 | 0.045 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reyes-Ruiz, J.M.; Avelino-Santiago, A.C.; Martínez-Mier, G.; López-López, C.V.; De Jesús-González, L.A.; León-Juárez, M.; Osuna-Ramos, J.F.; Farfan-Morales, C.N.; Palacios-Rápalo, S.N.; Bernal-Dolores, V.; et al. The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score Predicting Mortality Due to SARS-CoV-2 in Mexican Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 5777. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195777
Reyes-Ruiz JM, Avelino-Santiago AC, Martínez-Mier G, López-López CV, De Jesús-González LA, León-Juárez M, Osuna-Ramos JF, Farfan-Morales CN, Palacios-Rápalo SN, Bernal-Dolores V, et al. The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score Predicting Mortality Due to SARS-CoV-2 in Mexican Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(19):5777. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195777
Chicago/Turabian StyleReyes-Ruiz, José Manuel, Ana Citlali Avelino-Santiago, Gustavo Martínez-Mier, Claudia Vanessa López-López, Luis Adrián De Jesús-González, Moises León-Juárez, Juan Fidel Osuna-Ramos, Carlos Noe Farfan-Morales, Selvin Noé Palacios-Rápalo, Víctor Bernal-Dolores, and et al. 2024. "The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score Predicting Mortality Due to SARS-CoV-2 in Mexican Patients" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 19: 5777. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195777
APA StyleReyes-Ruiz, J. M., Avelino-Santiago, A. C., Martínez-Mier, G., López-López, C. V., De Jesús-González, L. A., León-Juárez, M., Osuna-Ramos, J. F., Farfan-Morales, C. N., Palacios-Rápalo, S. N., Bernal-Dolores, V., & Del Ángel, R. M. (2024). The Model for End-Stage Liver Disease (MELD) Score Predicting Mortality Due to SARS-CoV-2 in Mexican Patients. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(19), 5777. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13195777












