Bone Imaging of the Knee Using Short-Interval Delta Ultrashort Echo Time and Field Echo Imaging
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
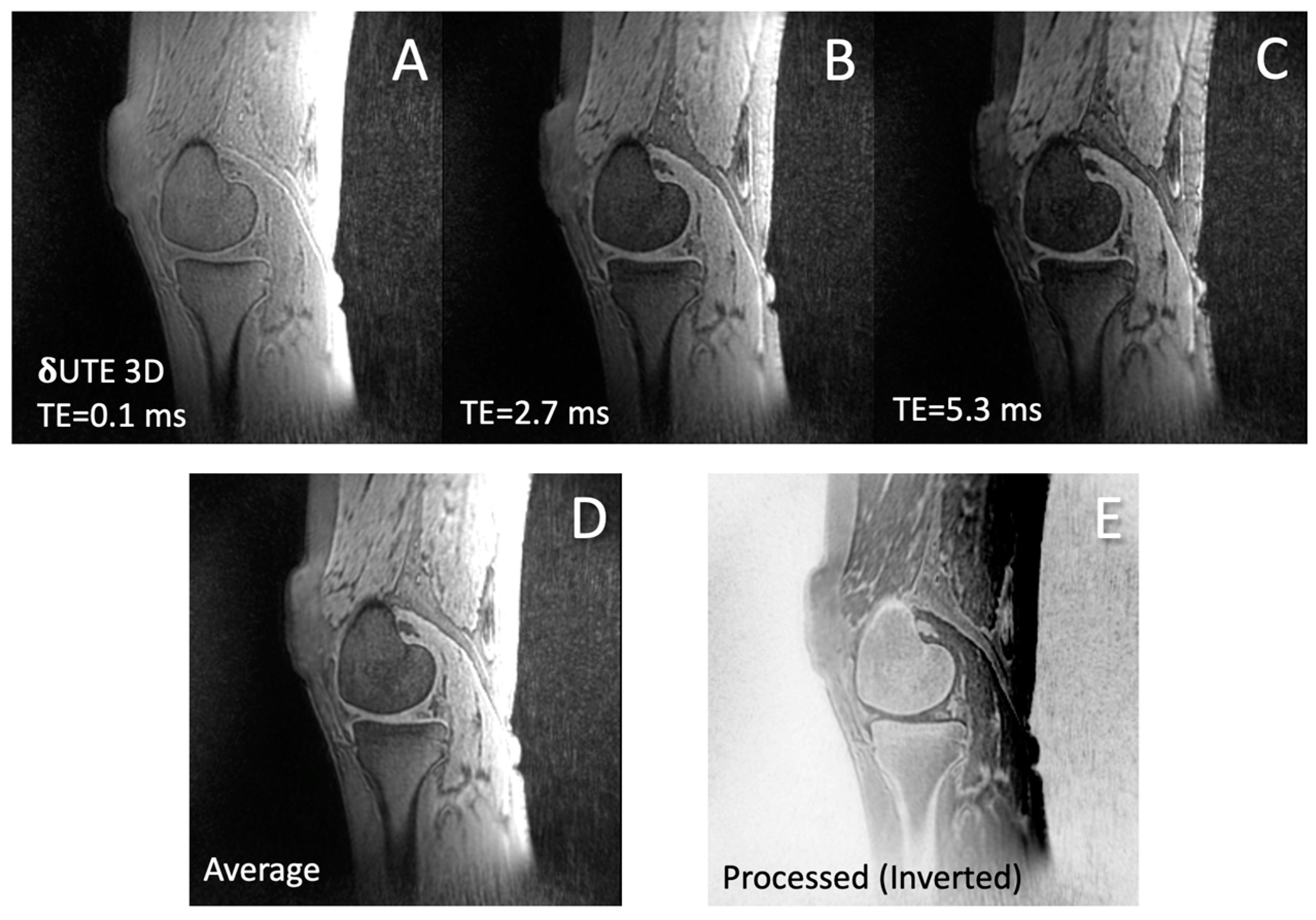
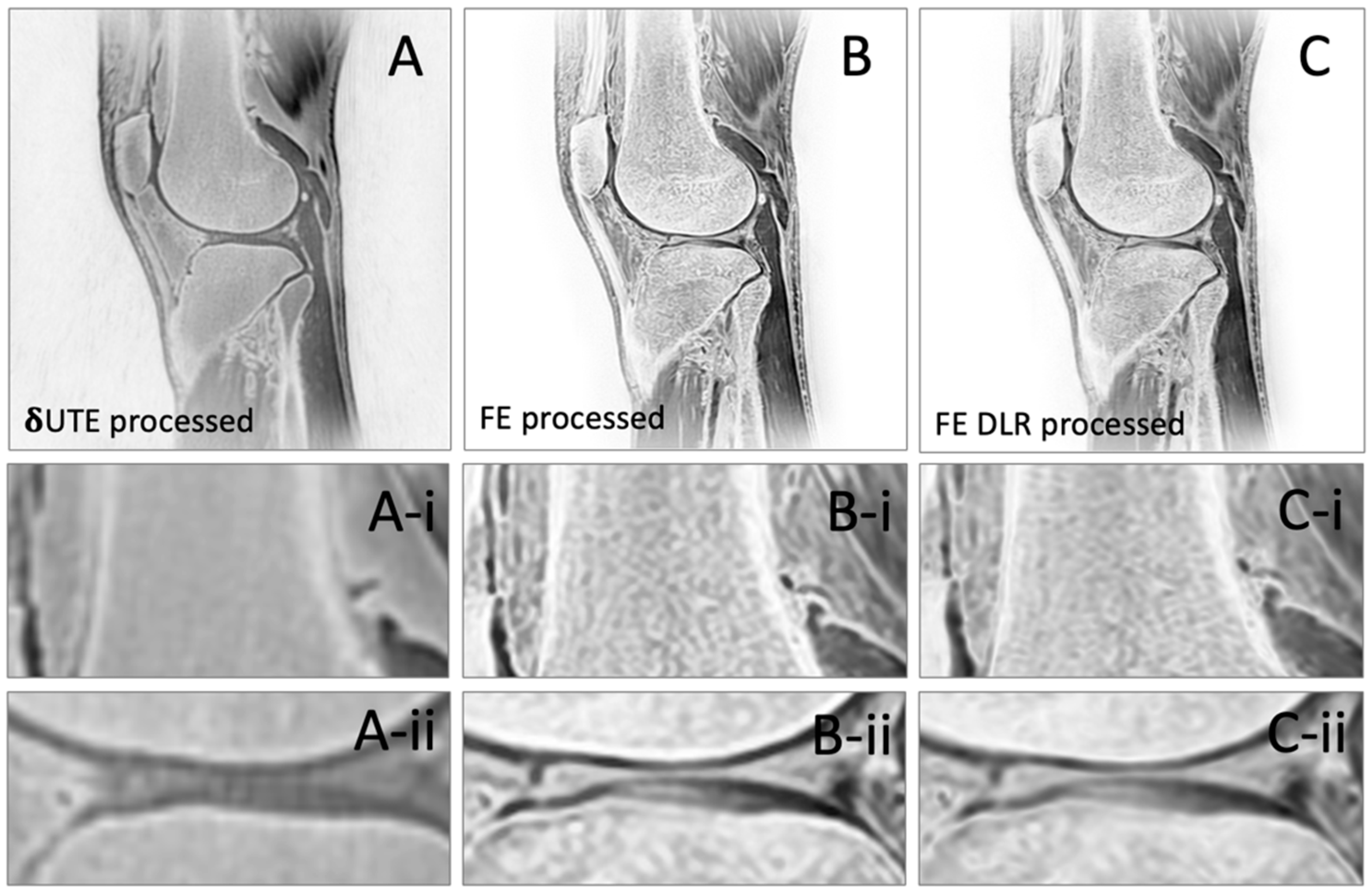
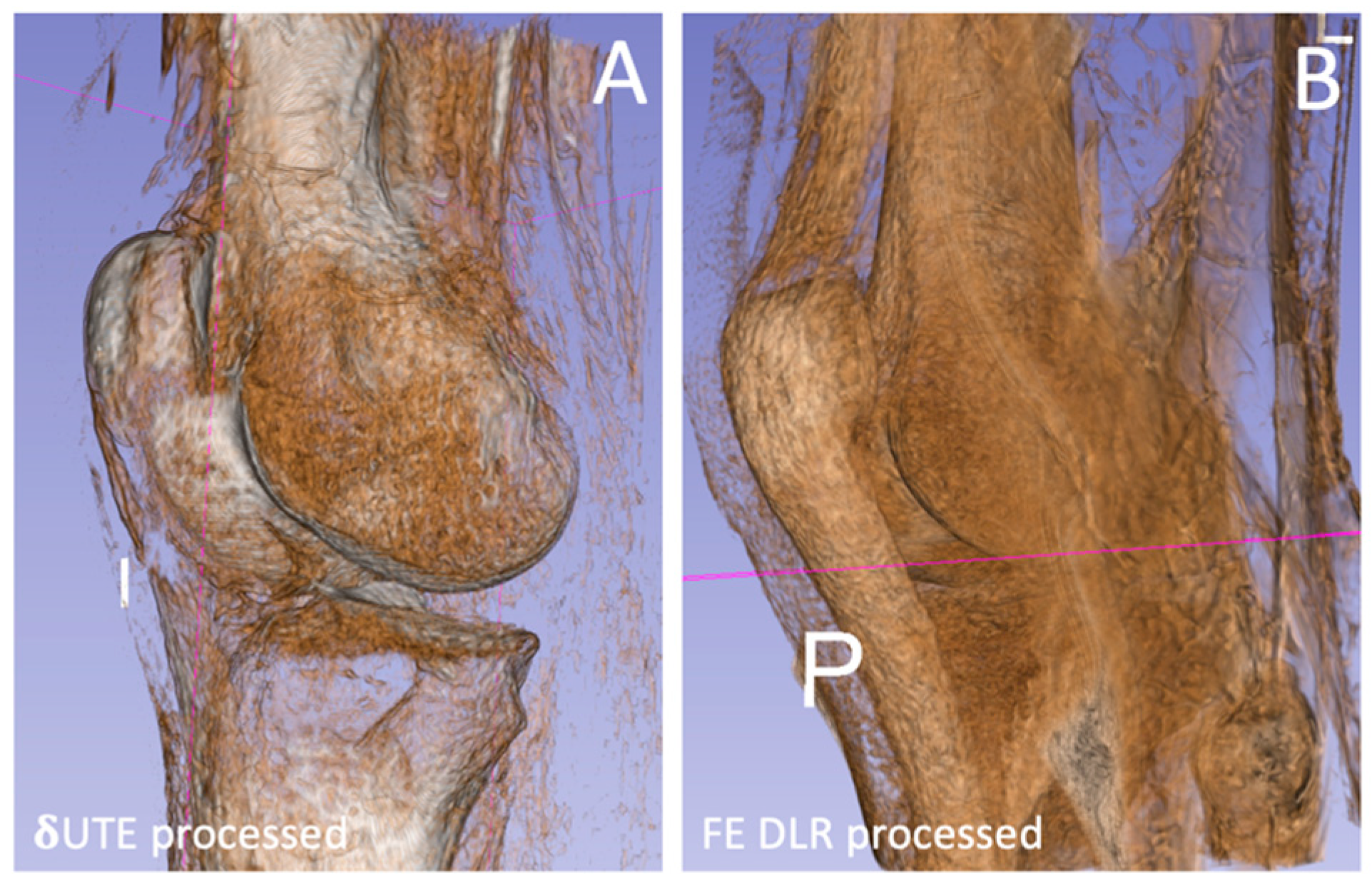
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hunter, D.J.; Bierma-Zeinstra, S. Osteoarthritis. Lancet 2019, 393, 1745–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brander, A.E.; Viikinkoski, V.P.; Nickels, J.I.; Kivisaari, L.M. Importance of thyroid abnormalities detected at US screening: A 5-year follow-up. Radiology 2000, 215, 801–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, K.Y.; Moazamian, D.; Ma, Y.; Jang, H.; Jerban, S.; Du, J.; Chung, C.B. Clinical application of ultrashort echo time (UTE) and zero echo time (ZTE) magnetic resonance (MR) imaging in the evaluation of osteoarthritis. Skeletal Radiol. 2023, 52, 2149–2157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bae, W.C.; Biswas, R.; Chen, K.; Chang, E.Y.; Chung, C.B. UTE MRI of the Osteochondral Junction. Curr. Radiol. Rep. 2014, 2, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bharadwaj, U.U.; Coy, A.; Motamedi, D.; Sun, D.; Joseph, G.B.; Krug, R.; Link, T.M. CT-like MRI: A qualitative assessment of ZTE sequences for knee osseous abnormalities. Skeletal Radiol. 2022, 51, 1585–1594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florkow, M.C.; Willemsen, K.; Mascarenhas, V.V.; Oei, E.H.G.; van Stralen, M.; Seevinck, P.R. Magnetic Resonance Imaging Versus Computed Tomography for Three-Dimensional Bone Imaging of Musculoskeletal Pathologies: A Review. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2022, 56, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eley, K.A.; Delso, G. Automated 3D MRI rendering of the craniofacial skeleton: Using ZTE to drive the segmentation of black bone and FIESTA-C images. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiger, M.; Pruessmann, K.P.; Bracher, A.K.; Kohler, S.; Lehmann, V.; Wolfram, U.; Hennel, F.; Rasche, V. High-resolution ZTE imaging of human teeth. NMR Biomed. 2012, 25, 1144–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torres, L.; Kammerman, J.; Hahn, A.D.; Zha, W.; Nagle, S.K.; Johnson, K.; Sandbo, N.; Meyer, K.; Schiebler, M.; Fain, S.B. Structure-Function Imaging of Lung Disease Using Ultrashort Echo Time MRI. Acad. Radiol. 2019, 26, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magland, J.F.; Wald, M.J.; Wehrli, F.W. Spin-echo micro-MRI of trabecular bone using improved 3D fast large-angle spin-echo (FLASE). Magn. Reson. Med. 2009, 61, 1114–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idiyatullin, D.; Corum, C.; Moeller, S.; Prasad, H.S.; Garwood, M.; Nixdorf, D.R. Dental magnetic resonance imaging: Making the invisible visible. J. Endod. 2011, 37, 745–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Idiyatullin, D.; Corum, C.; Park, J.Y.; Garwood, M. Fast and quiet MRI using a swept radiofrequency. J. Magn. Reson. 2006, 181, 342–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malis, V.; Kassai, Y.; Vucevic, D.; Bae, W.C.; Ohno, Y.; Yen, A.; Miyazaki, M. Lung T(2) * mapping using 3D ultrashort TE with tight intervals deltaTE. Magn. Reson. Med. 2023, 90, 2001–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, Y.; Koyama, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Kishida, Y.; Seki, S.; Takenaka, D.; Yui, M.; Miyazaki, M.; Sugimura, K. Standard-, Reduced-, and No-Dose Thin-Section Radiologic Examinations: Comparison of Capability for Nodule Detection and Nodule Type Assessment in Patients Suspected of Having Pulmonary Nodules. Radiology 2017, 284, 562–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohno, Y.; Koyama, H.; Yoshikawa, T.; Seki, S.; Takenaka, D.; Yui, M.; Lu, A.; Miyazaki, M.; Sugimura, K. Pulmonary high-resolution ultrashort TE MR imaging: Comparison with thin-section standard- and low-dose computed tomography for the assessment of pulmonary parenchyma diseases. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2016, 43, 512–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, A.; Qian, Y.; Chu, C.R. UTE-T2 * mapping of human articular cartilage in vivo: A repeatability assessment. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2011, 19, 84–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filho, G.H.; Du, J.; Pak, B.C.; Statum, S.; Znamorowski, R.; Haghighi, P.; Bydder, G.; Chung, C.B. Quantitative characterization of the Achilles tendon in cadaveric specimens: T1 and T2* measurements using ultrashort-TE MRI at 3 T. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2009, 192, W117–W124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, B.; Alizai, H.; Dempsey, M. Fast field echo resembling a CT using restricted echo-spacing (FRACTURE): A novel MRI technique with superior bone contrast. Skeletal Radiol. 2021, 50, 1705–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwaiger, B.J.; Schneider, C.; Kronthaler, S.; Gassert, F.T.; Bohm, C.; Pfeiffer, D.; Baum, T.; Kirschke, J.S.; Karampinos, D.C.; Makowski, M.R.; et al. CT-like images based on T1 spoiled gradient-echo and ultra-short echo time MRI sequences for the assessment of vertebral fractures and degenerative bone changes of the spine. Eur. Radiol. 2021, 31, 4680–4689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Bydder, M.; Takahashi, A.M.; Carl, M.; Chung, C.B.; Bydder, G.M. Short T2 contrast with three-dimensional ultrashort echo time imaging. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2011, 29, 470–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, G.; Uetani, H.; Nakaura, T.; Nakahara, K.; Morita, K.; Nagayama, Y.; Kidoh, M.; Iwashita, K.; Yoshida, N.; Hokamura, M.; et al. Optimizing High-Resolution MR Angiography: The Synergistic Effects of 3D Wheel Sampling and Deep Learning-Based Reconstruction. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashiwagi, N.; Tanaka, H.; Yamashita, Y.; Takahashi, H.; Kassai, Y.; Fujiwara, M.; Tomiyama, N. Applicability of deep learning-based reconstruction trained by brain and knee 3T MRI to lumbar 1.5T MRI. Acta Radiol. Open 2021, 10, 20584601211023939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goerner, F.L.; Clarke, G.D. Measuring signal-to-noise ratio in partially parallel imaging MRI. Med. Phys. 2011, 38, 5049–5057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zerunian, M.; Pucciarelli, F.; Caruso, D.; Polici, M.; Masci, B.; Guido, G.; De Santis, D.; Polverari, D.; Principessa, D.; Benvenga, A.; et al. Artificial intelligence based image quality enhancement in liver MRI: A quantitative and qualitative evaluation. La Radiol. Medica 2022, 127, 1098–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edelstein, W.; Bottomley, P.; Hart, H.; Leue, W.; Schenck, J.; Redington, R. NMR imaging at 5.1 MHz: Work in progress. In International Symposium on NMR Imaging; Witcofski, R., Karstaedt, N., Partain, C., Eds.; Bowman Gray School of Medicine: Winston-Salem, NC, USA, 1982; pp. 139–145. [Google Scholar]
- Mishra, P.; Singh, U.; Pandey, C.M.; Mishra, P.; Pandey, G. Application of student’s t-test, analysis of variance, and covariance. Ann. Card. Anaesth. 2019, 22, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hazra, A.; Gogtay, N. Biostatistics Series Module 3: Comparing Groups: Numerical Variables. Indian. J. Dermatol. 2016, 61, 251–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yushkevich, P.A.; Piven, J.; Hazlett, H.C.; Smith, R.G.; Ho, S.; Gee, J.C.; Gerig, G. User-guided 3D active contour segmentation of anatomical structures: Significantly improved efficiency and reliability. Neuroimage 2006, 31, 1116–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiya, K.; Gomyo, M.; Katase, S.; Hiraoka, S.; Tateishi, H. Magnetic resonance bone imaging: Applications to vertebral lesions. Jpn. J. Radiol. 2023, 41, 1173–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deininger-Czermak, E.; Villefort, C.; von Knebel Doeberitz, N.; Franckenberg, S.; Kalin, P.; Kenkel, D.; Gascho, D.; Piccirelli, M.; Finkenstaedt, T.; Thali, M.J.; et al. Comparison of MR Ultrashort Echo Time and Optimized 3D-Multiecho In-Phase Sequence to Computed Tomography for Assessment of the Osseous Craniocervical Junction. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2021, 53, 1029–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, D.; Bae, W.C.; Statum, S.; Du, J.; Chung, C.B. Quantitative 3D ultrashort time-to-echo (UTE) MRI and micro-CT (muCT) evaluation of the temporomandibular joint (TMJ) condylar morphology. Skeletal Radiol. 2013, 43, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breighner, R.E.; Endo, Y.; Konin, G.P.; Gulotta, L.V.; Koff, M.F.; Potter, H.G. Technical Developments: Zero Echo Time Imaging of the Shoulder: Enhanced Osseous Detail by Using MR Imaging. Radiology 2018, 286, 960–966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Achar, S.; Hwang, D.; Finkenstaedt, T.; Malis, V.; Bae, W.C. Deep-Learning-Aided Evaluation of Spondylolysis Imaged with Ultrashort Echo Time Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Sensors 2023, 23, 8001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finkenstaedt, T.; Siriwanarangsun, P.; Achar, S.; Carl, M.; Finkenstaedt, S.; Abeydeera, N.; Chung, C.B.; Bae, W.C. Ultrashort Time-to-Echo Magnetic Resonance Imaging at 3 T for the Detection of Spondylolysis in Cadaveric Spines: Comparison with CT. Investig. Radiol. 2019, 54, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morbee, L.; Vereecke, E.; Laloo, F.; Chen, M.; Herregods, N.; Jans, L. MR Imaging of the Pelvic Bones: The Current and Cutting-Edge Techniques. J. Belg. Soc. Radiol. 2022, 106, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

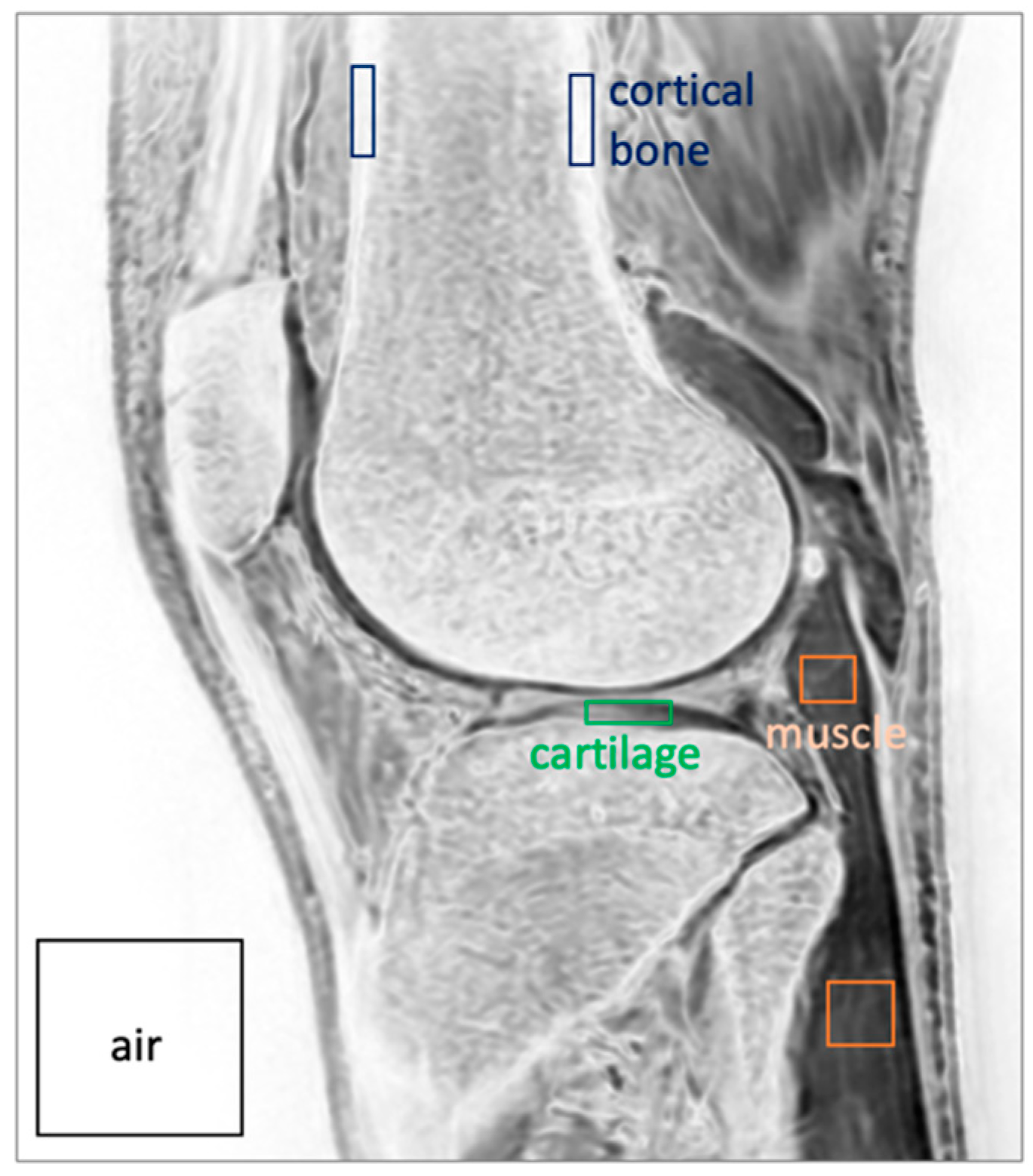
| Mean (+/−Std. Dev.) Values for Each Sequence | ANOVA | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Measurement | δUTE processed | FE processed | FE HR-DLR processed | p-value |
| Bone SNR | 104 (19.3) | 304 (271) | 410 (179) | 0.086 |
| Muscle SNR | 63.1 (22.2) | 116 (70.0) | 168 (64.4) | 0.716 |
| Cartilage SNR | 69.8 (23.5) | 166 (141) | 233 (96.1) | 0.067 |
| Bone-Muscle CNR | 40.5 (8.4) | 187 (205) | 242 (139) | 0.137 |
| Bone-Cart CNR | 33.8 (6.6) | 138 (148) | 177 (103) | 0.124 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Bae, W.C.; Malis, V.; Yamashita, Y.; Mesa, A.; Vucevic, D.; Miyazaki, M. Bone Imaging of the Knee Using Short-Interval Delta Ultrashort Echo Time and Field Echo Imaging. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164595
Bae WC, Malis V, Yamashita Y, Mesa A, Vucevic D, Miyazaki M. Bone Imaging of the Knee Using Short-Interval Delta Ultrashort Echo Time and Field Echo Imaging. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(16):4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164595
Chicago/Turabian StyleBae, Won C., Vadim Malis, Yuichi Yamashita, Anya Mesa, Diana Vucevic, and Mitsue Miyazaki. 2024. "Bone Imaging of the Knee Using Short-Interval Delta Ultrashort Echo Time and Field Echo Imaging" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 16: 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164595
APA StyleBae, W. C., Malis, V., Yamashita, Y., Mesa, A., Vucevic, D., & Miyazaki, M. (2024). Bone Imaging of the Knee Using Short-Interval Delta Ultrashort Echo Time and Field Echo Imaging. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(16), 4595. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13164595







