Deep Learning in Cardiothoracic Ratio Calculation and Cardiomegaly Detection
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Radiological Phase
2.2. Technical Materials
2.3. Slicer and Custom Workflow
2.4. Data Preparation and Dataset
- Inversion of values of Monochrome1 to Monochrome2 images.
- Scaling to Hounsfield units (HU).
- Downsampling to 256 × 256.
- Standardization to zero mean and unit variance (computed with training dataset).
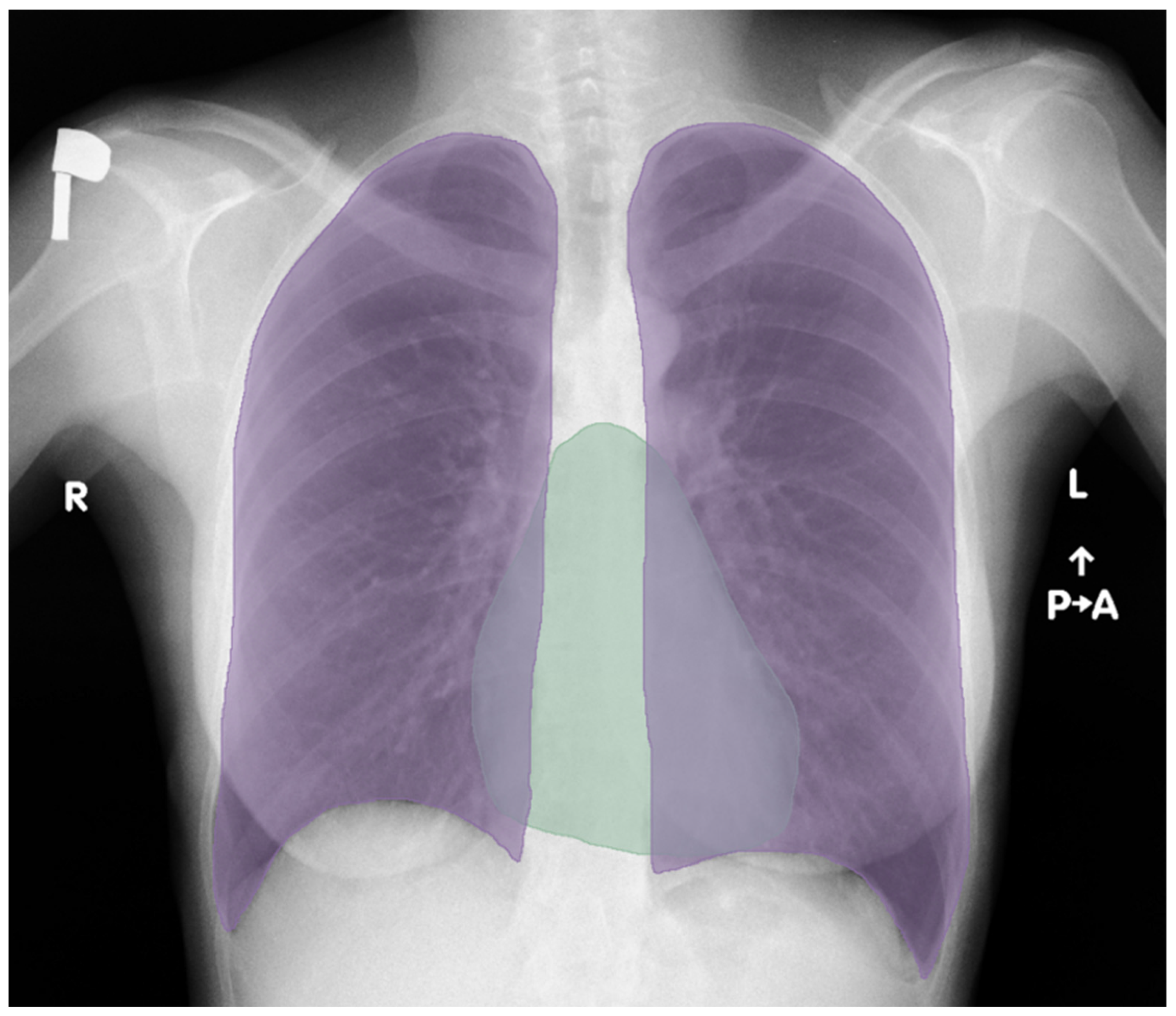
2.5. Semantic Segmentation—U-Net
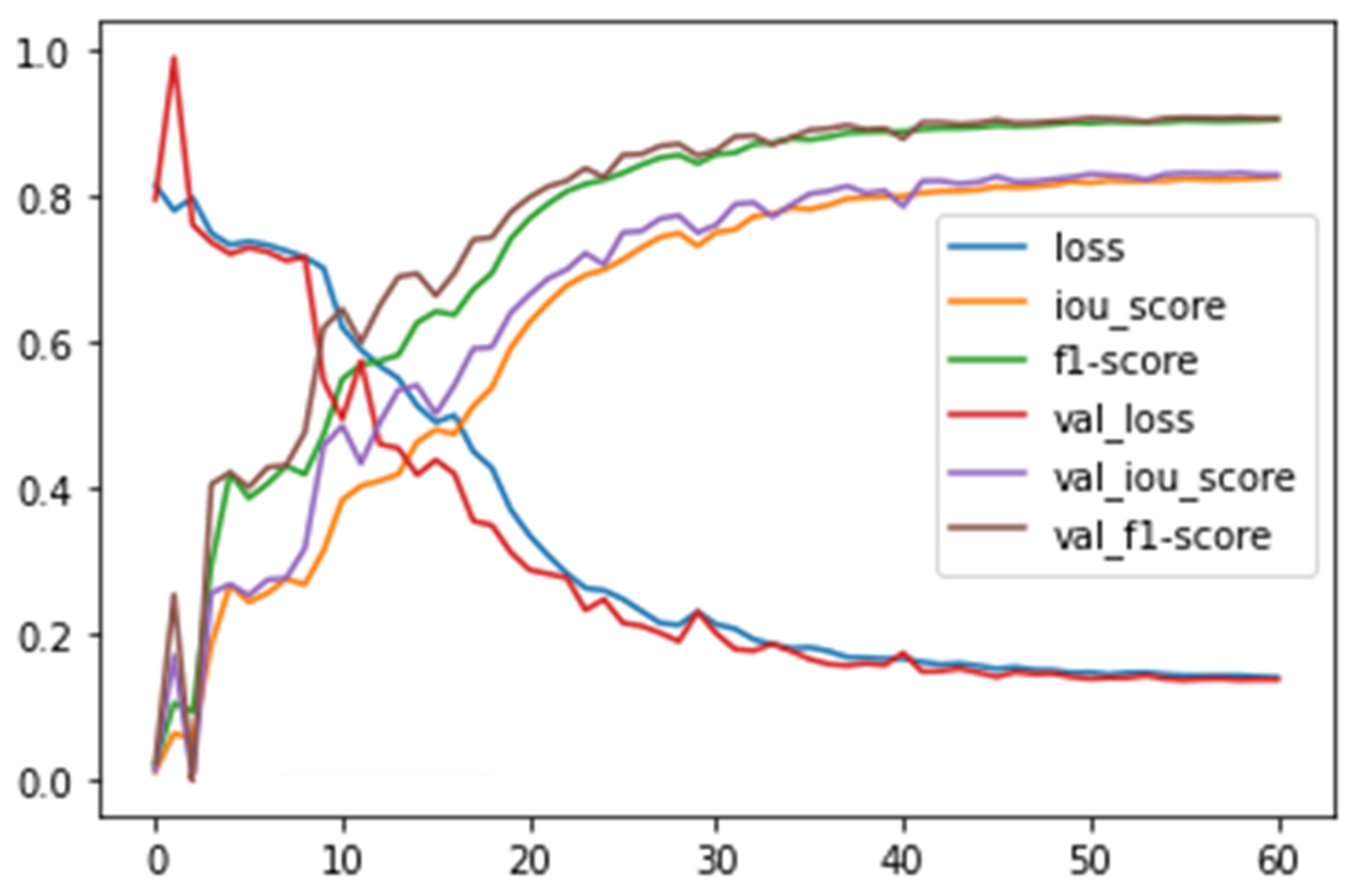
2.6. Model—Training Details
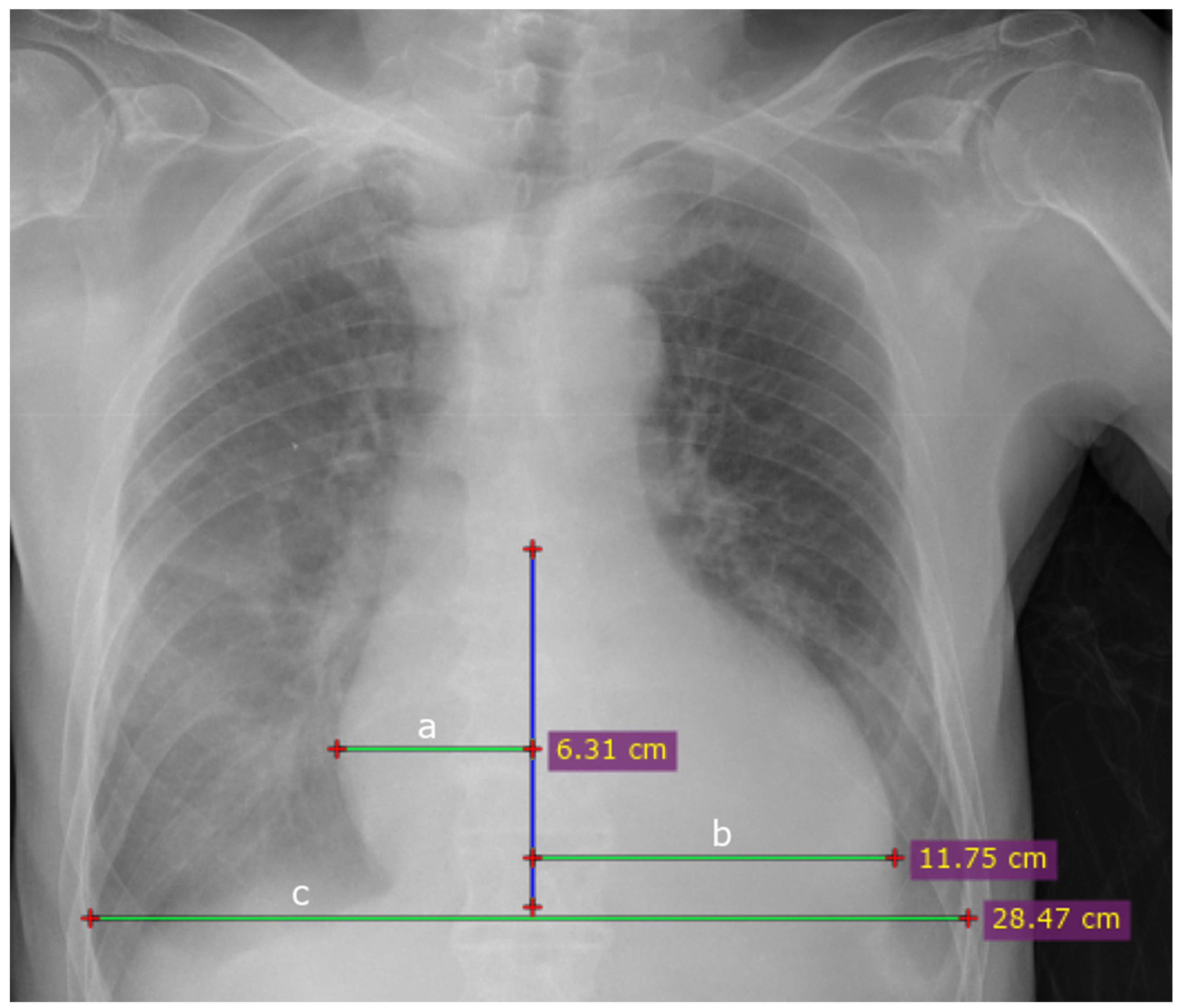
2.7. Postprocessing and CTR Calculation
3. Results
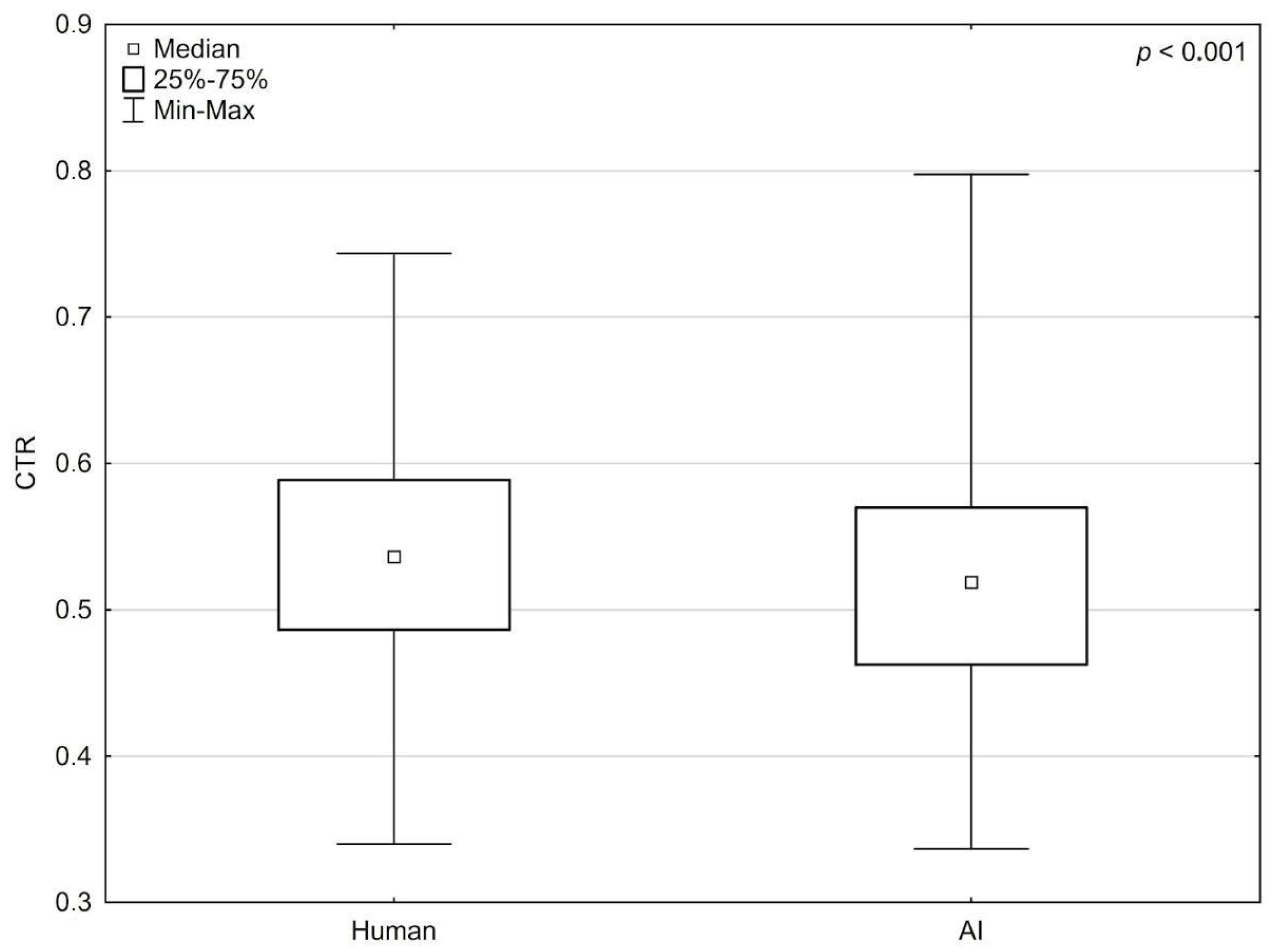
3.1. Comparative Analysis AI vs. Humans
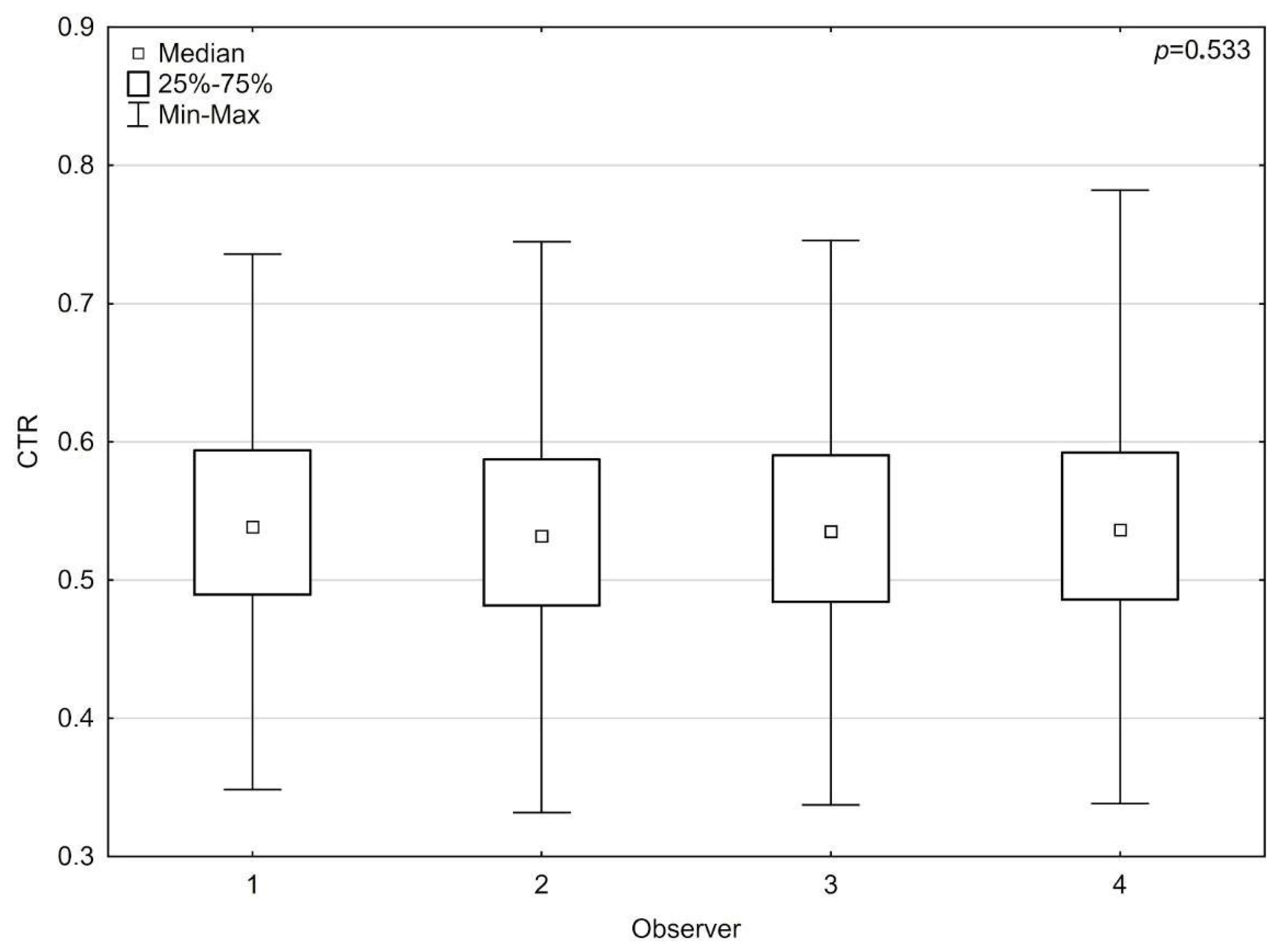
3.2. Comparative Analysis of the Observer vs. Observer
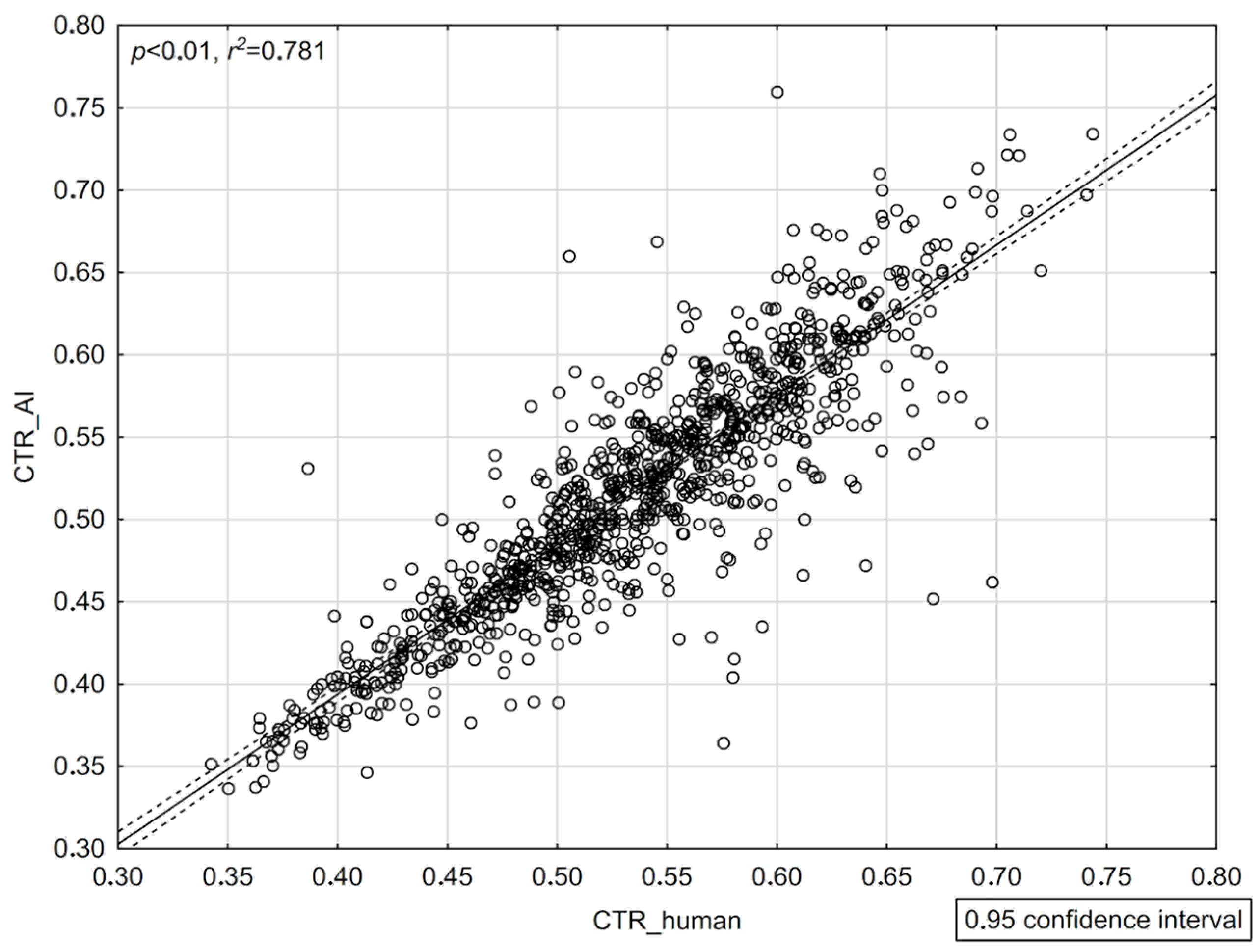
3.3. Correlation Strength Analysis (CTR_AI vs. CTR_Human)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Murphy, K. How data will improve healthcare without adding staff or beds. In The Global Innovation Index 2019; World Intellectual Property Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 129–132. [Google Scholar]
- NHS England. Diagnostic Imaging Dataset Annual Statistical Release 2017/18. Available online: https://www.england.nhs.uk/statistics/wp-content/uploads/sites/2/2018/11/Annual-Statistical-Release-2017-18-PDF-1.6MB-1.pdf (accessed on 31 October 2022).
- X-ray Diagnostics: Frequency and Radiation Exposure of the German Population. Available online: https://www.bfs.de/EN/topics/ion/medicine/diagnostics/x-rays/frequency-exposure.html (accessed on 4 November 2022).
- Gaillard, F.; Sharma, R.; Bell, D. Cardiothoracic ratio. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org. Available online: https://radiopaedia.org/articles/cardiothoracic-ratio?lang=us (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- van der Jagt, E.J.; Smits, H.J. Cardiac size in the supine chestfilm. Eur. J. Radiol. 1992, 14, 173–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Milne, E.N.C.; Burnett, K.; Aufrichtig, D.; McMillan, J.; Imray, T.J. Assessment of cardiac size on portable chest films. J. Thorac. Imaging 1988, 3, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truszkiewicz, K.; Poręba, R.; Gać, P. Radiological Cardiothoracic Ratio in Evidence-Based Medicine. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simkus, P.; Gutierrez Gimeno, M.; Banisauskaite, A.; Noreikaite, J.; McCreavy, D.; Penha, D.; Arzanauskaite, M. Limitations of cardiothoracic ratio derived from chest radiographs to predict real heart size: Comparison with magnetic resonance imaging. Insights Imaging 2021, 12, 158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amin, H.; Siddiqui, W.J. Cardiomegaly. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Bui, A.L.; Horwich, T.B.; Fonarow, G.C. Epidemiology and risk profile of heart failure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 30–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.; Shpanskaya, K.; et al. CheXNet: Radiologist-Level Pneumonia Detection on Chest X-rays with Deep Learning. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05225. [Google Scholar]
- Rajpurkar, P.; Irvin, J.; Ball, R.L.; Zhu, K.; Yang, B.; Mehta, H.; Duan, T.; Ding, D.; Bagul, A.; Langlotz, C.P.; et al. Deep learning for chest radiograph diagnosis: A retrospective comparison of the CheXNeXt algorithm to practicing radiologists. PLoS Med. 2018, 15, e1002686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabala, J.E.; Wilde, P. The measurement of heart size in the antero-posterior chest radiograph. Br. J. Radiol. 1987, 60, 981–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keats, T.E.; Anderson, M.W. Atlas of Normal Roentgen Variants That May Simulate Disease, 9th ed.; Saunders: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Keats, T.E. Atlas of Roentgenographic Measurement, 6th ed.; Mosby Year Book: Saint Louis, MO, USA, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Fedorov, A.; Beichel, R.; Kalpathy-Cramer, J.; Finet, J.; Fillion-Robin, J.-C.; Pujol, S.; Bauer, C.; Jennings, D.; Fennessy, F.; Sonka, M.; et al. 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2012, 30, 1323–1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- NEMA PS3/ISO 12052; Digital Imaging and Communications in Medicine (DICOM) Standard. National Electrical Manufacturers Association: Rosslyn, VA, USA. Available online: http://medical.nema.org/ (accessed on 31 October 2022).
- van Rossum, G.; Drake, F.L. The Python Language Reference. Release 3.0.1 [Repr.]; Python Software Foundation: Hampton, NH, USA, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Zarr-Python. Available online: https://zarr.readthedocs.io/en/stable/ (accessed on 31 October 2022).
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-Net: Convolutional Networks for Biomedical Image Segmentation. In Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention–MICCAI 2015: 18th International Conference, Munich, 5–9 Germany, October 2015, Proceedings, Part III 18; Springer International Publishing: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kearney, M.T.; Fox, K.A.A.; Lee, A.J.; Prescott, R.J.; Shah, A.M.; Batin, P.D.; Baig, W.; Lindsay, S.; Callahan, T.S.; Shell, W.E.; et al. Predicting death due to progressive heart failure in patients with mild-to-moderate chronic heart failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2002, 40, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dimopoulos, K.; Giannakoulas, G.; Bendayan, I.; Liodakis, E.; Petraco, R.; Diller, G.-P.; Piepoli, M.F.; Swan, L.; Mullen, M.; Best, N.; et al. Cardiothoracic ratio from postero-anterior chest radiographs: A simple, reproducible and independent marker of disease severity and outcome in adults with congenital heart disease. Int. J. Cardiol. 2013, 166, 453–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chamveha, I.; Promwiset, T.; Tongdee, T.; Saiviroonporn, P.; Chaisangmongkon, W. Automated Cardiothoracic Ratio Calculation and Cardiomegaly Detection using Deep Learning Approach. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2002.07468. [Google Scholar]
- Que, Q.; Tang, Z.; Wang, R.; Zeng, Z.; Wang, J.; Chua, M.; Gee, T.S.; Yang, X.; Veeravalli, B. CardioXNet: Automated Detection for Cardiomegaly Based on Deep Learning. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 612–615. [Google Scholar]
- Saiviroonporn, P.; Rodbangyang, K.; Tongdee, T.; Chaisangmongkon, W.; Yodprom, P.; Siriapisith, T.; Wonglaksanapimon, S. Cardiothoracic ratio measurement using artificial intelligence: Observer and method validation studies. BMC Med. Imaging 2021, 21, 95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arsalan, M.; Owais, M.; Mahmood, T.; Choi, J.; Park, K.R. Artificial Intelligence-Based Diagnosis of Cardiac and Related Diseases. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajmera, P.; Kharat, A.; Gupte, T.; Pant, R.; Kulkarni, V.; Duddalwar, V.; Lamghare, P. Observer performance evaluation of the feasibility of a deep learning model to detect cardiomegaly on chest radiographs. Acta Radiol. Open 2022, 11, 205846012211073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Obuchowicz, R.; Strzelecki, M.; Piórkowski, A. Clinical Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Medical Imaging and Image Processing—A Review. Cancers 2024, 16, 1870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kufel, J.; Paszkiewicz, I.; Kocot, S.; Lis, A.; Dudek, P.; Czogalik, Ł.; Janik, M.; Bargieł-Łączek, K.; Bartnikowska, W.; Koźlik, M.; et al. Deep Learning in Cardiothoracic Ratio Calculation and Cardiomegaly Detection. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144180
Kufel J, Paszkiewicz I, Kocot S, Lis A, Dudek P, Czogalik Ł, Janik M, Bargieł-Łączek K, Bartnikowska W, Koźlik M, et al. Deep Learning in Cardiothoracic Ratio Calculation and Cardiomegaly Detection. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(14):4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144180
Chicago/Turabian StyleKufel, Jakub, Iga Paszkiewicz, Szymon Kocot, Anna Lis, Piotr Dudek, Łukasz Czogalik, Michał Janik, Katarzyna Bargieł-Łączek, Wiktoria Bartnikowska, Maciej Koźlik, and et al. 2024. "Deep Learning in Cardiothoracic Ratio Calculation and Cardiomegaly Detection" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 14: 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144180
APA StyleKufel, J., Paszkiewicz, I., Kocot, S., Lis, A., Dudek, P., Czogalik, Ł., Janik, M., Bargieł-Łączek, K., Bartnikowska, W., Koźlik, M., Cebula, M., Gruszczyńska, K., & Nawrat, Z. (2024). Deep Learning in Cardiothoracic Ratio Calculation and Cardiomegaly Detection. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(14), 4180. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13144180










