3D Printing for Customized Bone Reconstruction in Spheno-Orbital Meningiomas: A Systematic Literature Review and Institutional Experience
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search Methods
2.2. Selection Criteria and Data Extraction
2.3. Clinical Study
3. Results
3.1. Review of the Literature
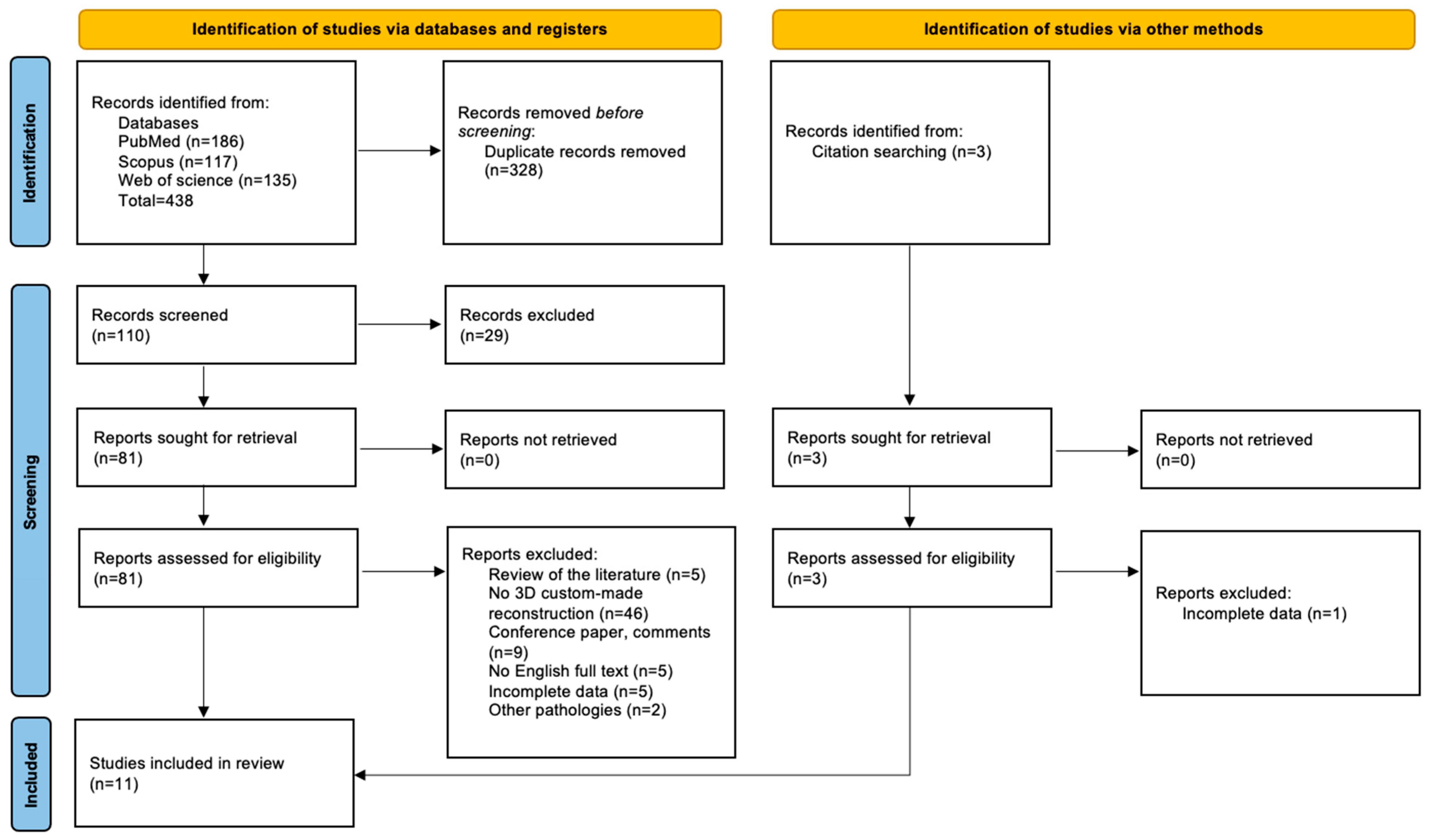
3.1.1. Study Selection
3.1.2. Summary of Results
3.2. Institutional Case Series
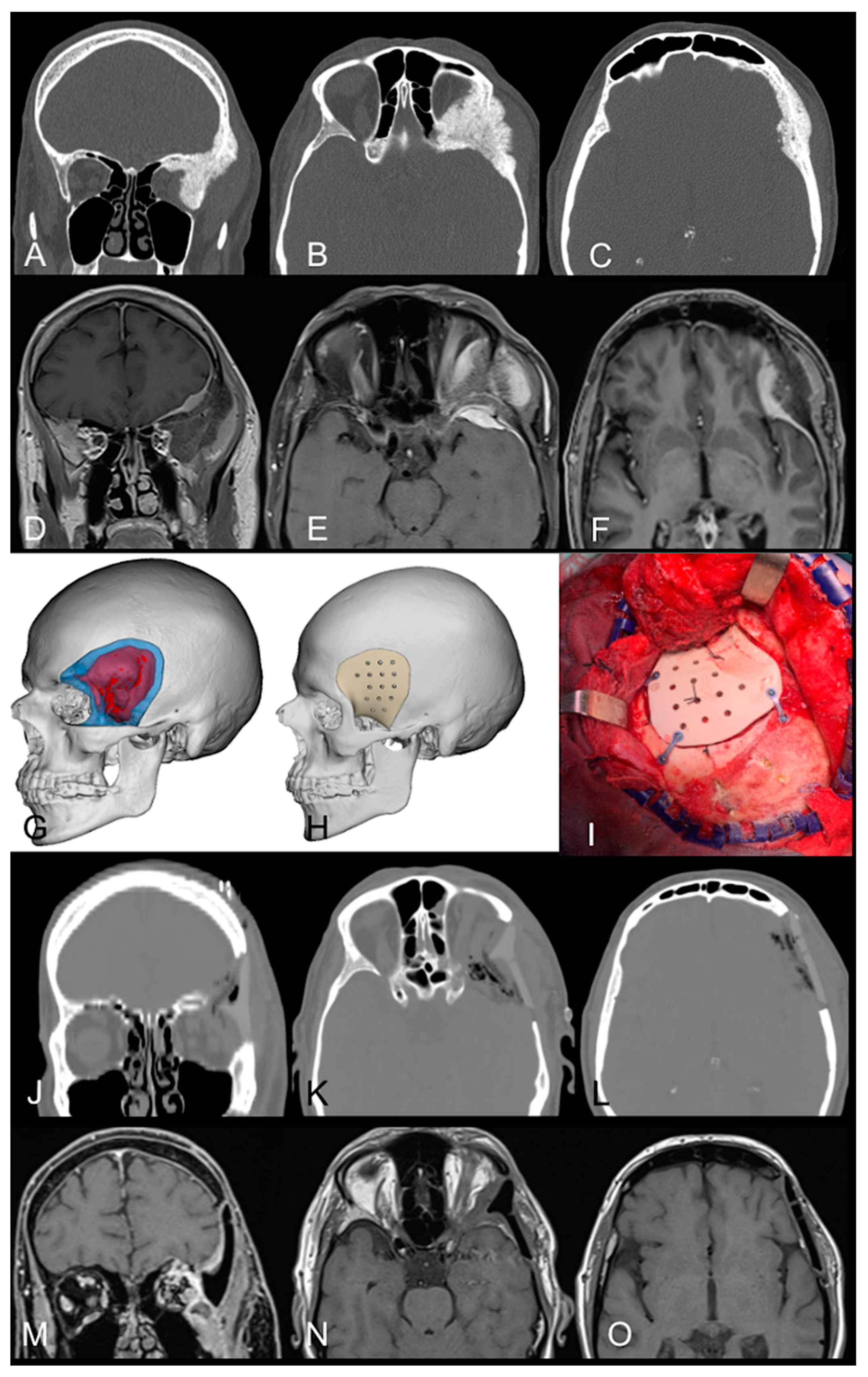
3.2.1. Case Example 1
3.2.2. Case Example 2
4. Discussion
5. Limitations of the Study
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Lasunin, N.; Cherekaev, V.; Abdullaev, A.; Gadzhiagaev, V.; Danilov, G.; Strunina, Y.; Golbin, D.; Okishev, D. Reconstruction of orbital walls after resection of cranioorbital meningiomas: A systematic review and meta-analysis of individual patient data. Neurosurg. Rev. 2023, 46, 268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fisher, F.L.; Najafabadi, A.H.Z.; Schoones, J.W.; Genders, S.W.; van Furth, W.R. Surgery as a safe and effective treatment option for spheno-orbital meningioma: A systematic review and meta-analysis of surgical techniques and outcomes. Acta Ophthalmol. 2021, 99, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachelet, J.-T.; Cordier, G.; Porcheray, M.; Bourlet, J.; Gleizal, A.; Foletti, J.-M. Orbital Reconstruction by Patient-Specific Implant Printed in Porous Titanium: A Retrospective Case Series of 12 Patients. J Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 76, 2161–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ore, C.L.D.; Magill, S.T.; Rubio, R.R.; Shahin, M.N.; Aghi, M.K.; Theodosopoulos, P.V.; Villanueva-Meyer, J.E.; Kersten, R.C.; Idowu, O.O.; Vagefi, M.R.; et al. Hyperostosing sphenoid wing meningiomas: Surgical outcomes and strategy for bone resection and multidisciplinary orbital reconstruction. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 711–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biglioli, F.; Mortini, P.; Pedrazzoli, M.; D’alessandro, L.; Bardazzi, A.; Colletti, G. The reconstruction of the spheno-orbital region using latissimus dorsi flap and costal graft. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2013, 24, e379–e383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambless, L.B.; Mawn, L.A.; Forbes, J.A.; Thompson, R.C. Porous polyethylene implant reconstruction of the orbit after resection of spheno-orbital meningiomas: A novel technique. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2012, 40, e28–e32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrizo, A.; Basso, A. Current surgical treatment for sphenoorbital meningiomas. Surg. Neurology. 1998, 50, 574–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gonen, L.; Nov, E.; Shimony, N.; Shofty, B.; Margalit, N. Sphenoorbital meningioma: Surgical series and design of an intraoperative management algorithm. Neurosurg. Rev. 2018, 41, 291–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rochlin, D.H.; Mittermiller, P.A.; DeMitchell-Rodriguez, E.B.; Weiss, H.; Dastagirzada, Y.; Patel, V.; Hagiwara, M.; Flores, R.; Sen, C.; Staffenberg, D.A. Reconstructive Approaches Following Sphenoorbital Meningioma Resection. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2023, 34, e10–e15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L. How I do it: Micro-neurosurgical resection of spheno-orbital meningioma with customized orbit reconstruction technique. Acta Neurochir. 2023, 165, 2943–2949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pritz, M.B.; Burgett, R.A. Spheno-orbital Reconstruction after Meningioma Resection. Skull Base. 2009, 19, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carolus, A.; Weihe, S.; Schmieder, K.; Brenke, C. One-step CAD/CAM titanium cranioplasty after drilling template-assisted resection of intraosseous skull base meningioma: Technical note. Acta Neurochir. 2017, 159, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goertz, L.; Stavrinou, P.; Stranjalis, G.; Timmer, M.; Goldbrunner, R.; Krischek, B. Single-Step Resection of Sphenoorbital Meningiomas and Orbital Reconstruction Using Customized CAD/CAM Implants. J. Neurol. Surg. B Skull Base 2020, 81, 142–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laroche, J.; Kulker, D.; Laure, B.; Paré, A. Massive orbital reconstruction with custom 3D implant after exenteration for spheno-orbital meningioma. J. Français Ophtalmol. 2022, 45, e237–e240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korn, P.; Spalthoff, S.; Gellrich, N.-C.; Lentge, F.; Hermann, E.; Krauss, J.K.; Jehn, P. Patient-specific implants for reconstruction of orbit and skull following resection of spheno-orbital meningiomas: A two-implant concept. J. Stomatol. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 124, 101408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schebesch, K.M.; Höhne, J.; Gassner, H.G.; Brawanski, A. Preformed titanium cranioplasty after resection of skull base meningiomas—A technical note. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2013, 41, 803–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gerbino, G.; Bianchi, F.A.; Zavattero, E.; Tartara, F.; Garbossa, D.; Ducati, A. Single-step resection and reconstruction using patient-specific implants in the treatment of benign cranio-orbital tumors. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2013, 71, 1969–1982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jalbert, F.; Boetto, S.; Nadon, F.; Lauwers, F.; Schmidt, E.; Lopez, R. One-step primary reconstruction for complex craniofacial resection with PEEK custom-made implants. J. Craniomaxillofac. Surg. 2014, 42, 141–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bassi, M.; Antonelli, V.; Tomassini, A.; Maimone, G.; D’andrea, M.; Campobassi, A.; Gessaroli, M.; Tosatto, L. Synchronized “One-Step” Resection and Cranio-Orbital Reconstruction for Spheno-Orbital Lesions with Custom Made Implant. J. Craniofac. Surg. 2021, 32, 1870–1873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- d’Avella, E.; Somma, T.; Fabozzi, G.L.; Committeri, U.; Romano, A.; Cappabianca, P.; Cavallo, L.M. Endoscopic transorbital and transcranial multiportal resection of a sphenoorbital meningiomas with custom bone 3D printing reconstruction: Case report. Head Neck. 2024, 46, E18–E25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Louis, R.G.; Eisenberg, A.; Barkhoudarian, G.; Griffiths, C.; Kelly, D.F. Evolution of minimally invasive approaches to the sella and parasellar region. Int. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2014, 18 (Suppl. S2), S136–S148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.K.; Gottfried, O.N.; Cole, C.D.; Dougherty, W.R.; Couldwell, W.T. Porous polyethylene implant for cranioplasty and skull base reconstruction. Neurosurg. Focus 2004, 16, ECP1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhry, O.J.; Christiano, L.D.; Arnaout, O.; Adel, J.G.; Liu, J.K. Reconstruction of pterional defects after frontotemporal and orbitozygomatic craniotomy using Medpor Titan implant: Cosmetic results in 98 patients. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2013, 115, 1716–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, S.; Ferrer, A.; Vela, J.; Granados, F. Spheno-Orbital Meningioma Resection and Reconstruction: The Role of Piezosurgery and Premolded Titanium Mesh. Craniomaxillofac. Trauma Reconstr. 2011, 4, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringel, F.; Cedzich, C.; Schramm, J. Microsurgical technique and results of a series of 63 spheno-orbital meningiomas. Neurosurgery 2007, 60, 214–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariniello, G.; Maiuri, F.; Strianese, D.; Donzelli, R.; Iuliano, A.; Tranfa, F.; de Divitiis, E.; Bonavolontà, G. Spheno-orbital Meningiomas: Surgical Approaches and Outcome According to the Intraorbital Tumor Extent. Zentralbl. Neurochir. 2008, 69, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajibandeh, J.; Lee, C. Patient-specific implants in orbital reconstruction. Curr. Opin. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2022, 30, 230–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattavelli, D.; Fiorentino, A.; Tengattini, F.; Colpani, A.; Agnelli, S.; Buffoli, B.; Ravanelli, M.; Ferrari, M.; Schreiber, A.; Rampinelli, V.; et al. Additive Manufacturing for Personalized Skull Base Reconstruction in Endoscopic Transclival Surgery: A Proof-of-Concept Study. World Neurosurg. 2021, 155, e439–e452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Belotti, F.; Tengattini, F.; Mattavelli, D.; Ferrari, M.; Fiorentino, A.; Agnelli, S.; Schreiber, A.; Nicolai, P.; Fontanella, M.M.; Doglietto, F. Transclival approaches for intradural pathologies: Historical overview and present scenario. Neurosurg. Rev. 2021, 44, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosameldin, A.; Osman, A.; Hussein, M.; Gomaa, A.F.; Abdellatif, M. Three dimensional custom-made PEEK cranioplasty. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2021, 12, 587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antonelli, V.; Maimone, G.; D’andrea, M.; Tomassini, A.; Bassi, M.; Tosatto, L. “Single-step” resection and cranio-orbital reconstruction for spheno-orbital metastasis with custom made implant. A case report and review of the literature. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2021, 81, 105755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerrini, F.; Dallolio, V.; Grimod, G.; Cesana, C.; Vismara, D.; Franzin, A.B. It Is Time to Reduce Free-Hand Manipulation: Case Report of Our Proposal for an Innovative 1-Step Cranioplasty. World Neurosurg. 2017, 107, e7–e1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| First Author, Year of Publication | Age (Mean; Range) | Sex (%) | MAT (%) | Surgical Approach (%) | Steps (m §) | Pre-op. Symptoms | Resection | Post-op. Neurology | Complications (%) | Outcome (mRS) [FU-mo] | Cosmetic Outcome | RT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pritz, 2009 [11] | 52 | F | PMMA | FT | 1 | Vis. I, V1 Medial rectus dysfunction | NT | Intact | N | 1 [1.2] | 3 | NR |
| 33 | F | PMMA | FT | 1 | Anis, Ex | ST | D | N | 1 [1.2] | - | NR | |
| Gerbino, 2013 [17] | 54 | F | PEEK | FT | 1 | Dyst, Ex | NR | tD | N | 0 [24] | 1 | N |
| 56 | M | PEEK | FT | 1 | Vis. I, D, Ex | NR | tD | N | 0 [24] | 1 | N | |
| Schebesch, 2013 [16] | 40 | F | PT | FT ^ | 1 | Sw, Ex | NT | NR | N | NR | - | NR |
| 64 | F | PT | FT ^ | 1 | Temp. Sw | NT | NR | N | NR | - | NR | |
| Jalbert, 2014 [18] | 46 | F | PEEK | FT | 1 | Ex | NR | Ptosis, scalp HyperE | N | 2 [12] | 1 | N |
| Carolus, 2017 [12] | 43 | F | PT | FT | 1 | NR | NR | NR | N | 0 [6] | 3 | N |
| 64 | F | PT | FT | 1 | Ex | ST | NR | N | 1 [6] | 3 | Y | |
| Bachelet, 2018 [3] | 52 | F | PT | SC | 2 (19) | Eno, D | NR | Intact | N | NR | 1 | NR |
| 42 | F | PT | SC | 2 (24) | Eno, D | NR | Intact | N | NR | 1 | NR ç | |
| 49 | F | PT | TP | 2 (22) | Eno, D | NR | D | Eno, SubO position | NR | 3 | NR | |
| Bassi, 2020 [19] | NR | NR | PMMA | FT | 1 | Ex, Dyst | NR | Intact | N | 0 [36] | - | NR |
| NR | NR | PMMA | FT | 1 | Ex, Dyst | NR | Intact | N | 0 [32] | - | NR | |
| NR | NR | PMMA | FT | 1 | Ex, Dyst, Vis. I | NR | Intact | N | 0 [30] | - | NR | |
| Goertz, 2020 [13] | 63 | F | PT | FT | 1 | Ex, Dyst, Vis. I | ST | Intact | Epidural | 1 [17] | 1 | Y |
| 54 | F | PMMA | FT | 1 | Ex | NR | Intact | SubO position | 2 [25] | 4 | N | |
| 46 | F | PMMA | FT | 1 | Ex, D, Vis. I | ST | Vis. I | N | 1 [18] | 1 | Y | |
| Laroche, 2022 [14] | 39 | F | PT | FT + OEx | 2 (12) | Ex, no functional eye | NT | Intact | N | 2 [36] | 4 | Y |
| D’Avella, 2023 [20] | 70 | F | PMMA | FT + TOE | 1 | Ex | ST | tD | N | 0 [3] | 1 | NR |
| Korn, 2023 [15] * | (56; 41–89) | F (70) | PT (100) | FT (100) | 1 | D (70%) | NR | NR | N | 0–1 * [NR] (100) | NR |
| Patient | Age | Sex | MAT | Surgical Approach | Steps | Pre-op. Symptoms | Resection | Post-op. Neurology | Complications | Outcome (mRS) [FU-mo] | Cosmetic Outcome | RT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 60 | M | PEEK | FT | 1 | Ex, D, Ptosis | NT | tVII bleph | N | 0 [9] | 1 | N |
| 2 | 58 | F | PEEK | FT | 1 | Ex, Vis. I Conj Hyp | ST | Intact | N | 0 [19] | 1 | N |
| 3 | 63 | F | PEEK | FT | 1 | Ex | ST | Intact | N | 0 [32] | 1 | N |
| 4 | 53 | F | PEEK | FT | 1 | Ex, Vis. I, D | NT | III, tV2 | N | 1 [41] | 1 | N |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Serioli, S.; Pietrantoni, A.; Benato, A.; Galeazzi, M.; Piazza, A.; Lauretti, L.; Mattogno, P.P.; Olivi, A.; Fontanella, M.M.; Doglietto, F. 3D Printing for Customized Bone Reconstruction in Spheno-Orbital Meningiomas: A Systematic Literature Review and Institutional Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133968
Serioli S, Pietrantoni A, Benato A, Galeazzi M, Piazza A, Lauretti L, Mattogno PP, Olivi A, Fontanella MM, Doglietto F. 3D Printing for Customized Bone Reconstruction in Spheno-Orbital Meningiomas: A Systematic Literature Review and Institutional Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133968
Chicago/Turabian StyleSerioli, Simona, Alberto Pietrantoni, Alberto Benato, Marco Galeazzi, Amedeo Piazza, Liverana Lauretti, Pier Paolo Mattogno, Alessandro Olivi, Marco Maria Fontanella, and Francesco Doglietto. 2024. "3D Printing for Customized Bone Reconstruction in Spheno-Orbital Meningiomas: A Systematic Literature Review and Institutional Experience" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133968
APA StyleSerioli, S., Pietrantoni, A., Benato, A., Galeazzi, M., Piazza, A., Lauretti, L., Mattogno, P. P., Olivi, A., Fontanella, M. M., & Doglietto, F. (2024). 3D Printing for Customized Bone Reconstruction in Spheno-Orbital Meningiomas: A Systematic Literature Review and Institutional Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3968. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133968








