Chuna Manual Therapy or Electroacupuncture with Pregabalin for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
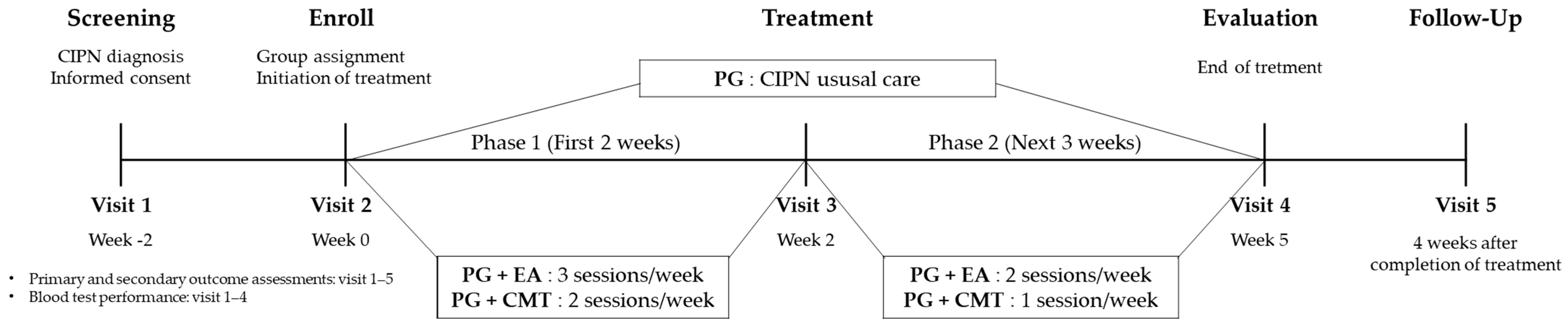
2.1. Study Design
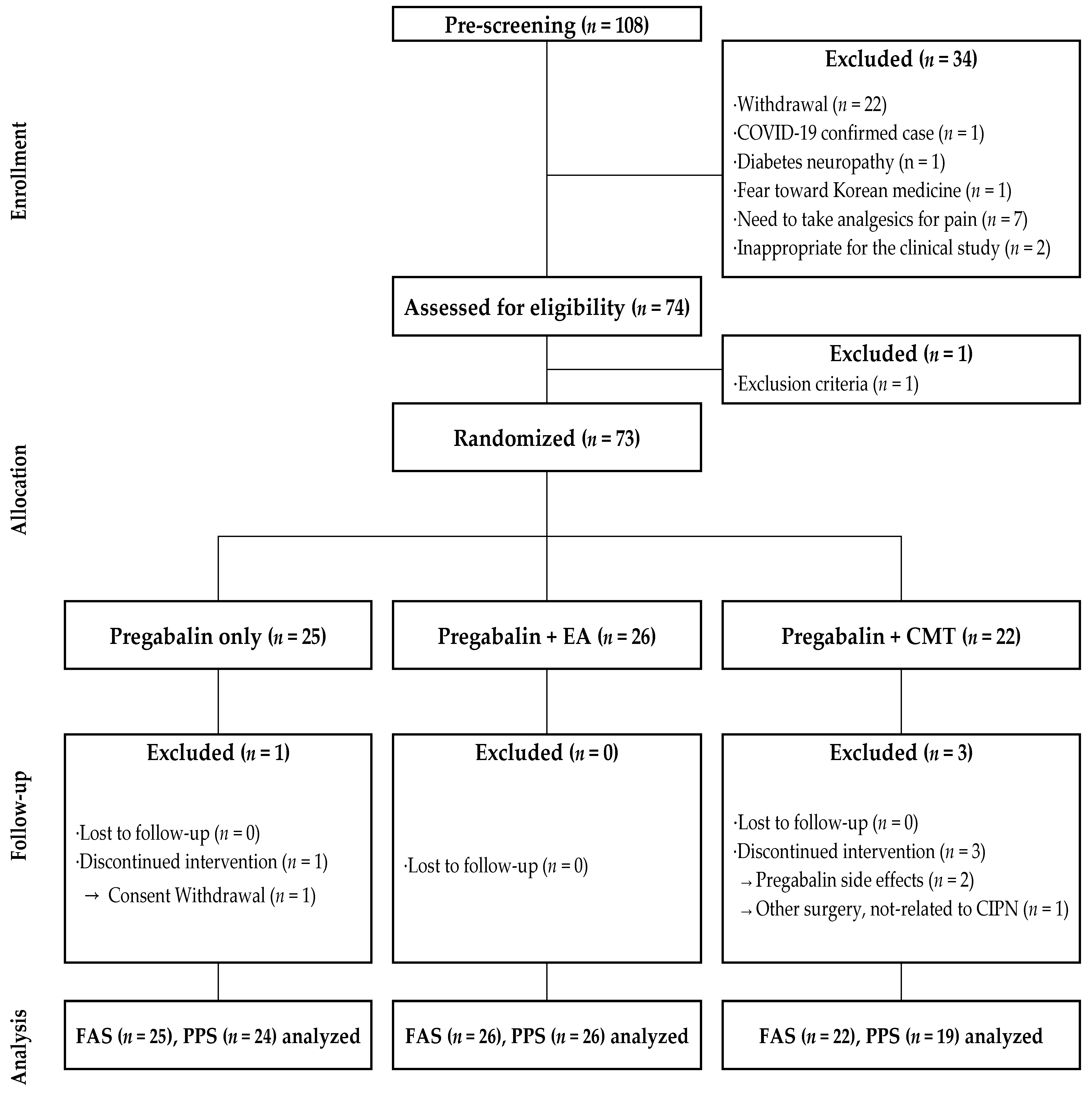
2.2. Participants
- (1)
- Inclusion Criteria
- (2)
- Exclusion Criteria
2.3. Randomization and Blinding
2.4. Intervention
2.4.1. PG Group
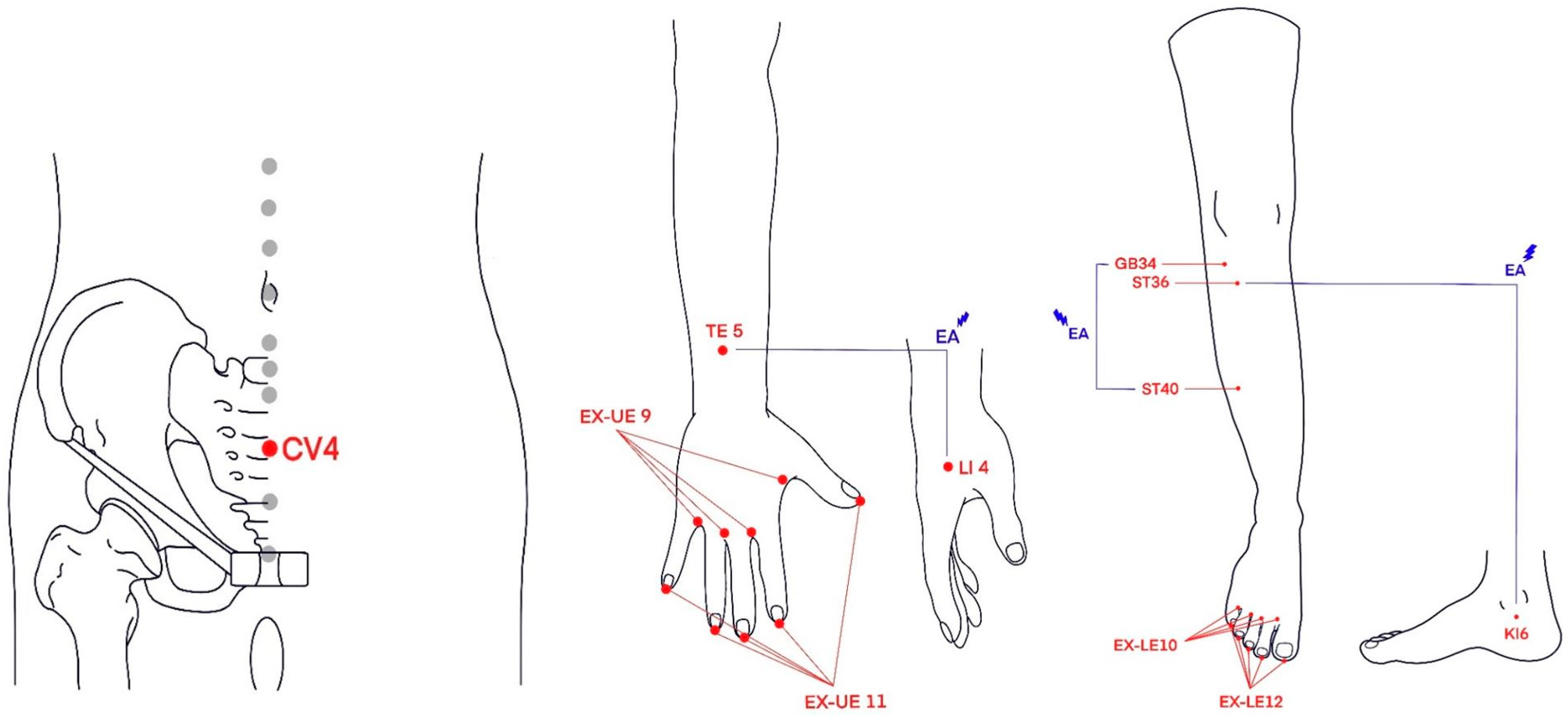
2.4.2. PG + EA Group
2.4.3. PG + CMT Group
3. Outcome Measurements
3.1. Primary Outcome
3.2. Secondary Outcomes
3.3. Exploratory Efficacy
3.4. Safety and Adverse Event Monitoring
3.5. Statistical Analysis
4. Results
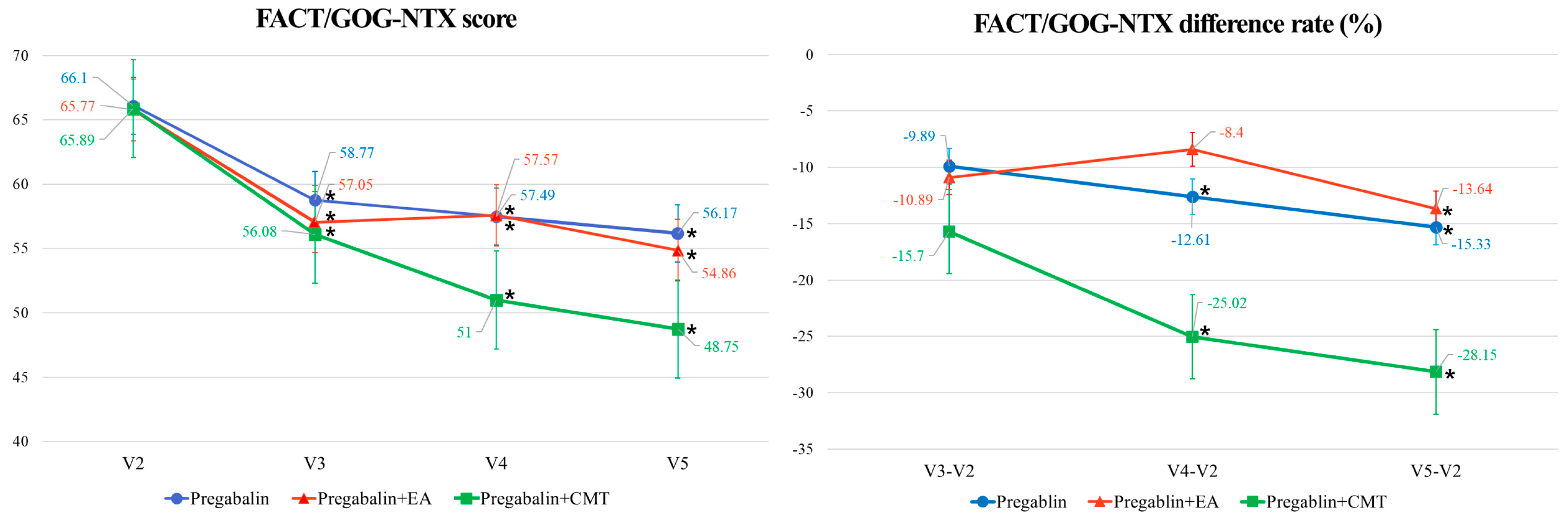
4.1. Primary Outcome
4.2. Secondary Outcomes
4.3. Exploratory Efficacy
4.4. Safety and Adverse Event Monitoring
5. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- André, T.; Vernerey, D.; Mineur, L.; Bennouna, J.; Desrame, J.; Faroux, R.; Fratte, S.; Hug de Larauze, M.; Paget-Bailly, S.; Chibaudel, B.; et al. Three Versus 6 Months of Oxaliplatin-Based Adjuvant Chemotherapy for Patients with Stage III Colon Cancer: Disease-Free Survival Results From a Randomized, Open-Label, International Duration Evaluation of Adjuvant (IDEA) France, Phase III Trial. J. Clin. Oncol. 2018, 36, 1469–1477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilkes, G. Peripheral neuropathy related to chemotherapy. Semin. Oncol. Nurs. 2007, 23, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Streckmann, F.; Zopf, E.M.; Lehmann, H.C.; May, K.; Rizza, J.; Zimmer, P.; Gollhofer, A.; Bloch, W.; Baumann, F.T. Exercise intervention studies in patients with peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review. Sports Med. 2014, 44, 1289–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seretny, M.; Currie, G.L.; Sena, E.S.; Ramnarine, S.; Grant, R.; MacLeod, M.R.; Colvin, L.A.; Fallon, M. Incidence, prevalence, and predictors of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Pain 2014, 155, 2461–2470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Majithia, N.; Temkin, S.M.; Ruddy, K.J.; Beutler, A.S.; Hershman, D.L.; Loprinzi, C.L. National Cancer Institute-supported chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy trials: Outcomes and lessons. Support. Care Cancer 2016, 24, 1439–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.Y.; Mi, W.L.; Wu, G.C.; Wang, Y.Q.; Mao-Ying, Q.L. Prevention and Treatment for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: Therapies Based on CIPN Mechanisms. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2019, 17, 184–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loprinzi, C.L.; Lacchetti, C.; Bleeker, J.; Cavaletti, G.; Chauhan, C.; Hertz, D.L.; Kelley, M.R.; Lavino, A.; Lustberg, M.B.; Paice, J.A.; et al. Prevention and Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Survivors of Adult Cancers: ASCO Guideline Update. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020, 38, 3325–3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, R.A.; Straube, S.; Wiffen, P.J.; Derry, S.; McQuay, H.J. Pregabalin for acute and chronic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2009, 3, Cd007076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Onakpoya, I.J.; Thomas, E.T.; Lee, J.J.; Goldacre, B.; Heneghan, C.J. Benefits and harms of pregabalin in the management of neuropathic pain: A rapid review and meta-analysis of randomised clinical trials. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e023600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derry, S.; Bell, R.F.; Straube, S.; Wiffen, P.J.; Aldington, D.; Moore, R.A. Pregabalin for neuropathic pain in adults. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2019, 1, Cd007076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beijers, A.J.; Mols, F.; Tjan-Heijnen, V.C.; Faber, C.G.; van de Poll-Franse, L.V.; Vreugdenhil, G. Peripheral neuropathy in colorectal cancer survivors: The influence of oxaliplatin administration. Results from the population-based PROFILES registry. Acta Oncol. 2015, 54, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ness, K.K.; Jones, K.E.; Smith, W.A.; Spunt, S.L.; Wilson, C.L.; Armstrong, G.T.; Srivastava, D.K.; Robison, L.L.; Hudson, M.M.; Gurney, J.G. Chemotherapy-related neuropathic symptoms and functional impairment in adult survivors of extracranial solid tumors of childhood: Results from the St. Jude Lifetime Cohort Study. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2013, 94, 1451–1457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derksen, T.M.; Bours, M.J.; Mols, F.; Weijenberg, M.P. Lifestyle-Related Factors in the Self-Management of Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Colorectal Cancer: A Systematic Review. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2017, 2017, 7916031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macone, A.; Otis, J.A.D. Neuropathic Pain. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 644–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rostock, M.; Jaroslawski, K.; Guethlin, C.; Ludtke, R.; Schröder, S.; Bartsch, H.H. Chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in cancer patients: A four-arm randomized trial on the effectiveness of electroacupuncture. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2013, 2013, 349653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenlee, H.; Crew, K.D.; Capodice, J.; Awad, D.; Buono, D.; Shi, Z.; Jeffres, A.; Wyse, S.; Whitman, W.; Trivedi, M.S.; et al. Randomized sham-controlled pilot trial of weekly electro-acupuncture for the prevention of taxane-induced peripheral neuropathy in women with early stage breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2016, 156, 453–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Wu, T.; Zhang, H.; Yang, Y.; Jiang, H.; Cao, S.; Xie, F.; Xia, X.; Lü, J.; Zhong, Y. Effect of electroacupuncture on chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy in patients with malignant tumor: A single-blinded, randomized controlled trial. J. Tradit. Chin. Med. 2017, 37, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, E.; Kim, H. Effects of Manual Therapy on Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials. Phys. Ther. Rehabil. Sci. 2023, 12, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, M.-Y.; Song, Y.-K.; Lim, H.-H. Effect of Chuna on Nervous System- Based on Experimental Chuna Science. J. Korea CHUNA Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2013, 8, 47–56. [Google Scholar]
- Bishop, M.D.; Torres-Cueco, R.; Gay, C.W.; Lluch-Girbés, E.; Beneciuk, J.M.; Bialosky, J.E. What effect can manual therapy have on a patient's pain experience? Pain Manag. 2015, 5, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.-W.; Kim, J.-I.; Lee, J.-H.; Jo, D.-C.; Kang, S.-B.; Lee, J.-W.; Park, T.-Y.; Ko, Y.-S. Optimal Combination of Acupoints Based on Network Analysis for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy. J. Korean Med. Rehabil. 2022, 32, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.-Y.; Yang, N.-R.; Do, K.-S.; Sunu, Y.-Y. Introduction of Sunu Manual Therapy; Principle, Technique. J. Korea CHUNA Man. Med. Spine Nerves 2017, 12, 71–81. [Google Scholar]
- Park, E.H.; Jung, K.W.; Park, N.J.; Kang, M.J.; Yun, E.H.; Kim, H.J.; Kim, J.E.; Kong, H.J.; Im, J.S.; Seo, H.G. Cancer Statistics in Korea: Incidence, Mortality, Survival, and Prevalence in 2021. Cancer Res. Treat. 2024, 56, 357–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FACIT. FACT/GOG-NTX (Version 4). Available online: https://www.facit.org/_files/ugd/626819_bb41f4bd0c89499a8675a32e138e4ce2.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- EORTC. EORTC QLQ—CIPN20. Available online: https://www.eortc.org/app/uploads/sites/2/2018/08/Specimen-CIPN20-English.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- EORTC. EORTC QLQ-C30 (Version 3). Available online: https://www.eortc.org/app/uploads/sites/2/2018/08/Specimen-QLQ-C30-English.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Cella, D.; Peterman, A.; Hudgens, S.; Webster, K.; Socinski, M.A. Measuring the side effects of taxane therapy in oncology: The functional assesment of cancer therapy-taxane (FACT-taxane). Cancer 2003, 98, 822–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Postma, T.J.; Aaronson, N.K.; Heimans, J.J.; Muller, M.J.; Hildebrand, J.G.; Delattre, J.Y.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Lantéri-Minet, M.; Grant, R.; Huddart, R.; et al. The development of an EORTC quality of life questionnaire to assess chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: The QLQ-CIPN20. Eur. J. Cancer 2005, 41, 1135–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aaronson, N.K.; Ahmedzai, S.; Bergman, B.; Bullinger, M.; Cull, A.; Duez, N.J.; Filiberti, A.; Flechtner, H.; Fleishman, S.B.; de Haes, J.C.; et al. The European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer QLQ-C30: A quality-of-life instrument for use in international clinical trials in oncology. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 1993, 85, 365–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- EORTC. EORTC QLQ-C30 Scoring Manual. Available online: https://www.eortc.org/app/uploads/sites/2/2018/02/SCmanual.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Kim, J.H.; Kim, E.J.; Seo, B.K.; Lee, S.; Lee, S.; Jung, S.Y.; Lee, M.H.; Kim, A.R.; Park, H.J.; Shin, M.S.; et al. Electroacupuncture for chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: Study protocol for a pilot multicentre randomized, patient-assessor-blinded, controlled trial. Trials 2013, 14, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Youn, B.Y. Integrative Medicine in Diagnostics: Current Advances and Future Prospects. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 3052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyun, M.K. How can the concurrent use of conventional medicine and Korean medicine be defined in the National Health Insurance Service database? Integr. Med. Res. 2021, 10, 100485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, W.; Giobbie-Hurder, A.; Freedman, R.A.; Shin, I.H.; Lin, N.U.; Partridge, A.H.; Rosenthal, D.S.; Ligibel, J.A. Acupuncture for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy in Breast Cancer Survivors: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Trial. Oncologist 2020, 25, 310–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.L.; Lopez, V.; Lam, S.C.; Leung, A.K.T.; Li, Y.C.; Wong, K.H.; Au, J.S.K.; Sundar, R.; Chan, A.; De Ng, T.R.; et al. Psychometric testing of the Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy/Gynecologic Oncology Group-Neurotoxicity (FACT/GOG-Ntx) subscale in a longitudinal study of cancer patients treated with chemotherapy. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2020, 18, 246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desforges, A.D.; Hebert, C.M.; Spence, A.L.; Reid, B.; Dhaibar, H.A.; Cruz-Topete, D.; Cornett, E.M.; Kaye, A.D.; Urits, I.; Viswanath, O. Treatment and diagnosis of chemotherapy-induced peripheral neuropathy: An update. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2022, 147, 112671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NIH; National Cancer Institute Division of Cancer Treatment & Diagnosis (DCTD). Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE). Version 5.0. 27 November 2017. Available online: https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/docs/CTCAE_v5_Quick_Reference_5x7.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Oken, M.M.; Creech, R.H.; Tormey, D.C.; Horton, J.; Davis, T.E.; McFadden, E.T.; Carbone, P.P. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG). Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 1982, 5, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| PG (n = 25) | PG + EA (n = 26) | PG + CMT (n = 22) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean, SD; years) | 61.6, 10.3 | 54.3, 9.6 | 56.6, 12.6 | 0.0543 |
| Sex (n, %) ‡ | ||||
| Male | 6 (24.00) | 7 (26.92) | 2 (9.09) | 0.2727 |
| Female | 19 (76.00) | 19 (73.08) | 20 (90.91) | |
| Height (mean, SD; cm) | 159.2, 6.6 | 160.5, 7.4 | 157.3, 5.8 | 0.2507 |
| Weight (mean, SD; kg) | 62.7, 12.0 | 62.6, 10.3 | 59.1, 7.3 | 0.3938 |
| BMI (mean, SD; kg/m2) | 24.7, 3.8 | 24.4, 4.0 | 23.9, 2.9 | 0.7947 |
| SBP (mean, SD; mmHg) | 121.4, 13.6 | 119.4, 18.5 | 121.9, 20.3 | 0.8762 |
| DBP (mean, SD; mmHg) | 71.2, 10.4 | 73.2, 12.7 | 75.3, 7.3 | 0.4279 |
| Type of cancer (n, %) ‡ | ||||
| Colorectal cancer | 11 (44.00) | 11 (42.31) | 9 (40.91) | 0.977 |
| Brest cancer | 14 (56.00) | 15 (57.69) | 13 (59.09) |
| Mean Difference | Difference Rate (%) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Visit | PG (n = 25) | PG + EA (n = 26) | PG + CMT (n = 22) | p-Value | PG (n = 25) | PG + EA (n = 26) | PG + CMT (n = 22) | p-Value | |
| FACT/GOG-Ntx score | V3–V2 | −7.32 (−13.77, −0.87) * | −7.31 (−13.09, −1.53) * | −11.50 (−19.62, −3.38) * | 0.7926 | −9.89 (−21.35, 1.58) | −10.89 (−22.08, 0.30) | −15.70 (−26.86, −4.53) * | 0.7019 |
| V4–V2 | −8.60 (−14.93, −2.27) ¶,* | −6.73 (−12.34, −1.13) ¶,* | −16.64 (−25.16, −8.11) ¶,* | 0.2075 | −12.61 (−23.78, −1.43) * | −8.40 (−17.20, 0.40) | −25.02 (−38.20, −11.83) * | 0.0738 | |
| V5–V2 | −9.92 (−15.77, −4.07) * | −9.58 (−15.31, −3.85) * | −18.73 (−26.59, −10.87) * | 0.1737 | −15.33 (−25.23, −5.44) * | −13.64 (−22.37, −4.91) * | −28.15 (−40.62, −15.69) * | 0.1112 | |
| EORTC QLQ-CIPN 20 | V3–V2 | −4.16 (−7.83, −0.49) * | −5.00 (−7.96, −2.04) * | −6.50 (−11.68, −1.32) * | 0.5673 | −11.92 (−22.90, −0.95) * | −12.00 (−18.75, −5.24) * | −17.28 (−32.77, −1.79) * | 0.8038 |
| V4–V2 | −5.12 (−8.69, −1.55) * | −7.00 (−9.51, −4.49) * | −7.64 (−13.07, −2.20) * | 0.5668 | −14.32 (−24.86, −3.79) * | −18.08 (−23.35, −12.81) * | −19.01 (−34.43, −3.59) * | 0.4870 | |
| V5–V2 | −5.80 (−9.25, −2.35) * | −7.42 (−10.42, −4.43) * | −7.77 (−13.65, −1.90) * | 0.6945 | −15.89 (−26.42, −5.36) * | −19.09 (−25.63, −12.55) * | −17.74 (−35.33, −0.15) * | 0.2630 | |
| EORTC QLQ-C30 | V3–V2 | 1.19 (−1.59, 3.96) | 2.38 (−0.32, 5.09) | 1.67 (−1.30, 4.64) | 0.7994 | 2.78 (−4.96, 10.51) | 6.92 (−0.67, 14.51) | 8.50 (0.03, 16.97) * | 0.5855 |
| V4–V2 | 0.05 (−2.73, 2.83) | 2.95 (0.28, 5.61) * | 0.21 (−2.82, 3.24) | 0.1970 | 0.23 (−7.50, 7.97) | 7.50 (0.07, 14.94) * | 5.66 (−3.03, 14.35) | 0.3900 | |
| V5–V2 | 0.18 (−2.60, 2.95) | 1.33 (−1.34, 3.99) | 1.46 (−1.57, 4.49) | 0.7491 | 1.19 (−6.54, 8.93) | 4.28 (−3.15, 11.71) | 8.06 (−0.64, 16.75) | 0.5088 | |
| PG (n = 5) | PG + EA (n = 3) | PG + CMT (n = 3) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anticancer completion rate (%) | 5.56 (0, 10) | 16.67 (0, 20) | 7.14 (5.56, 11.11) | 0.5752 |
| PG (n = 25) | PG + EA (n = 26) | PG + CMT (n = 22) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adverse events (n, %) ‡ | ||||
| Yes | 3 (12.00) | 5 (19.23) | 9 (40.91) | 0.0538 |
| No | 22 (88.00) | 21 (80.77) | 13 (59.09) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Lee, Y.-W.; Lee, I.; Lee, J.-H.; Park, M.-G.; Kim, J.-H.; Sunwoo, Y.-Y.; Hwang, M.-S.; Park, T.-Y. Chuna Manual Therapy or Electroacupuncture with Pregabalin for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133916
Lee Y-W, Lee I, Lee J-H, Park M-G, Kim J-H, Sunwoo Y-Y, Hwang M-S, Park T-Y. Chuna Manual Therapy or Electroacupuncture with Pregabalin for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133916
Chicago/Turabian StyleLee, Yeon-Woo, Ilkyun Lee, Jin-Hyun Lee, Min-Geun Park, Ji-Hoon Kim, Yoon-Young Sunwoo, Man-Suk Hwang, and Tae-Yong Park. 2024. "Chuna Manual Therapy or Electroacupuncture with Pregabalin for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133916
APA StyleLee, Y.-W., Lee, I., Lee, J.-H., Park, M.-G., Kim, J.-H., Sunwoo, Y.-Y., Hwang, M.-S., & Park, T.-Y. (2024). Chuna Manual Therapy or Electroacupuncture with Pregabalin for Chemotherapy-Induced Peripheral Neuropathy: A Randomized Controlled Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3916. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133916







