Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy: Exploring Shared Pathways and Promising Biomarkers for Future Treatments
Abstract
1. Introduction
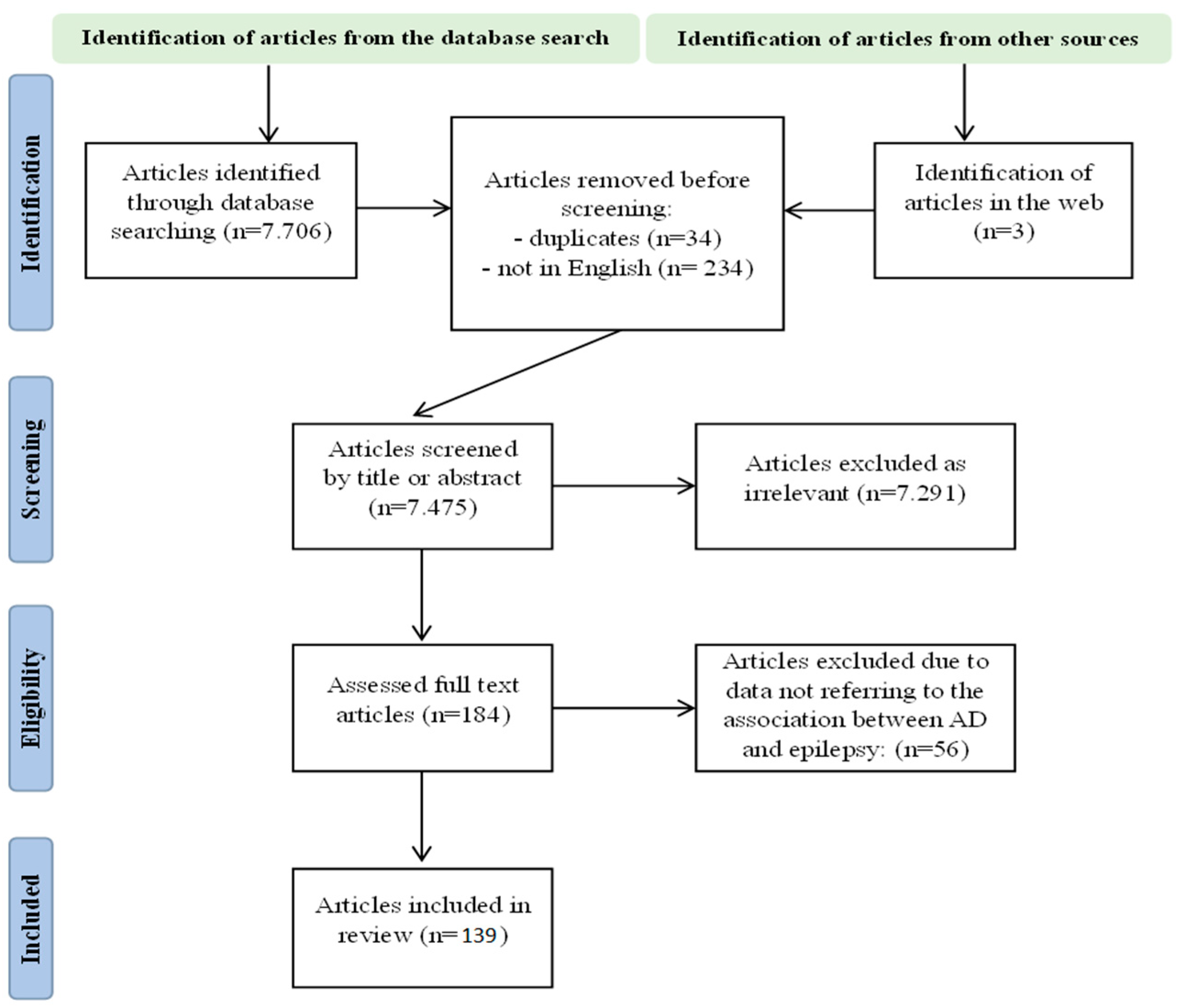
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Epidemiological Data Describing the Comorbidity of Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy
3.2. Risk Factors Implicated in Both Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy
3.2.1. Shared Risk Factors between Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy
3.2.2. Risk Factors for Epilepsy in Individuals with Alzheimer’s Disease
3.2.3. Risk Factors for Dementia in Epileptic Patients
3.3. Shared Pathogenetic Mechanisms between Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy
3.3.1. Amyloid-β
3.3.2. Hyperphosphorylated Tau Protein
3.3.3. Glutamate
3.3.4. Gamma-Aminobutyric Acid
3.3.5. Neuroinflammation
3.3.6. Acetylcholine—Noradrenaline—Serotonin Activity
3.3.7. Voltage-Gated Ion Channels
3.3.8. Mitochondria–Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress
3.3.9. Astrocytes
3.3.10. Beta-Secretase 1
3.3.11. Mechanistic Target of Rapamycin
3.3.12. Triggering Receptor Expressed on Myeloid Cells
3.3.13. α-Synuclein
3.3.14. Neural Network
3.3.15. The Role of Sleep
3.3.16. Others
3.4. Seizure Types
3.5. Electroencephalography
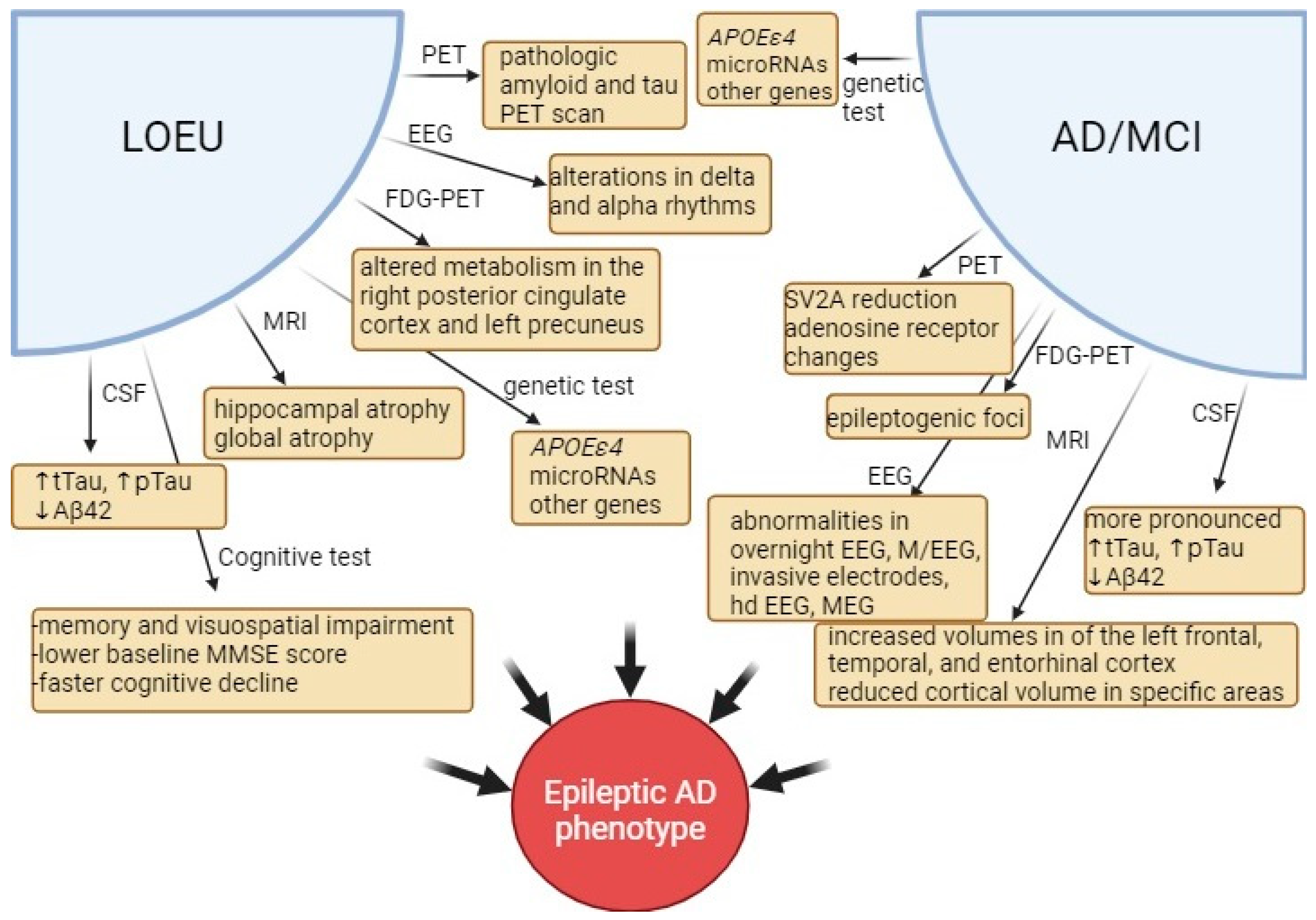
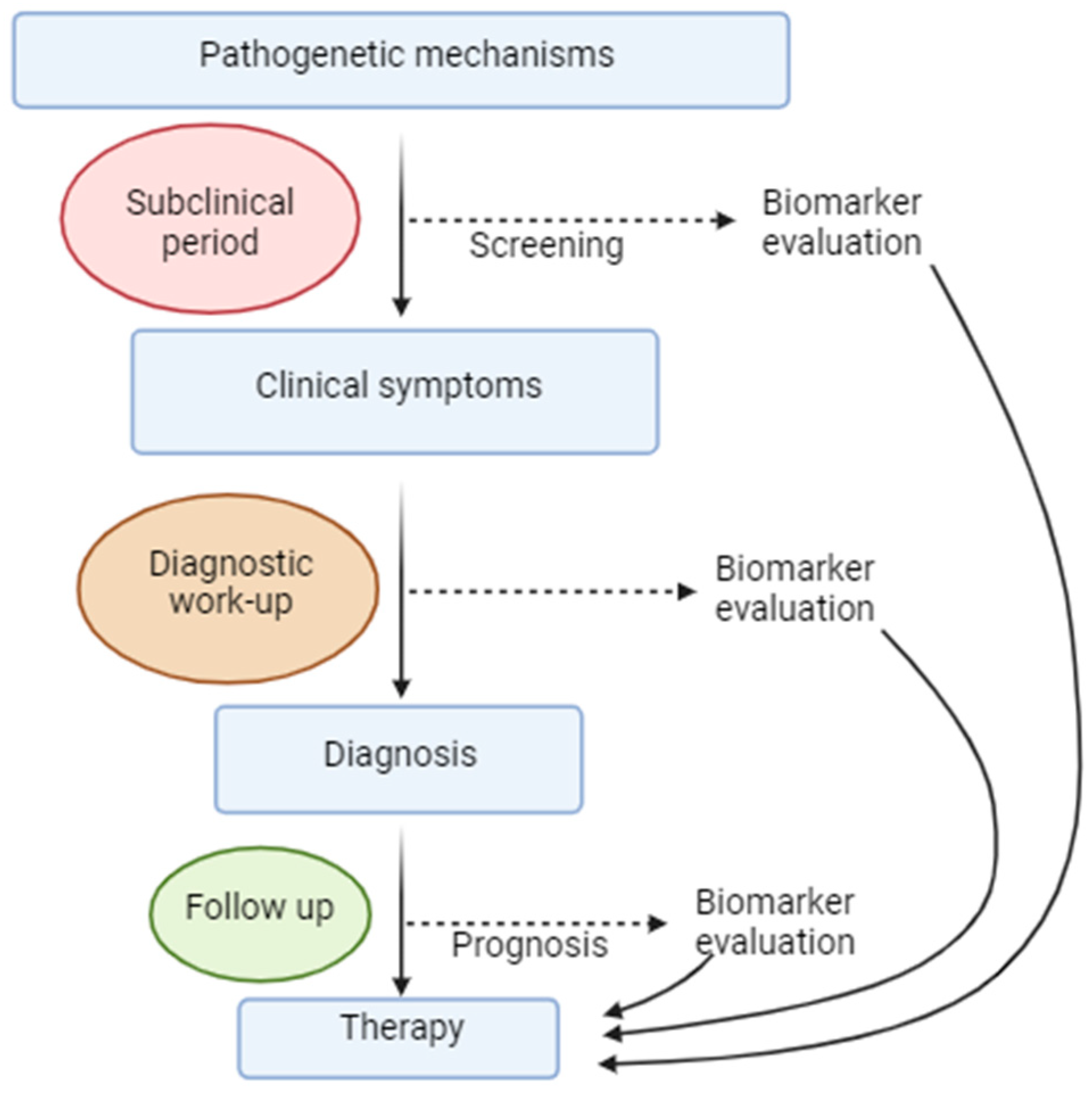
3.6. Biomarkers
3.6.1. Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers
3.6.2. Neuroimaging Findings
3.6.3. Cognitive Testing
3.6.4. Genetic Associations
3.6.5. Electroencephalographic Markers
3.7. Therapy
4. Discussion
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- World Health Organization. Dementia 2023. (Updated 15 March 2023). Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. A Public Health Approach to Alzheimer’s and Other Dementias. 2019. Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/aging/services/pdf/Public-Health-Approach-to-Alzheimers-and-Other-Dementias-complete-course-508.pdf (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- World Health Organization. Epilepsy: A Public Health Imperative; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Vicente, M.; Addo-Osafo, K.; Vossel, K. Latest advances in mechanisms of epileptic activity in Alzheimer’s disease and dementia with Lewy Bodies. Front. Neurol. 2024, 15, 1277613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.A.; Lee, H.J.; Kim, S.E.; Park, K.M. Brain networks and epilepsy development in patients with Alzheimer disease. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helmstaedter, C.; Lutz, T.; Wolf, V.; Witt, J.A. Prevalence of dementia in a level 4 university epilepsy center: How big is the problem? Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1217594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hickman, L.B.; Stern, J.M.; Silverman, D.H.S.; Salamon, N.; Vossel, K. Clinical, imaging, and biomarker evidence of amyloid- and tau-related neurodegeneration in late-onset epilepsy of unknown etiology. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1241638. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Z.; Wang, F.Y.; Wu, W.P.; Yu, L.Z.; Wu, J.C.; Wang, L. Bidirectional relationship between late-onset epilepsy (LOE) and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis of cohort studies. Epilepsy Behav. 2024, 153, 109723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Chen, S.; Xu, S.; Wu, J.; Zhuang, Y.; Cao, W.; Chen, X.; Li, X. The clinical correlation between Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 922535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, N.; Chen, H.; Zhang, W.; Yao, J.; Tu, Q.; Yu, X.; Sun, X. Bidirectional influences between seizures and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Int. J. Geriatr. Psychiatry 2022, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, F.; Chen, L.; Yu, Y.; Xu, T.; Chen, L.; Yang, W.; Wu, Q.; Han, Y. Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy: An increasingly recognized comorbidity. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 940515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Yang, W.; Yang, F.; Yu, Y.; Xu, T.; Wang, D.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, Q.; Han, Y. The crosstalk between epilepsy and dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Epilepsy Behav. 2024, 152, 109640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nous, A.; Seynaeve, L.; Feys, O.; Wens, V.; De Tiège, X.; Van Mierlo, P.; Baroumand, A.G.; Nieboer, K.; Allemeersch, G.J.; Mangelschots, S.; et al. Subclinical epileptiform activity in the Alzheimer continuum: Association with disease, cognition and detection method. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2024, 16, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.C.; Kim, B.K.; Kang, K.; Lee, W.W.; Yoo, I.; Kim, Y.S.; Lee, J.J. Aphasic Status Epilepticus Associated with Alzheimer’s Disease: Clinical and Electrographic Characteristics. J. Epilepsy Res. 2023, 13, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, O.; Kouser, T.; Skylar-Scott, I.A. Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy: Shared neuropathology guides current and future treatment strategies. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1241339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, C.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, J.; Su, B.; Peng, X.; Liu, L. Bi-directional associations of epilepsy with dementia and Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis of longitudinal studies. Age Ageing 2022, 51, afac010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, S.F.; Hu, J.J.; Zhang, Y.B.; Chen, G.R.; Lin, Y.X.; Kang, D.Z.; Lin, Z.Y.; Yao, P.S. Lack of causal association between epilepsy and dementia: A Mendelian randomization analysis. Epilepsy Behav. 2024, 150, 109570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawakami, O.; Koike, Y.; Ando, T.; Sugiura, M.; Kato, H.; Hiraga, K.; Kito, H.; Kondo, H. Incidence of dementia in patients with adult-onset epilepsy of unknown causes. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 395, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Pozo, A.; Knox, K.M.; Lehmann, L.M.; Davidson, S.; Rho, S.L.; Jayadev, S.; Barker-Haliski, M. Chronic evoked seizures in young pre-symptomatic APP/PS1 mice induce serotonin changes and accelerate onset of Alzheimer’s disease-related neuropathology. Prog. Neurobiol. 2024, 235, 102591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haoudy, S.; Jonveaux, T.; Puisieux, S.; Epstein, J.; Hopes, L.; Maillard, L.; Aron, O.; Tyvaert, L. Epilepsy in Early Onset Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2022, 85, 615–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cano, A.; Fonseca, E.; Ettcheto, M.; Sánchez-López, E.; de Rojas, I.; Alonso-Lana, S.; Morató, X.; Souto, E.B.; Toledo, M.; Boada, M.; et al. Epilepsy in Neurodegenerative Diseases: Related Drugs and Molecular Pathways. Pharmaceuticals 2021, 14, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciliento, R.; Gjini, K.; Dabbs, K.; Hermann, B.; Riedner, B.; Jones, S.; Fatima, S.; Johnson, S.; Bendlin, B.; Lam, A.D.; et al. Prevalence and localization of nocturnal epileptiform discharges in mild cognitive impairment. Brain Commun. 2023, 5, fcad302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vöglein, J.; Noachtar, S.; McDade, E.; Quaid, K.A.; Salloway, S.; Ghetti, B.; Noble, J.; Berman, S.; Chhatwal, J.; Mori, H.; et al. Seizures as an early symptom of autosomal dominant Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2019, 76, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cortini, F.; Cantoni, C.; Villa, C. Epileptic seizures in autosomal dominant forms of Alzheimer’s disease. Seizure—Eur. J. Epilepsy 2018, 61, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagino, N.; Kubota, Y.; Nakamoto, H.; Miyao, S.; Kodama, T.; Ito, S.; Oguni, H.; Chernov, M. Non-lesional late-onset epilepsy in the elderly Japanese patients: Presenting characteristics and seizure outcomes with regard to comorbid dementia. J. Clin. Neurosci. 2022, 103, 100–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, D.F.; Kanshin, E.; Faustin, A.; Thierry, M.; Friedman, D.; Devore, S.; Ueberheide, B.; Devinsky, O.; Wisniewski, T. Localized proteomic differences in the choroid plexus of Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy patients. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1221775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Altuna, M.; Olmedo-Saura, G.; Carmona-Iragui, M.; Fortea, J. Mechanisms Involved in Epileptogenesis in Alzheimer’s Disease and Their Therapeutic Implications. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 4307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kazim, S.F.; Seo, J.H.; Bianchi, R.; Larson, C.S.; Sharma, A.; Wong, R.K.S.; Gorbachev, K.Y.; Pereira, A.C. Neuronal Network Excitability in Alzheimer’s Disease: The Puzzle of Similar versus Divergent Roles of Amyloid β and Tau. eNeuro 2021, 8, 1–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Csernus, E.A.; Werber, T.; Kamondi, A.; Horvath, A.A. The Significance of Subclinical Epileptiform Activity in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Review. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 856500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horvath, A.A.; Papp, A.; Zsuffa, J.; Szucs, A.; Luckl, J.; Radai, F.; Nagy, F.; Hidasi, Z.; Csukly, G.; Barcs, G.; et al. Subclinical epileptiform activity accelerates the progression of Alzheimer’s disease: A long-term EEG study. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2021, 132, 1982–1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeh, W.-C.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Li, K.-Y.; Chien, C.-F.; Huang, L.-C.; Yang, Y.-H. Association between Subclinical Epileptiform Discharge and the Severity of Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Longitudinal Cohort Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2022, 90, 305–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devulder, A.; Macea, J.; Kalkanis, A.; De Winter, F.L.; Vandenbulcke, M.; Vandenberghe, R.; Testelmans, D.; Van Den Bossche, M.J.A.; Van Paesschen, W. Subclinical epileptiform activity and sleep disturbances in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, J.; Libretto, T.; Henley, W.; Zeman, A. A Longitudinal Study of Epileptic Seizures in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehmann, L.; Lo, A.; Knox, K.M.; Barker-Haliski, M. Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy: A Perspective on the Opportunities for Overlapping Therapeutic Innovation. Neurochem. Res. 2021, 46, 1895–1912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, M.; Mao, W.; Voskobiynyk, Y.; Necula, D.; Lew, I.; Petersen, C.; Zahn, A.; Yu, G.Q.; Yu, X.; Smith, N.; et al. Alzheimer risk-increasing TREM2 variant causes aberrant cortical synapse density and promotes network hyperexcitability in mouse models. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 186, 106263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, M.; Tran, T.; Eskin, E.; Lajonchere, C.; Pasaniuc, B.; Geschwind, D.H.; Vossel, K.; Chang, T.S. Multi-class Modeling Identifies Shared Genetic Risk for Late-onset Epilepsy and Alzheimer’s Disease. medRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijaya, A.; Setiawan, N.A.; Ahmad, A.H.; Zakaria, R.; Othman, Z. Electroencephalography and mild cognitive impairment research: A scoping review and bibliometric analysis (ScoRBA). AIMS Neurosci. 2023, 10, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyou, H.J.; Seo, K.D.; Lee, J.E.; Pak, H.Y.; Lee, J.H. Association of Alzheimer’s Disease with the Risk of Developing Epilepsy: A 10-Year Nationwide Cohort Study. Dement. Neurocogn Disord. 2018, 17, 156–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamoureux, L.; Marottoli, F.M.; Tseng, K.Y.; Tai, L.M. APOE4 Promotes Tonic-Clonic Seizures, an Effect Modified by Familial Alzheimer’s Disease Mutations. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 656521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keret, O.; Hoang, T.D.; Xia, F.; Rosen, H.J.; Yaffe, K. Association of Late-Onset Unprovoked Seizures of Unknown Etiology with the Risk of Developing Dementia in Older Veterans. JAMA Neurol. 2020, 77, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cretin, B.; Bousiges, O.; Hautecloque, G.; Philippi, N.; Blanc, F.; Dibitonto, L.; Martin-Hunyadi, C.; Sellal, F. CSF in Epileptic Prodromal Alzheimer’s Disease: No Diagnostic Contribution but a Pathophysiological One. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 623777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, G.; Ziso, B.; Larner, A.J. The overlap between epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease and the consequences for treatment. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2019, 19, 653–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emsley, H.C.A.; Parkes, L.M. Seizures in the context of occult cerebrovascular disease. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 104 Pt B, 106396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turon, M.; Abraira, L.; Cazorla, S.; Fonseca, E.; Quintana, M.; Toledo, M.; Salas-Puig, X.; Santamarina, E. Vascular risk factors as independent predictors of neurocognitive impairments in patients with late-onset epilepsy who have small-vessel disease. Epilepsy Behav. 2020, 104 Pt B, 106443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, L.; Fu, C.; Li, J.; Peng, S. Late-onset epilepsy and the risk of dementia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Aging Clin. Exp. Res. 2022, 34, 1771–1779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milikovsky, D.Z.; Ofer, J.; Senatorov, V.V.; Friedman, A.R.; Prager, O.; Sheintuch, L.; Elazari, N.; Veksler, R.; Zelig, D.; Weissberg, I.; et al. Paroxysmal slow cortical activity in Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy is associated with blood-brain barrier dysfunction. Sci. Transl. Med. 2019, 11, eaaw8954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, A.; Capelli, V.; Husain, M. Cognition and dementia in older patients with epilepsy. Brain 2018, 141, 1592–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, Y.N.; Angelopoulou, E.; Jones, N.C.; O’Brien, T.J.; Kwan, P.; Piperi, C.; Othman, I.; Shaikh, M.F. Tau Related Pathways as a Connecting Link between Epilepsy and Alzheimer’s Disease. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2019, 10, 4199–4212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lavrencic, L.; Radford, K.; Booth, A.; Yoshimura, S.; Anstey, K.J.; Anderson, C.S.; Peters, R. Systematic review of coexistent epileptic seizures and Alzheimer’s disease: Incidence and prevalence. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2021, 69, 2011–2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asadollahi, M.; Atazadeh, M.; Noroozian, M. Seizure in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Underestimated Phenomenon. Am. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. Other Dement. 2018, 34, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horváth, A.; Szűcs, A.; Hidasi, Z.; Csukly, G.; Barcs, G.; Kamondi, A. Prevalence, Semiology, and Risk Factors of Epilepsy in Alzheimer’s Disease: An Ambulatory EEG Study. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2018, 63, 1045–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tábuas-Pereira, M.; Durães, J.; Lopes, J.; Sales, F.; Bento, C.; Duro, D.; Santiago, B.; Almeida, M.R.; Leitão, M.J.; Baldeiras, I.; et al. Increased CSF tau is associated with a higher risk of seizures in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 98, 207–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, X.Y.; Torzillo, E.; Lyall, D.M.; Manohar, S.; Husain, M.; Sen, A. Association of Dementia Risk With Focal Epilepsy and Modifiable Cardiovascular Risk Factors. JAMA Neurol. 2023, 80, 445–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández, G.; Sala-Padró, J.; Adell, V.; Rico, I.; Gasa-Roqué, A.; Morandeira, F.; Campdelacreu, J.; Gascon, J.; Falip, M. Cognitive decline in adult-onset temporal lobe epilepsy: Insights from aetiology. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2024, 237, 108159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Z.R.; Zhang, H.W.; Tseng, C.H.; Peng, H.C.; Kok, V.C.; Li, G.P.; Hsiung, C.A.; Hsu, C.Y. Late-onset epilepsy and subsequent increased risk of dementia. Aging 2021, 13, 3573–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Wang, Q. The bidirectional relationship between Alzheimer’s disease (AD) and epilepsy: A Mendelian randomization study. Brain Behav. 2023, 13, e3221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, R.; Hu, M.; Liu, X.; Ye, L.; Xu, B.; Sun, M.; Xu, S.; Shao, W.; Tan, Y.; Xu, Y.; et al. Impairments of GABAergic transmission in hippocampus mediate increased susceptibility of epilepsy in the early stage of Alzheimer’s disease. Cell Commun. Signal 2024, 22, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.P.; Leeman-Markowski, B.A. Proposed mechanisms of tau: Relationships to traumatic brain injury, Alzheimer’s disease, and epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1287545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, D.; Pires, G.; Kavanagh, T.; Kanshin, E.; Askenazi, M.; Ueberheide, B.; Devinsky, O.; Wisniewski, T.; Drummond, E. Similar brain proteomic signatures in Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy. Acta Neuropathol. 2024, 147, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szabo, A.B.; Cretin, B.; Gérard, F.; Curot, J.; Barbeau, E.J.; Pariente, J.; Dahan, L.; Valton, L. Sleep: The Tip of the Iceberg in the Bidirectional Link Between Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 836292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hector, A.; Brouillette, J. Hyperactivity Induced by Soluble Amyloid-β Oligomers in the Early Stages of Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2020, 13, 600084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosco, F.; Guarnieri, L.; Rania, V.; Palma, E.; Citraro, R.; Corasaniti, M.T.; Leo, A.; De Sarro, G. Antiseizure Medications in Alzheimer’s Disease from Preclinical to Clinical Evidence. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 2639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lemus, H.N.; Sarkis, R.A. Interictal epileptiform discharges in Alzheimer’s disease: Prevalence, relevance, and controversies. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1261136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toral-Rios, D.; Pichardo-Rojas, P.S.; Alonso-Vanegas, M.; Campos-Peña, V. GSK3β and Tau Protein in Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy. Front. Cell Neurosci. 2020, 14, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkis, R.A.; Willment, K.C.; Pennell, P.B.; Marshall, G. Late-onset unexplained epilepsy: What are we missing? Epilepsy Behav. 2019, 99, 106478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leo, A.; Tallarico, M.; Sciaccaluga, M.; Citraro, R.; Costa, C. Epilepsy and Alzheimer’s Disease: Current Concepts and Treatment Perspective on Two Closely Related Pathologies. Curr. Neuropharmacol. 2022, 20, 2029–2033. [Google Scholar]
- Yook, Y.; Lee, K.Y.; Kim, E.; Lizarazo, S.; Yu, X.; Tsai, N.P. Hyperfunction of post-synaptic density protein 95 promotes seizure response in early-stage aβ pathology. EMBO Rep. 2024, 25, 1233–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banote, R.K.; Håkansson, S.; Zetterberg, H.; Zelano, J. CSF biomarkers in patients with epilepsy in Alzheimer’s disease: A nation-wide study. Brain Commun. 2022, 4, fcac210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawar, I.; Kapur, J. Does Alzheimer’s disease with mesial temporal lobe epilepsy represent a distinct disease subtype? Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 2697–2706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, J.C.; Vivash, L.; Malpas, C.B.; Hao, Y.; McLean, C.; Chen, Z.; O’Brien, T.J.; Jones, N.C.; Kwan, P. Low prevalence of amyloid and tau pathology in drug-resistant temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsia 2021, 62, 3058–3067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carello-Collar, G.; Bellaver, B.; Ferreira, P.C.L.; Ferrari-Souza, J.P.; Ramos, V.G.; Therriault, J.; Tissot, C.; De Bastiani, M.A.; Soares, C.; Pascoal, T.A.; et al. The GABAergic system in Alzheimer’s disease: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 5025–5036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, T.; Li, X.; Yu, E.; Li, M.; Pan, X. Identification of common core ion channel genes in epilepsy and Alzheimer’s disease. Ir. J. Med. Sci. 2024, 193, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liew, Y.; Retinasamy, T.; Arulsamy, A.; Ali, I.; Jones, N.C.; O’Brien, T.J.; Shaikh, M.F. Neuroinflammation: A Common Pathway in Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 94, S253–s265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Y.; Zhang, H.C.; Lv, Y.D.; Jin, F.Y.; Wu, X.J.; Zhu, J.; Ruan, Y. Levetiracetam alleviates cognitive decline in Alzheimer’s disease animal model by ameliorating the dysfunction of the neuronal network. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 888784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.R.; Huang, J.B.; Yang, S.L.; Hong, F.F. Role of Cholinergic Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules 2022, 27, 1816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Tan, B.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Z. Cholinergic Signaling, Neural Excitability, and Epilepsy. Molecules 2021, 26, 2258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giorgi, F.S.; Saccaro, L.F.; Busceti, C.L.; Biagioni, F.; Fornai, F. Epilepsy and Alzheimer’s Disease: Potential mechanisms for an association. Brain Res. Bull. 2020, 160, 107–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yun, H.M.; Park, K.R.; Kim, E.C.; Kim, S.; Hong, J.T. Serotonin 6 receptor controls Alzheimer’s disease and depression. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 26716–26728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, J.; Du, E.; Guo, L. Mitochondrial Interaction with Serotonin in Neurobiology and Its Implication in Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. Rep. 2023, 7, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acquarone, E.; Argyrousi, E.K.; Arancio, O.; Watterson, D.M.; Roy, S.M. The 5HT2b Receptor in Alzheimer’s Disease: Increased Levels in Patient Brains and Antagonist Attenuation of Amyloid and Tau Induced Dysfunction. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2024, 98, 1349–1360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eremin, D.V.; Kondaurova, E.M.; Rodnyy, A.Y.; Molobekova, C.A.; Kudlay, D.A.; Naumenko, V.S. Serotonin Receptors as a Potential Target in the Treatment of Alzheimer’s Disease. Biochemistry 2023, 88, 2023–2042. [Google Scholar]
- Sayahi, Z.; Komaki, A.; Saidi Jam, M.; Karimi, S.A.; Raoufi, S.; Mardani, P.; Naderishahab, M.; Sarihi, A.; Mirnajafi-Zadeh, J. Effect of ramosetron, a 5-HT(3) receptor antagonist on the severity of seizures and memory impairment in electrical amygdala kindled rats. J. Physiol. Sci. 2022, 72, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, L.; Xu, Z.; Luo, H.; He, Q.; Diao, L.; Gui, X.; Wei, L. The association between 5-HT1A binding and temporal lobe epilepsy: A meta-analysis of molecular imaging studies. Epilepsy Behav. 2023, 145, 109354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzello, E.; Pimpinella, D.; Pignataro, A.; Titta, G.; Merenda, E.; Saviana, M.; Porcheddu, G.F.; Paolantoni, C.; Malerba, F.; Giorgi, C.; et al. Lamotrigine rescues neuronal alterations and prevents seizure-induced memory decline in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 181, 106106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, J.Q. Epileptic Mechanisms Shared by Alzheimer’s Disease: Viewed via the Unique Lens of Genetic Epilepsy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 7133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bosco, D.B.; Kremen, V.; Haruwaka, K.; Zhao, S.; Wang, L.; Ebner, B.A.; Zheng, J.; Dheer, A.; Perry, J.F.; Xie, M.; et al. Impaired microglial phagocytosis promotes seizure development. bioRxiv 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosun, D.; Hausle, Z.; Iwaki, H.; Thropp, P.; Lamoureux, J.; Lee, E.B.; MacLeod, K.; McEvoy, S.; Nalls, M.; Perrin, R.J.; et al. A cross-sectional study of α-synuclein seed amplification assay in Alzheimer’s disease neuroimaging initiative: Prevalence and associations with Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers and cognitive function. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, A.A.; Csernus, E.A.; Lality, S.; Kaminski, R.M.; Kamondi, A. Inhibiting Epileptiform Activity in Cognitive Disorders: Possibilities for a Novel Therapeutic Approach. Front. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 557416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanke, J.M.; Schindler, K.A.; Seiler, A. On the relationships between epilepsy, sleep, and Alzheimer’s disease: A narrative review. Epilepsy Behav. 2022, 129, 108609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez, M.P.; García-Cabrero, A.M.; Sánchez-Elexpuru, G.; Burgos, D.F.; Serratosa, J.M. Tau-Induced Pathology in Epilepsy and Dementia: Notions from Patients and Animal Models. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, Y.; Si, X.; Wang, J.; Wang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Yan, Y.; Tian, J.; Zhang, B.; Pu, J. Alzheimer Disease and Epilepsy: A Mendelian Randomization Study. Neurology 2023, 101, e399–e409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rey, C.; Cattaud, V.; Rampon, C.; Verret, L. What’s New on Alzheimer’s Disease? Insights From AD Mouse Models; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Song, S.; Chen, J.; Xiao, P.; Duan, H.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, F.; Wang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Geng, Z. Role of Macrophages in Status Epilepticus Predisposing to Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2020, 73, 375–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.; Jones, N.C.; Kwan, P. Unravelling the Role of Glycogen Synthase Kinase-3 in Alzheimer’s Disease-Related Epileptic Seizures. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.; Lu, H.; Liu, W.; Wu, Z.; Wu, Q.; Li, X.; Xu, Z.; Hui, F.; Zhao, Q. The overlap between Alzheimer’s disease and epilepsy uncovered by transcriptome sequencing. Clin. Transl. Med. 2020, 10, e169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fu, C.H.; Iascone, D.M.; Petrof, I.; Hazra, A.; Zhang, X.; Pyfer, M.S.; Tosi, U.; Corbett, B.F.; Cai, J.; Lee, J.; et al. Early Seizure Activity Accelerates Depletion of Hippocampal Neural Stem Cells and Impairs Spatial Discrimination in an Alzheimer’s Disease Model. Cell Rep. 2019, 27, 3741–3751.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lehmann, L.M.; Barker-Haliski, M. Loss of normal Alzheimer’s disease-associated Presenilin 2 function alters antiseizure medicine potency and tolerability in the 6-Hz focal seizure model. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1223472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cope, Z.A.; Murai, T.; Sukoff Rizzo, S.J. Emerging Electroencephalographic Biomarkers to Improve Preclinical to Clinical Translation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2022, 14, 805063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, T.; Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Wang, Q. Electrophysiological Biomarkers of Epileptogenicity in Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2021, 15, 747077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lam, A.D.; Sarkis, R.A.; Pellerin, K.R.; Jing, J.; Dworetzky, B.A.; Hoch, D.B.; Jacobs, C.S.; Lee, J.W.; Weisholtz, D.S.; Zepeda, R.; et al. Association of epileptiform abnormalities and seizures in Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2020, 95, e2259–e2270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musaeus, C.S.; Frederiksen, K.S.; Andersen, B.B.; Høgh, P.; Kidmose, P.; Fabricius, M.; Hribljan, M.C.; Hemmsen, M.C.; Rank, M.L.; Waldemar, G.; et al. Detection of subclinical epileptiform discharges in Alzheimer’s disease using long-term outpatient EEG monitoring. Neurobiol. Dis. 2023, 183, 106149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnson, E.L.; Sullivan, K.J.; Schneider, A.L.C.; Simino, J.; Mosley, T.H.; Kucharska-Newton, A.; Knopman, D.S.; Gottesman, R.F. Association of Plasma Aβ(42)/Aβ(40) Ratio and Late-Onset Epilepsy: Results From the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities Study. Neurology 2023, 101, e1319–e1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nardi Cesarini, E.; Babiloni, C.; Salvadori, N.; Farotti, L.; Del Percio, C.; Pascarelli, M.T.; Noce, G.; Lizio, R.; Da Re, F.; Isella, V.; et al. Late-Onset Epilepsy With Unknown Etiology: A Pilot Study on Neuropsychological Profile, Cerebrospinal Fluid Biomarkers, and Quantitative EEG Characteristics. Front. Neurol. 2020, 11, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lam, A.D.; Noebels, J. Night Watch on the Titanic: Detecting Early Signs of Epileptogenesis in Alzheimer Disease. Epilepsy Curr. 2020, 20, 369–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hahm, J.; Kim, K.K.; Kim, D.W. Seizure-Related Cortical Volume Alterations in Alzheimer’s Disease: A Preliminary Study. J. Epilepsy Res. 2018, 8, 33–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaestner, E.; Reyes, A.; Chen, A.; Rao, J.; Macari, A.C.; Choi, J.Y.; Qiu, D.; Hewitt, K.; Wang, Z.I.; Drane, D.L.; et al. Atrophy and cognitive profiles in older adults with temporal lobe epilepsy are similar to mild cognitive impairment. Brain 2021, 144, 236–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Li, W.; Shen, W.; Zhang, L.; Pu, X.; Chen, L. (Eds.) Automatic Identification of Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy Based on MRI. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 31st International Conference on Tools with Artificial Intelligence (ICTAI), Portland, OR, USA, 4–6 November 2019; pp. 614–620. [Google Scholar]
- Purushotham, M.; Tashrifwala, F.; Jena, R.; Vudugula, S.A.; Patil, R.S.; Agrawal, A. The Association Between Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy: A Narrative Review. Cureus 2022, 14, e30195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marcus, C.; Mena, E.; Subramaniam, R.M. Brain PET in the diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease. Clin. Nucl. Med. 2014, 39, e413–e422, quiz e423–e426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colom-Cadena, M.; Spires-Jones, T.; Zetterberg, H.; Blennow, K.; Caggiano, A.; DeKosky, S.T.; Fillit, H.; Harrison, J.E.; Schneider, L.S.; Scheltens, P.; et al. The clinical promise of biomarkers of synapse damage or loss in Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimer’s Res. Ther. 2020, 12, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horvath, A.; Kiss, M.; Szucs, A.; Kamondi, A. Precuneus-Dominant Degeneration of Parietal Lobe Is at Risk of Epilepsy in Mild Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Neurol. 2019, 10, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Novak, A.; Vizjak, K.; Gacnik, A.; Rakusa, M. Cognitive impairment in people with epilepsy: Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) as a screening tool. Acta Neurol. Belg. 2023, 123, 451–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Filippov, M.A.; Vorobyov, V.V. Detrimental and synergistic role of epilepsy—Alzheimer’s disease risk factors. Neural Regen. Res. 2019, 14, 1376–1377. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wu, J.; Zhu, S.; Zhao, C.; Xu, X. A Comprehensive Investigation of Molecular Signatures and Pathways Linking Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy via Bioinformatic Approaches. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2022, 19, 146–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juźwik, C.A.; Drake, S.S.; Zhang, Y.; Paradis-Isler, N.; Sylvester, A.; Amar-Zifkin, A.; Douglas, C.; Morquette, B.; Moore, C.S.; Fournier, A.E. microRNA dysregulation in neurodegenerative diseases: A systematic review. Progress. Neurobiol. 2019, 182, 101664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, X.-w.; Lu, H.-y.; Xu, Z.; Liu, T.-y.; Wu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Q.-c.; Gao, H.-y. In Silico Analyses for Key Genes and Molecular Genetic Mechanism in Epilepsy and Alzheimer’s Disease. CNS Neurol. Disord.—Drug Targets 2018, 17, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harutyunyan, A.; Jones, N.C.; Kwan, P.; Anderson, A. Network Preservation Analysis Reveals Dysregulated Synaptic Modules and Regulatory Hubs Shared Between Alzheimer’s Disease and Temporal Lobe Epilepsy. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 821343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossel, K.A.; Ranasinghe, K.G.; Beagle, A.J.; Mizuiri, D.; Honma, S.M.; Dowling, A.F.; Darwish, S.M.; Van Berlo, V.; Barnes, D.E.; Mantle, M.; et al. Incidence and impact of subclinical epileptiform activity in Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Neurol. 2016, 80, 858–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musaeus, C.S.; Engedal, K.; Høgh, P.; Jelic, V.; Mørup, M.; Naik, M.; Oeksengaard, A.R.; Snaedal, J.; Wahlund, L.O.; Waldemar, G.; et al. EEG Theta Power Is an Early Marker of Cognitive Decline in Dementia due to Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 64, 1359–1371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitchigina, V.F. Alterations of Coherent Theta and Gamma Network Oscillations as an Early Biomarker of Temporal Lobe Epilepsy and Alzheimer’s Disease. Front. Integr. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tombini, M.; Boscarino, M.; Di Lazzaro, V. Tackling seizures in patients with Alzheimer’s disease. Expert. Rev. Neurother. 2023, 23, 1131–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hautecloque-Raysz, G.; Sellal, F.; Bousiges, O.; Phillipi, N.; Blanc, F.; Cretin, B. Epileptic Prodromal Alzheimer’s Disease Treated with Antiseizure Medications: Medium-Term Outcome of Seizures and Cognition. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 94, 1057–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, C.Y.; Chang, M.C.; Jhou, H.J. Effect of Levetiracetam on Cognition: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis of Double-Blind Randomized Placebo-Controlled Trials. CNS Drugs 2024, 38, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vossel, K.; Ranasinghe, K.G.; Beagle, A.J.; La, A.; Ah Pook, K.; Castro, M.; Mizuiri, D.; Honma, S.M.; Venkateswaran, N.; Koestler, M.; et al. Effect of Levetiracetam on Cognition in Patients With Alzheimer Disease With and Without Epileptiform Activity: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 1345–1354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Isla, A.G.; Balleza-Tapia, H.; Chu, F.; Chen, G.; Johansson, J.; Nilsson, P.; Fisahn, A. Low dose of levetiracetam counteracts amyloid β-induced alterations of hippocampal gamma oscillations by restoring fast-spiking interneuron activity. Exp. Neurol. 2023, 369, 114545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vossel, K. Putting the Brakes on Accelerated Cognitive Decline in Alzheimer’s Disease with Epileptic Activity. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2023, 94, 1075–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musaeus, C.S.; Nilsson, C.; Cooper, C.; Kramberger, M.G.; Verdelho, A.; Stefanova, E.; Religa, D.; Waldemar, G.; Frederiksen, K.S. Pharmacological Medical Treatment of Epilepsy in Patients with Dementia: A Systematic Review. Curr. Alzheimer Res. 2021, 18, 689–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rohracher, A.; Kalss, G.; Kuchukhidze, G.; Neuray, C.; Leitinger, M.; Höfler, J.; Kreidenhuber, R.; Rossini, F.; Volna, K.; Mauritz, M.; et al. New anti-seizure medication for elderly epilepsy patients—A critical narrative review. Expert. Opin. Pharmacother. 2021, 22, 621–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Jiang, H.Y.; Liu, W.J. Anti-seizure medication exposure and the risk of dementia: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Front. Neurol. 2023, 14, 1133816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dusanter, C.; Houot, M.; Mere, M.; Denos, M.; Samson, S.; Herlin, B.; Navarro, V.; Dupont, S. Cognitive effect of antiseizure medications in medial temporal lobe epilepsy. Eur. J. Neurol. 2023, 30, 3692–3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schnier, C.; Duncan, S.; Wilkinson, T.; Mbizvo, G.K.; Chin, R.F.M. A nationwide, retrospective, data-linkage, cohort study of epilepsy and incident dementia. Neurology 2020, 95, e1686–e1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayala, H.; Kapur, J.; El-Haija, H.A.; Parikh, P.; Zawar, I. Memantine’s double duty? Investigating its impact on epilepsy control in Alzheimer’s disease. Epileptic Disord. 2024, 26, 261–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vico Varela, E.; Etter, G.; Williams, S. Excitatory-inhibitory imbalance in Alzheimer’s disease and therapeutic significance. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 127, 605–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourmaud, S.; Stewart, D.A.; Irwin, D.J.; Roberts, N.; Barbour, A.J.; Eberwine, G.; O’Brien, W.T.; Vassar, R.; Talos, D.M.; Jensen, F.E. The role of mTORC1 activation in seizure-induced exacerbation of Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2022, 145, 324–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourmaud, S.; Shou, H.; Irwin, D.J.; Sansalone, K.; Jacobs, L.M.; Lucas, T.H.; Marsh, E.D.; Davis, K.A.; Jensen, F.E.; Talos, D.M. Alzheimer-like amyloid and tau alterations associated with cognitive deficit in temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 2020, 143, 191–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranasinghe, K.G.; Kudo, K.; Hinkley, L.; Beagle, A.; Lerner, H.; Mizuiri, D.; Findlay, A.; Miller, B.L.; Kramer, J.H.; Gorno-Tempini, M.L.; et al. Neuronal synchrony abnormalities associated with subclinical epileptiform activity in early-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2022, 145, 744–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, M.; Kolesar, T.A.; Goertzen, A.L.; Ng, M.C.; Ko, J.H. Do Epilepsy Patients with Cognitive Impairment Have Alzheimer’s Disease-like Brain Metabolism? Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, M.; Manfredi, N.; Aluisantonio, L.; Franchini, F.; Chiaravalloti, A.; Izzi, F.; Di Santo, S.; Schillaci, O.; Mercuri, N.B.; Placidi, F.; et al. Cognitive functioning, cerebrospinal fluid Alzheimer’s disease biomarkers and cerebral glucose metabolism in late-onset epilepsy of unknown aetiology: A prospective study. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2022, 56, 5384–5396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, X.; Ahmed, R.; Thayer, Z.; Breen, N.; McMillan, J.; Fulham, M.; Nikpour, A. Late-onset epilepsy with cognitive symptoms: Comparison of cognitive and imaging profiles with probable Alzheimer’s disease. Epilepsy Behav. 2023, 146, 109371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Genetic:
|
| Age [7,37] |
| Mild cognitive impairment [37] |
Vascular [7]:
|
| History of brain traumatic injury [27] |
| Blood–brain barrier dysfunction [27] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kalyvas, A.-C.; Dimitriou, M.; Ioannidis, P.; Grigoriadis, N.; Afrantou, T. Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy: Exploring Shared Pathways and Promising Biomarkers for Future Treatments. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133879
Kalyvas A-C, Dimitriou M, Ioannidis P, Grigoriadis N, Afrantou T. Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy: Exploring Shared Pathways and Promising Biomarkers for Future Treatments. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133879
Chicago/Turabian StyleKalyvas, Athanasios-Christos, Maria Dimitriou, Panagiotis Ioannidis, Nikolaos Grigoriadis, and Theodora Afrantou. 2024. "Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy: Exploring Shared Pathways and Promising Biomarkers for Future Treatments" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133879
APA StyleKalyvas, A.-C., Dimitriou, M., Ioannidis, P., Grigoriadis, N., & Afrantou, T. (2024). Alzheimer’s Disease and Epilepsy: Exploring Shared Pathways and Promising Biomarkers for Future Treatments. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133879








