Long-Term Persistence Rate of Secukinumab in Psoriatic Patients: A Six-Year Multicenter, Real-World Experience, Retrospective Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Patients and Methods
2.1. Methods and Data Extraction from Patient Database
2.2. Study Measures
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Demographic Characteristics of the General Population
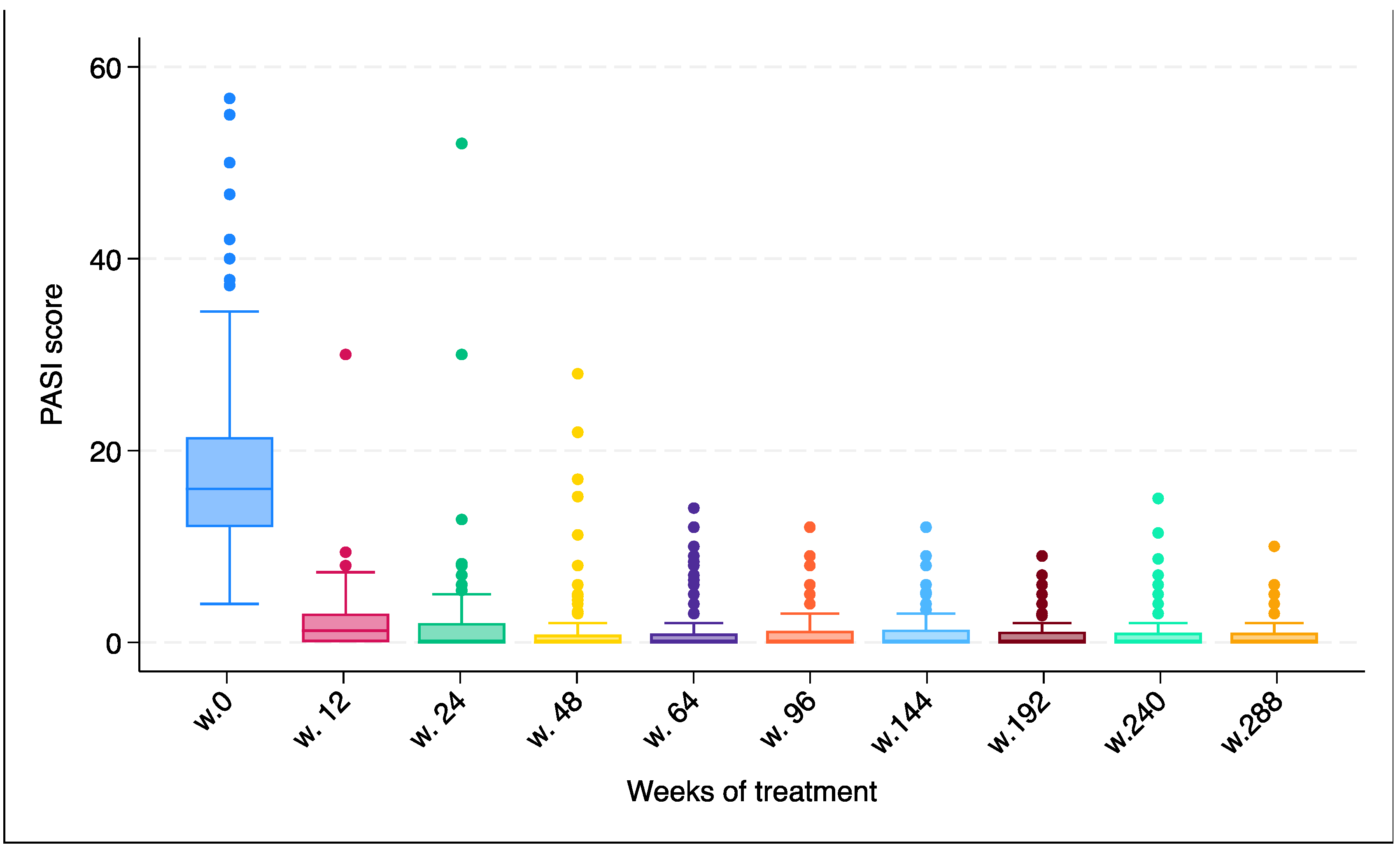
3.2. Secukinumab Effectiveness and Safety throughout 6 Years of Observation
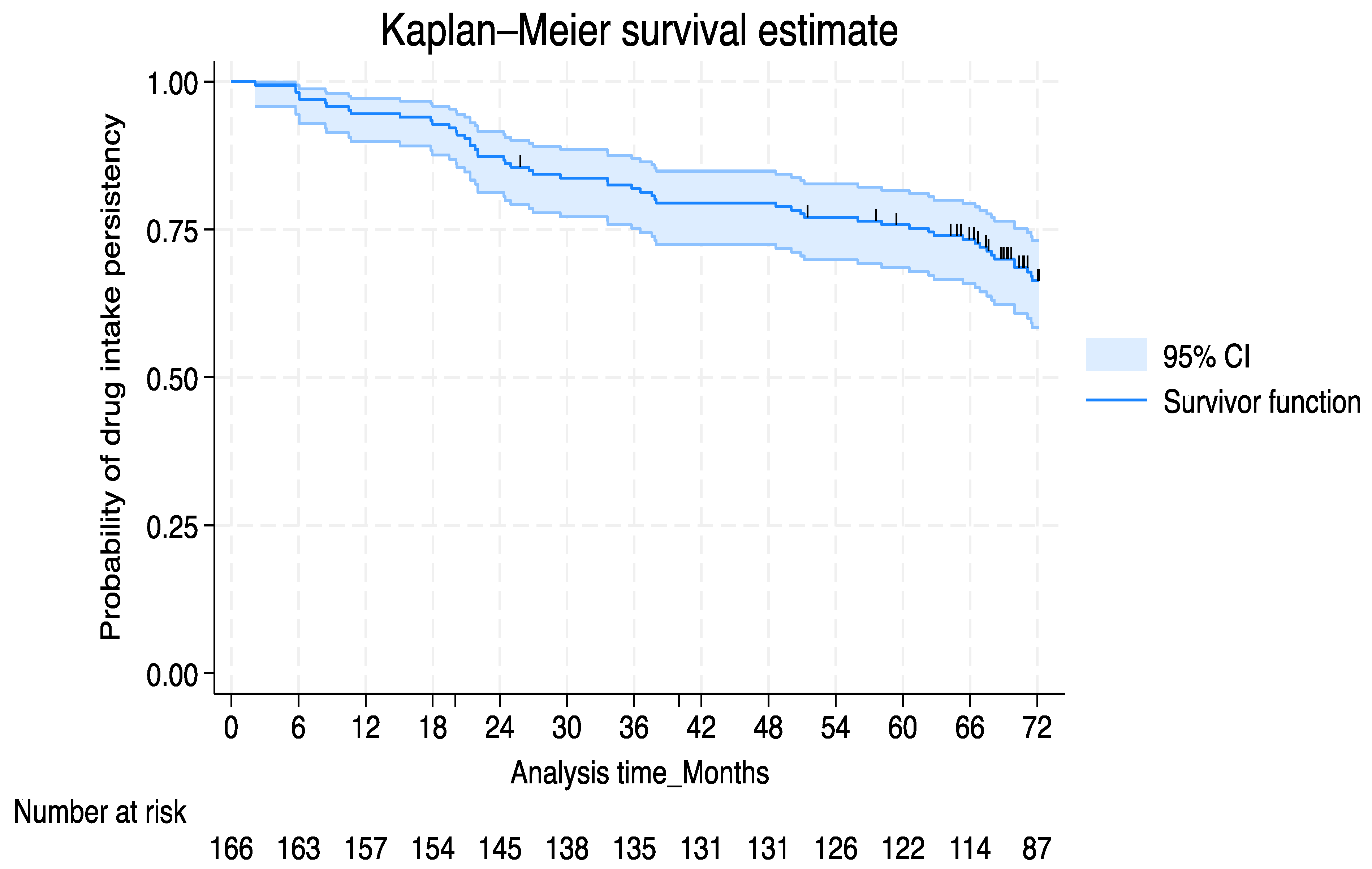
3.3. Secukinumab Persistence Rate
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Augustin, M.; Sator, P.G.; von Kiedrowski, R.; Conrad, C.; Rigopoulos, D.; Romanelli, M.; Ghislain, P.D.; Torres, T.; Ioannides, D.; Aassi, M.; et al. Secukinumab demonstrated sustained retention, effectiveness and safety in a real-world setting in patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, long-term results from an interim analysis of the SERENA study. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, 1796–1804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gargiulo, L.; Ibba, L.; Malagoli, P.; Balato, A.; Bardazzi, F.; Burlando, M.; Carrera, C.G.; Damiani, G.; Dapavo, P.; Dini, V.; et al. Drug survival of IL-12/23, IL-17 and IL-23 inhibitors for moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis, a retrospective multicenter real-world experience on 5932 treatment courses—IL PSO (Italian landscape psoriasis). Front. Immunol. 2024, 14, 1341708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tada, Y.; Morita, A.; Yamanaka, K.; Kono, M.; Imafuku, S.; Okubo, Y.; Yamazaki, F.; Kawamura, T.; Itakura, A.; Ohtsuki, M. Real-world retention rates and effectiveness of secukinumab in psoriasis, Results from a multicenter cohort study (RAILWAY). J. Dermatol. 2023, 50, 1415–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asawanonda, P.; Pattamadilok, B.; Chularojanamontri, L.; Chuamanochan, M.; Choonhakarn, C.; Chakkavittumrong, P.; Sangob, N.; Rajatanavin, N. Real-world experience of secukinumab in moderate to severe psoriasis patients in Thailand, Characteristics, effectiveness, and safety. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foley, P.; Manuelpillai, N.; Dolianitis, C.; Cains, G.D.; Mate, E.; Tronnberg, R.; Baker, C. Secukinumab treatment demonstrated high drug survival and sustained effectiveness in patients with severe chronic plaque psoriasis: 21-month analysis in Australian routine clinical practice (SUSTAIN study). Australas. J. Dermatol. 2022, 63, 303–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foley, P.; Tsai, T.F.; Rodins, K.; Hamadah, I.R.; Ammoury, A.; Dayem, H.A.; Abdallah, M.; Crowe, S.; Haas, S.; Pournara, E.; et al. Effectiveness and Safety of Secukinumab for Psoriasis in a Real-World Clinical Setting in the Asia-Pacific and Middle East Regions, Results from the REALIA Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 12, 511–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camela, E.; Potestio, L.; Ruggiero, A.; Ocampo-Garza, S.S.; Fabbrocini, G.; Megna, M. Towards personalized medicine in psoriasis: Current progress. Psoriasis 2022, 12, 231–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Torisu-Itakura, H.; Hanada, T.; Matsuo, T.; Cai, Z.; Osaga, S.; Aranishi, T. Treatment persistence of interleukin-17 inhibitor class drugs among patients with psoriasis in Japan, a retrospective database study. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2023, 34, 2229465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, Y.; Li, W.; Guan, X.; Liu, N.; Zhou, Y.; Li, G.; Wang, X.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, X.; Yang, B.; et al. Treatment outcomes of secukinumab in adult patients with moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis in China, A real-world multicenter retrospective study. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2023, 16, 1803–1814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galluzzo, M.; D’Adamio, S.; Silvaggio, D.; Lombardo, P.; Bianchi, L.; Talamonti, M. In which patients the best efficacy of secukinumab? Update of a real-life analysis after 136 weeks of treatment with secukinumab in moderate-to-severe plaque psoriasis. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2020, 20, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diotallevi, F.; Gambini, D.; Radi, G.; Simonetti, O.; Offidani, A. Should we be concerned about gastrointestinal-related adverse events in patients with plaque psoriasis receiving secukinumab therapy? A retrospective, real-life study. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chicharro, P.; Llamas-Velasco, M.; Armesto, S.; Herrera Acosta, E.; Vidal, D.; Vilarrasa, E.; Rivera-Diaz, R.; De-la-Cueva, P.; Martorell-Calatayud, A.; Ballescà, F.; et al. Secukinumab is effective and safe in the long-term treatment of plaque psoriasis in a daily practice setting, Multicenter study in 384 Spanish patients. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dastoli, S.; Passante, M.; Loconsole, F.; Mortato, E.; Balato, A.; Piccolo, V.; Guarneri, C.; Macca, L.; Provenzano, E.; Valenti, G.; et al. Long-term efficacy and safety of secukinumab in real life, a 240 weeks multicenter study from Southern Italy. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2023, 34, 2200868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaçar, N.; Balcı, D.D.; Doğan, S.; Türkmen, M.; Gönülal, M.; Çınar, G. Real-life efficacy and drug continuation of secukinumab in treating moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in Aegean region of Turkey, a multicenter retrospective study and systematic review of the literature. Asian. Pac. J. Allergy Immunol. 2022; Epub ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martos-Cabrera, L.; Llamas-Velasco, M.; Armesto, S.; Herrera-Acosta, E.; Vidal, D.; Vilarrasa, E.; Rivera-Diaz, R.; de la Cueva, P.; Martorell-Calatayud, A.; Ballescá, F.; et al. High adherence to secukinumab in patients with moderate to severe psoriasis, a long-term multicenter study in a daily practice setting. Int. J. Dermatol. 2023, 62, e146–e149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendes-Bastos, P.; Morais, P.; Ferreira, P.; Loureiro, M.; Sanganha, J.; Santiago, L.; Basto, A.S.; Henrique, M. Persistence, effectiveness, and real-world outcomes in psoriasis patients treated with secukinumab in Portugal. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sotiriou, E.; Bakirtzi, K.; Vakirlis, E.; Papadimitriou, I.; Eftychidou, P.; Trifona, M.; Lallas, A.; Ioannides, D. Long-term drug survival of secukinumab in real life in the era of novel biologics, a 5-year, retrospective study, including difficult-to-treat areas. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2022, 36, e626–e627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Russo, F.; Galluzzo, M.; Stingeni, L.; Persechino, S.; Zichichi, L.; Conti, A.; Giofrè, C.; Dini, V.; Vispi, M.; Atzori, L.; et al. Long-term drug survival and effectiveness of secukinumab in patients with moderate to severe chronic plaque psoriasis, 42-month results from the SUPREME 2.0 study. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 16, 3561–3574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, H.T.; Pham, N.T.U.; Tran, T.N.A.; Pham, N.N.; Bui, Y.T.; Vu, T.T.P. Long-Term Effectiveness and Drug Survival of Secukinumab in Vietnamese Patients with Psoriasis, Results from a Retrospective ENHANCE Study. Dermatol. Ther. 2023, 13, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Yuan, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chu, M.; Liu, H.; Liu, Q.; Wang, R.; Shao, S.; Wang, G.; Yu, C. Effectiveness and safety of secukinumab in Chinese patients with moderate to severe plaque psoriasis in real-world practice. Exp. Dermatol. 2024, 33, e14890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, T.; Puig, L.; Vender, R.; Yeung, J.; Carrascosa, J.M.; Piaserico, S.; Gisondi, P.; Lynde, C.; Ferreira, P.; Bastos, P.M.; et al. Drug Survival of Interleukin (IL) 17 and IL 23 Inhibitors for the Treatment of Psoriasis, A Retrospective Multi country, Multicentric Cohort Study. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2022, 23, 891–904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savage, L.; Hughes, J.; Matthews, K.; Rhodes, L. P80 Real-world evidence of the effectiveness of secukinumab in patients with psoriasis with and without scalp involvement from the British Association of Dermatologists Biologics and Immunomodulators Register. Br. J. Dermatol. 2023, 188, ljad113.108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Living EuroGuiDerm Guideline for the Systemic Treatment of Psoriasis Vulgaris. Available online: www.guidelines.edf.one/guidelines (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Saunte, D.M.; Mrowietz, U.; Puig, L.; Zachariae, C. Candida infections in patients with psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis treated with interleukin-17 inhibitors and their practical management. Br. J. Dermatol. 2017, 177, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mease, P.J.; McInnes, I.B.; Kirkham, B.; Kavanaugh, A.; Rahman, P.; van der Heijde, D.; Landewé, R.; Nash, P.; Pricop, L.; Yuan, J.; et al. Secukinumab Inhibition of Interleukin-17A in Patients with Psoriatic Arthritis. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 373, 1329–1339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blauvelt, A.; Prinz, J.C.; Gottlieb, A.B.; Kingo, K.; Sofen, H.; Ruer-Mulard, M.; Singh, V.; Pathan, R.; Papavassilis, C.; Cooper, S.; et al. Secukinumab administration by pre-filled syringe, efficacy, safety and usability results from a randomized controlled trial in psoriasis (FEATURE). Br. J. Dermatol. 2015, 172, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McInnes, I.B.; Mease, P.J.; Kirkham, B.; Kavanaugh, A.; Ritchlin, C.T.; Rahman, P.; van der Heijde, D.; Landewé, R.; Conaghan, P.G.; Gottlieb, A.B.; et al. Secukinumab, a human anti-interleukin-17A monoclonal antibody, in patients with psoriatic arthritis (FUTURE 2), a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet 2015, 386, 1137–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brezinski, E.A.; Dhillon, J.S.; Armstrong, A.W. Economic Burden of Psoriasis in the United States, A Systematic Review. JAMA Dermatol. 2015, 151, 651–658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saisyo, A.; Yamaguchi, M.; Kashibe, K.; Ishida, H.; Hirano, Y.; Oka, T.; Tamura, M.; Takasago, M.; Uchida, Y.; Kouda, K.; et al. Pharmacoeconomic study of biologics for psoriasis treatment based on real-world drug survival. Dermatol. Ther. 2022, 35, e15375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Baseline Characteristics | n (%)/Mean ± SD |
|---|---|
| Total patients | n = 166 |
| Sex | |
| Males | 115 (69.3) |
| Females | 51 (30.7) |
| Age (years) | 53.9 ± 12.9 |
| BMI ≥30 (kg/m2) | 26.5 ± 4.9 |
| Smoke | |
| Yes | 70 (42.2) |
| No | 96 (57.8) |
| Bio-experienced patients * | |
| Yes | 64 (38.6) |
| No | 102 (61.4) |
| Age at onset (years) | 27.7 ± 14.8 |
| Categorized age at onset (years) | |
| Early (0–11) | 28 (16.9) |
| Adolescent (11–17) | 20 (12.1) |
| Adult (≥18) | 118 (71.1) |
| Disease duration (years) | 24.5 ± 12.1 |
| PsA development during treatment | 15 (9.0) |
| Comorbidity † | |
| Chronic infections | 20 (12.1) |
| HCVAg+ | 0 |
| HBVAg+ | 1 (5.0) |
| TB-Gold+ | 8 (40.0) |
| Obesity * | |
| Yes (BMI ≥ 30) | 32 (19.4) |
| No (BMI ≤ 30) | 133 (80.6) |
| Cardiovascular | 116 (9.9) |
| Metabolic | 28 (18.1) |
| Autoimmune | 6 (3.6) |
| Psychiatric | 4 (2.4) |
| Other (renal, gastro, ocular, respiratory) | 18 (10.8) |
| PASI score | 18.1 ± 9.1 |
| Overall AEs or new comorbidities arising during drug administration | |
| Total observation | 32 (19.9) |
| Cutaneous | 4 (12.1) |
| Cardiovascular | 5 (15.2) |
| Metabolic | 1 (9.1) |
| HBV reactivation | 1 (3.0) |
| Mucocutaneous fungal infections | 5 (15.2) |
| Other [transaminasemia, abortion, joint pain, recurrent conjunctivitis, neoplasia (prostate, breast, and squamous cell carcinoma), weight loss, diverticulitis, orchitis, retinopathy, glossitis, stomatitis] | 15 (45.4) |
| Anatomical site involvement | |
| Nails | 51 (30.7) |
| Scalp | 86 (51.8) |
| Palmoplantar | 25 (15.1) |
| Genitals | 47 (28.3) |
| Drug discontinuation | 70 (42.2) |
| Loss of efficacy | 41 (58.6) |
| Primary inefficacy | 1 (5.7) |
| Adverse events | 12 (17.1) |
| Loss to follow-up | 12 (17.1) |
| Other reasons | 1 (1.4) |
| Baseline | Week 12 | Week 24 | Week 48 | Week 64 | Week 96 | Week 144 | Week 192 | Week 240 | Week 288 | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of patients | 166 | 163 | 160 | 147 | 144 | 130 | 120 | 112 | 109 | 101 | |
| PASI (mean ± SD) | 18.1 ± 9.1 | 2.5 ± 3.1 | 1.7 ± 5.9 | 1.4 ± 3.8 | 1.2 ± 2.6 | 1.1 ± 2.3 | 1.1 ± 2.3 | 0.9 ± 1.7 | 0.9 ± 2.3 | 0.7 ± 1.6 | <0.0001 |
| Overall Drug Discontinuation | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Univariable Analysis | HR | p > |z| | 95% CI |
| Anatomical Disease Localization | |||
| Scalp | 1.72 | 0.026 | 1.06–2.79 |
| Nail | 1.15 | 0.567 | 0.70–1.90 |
| Palmoplantar | 1.49 | 0.181 | 0.83–2.68 |
| Genitals | 2.03 | 0.004 | 1.26–3.29 |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 30) | 1.74 | 0.043 | 1.02–2.98 |
| Baseline PASI score | 1.02 | 0.070 | 0.99–1.05 |
| Last follow-up PASI score | 1.32 | 0.013 | 1.06–1.66 |
| Smoking habit | 1.08 | 0.736 | 0.68–1.74 |
| Sex | |||
| Female | ref | ||
| Male | 1.12 | 0.648 | 0.67–1.88 |
| PsO onset | |||
| Early (<11 years) | ref | ||
| Adolescent (11–17 years) | 1.89 | 0.158 | 0.78–4.56 |
| Adult (≥18 years) | 1.36 | 0.396 | 0.67–2.77 |
| Age at treatment initiation | 1.02 | 0.034 | 1.00–1.04 |
| Chronic infectious disease | 0.75 | 0.472 | 0.34–1.64 |
| HBV DNA+ | 7.35 | 0.051 | 0.99–54.66 |
| TB-GOLD+ | 2.56 | 0.028 | 1.10–6.01 |
| Disease duration prior to secukinumab start | 1.02 | 0.060 | 0.99–1.04 |
| PsA development during secukinumab intake | 1.15 | 0.726 | 0.53–2.51 |
| Biological-naïve patients | 1.28 | 0.299 | 0.80–2.06 |
| Multivariable analysis | |||
| Anatomical disease localization | |||
| Scalp | 1.51 | 0.112 | 0.91–2.53 |
| Genitals | 2.30 | 0.002 | 1.36–3.89 |
| Obesity (BMI ≥ 30) | 1.61 | 0.094 | 0.92–2.81 |
| Age at treatment initiation | 1.02 | 0.024 | 1.003–1.045 |
| Sex | |||
| Female | ref | ||
| Male | 0.90 | 0.718 | 0.52–1.56 |
| TB-GOLD+ | 1.59 | 0.327 | 0.63–4.03 |
| HBV DNA+ | 2.29 | 0.468 | 0.24–21.38 |
| Baseline PASI score | 1.00 | 0.913 | 0.97–1.03 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Galluzzo, M.; Trovato, E.; Talamonti, M.; Caldarola, G.; Di Nardo, L.; Lazzeri, L.; Mugheddu, C.; Burlando, M.; Balestri, R.; Bernardini, N.; et al. Long-Term Persistence Rate of Secukinumab in Psoriatic Patients: A Six-Year Multicenter, Real-World Experience, Retrospective Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3864. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133864
Galluzzo M, Trovato E, Talamonti M, Caldarola G, Di Nardo L, Lazzeri L, Mugheddu C, Burlando M, Balestri R, Bernardini N, et al. Long-Term Persistence Rate of Secukinumab in Psoriatic Patients: A Six-Year Multicenter, Real-World Experience, Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3864. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133864
Chicago/Turabian StyleGalluzzo, Marco, Emanuele Trovato, Marina Talamonti, Giacomo Caldarola, Lucia Di Nardo, Laura Lazzeri, Cristina Mugheddu, Martina Burlando, Riccardo Balestri, Nicoletta Bernardini, and et al. 2024. "Long-Term Persistence Rate of Secukinumab in Psoriatic Patients: A Six-Year Multicenter, Real-World Experience, Retrospective Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3864. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133864
APA StyleGalluzzo, M., Trovato, E., Talamonti, M., Caldarola, G., Di Nardo, L., Lazzeri, L., Mugheddu, C., Burlando, M., Balestri, R., Bernardini, N., Biondi, G., Vellucci, L., Russo, F., De Simone, C., Paganini, C., Rech, G., Cozzani, E. C., Atzori, L., Montesu, M. A., ... Rubegni, P. (2024). Long-Term Persistence Rate of Secukinumab in Psoriatic Patients: A Six-Year Multicenter, Real-World Experience, Retrospective Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3864. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133864








