Comparison between Classical- and Rotational-Mechanical-Chair-Assisted Maneuvers in a Population of Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo
Abstract
1. Introduction
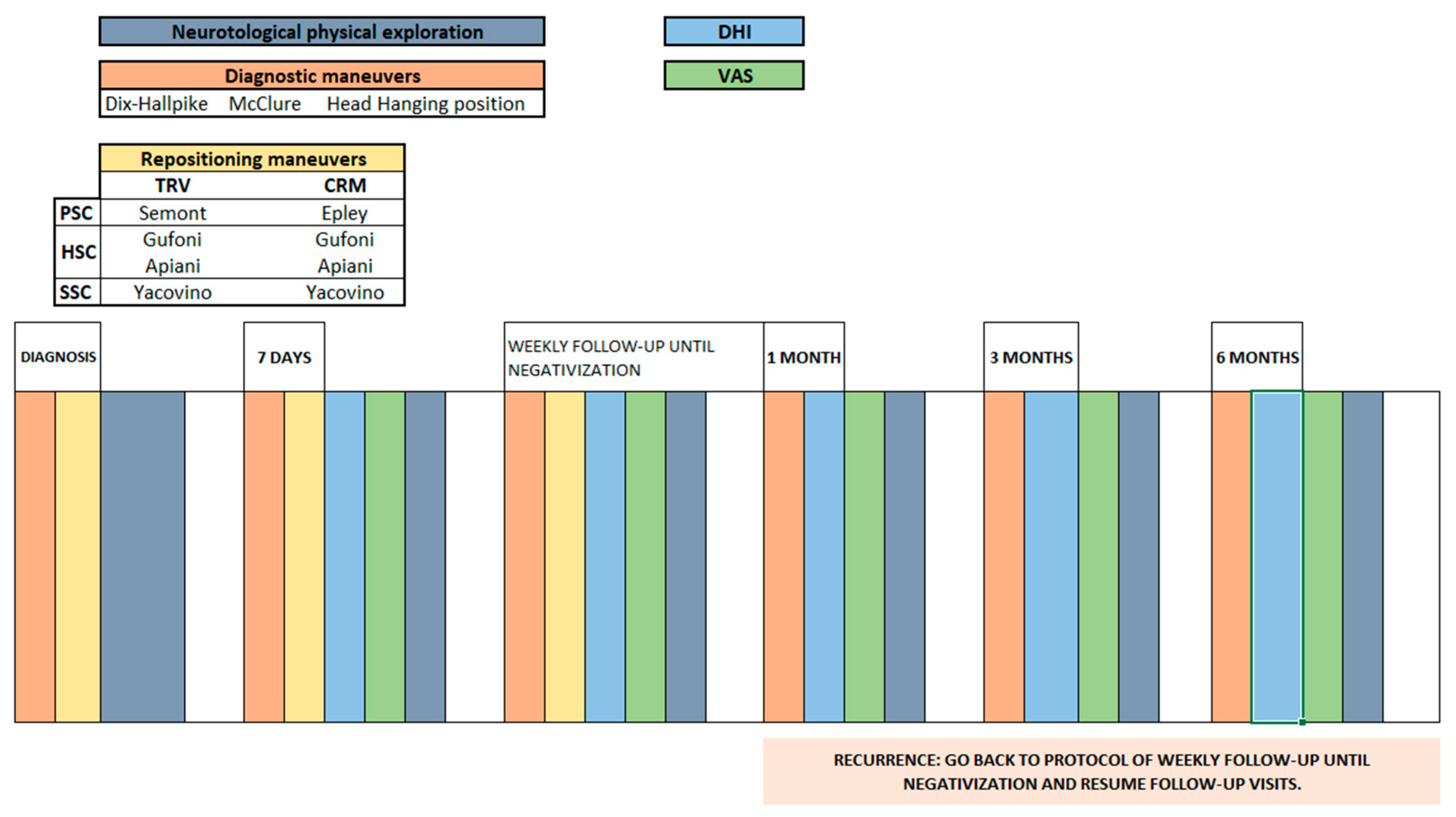
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Patient Assessment
2.3. Handicap Measurements
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Risk Factors Distribution
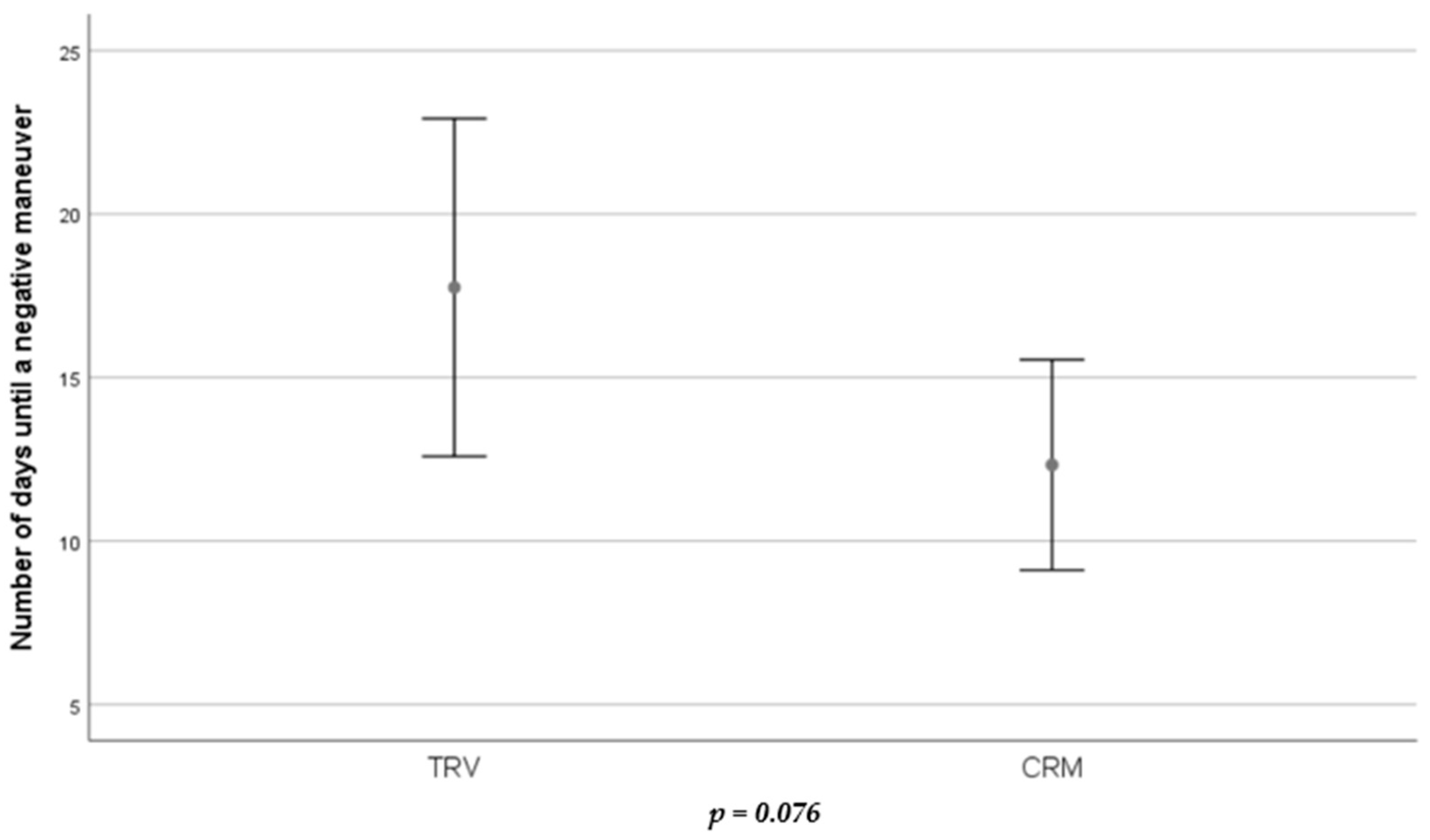
3.2. Number of Treatments and Days until Resolution of BPPV
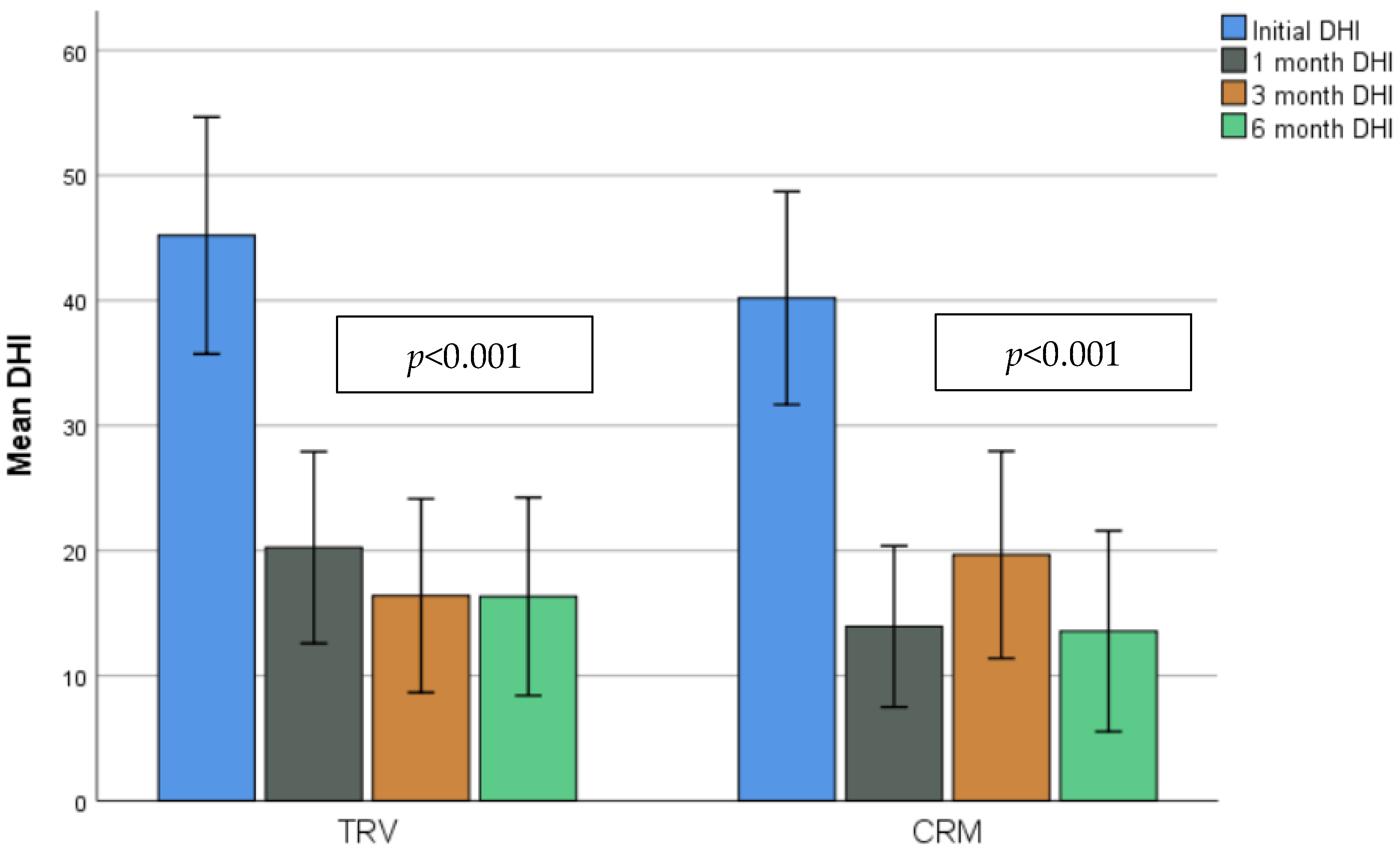
3.3. Quality of Life Evaluation: DHI, VAS and Sort FES-I Scores
3.4. Recurrence
4. Discussion
4.1. Treatment Efficacy
4.2. Quality of Life
4.3. Recurrence
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pérez-Vázquez, P.; Franco-Gutiérrez, V.; Soto-Varela, A.; Amor-Dorado, J.C.; Martín-Sanz, E.; Oliva-Domínguez, M.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. Guía de Práctica Clínica Para el Diagnóstico y Tratamiento del Vértigo Posicional Paroxístico Benigno. Documento de Consenso de la Comisión de Otoneurología Sociedad Española de Otorrinolaringlogía y Cirugía de Cabeza y Cuello. Acta Otorrinolaringológica Española 2018, 69, 345–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aw, S.T.; Todd, M.J.; Aw, G.E.; McGarvie, L.A.; Halmagyi, G.M. Benign Positional Nystagmus: A Study of Its Three-Dimensional Spatio-Temporal Characteristics. Neurology 2005, 64, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Honrubia, V.; Baloh, R.W.; Harris, M.R.; Jacobson, K.M. Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Syndrome. Am. J. Otol. 1999, 20, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Caruso, G.; Nuti, D. Epidemiological Data from 2270 PPV Patients. Audiol. Med. 2005, 3, 7–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Brevern, M.; Radtke, A.; Lezius, F.; Feldmann, M.; Ziese, T.; Lempert, T.; Neuhauser, H. Epidemiology of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: A Population Based Study. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 78, 710–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gámiz, M.J.; Lopez-Escamez, J.A. Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients over Sixty Years Old with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Gerontology 2004, 50, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindell, E.; Kollén, L.; Johansson, M.; Karlsson, T.; Rydén, L.; Falk Erhag, H.; Wetterberg, H.; Zettergren, A.; Skoog, I.; Finizia, C. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo, Dizziness, and Health-Related Quality of Life among Older Adults in a Population-Based Setting. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2021, 278, 1637–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huebner, A.C.; Lytle, S.R.; Doettl, S.M.; Plyler, P.N.; Thelin, J.T. Treatment of Objective and Subjective Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. J. Am. Acad. Audiol. 2013, 24, 600–606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, T.; Ito, M.; Takeda, N.; Uno, A.; Matsunaga, T.; Sekine, K.; Kubo, T. Natural Course of the Remission of Vertigo in Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Neurology 2005, 64, 920–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharyya, N.; Gubbels, S.P.; Schwartz, S.R.; Edlow, J.A.; El-Kashlan, H.; Fife, T.; Holmberg, J.M.; Mahoney, K.; Hollingsworth, D.B.; Roberts, R.; et al. Clinical Practice Guideline: Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (Update). Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2017, 156, S1–S47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nunez, R.A.; Cass, S.P.; Furman, J.M. Short- and Long-Term Outcomes of Canalith Repositioning for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 2000, 122, 647–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Cesare, T.; Tricarico, L.; Passali, G.C.; Sergi, B.; Paludetti, G.; Galli, J.; Picciotti, P.M. Traumatic Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Personal Experience and Comparison with Idiopathic BPPV. Int. J. Audiol. 2021, 60, 393–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epley, J.M. The Canalith Repositioning Procedure: For Treatment of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Otolaryngol. Head Neck Surg. 1992, 107, 399–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Semont, A.; Freyss, G.; Vitte, E. Curing the BPPV with a Liberatory Maneuver. Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 1988, 42, 290–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batuecas-Caletrio, A.; Trinidad-Ruiz, G.; Zschaeck, C.; del Pozo de Dios, J.C.; de Toro Gil, L.; Martin-Sanchez, V.; Martin-Sanz, E. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo in the Elderly. Gerontology 2013, 59, 408–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richard-Vitton, T.; Seidermann, L.; Fraget, P.; Mouillet, J.; Astier, P.; Chays, A. Vertige positionnel paroxystique bénin, un fauteuil au service du diagnostic et du traitement: Description et intérêt [Benign positional vertigo, an armchair for diagnosis and for treatment: Description and significance]. Rev. Laryngol.-Otol.-Rhinol. 2005, 126, 249–251. [Google Scholar]
- Hougaard, D.D.; Valsted, S.H.; Bruun, N.H.; Bech, M.W.; Talebnasab, M.H. Seven Years of Experience with Treatment of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo with a Mechanical Rotational Chair. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 981216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- West, N.; Hansen, S.; Møller, M.N.; Bloch, S.L.; Klokker, M. Repositioning Chairs in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Implications and Clinical Outcome. Eur. Arch. Otorhinolaryngol. 2016, 273, 573–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, M.F.; Eriksen, H.H.; Kjaersgaard, J.B.; Abrahamsen, E.R.; Hougaard, D.D. Treatment of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo with the TRV Reposition Chair. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2020, 16, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, J.; Yu, D.; Feng, Y.; Song, Q.; You, J.; Shi, H.; Yin, S. Comparative Study of the Efficacy of the Canalith Repositioning Procedure versus the Vertigo Treatment and Rehabilitation Chair. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2014, 134, 704–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdulovski, S.; Klokker, M. Repositioning Chairs in the Diagnosis and Treatment of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo—A Systematic Review. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2021, 17, 353–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Brevern, M.; Bertholon, P.; Brandt, T.; Fife, T.; Imai, T.; Nuti, D.; Newman-Toker, D. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Diagnostic Criteria: Consensus Document of the Committee for the Classification of Vestibular Disorders of the Bárány Society. VES 2015, 25, 105–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pérez, N.; Garmendia, I.; Martín, E.; García-Tapia, R. Cultural adaptation of 2 questionnaires for health measurement in patients with vertigo. Acta Otorrinolaringol. Esp. 2000, 51, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jacobson, G.P.; Newman, C.W. The Development of the Dizziness Handicap Inventory. Arch. Otolaryngol.—Head Neck Surg. 1990, 116, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kempen, G.I.J.M.; Yardley, L.; van Haastregt, J.C.M.; Zijlstra, G.A.R.; Beyer, N.; Hauer, K.; Todd, C. The Short FES-I: A Shortened Version of the Falls Efficacy Scale-International to Assess Fear of Falling. Age Ageing 2008, 37, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baydan-Aran, M.; Binay-Bolat, K.; Hançer-Aslan, G.; Avcı-Can, S.; Yeğin, S.; Öztaş, S.; Tokgoz-Yilmaz, S.; Yorulmaz, İ. Outcomes of Treatment of Multicanal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo by Means of TRV Chair. Audiol. Neurotol. 2023, 28, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuricht, A.; Hougaard, D.D. Is a Mechanical Rotational Chair Superior to Manual Treatment Maneuvers on an Examination Bed in the Treatment of Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo? Otol. Neurotol. 2022, 43, e235–e242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopez-Escámez, J.A.; Gámiz, M.J.; Fiñana, M.G.; Perez, A.F.; Canet, I.S. Position in Bed Is Associated with Left or Right Location in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo of the Posterior Semicircular Canal. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2002, 23, 263–266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Brevern, M. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo Predominantly Affects the Right Labyrinth. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2004, 75, 1487–1488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molnár, A.; Maihoub, S.; Tamás, L.; Szirmai, Á. A possible objective test to detect benign paroxysmal positional vertigo. The role of the caloric and video-head impulse tests in the diagnosis. J. Otol. 2022, 17, 46–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korres, S.; Balatsouras, D.G.; Kaberos, A.; Economou, C.; Kandiloros, D.; Ferekidis, E. Occurrence of Semicircular Canal Involvement in Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Otol. Neurotol. 2002, 23, 926–932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Brevern, M. Short-Term Efficacy of Epley’s Manoeuvre: A Double-Blind Randomised Trial. J. Neurol. Neurosurg. Psychiatry 2006, 77, 980–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Munoz, J.E.; Miklea, J.T.; Howard, M.; Springate, R.; Kaczorowski, J. Canalith Repositioning Maneuver for Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo: Randomized Controlled Trial in Family Practice. Can. Fam. Physician 2007, 53, 1048–1053. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Álvarez-Morujo De Sande, M.G.; González-Aguado, R.; Guerra-Jiménez, G.; Domènech-Vadillo, E.; Galera-Ruiz, H.; Figuerola-Massana, E.; Ramos-Macías, Á.; Morales-Angulo, C.; Martín-Mateos, A.J.; Domínguez-Durán, E. Probable Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo, Spontaneously Resolved: Incidence in Medical Practice, Patients’ Characteristics and the Natural Course. J. Otol. 2019, 14, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Instrum, R.S.; Parnes, L.S. Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Adv. Otorhinolaryngol. 2019, 82, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luryi, A.L.; Wright, D.; Lawrence, J.; Babu, S.; LaRouere, M.; Bojrab, D.I.; Sargent, E.W.; Zappia, J.; Schutt, C.A. Analysis of Non-Posterior Canal Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo in Patients Treated Using the Particle Repositioning Chair: A Large, Single-Institution Series. Am. J. Otolaryngol. 2018, 39, 313–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- West, N.; Bloch, S.L.; Moller, M.N.; Hansen, S.; Klokker, M. Reposition Chair Treatment Improves Subjective Outcomes in Refractory Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. J. Int. Adv. Otol. 2019, 15, 146–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandt, T.; Huppert, D.; Hecht, J.; Karch, C.; Strupp, M. Benign Paroxysmal Positioning Vertigo: A Long-Term Follow-up (6–17 Years) of 125 Patients. Acta Oto-Laryngol. 2006, 126, 160–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| TRV 1 (n = 32) | CRM 2 (n = 31) | TOTAL | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | 0.11 | |||
| 14 (43.75%) | 4 (12.9%) | 18 (28.57%) | |
| 18 (56.25%) | 27 (87.1%) | 45 (71.43%) | |
| Age (years), mean (SD 3) | 63.28 (17.32) | 61.26 (18.25) | 62.29 (17.67) | 0.654 |
| BMI 4 (Kg/m2), mean (SD) | 26.15 (4.21) | 19.73 (18.94) | 28.55 (13.73) | 0.171 |
| Affected canal, n (%) | 1 | |||
| 31 (49.21%) | 30 (47.61%) | 61 (96.82%) | |
| 1 (1.58%) | 1 (1.58%) | 2 (3.16%) | |
| Side n (%) | 0.118 | |||
| 17 (26.99%) | 10 (15.87%) | 27 (42.86%) | |
| 15 (23.81%) | 19 (30.16%) | 34 (53.97%) | |
| 0 (0%) | 2 (3.17%) | (3.17%) |
| TRV 1 (n = 32) | CRM 2 (n = 31) | TOTAL | p-Value * | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| History of BPPV, n (%) | 16 (50%) | 19 (61.29%) | 35 (55.56%) | 0.450 |
| Low vitamin D | 9 (28.13%) | 10 (32.26%) | 19 (30.16%) | 0.788 |
| Head trauma | 3 (9.37%) | 2 (6.45%) | 5 (7.94%) | 1 |
| Falls | 4 (12.5%) | 2 (6.45%) | 6 (9.52%) | 0.672 |
| Dyslipidemia | 4 (12.5%) | 10 (32.26%) | 14 (22.22%) | 0.075 |
| Osteoporosis | 2 (6.25%) | 7 (22.58%) | 9 (14.29%) | 0.082 |
| Recent surgery | 1 (3.13) | 2 (6.45%) | 3 (4.76%) | 0.613 |
| 1 | 2–4 | ≥5 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| TRV 1 group (n = 32), n (%) | 15 (46.87%) | 12 (37.5%) | 5 (15.63%) |
| CRM 2 (n = 31), n (%) | 20 (64.52%) | 9 (29.03%) | 2 (6.45%) |
| TOTAL | 35 (55.56%) | 21 (33.33%) | (11.11%) |
| First Visit | p-Value | One Month | p-Value | Three Months | p-Value | Six Months | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Short FES-I 1 | TRV (n = 32), mean (SD) | 9.22 (2.68) | 0.656 | 7.72 (1.25) | 0.317 | ||||
| CRM (n = 31), mean (SD) | 9.58 (3.64) | 7.45 (0.81) | |||||||
| VAS 2 | TRV (n = 32), mean (SD) | 5.42 (2.38) | 0.292 | 2.16 (2) | 0.265 | 1.61 (1.5) | 0.364 | 1.61 (1.78) | 0.273 |
| CRM (n = 31), mean (SD) | 4.1 (1.84) | 1.63 (1.71) | 1.23 (1.82) | 1.08 (1.95) | |||||
| DHI (mean total score) 3 | TRV (n = 32), mean (SD) | 45.19 (26.28) | 0.427 | 20.25 (21.26) | 0.203 | 16.4 (20.79) | 0.559 | 16.33 (21.27) | 0.618 |
| CRM (n = 31), mean (SD) | 40.19 (23.22) | 13.94 (17.57) | 19.67 (22.2) | 13.57 (21.53) | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chaure-Cordero, M.; Garrote-Garrote, M.; Esteban-Sánchez, J.; Morales-Chacchi, P.; Del Valle-Díaz, M.; Martin-Sanz, E. Comparison between Classical- and Rotational-Mechanical-Chair-Assisted Maneuvers in a Population of Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133863
Chaure-Cordero M, Garrote-Garrote M, Esteban-Sánchez J, Morales-Chacchi P, Del Valle-Díaz M, Martin-Sanz E. Comparison between Classical- and Rotational-Mechanical-Chair-Assisted Maneuvers in a Population of Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(13):3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133863
Chicago/Turabian StyleChaure-Cordero, Marta, Maria Garrote-Garrote, Jonathan Esteban-Sánchez, Paula Morales-Chacchi, Marina Del Valle-Díaz, and Eduardo Martin-Sanz. 2024. "Comparison between Classical- and Rotational-Mechanical-Chair-Assisted Maneuvers in a Population of Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 13: 3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133863
APA StyleChaure-Cordero, M., Garrote-Garrote, M., Esteban-Sánchez, J., Morales-Chacchi, P., Del Valle-Díaz, M., & Martin-Sanz, E. (2024). Comparison between Classical- and Rotational-Mechanical-Chair-Assisted Maneuvers in a Population of Patients with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(13), 3863. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13133863







