Evaluation of the Dimensional Accuracy of Robot-Guided Laser Osteotomy in Reconstruction with Patient-Specific Implants—An Accuracy Study of Digital High-Tech Procedures
Abstract
1. Introduction
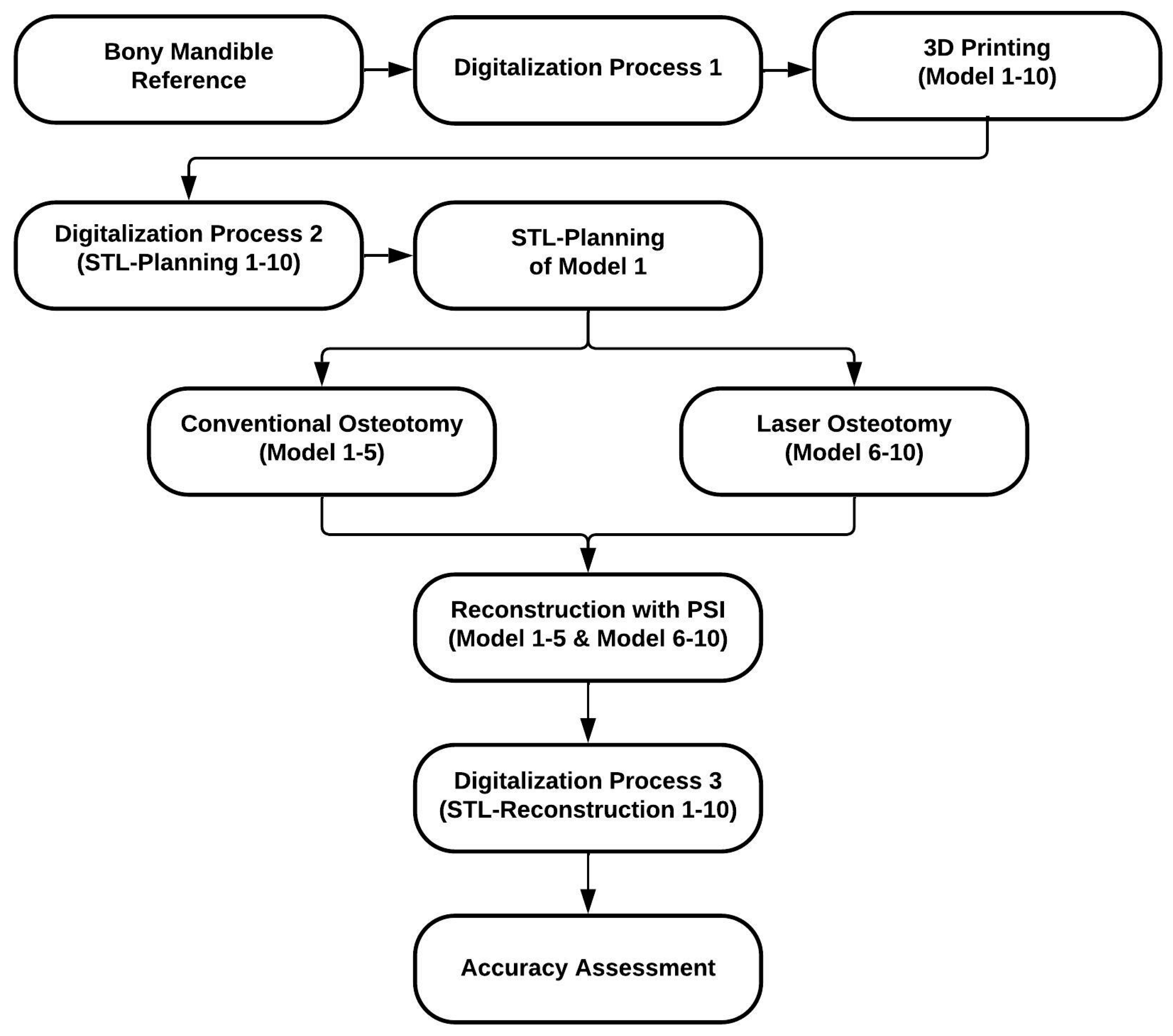
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Protocol
2.2. CARLO®
2.3. Fabrication Process of the Mandibular Models
2.3.1. Digitalization Process 1 (Reference Model)
2.3.2. 3D Printing of the Models (Replicas) and Digitalization Process 2
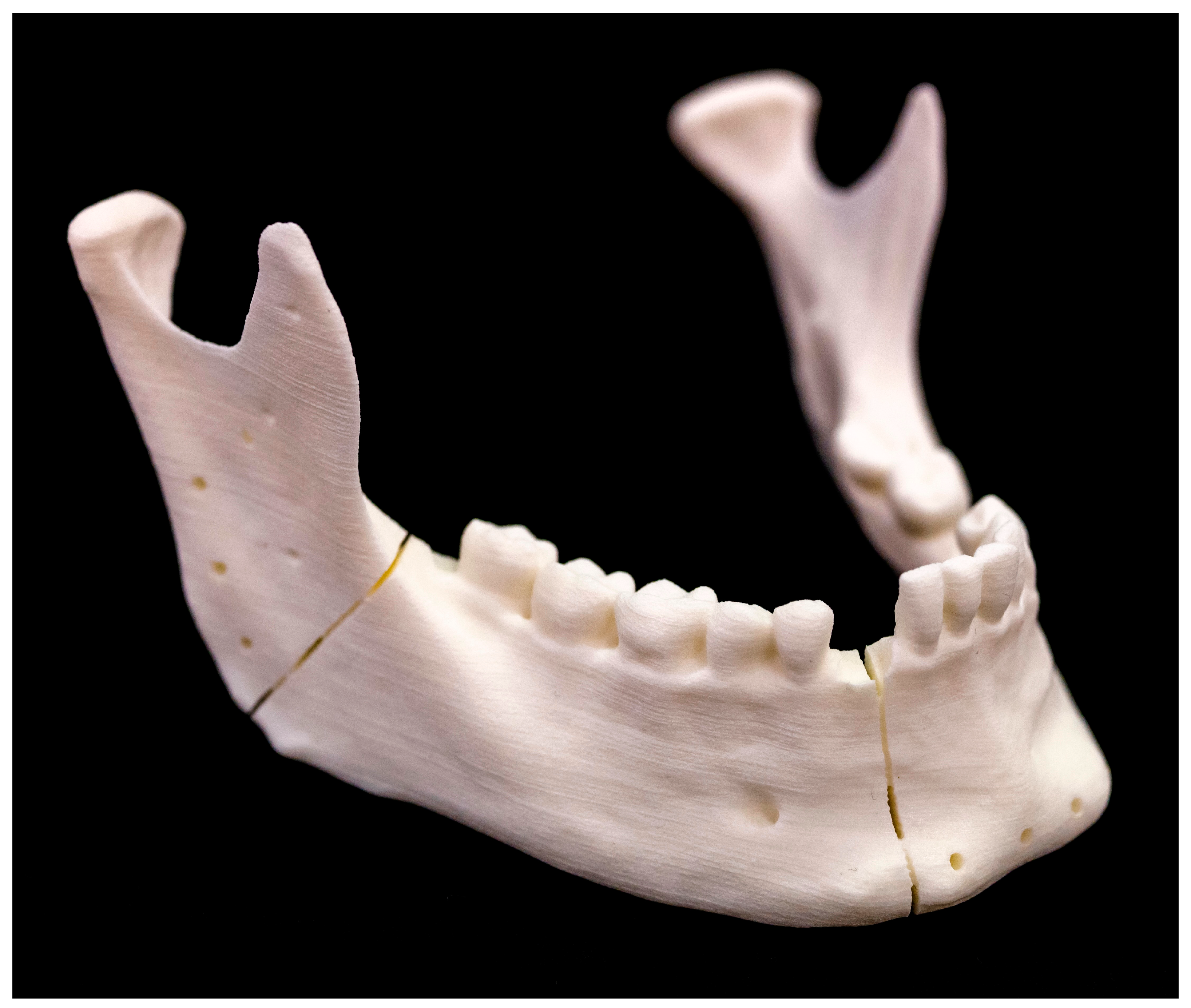
2.4. Conventional Osteotomy by Saw
2.4.1. Osteotomy Design and Cutting Guide Planning
2.4.2. Conventional Osteotomy (Models 1–5)
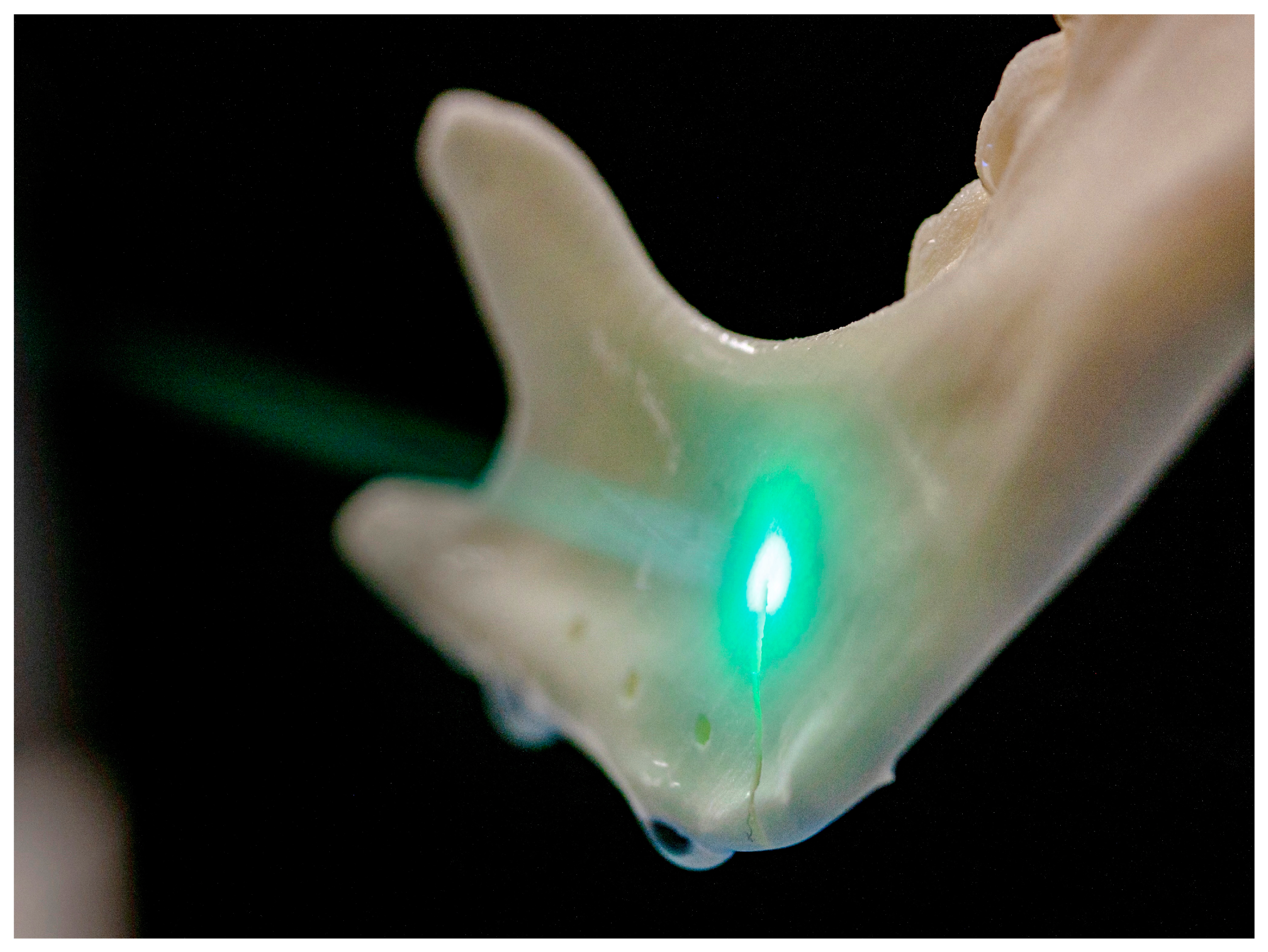
2.5. Laser Osteotomy by Robot Guidance
2.5.1. Osteotomy Design
2.5.2. Laser Osteotomy (Models 6–10)
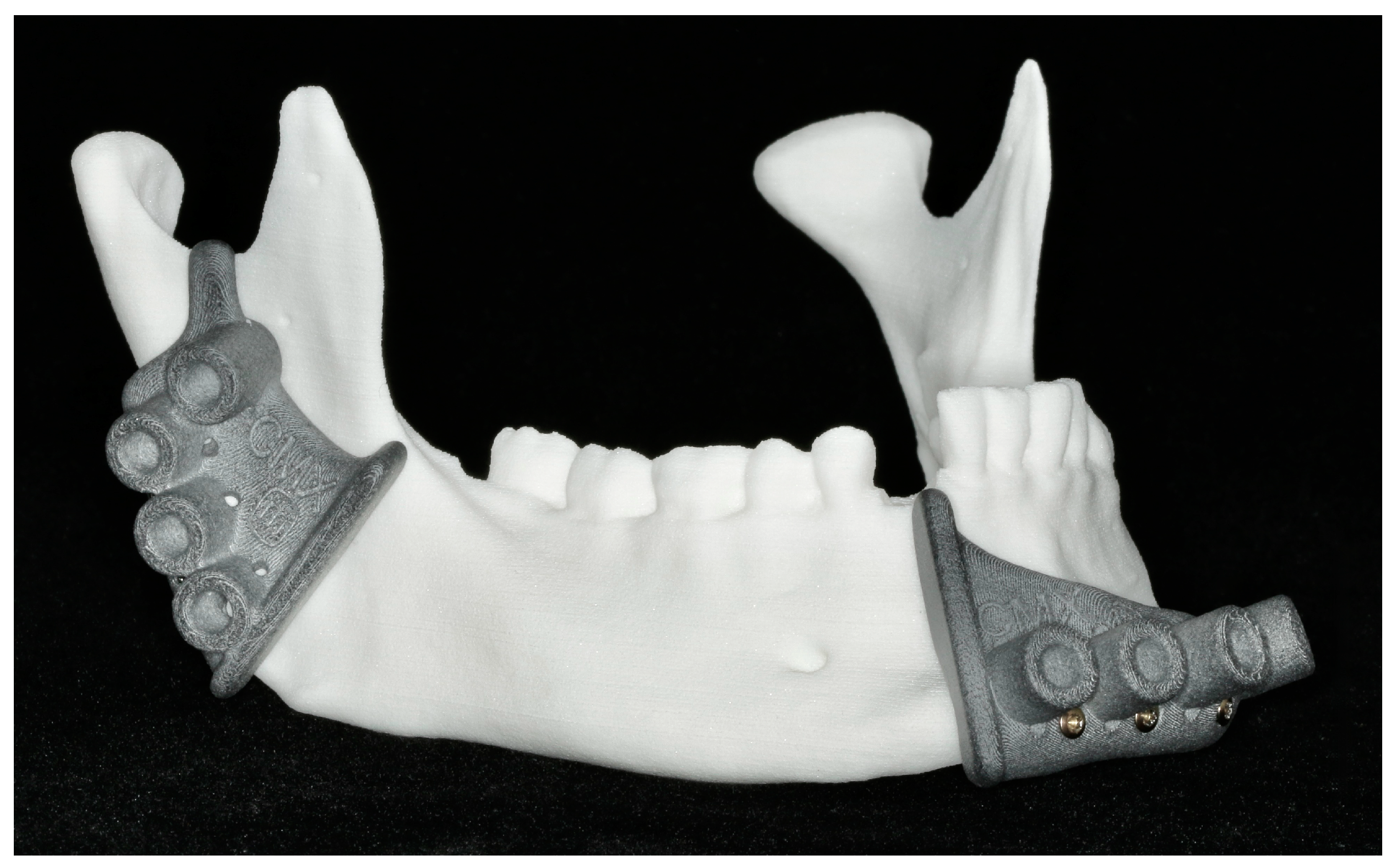
2.6. Patient-Specific Reconstruction
2.6.1. Patient-Specific Implant Planning and Fabrication
2.6.2. Reconstruction with Patient-Specific Implant
2.6.3. Digitalization Process 3
2.7. Accuracy Assessment
2.8. Evaluation
2.9. Statistics
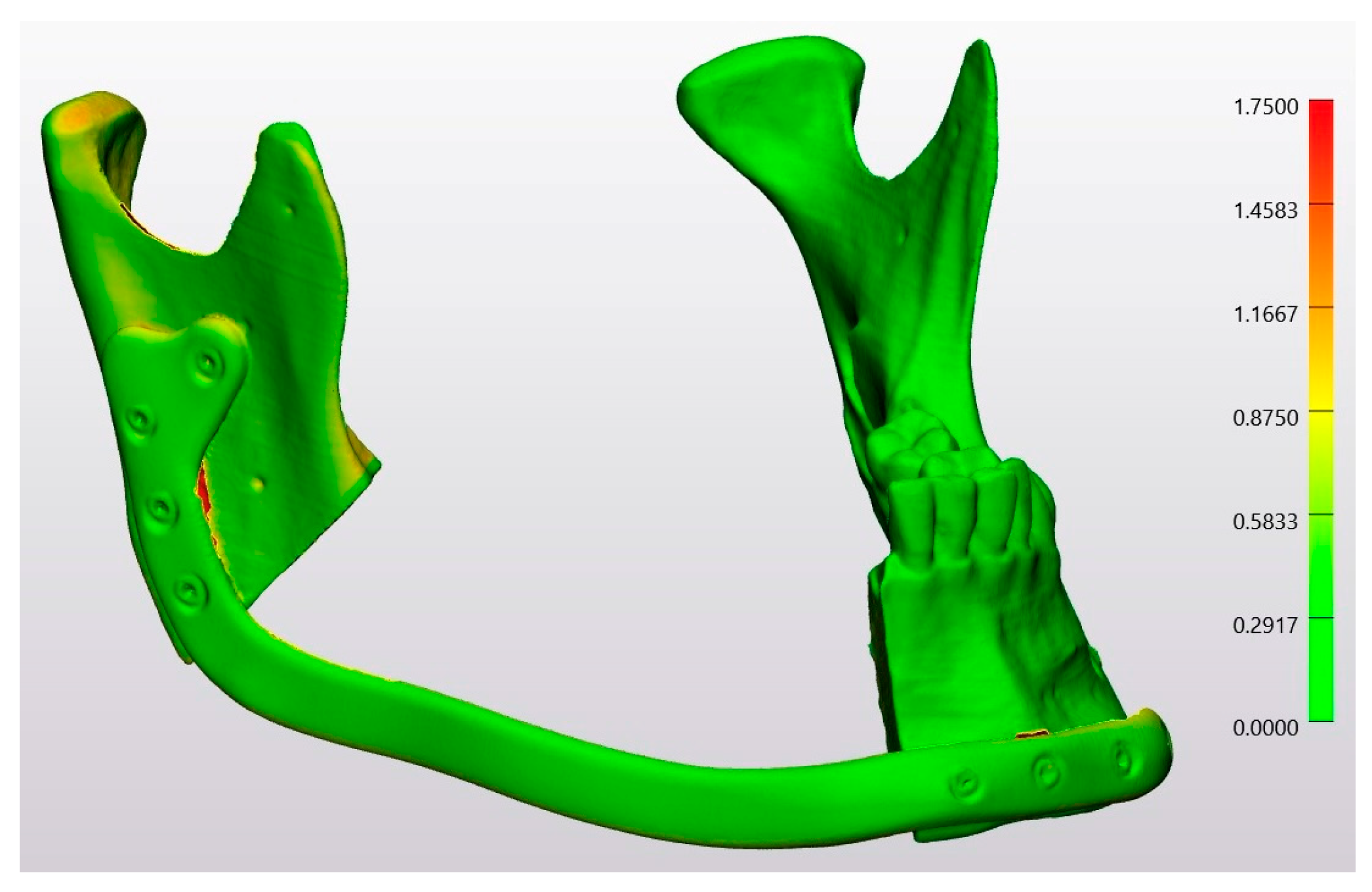
3. Results
3.1. Trueness
3.2. Precision
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| 3D | three-dimensional |
| CARLO | cold ablation robot-guided laser osteotome |
| CO2 | carbon dioxide |
| CT | computed tomography |
| Er:YAG | Erbium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet |
| IQR | interquartile range |
| ISO | International Organization for Standardization |
| Nd:YAG | Neodymium-doped Yttrium Aluminum Garnet |
| quantile–quantile | |
| RMS | root mean square |
| SD | standard deviation |
| SLS | selective laser sintering |
| STL | standard tessellation language |
References
- Panduric, D.G.; Juric, I.B.; Music, S.; Molčanov, K.; Sušic, M.; Anic, I. Morphological and Ultrastructural Comparative Analysis of Bone Tissue after Er:YAG Laser and Surgical Drill Osteotomy. Photomed. Laser Surg. 2014, 32, 401–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ureel, M.; Augello, M.; Holzinger, D.; Wilken, T.; Berg, B.I.; Zeilhofer, H.F.; Millesi, G.; Juergens, P.; Mueller, A.A. Cold Ablation Robot-Guided Laser Osteotome (Carlo®): From Bench to Bedside. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagova, B.; Krastev, D.; Krastev, N.; Malinova, L. Tissue Changes and Tissue Reactivity Following Osteotomy by a Conventional Rotary Device, an Ultrasonic Unit, and an Er: YAG Laser—A Comparative Study in Humans. J. Stomatol. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 125, 101750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moslemi, N.; Shahnaz, A.; Masoumi, S.; Torabi, S.; Akbari, S. Laser-Assisted Osteotomy for Implant Site Preparation: A Literature Review. Implant. Dent. 2017, 26, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanazirski, N.; Vladova, D.; Neychev, D.; Raycheva, R.; Kanazirska, P. Effect of Er: YAG Laser Exposure on the Amorphous Smear Layer in the Marginal Zone of the Osteotomy Site for Placement of Dental Screw Implants: A Histomorphological Study. J. Funct. Biomater. 2023, 14, 376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gabrić, D.; Blašković, M.; Gjorgijevska, E.; Mladenov, M.; Tašič, B.; Jurič, I.B.; Ban, T. Evaluation of Bone Healing after Osteotomies Prepared with Er: YAG Laser in Contact and Noncontact Modes and Piezosurgery—An Animal Study. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2016, 74, 18–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burgner, J.; Müller, M.; Raczkowsky, J.; Wörn, H. Ex Vivo Accuracy Evaluation for Robot Assisted Laser Bone Ablation. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2010, 6, 489–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papadaki, M.; Doukas, A.; Farinelli, W.A.; Kaban, L.; Troulis, M. Vertical Ramus Osteotomy with Er:YAG Laser: A Feasibility Study. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2007, 36, 1193–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gottsauner, M.; Morawska, M.M.; Tempel, S.; Müller-Gerbl, M.; Dalcanale, F.; de Wild, M.; Ettl, T. Geometric Cuts by an Autonomous Laser Osteotome Increase Stability in Mandibular Reconstruction With Free Fibula Grafts: A Cadaver Study. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2024, 82, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farronato, G.; Galbiati, G.; Esposito, L.; Mortellaro, C.; Zanoni, F.; Maspero, C. Three-Dimensional Virtual Treatment Planning: Presurgical Evaluation. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2018, 29, e433–e437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annino, D.J.; Sethi, R.K.; Hansen, E.E.; Horne, S.; Dey, T.; Rettig, E.M.; Uppaluri, R.; Kass, J.I.; Goguen, L.A. Virtual Planning and 3D-Printed Guides for Mandibular Reconstruction: Factors Impacting Accuracy. Laryngoscope Investig. Otolaryngol. 2022, 7, 1798–1807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holzinger, D.; Ureel, M.; Wilken, T.; Müller, A.A.; Schicho, K.; Millesi, G.; Juergens, P. First-in-Man Application of a Cold Ablation Robot Guided Laser Osteotome in Midface Osteotomies. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2021, 49, 531–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chao, A.H.; Weimer, K.; Raczkowsky, J.; Zhang, Y.; Kunze, M.; Cody, D.; Selber, J.C.; Hanasono, M.M.; Skoracki, R.J. Pre-Programmed Robotic Osteotomies for Fibula Free Flap Mandible Reconstruction: A Preclinical Investigation. Microsurgery 2016, 36, 246–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augello, M.; Baetscher, C.; Segesser, M.; Zeilhofer, H.F.; Cattin, P.; Juergens, P. Performing Partial Mandibular Resection, Fibula Free Flap Reconstruction and Midfacial Osteotomies with a Cold Ablation and Robot-Guided Er:YAG Laser Osteotome (CARLO®)—A Study on Applicability and Effectiveness in Human Cadavers. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2018, 46, 1850–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augello, M.; Deibel, W.; Nuss, K.; Cattin, P.; Jürgens, P. Comparative Microstructural Analysis of Bone Osteotomies after Cutting by Computer-Assisted Robot-Guided Laser Osteotome and Piezoelectric Osteotome: An in Vivo Animal Study. Lasers Med. Sci. 2018, 33, 1471–1478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, S.; Bianchi, A.; Schiariti, G.; Badiali, G.; Marchetti, C. Computer-Aided Design and Computer-Aided Manufacturing Cutting Guides and Customized Titanium Plates Are Useful in Upper Maxilla Waferless Repositioning. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 73, 701–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajitha Gunaratne, G.D.; Khan, R.; Fick, D.; Robertson, B.; Dahotre, N.; Ironside, C. A Review of the Physiological and Histological Effects of Laser Osteotomy. J. Med. Eng. Technology. 2017, 41, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zavattero, E.; Romano, M.; Gerbino, G.; Rossi, D.S.; Giannì, A.B.; Ramieri, G.; Baj, A. Evaluation of the Accuracy of Virtual Planning in Orthognathic Surgery: A Morphometric Study. J. Craniofacial Surg. 2019, 30, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baek, K.W.; Deibel, W.; Marinov, D.; Griessen, M.; Bruno, A.; Zeilhofer, H.F.; Cattin, P.; Juergens, P. Clinical Applicability of Robot-Guided Contact-Free Laser Osteotomy in Cranio-Maxillo-Facial Surgery: In-Vitro Simulation and in-Vivo Surgery in Minipig Mandibles. Br. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2015, 53, 976–981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giger, A.; Jud, C.; Cattin, P.C. Respiratory Motion Compensation for the Robot-Guided Laser Osteotome. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2017, 12, 1751–1762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deibel, W. The Physics and Engineering of Laser Ablation of Hard Tissue for Osteotomy Purposes Inauguraldissertation Zur Erlangung Der Würde Eines. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Basel, Basel, Switzerland, 2021. Available online: http://edoc.unibas.ch/ (accessed on 15 December 2023).
- Ebeling, M.; Scheurer, M.; Sakkas, A.; Wilde, F.; Schramm, A. First-Hand Experience and Result with New Robot-Assisted Laser LeFort-I Osteotomy in Orthognathic Surgery: A Case Report. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, J.J.; Woo, S.Y.; Yi, W.J.; Hwang, S.J. Robot-Assisted Maxillary Positioning in Orthognathic Surgery: A Feasibility and Accuracy Evaluation. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martins, G.L.; Puricelli, E.; Baraldi, C.E.; Ponzoni, D. Bone Healing after Bur and Er: YAG Laser Ostectomies. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 69, 1214–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blagova, B.; Krastev, D.; Malinova, L. Conventional Drilling versus Ultrasound and Laser Osteotomy in Mandibular Third Molar Surgery: A Comparative Study. Lasers Surg. Med. 2023, 55, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Mello, E.D.A.; Pagnoncelli, R.M.; Munin, E.; Filho, M.S.A.; De Mello, G.P.S.; Arisawa, E.A.L.; De Oliveira, M.G. Comparative Histological Analysis of Bone Healing of Standardized Bone Defects Performed with the Er: YAG Laser and Steel Burs. Lasers Med. Sci. 2008, 23, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandurić, D.G.; Bago, I.; Katanec, D.; Žabkar, J.; Miletić, I.; Anić, I. Comparison of Er:YAG Laser and Surgical Drill for Osteotomy in Oral Surgery: An Experimental Study. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2012, 70, 2515–2521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiao, L.; Guo, J.; Wang, H.; He, Q.; Xu, Y.; Yuan, L.; Yi, Q.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, J.; Min, S.; et al. Thermal Damage and the Prognostic Evaluation of Laser Ablation of Bone Tissue—A Review. In Lasers in Medical Science; Springer Science and Business Media Deutschland GmbH: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 5725-1; International Organization for Standardization. Accuracy (Trueness and Precision) of Measurement Methods and Results—Part 1: General Principles and Definitions. Beuth Verlag Berlin: Berlin, Germany, 1994.
- Mehl, A.; Reich, S.; Beuer, F.; Güth, J.-F. Accuracy, Trueness, and Precision-a Guideline for the Evaluation of These Basic Values in Digital Dentistry. Int. J. Comput. Dent. 2021, 24, 341–352. [Google Scholar]
- Kakarala, K.; Shnayder, Y.; Tsue, T.T.; Girod, D.A. Mandibular Reconstruction. Oral Oncol. 2018, 77, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msallem, B.; Sharma, N.; Cao, S.; Halbeisen, F.S.; Zeilhofer, H.F.; Thieringer, F.M. Evaluation of the Dimensional Accuracy of 3D-Printed Anatomical Mandibular Models Using FFF, SLA, SLS, MJ, and BJ Printing Technology. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9, 817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jivraj, J.; Deorajh, R.; Lai, P.; Chen, C.; Nguyen, N.; Ramjist, J.; Yang, V.X.D. Robotic Laser Osteotomy through Penscriptive Structured Light Visual Servoing. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2019, 14, 809–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ter Braak, T.P.; Brouwer de Koning, S.G.; van Alphen, M.J.A.; van der Heijden, F.; Schreuder, W.H.; van Veen, R.L.P.; Karakullukcu, M.B. A Surgical Navigated Cutting Guide for Mandibular Osteotomies: Accuracy and Reproducibility of an Image-Guided Mandibular Osteotomy. Int. J. Comput. Assist. Radiol. Surg. 2020, 15, 1719–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, S.; Wei, H.; Zeng, F.; Wang, X. The Use of Patient-Specific Implants in Genioplasty and Its Clinical Accuracy: A Preliminary Study. Int. J. Oral. Maxillofac. Surg. 2020, 49, 461–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stübinger, S.; Ghanaati, S.; Saldamli, B.; Kirkpatrick, C.J.; Sader, R. Er: YAG Laser Osteotomy: Preliminary Clinical and Histological Results of a New Technique for Contact-Free Bone Surgery. Eur. Surg. Res. 2009, 42, 150–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msallem, B.; Maintz, M.; Halbeisen, F.S.; Meyer, S.; Sigron, G.R.; Sharma, N.; Cao, S.; Thieringer, F.M. Biomechanical Evaluation of Patient-Specific Polymethylmethacrylate Cranial Implants for Virtual Surgical Planning: An In-Vitro Study. Materials 2022, 15, 1970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Msallem, B.; Beiglboeck, F.; Honigmann, P.; Jaquiéry, C.; Thieringer, F. Craniofacial Reconstruction by a Cost-Efficient Template-Based Process Using 3D Printing. In Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery—Global Open; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2017; Volume 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzoni, S.; Marchetti, C.; Sgarzani, R.; Cipriani, R.; Scotti, R.; Ciocca, L. Prosthetically Guided Maxillofacial Surgery: Evaluation of the Accuracy of a Surgical Guide and Custom-Made Bone Plate in Oncology Patients after Mandibular Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 131, 1376–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojcik, T.; Morawska, M.; Ferri, J.; Müller-Gerbl, M.; Nicot, R. Robotic Calvarial Bone Sampling. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2023, 51, 603–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roessler, K.; Winter, F.; Wilken, T.; Pataraia, E.; Mueller-Gerbl, M.; Dorfer, C. Robotic Navigated Laser Craniotomy for Depth Electrode Implantation in Epilepsy Surgery: A Cadaver Lab Study. J. Neurol. Surg. A Cent. Eur. Neurosurg. 2021, 82, 125–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honigmann, P.; Hofer, M.; Hirsch, S.; Morawska, M.; Müller-Gerbl, M.; Thieringer, F.M.; Coppo, E. Cold Ablation Robot-Guided Laser Osteotomy in Hand, Wrist and Forearm Surgery—A Feasibility Study. Int. J. Med. Robot. Comput. Assist. Surg. 2022, 18, e2438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, S.; Tangermann, K.; Kessler, P.; Neukam, F.W.; Wiltfang, J. Er: YAG Laser Osteotomy Directed by Sensor Controlled Systems. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2003, 31, 337–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stübinger, S. Clinical, Cosmetic and Investigational Dentistry Dovepress Advances in Bone Surgery: The Er: YAG Laser in Oral Surgery and Implant Dentistry. 2010. Available online: www.dovepress.com (accessed on 18 May 2024).
- Zeitouni, J.; Clough, B.; Zeitouni, S.; Saleem, M.; Al Aisami, K.; Gregory, C. The Effects of the Er: YAG Laser on Trabecular Bone Micro-Architecture: Comparison with Conventional Dental Drilling by Micro-Computed Tomographic and Histological Techniques. F1000Res 2017, 6, 1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Advanced Osteotomy Tools—AOT AG. CARLO Primo+ Instructions for Use Cold Ablation Robot-Guided Laser Osteotome; Advanced Osteotomy Tools—AOT AG: Basel, Switzerland, 2022. [Google Scholar]

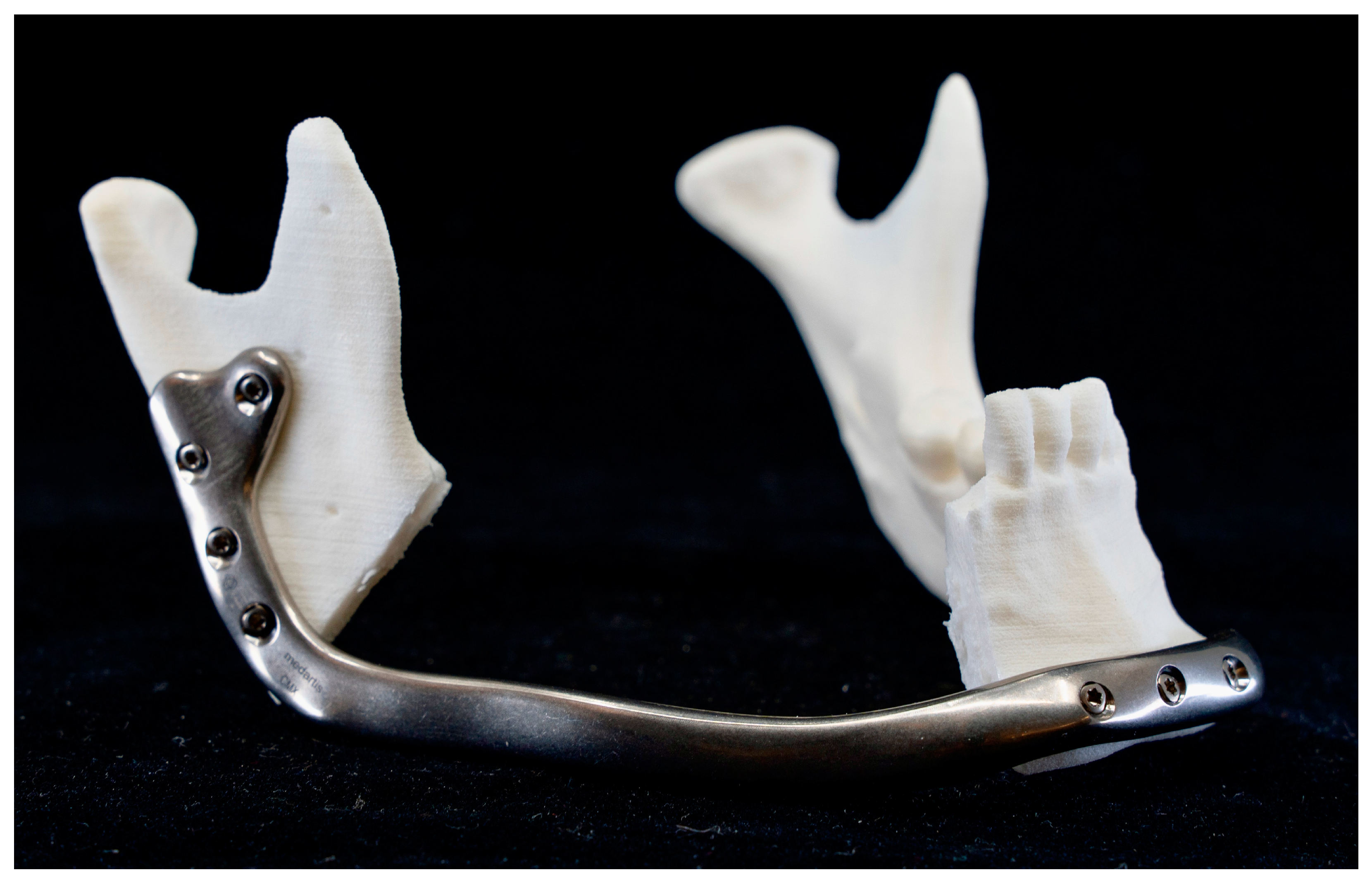
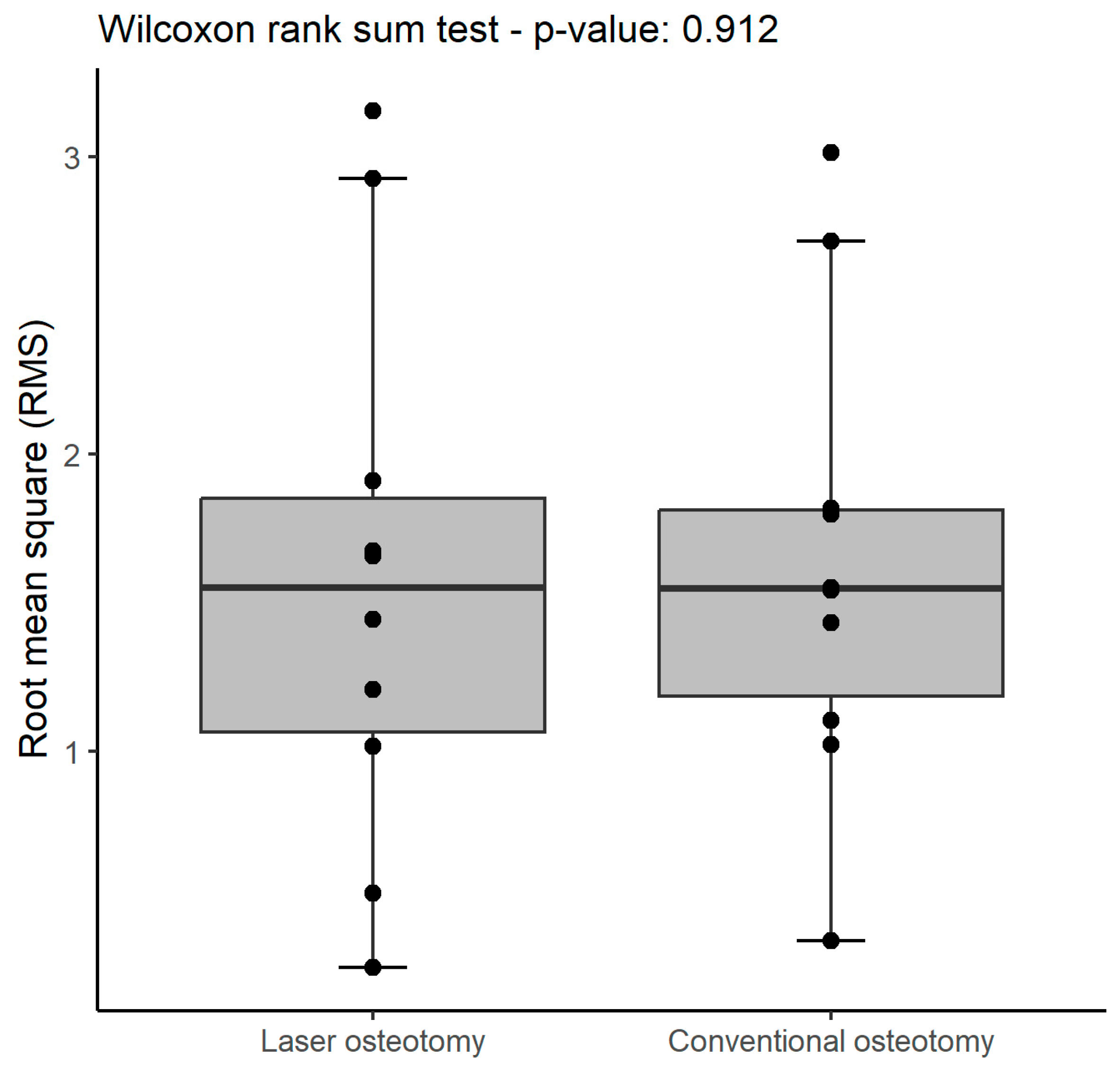

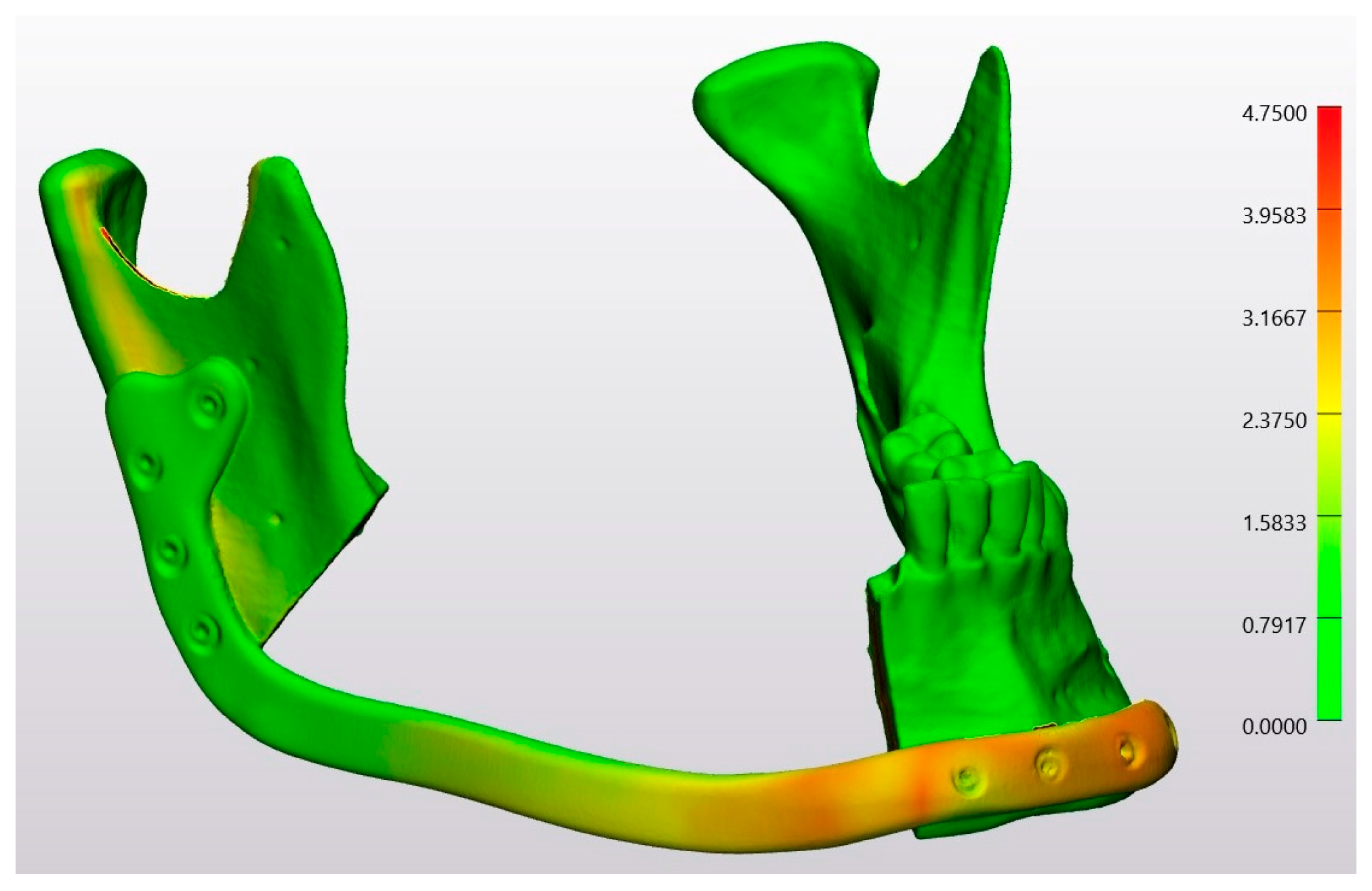
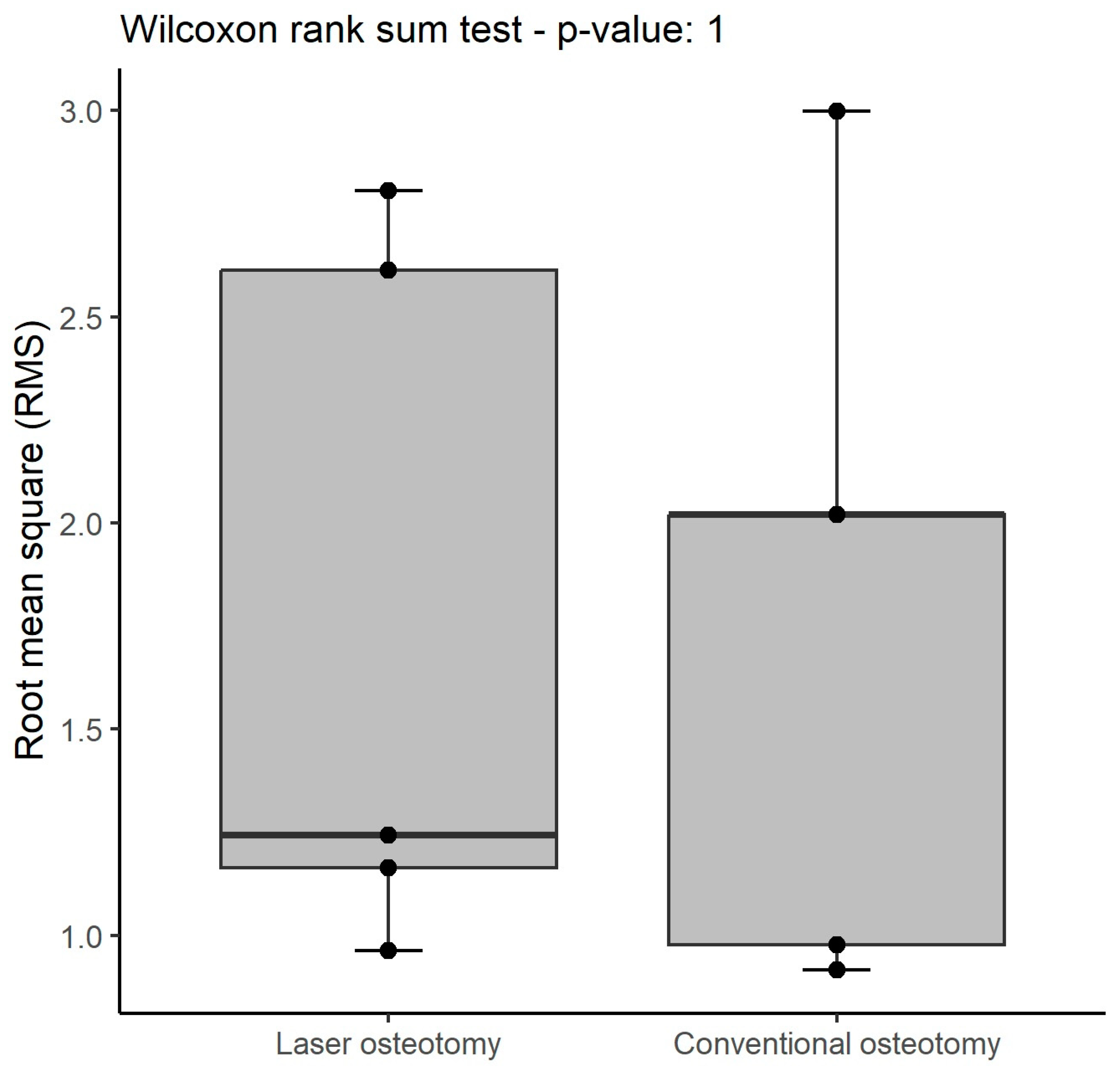

| Technology | RMS | Mean | SD | Median | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Osteotomy | 1.2 | 0.9 | 1.1 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 15 |
| Conventional Osteotomy | 2.0 | 0.9 | 1.7 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 12 |
| Laser Osteotomy | Conventional Osteotomy | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | p-Value | |
| RMS (all) | 1.2 (1.2 to 2.6) | 2.0 (1.0 to 2.0) | 1 |
| Technology | RMS | Mean | SD | Median | Minimum | Maximum |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser Osteotomy | 1.6 | 0.7 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 17 |
| Conventional Osteotomy | 1.6 | 0.8 | 1.4 | 0.1 | 0.0 | 15 |
| Laser Osteotomy | Conventional Osteotomy | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Median (IQR) | Median (IQR) | ||
| RMS (all) | 1.6 (1.1 to 1.9) | 1.6 (1.2 to 1.8) | 0.9 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Msallem, B.; Veronesi, L.; Beyer, M.; Halbeisen, F.S.; Maintz, M.; Franke, A.; Korn, P.; Dragu, A.; Thieringer, F.M. Evaluation of the Dimensional Accuracy of Robot-Guided Laser Osteotomy in Reconstruction with Patient-Specific Implants—An Accuracy Study of Digital High-Tech Procedures. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123594
Msallem B, Veronesi L, Beyer M, Halbeisen FS, Maintz M, Franke A, Korn P, Dragu A, Thieringer FM. Evaluation of the Dimensional Accuracy of Robot-Guided Laser Osteotomy in Reconstruction with Patient-Specific Implants—An Accuracy Study of Digital High-Tech Procedures. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(12):3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123594
Chicago/Turabian StyleMsallem, Bilal, Lara Veronesi, Michel Beyer, Florian S. Halbeisen, Michaela Maintz, Adrian Franke, Paula Korn, Adrian Dragu, and Florian M. Thieringer. 2024. "Evaluation of the Dimensional Accuracy of Robot-Guided Laser Osteotomy in Reconstruction with Patient-Specific Implants—An Accuracy Study of Digital High-Tech Procedures" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 12: 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123594
APA StyleMsallem, B., Veronesi, L., Beyer, M., Halbeisen, F. S., Maintz, M., Franke, A., Korn, P., Dragu, A., & Thieringer, F. M. (2024). Evaluation of the Dimensional Accuracy of Robot-Guided Laser Osteotomy in Reconstruction with Patient-Specific Implants—An Accuracy Study of Digital High-Tech Procedures. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(12), 3594. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13123594







