Variation in Systemic Antibiotic Treatment for Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis in England and Wales: A Multi-Centre Case Review †
Abstract
1. Introduction
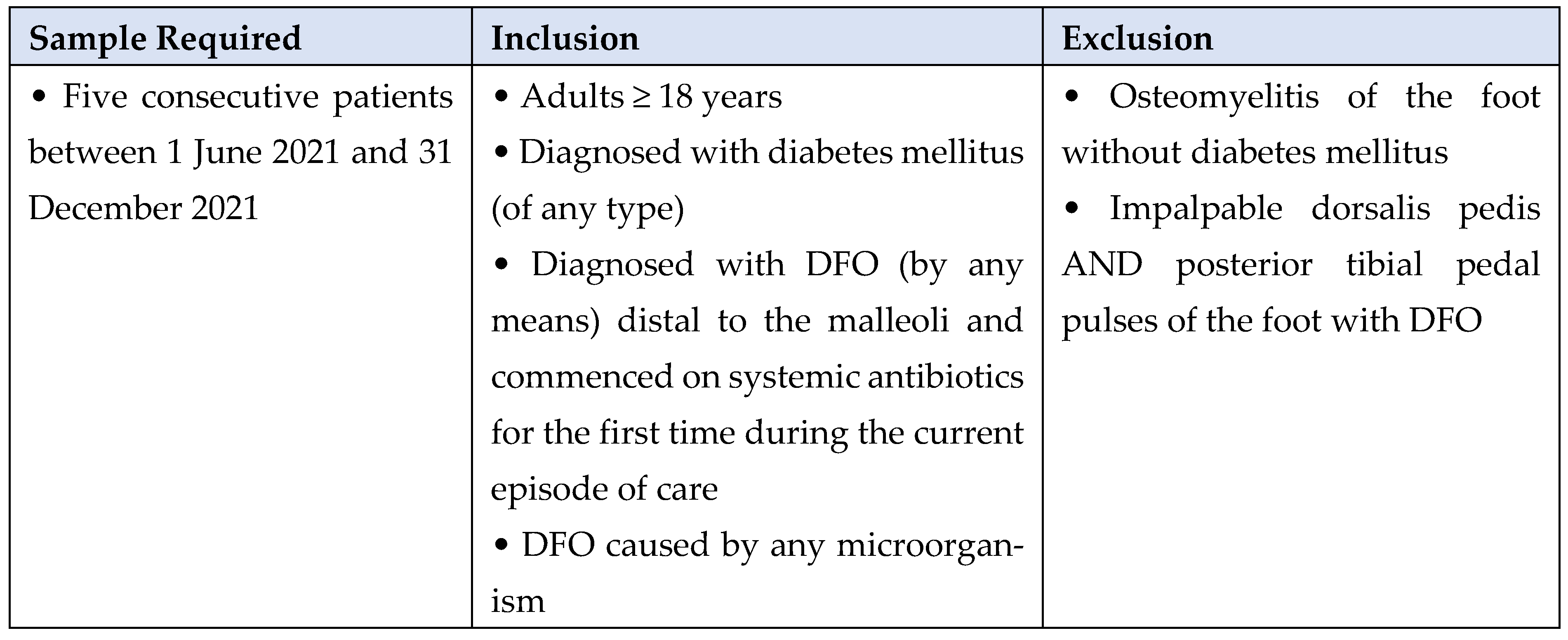
2. Methods
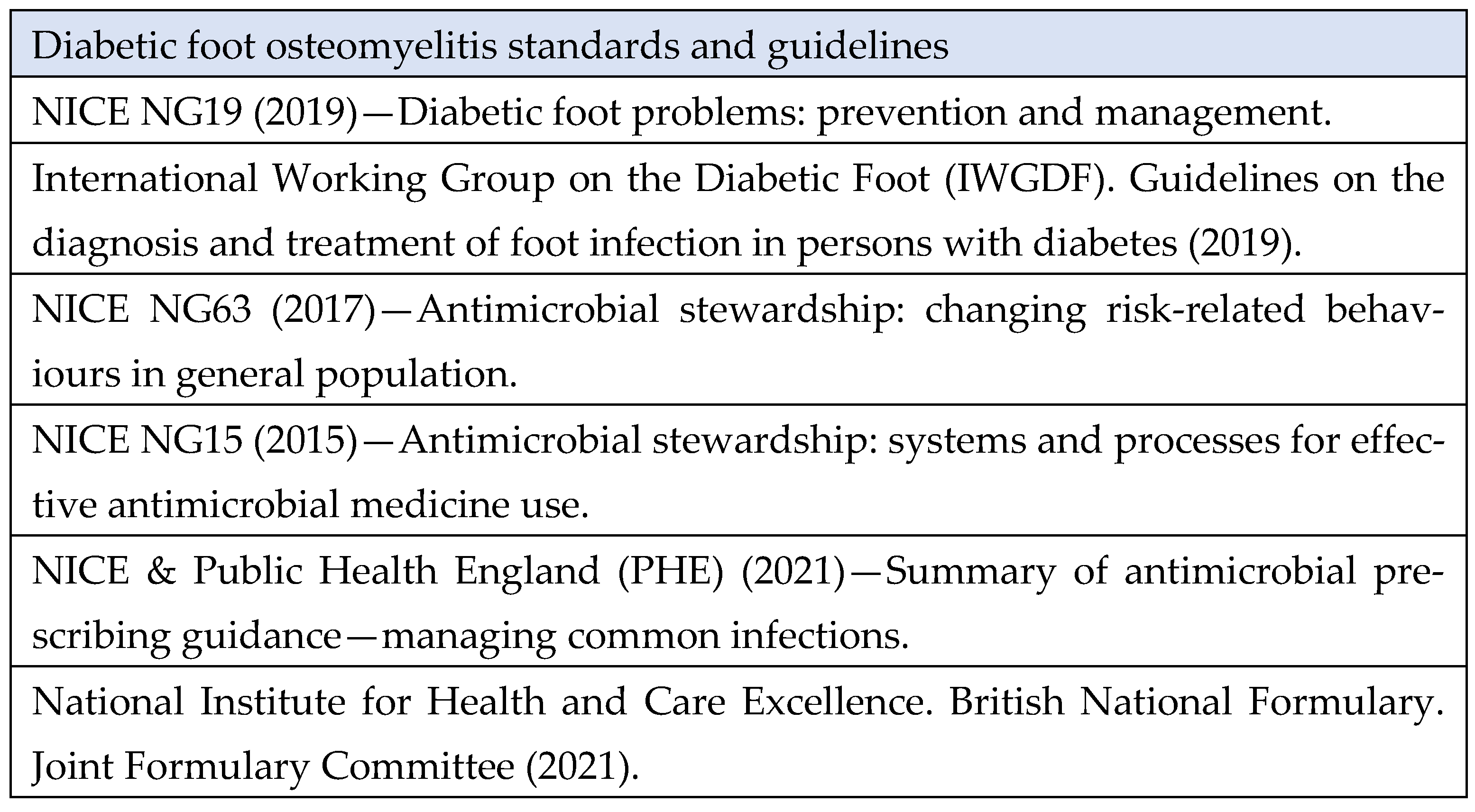
3. Case Review Standards
4. Results
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, S.; Liu, M.; Yao, S.; Fang, S.; Cheng, H.; Chen, Q. Adjunctive Rifampin Therapy for Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis. Medicine 2020, 99, e20375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niazi, N.S.; Drampalos, E.; Morrissey, N.; Jahangir, N.; Wee, A.; Pillai, A. Adjuvant Antibiotic Loaded Bio Composite in the Management of Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis—A Multicentre Study. Foot 2019, 39, 22–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hospital Episode Statistics (HES). National Diabetes Foot Care Report. Available online: https://fingertips.phe.org.uk/static-reports/diabetes-footcare/national-diabetic-footcare-report.html (accessed on 10 February 2024).
- Robineau, O.; Nguyen, S.; Senneville, E. Optimising the Quality and Outcomes of Treatments for Diabetic Foot Infections. Expert. Rev. Anti Infect. Ther. 2016, 14, 817–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Geraghty, T.; LaPorta, G. Current Health and Economic Burden of Chronic Diabetic Osteomyelitis. Expert. Rev. Pharmacoecon. Outcomes Res. 2019, 19, 279–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, A.; Berkache, M.; Morency-Potvin, P.; Juneau, D.; Koenig, M.; Bourduas, K.; Freire, V. Diabetic Foot Infections: How to Investigate More Efficiently? A Retrospective Study in a Quaternary University Center. Insights Imaging 2022, 13, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Birt, M.C.; Anderson, D.W.; Bruce Toby, E.; Wang, J. Osteomyelitis: Recent Advances in Pathophysiology and Therapeutic Strategies. J. Orthop. 2017, 14, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senneville, É.; Albalawi, Z.; van Asten, S.A.; Abbas, Z.G.; Allison, G.; Aragón-Sánchez, J.; Embil, J.M.; Lavery, L.A.; Alhasan, M.; Oz, O.; et al. IWGDF/IDSA Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Diabetes-Related Foot Infections (IWGDF/IDSA 2023). Clin. Infect. Dis. 2023, 40, e3687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weng, B.; Oskooilar, Y.; Zakhary, B.; Chiu, C.A.; Wu, P.; Mulligan, N.; Sutjita, M. Evaluating Predictive Value of Surgical Resected Proximal Bone Margins in Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis With Clinical Outcomes at 1 Year. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2023, 10, ofac689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, A.D.; Simon, G.L. Diabetic Foot Infections: The Role of Microbiology and Antibiotic Treatment. Semin. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 25, 75–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aragón-Sánchez, J.; Luis Lázaro-Martínez, J.; Pulido-Duque, J.; Maynar, M. From the Diabetic Foot Ulcer and beyond: How Do Foot Infections Spread in Patients with Diabetes? Diabet. Foot Ankle 2012, 3, 18693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoropoulou, P.; Eleftheriadou, I.; Jude, E.B.; Tentolouris, N. Diabetic Foot Infections: An Update in Diagnosis and Management. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2017, 17, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, E.J.G.; Lipsky, B.A.; Berendt, A.R.; Embil, J.M.; Lavery, L.A.; Senneville, E.; Urbančič-Rovan, V.; Bakker, K.; Jeffcoate, W.J. A Systematic Review of the Effectiveness of Interventions in the Management of Infection in the Diabetic Foot. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2012, 28, 142–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bessesen, M.T.; Doros, G.; Henrie, A.M.; Harrington, K.M.; Hermos, J.A.; Bonomo, R.A.; Ferguson, R.E.; Huang, G.D.; Brown, S.T. A Multicenter Randomized Placebo Controlled Trial of Rifampin to Reduce Pedal Amputations for Osteomyelitis in Veterans with Diabetes (VA INTREPID). BMC Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miller, W.; Berg, C.; Wilson, M.L.; Heard, S.; Knepper, B.; Young, H. Risk Factors for Below-the-Knee Amputation in Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis After Minor Amputation. J. Am. Podiatr. Med. Assoc. 2019, 109, 91–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lipsky, B.A.; Senneville, É.; Abbas, Z.G.; Aragón-Sánchez, J.; Diggle, M.; Embil, J.M.; Kono, S.; Lavery, L.A.; Malone, M.; van Asten, S.A.; et al. Guidelines on the Diagnosis and Treatment of Foot Infection in Persons with Diabetes (IWGDF 2019 Update). Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36, e3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NICE NG19. NICE Guideline [NG19]: Diabetic Foot Problems: Prevention and Management. 2019. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng19 (accessed on 11 February 2024).
- Game, F.L.; Jeffcoate, W.J. Primarily Non-Surgical Management of Osteomyelitis of the Foot in Diabetes. Diabetologia 2008, 51, 962–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Embil, J.M.; Rose, G.; Trepman, E.; Math, M.C.M.; Duerksen, F.; Simonsen, J.N.; Nicolle, L.E. Oral Antimicrobial Therapy for Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis. Foot Ankle Int. 2006, 27, 771–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gariani, K.; Pham, T.-T.; Kressmann, B.; Jornayvaz, F.R.; Gastaldi, G.; Stafylakis, D.; Philippe, J.; Lipsky, B.A.; Uçkay, L. Three Weeks Versus Six Weeks of Antibiotic Therapy for Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: A Prospective, Randomized, Noninferiority Pilot Trial. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2021, 73, e1539–e1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, A.; Nguyen, S.; Devemy, F.; Topolinski, H.; Valette, M.; Cazaubiel, M.; Fayard, A.; Beltrand, É.; Lemaire, C.; Senneville, É. Six-Week Versus Twelve-Week Antibiotic Therapy for Nonsurgically Treated Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: A Multicenter Open-Label Controlled Randomized Study. Diabetes Care 2015, 38, 302–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Truong, D.H.; Bedimo, R.; Malone, M.; Wukich, D.K.; Oz, O.K.; Killeen, A.L.; Lavery, L.A. Meta-Analysis: Outcomes of Surgical and Medical Management of Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tardáguila-García, A.; Sanz-Corbalán, I.; García-Alamino, J.M.; Ahluwalia, R.; Uccioli, L.; Lázaro-Martínez, J.L. Medical Versus Surgical Treatment for the Management of Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Soldevila-Boixader, L.; Fernández, A.P.; Laguna, J.M.; Uçkay, I. Local Antibiotics in the Treatment of Diabetic Foot Infections: A Narrative Review. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaper, N.; Van Netten, J.; Apelqvist, J.; Bus, C.; Hinchliffe, R.; Lipsky, B. IWGDF Practical Guidelines on the Prevention and Magement of Diabetic Foot Disease. Diabetes Metab. Res. Rev. 2020, 36 (Suppl. 1), e3266. [Google Scholar]
- Antimicrobial Stewardship: Changing Risk-Related Behaviours in the General Population NICE Guideline. 2017. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng63 (accessed on 11 February 2024).
- Antimicrobial Stewardship: Systems and Processes for Effective Antimicrobial Medicine Use NICE Guideline. 2015. Available online: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/ng15 (accessed on 11 February 2024).
- Phe. Summary of Antimicrobial Prescribing Guidance: Managing Common Infections PHE Context, References and Rationales for Clinical Commissioning Groups, Commissioning Support Units and Primary Care Providers. 2021. Available online: https://www.facebook.com/PublicHealthEngland (accessed on 11 February 2024).
- Medicines Information Services. Available online: https://www.sps.nhs.uk/ukdilas (accessed on 11 February 2024).
- Schechter, M.C.; Ali, M.K.; Risk, B.B.; Singer, A.D.; Santamarina, G.; Rogers, H.K.; Rajani, R.R.; Umpierrez, G.; Fayfman, M.; Kempker, R.R. Percutaneous Bone Biopsy for Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2020, 7, ofaa393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- British National Formulary. Diabetic Foot Infections, Antibacterial Therapy. Available online: https://bnf.nice.org.uk/ (accessed on 11 February 2024).
- Akbari, R.; Javaniyan, M.; Fahimi, A.; Sadeghi, M. Renal Function in Patients with Diabetic Foot Infection; Does Antibiotherapy Affect It? J. Renal Inj. Prev. 2016, 6, 117–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Björnsson, E.S. Drug-Induced Liver Injury Due to Antibiotics. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 52, 617–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maurer, S.M.; Hepp, Z.S.; McCallin, S.; Waibel, F.W.A.; Romero, F.C.; Zorman, Y.; Lipsky, B.A.; Uçkay, İ. Short and Oral Antimicrobial Therapy for Diabetic Foot Infection: A Narrative Review of Current Knowledge. J. Bone Jt. Infect. 2022, 7, 61–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavery, L.A.; Ahn, J.; Ryan, E.C.; Bhavan, K.; Oz, O.K.; La Fontaine, J.; Wukich, D.K. What Are the Optimal Cutoff Values for ESR and CRP to Diagnose Osteomyelitis in Patients with Diabetes-Related Foot Infections? Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 2019, 477, 1594–1602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Sharma, S.; Krishnan, A.; Yuan, D.; Vangaveti, V.N.; Malabu, U.H.; Haleagrahara, N. The Efficacy of Inflammatory Markers in Diagnosing Infected Diabetic Foot Ulcers and Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0267412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Characteristic | Total Population n (%) | MDFT Centre 1 | MDFT Centre 2 | MDFT Centre 3 | MDFT Centre 4 | MDFT Centre 5 | MDFT Centre 6 | MDFT Centre 7 | MDFT Centre 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patients (n = 40) | 40 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Male n (%) | 34 (85%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 4 (80%) | 5 (100%) | 4 (80%) | 3 (60%) | 4 (80%) | 4 (80%) |
| Female n (%) | 6 (15%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 2 (40%) | 1 (20%) | 1 (20%) |
| Age at diagnosis of DFO, years, mean (SD) | Mean 62.3 (SD 13.0) | 59.4 (SD 9.2) | 71.6 (SD 8.2) | 53.4 (SD 14.6) | 68.2 (SD 13.2) | 62.6 (SD 14.7) | 64.6 (SD 12.4) | 60.6 (SD 9.6) | 58.2 (SD 10.7) |
| Diabetes type I, II or other | Type 1 8 (20%) Male = 6 (15%) Female = 2 (5%) Type 2 31 (77.5%) Male = 27 (67.5%) Female = 4 (10%) Other 1 (2.5%) Male = 1 (1%) Female = 0 (0%) | Type 1 1 (20%) Type 2 4 (80%) | Type 1 0 (0%) Type 2 5 (100%) | Type 1 2 (40%) Type 2 3 (60%) | Type 1 0 (0%) Type 2 5 (100%) | Type 1 1 (20%) Type 2 4 (80%) | Type 1 1 (20%) Type 2 4 (80%) | Type 1 0 (0%) Type 2 4 (%) Other 1 (20%) | Type 1 3 (60%) Type 2 2 (40%) |
| DFO: Digit | 33 (80.5%) | 4 | 3 | 5 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 4 | 4 |
| DFO: Metatarsals | 5 (12.2%) | 1 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| DFO: Mid-foot | 2 (4.9%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| DFO: Calcaneus | 1 (2.4%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| TOTAL | MDFT Centre 1 | MDFT Centre 2 | MDFT Centre 3 | MDFT Centre 4 | MDFT Centre 5 | MDFT Centre 6 | MDFT Centre 7 | MDFT Centre 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Oral | 26 (65%) | 3 (60%) | 5 (100%) | 4 (80%) | 3 (60%) | 2 (40%) | 3 (60%) | 4 (80%) | 2 (40%) |
| IV | 14 (35%) | 2 (40%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 2 (40%) | 3 (60%) | 2 (40%) | 1 (20%) | 3 (60%) |
| Antibiotic(s) and Mode of Delivery | Frequency (n = 40) | Mild Allergic Reaction (Sensitivity) to Antibiotic(s) | Severe Allergic Reaction (Anaphylaxis) to Antibiotic(s) | Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) | Abnormal Liver Test | Clostridium Difficile |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceftriaxone IV | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ciprofloxacin oral | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Clindamycin oral | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Clindamycin and ciprofloxacin oral | 9 | 2 (5%) | 0 | 1 (2.5%) | 2 (5%) | 0 |
| Clindamycin and meropenem IV | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Co-Amoxiclav oral | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Co-Amoxiclav IV | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Co-Amoxiclav and amoxicillin oral | 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 (2.5%) | 0 |
| Co-trimoxazole IV | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Doxycycline oral | 1 | 1 (2.5%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ertapenem and metronidazole IV | 1 | 1 (2.5%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ertapenem and clindamycin IV | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Flucloxacillin oral | 3 | 1 (2.5%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Flucloxacillin and fusidic acid oral | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Flucloxacillin and metronidazole IV | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 (2.5%) | 1 (2.5%) | 0 |
| Linezolid oral | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam IV | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Teicoplanin IV | 3 | 0 | 0 | 2 (5%) | 2 (5%) | 0 |
| Total | 40 | 5 (12.5%) | 0 | 4 (10%) | 6 (15%) | 0 |
| TOTAL N (%) | MDFT Centre 1 N (%) | MDFT Centre 2 N (%) | MDFT Centre 3 N (%) | MDFT Centre 4 N (%) | MDFT Centre 5 N (%) | MDFT Centre 6 N (%) | MDFT Centre 7 N (%) | MDFT Centre 8 N (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray | 37 (92.5%) | 5 (100%) | 4 (80%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 3 (60%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) |
| MRI | 10 (25%) | 2 (40%) | 3 (60%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 1 (20%) | 1 (20%) | 1 (20%) |
| CT | 1 (2.5%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| SPECT-CT | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| 18F-FDG PET/CT | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Radioisotope bone scan | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Total Number of Tests N (%) | MDFT Centre 1 N | MDFT Centre 2 N | MDFT Centre 3 N | MDFT Centre 4 N | MDFT Centre 5 N | MDFT Centre 6 N | MDFT Centre 7 N | MDFT Centre 8 N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| X-ray | 57 (83.8%) | 6 | 1 | 8 | 8 | 3 | 1 | 16 | 14 |
| MRI | 10 (14.7%) | 2 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| CT | 1 (1.4%) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| SPECT-CT | 0 (0%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| 18F-FDG PET/CT | 0 (0%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Radioisotope bone scan | 0 (0%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total number of investigations | 68 | 9 | 4 | 9 | 8 | 4 | 2 | 17 | 15 |
| Total N (%) | MDFT Centre 1 N (%) | MDFT Centre 2 N (%) | MDFT Centre 3 N (%) | MDFT Centre 4 N (%) | MDFT Centre 5 N (%) | MDFT Centre 6 N (%) | MDFT Centre 7 N (%) | MDFT Centre 8 N (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBC | 32 (80%) | 5 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 4 (80%) | 3 (60%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) |
| eGFR | 34 (85%) | 5 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 4(80%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) |
| U&E profile | 28 (70%) | 5 (100%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 4 (80%) | 4 (80%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) |
| ESR | 14 (35%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 3 (60%) | 2 (40%) | 3 (60%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (100%) |
| CRP | 33 (82.5%) | 5 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (100% | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 3 (60%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) |
| LFT | 31 (77.5%) | 4 (80%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (100%) | 3 (60%) | 5 (100%) | 4 (80%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) |
| Bicarbonate | 10 (25%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) |
| Procalcitonin | 0 (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Total N (%) | MDFT Centre 1 N | MDFT Centre 2 N | MDFT Centre 3 N | MDFT Centre 4 N | MDFT Centre 5 N | MDFT Centre 6 N | MDFT Centre 7 N | MDFT Centre 8 N | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| FBC | 226 (19%) | 72 | 0 | 12 | 27 | 24 | 12 | 28 | 51 |
| eGFR | 161 (13.4%) | 81 | 0 | 14 | 28 | 24 | 14 | 0 | 0 |
| U&E profile | 241 (20.1%) | 77 | 0 | 14 | 28 | 24 | 15 | 34 | 49 |
| ESR | 56 (4.6%) | 0 | 0 | 3 | 19 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 32 |
| CRP | 234 (19.5%) | 72 | 0 | 13 | 28 | 22 | 14 | 36 | 49 |
| LFT | 232 (19.3%) | 72 | 0 | 14 | 27 | 24 | 14 | 36 | 45 |
| Bicarbonate | 49 (4.1%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 36 | 13 |
| Procalcitonin | 0 (0%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Total tests | 1199 | 374 | 0 | 70 | 157 | 118 | 71 | 170 | 239 |
| Total N (%) | MDFT Centre 1 N (%) | MDFT Centre 2 N (%) | MDFT Centre 3 N (%) | MDFT Centre 4 N (%) | MDFT Centre 5 N (%) | MDFT Centre 6 N (%) | MDFT Centre 7 N (%) | MDFT Centre 8 N (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wound swab for microscopy culture and sensitivity | 29 (72.5%) | 5 (100%) | 2 (40%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 1 (20%) | 1 (20%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) |
| Tissue sample for microscopy culture and sensitivity | 14 (35%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 3 (60%) | 4 (80%) | 2 (40%) | 0 (0%) | 4 (80%) |
| Fluid aspirate for microscopy culture and sensitivity | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Bone sample for microscopy culture and sensitivity | 8 (20%) | 3 (60%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 2 (40%) | 0 (%) | 2 (40%) | 0 (0%) |
| Bone sample for histological examination | 1 (2.5%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) |
| Thermographic scan of the foot with DFO | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Clinician assessment | 40 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) | 5 (100%) |
| Total N (%) | MDFT Centre 1 | MDFT Centre 2 | MDFT Centre 3 | MDFT Centre 4 | MDFT Centre 5 | MDFT Centre 6 | MDFT Centre 7 | MDFT Centre 8 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wound swab for microscopy culture and sensitivity | 88 (17.5%) | 31 | 3 | 5 | 11 | 0 | 0 | 6 | 32 |
| Tissue sample for microscopy culture and sensitivity | 8 (1.6%) | 2 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Fluid aspirate for microscopy culture and sensitivity | 0 (0%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Bone sample for microscopy culture and sensitivity | 8 (1.6%) | 3 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 0 |
| Bone sample for histological examination | 1 (0.2%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| Thermographic scan of the foot with DFO | 0 (0%) | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Clinician assessment | 396 (78.8%) | 106 | 17 | 40 | 67 | 33 | 20 | 60 | 53 |
| Total | 501 | 143 | 20 | 45 | 82 | 36 | 20 | 69 | 87 |
| Outcome | Total N (%) | MDFT Centre 1 | MDFT Centre 2 | MDFT Centre 3 | MDFT Centre 4 | MDFT Centre 5 | MDFT Centre 6 | MDFT Centre 7 | MDFT Centre 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Systemic antibiotics continued | 12 (30%) | 1 (20%) | 2 (40%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 1 (20%) | 2 (40%) | 3 (60%) | 2 (40%) |
| Systemic antibiotics stopped | 28 (70%) | 4 (80%) | 3 (60%) | 5 (100%) | 4 (80%) | 4 (80%) | 3 (60%) | 2 (40%) | 3 (60%) |
| Quiescence of DFO | 27 (67.5%) | 5 (100%) | 2 (40%) | 5 (100%) | 4 (80%) | 4 (80%) | 2 (40%) | 2 (40%) | 3 (60%) |
| No recurrence of DFO | 21 (52.5%) | 4 (80%) | 4 (80%) | 4 (80%) | 4 (80%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 3 (60%) | 1 (20%) |
| Surgery debridement only | 6 (15%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 4 (80%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Surgery minor amputation | 12 (30%) | 2 (40%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 1 (20%) | 3 (60%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (40%) | 3 (60%) |
| Surgery major amputation | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Surgery with biological agent impregnated with antibiotics | 3 (7.5%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (40%) |
| Death due to DFO | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Antibiotic(s) and Mode of Delivery | Patients (n = 40) | Systemic Antibiotics Continued | Systemic Antibiotics Stopped | Quiescence of DFO | No Recurrence of DFO | Surgery Debridement Only | Surgery Minor Amputation | Surgery Major Amputation | Surgery with Biological Agent Impregnated with Antibiotics | Death |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ceftriaxone IV | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ciprofloxacin oral | 2 | 0 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Clindamycin oral | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Clindamycin and ciprofloxacin oral | 9 | 2 | 7 | 6 | 5 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Clindamycin and meropenem IV | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Co-Amoxiclav oral | 2 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Co-Amoxiclav IV | 3 | 0 | 2 | 2 | 0 | 3 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Co-Amoxiclav and amoxicillin oral | 4 | 3 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Co-Trimoxazole IV | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Doxycycline oral | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| Ertapenem and metronidazole IV | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Ertapenem and clindamycin IV | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Flucloxacillin oral | 3 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Flucloxacillin and fusidic acid oral | 3 | 0 | 3 | 3 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Flucloxacillin and metronidazole IV | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Linezolid oral | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Piperacillin/tazobactam IV | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Teicoplanin IV | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 |
| TOTAL | 40 | 12 (30%) | 28 (70%) | 27 (67.5%) | 21 (52.5%) | 6 (15%) | 12 (30%) | 0 (%) | 3 (7.5%) | 0 (0%) |
| Total N (%) | MDFT Centre 1 N (%) | MDFT Centre 2 N (%) | MDFT Centre 3 N (%) | MDFT Centre 4 N (%) | MDFT Centre 5 N (%) | MDFT Centre 6 N (%) | MDFT Centre 7 N (%) | MDFT Centre 8 N (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mild allergic reaction (sensitivity) to antibiotic(s) | 5 (12.5%) | 0 (%) | 1 (20%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (40%) | 1 (20%) |
| Severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) to antibiotic(s) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0(%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (%) |
| Acute kidney injury (AKI) | 4 (10%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) |
| Abnormal liver test | 6 (15%) | 2 (40%) | 0 (0%) | 2 (40%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0%) | 1 (20%) | 0 (0% | 0 (0%) |
| Clostridium difficile | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) | 0 (0%) |
| Total | 15 | 3 | 1 | 4 | 2 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Uddin, A.; Russell, D.A.; Game, F.; Santos, D.; Siddle, H.J. Variation in Systemic Antibiotic Treatment for Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis in England and Wales: A Multi-Centre Case Review. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3083. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113083
Uddin A, Russell DA, Game F, Santos D, Siddle HJ. Variation in Systemic Antibiotic Treatment for Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis in England and Wales: A Multi-Centre Case Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(11):3083. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113083
Chicago/Turabian StyleUddin, Akram, David A. Russell, Fran Game, Derek Santos, and Heidi J. Siddle. 2024. "Variation in Systemic Antibiotic Treatment for Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis in England and Wales: A Multi-Centre Case Review" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 11: 3083. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113083
APA StyleUddin, A., Russell, D. A., Game, F., Santos, D., & Siddle, H. J. (2024). Variation in Systemic Antibiotic Treatment for Diabetic Foot Osteomyelitis in England and Wales: A Multi-Centre Case Review. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(11), 3083. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13113083