Trochleoplasty Provides Good Outcomes for Recurrent Patellofemoral Dislocations with No Clear Superiority across Different Techniques
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Systematic Review
2.2. Data Abstraction
2.3. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Quality of Studies
3.2. Outcome Scores
3.3. Complications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Balcarek, P.; Rehn, S.; Howells, N.R.; Eldridge, J.D.; Kita, K.; Dejour, D.; Nelitz, M.; Banke, I.J.; Lambrecht, D.; Harden, M.; et al. Results of medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction compared with trochleoplasty plus individual extensor apparatus balancing in patellar instability caused by severe trochlear dysplasia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 3869–3877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemstra, L.A.; Peterson, D.; Youssef, M.; Soliman, J.; Banfield, L.; Ayeni, O.R. Trochleoplasty provides good clinical outcomes and an acceptable complication profile in both short and long-term follow-up. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2019, 27, 2967–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Longo, U.G.; Vincenzo, C.; Mannering, N.; Ciuffreda, M.; Salvatore, G.; Berton, A.; Denaro, V. Trochleoplasty techniques provide good clinical results in patients with trochlear dysplasia. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2018, 26, 2640–2658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ntagiopoulos, P.G.; Byn, P.; Dejour, D. Midterm results of comprehensive surgical reconstruction including sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty in recurrent patellar dislocations with high-grade trochlear dysplasia. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 998–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, G.Y.; Hong, L.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, J.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Feng, H. Trochleoplasty versus nontrochleoplasty procedures in treating patellar instability caused by severe trochlear dysplasia. Arthroscopy 2014, 30, 523–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Testa, E.A.; Camathias, C.; Amsler, F.; Henle, P.; Friederich, N.F.; Hirschmann, M.T. Surgical treatment of patellofemoral instability using trochleoplasty or MPFL reconstruction: A systematic review. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2017, 25, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albee, F. Bone graft wedge in the treatment of habitual dislocation of the patella. Med. Rec. 1915, 88, 257–259. [Google Scholar]
- Masse, Y. Trochleoplasty. Restoration of the intercondylar groove in subluxations and dislocations of the patella. Rev. Chir. Orthop. Reparatrice Appar. Mot. 1978, 64, 3–17. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dejour, H.; Walch, G.; Neyret, P.; Adeleine, P. Dysplasia of the femoral trochlea. Rev. Chir. Orthop. Reparatrice Appar. Mot. 1990, 76, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dejour, D.; Saggin, P. The sulcus deepening trochleoplasty-the Lyon’s procedure. Int. Orthop. 2010, 34, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Knoch, F.; Böhm, T.; Bürgi, M.L.; von Knoch, M.; Bereiter, H. Trochleaplasty for recurrent patellar dislocation in association with trochlear dysplasia. A 4- to 14-year follow-up study. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2006, 88, 1331–1335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bereiter, H.; Gautier, E. Die trochleaplastik als chirurgische Therapie der rezidivierenden Patellaluxation bei Trochleadysplasie des Femurs. Arthroskopie 1994, 7, 281–286. [Google Scholar]
- Goutallier, D.; Raou, D.; Van Driessche, S. Retro-trochlear wedge reduction trochleoplasty for the treatment of painful patella syndrome with protruding trochleae. Technical note and early results. Rev. Chir. Orthop. Reparatrice Appar. Mot. 2002, 88, 678–685. [Google Scholar]
- Arendt, E.A. MPFL reconstruction for PF instability. The soft (tissue) approach. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2009, 95 (Suppl. S1), S97–S100. [Google Scholar]
- Dejour, D.; Le Coultre, B. Osteotomies in patello-femoral instabilities. Sports Med. Arthrosc. Rev. 2007, 15, 39–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dejour, H.; Walch, G.; Nove-Josserand, L.; Guier, C. Factors of patellar instability: An anatomic radiographic study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 1994, 2, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McNamara, I.; Bua, N.; Smith, T.O.; Ali, K.; Donell, S.T. Deepening Trochleoplasty with a Thick Osteochondral Flap for Patellar Instability: Clinical and Functional Outcomes at a Mean 6-Year Follow-up. Am. J. Sports Med. 2015, 43, 2706–2713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelitz, M.; Dreyhaupt, J.; Lippacher, S. Combined trochleoplasty and medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for recurrent patellar dislocations in severe trochlear dysplasia: A minimum 2-year follow-up study. Am. J. Sports Med. 2013, 41, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Engelhardt, L.V.; Weskamp, P.; Lahner, M.; Spahn, G.; Jerosch, J. Deepening trochleoplasty combined with balanced medial patellofemoral ligament reconstruction for an adequate graft tensioning. World J. Orthop. 2017, 8, 935–945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kon, E.; Altadonna, G.; Filardo, G.; Matteo, B.D.; Marcacci, M. Knee Scoring Systems. In European Surgical Orthopaedics and Traumatology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; pp. 3371–3388. [Google Scholar]
- Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G.; Bradburn, M.J. Statistical methods for examining heterogeneity and combining results from several studies in meta-analysis. In Systematic Reviews in Health Care: Meta-Analysis in Context; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 2001; pp. 285–321. [Google Scholar]
- Fleiss, J.L. The statistical basis of meta-analysis. Stat. Methods Med. Res. 1993, 2, 121–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.; Thompson, S.G.; Deeks, J.J.; Altman, D.G. Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. BMJ 2003, 327, 557–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, J.P.T.; Thompson, S.G. Quantifying heterogeneity in a meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 2002, 21, 1539–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitehead, A. Meta-Analysis of Controlled Clinical Trials; John Wiley and Sons: West Sussex, UK, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Banke, I.J.; Kohn, L.M.; Meidinger, G.; Otto, A.; Hensler, D.; Beitzel, K.; Imhoff, A.B.; Schöttle, P.B. Combined trochleoplasty and MPFL reconstruction for treatment of chronic patellofemoral instability: A prospective minimum 2-year follow-up study. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 2591–2598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blønd, L.; Haugegaard, M. Combined arthroscopic deepening trochleoplasty and reconstruction of the medial patellofemoral ligament for patients with recurrent patella dislocation and trochlear dysplasia. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2014, 22, 2484–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Camathias, C.; Studer, K.; Kiapour, A.; Rutz, E.; Vavken, P. Trochleoplasty as a Solitary Treatment for Recurrent Patellar Dislocation Results in Good Clinical Outcome in Adolescents. Am. J. Sports Med. 2016, 44, 2855–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dejour, D.; Byn, P.; Ntagiopoulos, P.G. The Lyon’s sulcus-deepening trochleoplasty in previous unsuccessful patellofemoral surgery. Int. Orthop. 2013, 37, 433–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donell, S.T.; Joseph, G.; Hing, C.B.; Marshall, T.J. Modified Dejour trochleoplasty for severe dysplasia: Operative technique and early clinical results. Knee 2006, 13, 266–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falkowski, A.L.; Camathias, C.; Jacobson, J.A.; Magerkurth, O. Increased Magnetic Resonance Imaging Signal of the Lateral Patellar Facet Cartilage: A Functional Marker for Patellar Instability? Am. J. Sports Med. 2017, 45, 2276–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fucentese, S.F.; Zingg, P.O.; Schmitt, J.; Pfirrmann, C.W.; Meyer, D.C.; Koch, P.P. Classification of trochlear dysplasia as predictor of clinical outcome after trochleoplasty. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2011, 19, 1655–1661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koëter, S.; Pakvis, D.; van Loon, C.J.; van Kampen, A. Trochlear osteotomy for patellar instability: Satisfactory minimum 2-year results in patients with dysplasia of the trochlea. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2007, 15, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Metcalfe, A.J.; Clark, D.A.; Kemp, M.A.; Eldridge, J.D. Trochleoplasty with a flexible osteochondral flap: Results from an 11-year series of 214 cases. Bone Jt. J. 2017, 99, 344–350. [Google Scholar]
- Neumann, M.V.; Stalder, M.; Schuster, A.J. Reconstructive surgery for patellofemoral joint incongruency. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2016, 24, 873–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pesenti, S.; Blondel, B.; Armaganian, G.; Parratte, S.; Bollini, G.; Launay, F.; Jouve, J.L. The lateral wedge augmentation trochleoplasty in a pediatric population: A 5-year follow-up study. J. Pediatr. Orthop. B. 2017, 26, 458–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rouanet, T.; Gougeon, F.; Fayard, J.M.; Rémy, F.; Migaud, H.; Pasquier, G. Sulcus deepening trochleoplasty for patellofemoral instability: A series of 34 cases after 15 years postoperative follow-up. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2015, 101, 443–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöttle, P.B.; Fucentese, S.F.; Pfirrmann, C.; Bereiter, H.; Romero, J. Trochleaplasty for patellar instability due to trochlear dysplasia: A minimum 2-year clinical and radiological follow-up of 19 knees. Acta Orthop. 2005, 76, 693–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thaunat, M.; Bessiere, C.; Pujol, N.; Boisrenoult, P.; Beaufils, P. Recession wedge trochleoplasty as an additional procedure in the surgical treatment of patellar instability with major trochlear dysplasia: Early results. Orthop. Traumatol. Surg. Res. 2011, 97, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utting, M.R.; Mulford, J.S.; Eldridge, J.D. A prospective evaluation of trochleoplasty for the treatment of patellofemoral dislocation and instability. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 2008, 90, 180–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verdonk, R.; Jansegers, E.; Stuyts, B. Trochleoplasty in dysplastic knee trochlea. Knee Surg. Sports Traumatol. Arthrosc. 2005, 13, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, S.A.; Helmer, R.; Terk, M.R. Analysis of the patellofemoral region on MRI: Association of abnormal trochlear morphology with severe cartilage defects. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2010, 194, 721–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jungmann, P.M.; Tham, S.C.; Liebl, H.; Nevitt, M.C.; McCulloch, C.E.; Lynch, J.; Link, T.M. Association of trochlear dysplasia with degenerative abnormalities in the knee: Data from the Osteoarthritis Initiative. Skeletal Radiol. 2013, 42, 1383–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pap, T.; Korb-Pap, A. Cartilage damage in osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis—Two unequal siblings. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2015, 11, 606–615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arnbjörnsson, A.; Egund, N.; Rydling, O.; Stockerup, R.; Ryd, L. The natural history of recurrent dislocation of the patella. Long-term results of conservative and operative treatment. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1992, 74, 140–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heywood, A.W.B. Recurrent dislocation of the patella. A study of its pathology and treatment in 106 knees. J. Bone Jt. Surg. Br. 1961, 43, 508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mäenpää, H.; Lehto, M.U. Patellofemoral osteoarthritis after patellar dislocation. Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. 1997, 339, 156–162. [Google Scholar]
- Barlow, T.; Griffin, D.; Barlow, D.; Realpe, A. Patients’ decision making in total knee arthroplasty: A systematic review of qualitative research. Bone Jt. Res. 2015, 4, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gagnier, J.J. Patient reported outcomes in orthopaedics. J. Orthop. Res. 2017, 35, 2098–2108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, D.F.; Ghert, M.; Simpson, A.H. Interpreting regression models in clinical outcome studies. Bone Jt. Res. 2015, 4, 152–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamilton, D.F.; Giesinger, J.M.; Patton, J.T.; MacDonald, D.J.; Simpson, A.H.R.W.; Howie, C.R.; Giesinger, K. Making the Oxford Hip and Knee Scores meaningful at the patient level through normative scoring and registry data. Bone Jt. Res. 2015, 4, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kingsbury, S.R.; Dube, B.; Thomas, C.M.; Conaghan, P.G.; Stone, M.H. Is a questionnaire and radiograph-based follow-up model for patients with primary hip and knee arthroplasty a viable alternative to traditional regular outpatient follow-up clinic? Bone Jt. J. 2016, 98, 201–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kleinlugtenbelt, Y.V.; Nienhuis, R.W.; Bhandari, M.; Goslings, J.C.; Poolman, R.W.; Scholtes, V.A. Are validated outcome measures used in distal radial fractures truly valid? A critical assessment using the COnsensus-based Standards for the selection of health Measurement INstruments (COSMIN) checklist. Bone Jt. Res. 2016, 5, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malak, T.T.; Broomfield, J.A.; Palmer, A.J.; Hopewell, S.; Carr, A.; Brown, C.; Prieto-Alhambra, D.; Glyn-Jones, S. Surrogate markers of long-term outcome in primary total hip arthroplasty: A systematic review. Bone Jt. Res. 2016, 5, 206–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parsons, N.; Griffin, X.L.; Achten, J.; Costa, M.L. Outcome assessment after hip fracture: Is EQ-5D the answer? Bone Jt. Res. 2014, 3, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poitras, S.; Wood, K.S.; Savard, J.; Dervin, G.F.; Beaule, P.E. Predicting early clinical function after hip or knee arthroplasty. Bone Jt. Res. 2015, 4, 145–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiemstra, L.A.; Page, J.L.; Kerslake, S. Patient-Reported Outcome Measures for Patellofemoral Instability: A Critical Review. Curr. Rev. Musculoskelet. Med. 2019, 12, 124–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Author | Year | Level of Evidence | Sample Size (Number of Knees) | Type of Trocheoplasty | Age (Years) | Sex * | Follow Up (Months) | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | Minimum | Maximum | Male | Female | Mean | Minimum | Maximum | |||||
| Banke | 2014 | IV | 18 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 22.2 | 15 | 31 | 6 | 11 | 30.5 | 24 | 40 |
| Blønd | 2014 | IV | 29 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 19 | 12 | 39 | 10 | 21 | 29 | 12 | 57 |
| Camathias | 2016 | IV | 50 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 15.6 | 13 | 20.4 | 20 | 30 | 33 | 24 | 64 |
| Dejour | 2013 | IV | 24 | Thick Trocheoplasty | 23 | 14 | 33 | 9 | 13 | 66 | 24 | 191 |
| Donell | 2006 | IV | 17 | Thick Trocheoplasty | 25 | 15 | 47 | 3 | 12 | 36 | 12 | 108 |
| Falkowski | 2017 | IV | 22 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 16.3 | 13.9 | 19 | 4 | 18 | 8.8 | 3 | 12 |
| Fucentese | 2011 | IV | 44 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 18 | 14 | 40 | 10 | 28 | 48 | 24 | 93.6 |
| Koëter | 2007 | IV | 19 | Lateral Condyle Elevating | 25 | 15 | 34 | 4 | 12 | 51 | 24 | 110 |
| McNamara | 2015 | IV | 107 | Thick Trocheoplasty | 23 | 12 | 49 | 36 | 54 | 72 | 24 | 228 |
| Metcalfe | 2017 | IV | 199 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 21.3 | 14 | 38 | 52 | 133 | 53.16 | 12 | 144 |
| Nelitz | 2013 | IV | 26 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 19.2 | 15.4 | 23.6 | 14 | 9 | 36 | 24 | 42 |
| Neumann | 2016 | IV | 46 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 27.6 # | 16 | 53 | 13 | 33 | 56.7 # | 24 | 109 |
| Ntagiopoulos | 2013 | IV | 31 | Thick Trocheoplasty | 21 | 14 | 47 | 14 | 13 | 84 | 24 | 108 |
| Pesenti | 2017 | IV | 27 | Lateral Condyle Elevating | 12.5 | 8 | 17 | 11 | 12 | NR | 60 | NR |
| Rouanet | 2015 | IV | 34 | Thick Trocheoplasty | 27.8 | 16 | 49 | 10 | 24 | 183.6 | 144 | 228 |
| Schöttle | 2005 | IV | 19 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 22 | 17 | 40 | 3 | 13 | 36 | 24 | 48 |
| Thaunat | 2011 | IV | 19 | Recession Wedge | 23 | 18 | 45 | 8 | 9 | 34 | 12 | 71 |
| Utting | 2008 | IV | 59 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 21.5 | 14.3 | 33.9 | 15 | 39 | 24 | 12 | 58 |
| Verdonk | 2005 | IV | 13 | Thick Trocheoplasty | 27 | 14 | 39 | 3 | 9 | 18 | 8 | 34 |
| von Engelhardt | 2017 | IV | 33 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 24 | SD 9 + | SD 9 + | 12 | 21 | 29 | SD 23 + | SD 23 + |
| von Knoch | 2006 | IV | 45 | Thin Trochleoplasty | 22.2 | 15 | 31 | 16 | 22 | ] | 48 | 168 |
| Outcomes | Meta-Analysis | Tests for Heterogeneity | Egger’s Test | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pooled Estimate | 95% Confidence Interval | p-Value | I2 | p-Value | ||||
| Kujala | SMD | 1.74 | 1.31 | - | 2.17 | 0.000 | 90.6% | 0.158 |
| IKDC | SMD | 1.20 | 0.90 | - | 1.50 | 0.032 | 59.1% | 0.169 |
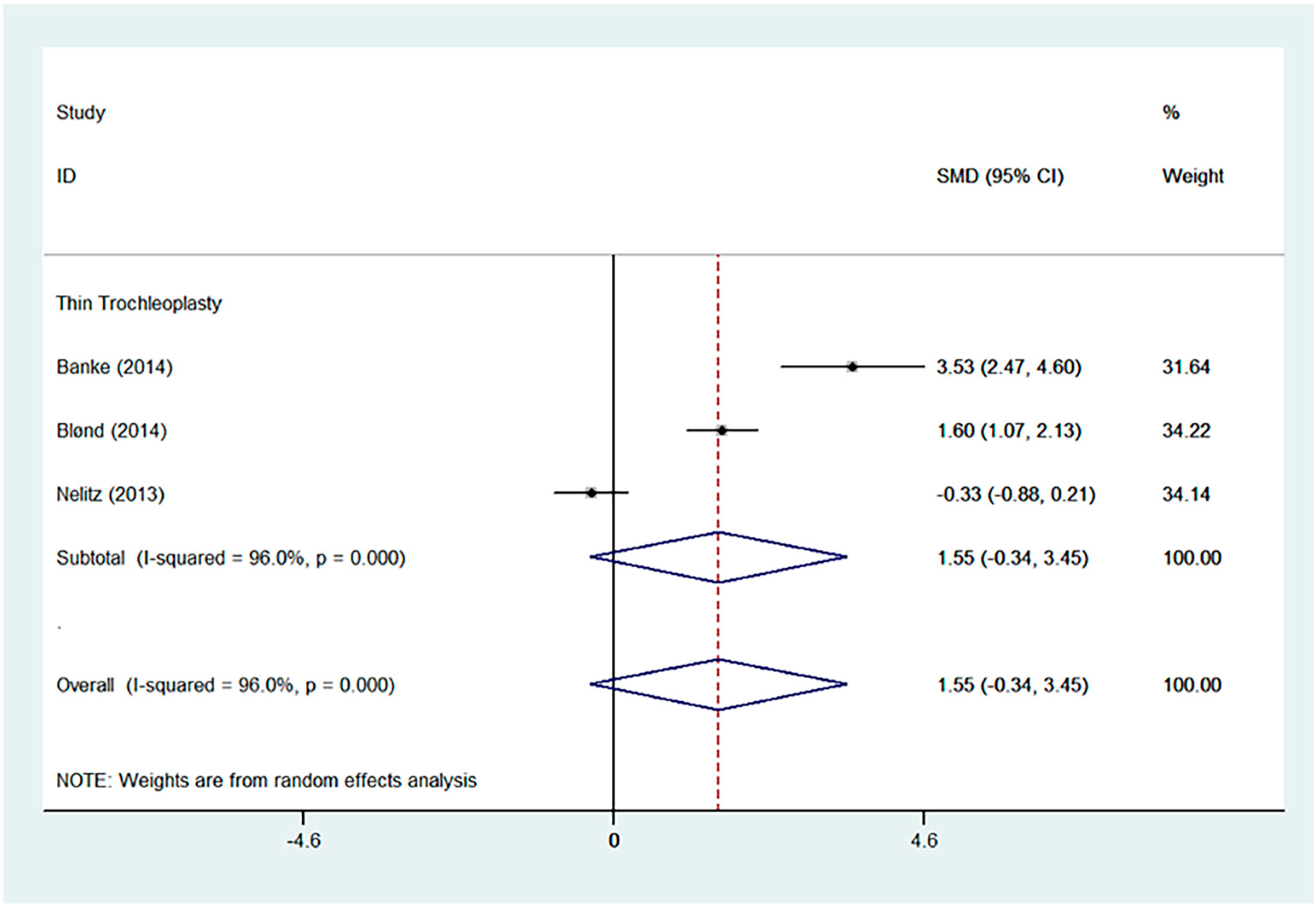
| Tegner | SMD | 1.55 | −0.34 | - | 3.45 | 0.000 | 96.0% | 0.828 |
| Lysholm | SMD | 1.65 | 0.99 | - | 2.32 | 0.003 | 82.5% | 0.960 |
| Dislocation | RR | 0.04 | 0.03 | - | 0.07 | 0.125 | 27.4% | 0.999 |
| Satisfaction | RR | 67.94 | 36.13 | - | 127.76 | 1.000 | 0.0% | 0.999 |
| Author | Year | Sample Size (Number of Knees) | Pain | Residual Symptoms and Signs | Complications | Re-Operations |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Banke | 2014 | 18 | VAS 5.6 (2.8) to 2.5 (1.7) | NR | 1 over tight MPFLR (5.6%) 2 arthrofibrosis (11.1%) | 1 re-tension MPFLR 2 arthroscopic arthrolysis |
| Blønd | 2014 | 29 | NR | 2 residual instability, J sign positive (6.9%) | 2 symptomatic subluxations (6.9%) 3 anterior knee pain secondary to tight lateral retinaculum (10.3%) | 2 medialisation of tibial tubercle 3 lateral release |
| Camathias | 2016 | 50 | NR | 6 J sign positive (12%) 8 apprehension positive (16%) | 1 dislocation (2%) 4 arthrofibrosis (8%) | 1 revision with retrochleoplasty, MPFL-plasty 4 arthroscopic arthrolysis |
| Dejour | 2013 | 24 | Pain decreased in 72% of cases, unchanged, or increased in 28% | 6 apprehension positive (25%) | No patellofemoral osteoarthritis No postoperative stiffness No dislocation | 1 removal of hardware after staple breakage |
| Donell | 2006 | 17 | NR | 7 apprehension positive | 11 crepitus | 5 arthroscopic arthrolysis 1 re-medial reefing 1 patellar chondroplasty 1 autologous chondrocyte implantation in lateral femoral condyle 1 removal of loose screw head 4 removal of screws only |
| Falkowski | 2017 | 22 | NR | 6 apprehension positive | NR | NR |
| Fucentese | 2011 | 44 | VAS 8 (3–10) to 8 (3–10); p = 0.027) | 11 apprehension positive (25%) 11 residual instability (25%) | 1 dislocation (2.3%) 1 transient postoperative femoral nerve palsy after peripheral anaesthesia (2.3%) 1 poor wound healing (2.3%) 1 CRPS (2.3%) | 1 MPFL reconstruction 1 anteromedialization of tibial tuberosity |
| Koëter | 2007 | 19 | 13 patients reported pain relieved at rest 12 patients reported pain relieved during activities | 1 residual instability | 2 progression of osteoarthritis 1 post-operative haematoma 2 subluxation after rotational trauma 1 failure (persisting pain requiring revision arthroplasty) No arthrofibrosis | 1 patellofemoral arthroplasty 1 evacuation of post-operative haematoma 1 tibial tubercle repositioning |
| McNamara | 2015 | 107 | 34% | 34.3–74.5% apprehension positive 12 residual instability | 1 DVT 1 pulmonary embolism 8 arthrofibrosis 4 superficial wound infection 4 crepitus | 10 MPFL-R 8 arthrolysis 2 removal of loose screw head 1 arthroscopic debridement 2 patelloplasty |
| Metcalfe | 2017 | 199 | 25% had residual pain | 12 residual instability 2 quadriceps weakness | 16 dislocation 2 arthrofibrosis 1 over tight MPFLR 1 partial detachment of cartilage flap 1 recurrent knee effusion 2 intraarticular loose bodies 1 CRPS 1 foot drop | 9 MPFLR 7 TTO 2 MUA 1 release of tight MPFL reconstruction 6 arthroscopy 2 removal of TTO screw |
| Nelitz | 2013 | 26 | VAS 3 (1–7) to 1 (0–5); p =< 0.01 | 1 apprehension positive | 1 poor post-operative knee flexion requiring prolonged rehabilitation to achieve full range of motion No recurrent dislocation No wound infection 3 patellofemoral crepitus | NR |
| Neumann | 2014 | 46 | NR | No apprehension | No dislocation 3 with preexisting patellofemoral osteoarthritis showed radiological progression of osteoarthritis | NR |
| Ntagiopoulos | 2013 | 31 | 75% reported decrease in pain | No residual instability 6 apprehension positive | No dislocation recurrence 2 hardware (staple) breakage 1 DVT No patellofemoral arthritis | 2 arthroscopic removal of hardware |
| Pesenti | 2017 | 27 | 3 had occasional knee pain after prolonged physical activity. The rest of the patients were pain free on follow up. | 2 residual instability | No dislocation 4 developed lateral patellofemoral osteoarthritis | NR |
| Rouanet | 2015 | 34 | Out of 27 patients without revision, 18 had no pain or only occasional pain, 1 had significant pain | Out of 27 patients without revision, 10 residual instability 3 apprehension positive | 7 failures (6 osteoarthritis, 1 gives way frequently) 8 arthrofibrosis Pre-operatively, 10 had patellofemoral osteoarthritis (none > Iwano 2) Post-operatively, 33 had patellofemoral osteoarthritis [20 (65%) > Iwano 2)] | 3 total knee arthroplasty 3 patellofemoral arthroplasty 1 tibial tubercle transfer 6 MUA 2 arthroscopic release |
| Schöttle | 2005 | 19 | Pain improved in 12 knees and worsened in 2 knees | 4 apprehension positive | No dislocation | NR |
| Thaunat | 2011 | 19 | All but 1 patient had slight pain on follow up. Pain was generally localised at the level of the tibial tubercle screw site for those operated for pain-free instability. Significant pain improvement was reported in all but one patient for those with pain preoperatively. | 6 apprehension positive (31.6%) | 2 dislocation (10.5%) 1 arthrofibrosis (5.3%) 9 patellofemoral crepitus (50.0%) | 1 arthroscopic arthrolysis 1 arthroscopic supratrochlear exostosectomy 8 removal of screws from anterior tibial tubercle and trochlea 2 for tibial tubercle pseudoarthrosis |
| Utting | 2008 | 59 | 8 had residual pain | 8 had continued swelling or crepitation (14.8%) No recurrent instability | 2 superficial infection 1 arthrofibrosis 1 traumatic dislocation 1 anaphylaxis to prophylactic antibiotic | 1 MUA |
| Verdonk | 2005 | 13 | 2 persistent retropatellar pain (15.4%) | 7 patellofemoral crepitus (53.8%) | No dislocation 5 arthrofibrosis 3 impingement of fixation material 1 complete failure | 5 MUA 3 arthroscopic removal of fixation material 1 total knee arthroplasty |
| von Engelhardt | 2017 | 33 | VAS 4.8 (2.0) to 1.3 (3.4); p < 0.0001) | 2 avoidance behaviour (6.1%) | 5 arthrofibrosis (15.2%) | 2 arthroscopic arthrolysis (6.1%) |
| von Knoch | 2006 | 45 | Post-operative pain increased in 15 knees (33.4%), remained unchanged in 4 (8.8%) and improved in 22 (49%). 4 knees (8.8%) which were pain free pre-operatively remained pain free post-operatively | No apprehension 1 residual instability | 1 patella baja No dislocation Development of patellofemoral osteoarthritis in 22 of 31 knees (72.7%) and tibiofemoral osteoarthritis in 4 of 33 knees (15.2%) with no pre-existing osteoarthritis radiologically prior to surgery 28 patellofemoral crepitus (62.2%) | 1 Elmslie–Trillat procedure for distal realignment |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tan, S.S.H.; Law, G.W.; Kim, S.S.; Sethi, E.; Lim, A.K.S.; Hui, J.H.P. Trochleoplasty Provides Good Outcomes for Recurrent Patellofemoral Dislocations with No Clear Superiority across Different Techniques. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13103009
Tan SSH, Law GW, Kim SS, Sethi E, Lim AKS, Hui JHP. Trochleoplasty Provides Good Outcomes for Recurrent Patellofemoral Dislocations with No Clear Superiority across Different Techniques. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(10):3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13103009
Chicago/Turabian StyleTan, Sharon Si Heng, Gin Way Law, Sunny Sunwoo Kim, Ervin Sethi, Andrew Kean Seng Lim, and James Hoi Po Hui. 2024. "Trochleoplasty Provides Good Outcomes for Recurrent Patellofemoral Dislocations with No Clear Superiority across Different Techniques" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 10: 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13103009
APA StyleTan, S. S. H., Law, G. W., Kim, S. S., Sethi, E., Lim, A. K. S., & Hui, J. H. P. (2024). Trochleoplasty Provides Good Outcomes for Recurrent Patellofemoral Dislocations with No Clear Superiority across Different Techniques. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(10), 3009. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13103009