High Prevalence of the Lung Ultrasound Interstitial Syndrome in Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Normal HRCT and Lung Function—A Pilot Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
2.1. Patients and Inclusion
2.2. Intervention
2.2.1. Lung Ultrasound
2.2.2. Echocardiography and High-Resolution Computed Tomography
2.2.3. Pulmonary Functional Test and Cardiopulmonary Exercise Testing
2.3. Number of Subjects Required
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
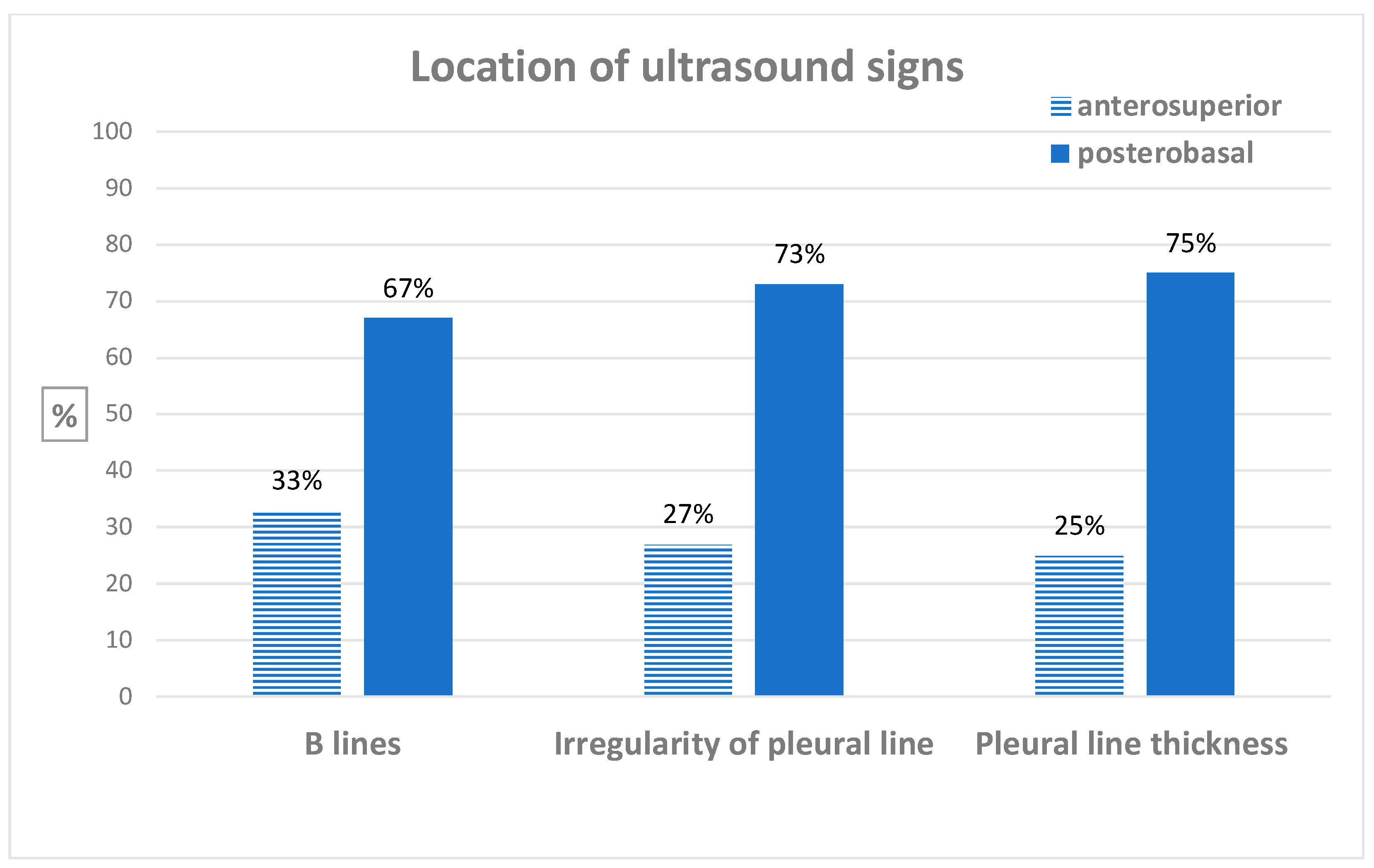
3.2. Diagnosis of Ultrasound Interstitial Syndrome and Inter-Reader Agreement
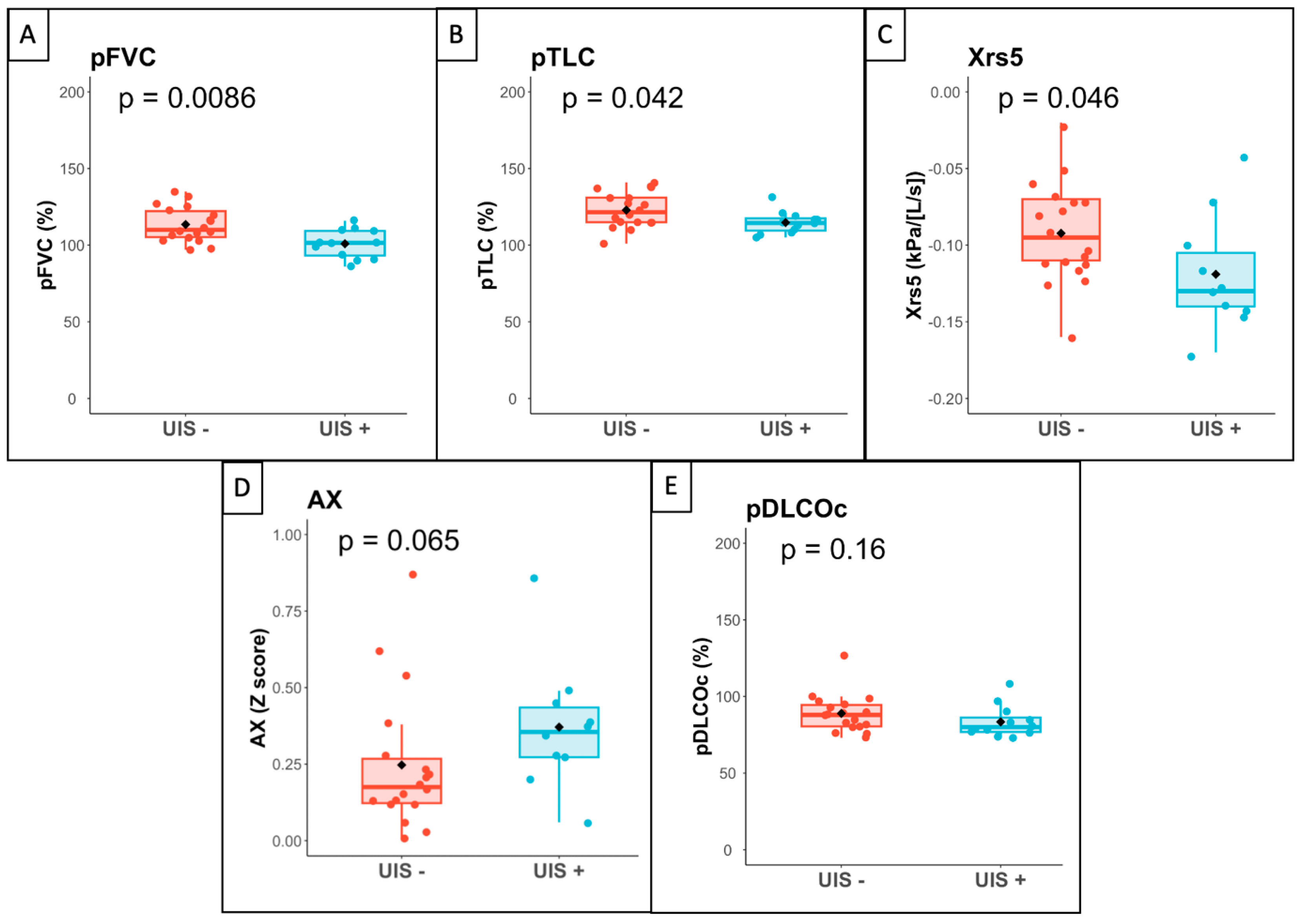
3.3. Association between Ultrasound Interstitial Syndrome and Lung Function
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thoreau, B.; Chaigne, B.; Renaud, A.; Mouthon, L. Pathophysiology of systemic sclerosis. Presse Medicale 1983 2021, 50, 104087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhai, M.; Meune, C.; Boubaya, M.; Avouac, J.; Hachulla, E.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Riemekasten, G.; Airò, P.; Joven, B.; Vettori, S.; et al. Mapping and predicting mortality from systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2017, 76, 1897–1905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perelas, A.; Silver, R.M.; Arrossi, A.V.; Highland, K.B. Systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Lancet Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 304–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann-Vold, A.-M.; Maher, T.M.; Philpot, E.E.; Ashrafzadeh, A.; Barake, R.; Barsotti, S.; Bruni, C.; Carducci, P.; Carreira, P.E.; Castellví, I.; et al. The identification and management of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: Evidence-based European consensus statements. Lancet Rheumatol. 2020, 2, e71–e83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeMizio, D.J.; Bernstein, E.J. Detection and Classification of Systemic Sclerosis-Related Interstitial Lung Disease: A Review. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2019, 31, 553–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radić, M.; Đogaš, H.; Gelemanović, A.; Jurić Petričević, S.; Škopljanac, I.; Radić, J. Pulmonary Ultrasonography in Systemic Sclerosis-Induced Interstitial Lung Disease-A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diagnostics 2023, 13, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sperandeo, M.; De Cata, A.; Molinaro, F.; Trovato, F.; Catalano, D.; Simeone, A.; Varriale, A.; Martines, G.; Trovato, G. Ultrasound signs of pulmonary fibrosis in systemic sclerosis as timely indicators for chest computed tomography. Scand. J. Rheumatol. 2015, 44, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinal-Fernandez, I.; Pallisa-Nuñez, E.; Selva-O’Callaghan, A.; Castella-Fierro, E.; Simeon-Aznar, C.P.; Fonollosa-Pla, V.; Vilardell-Tarres, M. Pleural irregularity, a new ultrasound sign for the study of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis and antisynthetase syndrome. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Fairchild, R.; Chung, M.; Yang, D.; Sharpless, L.; Li, S.; Chung, L. Development and Assessment of Novel Lung Ultrasound Interpretation Criteria for the Detection of Interstitial Lung Disease in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res. 2021, 73, 1338–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; Matucci-cerinic, M.; Naden, R.P.; Medsger, T.A.; Carreira, P.E.; et al. 2013 Classification Criteria for Systemic Sclerosis: An American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism Collaborative Initiative. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2013, 65, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galiè, N.; Humbert, M.; Vachiery, J.-L.; Gibbs, S.; Lang, I.; Torbicki, A.; Simonneau, G.; Peacock, A.; Vonk Noordegraaf, A.; Beghetti, M.; et al. 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: The Joint Task Force for the Diagnosis and Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and the European Respiratory Society (ERS): Endorsed by: Association for European Paediatric and Congenital Cardiology (AEPC), International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation (ISHLT). Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 903–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gutierrez, M.; Salaffi, F.; Carotti, M.; Tardella, M.; Pineda, C.; Bertolazzi, C.; Bichisecchi, E.; Filippucci, E.; Grassi, W. Utility of a simplified ultrasound assessment to assess interstitial pulmonary fibrosis in connective tissue disorders—preliminary results. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2011, 13, R134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tardella, M.; Di Carlo, M.; Carotti, M.; Filippucci, E.; Grassi, W.; Salaffi, F. Ultrasound B-lines in the evaluation of interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis. Medicine 2018, 97, e0566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legué, S.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Plantier, L.; Bayeh, B.A.; Morel, H.; Mangiapan, G.; Flament, T. ThOracic Ultrasound in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis Evolution (TOUPIE): Research protocol of a multicentric prospective study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e039078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- King, G.G.; Bates, J.; Berger, K.I.; Calverley, P.; de Melo, P.L.; Dellacà, R.L.; Farré, R.; Hall, G.L.; Ioan, I.; Irvin, C.G.; et al. Technical standards for respiratory oscillometry. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1900753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quanjer, P.H.; Stanojevic, S.; Cole, T.J.; Baur, X.; Hall, G.L.; Culver, B.H.; Enright, P.L.; Hankinson, J.L.; Ip, M.S.M.; Zheng, J.; et al. Multi-ethnic reference values for spirometry for the 3-95-yr age range: The global lung function 2012 equations. Eur. Respir. J. 2012, 40, 1324–1343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stanojevic, S.; Graham, B.L.; Cooper, B.G.; Thompson, B.R.; Carter, K.W.; Francis, R.W.; Hall, G.L.; Global Lung Function Initiative TLCO Working Group; Global Lung Function Initiative (GLI) TLCO. Official ERS technical standards: Global Lung Function Initiative reference values for the carbon monoxide transfer factor for Caucasians. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oostveen, E.; Boda, K.; van der Grinten, C.P.M.; James, A.L.; Young, S.; Nieland, H.; Hantos, Z. Respiratory impedance in healthy subjects: Baseline values and bronchodilator response. Eur. Respir. J. 2013, 42, 1513–1523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- American Thoracic Society; American College of Chest Physicians ATS/ACCP Statement on cardiopulmonary exercise testing. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 211–277. [CrossRef]
- Conway, A.; Tipton, E.; Liu, W.-H.; Conway, Z.; Soalheira, K.; Sutherland, J.; Fingleton, J. Accuracy and precision of transcutaneous carbon dioxide monitoring: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Thorax 2019, 74, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leprat, T.; Ivanes, F.; Bernard, A.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Plantier, L. Transcutaneous PCO2 -based dead space ventilation at submaximal exercise accurately discriminates healthy controls from patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin. Physiol. Funct. Imaging 2021, 41, 253–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D’Angelo, W.A.; Fries, J.F.; Masi, A.T.; Shulman, L.E. Pathologic observations in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). A study of fifty-eight autopsy cases and fifty-eight matched controls. Am. J. Med. 1969, 46, 428–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaminsky, D.A.; Simpson, S.J.; Berger, K.I.; Calverley, P.; de Melo, P.L.; Dandurand, R.; Dellacà, R.L.; Farah, C.S.; Farré, R.; Hall, G.L.; et al. Clinical significance and applications of oscillometry. Eur. Respir. Rev. Off. J. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2022, 31, 210208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotes, J.E.; Chinn, D.J.; Miller, M.R. Lung Function: Physiology, Measurement and Application in Medicine, 6th ed.; Blackwell Pub: Malden, MA, USA; Oxford, UK, 2006; 636p, ISBN 978-0-632-06493-9. [Google Scholar]
- Graham, B.L.; Brusasco, V.; Burgos, F.; Cooper, B.G.; Jensen, R.; Kendrick, A.; MacIntyre, N.R.; Thompson, B.R.; Wanger, J. 2017 ERS/ATS standards for single-breath carbon monoxide uptake in the lung. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 49, 1600016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nihtyanova, S.I.; Sari, A.; Harvey, J.C.; Leslie, A.; Derrett-Smith, E.C.; Fonseca, C.; Ong, V.H.; Denton, C.P. Using Autoantibodies and Cutaneous Subset to Develop Outcome-Based Disease Classification in Systemic Sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2020, 72, 465–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, M.; Heal, C.; Henes, J.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Distler, J.H.W.; Airò, P.; Müller-Ladner, U.; Hunzelmann, N.; Kerzberg, E.; Rudnicka, L.; et al. Digital pitting scars are associated with a severe disease course and death in systemic sclerosis: A study from the EUSTAR cohort. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 1141–1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magnant, J.; de Monte, M.; Guilmot, J.-L.; Lasfargues, G.; Diot, P.; Asquier, E.; Degenne, D.; Boissinot, E.; Diot, E. Relationship between occupational risk factors and severity markers of systemic sclerosis. J. Rheumatol. 2005, 32, 1713–1718. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Zanatta, E.; Huscher, D.; Ortolan, A.; Avouac, J.; Airò, P.; Balbir-Gurman, A.; Siegert, E.; Cerinic, M.M.; Cozzi, F.; Riemekasten, G.; et al. Phenotype of limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis patients with positive anti-topoisomerase I antibodies: Data from EUSTAR cohort. Rheumatology 2022, 61, 4786–4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thoreau, B.; Eustache, M.; Fievet, A.; Lasfargues, G.; Plantier, L.; Diot, E. Independent Association Between Occupational Exposure and Decline of FVC in Systemic Sclerosis: A Multicenter Recruitment Retrospective Cohort Study. Chest 2022, 161, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laursen, C.B.; Clive, A.; Hallifax, R.; Pietersen, P.I.; Asciak, R.; Davidsen, J.R.; Bhatnagar, R.; Bedawi, E.O.; Jacobsen, N.; Coleman, C.; et al. European Respiratory Society statement on thoracic ultrasound. Eur. Respir. J. 2021, 57, 2001519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, H.Q.; Zhang, W.W.; Sun, D.S.; Chen, X.M.; Yuan, S.F.; Gong, Z.H.; Liu, L. A simplified lung ultrasound for the diagnosis of interstitial lung disease in connective tissue disease: A meta-analysis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2019, 21, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammadi, A.; Pourahmadazar, R.; Broofeh, B.; Oshnoei, S.; Ghasemi-Rad, M. Comparison of a new, modified lung ultrasonography technique with high-resolution CT in the diagnosis of the alveolo-interstitial syndrome of systemic scleroderma. Med. Ultrason. 2014, 16, 27–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plantier, L.; Cazes, A.; Dinh-Xuan, A.-T.; Bancal, C.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Crestani, B. Physiology of the lung in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2018, 27, 170062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandmeier, B.; Jäger, V.K.; Nagy, G.; Carreira, P.E.; Tzankov, A.; Widuchowska, M.; Antic, M.; Distler, O.; Reichert, H.; Distler, J.H.W.; et al. Autopsy versus clinical findings in patients with systemic sclerosis in a case series from patients of the EUSTAR database. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2015, 33, S75–S79. [Google Scholar]
- Vandecasteele, E.; Melsens, K.; Vanhaecke, A.; Blockmans, D.; Bonroy, C.; Carton, C.; Deschepper, E.; De Keyser, F.; Houssiau, F.; Piette, Y.; et al. Incidence, prevalence and long-term progression of Goh algorithm rated interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis in two independent cohorts in flanders: A retrospective cohort study. Semin. Arthritis Rheum. 2021, 51, 969–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergamasco, A.; Hartmann, N.; Wallace, L.; Verpillat, P. Epidemiology of systemic sclerosis and systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease. Clin. Epidemiol. 2019, 11, 257–273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schneider, F.; Gruden, J.; Tazelaar, H.D.; Leslie, K.O. Pleuropulmonary pathology in patients with rheumatic disease. Arch. Pathol. Lab. Med. 2012, 136, 1242–1252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoneff, E.R.; Baker, K.; Sweeny, A.; Keijzers, G.; Sanderson, J.; Watkins, S. The prevalence of lung surface abnormalities in a healthy population as detected by a screening lung ultrasound protocol: Comparison between young and older volunteers. Australas. J. Ultrasound Med. 2019, 22, 129–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, A.; Rossi Fanelli, F.; Lucci, S.; Barilaro, G.; Quarta, S.; Barbano, B.; Giovannetti, A.; Amoroso, A.; Rosato, E. Lung ultrasound in systemic sclerosis: Correlation with high-resolution computed tomography, pulmonary function tests and clinical variables of disease. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2016, 11, 213–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohammad Reza Beigi, D.; Pellegrino, G.; Loconte, M.; Landini, N.; Mattone, M.; Paone, G.; Truglia, S.; Di Ciommo, F.R.; Bisconti, I.; Cadar, M.; et al. Lung ultrasound compared to computed tomography detection and automated quantification of systemic sclerosis-associated interstitial lung disease: Preliminary study. Rheumatology 2023, 63, 1240–1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Overall N = 30 | Patients with Ultrasound Interstitial Syndrome N = 12 | Patients without Ultrasound Interstitial Syndrome N = 18 | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sex: Female | 27 (90%) | 11 (92%) | 16 (89%) | 0.999 |
| Age (years) | 58 (46, 64) | 47 (36, 54) | 60 (58, 67) | 0.003 |
| Age onset (years) | 48 (38, 58) | 37 (22, 50) | 53 (43, 59) | 0.009 |
| Time from Raynaud phenomenon to SSc (months) | 26 (4, 148) | 9 (2, 26) | 114 (14, 294) | 0.016 |
| mRSS | 5 (3, 6) | 5 (4, 7) | 5 (3, 5) | 0.617 |
| Puffy fingers | 21 (70%) | 6 (50%) | 15 (83%) | 0.102 |
| Sclerodactylia | 9 (30%) | 6 (50%) | 3 (17%) | 0.102 |
| Digital ulcer | 2 (7%) | 2 (17%) | 0 (0%) | 0.152 |
| Pitting scars | 10 (33%) | 7 (58%) | 3 (17%) | 0.045 |
| Telangiectasias | 23 (77%) | 9 (75%) | 14 (78%) | 0.999 |
| Anti-centromere Antibodies | 24 (80%) | 10 (83%) | 14 (78%) | 0.999 |
| Anti-topoisomerase I Antibodies | 3 (11%) | 1 (10%) | 2 (11%) | 0.999 |
| Pulmonary function tests | ||||
| FEV1 (% pred) | 108 (101, 116) | 99 (92, 106) | 108 (104, 122) | 0.010 |
| FVC (% pred) | 106 (99, 111) | 102 (93, 109) | 110 (105, 122) | 0.009 |
| TLC (% pred) | 117 (113, 127) | 114 (110, 118) | 122 (115, 131) | 0.042 |
| DLCOc (% pred) | 84 (78, 92) | 80 (77, 86) | 88 (80, 94) | 0.162 |
| Xrs5 (Z-score) | −0.11 (−0.13, −0.07) | 0.16 (−0.41, 0.82) | 1.02 (0.76, 1.34) | 0.018 |
| Rrs5 (Z-score) | 0.84 (0.26, 1.22) | 0.59 (0.41, 1.06) | 0.21 (0.02, 0.81) | 0.44 |
| AX (Z-score) | −0.64 (−1.31, 0.22) | 0.200 (−0.46, 0.43) | −0.87 (−1.54, −0.59) | 0.016 |
| Fres (Z-score) | 2.72 (2.47, 3.24) | 3.11 (2.78, 3.32) | 2.57 (2.41, 2.94) | 0.049 |
| N = 30 | |
|---|---|
| Reader 1 | |
| Number of B-lines | 2.5 (1.0–6.0) |
| Number of patients with sum of B-lines > 10 | 4 (13.3%) |
| Pleural line irregularity score (%) | 14.3 (7.1–13.3) |
| Number of patients with irregularity > 16% | 5 (16.7%) |
| Pleural line thickness (mm) | 1.5 (1.4–1.6) |
| Number of patients with thickness > 3 mm | 3 (10.0%) |
| Number of patients with ultrasound interstitial syndrome | 12 (40.0%) |
| Reader 2 | |
| Number of B-lines | 2.0 (1.0–4.0) |
| Number of patients with sum of B-lines > 10 | 3 (10.0%) |
| Pleural line irregularity score (%) | 10.7 (7.1–19.6) |
| Number of patients with irregularity > 16% | 8 (26.7%) |
| Pleural line thickness (mm) | 1.6 (1.4–1.6) |
| Number of patients with thickness > 3 mm | 2 (6.7%) |
| Number of patients with ultrasound interstitial syndrome | 11 (36.7%) |
| Kappa Coefficient | ICC | 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number of B-lines | |||
| Ultrasound interstitial syndrome based on B-lines | 0.84 | - | 0.53 to 1.00 |
| Absolute B line quotation | - | 0.77 | 0.76 to 0.77 |
| Pleural irregularity | |||
| Ultrasound interstitial syndrome based on irregularity | 0.71 | - | 0.41 to 1.00 |
| Absolute irregularity quotation | - | 0.57 | 0.56 to 0.59 |
| Pleural thickness | |||
| Ultrasound interstitial syndrome based on thickness | 0.78 | - | 0.37 to 1.00 |
| Absolute pleural thickness quotation | - | 0.32 | 0.31 to 0.33 |
| Total ultrasound interstitial syndrome assessment | 0.93 | - | 0.79 to 1.00 |
| CPET Data | Coefficient | p 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Peak load | 16.8908 | 0.355 |
| Peak VO2 | 0.2238 | 0.333 |
| VE/VCO2 slope | −3.4572 | 0.166 |
| Peak SpO2 | 0.1689 | 0.566 |
| PtcCO2-based. Vd/Vt VT1 | −0.0143 | 0.653 |
| Ventilatory reserve | −16.7918 | 0.023 |
| Vd/Vt VT1 | −0.0285 | 0.329 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mercier, C.; Thoreau, B.; Flament, T.; Legué, S.; Pearson, A.; Jobard, S.; Marchand-Adam, S.; Plantier, L.; Diot, E. High Prevalence of the Lung Ultrasound Interstitial Syndrome in Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Normal HRCT and Lung Function—A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13102885
Mercier C, Thoreau B, Flament T, Legué S, Pearson A, Jobard S, Marchand-Adam S, Plantier L, Diot E. High Prevalence of the Lung Ultrasound Interstitial Syndrome in Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Normal HRCT and Lung Function—A Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(10):2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13102885
Chicago/Turabian StyleMercier, Camille, Benjamin Thoreau, Thomas Flament, Sylvie Legué, Arthur Pearson, Stephanie Jobard, Sylvain Marchand-Adam, Laurent Plantier, and Elisabeth Diot. 2024. "High Prevalence of the Lung Ultrasound Interstitial Syndrome in Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Normal HRCT and Lung Function—A Pilot Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 10: 2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13102885
APA StyleMercier, C., Thoreau, B., Flament, T., Legué, S., Pearson, A., Jobard, S., Marchand-Adam, S., Plantier, L., & Diot, E. (2024). High Prevalence of the Lung Ultrasound Interstitial Syndrome in Systemic Sclerosis Patients with Normal HRCT and Lung Function—A Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(10), 2885. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13102885






