Beyond VEGF: Angiopoietin–Tie Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Retinopathy
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. The Angiopoietins and Tie Signaling Pathway
2.1. The Angiopoietins
2.2. TIE Receptors
2.3. Vascular Endothelial-Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase (VE-PTP)
2.4. Ang/Tie Signaling Pathway in the Retina
3. Molecular Mechanisms and Pathophysiology of Diabetic Retinopathy
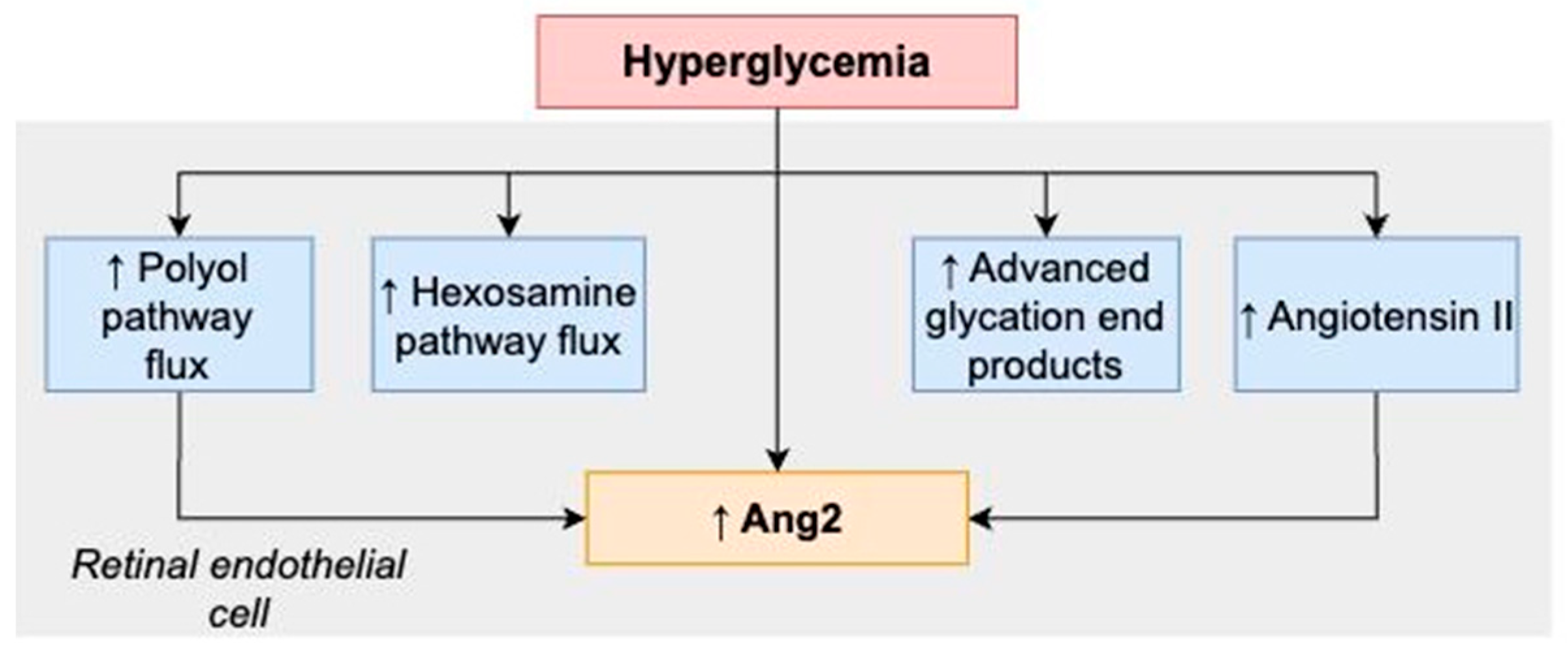
3.1. Effects of Hyperglycemia and Ang–Tie Signaling
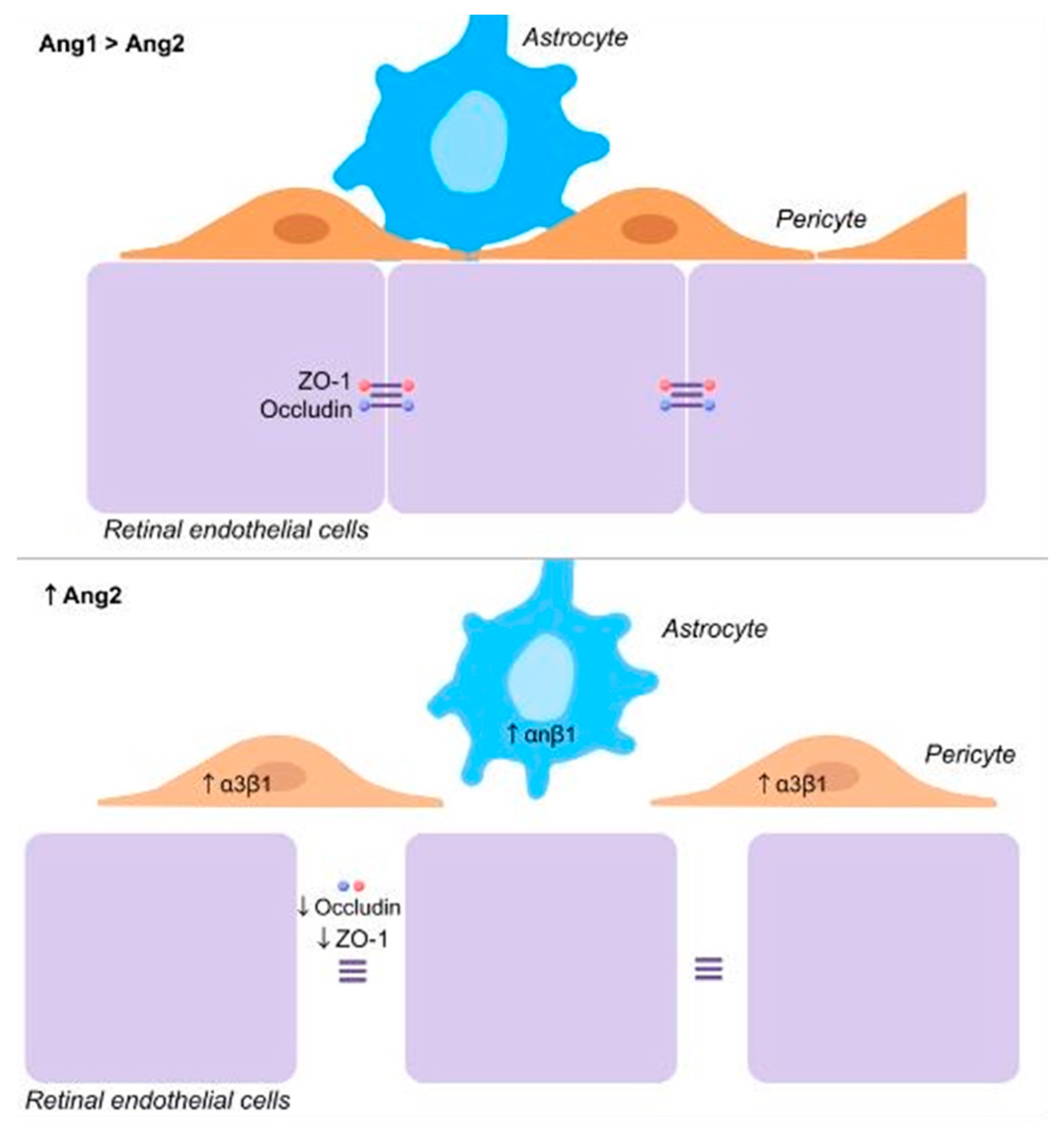
3.2. Ang–Tie Signaling and Blood Retinal Barrier
3.3. Vascular Regression and Ang–Tie Signaling
3.4. Retinal Neovascularization and Ang–Tie Signaling
3.5. Diabetic Patients and Ang–Tie Signaling
4. Targeting the Ang–Tie Signaling Pathway in DR
4.1. Combination Therapy of Anti-Ang2 and Anti-VEGF
- Faricimab (RO6867461, RG7716, Roche)
- ii.
- Nesvacumab (REGN910-3) plus aflibercept
4.2. VE-PTP Inhibitors
- Razuprotafib
- ii.
- ARP-1536
4.3. Integrin Binding Peptide
- Gersizangitide (AXT107)
4.4. Surrobodies
- RO101
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ogurtsova, K.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Huang, Y.; Linnenkamp, U.; Guariguata, L.; Cho, N.H.; Cavan, D.; Shaw, J.E.; Makaroff, L.E. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates for the prevalence of diabetes for 2015 and 2040. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2017, 128, 40–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.; Moss, S.E. Visual impairment in diabetes. Ophthalmology 1984, 91, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, R.; Airey, M.; Baxter, H.; Forrester, J.; Kennedy-Martin, T.; Girach, A. Epidemiology of diabetic retinopathy and macular oedema: A systematic review. Eye 2004, 18, 963–983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.M.; Brown, G.C.; Sharma, S.; Shah, G. Utility values and diabetic retinopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 128, 324–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javitt, J.C.; Aiello, L.P.; Chiang, Y.; Ferris, F.L., 3rd; Canner, J.K.; Greenfield, S. Preventive eye care in people with diabetes is cost-saving to the federal government. Implications for health-care reform. Diabetes Care 1994, 17, 909–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Javitt, J.C.; Aiello, L.P. Cost-effectiveness of detecting and treating diabetic retinopathy. Ann. Intern. Med. 1996, 124, 164–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, T.E.; Wong, T.Y. Diabetic retinopathy: Looking forward to 2030. Front. Endocrinol 2023, 13, 1077669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engerman, R.L.; Kern, T.S. Retinopathy in animal models of diabetes. Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 1995, 11, 109–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klein, R.; Klein, B.E.; Moss, S.E.; Cruickshanks, K.J. The Wisconsin Epidemiologic Study of diabetic retinopathy, X.I.V. Ten-year incidence and progression of diabetic retinopathy. Arch. Ophthalmol. 1994, 112, 1217–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Stewart, J.M. Pathophysiology of diabetic macular edema. Int. Ophthalmol. Clin. 2009, 49, 270–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Acon, D.; Wu, A.; Wu, M. Vascular endothelial growth factor inhibition and proliferative diabetic retinopathy, a changing treatment paradigm? Taiwan J. Ophthalmol. 2019, 9, 216–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, M.B.; Afzal, A.; Spoerri, P.; Pan, H.; Shaw, L.C.; Mames, R.N. The role of growth factors in the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Expert Opin. Investig. Drugs 2004, 13, 1275–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Owen, L.A.; Hartnett, M.E. Soluble mediators of diabetic macular edema: The diagnostic role of aqueous VEGF and cytokine levels in diabetic macular edema. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2013, 13, 476–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, D.M.; Schmidt-Erfurth, U.; Do, D.V.; Holz, F.G.; Boyer, D.S.; Midena, E.; Heier, J.S.; Terasaki, H.; Kaiser, P.K.; Marcus, D.M.; et al. Intravitreal Aflibercept for Diabetic Macular Edema: 100-Week Results From the VISTA and VIVID Studies. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 2044–2052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Brown, D.M.; Marcus, D.M.; Boyer, D.S.; Patel, S.; Feiner, L.; Gibson, A.; Sy, J.; Rundle, A.C.; Hopkins, J.J.; et al. Ranibizumab for diabetic macular edema: Results from 2 phase III randomized trials: RISE and RIDE. Ophthalmology 2012, 119, 789–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rajendram, R.; Fraser-Bell, S.; Kaines, A.; Michaelides, M.; Hamilton, R.D.; Esposti, S.D.; Peto, T.; Egan, C.; Bunce, C.; Leslie, R.D.; et al. A 2-year prospective randomized controlled trial of intravitreal bevacizumab or laser therapy (BOLT) in the management of diabetic macular edema: 24-month data: Report 3. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2012, 130, 972–979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arevalo, J.F.; Lasave, A.F.; Wu, L.; Acon, D.; Farah, M.E.; Gallego-Pinazo, R.; Alezzandrini, A.A.; Fortuna, V.; Quiroz-Mercado, H.; Salcedo-Villanueva, G.; et al. Intravitreal bevacizumab for diabetic macular oedema: 5-year results of the Pan-American Collaborative Retina Study group. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2016, 100, 1605–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ciulla, T.A.; Bracha, P.; Pollack, J.; Williams, D.F. Real-world Outcomes of Anti-Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Therapy in Diabetic Macular Edema in the United States. Ophthalmol. Retin. 2018, 2, 1179–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, J.A.; Glassman, A.R.; Ayala, A.R.; Jampol, L.M.; Bressler, N.M.; Bressler, S.B.; Brucker, A.J.; Ferris, F.L.; Hampton, G.R.; Jhaveri, C.; et al. Aflibercept, Bevacizumab, or Ranibizumab for Diabetic Macular Edema: Two-Year Results from a Comparative Effectiveness Randomized Clinical Trial. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1351–1359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Aldrich, T.H.; Jones, P.F.; Acheson, A.; Compton, D.L.; Jain, V.; Ryan, T.E.; Bruno, J.; Radziejewski, C.; Maisonpierre, P.C.; et al. Isolation of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, by secretion-trap expression cloning. Cell 1996, 87, 1161–1169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maisonpierre, P.C.; Goldfarb, M.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Gao, G. Distinct rat genes with related profiles of expression define a TIE receptor tyrosine kinase family. Oncogene 1993, 8, 1631–1637. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Maisonpierre, P.C.; Suri, C.; Jones, P.F.; Bartunkova, S.; Wiegand, S.J.; Radziejewski, C.; Compton, D.; McClain, J.; Aldrich, T.H.; Papadopoulos, N.; et al. Angiopoietin-2, a natural antagonist for Tie2 that disrupts in vivo angiogenesis. Science 1997, 277, 55–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.W.; Yun, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, K.W.; Cho, C.H.; Kim, J.H. Angiopoietin 2 induces pericyte apoptosis via alpha3beta1 integrin signaling in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 2014, 63, 3057–3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.H.; Park, S.W.; Kim, J.H.; Park, Y.J.; Cho, C.H.; Kim, J.H. Angiopoietin 2 induces astrocyte apoptosis via alphavbeta5-integrin signaling in diabetic retinopathy. Cell Death. Dis. 2016, 7, e2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Chen, T.; Li, Y.; You, J.; Deng, X.; Chen, N.; Li, T.; Zheng, Y.; Li, R.; Luo, M.; et al. Glycation of Tie-2 Inhibits Angiopoietin-1 Signaling Activation and Angiopoietin-1-Induced Angiogenesis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 7137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joussen, A.M.; Poulaki, V.; Tsujikawa, A.; Qin, W.; Qaum, T.; Xu, Q.; Moromizato, Y.; Bursell, S.E.; Wiegand, S.J.; Rudge, J.; et al. Suppression of diabetic retinopathy with angiopoietin-1. Am. J. Pathol. 2002, 160, 1683–1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, S.; Cree, I.A.; Alexander, R.; Turowski, P.; Ockrim, Z.; Patel, J.; Boyd, S.R.; Joussen, A.M.; Ziemssen, F.; Hykin, P.G.; et al. Angiopoietin modulation of vascular endothelial growth factor: Effects on retinal endothelial cell permeability. Cytokine 2007, 40, 144–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rangasamy, S.; Srinivasan, R.; Maestas, J.; McGuire, P.G.; Das, A. A potential role for angiopoietin 2 in the regulation of the blood-retinal barrier in diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Opthalmology Vis. Sci. 2011, 52, 3784–3791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boone, C.V.; Wykoff, C.C.; Fine, H.F. From Bench to Bedside: Faricimab Enters the Clinic. Ophthalmic Surg. Lasers Imaging Retin. 2022, 53, 305–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustonen, T.; Alitalo, K. Endothelial receptor tyrosine kinases involved in angiogenesis. J. Cell Biol. 1995, 129, 895–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davis, S.; Papadopoulos, N.; Aldrich, T.H.; Maisonpierre, P.C.; Huang, T.; Kovac, L.; Xu, A.; Leidich, R.; Radziejewska, E.; Rafique, A.; et al. Angiopoietins have distinct modular domains essential for receptor binding, dimerization and superclustering. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2002, 10, 38–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Procopio, W.N.; Pelavin, P.I.; Lee, W.M.; Yeilding, N.M. Angiopoietin-1 and -2 coiled coil domains mediate distinct homo-oligomerization patterns, but fibrinogen-like domains mediate ligand activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 30196–30201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yee, V.C.; Pratt, K.P.; Cote, H.C.; Trong, I.L.; Chung, D.W.; Davie, E.W.; Stenkamp, R.E.; Teller, D.C. Crystal structure of a 30 kDa C-terminal fragment from the gamma chain of human fibrinogen. Structure 1997, 5, 125–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, B.O.; Ding, L.; Morrison, S.J. Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells regulate the regeneration of their niche by secreting Angiopoietin-1. eLife 2015, 4, e05521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, D.Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, J.; Kim, K.; Hong, S.; Han, S.; Kubota, Y.; Augustin, H.G.; Ding, L.; Kim, J.W.; et al. Plastic roles of pericytes in the blood-retinal barrier. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 15296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, B.J.; Tripathi, R.C. Neural crest origin of human trabecular meshwork and its implications for the pathogenesis of glaucoma. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1989, 107, 583–590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gage, P.J.; Rhoades, W.; Prucka, S.K.; Hjalt, T. Fate maps of neural crest and mesoderm in the mammalian eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2005, 46, 4200–4208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bharti, K.; Nguyen, M.T.; Skuntz, S.; Bertuzzi, S.; Arnheiter, H. The other pigment cell: Specification and development of the pigmented epithelium of the vertebrate eye. Pigment. Cell Res. 2006, 19, 380–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, K.T.; Choi, H.H.; Steinmetz, M.O.; Maco, B.; Kammerer, R.A.; Ahn, S.Y.; Kim, H.Z.; Lee, G.M.; Koh, G.Y. Oligomerization and multimerization are critical for angiopoietin-1 to bind and phosphorylate Tie2. J. Biol. Chem. 2005, 280, 20126–20131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saharinen, P.; Kerkela, K.; Ekman, N.; Marron, M.; Brindle, N.; Lee, G.M.; Augustin, H.; Koh, G.Y.; Alitalo, K. Multiple angiopoietin recombinant proteins activate the Tie1 receptor tyrosine kinase and promote its interaction with Tie2. J. Cell Biol. 2005, 169, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dallabrida, S.M.; Ismail, N.; Oberle, J.R.; Himes, B.E.; Rupnick, M.A. Angiopoietin-1 promotes cardiac and skeletal myocyte survival through integrins. Circ. Res. 2005, 96, e8–e24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlson, T.R.; Feng, Y.; Maisonpierre, P.C.; Mrksich, M.; Morla, A.O. Direct cell adhesion to the angiopoietins mediated by integrins. J. Biol. Chem. 2001, 276, 26516–26525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.Q.; Li, J.J.; Hu, L.; Karpatkin, S. Thrombin induces increased expression and secretion of angiopoietin-2 from human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Blood 2002, 99, 1646–1650. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, B.D.; Hackett, S.F.; Hirota, K.; Oshima, Y.; Cai, Z.; Berg-Dixon, S.; Rowan, A.; Yan, Z.; Campochiaro, P.A.; Semenza, G.L. Cell type-specific regulation of angiogenic growth factor gene expression and induction of angiogenesis in nonischemic tissue by a constitutively active form of hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Circ. Res. 2003, 93, 1074–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Lash, G.E. Angiopoietin 2 in placentation and tumor biology: The yin and yang of vascular biology. Placenta 2017, 56, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sfiligoi, C.; de Luca, A.; Cascone, I.; Sorbello, V.; Fuso, L.; Ponzone, R.; Biglia, N.; Audero, E.; Arisio, R.; Bussolino, F.; et al. Angiopoietin-2 expression in breast cancer correlates with lymph node invasion and short survival. Int. J. Cancer 2002, 103, 466–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, B.; Cheng, S.Y. Angiopoietin-2: Development of inhibitors for cancer therapy. Curr. Oncol. Rep. 2009, 11, 111–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammes, H.P.; Lin, J.; Wagner, P.; Feng, Y.; Vom Hagen, F.; Krzizok, T.; Renner, O.; Breier, G.; Brownlee, M.; Deutsch, U. Angiopoietin-2 causes pericyte dropout in the normal retina: Evidence for involvement in diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 2004, 53, 1104–1110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiedler, U.; Scharpfenecker, M.; Koidl, S.; Hegen, A.; Grunow, V.; Schmidt, J.M.; Kriz, W.; Thurston, G.; Augustin, H.G. The Tie-2 ligand angiopoietin-2 is stored in and rapidly released upon stimulation from endothelial cell Weibel-Palade bodies. Blood 2004, 103, 4150–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saharinen, P.; Eklund, L.; Alitalo, K. Therapeutic targeting of the angiopoietin-TIE pathway. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 635–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenzuela, D.M.; Griffiths, J.A.; Rojas, J.; Aldrich, T.H.; Jones, P.F.; Zhou, H.; McClain, J.; Copeland, N.G.; Gilbert, D.J.; Jenkins, N.A.; et al. Angiopoietins 3 and 4: Diverging gene counterparts in mice and humans. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 1904–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elamaa, H.; Kihlstrom, M.; Kapiainen, E.; Kaakinen, M.; Miinalainen, I.; Ragauskas, S.; Cerrada-Gimenez, M.; Mering, S.; Nätynki, M.; Eklund, L. Angiopoietin-4-dependent venous maturation and fluid drainage in the peripheral retina. eLife 2018, 7, e37776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapiainen, E.; Elamaa, H.; Miinalainen, I.; Izzi, V.; Eklund, L. Cooperation of Angiopoietin-2 and Angiopoietin-4 in Schlemm’s Canal Maintenance. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2022, 63, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullrich, A.; Schlessinger, J. Signal transduction by receptors with tyrosine kinase activity. Cell 1990, 61, 203–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlessinger, J.; Ullrich, A. Growth factor signaling by receptor tyrosine kinases. Neuron 1992, 9, 383–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, D.J.; Yamaguchi, T.P.; Conlon, R.A.; Rossant, J.; Breitman, M.L. Tek, a novel tyrosine kinase gene located on mouse chromosome 4, is expressed in endothelial cells and their presumptive precursors. Oncogene 1992, 7, 1471–1480. [Google Scholar]
- Runting, A.S.; Stacker, S.A.; Wilks, A.F. tie2, a putative protein tyrosine kinase from a new class of cell surface receptor. Growth Factors 1993, 9, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Barton, W.A.; Dalton, A.C.; Seegar, T.C.; Himanen, J.P.; Nikolov, D.B. Tie2 and Eph receptor tyrosine kinase activation and signaling. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2014, 6, a009142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, X.; Seegar, T.C.; Dalton, A.C.; Tzvetkova-Robev, D.; Goldgur, Y.R.; Tajashankar, K.R.; Nikolov, D.B.; Barton, W.A. Structural basis for angiopoietin-1-mediated signaling initiation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, 7205–7210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumont, D.J.; Fong, G.H.; Puri, M.C.; Gradwohl, G.; Alitalo, K.; Breitman, M.L. Vascularization of the mouse embryo: A study of flk-1, tek, tie, and vascular endothelial growth factor expression during development. Dev. Dyn. 1995, 203, 80–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato, T.N.; Qin, Y.; Kozak, C.A.; Audus, K.L. Tie-1 and tie-2 define another class of putative receptor tyrosine kinase genes expressed in early embryonic vascular system. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1993, 90, 9355–9358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziegler, S.F.; Bird, T.A.; Schneringer, J.A.; Schooley, K.A.; Baum, P.R. Molecular cloning and characterization of a novel receptor protein tyrosine kinase from human placenta. Oncogene 1993, 8, 663–670. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schnurch, H.; Risau, W. Expression of tie-2, a member of a novel family of receptor tyrosine kinases, in the endothelial cell lineage. Development 1993, 119, 957–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macdonald, P.R.; Progias, P.; Ciani, B.; Patel, S.; Mayer, U.; Steinmetz, M.O.; Kammerer, R.A. Structure of the extracellular domain of Tie receptor tyrosine kinases and localization of the angiopoietin-binding epitope. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 28408–28414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Partanen, J.; Armstrong, E.; Makela, T.P.; Korhonen, J.; Sandberg, M.; Renkonen, R.S.; Huebner, K.; Alitalo, K. A novel endothelial cell surface receptor tyrosine kinase with extracellular epidermal growth factor homology domains. Mol. Cell Biol. 1992, 12, 1698–1707. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.L.; Shin, I.S.; Kim, J.M.; Choi, J.H.; Byun, J.; Jeon, E.S.; Suh, W.; Kim, D.K. Interaction between Tie receptors modulates angiogenic activity of angiopoietin2 in endothelial progenitor cells. Cardiovasc. Res. 2006, 72, 394–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seegar, T.C.; Eller, B.; Tzvetkova-Robev, D.; Kolev, M.V.; Hemderson, S.C.; Nikolov, D.B.; Barton, W.A. Tie1-Tie2 interactions mediate functional differences between angiopoietin ligands. Mol. Cell 2010, 37, 643–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, A.L.; Haroon, Z.A.; Werner, S.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Greenberg, C.S.; Peters, K.G. Tie2 expression and phosphorylation in angiogenic and quiescent adult tissues. Circ. Res. 1997, 81, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krueger, N.X.; Streuli, M.; Saito, H. Structural diversity and evolution of human receptor-like protein tyrosine phosphatases. EMBO J. 1990, 9, 3241–3252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, L.J.; Zinnhardt, M.; Vockel, M.; Drexel, H.C.; Peters, K.; Vestweber, D. VE-PTP inhibition stabilizes endothelial junctions by activating FGD5. Embo Rep. 2019, 20, e47046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellberg, S.; Dimberg, A.; Bahram, F.; Makoto, H.; Rennel, E.; Ameur, A.; Westholm, J.O.; Larsson, E.; Lindahl, P.; Cross, M.J. Transcriptional profiling reveals a critical role for tyrosine phosphatase VE-PTP in regulation of VEGFR2 activity and endothelial cell morphogenesis. FASEB J. 2009, 23, 1490–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yacyshyn, O.K.; Lai, P.F.; Forse, K.; Teichert-Kuliszewska, K.; Jurasz, P.; Stewart, D.J. Tyrosine phosphatase beta regulates angiopoietin-Tie2 signaling in human endothelial cells. Angiogenesis 2009, 12, 25–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Winderlich, M.; Keller, L.; Cagna, G.; Broermann, A.; Kamenyeva, O.; Kiefer, F.; Deutsch, U.; Nottebaum, A.F.; Vestweber, D. VE-PTP controls blood vessel development by balancing Tie-2 activity. J. Cell Biol. 2009, 185, 657–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fachinger, G.; Deutsch, U.; Risau, W. Functional interaction of vascular endothelial-protein-tyrosine phosphatase with the angiopoietin receptor Tie-2. Oncogene 1999, 18, 5948–5953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestweber, D. Vascular Endothelial Protein Tyrosine Phosphatase Regulates Endothelial Function. Physiology 2021, 36, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allingham, M.J.; van Buul, J.D.; Burridge, K. ICAM-1-mediated, Src- and Pyk2-dependent vascular endothelial cadherin tyrosine phosphorylation is required for leukocyte transendothelial migration. J. Immunol. 2007, 179, 4053–4064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turowski, P.; Martinelli, R.; Crawford, R.; Wateridge, D.; Papageorgiou, A.P.; Lampugnani, M.G.; Gamp, A.C.; Vestweber, D.; Adamson, P.; Dejana, E. Phosphorylation of vascular endothelial cadherin controls lymphocyte emigration. J. Cell Sci. 2008, 121, 29–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wallez, Y.; Cand, F.; Cruzalegui, F.; Souchelnytskyi, S.; Vilgrain, I.; Huber, P. Src kinase phosphorylates vascular endothelial-cadherin in response to vascular endothelial growth factor: Identification of tyrosine 685 as the unique target site. Oncogene 2006, 26, 1067–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wessel, F.; Winderlich, M.; Holm, M.; Frye, M.; Rivera-Galdos, R.; Vockel, M.; Linnepe, R.; Ipe, U.; Stadtmann, A.; Zarbock, A.; et al. Leukocyte extravasation and vascular permeability are each controlled in vivo by different tyrosine residues of VE-cadherin. Nat. Immunol. 2014, 15, 223–230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orsenigo, F.; Giampietro, C.; Ferrari, A.; Corada, M.; Galaup, A.; Sigismund, S.; Ristagno, G.; Maddaluno, L.; Koh, G.Y.; Franco, D.; et al. Phosphorylation of VE-cadherin is modulated by haemodynamic forces and contributes to the regulation of vascular permeability in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2012, 3, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corada, M.; Mariotti, M.; Thurston, G.; Smith, K.; Kunkel, R.; Brockhaus, M.; Lampugnani, M.G.; Martin-Padura, I.; Stoppacciaro, A.; Ruco, L.; et al. Vascular endothelial-cadherin is an important determinant of microvascular integrity in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 9815–9820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gotsch, U.; Borges, E.; Bosse, R.; Böggemeyer, E.; Simon, M.; Mossmann, H.; Vestweber, D. VE-cadherin antibody accelerates neutrophil recruitment in vivo. J. Cell Sci. 1997, 110 Pt 5, 583–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breviario, F.; Caveda, L.; Corada, M.; Martin-Padura, I.; Navarro, P.; Golay, J.; Introna, M.; Gulino, D.; Lampugnani, M.G.; Dejana, E. Functional properties of human vascular endothelial cadherin (7B4/cadherin-5), an endothelium-specific cadherin. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 1995, 15, 1229–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nawroth, R.; Poell, G.; Ranft, A.; Kloep, S.; Samulowitz, U.; Fachinger, G.; Golding, M.; Shima, D.T.; Deutsch, U.; Vestweber, D. VE-PTP and VE-cadherin ectodomains interact to facilitate regulation of phosphorylation and cell contacts. EMBO J. 2002, 21, 4885–4895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nottebaum, A.F.; Cagna, G.; Winderlich, M.; Gamp, A.C.; Linnepe, R.; Polaschegg, C.; Filippova, K.; Lyck, R.; Engelhardt, B.; Kamenyeva, O.; et al. VE-PTP maintains the endothelial barrier via plakoglobin becomes dissociated from VE-cadherin by leukocytes by, V.E.G.F. J. Exp. Med. 2008, 205, 2929–2945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, J.; Frye, M.; Lee, B.L.; Reinardy, J.L.; McClung, J.M.; Ding, K.; Kojima, M.; Xia, H.; Seidel, C.; Lima e Silva, R.; et al. Targeting VE-PTP activates TIE2 and stabilizes the ocular vasculature. J. Clin. Investig. 2014, 124, 4564–4576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dominguez, M.G.; Hughes, V.C.; Pan, L.; Simmons, M.; Daly, C.; Anderson, K.; Noguera-Troise, I.; Murphy, A.J.; Valenzuela, D.M.; Davis, S.; et al. Vascular endothelial tyrosine phosphatase (VE-PTP)-null mice undergo vasculogenesis but die embryonically because of defects in angiogenesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 3243–3248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frye, M.; Dierkes, M.; Kuppers, V.; Vockel, M.; Tomm, J.; Zeuschner, D.; Rossaint, J.; Zarbock, A.; Koh, G.Y.; Peters, K.; et al. Interfering with VE-PTP stabilizes endothelial junctions in vivo via Tie-2 in the absence of VE-cadherin. J. Exp. Med. 2015, 212, 2267–2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baumer, S.; Keller, L.; Holtmann, A.; Funke, R.; August, B.; Gamp, A.; Wolburg, H.; Wolburg-Buchholz, K.; Deutsch, U.; Vestweber, D. Vascular endothelial cell-specific phosphotyrosine phosphatase (VE-PTP) activity is required for blood vessel development. Blood 2006, 107, 4754–4762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dumont, D.J.; Gradwohl, G.; Fong, G.H.; Puri, M.C.; Gertsenstein, M.; Auerbach, A.; Breitman, M.L. Dominant-negative and targeted null mutations in the endothelial receptor tyrosine kinase, tek, reveal a critical role in vasculogenesis of the embryo. Genes Dev. 1994, 8, 1897–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suri, C.; Jones, P.F.; Patan, S.; Bartunkova, S.; Maisonpierre, P.C.; Davis, S.; Sato, T.N.; Yancopoulos, G.D. Requisite role of angiopoietin-1, a ligand for the TIE2 receptor, during embryonic angiogenesis. Cell 1996, 87, 1171–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reynolds, L.P.; Killilea, S.D.; Redmer, D.A. Angiogenesis in the female reproductive system. FASEB J. 1992, 6, 886–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohashi, H.; Takagi, H.; Koyama, S.; Oh, H.; Watanabe, D.; Antonetti, D.A.; Matsubara, T.; Nagai, K.; Arai, H.; Kita, T.; et al. Alterations in expression of angiopoietins and the Tie-2 receptor in the retina of streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Mol. Vis. 2004, 10, 608–617. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Heier, J.S.; Singh, R.P.; Wykoff, C.C.; Csaky, K.G.; Lai, T.Y.Y.; Loewenstein, A.; Schlottmann, P.G.; Paris, L.P.; Westenskow, P.D.; Quezada-Ruiz, C. The Angiopoietin/Tie Pathway in Retinal Vascular Diseases: A Review. Retina 2021, 41, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hammes, H.P.; Lin, J.; Renner, O.; Wang, Y.; Stock, O.; Vom Hagen, F.; Wolburg, H.; Hoffmann, S.; Deutsch, U.; Hammes, H.P. Pericytes and the pathogenesis of diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 2002, 51, 3107–3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao-Cheng, J.H.; Nagy, Z.; Brightman, M.W. Tight junctions of brain endothelium in vitro are enhanced by astroglia. J. Neurosci. 1987, 7, 3293–3299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janzer, R.C.; Raff, M.C. Astrocytes induce blood-brain barrier properties in endothelial cells. Nature 1987, 325, 253–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gardner, T.W.; Lieth, E.; Khin, S.A.; Barber, A.J.; Bonsall, D.J.; Lesher, T.; Rice, K.; Brennan, W.A., Jr. Astrocytes increase barrier properties and ZO-1 expression in retinal vascular endothelial cells. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997, 38, 2423–2427. [Google Scholar]
- Gaonac’h-Lovejoy, V.; Boscher, C.; Delisle, C.; Gratton, J.P. Rap1 is Involved in Angiopoietin-1-Induced Cell-Cell Junction Stabilization and Endothelial Cell Sprouting. Cells 2020, 9, 155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peters, K.G.; Kontos, C.D.; Lin, P.C.; Wong, A.L.; Rao, P.; Huang, L.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Sankar, S. Functional significance of Tie2 signaling in the adult vasculature. Recent Prog. Horm. Res. 2004, 59, 51–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asahara, T.; Chen, D.; Takahashi, T.; Fujikawa, K.; Kearney, M.; Magner, M.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Isner, J.M. Tie2 receptor ligands, angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2, modulate VEGF-induced postnatal neovascularization. Circ. Res. 1998, 83, 233–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, P.; Polverini, P.; Dewhirst, M.; Shan, S.; Rao, P.S.; Peters, K. Inhibition of tumor angiogenesis using a soluble receptor establishes a role for Tie2 in pathologic vascular growth. J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 100, 2072–2078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eklund, L.; Olsen, B.R. Tie receptors and their angiopoietin ligands are context-dependent regulators of vascular remodeling. Exp. Cell Res. 2006, 312, 630–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fukuhara, S.; Sako, K.; Minami, T.; Noda, K.; Kim, H.Z.; Kodama, T.; Shibuya, M.; Takakura, N.; Koh, G.Y.; Mochizuki, N. Differential function of Tie2 at cell-cell contacts and cell-substratum contacts regulated by angiopoietin-1. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 513–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saharinen, P.; Eklund, L.; Miettinen, J.; Wirkkala, R.; Anisimov, A.; Winderlich, M.; Nottebaum, A.; Vestweber, D.; Deutsch, U.; Koh, G.Y.; et al. Angiopoietins assemble distinct Tie2 signalling complexes in endothelial cell-cell and cell-matrix contacts. Nat. Cell Biol. 2008, 10, 527–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thurston, G.; Daly, C. The complex role of angiopoietin-2 in the angiopoietin-tie signaling pathway. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2012, 2, a006550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harfouche, R.; Hussain, S.N. Signaling and regulation of endothelial cell survival by angiopoietin-2. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2006, 291, H1635–H1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBusk, L.M.; Hallahan, D.E.; Lin, P.C. Akt is a major angiogenic mediator downstream of the Ang1/Tie2 signaling pathway. Exp. Cell Res. 2004, 298, 167–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackett, S.F.; Ozaki, H.; Strauss, R.W.; Wahlin, K.; Suri, C.; Maisonpierre, P.; Yancopoulos, G.; Campochiaro, P.A. Angiopoietin 2 expression in the retina: Upregulation during physiologic and pathologic neovascularization. J. Cell. Physiol. 2000, 184, 275–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gale, N.W.; Thurston, G.; Hackett, S.F.; Renard, R.; Wang, Q.; McClain, J.; Martin, C.; Witte, C.; Witte, M.H.; Jackson, D.; et al. Angiopoietin-2 is required for postnatal angiogenesis and lymphatic patterning, and only the latter role is rescued by Angiopoietin-1. Dev. Cell 2002, 3, 411–423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, H.; Takagi, H.; Suzuma, K.; Otani, A.; Matsumura, M.; Honda, Y. Hypoxia and vascular endothelial growth factor selectively up-regulate angiopoietin-2 in bovine microvascular endothelial cells. J. Biol. Chem. 1999, 274, 15732–15739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hackett, S.F.; Wiegand, S.; Yancopoulos, G.; Campochiaro, P.A. Angiopoietin-2 plays an important role in retinal angiogenesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2002, 192, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.S.; Kim, N.H.; Jo, I. Hypoxia and vascular endothelial growth factor acutely up-regulate angiopoietin-1 and Tie2 mRNA in bovine retinal pericytes. Microvasc. Res. 2003, 65, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandriota, S.J.; Pepper, M.S. Regulation of angiopoietin-2 mRNA levels in bovine microvascular endothelial cells by cytokines and hypoxia. Circ. Res. 1998, 83, 852–859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wagner, D.D. The Weibel-Palade body: The storage granule for von Willebrand factor and P-selectin. Thromb. Haemost. 1993, 70, 105–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hop, C.; Guilliatt, A.; Daly, M.; de Leeuw, H.P.; Brinkman, H.J.; Peake, I.R.; van Mourik, J.A.; Pannekoek, H. Assembly of multimeric von Willebrand factor directs sorting of P-selectin. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Teichert-Kuliszewska, K.; Maisonpierre, P.C.; Jones, N.; Campbell, A.I.; Master, Z.; Bendeck, M.P.; Alitalo, K.; Dumont, D.J.; Yancopoulos, G.D.; Stewart, D.J. Biological action of angiopoietin-2 in a fibrin matrix model of angiogenesis is associated with activation of Tie2. Cardiovasc. Res. 2001, 49, 659–670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Augustin, H.G.; Koh, G.Y.; Thurston, G.; Alitalo, K. Control of vascular morphogenesis and homeostasis through the angiopoietin-Tie system. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 165–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mochizuki, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Kanetake, H.; Kanda, S. Angiopoietin 2 stimulates migration and tube-like structure formation of murine brain capillary endothelial cells through c-Fes and c-Fyn. J. Cell Sci. 2002, 115, 175–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Kontos, C.D.; Annex, B.H.; Popel, A.S. A systems biology model of junctional localization and downstream signaling of the Ang–Tie signaling pathway. Npj Syst. Biol. Appl. 2021, 7, 34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Kehoe, O.; Smith, G.M.; Hykin, P.; Boulton, M.E. The angiopoietin/Tie-2 system regulates pericyte survival and recruitment in diabetic retinopathy. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2008, 49, 2163–2171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, D.; Taguchi, T.; Matsumura, T.; Pestell, R.; Edelstein, D.; Giardino, I.; Suske, G.; Rabbani, N.; Thornalley, P.J.; Sarthy, V.P.; et al. High glucose increases angiopoietin-2 transcription in microvascular endothelial cells through methylglyoxal modification of, m.S.i.n.3.A. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 31038–31045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Okamoto, T.; Yamagishi, S.; Inagaki, Y.; Amano, S.; Koga, K.; Abe, R.; Takeuchi, M.; Ohno, S.; Yoshimura, A.; Makita, Z. Angiogenesis induced by advanced glycation end products and its prevention by cerivastatin. FASEB J. 2002, 16, 1928–1930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brownlee, M. Biochemistry and molecular cell biology of diabetic complications. Nature 2001, 414, 813–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gamble, J.R.; Drew, J.; Trezise, L.; Underwood, A.; Parsons, M.; Kasminkas, L.; Rudge, J.; Yancopoulos, G.; Vadas, M.A. Angiopoietin-1 is an antipermeability and anti-inflammatory agent in vitro and targets cell junctions. Circ. Res. 2000, 87, 603–607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavard, J.; Patel, V.; Gutkind, J.S. Angiopoietin-1 prevents VEGF-induced endothelial permeability by sequestering Src through mDia. Dev. Cell 2008, 14, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.A.; Lee, E.H.; Lee, S.D.; Park, J.B.; Jeon, B.H.; Cho, C.H. COMP-Ang1 ameliorates leukocyte adhesion and reinforces endothelial tight junctions during endotoxemia. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2009, 381, 592–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, K.; Khosrof, S.; Bursell, S.E.; Rohan, R.; Murata, T.; Clermont, A.C.; Aiello, L.P.; Ogura, Y.; Adamis, A.P. Prevention of leukostasis and vascular leakage in streptozotocin-induced diabetic retinopathy via intercellular adhesion molecule-1 inhibition. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 10836–10841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joussen, A.M.; Murata, T.; Tsujikawa, A.; Kirchhof, B.; Bursell, S.E.; Adamis, A.P. Leukocyte-mediated endothelial cell injury and death in the diabetic retina. Am. J. Pathol. 2001, 158, 147–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; Gross, S.; Wolf, N.M.; Butenschon, V.M.; Qiu, Y.; Devraj, K.; Liebner, S.; Kroll, J.; Skolnik, E.Y.; Hammes, H.P.; et al. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase B regulates angiogenesis through modulation of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor type 2 and endothelial adherens junction proteins. Arter. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2014, 34, 2292–2300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, S.; Devraj, K.; Feng, Y.; Macas, J.; Liebner, S.; Wieland, T. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase B regulates angiogenic responses in the endothelium via caveolae formation and c-Src-mediated caveolin-1 phosphorylation. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 37, 2471–2484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Y.; Zhao, D.; Butenschon, V.M.; Bauer, A.T.; Schneider, S.W.; Skolnik, E.Y.; Hammes, H.P.; Wieland, T.; Feng, Y. Nucleoside diphosphate kinase B deficiency causes a diabetes-like vascular pathology via up-regulation of endothelial angiopoietin-2 in the retina. Acta Diabetol. 2015, 53, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danser, A.H.; Derkx, F.H.; Admiraal, P.J.; Deinum, J.; de Jong, P.T.; Schalekamp, M.A. Angiotensin levels in the eye. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 1008–1018. [Google Scholar]
- Danser, A.H.; van den Dorpel, M.A.; Deinum, J.; Derkx, F.H.; Franken, A.A.; Peperkamp, E.; de Jong, P.T.; Schalekamp, M.A. Renin, prorenin, and immunoreactive renin in vitreous fluid from eyes with and without diabetic retinopathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 1989, 68, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, A.; Takagi, H.; Oh, H.; Suzuma, K.; Matsumura, M.; Ikeda, E.; Honda, Y. Angiotensin II-stimulated vascular endothelial growth factor expression in bovine retinal pericytes. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2000, 41, 1192–1199. [Google Scholar]
- Otani, A.; Takagi, H.; Oh, H.; Koyama, S.; Honda, Y. Angiotensin II induces expression of the Tie2 receptor ligand, angiopoietin-2, in bovine retinal endothelial cells. Diabetes 2001, 50, 867–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funatsu, H.; Yamashita, H.; Ikeda, T.; Mimura, T.; Eguchi, S.; Hori, S. Vitreous levels of interleukin-6 and vascular endothelial growth factor are related to diabetic macular edema. Ophthalmology 2003, 110, 1690–1696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, H.; Pardoll, D.; Jove, R. STATs in cancer inflammation and immunity: A leading role for STAT3. Nat. Rev. Cancer 2009, 9, 798–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.H.; Park, S.W.; Kim, K.J.; Bae, J.S.; Lee, E.H.; Paek, S.H.; Kim, S.U.; Ye, S.; Kim, J.H.; Cho, C.H. Endothelial STAT3 Activation Increases Vascular Leakage Through Downregulating Tight Junction Proteins: Implications for Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Cell. Physiol. 2017, 232, 1123–1134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yun, J.H.; Han, M.H.; Jeong, H.S.; Lee, D.H.; Cho, C.H. Angiopoietin 1 attenuates interleukin-6-induced endothelial cell permeability through SHP-1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2019, 518, 286–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feng, Y.; vom Hagen, F.; Pfister, F.; Djokic, S.; Hoffmann, S.; Back, W.; Wagner, P.; Lin, J.; Deutsch, U.; Hammes, H.P. Impaired pericyte recruitment and abnormal retinal angiogenesis as a result of angiopoietin-2 overexpression. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2007, 97, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bresnick, G.H.; Engerman, R.; Davis, M.D.; de Venecia, G.; Myers, F.L. Patterns of ischemia in diabetic retinopathy. Trans. Sect. Ophthalmol. Am. Acad. Ophthalmol. Otolaryngol. 1976, 81, OP694–OP709. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kohner, E.M.; Henkind, P. Correlation of fluorescein angiogram and retinal digest in diabetic retinopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1970, 69, 403–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Stone, J. Role of astrocytes in the control of developing retinal vessels. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1997, 38, 1653–1666. [Google Scholar]
- Pfister, F.; Wang, Y.; Schreiter, K.; vom Hagen, F.; Altvater, K.; Hoffmann, S.; Deutsch, U.; Hammes, H.P.; Feng, Y. Retinal overexpression of angiopoietin-2 mimics diabetic retinopathy and enhances vascular damages in hyperglycemia. Acta Diabetol. 2009, 47, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfister, F.; Feng, Y.; vom Hagen, F.; Hoffmann, S.; Molema, G.; Hillebrands, J.L.; Shani, M.; Deutsch, U.; Hammes, H.P. Pericyte migration: A novel mechanism of pericyte loss in experimental diabetic retinopathy. Diabetes 2008, 57, 2495–2502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Pfister, F.; Schreiter, K.; Wang, Y.; Stock, O.; Vom Hagen, F.; Wolburg, H.; Hoffmann, S.; Deutsch, U.; Hammes, H.P. Angiopoietin-2 deficiency decelerates age-dependent vascular changes in the mouse retina. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2008, 21, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Vom Hagen, F.; Wang, Y.; Beck, S.; Schreiter, K.; Pfister, F.; Hoffmann, S.; Wagner, P.; Seeliger, M.; Molema, G.; et al. The absence of angiopoietin-2 leads to abnormal vascular maturation and persistent proliferative retinopathy. Thromb. Haemost. 2009, 102, 120–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lobov, I.B.; Brooks, P.C.; Lang, R.A. Angiopoietin-2 displays VEGF-dependent modulation of capillary structure and endothelial cell survival in vivo. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11205–11210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, R.K. Molecular regulation of vessel maturation. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 685–693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hanahan, D. Signaling vascular morphogenesis and maintenance. Science 1997, 277, 48–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmeliet, P. Angiogenesis in health and disease. Nat. Med. 2003, 9, 653–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.; Koh, G.Y. Ang2, the instigator of inflammation. Blood 2011, 118, 4767–4768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stratmann, A.; Risau, W.; Plate, K.H. Cell type-specific expression of angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 suggests a role in glioblastoma angiogenesis. Am. J. Pathol. 1998, 153, 1459–1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Collazos-Aleman, J.D.; Gnecco-Gonzalez, S.; Jaramillo-Zarama, B.; Jimenez-Mora, M.A.; Mendivil, C.O. The Role of Angiopoietins in Neovascular Diabetes-Related Retinal Diseases. Diabetes Ther. 2022, 13, 1811–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Yan, H. Simvastatin increases circulating endothelial progenitor cells and reduces the formation and progression of diabetic retinopathy in rats. Exp. Eye Res. 2012, 105, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G.; Kim, J.L.; Lee, H.K.; Ryu, G.W.; Hur, D.Y.; Yun, I.H.; Yang, J.W.; Kim, H.W. Simvastatin suppresses expression of angiogenic factors in the retinas of rats with streptozotocin-induced diabetes. Graefe’s Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2010, 249, 389–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tuuminen, R.; Sahanne, S.; Loukovaara, S. Low intravitreal angiopoietin-2 and VEGF levels in vitrectomized diabetic patients with simvastatin treatment. Acta Ophthalmol. 2014, 92, 675–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, L.E.; Wesolowski, E.; McLellan, A.; Kostyk, S.K.; D’Amato, R.; Sullivan, R.; D’Amore, P.A. Oxygen-induced retinopathy in the mouse. Investg. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 1994, 35, 101–111. [Google Scholar]
- Hangai, M.; Moon, Y.S.; Kitaya, N.; Chan, C.K.; Wu, D.Y.; Peters, K.G.; Ryan, S.J.; Hinton, D.R. Systemically expressed soluble Tie2 inhibits intraocular neovascularization. Hum. Gene Ther. 2001, 12, 1311–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, C.; Ruan, L.; Zhang, J.; Huang, X. Inhibitory Effects On Retinal Neovascularization by Ranibizumab and sTie2-Fc in An Oxygen-Induced Retinopathy Mouse Model. Curr. Eye Res. 2018, 43, 1190–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, C.; Yi, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lv, Y. Soluble Tei2 fusion protein inhibits retinopathy of prematurity occurrence via regulation of the Ang/Tie2 pathway. Exp. Ther. Med. 2019, 18, 614–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, H.S.; Lip, G.Y.; Blann, A.D. Angiopoietin-1 and angiopoietin-2 in diabetes mellitus: Relationship to VEGF, glycaemic control, endothelial damage/dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 2005, 180, 113–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anuradha, S.; Mohan, V.; Gokulakrishnan, K.; Dixit, M. Angiopoietin-2 levels in glucose intolerance, hypertension, and metabolic syndrome in Asian Indians (Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study-74). Metabolism 2010, 59, 774–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lip, P.L.; Chatterjee, S.; Caine, G.J.; Hope-Ross, M.; Gibson, J.; Blann, A.D.; Lip, G.Y. Plasma vascular endothelial growth factor, angiopoietin-2, and soluble angiopoietin receptor tie-2 in diabetic retinopathy: Effects of laser photocoagulation and angiotensin receptor blockade. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2004, 88, 1543–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Q.Y.; Zhuge, F.Y.; Zhu, Q.Q.; Si, X.W. Effects of laser photocoagulation on serum angiopoietin-1, angiopoietin-2, angiopoietin-1/angiopoietin-2 ratio, and soluble angiopoietin receptor Tie-2 levels in type 2 diabetic patients with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. Int. J. Ophthalmol. 2014, 7, 648–653. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Dieter, C.; Lemos, N.E.; de Faria Correa, N.R.; Costa, A.R.; Canani, L.H.; Crispim, D.; Bauer, A.C. The rs2442598 polymorphism in the ANGPT-2 gene is associated with risk for diabetic retinopathy in patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus in a Brazilian population. Arq. Bras. de Endocrinol. Metabol. 2021, 65, 794–800. [Google Scholar]
- Regula, J.T.; Lundh von Leithner, P.; Foxton, R.; Barathi, V.A.; Gemmy Cheung, C.M.; Bo Tun, S.B.; Wey, Y.S.; Iwata, D.; Dostalek, M.; Moelleken, J.; et al. Targeting key angiogenic pathways with a bispecific CrossMAb optimized for neovascular eye diseases. EMBO Mol. Med. 2017, 9, 985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tuuminen, R.; Haukka, J.; Loukovaara, S. Poor glycemic control associates with high intravitreal angiopoietin-2 levels in patients with diabetic retinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol. 2015, 93, e515–e516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klaassen, I.; Avery, P.; Schlingemann, R.O.; Steel, D.H.W. Vitreous protein networks around ANG2 and VEGF in proliferative diabetic retinopathy and the differential effects of aflibercept versus bevacizumab pre-treatment. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, R.H.; Minaker, S.A.; Lahaie Luna, G.; Bapat, P.; Farahvash, A.; Garg, A.; Bhambra, N.; Muni, R.H. Changes in aqueous and vitreous inflammatory cytokine levels in proliferative diabetic retinopathy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eye 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, T. Raff MC: Retinal astrocytes are immigrants from the optic nerve. Nature 1988, 332, 834–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, T.; Alwees, M.; Asaad, M.A.; Theile, J.; Kakkassery, V.; Dick, H.B.; Schultz, T.; Joachim, S.C. Increased Angiopoietin-1 and -2 levels in human vitreous are associated with proliferative diabetic retinopathy. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0280488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takagi, H.; Koyama, S.; Seike, H.; Oh, H.; Otani, A.; Matsumura, M.; Honda, Y. Potential role of the angiopoietin/tie2 system in ischemia-induced retinal neovascularization. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2003, 44, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Surowka, M.; Schaefer, W.; Klein, C. Ten years in the making: Application of CrossMab technology for the development of therapeutic bispecific antibodies and antibody fusion proteins. MAbs 2021, 13, 1967714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaefer, W.; Regula, J.T.; Bahner, M.; Schanzer, J.; Croasdale, R.; Durr, H.; Gassner, C.; Georges, G.; Kettenberger, H.; Imhof-Jung, S.; et al. Immunoglobulin domain crossover as a generic approach for the production of bispecific IgG antibodies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 11187–11192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, P.; Sanowar, S.; Lee, C.V.; Fuh, G. Tuning the specificity of a Two-in-One Fab against three angiogenic antigens by fully utilizing the information of deep mutational scanning. MAbs 2017, 9, 959–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sahni, J.; Patel, S.S.; Dugel, P.U.; Khanani, A.M.; Jhaveri, C.D.; Wykoff, C.C.; Hershberger, V.S.; Pauly-Evers, M.; Sadikhov, S.; Szczesny, P.; et al. Simultaneous Inhibition of Angiopoietin-2 and Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor-A with Faricimab in Diabetic Macular Edema: BOULEVARD Phase 2 Randomized Trial. Ophthalmology 2019, 126, 1155–1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eter, N.; Singh, R.P.; Abreu, F.; Asik, K.; Basu, K.; Baumal, C.; Chang, A.; Csaky, K.G.; Haskova, Z.; Lin, H.; et al. YOSEMITE and RHINE: Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trials of Faricimab for Diabetic Macular Edema: Study Design and Rationale. Ophthalmol. Sci. 2022, 2, 100111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wykoff, C.C.; Abreu, F.; Adamis, A.P.; Basu, K.; Eichenbaum, D.A.; Haskova, Z.; Lin, H.; Loewenstein, A.; Mohan, S.; Pearce, I.A.; et al. Efficacy, durability, and safety of intravitreal faricimab with extended dosing up to every 16 weeks in patients with diabetic macular oedema (YOSEMITE and RHINE): Two randomised, double-masked, phase 3 trials. Lancet 2022, 399, 741–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ishida, S.; Chen, S.J.; Murata, T.; Ogura, Y.; Ruamviboonsuk, P.; Sakamoto, T.; Fujita, T.; Kawano, M.; Ohsawa, S.; Abreu, F.; et al. Efficacy, Durability, and Safety of Faricimab in Patients From Asian Countries With Diabetic Macular Edema: 1-Year Subgroup Analysis of the Phase III YOSEMITE and RHINE Trials. Asia-Pac. J. Ophthalmol. 2023, 12, 451–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, T.Y.; Haskova, Z.; Asik, K.; Baumal, C.R.; Csaky, K.G.; Eter, N.; Ives, J.A.; Jaffe, G.J.; Korobelnik, J.F.; Lin, H.; et al. Faricimab Treat-and-Extend for Diabetic Macular Edema: 2-Year Results from the Randomized Phase 3 YOSEMITE and RHINE Trials. Ophthalmology 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watkins, C.; Paulo, T.; Buhrer, C.; Holekamp, N.M.; Bagijn, M. Comparative Efficacy, Durability and Safety of Faricimab in the Treatment of Diabetic Macular Edema: A Systematic Literature Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Adv. Ther. 2023, 40, 5204–5221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Zhu, N.; Ji, A. Comparative efficacy and safety of Faricimab and other anti-VEGF therapy for age-related macular degeneration and diabetic macular edema: A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized clinical trials. Medicine 2023, 102, e36370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rush, R.B. One Year Results of Faricimab for Aflibercept-Resistant Diabetic Macular Edema. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2023, 17, 2397–2403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rush, R.B.; Rush, S.W. Faricimab for Treatment-Resistant Diabetic Macular Edema. Clin. Ophthalmol. 2022, 16, 2797–2801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohara, H.; Harada, Y.; Hiyama, T.; Sadahide, A.; Minamoto, A.; Kiuchi, Y. Faricimab for Diabetic Macular Edema in Patients Refractory to Ranibizumab or Aflibercept. Medicina 2023, 59, 1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takamura, Y.; Yamada, Y.; Morioka, M.; Gozawa, M.; Matsumura, T.; Inatani, M. Turnover of Microaneurysms After Intravitreal Injections of Faricimab for Diabetic Macular Edema. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2023, 64, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kusuhara, S.; Kishimoto-Kishi, M.; Matsumiya, W.; Miki, A.; Imai, H.; Nakamura, M. Short-Term Outcomes of Intravitreal Faricimab Injection for Diabetic Macular Edema. Medicina 2023, 59, 665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawa, M.; Nakagawa, N.; Shunto, T.; Nishiyama, I. Two cases of diabetic macular edema with diminished areas of retinal non-perfusion and microaneurysms after intravitreal faricimab injections. Am. J. Ophthalmol. Case Rep. 2024, 33, 101973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D.M.; Boyer, D.S.; Csaky, K.; Vitti, R.; Perlee, L.; Chu, K.W.; Asmus, F.; Leal, S.; Zeitz, O.; Cheng, Y.; et al. Intravitreal Nesvacumab (Antiangiopoietin 2) Plus Aflibercept in Diabetic Macular Edema: Phase 2 RUBY Randomized Trial. Retina 2022, 42, 1111–1120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heier, J.S.; Ho, A.C.; Boyer, D.S.; Csaky, K.; Vitti, R.; Perlee, L.; Chu, K.W.; Asmus, F.; Leal, S.; Zeitz, O.; et al. Intravitreal Nesvacumab (Anti-Angiopoietin-2) Plus Aflibercept in Neovascular AMD: Phase 2 ONYX Randomized Trial. J. Vitr. Dis. 2022, 7, 8–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campochiaro, P.A.; Sophie, R.; Tolentino, M.; Miller, D.M.; Browning, D.; Boyer, D.S.; Heier, J.S.; Gambino, L.; Withers, B.; Brigell, M.; et al. Treatment of diabetic macular edema with an inhibitor of vascular endothelial-protein tyrosine phosphatase that activates Tie2. Ophthalmology 2015, 122, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, P.A.; Peters, K.G. Targeting Tie2 for Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Edema. Curr. Diab. Rep. 2016, 16, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, P.A.; Khanani, A.; Singer, M.; Patel, S.; Boyer, D.; Dugel, P.; Kherani, S.; Withers, B.; Gambino, L.; Peters, K.; et al. Enhanced Benefit in Diabetic Macular Edema from AKB-9778 Tie2 Activation Combined with Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor Suppression. Ophthalmology 2016, 123, 1722–1730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akwii, R.G.; Mikelis, C.M. Targeting the Angiopoietin/Tie Pathway: Prospects for Treatment of Retinal and Respiratory Disorders. Drugs 2021, 81, 1731–1749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Hove, I.; Hu, T.T.; Beets, K.; Van Bergen, T.; Etienne, I.; Stitt, A.W.; Vermassen, E.; Feyen, J.H.M. Targeting RGD-binding integrins as an integrative therapy for diabetic retinopathy and neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Prog. Retin. Eye Res. 2021, 85, 100966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parsons, J.T.; Horwitz, A.R.; Schwartz, M.A. Cell adhesion: Integrating cytoskeletal dynamics and cellular tension. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2010, 11, 633–643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cascone, I.; Audero, E.; Giraudo, E.; Napione, L.; Maniero, F.; Philips, M.R.; Collard, J.G.; Serini, G.; Bussolino, F. Tie-2-dependent activation of RhoA and Rac1 participates in endothelial cell motility triggered by angiopoietin-1. Blood 2003, 102, 2482–2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, N.; Iljin, K.; Dumont, D.J.; Alitalo, K. Tie receptors: New modulators of angiogenic and lymphangiogenic responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2001, 2, 257–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kontos, C.D.; Stauffer, T.P.; Yang, W.P.; York, J.D.; Huang, L.; Blanar, M.A.; Meyer, T.; Peters, K.G. Tyrosine 1101 of Tie2 is the major site of association of p85 and is required for activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and Akt. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998, 18, 4131–4140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, R.L.E.; Kanan, Y.; Mirando, A.C.; Kim, J.; Shmueli, R.B.; Lorenc, V.E.; Fortmann, S.D.; Sciamanna, J.; Pandey, N.B.; Green, J.J.; et al. Tyrosine kinase blocking collagen IV-derived peptide suppresses ocular neovascularization and vascular leakage. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaai8030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirando, A.C.; Shen, J.; Silva, R.L.E.; Chu, Z.; Sass, N.C.; Lorenc, V.E.; Green, J.J.; Campochiaro, P.A.; Popel, A.S.; Pandey, N.B. A collagen IV-derived peptide disrupts alpha5beta1 integrin and potentiates Ang2/Tie2 signaling. JCI Insight 2019, 4, e122043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, Q.D.; Heier, J.S.; Do, D.V.; Mirando, A.C.; Pandey, N.B.; Sheng, H.; Heah, T. The Tie2 signaling pathway in retinal vascular diseases: A novel therapeutic target in the eye. Int. J. Retin. Vitr. 2020, 6, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Estelles, A.; Briante, R.; Kurtzman, A.L.; Hannum, C.H.; Kashyap, A.K.; Horowitz, L.; Horowitz, M.; Bhatt, R.R.; Lerner, R.A. Surrobodies with functional tails. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 397, 352–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, L.; Yee, H.; Chan, C.; Kashyap, A.K.; Horowitz, L.; Horowitz, M.; Bhatt, R.R.; Lerner, R.A. Combinatorial surrobody libraries. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 10756–10761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen-Li, G.; Martinez-Archer, R.; Coghi, A.; Roca, J.A.; Rodriguez, F.J.; Acaba-Berrocal, L.; Berrocal, M.H.; Wu, L. Beyond VEGF: Angiopoietin–Tie Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Retinopathy. J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13102778
Chen-Li G, Martinez-Archer R, Coghi A, Roca JA, Rodriguez FJ, Acaba-Berrocal L, Berrocal MH, Wu L. Beyond VEGF: Angiopoietin–Tie Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Retinopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(10):2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13102778
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen-Li, Genesis, Rebeca Martinez-Archer, Andres Coghi, José A. Roca, Francisco J. Rodriguez, Luis Acaba-Berrocal, María H. Berrocal, and Lihteh Wu. 2024. "Beyond VEGF: Angiopoietin–Tie Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Retinopathy" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 10: 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13102778
APA StyleChen-Li, G., Martinez-Archer, R., Coghi, A., Roca, J. A., Rodriguez, F. J., Acaba-Berrocal, L., Berrocal, M. H., & Wu, L. (2024). Beyond VEGF: Angiopoietin–Tie Signaling Pathway in Diabetic Retinopathy. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(10), 2778. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13102778





