Optic Neuritis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms and Serum Levels of STAT4 (rs10181656, rs7574865, rs7601754, rs10168266)
Abstract
:1. Introduction
1.1. Clinic
- Retrobulbar neuritis with normal appearance of the optic disc;
- Papillitis with a swollen optic disc;
- Perineuritis, which affects the optic nerve sheath, while the optic disc may or may not be swollen;
1.2. STAT
1.3. STAT4 Gene
1.4. Optic Neuritis and Multiple Sclerosis
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics Statement
2.2. Subjects
2.3. Genotyping
2.4. Serum IL-9 Levels Measurement
2.5. Statistical Analysis
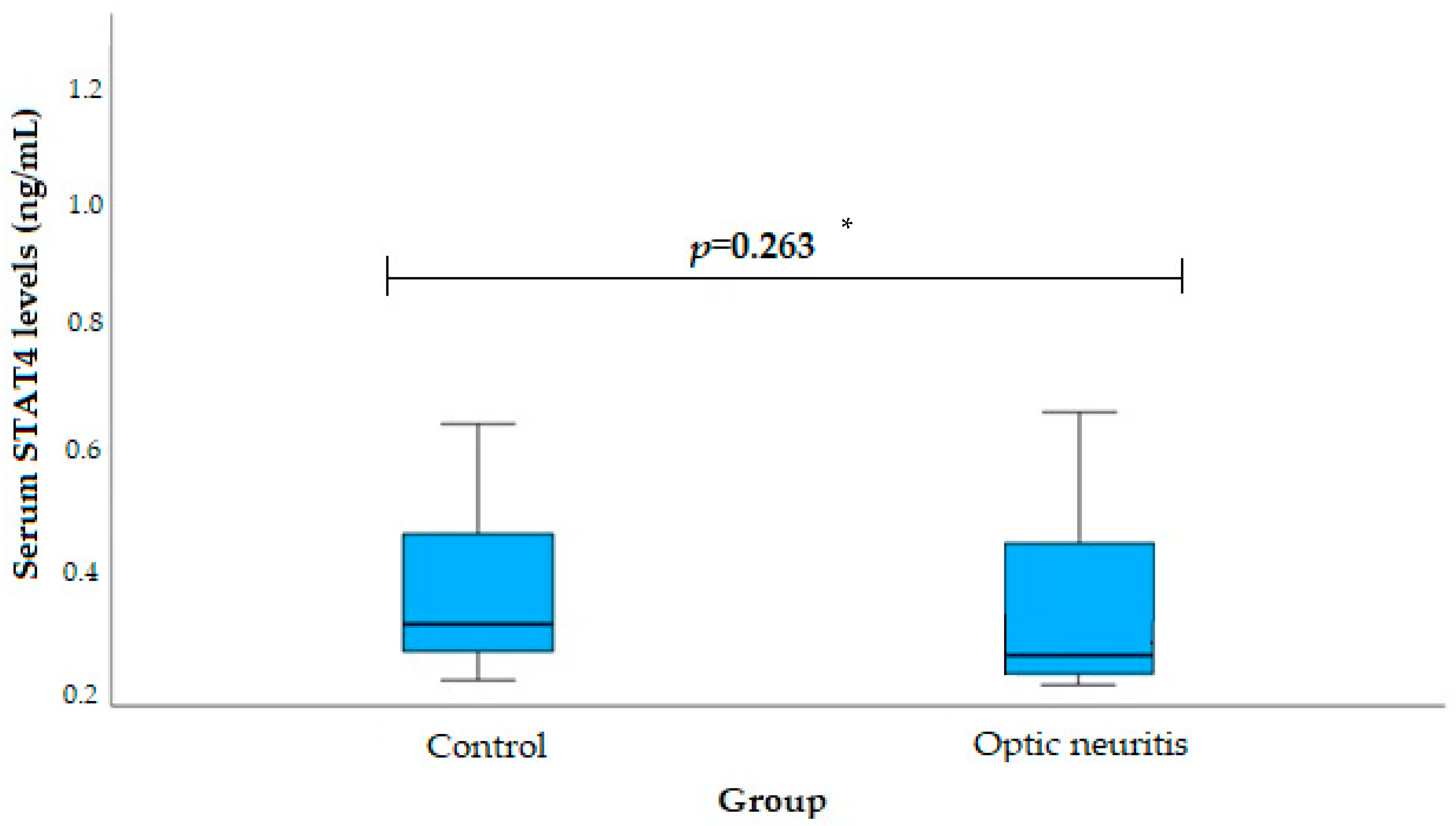
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pukenytė, R.; Šustickas, G.; Ščerbak, J.; Aukštikalnis, D.; Ašoklis, R. Regos nervo sužalojimas: Literatūros apžvalga. Liet. Chirurgija 2011, 9, 18–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhillon, N. Anatomy. In Current Diagnosis & Treatment Otolaryngology—Head and Neck Surgery, 4th ed.; Lalswani, A.K., Ed.; McGraw-Hill Education: New York, NY, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Punytė, V.; Liutkevičienė, R.; Gelžinis, A.; Žemaitienė, R. Optic neuritis. J. Med. Sci. 2020, 8, 170–175. [Google Scholar]
- Bennett, J.L. Optic Neuritis. In CONTINUUM Lifelong Learning in Neurology; Lippincott Williams and Wilkins: Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2019; Volume 25, pp. 1236–1264. [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, N.; De Bernardo, M.; Di Stasi, M.; Cione, F.; Capaldo, I. A-Scan Ultrasonographic Evaluation of Patients with Idiopathic Intracranial Hypertension: Comparison of Optic Nerves. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rosa, N.; De Bernardo, M.; Abbinante, G.; Vecchio, G.; Cione, F.; Capasso, L. Optic Nerve Drusen Evaluation: A Comparison between Ultrasound and OCT. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, M.J. Ischemic Optic Neuropathy. Continuum 2019, 25, 1215–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toosy, A.T.; Mason, D.F.; Miller, D.H. Optic neuritis. In The Lancet Neurology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2014; Volume 13, pp. 83–99. [Google Scholar]
- Verhoeven, Y.; Tilborghs, S.; Jacobs, J.; De Waele, J.; Quatannens, D.; Deben, C.; Prenen, H.; Pauwels, P.; Trinh, X.B.; Wouters, A.; et al. The Potential and Controversy of Targeting STAT Family Members in Cancer. In Seminars in Cancer Biology; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2020; Volume 60, pp. 41–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowman, T.; Garcia, R.; Turkson, J.; Jove, R. STATs in Oncogenesis. In Oncogene; Nature Publishing Group: Berlin, Germany, 2000; Volume 19, pp. 2474–2488. [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelm, H.; Schabet, M. The Diagnosis and Treatment of Optic Neuritis. Dtsch. Arztebl. Int. 2015, 112, 616–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, H.; Lian, Z.; Liu, J.; Feng, H.; Miao, X.; Du, Q.; Zhou, H. STAT4 Polymorphisms are Associated with Neuromyelitis Optica Spec-trum Disorders. NeuroMol. Med. 2017, 19, 493–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, N.J. The Optic Neuritis Treatment Trial. Ophthalmology 2020, 127, S172–S173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slavinskaitė, A.; Banevičius, M.; Kriaučiūnienė, L.; Zlatkutė, E.; Vilkevičiūtė, A.; Liutkevičienė, R. Regos nervo neurito pagrindiniai diagnostikos ir gydymo principai. Neurol. Semin. 2016, 20, 17–22. [Google Scholar]
- Sobhanian, M.J.; Agarwal, R.; Meltzer, E.; Kildebeck, E.; Frohman, B.S.; Frohman, A.N.; Galetta, S.L.; Saidha, S.; White, O.; Villoslada, P.; et al. Identification and treatment of the visual processing asymmetry in MS patients with optic neuritis: The Pulfrich phenomenon. J. Neurol. Sci. 2018, 387, 60–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, A.; Rosso, M.; Santoro, J.D. Wilhelm Uhthoff and Uhthoff’s phenomenon. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 1790–1796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoorbakht, H.; Bagherkashi, F. Optic neuritis, its differential diagnosis and management. Open Ophthalmol. J. 2012, 6, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pau, D.; Al Zubidi, N.; Yalamanchili, S.; Plant, G.T.; Lee, A.G. Optic neuritis. Eye 2011, 25, 833–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrpouya-Bahrami, P.; Moriarty, A.K.; De Melo, P.; Keeter, W.C.; Alakhras, N.S.; Nelson, A.S.; Hoover, M.; Barrios, M.S.; Nadler, J.L.; Serezani, C.H.; et al. STAT4 is expressed in neutrophils and promotes antimicrobial immunity. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 6, e141326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ihle, J.N. The Stat Family in Cytokine Signaling. In Current Opinion in Cell Biology; Elsevier Ltd.: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2001; Volume 13, pp. 211–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calò, V.; Migliavacca, M.; Bazan, V.; Macaluso, M.; Buscemi, M.; Gebbia, N.; Russo, A. STAT proteins: From normal control of cellular events to tumorigenesis. J. Cell. Physiol. 2003, 197, 157–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, C.; Li, B.; Cheng, Z.; Hu, Y.; Fang, Z.; Zhai, A. Association study of STAT4 polymorphisms and type 1 diabetes in Northeastern Chinese Han population. Tissue Antigens 2013, 81, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.-S.; Park, H.; Yang, S.; Kim, D.; Park, Y. STAT4 Polymorphism Is Associated with Early-Onset Type 1 Diabetes, but not with Late-Onset Type 1 Diabetes. In Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences; Blackwell Publishing Inc.: Oxford, UK, 2008; Volume 1150, pp. 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hauser, S.L.; Cree, B.A. Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis: A Review. Am. J. Med. 2020, 133, 1380–1390.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zafeiropoulos, P.; Katsanos, A.; Kitsos, G.; Stefaniotou, M.; Asproudis, I. The contribution of multifocal visual evoked potentials in patients with optic neuritis and multiple sclerosis: A review. Doc. Ophthalmol. 2021, 142, 283–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guier, C.P.; Stokkermans, T.J. Optic Neuritis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liutkeviciene, R.; Vilkeviciute, A.; Banevicus, M.; Miezyte, R.; Kriauciuniene, L. Association of MMP-2 (-1306 C/T) gene polymor-phism with predisposition of optic neuritis together with multiple sclerosis. Medicina 2018, 54, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gedvilaite, G.; Vilkeviciute, A.; Kriauciuniene, L.; Asmoniene, V.; Liutkeviciene, R. Does CETP rs5882, rs708272, SIRT1 rs12778366, FGFR2 rs2981582, STAT3 rs744166, VEGFA rs833068, IL6 rs1800795 polymorphisms play a role in optic neuritis development? Ophthalmic Genet. 2019, 40, 219–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanton, J.K.; Rovira, A.; Tintore, M.; Altmann, D.R.; Barkhof, F.; Filippi, M.; Huerga, E.; A Miszkiel, K.; Plant, G.T.; Polman, C.; et al. MRI criteria for multiple sclerosis in patients presenting with clinically isolated syndromes: A multicentre retrospective study. Lancet Neurol. 2007, 6, 677–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Remmers, E.F.; Plenge, R.M.; Lee, A.T.; Graham, R.R.; Hom, G.; Behrens, T.W.; de Bakker, P.I.; Le, J.M.; Lee, H.-S.; Batliwalla, F.; et al. STAT4 and the Risk of Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. N. Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 977–986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghanavati, F.; Nezhad, S.R.K.; Hajjari, M.R.; Akhoond, M.R. Association of Signal Transducer and Activator of Transcription 4 rs10181656 Polymorphism with Rheumatoid Arthritis and Systemic Sclerosis in Khuzestan Province in Southwestern Iran. Arch. Rheumatol. 2019, 34, 434–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.M.; Xu, W.D.; Huang, A.F. Association of STAT4 Gene Rs7574865, Rs10168266 Polymorphisms and Systemic Lupus Er-ythematosus Susceptibility: A Meta-analysis. Immunol. Investig. 2021, 50, 282–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhong, X.; Luo, M.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Yu, X.; Liu, L.; Chen, S. Genetic variants in STAT4 and their interactions with environmental factors for the incidence of hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Biomark. 2021, 32, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, W.; Dong, X.; Yang, Z.; Mao, G.; Xing, W. Association between rs7574865 polymorphism in STAT4 gene and rheumatoid arthritis: An updated meta-analysis. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 71, 101–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, Y.; Lee, H.-S.; Park, Y.; Min, D.; Yang, S.; Kim, D.; Cho, B. Evidence for the role of STAT4 as a general autoimmunity locus in the Korean population. Diabetes/Metab. Res. Rev. 2011, 27, 867–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaplan, M.H. STAT4: A Critical Regulator of Inflammation In Vivo. Immunol. Res. 2005, 31, 231–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Totoson, P.; Maguin-Gaté, K.; Prati, C.; Wendling, D.; Demougeot, C. Mechanisms of endothelial dysfunction in rheumatoid arthritis: Lessons from animal studies. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2014, 16, 202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Mai, H.; Peng, J.; Zhou, B.; Hou, J.; Jiang, D. STAT4: An immunoregulator contributing to diverse human diseases. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 1575–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker, J.G.; Ahern, M.J.; Coleman, M.; Weedon, H.; Papangelis, V.; Beroukas, D.; Roberts-Thomson, P.J.; Smith, M.D. Characterisation of a dendritic cell subset in synovial tissue which strongly expresses Jak/STAT transcription factors from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2007, 66, 992–999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, E.; Lu, J.; Xing, D.; Chen, X.; Xie, H.; Liang, J.; Li, L. Rs7574865 polymorphism in signal transducers and activators of transcription 4 gene and rheumatoid arthritis: An updated meta-analysis of 28 case-control comparisons. Int. J. Rheum. Dis. 2015, 18, 3–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hendric, A.M.; Gibson, M.V.; Kulshreshtha, A. Diabetic Retinopathy. In Primary Care: Clinics in Office Practice; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2015; Volume 42, pp. 451–464. ISBN 9780323395793. ISSN 0095-4543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campochiaro, P.A.; Peters, K.G. Targeting Tie2 for Treatment of Diabetic Retinopathy and Diabetic Macular Edema. Curr. Diabetes Rep. 2016, 16, 126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, J.; Fan, G.; Yin, X.; Gu, Y.; Wang, X.; Xin, Y.; Yao, Y. A novel transthyretin/STAT4/miR-223-3p/FBXW7 signaling pathway affects neovascularization in diabetic retinopathy. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2019, 498, 110541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cione, F.; Gioia, M.; Pagliarulo, S. Bias That Should Be Avoided to Obtain a Reliable Study of IOL Power Calculation After Myopic Refractive Surgery. J. Refract. Surg. 2023, 39, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Pan, H.-F.; Ye, D.-Q. Therapeutic potential of STAT4 in autoimmunity. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets 2014, 18, 945–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Symptoms | Typical ON |
|---|---|
| Age | Young patient < 50 years |
| Visual acuity loss time | Acute/subacute visual acuity loss |
| Visual acuity loss progression | Visual acuity loss progressing for few days or few weeks |
| Damage | Mostly one eye |
| Visual acuity | ↓ in 90% of cases |
| Visual field | Changes noticed in 97% of cases |
| Color vision | In acute period, blue-yellow color vision loss; in subacute period, red-green color vision loss |
| Visual evoked potentials (VEP) | ↓ VEP latency |
| Optical coherence tomography (OCT) | Optic nerve disc edema (mostly in superior and nasal quadrants), noticed in 20% of patients |
| Pain | Acute painful visual acuity loss, especially ↑ with eye movement |
| Optic nerve disc | Mostly normal optic nerve disc |
| Vitreous | Normal |
| Orbit | Normal |
| Anamnesis | ON in anamnesis or MS in anamnesis. Patients without MS had MS-like lesions but were not followed up after ON treatment in our study, only redirected for neurological follow-up. |
| Neurological symptoms | Neurological symptoms, allowing to suspect MS |
| Treatment effect using steroids | Shortens the duration of the disease |
| Improvement | Spontaneous improvement in 2–3 weeks |
| Prognosis | Mostly good |
| Recurrence (5–10 years) | 28% |
| Gene | Genotype | With MS | Without MS | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ON Group (n = 32) n (%) | Control Group (n = 158) n (%) | p-Value | ON Group (n = 42) n (%) | Control Group (n = 158) n (%) | p-Value | ||
| STAT4 (rs10181656) | CC | 20 (62.5) | 90 (56.96) | 0.721 | 26 (61.9) | 90 (56.96) | 0.827 |
| CG | 11 (34.38) | 58 (36.71) | 14 (33.33) | 58 (36.71) | |||
| GG | 1 (3.13) | 10 (6.33) | 2 (4.76) | 10 (6.33) | |||
| Allele: | 0.024 | 0.020 | |||||
| C | 51 (79.69) | 238 (65.38) | 66 (78.57) | 238 (65.38) | |||
| G | 13 (20.31) | 126 (34.62) | 18 (21.43) | 126 (34.62) | |||
| STAT4 (rs7574865) | GG | 23 (71.88) | 91 (57.59) | 0.303 | 25 (59.52) | 91 (57.59) | 0.968 |
| GT | 8 (25) | 56 (35.44) | 14 (33.33) | 56 (35.44) | |||
| TT | 1 (3.13) | 11 (6.96) | 3 (7.14) | 11 (6.96) | |||
| Allele: | 0.003 | 0.070 | |||||
| G | 54 (84.38) | 238 (65.93) | 64 (76.19) | 238 (65.93) | |||
| T | 10 (15.63) | 123 (34.07) | 20 (23.81) | 123 (34.07) | |||
| STAT4 (rs7601754) | AA | 22 (68.75) | 121 (76.58) | 0.631 | 31 (73.81) | 121 (76.58) | 0.927 |
| GA | 9 (28.13) | 34 (21.52) | 10 (23.81) | 34 (21.52) | |||
| GG | 1 (3.13) | 3 (1.9) | 1 (2.38) | 3 (1.9) | |||
| Allele: | 0.547 | 0.198 | |||||
| A | 53 (82.81) | 276 (79.54) | 72 (85.71) | 276 (79.54) | |||
| G | 11 (17.19) | 71 (20.46) | 12 (14.29) | 71 (20.46) | |||
| STAT4 (rs10168266) | CC | 26 (81.25) | 105 (66.46) | 0.213 | 27 (64.29) | 105 (66.46) | 0.873 |
| CT | 5 (15.63) | 49 (31.01) | 13 (30.95) | 49 (31.01) | |||
| TT | 1 (3.13) | 4 (2.53) | 2 (4.76) | 4 (2.53) | |||
| Allele: | 0.003 | 0.135 | |||||
| C | 57 (89.06) | 259 (71.75) | 67 (79.76) | 259 (71.75) | |||
| T | 7 (10.94) | 102 (28.25) | 17 (20.24) | 102 (28.25) | |||
| SNPs | ON vs. Controls | ||
|---|---|---|---|
| D’ | r2 | p-Value | |
| rs10181656–rs7574865 | 0.867 | 0.743 | <0.001 |
| rs10181656–rs7601754 | 0.858 | 0.034 | <0.001 |
| rs10181656–rs10168266 | 0.707 | 0.348 | <0.001 |
| rs7574865–rs7601754 | 0.998 | 0.046 | <0.001 |
| rs7574865–rs10168266 | 0.814 | 0.467 | <0.001 |
| rs7601754–rs10168266 | 0.998 | 0.032 | <0.001 |
| Haplotype | STAT4 rs10181656 | STAT4 rs7574865 | STAT4 rs7601754 | STAT4 rs10168266 | Frequency | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | ON | |||||||
| 1 | C | G | A | C | 59.43 | 58.29 | 1.00 | – |
| 2 | G | T | A | T | 14.57 | 11.01 | 0.55 (0.27–1.09) | 0.087 |
| 3 | C | G | G | C | 11.78 | 14.81 | 1.24 (0.69–2.24) | 0.470 |
| 4 | G | T | A | C | 9.16 | 4.15 | 0.47 (0.19–1.17) | 0.100 |
| 5 | C | G | A | T | 2.59 | 0.70 | 0.29 (0.05–1.62) | 0.160 |
| 6 | G | G | A | C | 0.64 | 5.17 | 11.51 (2.29–57.80) | 0.003 |
| 7 | C | T | A | T | 0.32 | 4.30 | 19.47 (2.25–168.17) | 0.008 |
| rare | * | * | * | * | NA | NA | 0.69 (0.06–7.49) | 0.760 |
| Haplotype | STAT4 rs10181656 | STAT4 rs7574865 | STAT4 rs7601754 | STAT4 rs10168266 | Frequency | OR (95% CI) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | ON | |||||||
| 1 | C | G | A | C | 59.43 | 55.58 | 1.00 | – |
| 2 | G | T | A | T | 14.57 | 11.52 | 0.57 (0.24–1.38) | 0.210 |
| 3 | C | G | G | C | 11.78 | 14.28 | 1.21 (0.57–2.61) | 0.620 |
| 4 | G | T | A | C | 9.16 | 4.81 | 0.50 (0.15–1.64) | 0.260 |
| 5 | C | G | A | T | 2.59 | 1.24 | 0.49 (0.06–4.41) | 0.530 |
| 6 | C | T | A | T | 0.32 | 7.47 | 32.55 (3.66–289.72) | 0.002 |
| 7 | G | G | A | C | 0.64 | 5.09 | 9.05 (1.53–53.35) | 0.016 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Gedvilaite, G.; Duseikaitė, M.; Dubinskaite, G.; Kriauciuniene, L.; Zemaitiene, R.; Liutkevicienė, R. Optic Neuritis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms and Serum Levels of STAT4 (rs10181656, rs7574865, rs7601754, rs10168266). J. Clin. Med. 2024, 13, 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010010
Gedvilaite G, Duseikaitė M, Dubinskaite G, Kriauciuniene L, Zemaitiene R, Liutkevicienė R. Optic Neuritis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms and Serum Levels of STAT4 (rs10181656, rs7574865, rs7601754, rs10168266). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2024; 13(1):10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010010
Chicago/Turabian StyleGedvilaite, Greta, Monika Duseikaitė, Gabrielė Dubinskaite, Loresa Kriauciuniene, Reda Zemaitiene, and Rasa Liutkevicienė. 2024. "Optic Neuritis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms and Serum Levels of STAT4 (rs10181656, rs7574865, rs7601754, rs10168266)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 13, no. 1: 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010010
APA StyleGedvilaite, G., Duseikaitė, M., Dubinskaite, G., Kriauciuniene, L., Zemaitiene, R., & Liutkevicienė, R. (2024). Optic Neuritis: The Influence of Gene Polymorphisms and Serum Levels of STAT4 (rs10181656, rs7574865, rs7601754, rs10168266). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 13(1), 10. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm13010010







