A Meta-Analysis of Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury: Geographical Differences and Associated Factors
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
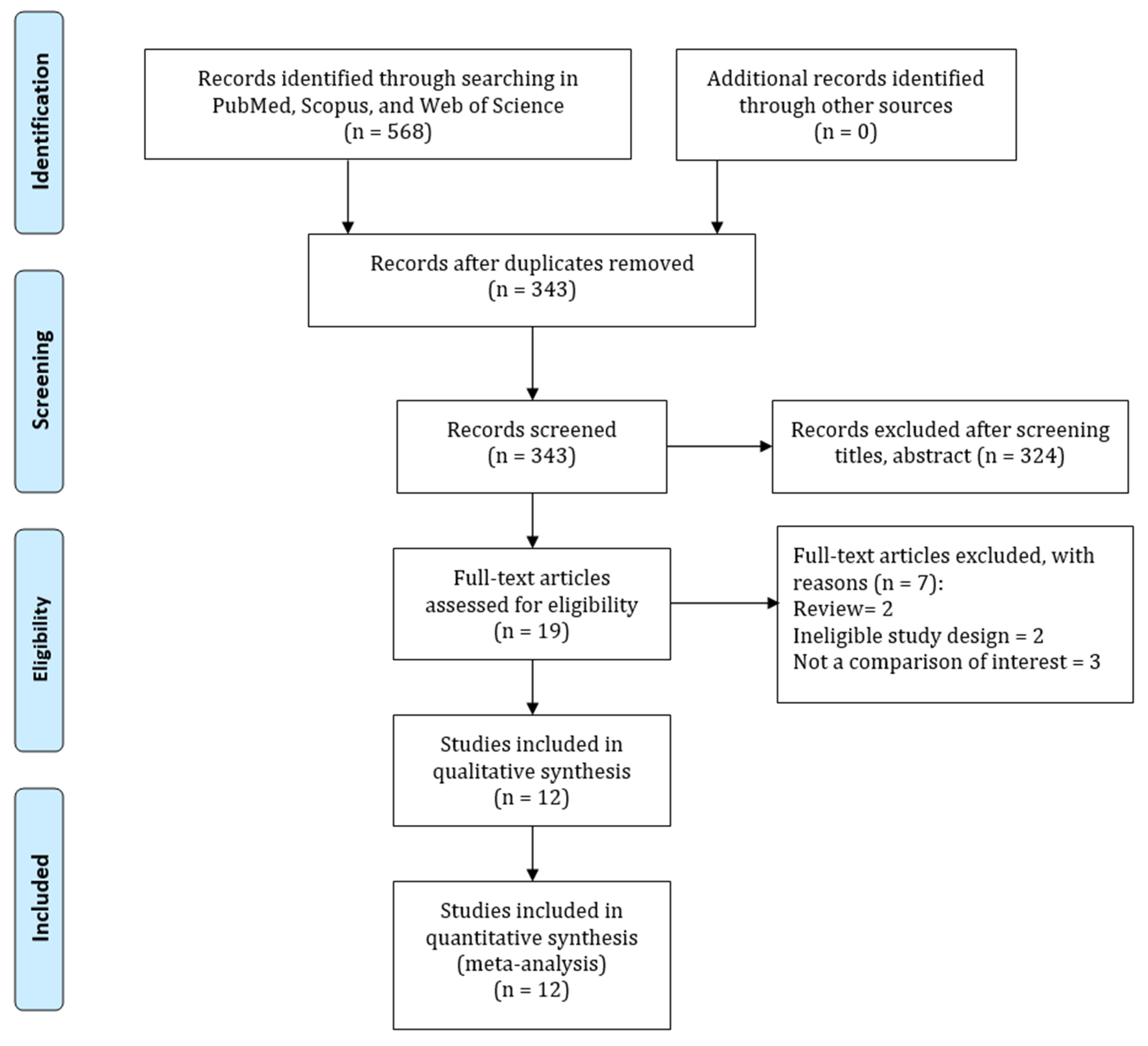
2.1. Search Strategy and Selection Criteria
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Risk-of-Bias Assessment
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Characteristics
3.2. Quality of Included Studies
3.3. Association between PPI Use and AKI Risk
3.4. Subgroup Analyses
3.5. Sensitivity Analysis
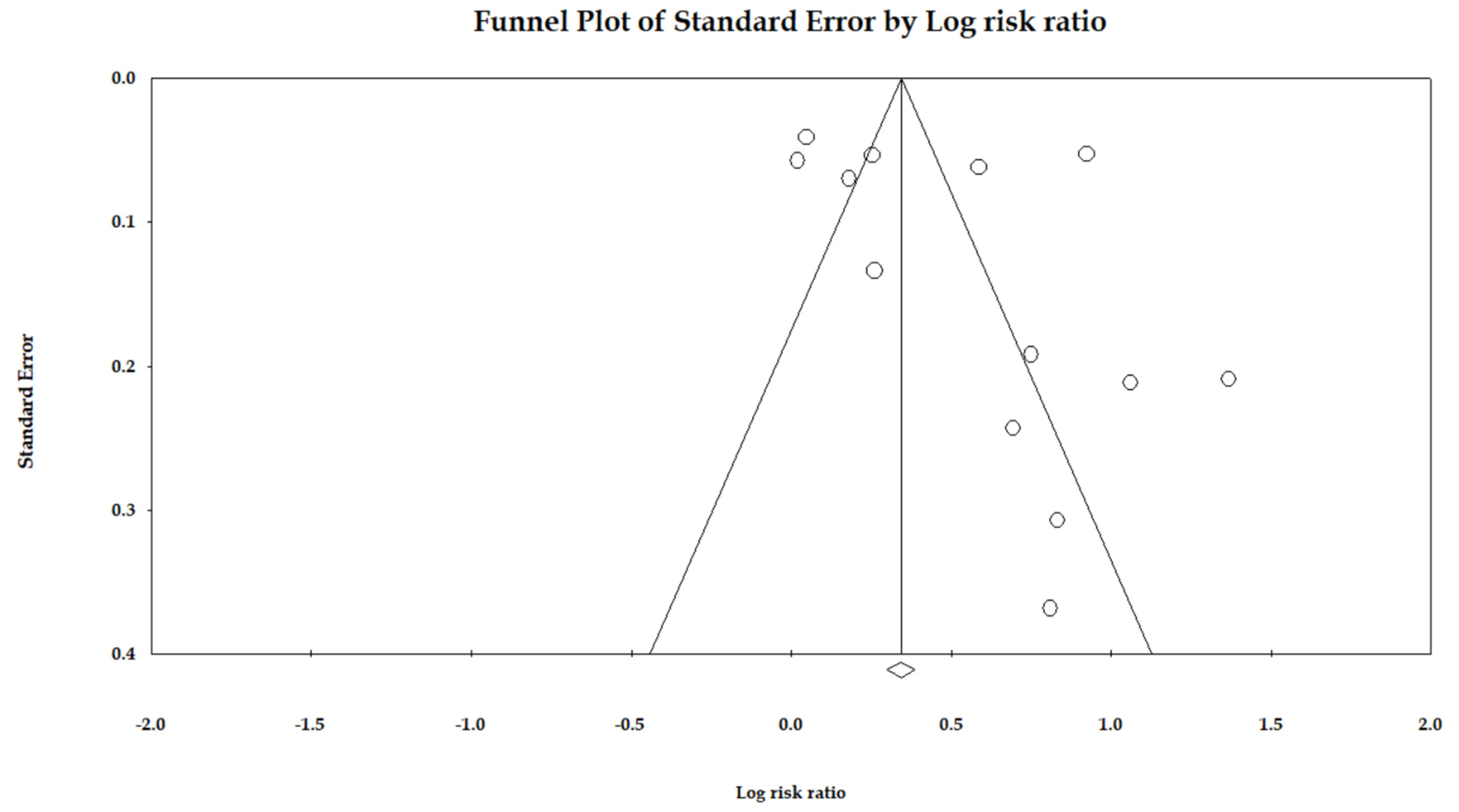
3.6. Publication Bias
4. Discussion
4.1. Main Findings
4.2. Biological Plausibility
4.3. Clinical Implications
4.4. Strengths and Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nugent, R.A.; Fathima, S.F.; Feigl, A.B.; Chyung, D. The burden of chronic kidney disease on developing nations: A 21st century challenge in global health. Nephron Clin. Pract. 2011, 118, c269–c277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Namazzi, R.; Batte, A.; Opoka, R.O.; Bangirana, P.; Schwaderer, A.L.; Berrens, Z.; Datta, D.; Goings, M.; Ssenkusu, J.M.; Goldstein, S.L.; et al. Acute kidney injury, persistent kidney disease, and post-discharge morbidity and mortality in severe malaria in children: A prospective cohort study. EClinicalMedicine 2022, 44, 101292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoste, E.A.; Kellum, J.A.; Selby, N.M.; Zarbock, A.; Palevsky, P.M.; Bagshaw, S.M.; Goldstein, S.L.; Cerdá, J.; Chawla, L.S. Global epidemiology and outcomes of acute kidney injury. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2018, 14, 607–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rewa, O.; Bagshaw, S.M. Acute kidney injury—Epidemiology, outcomes and economics. Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2014, 10, 193–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silver, S.A.; Chertow, G.M. The economic consequences of acute kidney injury. Nephron 2017, 137, 297–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, M.; Brattström, O.; Mårtensson, J.; Larsson, E.; Oldner, A. Acute kidney injury following severe trauma: Risk factors and long-term outcome. J. Trauma Acute Care Surg. 2015, 79, 407–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Sun, H.; Sun, Z.; Yang, X.; Zhou, S.; Wei, J. Intra-abdominal hypertension and increased acute kidney injury risk: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 03000605211016627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patschan, D.; Müller, G. Acute kidney injury in diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Nephrol. 2016, 2016, 6232909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abelha, F.J.; Botelho, M.; Fernandes, V.; Barros, H. Determinants of postoperative acute kidney injury. Crit. Care 2009, 13, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Rifkin, D.E.; Blantz, R.C. Chronic kidney disease: An inherent risk factor for acute kidney injury? Clin. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2010, 5, 1690–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poly, T.N.; Islam, M.M.; Walther, B.A.; Lin, M.-C.; Li, Y.-C. Proton Pump Inhibitors Use and the Risk of Pancreatic Cancer: Evidence from Eleven Epidemiological Studies, Comprising 1.5 Million Individuals. Cancers 2022, 14, 5357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fass, R.; Sifrim, D. Management of heartburn not responding to proton pump inhibitors. Gut 2009, 58, 295–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazarus, B.; Chen, Y.; Wilson, F.P.; Sang, Y.; Chang, A.R.; Coresh, J.; Grams, M.E. Proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of chronic kidney disease. JAMA Intern. Med. 2016, 176, 238–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Aly, Z.; Maddukuri, G.; Xie, Y. Proton pump inhibitors and the kidney: Implications of current evidence for clinical practice and when and how to deprescribe. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2020, 75, 497–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.; Poly, T.N.; Walther, B.A.; Dubey, N.K.; Anggraini Ningrum, D.N.; Shabbir, S.-A. Adverse outcomes of long-term use of proton pump inhibitors: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 1395–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Alamo, B.; Cases-Corona, C.; Fernandez-Juarez, G. Facing the challenge of drug-induced acute interstitial nephritis. Nephron 2022, 147, 78–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raghavan, R.; Shawar, S. Mechanisms of drug-induced interstitial nephritis. Adv. Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017, 24, 64–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brewster, U.; Perazella, M. Proton pump inhibitors and the kidney: Critical. Clin. Nephrol. 2007, 68, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lau, J.Y.; Sung, J.J.; Lee, K.K.; Yung, M.-y.; Wong, S.K.; Wu, J.C.; Chan, F.K.; Ng, E.K.; You, J.H.; Lee, C. Effect of intravenous omeprazole on recurrent bleeding after endoscopic treatment of bleeding peptic ulcers. N. Engl. J. Med. 2000, 343, 310–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Brady, P. Gastroesophageal reflux disease: Pathophysiology, diagnosis, and treatment. Gastroenterol. Nurs. 2019, 42, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antoniou, T.; Macdonald, E.M.; Hollands, S.; Gomes, T.; Mamdani, M.M.; Garg, A.X.; Paterson, J.M.; Juurlink, D.N. Proton pump inhibitors and the risk of acute kidney injury in older patients: A population-based cohort study. Can. Med. Assoc. Open Access J. 2015, 3, E166–E171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hart, E.; Dunn, T.E.; Feuerstein, S.; Jacobs, D.M. Proton pump inhibitors and risk of acute and chronic kidney disease: A retrospective cohort study. Pharmacother. J. Hum. Pharmacol. Drug Ther. 2019, 39, 443–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leonard, C.E.; Freeman, C.P.; Newcomb, C.W.; Reese, P.P.; Herlim, M.; Bilker, W.B.; Hennessy, S.; Strom, B.L. Proton pump inhibitors and traditional nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and the risk of acute interstitial nephritis and acute kidney injury. Pharmacoepidemiol. Drug Saf. 2012, 21, 1155–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Mark, R.G.; Celi, L.A.; Danziger, J. Proton pump inhibitors are not associated with acute kidney injury in critical illness. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2016, 56, 1500–1506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knobloch, K.; Yoon, U.; Vogt, P.M. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) statement and publication bias. J. Cranio-Maxillofac. Surg. 2011, 39, 91–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G.; Group, P. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wells, G.; Shea, B.; O’connell, D.; Peterson, J.; Welch, V.; Losos, M.; Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Quality Assessment Scale (NOS) for assessing the quality of nonrandomized studies in meta-analyses. Clin. Epidemiol. [Internet] 2017, 2017, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Biggerstaff, B.; Tweedie, R. Incorporating variability in estimates of heterogeneity in the random effects model in meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 1997, 16, 753–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poly, T.N.; Islam, M.M.; Walther, B.A.; Yang, H.-C.; Wu, C.-C.; Lin, M.-C.; Li, Y.-C. Association between use of statin and risk of dementia: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Neuroepidemiology 2020, 54, 214–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poly, T.N.; Islam, M.M.; Yang, H.C.; Lin, M.C.; Jian, W.-S.; Hsu, M.-H.; Jack Li, Y.-C. Obesity and mortality among patients diagnosed with COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 620044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Islam, M.M.; Nasrin, T.; Walther, B.A.; Wu, C.-C.; Yang, H.-C.; Li, Y.-C. Prediction of sepsis patients using machine learning approach: A meta-analysis. Comput. Methods Programs Biomed. 2019, 170, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikuta, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Yamawaki, C.; Itohara, K.; Hira, D.; Imai, S.; Yonezawa, A.; Nakagawa, T.; Sakuragi, M.; Sato, N. Use of proton pump inhibitors and macrolide antibiotics and risk of acute kidney injury: A self-controlled case series study. BMC Nephrol. 2022, 23, 383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klatte, D.C.; Gasparini, A.; Xu, H.; de Deco, P.; Trevisan, M.; Johansson, A.L.; Wettermark, B.; Ärnlöv, J.; Janmaat, C.J.; Lindholm, B. Association between proton pump inhibitor use and risk of progression of chronic kidney disease. Gastroenterology 2017, 153, 702–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klepser, D.G.; Collier, D.S.; Cochran, G.L. Proton pump inhibitors and acute kidney injury: A nested case–control study. BMC Nephrol. 2013, 14, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liabeuf, S.; Lambert, O.; Metzger, M.; Hamroun, A.; Laville, M.; Laville, S.M.; Frimat, L.; Pecoits-Filho, R.; Fouque, D.; Massy, Z.A. Adverse outcomes of proton pump inhibitors in patients with chronic kidney disease: The CKD-REIN cohort study. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 2967–2976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutton, S.S.; Magagnoli, J.; Cummings, T.H.; Hardin, J.W. Risk of acute kidney injury in patients with HIV receiving proton pump inhibitors. J. Comp. Eff. Res. 2019, 8, 781–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svanström, H.; Lund, M.; Melbye, M.; Pasternak, B. Use of proton pump inhibitors and the risk of acute kidney injury among patients with rheumatoid arthritis: Cohort study. Drug Saf. 2018, 41, 817–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, Y.; Bowe, B.; Yan, Y.; Xian, H.; Li, T.; Al-Aly, Z. Estimates of all cause mortality and cause specific mortality associated with proton pump inhibitors among US veterans: Cohort study. BMJ 2019, 365, l1580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; George, K.C.; Shang, W.-F.; Zeng, R.; Ge, S.-W.; Xu, G. Proton-pump inhibitors use, and risk of acute kidney injury: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2017, 11, 1291–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, I.J.; Marshall, M.R.; Pilmore, H.; Manley, P.; Williams, L.; Thein, H.; Voss, D. Proton pump inhibitors and acute interstitial nephritis: Report and analysis of 15 cases. Nephrology 2006, 11, 381–385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavan, R.; Eknoyan, G. Acute interstitial nephritis–a reappraisal and update. Clin. Nephrol. 2014, 82, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamal, F.; Khan, M.A.; Molnar, M.Z.; Howden, C.W. The association between proton pump inhibitor use with acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2018, 52, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corsonello, A.; Lattanzio, F.; Bustacchini, S.; Garasto, S.; Cozza, A.; Schepisi, R.; Lenci, F.; Luciani, F.; Maggio, M.G.; Ticinesi, A. Adverse events of proton pump inhibitors: Potential mechanisms. Curr. Drug Metab. 2018, 19, 142–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bignardi, G.E. Risk factors for Clostridium difficile infection. J. Hosp. Infect. 1998, 40, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dial, S.; Alrasadi, K.; Manoukian, C.; Huang, A.; Menzies, D. Risk of Clostridium difficile diarrhea among hospital inpatients prescribed proton pump inhibitors: Cohort and case–control studies. CMAJ 2004, 171, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leonard, J.; Marshall, J.K.; Moayyedi, P. Systematic review of the risk of enteric infection in patients taking acid suppression. Off. J. Am. Coll. Gastroenterol. ACG 2007, 102, 2047–2056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arrich, J.; Sodeck, G.H.; Sengölge, G.; Konnaris, C.; Müllner, M.; Laggner, A.N.; Domanovits, H. Clostridium difficile causing acute renal failure: Case presentation and review. World J. Gastroenterol. WJG 2005, 11, 1245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, B.; Seguro, A.; Andrade, L. Hypomagnesemia is a risk factor for nonrecovery of renal function and mortality in AIDS patients with acute kidney injury. Braz. J. Med. Biol. Res. 2010, 43, 316–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, S.C.; Tomasi, C.D.; Constantino, L.; Giombelli, V.; Candal, R.; Bristot, M.d.L.; Topanotti, M.F.; Burdmann, E.A.; Dal-Pizzol, F.; Fraga, C.M. Hypomagnesemia as a risk factor for the non-recovery of the renal function in critically ill patients with acute kidney injury. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2013, 28, 910–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Laecke, S.; Nagler, E.V.; Verbeke, F.; Van Biesen, W.; Vanholder, R. Hypomagnesemia and the risk of death and GFR decline in chronic kidney disease. Am. J. Med. 2013, 126, 825–831. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tannenbaum, H.; Peloso, P.; Russell, A.; Marlow, B. An evidence-based approach to prescribing NSAIDs in the treatment of osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis: The Second Canadian Consensus Conference. Can. J. Clin. Pharmacol. J. Can. Pharmacol. Clin. 2000, 7, 4A–16A. [Google Scholar]
- Members, W.C.; Bhatt, D.L.; Scheiman, J.; Abraham, N.S.; Antman, E.M.; Chan, F.K.; Furberg, C.D.; Johnson, D.A.; Mahaffey, K.W.; Quigley, E.M. ACCF/ACG/AHA 2008 expert consensus document on reducing the gastrointestinal risks of antiplatelet therapy and NSAID use: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation Task Force on Clinical Expert Consensus Documents. Circulation 2008, 118, 1894–1909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikuta, K.; Nakagawa, S.; Momo, K.; Yonezawa, A.; Itohara, K.; Sato, Y.; Imai, S.; Nakagawa, T.; Matsubara, K. Association of proton pump inhibitors and concomitant drugs with risk of acute kidney injury: A nested case–control study. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e041543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moledina, D.G.; Perazella, M.A. PPIs and kidney disease: From AIN to CKD. J. Nephrol. 2016, 29, 611–616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perico, N.; Remuzzi, G. Chronic kidney disease: A research and public health priority. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2012, 27 (Suppl. S3), iii19–iii26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silver, S.A.; Long, J.; Zheng, Y.; Chertow, G.M. Cost of acute kidney injury in hospitalized patients. J. Hosp. Med. 2017, 12, 70–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nash, D.M.; Markle-Reid, M.; Brimble, K.S.; McArthur, E.; Roshanov, P.S.; Fink, J.C.; Weir, M.A.; Garg, A.X. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug use and risk of acute kidney injury and hyperkalemia in older adults: A population-based study. Nephrol. Dial. Transplant. 2019, 34, 1145–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, C.K.; Au, I.C.; Cheng, W.Y.; Man, K.K.; Lau, K.T.; Mak, L.Y.; Lui, S.L.; Chung, M.S.; Xiong, X.; Lau, E.H. Remdesivir use and risks of acute kidney injury and acute liver injury among patients hospitalised with COVID-19: A self-controlled case series study. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2022, 56, 121–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, Y.J.; Dixon, S.N.; Reiss, J.P.; Wald, R.; Parikh, C.R.; Gandhi, S.; Shariff, S.Z.; Pannu, N.; Nash, D.M.; Rehman, F. Atypical antipsychotic drugs and the risk for acute kidney injury and other adverse outcomes in older adults: A population-based cohort study. Ann. Intern. Med. 2014, 161, 242–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haenisch, B.; von Holt, K.; Wiese, B.; Prokein, J.; Lange, C.; Ernst, A.; Brettschneider, C.; König, H.-H.; Werle, J.; Weyerer, S. Risk of dementia in elderly patients with the use of proton pump inhibitors. Eur. Arch. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2015, 265, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poly, T.; Islam, M.; Yang, H.-C.; Wu, C.; Li, Y.-C. Proton pump inhibitors and risk of hip fracture: A meta-analysis of observational studies. Osteoporos. Int. 2019, 30, 103–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kopitkó, C.; Medve, L.; Gondos, T.; Soliman, K.M.M.; Fülöp, T. Mediators of Regional Kidney Perfusion during Surgical Pneumo-Peritoneum Creation and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury—A Review of Basic Physiology. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murugan, R.; Kellum, J.A. Acute kidney injury: What’s the prognosis? Nat. Rev. Nephrol. 2011, 7, 209–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashani, K.; Macedo, E.; Burdmann, E.A.; Hooi, L.S.; Khullar, D.; Bagga, A.; Chakravarthi, R.; Mehta, R.; Group, C.; Initiative, A.D.Q. Acute kidney injury risk assessment: Differences and similarities between resource-limited and resource-rich countries. Kidney Int. Rep. 2017, 2, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jha, V.; Garcia-Garcia, G.; Iseki, K.; Li, Z.; Naicker, S.; Plattner, B.; Saran, R.; Wang, A.Y.-M.; Yang, C.-W. Chronic kidney disease: Global dimension and perspectives. Lancet 2013, 382, 260–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohammad, K.N.; Chan, E.Y.Y.; Lau, S.Y.-F.; Lam, H.C.Y.; Goggins, W.B.; Chong, K.C. Relationship between acute kidney injury, seasonal influenza, and environmental factors: A 14-year retrospective analysis. Environ. Int. 2021, 153, 106521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McTavish, R.K.; Richard, L.; McArthur, E.; Shariff, S.Z.; Acedillo, R.; Parikh, C.R.; Wald, R.; Wilk, P.; Garg, A.X. Association between high environmental heat and risk of acute kidney injury among older adults in a northern climate: A matched case-control study. Am. J. Kidney Dis. 2018, 71, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, P.A.; Islam, M.; Galvin, C.J.; Chang, C.-C.; An, S.Y.; Yang, H.-C.; Huang, C.-W.; Li, Y.-C.; Iqbal, U. Meta-analysis of proton pump inhibitors induced risk of community-acquired pneumonia. Int. J. Qual. Health Care 2020, 32, 292–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnstone, J.; Nerenberg, K.; Loeb, M. Meta-analysis: Proton pump inhibitor use and the risk of community-acquired pneumonia. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2010, 31, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
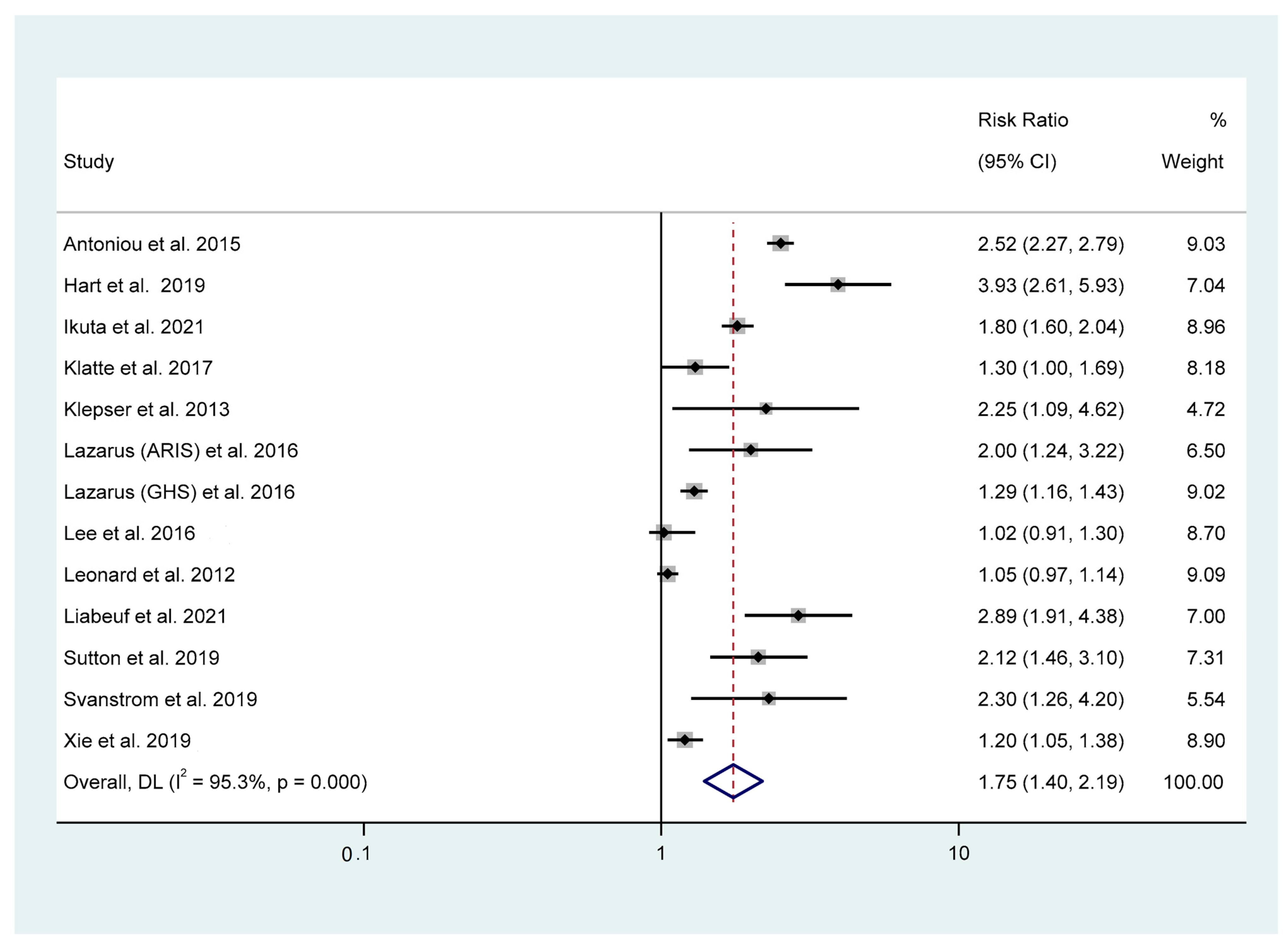
| Author, Year | Location | Study Design | Sample Size | Female | Age (Mean) | AKI Assessment | Duration | NOS |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antoniou 2015 [21] | Canada | Cohort | 290,592 | 56.7 | >65 | ICD | 2002–2011 | 8 |
| Hart 2019 [22] | USA | Cohort | 93,335 | 61.4 | 51.4/50.9 | ICD | 1993–2008 | 9 |
| Ikuta 2022 [32] | Japan | C-C | 3685 | 36.9 | 52 | ICD | 2005–2007 | 7 |
| Klatte 2017 [33] | Sweden | Cohort | 114,883 | 60.3 | 62.4 | ICD | 2007–2010 | 8 |
| Klepser 2013 [34] | USA | C-C | 802 | 57.4 | 44.6 | ICD | 2002–2005 | 7 |
| Lazarus 2016 [13] | USA | Cohort (ARIC) | 11,145 | 57.5 | 62.8 | ICD | 1996–2011 | 9 |
| Cohort (GHS) | 248,751 | 56.8 | 50.0 | ICD | 1997–2014 | 9 | ||
| Leonard 2012 [23] | UK | C-C | 1,351,832 | 50.3 | 68.6 | OXMIS | 1987–2002 | 8 |
| Lee 2016 [24] | USA | Cohort | 15,158 | 45.9 | 67.9 | KDIGO | 2001–2008 | 8 |
| Liabeuf 2020 [35] | France | Cohort | 3023 | 35 | 70 | ICD | 2013–2016 | 9 |
| Sutton 2019 [36] | USA | Cohort | 21,643 | 3 | 54.13 | ICD | 2005–2012 | 7 |
| Svanstrom 2018 [37] | Denmark | Cohort | 122,809 | 76 | 63 | ICD | 2004–2015 | 8 |
| Xie 2019 [38] | USA | Cohort | 21,4467 | 4.07 | 65.10 | ICD | 2002–2004 | 8 |
| Characteristics | Number of Studies | RR (95%CI) | p-Value | I2 Value | Q Value | τ2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| All studies | 12 | 1.75 (1.40–2.19) | <0.001 | 95.30 | 274.90 | 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Study design | |||||||
| Cohort | 9 | 1.82 (1.38–2.41) | <0.001 | 95.47 | 198.65 | 0.17 | <0.001 |
| Case–control | 3 | 1.52 (0.95–2.43) | 0.08 | 96.36 | 55.05 | 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Location | |||||||
| North America | 7 | 1.80 (1.31–2.48) | <0.001 | 96.26 | 187.36 | 0.18 | <0.001 |
| Europe | 4 | 1.64 (1.06–2.54) | 0.02 | 89.73 | 29.22 | 0.18 | <0.001 |
| Asia | 1 | 1.80 (1.59–2.03) | <0.001 | - | - | - | - |
| Methodological quality | |||||||
| High | 9 | 1.68 (1.29–2.199) | <0.001 | 96.39 | 249.93 | 0.15 | <0.001 |
| Moderate | 3 | 1.83 (1.63–2.06) | <0.001 | 0 | 0.96 | 0 | <0.001 |
| Types of PPI | |||||||
| Lansoprazole | 1 | 2.56 (1.85–3.55) | <0.05 | - | - | - | - |
| Omeprazole | 1 | 2.94 (2.21–3.91) | <0.05 | - | - | - | - |
| Pantoprazole | 1 | 2.43 (1.97–3.00) | <0.05 | - | - | - | - |
| Rabeprazole | 1 | 2.45 (2.12–2.83) | <0.05 | - | - | - | - |
| Characteristics | RR (95%CI) | p-Value | I2 Value | Q Value | τ2 | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Antoniou et al. [21] | 1.63 (1.35–1.96) | <0.001 | 91.48 | 129.10 | 0.07 | <0.001 |
| Hart et al. [22] | 1.63 (1.30–2.04) | <0.001 | 95.61 | 250.63 | 0.13 | <0.001 |
| Ikuta et al. [32] | 1.74 (1.36–2.22) | <0.001 | 95.72 | 257.18 | 0.15 | <0.001 |
| Klatte et al. [33] | 1.79 (1.41–2.26) | <0.001 | 95.99 | 274.54 | 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Klepser et al. [34] | 1.72 (1.37–2.16) | <0.001 | 95.97 | 273.28 | 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Lazarus (ARIS) et al. [13] | 1.72 (1.37–2.17) | <0.001 | 95.96 | 272.81 | 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Lazarus (GHS) et al. [13] | 1.80 (1.40–2.33) | <0.001 | 95.95 | 271.69 | 0.17 | <0.001 |
| Lee et al. [24] | 1.84 (1.45–2.33) | <0.001 | 95.38 | 238.44 | 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Leonard et al. [23] | 1.83 (1.45–2.32) | <0.001 | 94.65 | 205.83 | 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Liabeuf et al. [35] | 1.67 (1.33–2.10) | <0.001 | 95.82 | 263.26 | 0.13 | <0.001 |
| Sutton et al. [36] | 1.71 (1.36–2.16) | <0.001 | 95.93 | 270.32 | 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Svanstrom et al. [37] | 1.71 (1.36–2.15) | <0.001 | 95.96 | 272.34 | 0.14 | <0.001 |
| Xie et al. [38] | 1.81 (1.42–2.31) | <0.001 | 95.91 | 269.09 | 0.15 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, C.T.; Islam, M.M.; Poly, T.N.; Lu, Y.-C.; Lin, M.-C. A Meta-Analysis of Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury: Geographical Differences and Associated Factors. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072467
Han CT, Islam MM, Poly TN, Lu Y-C, Lin M-C. A Meta-Analysis of Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury: Geographical Differences and Associated Factors. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(7):2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072467
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Cheng Ta, Md. Mohaimenul Islam, Tahmina Nasrin Poly, Yu-Chun Lu, and Ming-Chin Lin. 2023. "A Meta-Analysis of Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury: Geographical Differences and Associated Factors" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 7: 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072467
APA StyleHan, C. T., Islam, M. M., Poly, T. N., Lu, Y.-C., & Lin, M.-C. (2023). A Meta-Analysis of Proton Pump Inhibitor Use and the Risk of Acute Kidney Injury: Geographical Differences and Associated Factors. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(7), 2467. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12072467







