Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Following the BNT162b2 (BioNTech/Pfizer) Vaccine Successfully Treated with Mepolizumab: A Case Report and Review of the Literature
Abstract
1. Introduction
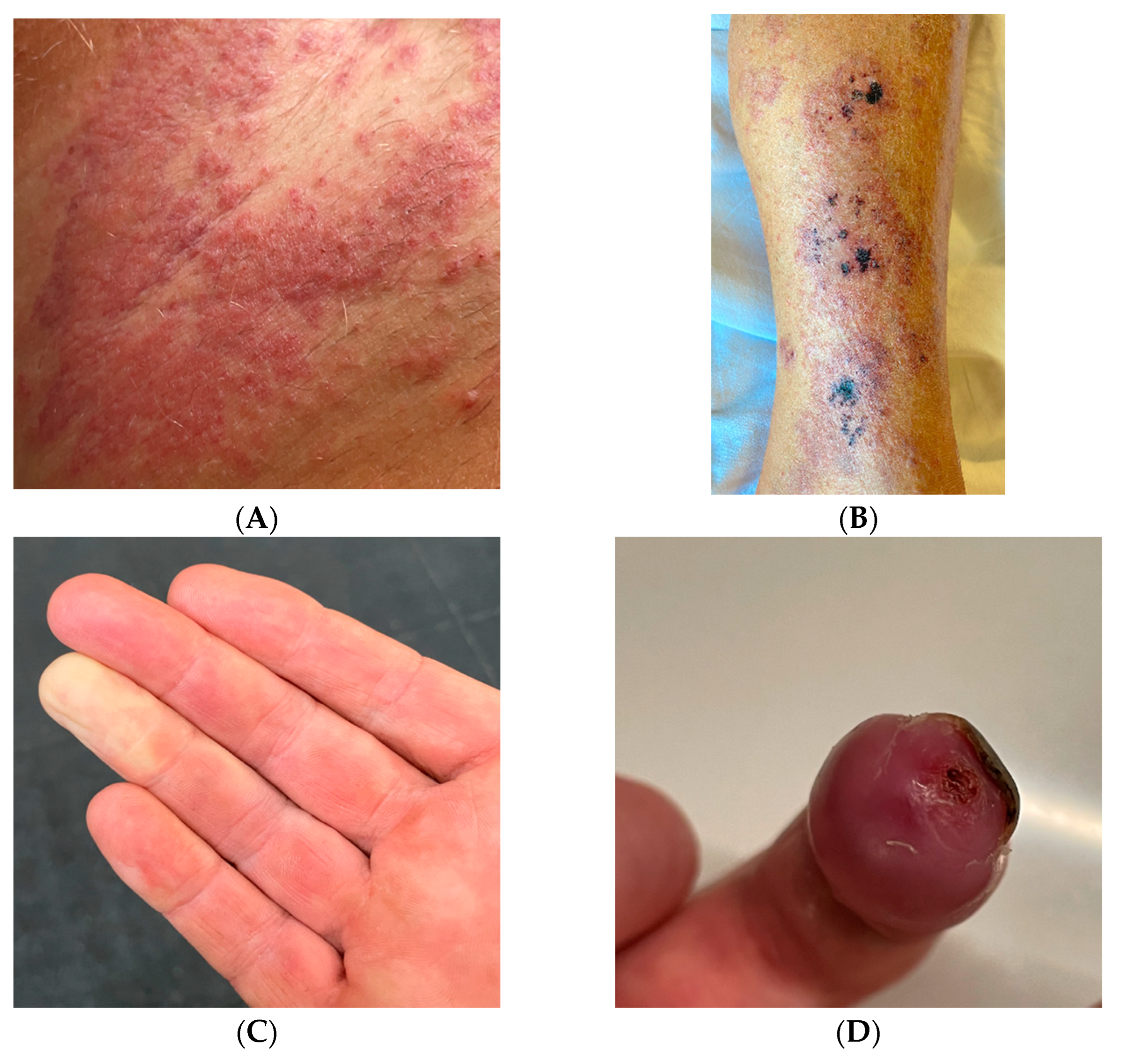
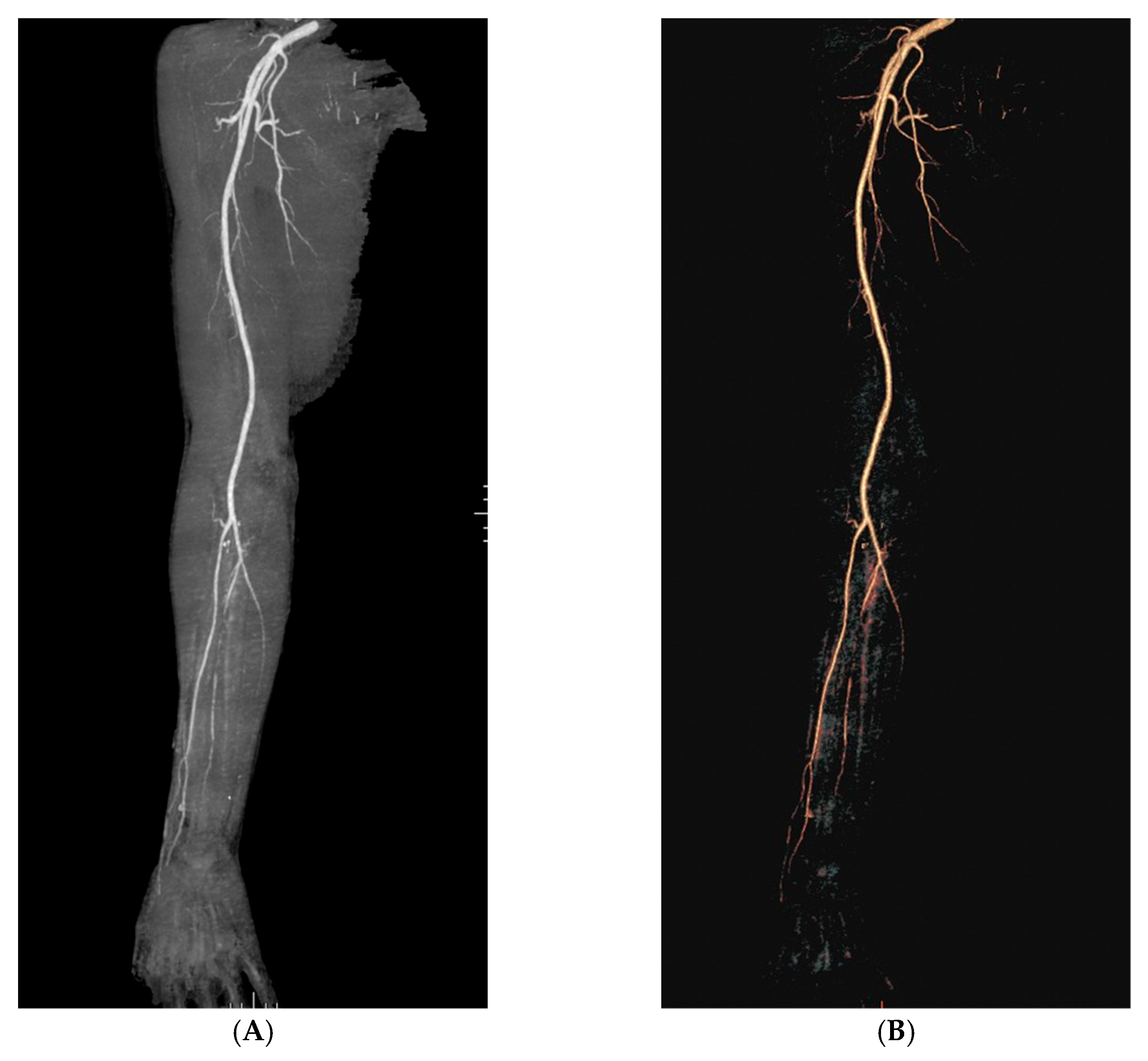
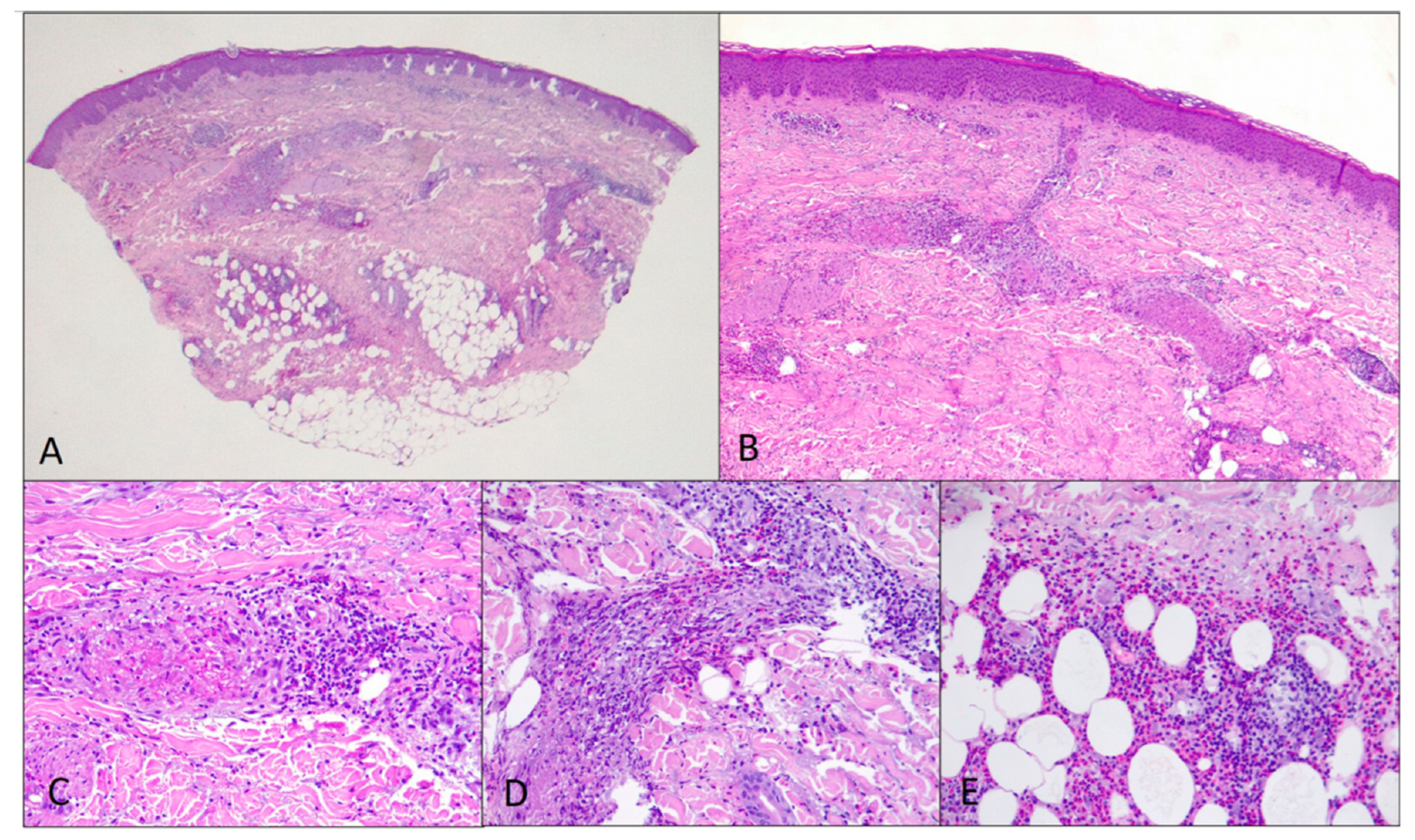
2. Case Description
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int (accessed on 31 January 2023).
- Polack, F.P.; Thomas, S.J.; Kitchin, N.; Absalon, J.; Gurtman, A.; Lockhart, S.; Perez, J.L.; Marc, G.P.; Moreira, E.D.; Zerbini, C.; et al. Safety and efficacy of the BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 vaccine. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 2603–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vacchi, C.; Testoni, S.; Visentini, M.; Zani, R.; Lauletta, G.; Gragnani, L.; Filippini, D.; Mazzaro, C.; Fraticelli, P.; Quartuccio, L.; et al. COVID-19 vaccination rate and safety profile in a multicentre Italian population affected by mixed cryoglobulinaemic vasculitis. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2022; in press. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pengo, V.; Del Ross, T.; Tonello, M.; Andreoli, L.; Tincani, A.; Gresele, P.; Silvestri, E.; Simioni, P.; Campello, E.; Hoxha, A. COVID-19 APS collaborators. Impact of COVID-19 and COVID-19 vaccination on high-risk patients with antiphospholipid syndrome: A nationwide survey. Rheumatology 2022, 28, SI136–SI142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Machado, P.M.; Lawson-Tovey, S.; Strangfeld, A.; Mateus, E.F.; Hyrich, K.L.; Gossec, L.; Carmona, L.; Rodrigues, A.; Raffeiner, B.; Duarte, C.; et al. Safety of vaccination against SARS-CoV-2 in people with rheumatic and musculoskeletal diseases: Results from the EULAR Coronavirus Vaccine (COVAX) physician-reported registry. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2022, 81, 695–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shomali, W.; Gotlib, J. World Health Organization-defined eosinophilic disorders: 2019 update on diagnosis, risk stratification, and management. Am. J. Hematol. 2019, 94, 1149–1167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valent, P.; Klion, A.D.; Horny, H.P.; Roufosse, F.; Gotlib, J.; Weller, P.F.; Hellmann, A.; Metzgeroth, G.; Leiferman, K.M.; Arock, M.; et al. Contemporary consensus proposal on criteria and classification of eosinophilic disorders and related syndromes. J. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. 2012, 130, 607–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, C.; Princess, O. Hypereosinopholis syndrome. Clinic. Rev. Allergy. Immunol. 2016, 50, 240–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lindsey, A.W.; Schwartz, J.T.; Rothenberg, M.E. Eosinophil responses during COVID-19 infections and coronavirus vaccination. J. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pornsuriyasak, P.; Suwatanapongched, T.; Klaewsongkram, J.; Buranapraditkun, S.; Rotjanapan, P. Acute respiratory failure secondary to eosinophilic pneumonia following influenza vaccination in an elderly man with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2014, 26, 14–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kikuchi, R.; Iwai, Y.; Watanabe, Y.; Nakamura, H.; Aoshiba, K. Acute respiratory failure due to eosinophilic pneumonia following pneumococcal vaccination. Hum. Vaccin. Immunother. 2019, 15, 2914–2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kapikian, A.; Mitchell, R.; Chanock, R.; Shvedoff, R.; Stewart, C. An epidemiological study of altered clinical reactivity to respiratory syncytial (RS) virus infection in children previously vaccinate with an inactivated RS virus vaccine. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1969, 89, 405–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tseng, C.T.; Sbrana, E.; Iwata-Yoshikawa, N.; Newman, P.C.; Garron, T.; Atmar, R.L.; Peters, C.J.; Couch, R.B. Immunization with SARS coronavirus vaccines leads to pulmonary immunopathology on challenge with the SARS virus. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e35421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cabanillas, B.; Novak, N. Allergy to COVID-19 vaccines: A current update. Allergol. Int. 2021, 70, 313–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ozturk, A.B.; Çağlayan, B.; Kapmaz, M.; Çalık, I.; Tekin, S.; İliaz, S.; Fırat, P. Hypersensitivity reactions to COVID-19 vaccines: A case of Eosinophilic pneumonia following Sinovac/CoronaVac vaccination. Eur. Ann. Allergy. Clin. Immunol. 2023, 55, 41–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May, J.; Draper, A.; Aul, R. Eosinophilic pneumonia and COVID-19 vaccination. QJM 2022, 115, 251–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiwari, A.; Karna, G.; Chakrabarti, S.S.; Panda, P.K.; Kaur, U. Hypereosinophilic syndrome with myocarditis after inactivated SARS-CoV-2 vaccination—A case study. Curr. Drug. Saf. 2022, 18, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa ESilva, M.; Sá Marques, M.; João, D.; Campainha, S. Eosinophilic Pneumonia Associated to SARS-CoV-2 Vaccine. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2022, 58, 51–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrio Piqueras, M.; Ezponda, A.; Felgueroso, C.; Urtasun, C.; Di Frisco, I.M.; Larrache, J.C.; Bastarrika, G.; Alcaide, A.B. Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia Following mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination: A Case Report. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2022, 58, 53–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miqdadi, A.; Herrag, M. Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia Associated with the Anti-COVID-19 Vaccine AZD1222. Cureus 2021, 13, e18959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harish, A.; Schwartz, S.A. Targeted Anti-IL-5 Therapies and Future Therapeutics for Hypereosinophilic Syndrome and Rare Eosinophilic Conditions. Clin. Rev. Allergy. Immunol. 2020, 59, 231–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Author, Year | Sex | Age (Years) | COVID-19 Vaccine | Time from Vaccine | Clinical Condition | Blood Eosinophils | Biopsy | Treatment | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ozturk et al., 2023 [15] | F | 73 | Sinovac/CoronaVac | 4 days | HES | 2300 μ/L | BAL: 36% eosinophils TBNA: eosinophile infiltration | MPN 1 mg/kg/day for 7 days and then 40 mg/daily tapered and discontinued over 3 months | Recovered with steroids |
| May et al., 2022 [16] | F | 55 | ChAdOx1 nCov-19 | 7 weeks | Eosinophilic pneumoniae | 900 μ/L | BAL: 50% eosinophils | MPN 500 mg then PDN 30 mg per day, tapered and discontinued over 12 weeks | Recovered with steroids |
| Tiwari et al., 2022 [17] | M | 33 | COVAXIN | 8 days | HES | 2767 μ/L | NA | Dexa 6 mg twice daily for five days | Recovered with steroids |
| Costa e Silva et al., 2022 [18] | F | 38 | NR | 2 weeks | Eosinophilic pneumoniae | 3250 μ/L | BAL: 13% eosinophils | Deflazacort 60 mg/die | Recovered with steroids |
| F | 47 | NR | 4 weeks | Eosinophilic pneumoniae | 800 μ/L | BAL: 11% eosinophils | PDN 40 mg/day for 14 days | Recovered with steroids | |
| Piqueras et al., 2022 [19] | M | 37 | Pfizer-BioNTech | 8–10 h | Eosinophilic pneumoniae | 4130 μ/L | BAL: 60.3% eosinophils | None | Spontaneous clinical improvement |
| Miqdadi et al., 2021 [20] | M | 66 | ChAdOx1 nCoV-19 | 5 h | Eosinophilic pneumoniae | 3960 μ/L | NA | MPN 240 mg/daily for 5 days and then tapered and discontinued over 3 months | Recovered with steroids |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Hoxha, A.; Tomaselli, T.; Minicucci, G.M.; Dall’Acqua, J.; Zardo, D.; Simioni, P.; Naldi, L. Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Following the BNT162b2 (BioNTech/Pfizer) Vaccine Successfully Treated with Mepolizumab: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062376
Hoxha A, Tomaselli T, Minicucci GM, Dall’Acqua J, Zardo D, Simioni P, Naldi L. Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Following the BNT162b2 (BioNTech/Pfizer) Vaccine Successfully Treated with Mepolizumab: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(6):2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062376
Chicago/Turabian StyleHoxha, Ariela, Tania Tomaselli, Giacomo Maria Minicucci, Jacopo Dall’Acqua, Davide Zardo, Paolo Simioni, and Luigi Naldi. 2023. "Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Following the BNT162b2 (BioNTech/Pfizer) Vaccine Successfully Treated with Mepolizumab: A Case Report and Review of the Literature" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 6: 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062376
APA StyleHoxha, A., Tomaselli, T., Minicucci, G. M., Dall’Acqua, J., Zardo, D., Simioni, P., & Naldi, L. (2023). Hypereosinophilic Syndrome Following the BNT162b2 (BioNTech/Pfizer) Vaccine Successfully Treated with Mepolizumab: A Case Report and Review of the Literature. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(6), 2376. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062376







