Rifaximin Improves Liver Functional Reserve by Regulating Systemic Inflammation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
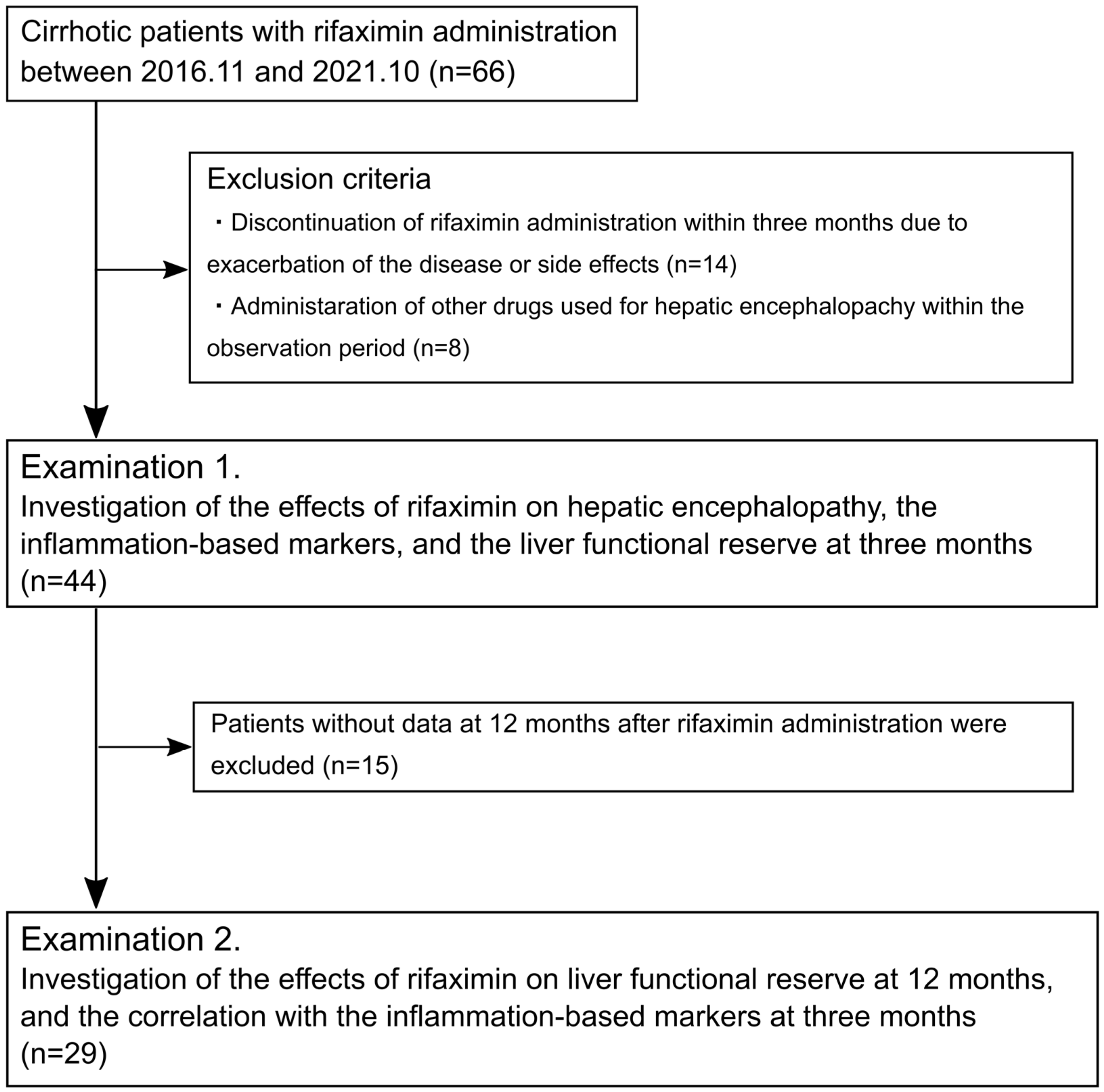
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Evaluations
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Impact of Rifaximin on Hepatic Encephalopathy and Serum Ammonia Levels
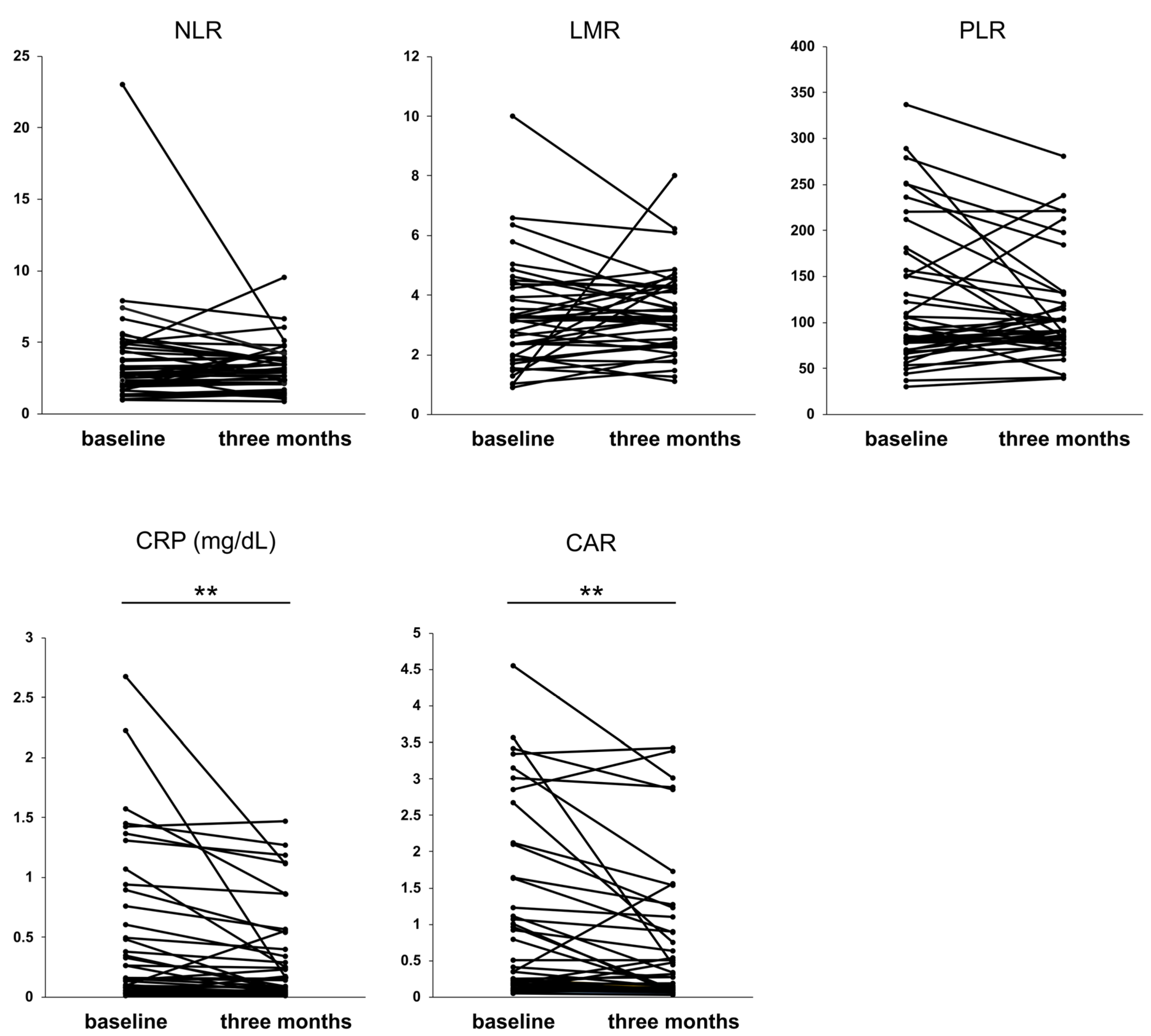
3.3. Impact of Rifaximin on Serological Inflammation-Based Markers
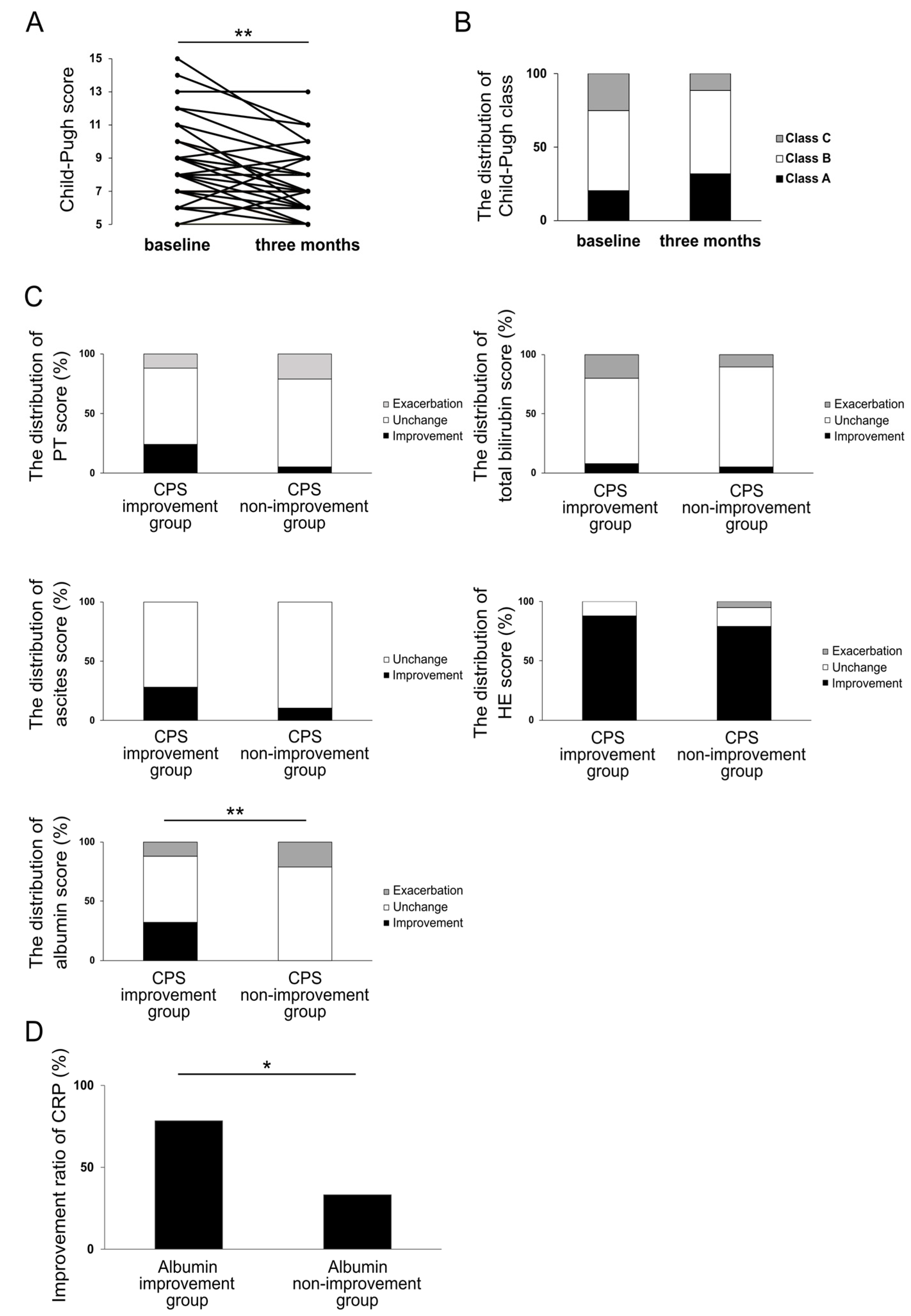
3.4. Impact of Rifaximin on Liver Functional Reserve at Three Months
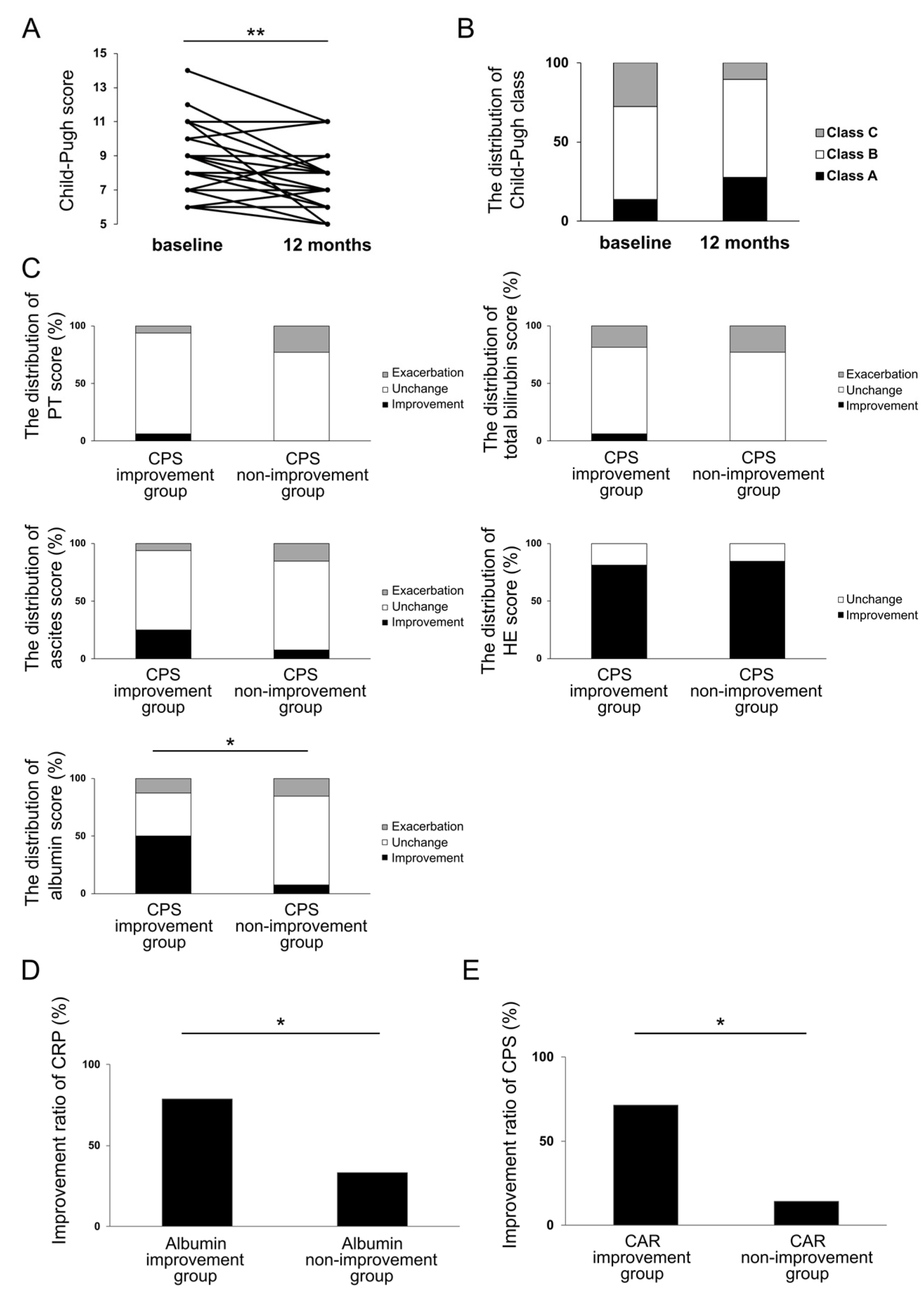
3.5. Investigation of the Effect of Rifaximin on Liver Functional Reserve at 12 Months and Its Relation to Inflammation-Based Markers
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Asrani, S.K.; Devarbhavi, H.; Eaton, J.; Kamath, P.S. Burden of liver diseases in the world. J. Hepatol. 2019, 70, 151–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsoris, A.; Marlar, C.A. Use of the child Pugh score in liver disease. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK542308/ (accessed on 25 December 2022).
- Infante-Rivard, C.; Esnaola, S.; Villeneuve, J.P. Clinical and statistical validity of conventional prognostic factors in predicting short-term survival among cirrhotics. Hepatology 1987, 7, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Backus, L.I.; Boothroyd, D.B.; Phillips, B.R.; Belperio, P.; Halloran, J.; Mole, L.A. A sustained virologic response reduces risk of all-cause mortality in patients with hepatitis C. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 509–516.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shayto, R.H.; Abou Mrad, R.A.; Sharara, A.I. Use of Rifaximin in gastrointestinal and liver diseases. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6638–6651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robins, G.W.; Wellington, K. Rifaximin: A review of its use in the management of traveller’s diarrhoea. Drugs 2005, 65, 1697–1713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, R.; Mullen, K.D. Mechanisms, diagnosis and management of hepatic encephalopathy. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2010, 7, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ponziani, F.R.; Gerardi, V.; Pecere, S.; D’Aversa, F.; Lopetuso, L.; Zocco, M.A.; Pompili, M.; Gasbarrini, A. Effect of Rifaximin on gut microbiota composition in advanced liver disease and its complications. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 12322–12333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlachogiannakos, J.; Viazis, N.; Vasianopoulou, P.; Vafiadis, I.; Karamanolis, D.G.; Ladas, S.D. Long-term administration of Rifaximin improves the prognosis of patients with decompensated alcoholic cirrhosis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 28, 450–455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girón-González, J.A.; Martínez-Sierra, C.; Rodriguez-Ramos, C.; Macías, M.A.; Rendón, P.; Díaz, F.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, C.; Martín-Herrera, L. Implication of inflammation-related cytokines in the natural history of liver cirrhosis. Liver Int. 2004, 24, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thabut, D.; Massard, J.; Gangloff, A.; Carbonell, N.; Francoz, C.; Nguyen-Khac, E.; Duhamel, C.; Lebrec, D.; Poynard, T.; Moreau, R. Model for end-stage liver disease score and systemic inflammatory response are major prognostic factors in patients with cirrhosis and acute functional renal failure. Hepatology 2007, 46, 1872–1882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, A.C. Nutrition and muscle in cirrhosis. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2017, 7, 340–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dondeti, M.F.; El-Maadawy, E.A.; Talaat, R.M. Hepatitis-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Insights into cytokine gene polymorphisms. World J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 22, 6800–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Luo, M.; Guo, J.Y.; Cao, W.K. Inflammation: A novel target of current therapies for hepatic encephalopathy in liver cirrhosis. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 11815–11824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, A.R.; Rama Rao, K.V.; Norenberg, M.D. Neuroinflammation in hepatic encephalopathy: Mechanistic aspects. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2015, 5, S21–S28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Noor, M.T.; Manoria, P. Immune dysfunction in cirrhosis. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2017, 5, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, Y.; Xu, D.; Song, H.; Qiu, B.; Tian, D.; Li, Z.; Ji, Y.; Wang, J. Inflammation and nutrition-based biomarkers in the prognosis of oesophageal cancer: A systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2021, 11, e048324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanno, H.; Hisaka, T.; Akiba, J.; Hashimoto, K.; Fujita, F.; Akagi, Y. C-reactive protein/albumin ratio and Glasgow prognostic score are associated with prognosis and infiltration of Foxp3+ or CD3+ lymphocytes in colorectal liver metastasis. BMC Cancer 2022, 22, 839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervoni, J.P.; Thévenot, T.; Weil, D.; Muel, E.; Barbot, O.; Sheppard, F.; Monnet, E.; di Martino, V. C-reactive protein predicts short-term mortality in patients with cirrhosis. J. Hepatol. 2012, 56, 1299–1304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biyik, M.; Ucar, R.; Solak, Y.; Gungor, G.; Polat, I.; Gaipov, A.; Cakir, O.O.; Ataseven, H.; Demir, A.; Turk, S.; et al. Blood neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio independently predicts survival in patients with liver cirrhosis. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2013, 25, 435–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalambokis, G.N.; Mouzaki, A.; Rodi, M.; Pappas, K.; Fotopoulos, A.; Xourgia, X.; Tsianos, E.V. Rifaximin improves systemic hemodynamics and renal function in patients with alcohol-related cirrhosis and ascites. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 10, 815–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferenci, P.; Lockwood, A.; Mullen, K.; Tarter, R.; Weissenborn, K.; Blei, A.T. Hepatic encephalopathy—Definition, nomenclature, diagnosis, and quantification: Final report of the working party at the 11th World Congresses of gastroenterology, Vienna, 1998. Hepatology 2002, 35, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanda, Y. Investigation of the freely available easy-to-use software ‘EZR’ for medical statistics. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2013, 48, 452–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- von Elm, E.; Altman, D.G.; Egger, M.; Pocock, S.J.; Gøtzsche, P.C.; Vandenbroucke, J.P.; STROBE Initiative. The Strengthening the Reporting of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (STROBE) statement: Guidelines for reporting observational studies. PLoS Med. 2007, 4, e296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bucci, L.; Palmieri, G.C. Double-blind, double-dummy comparison between treatment with Rifaximin and lactulose in patients with medium to severe degree hepatic encephalopathy. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 1993, 13, 109–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mas, A.; Rodés, J.; Sunyer, L.; Rodrigo, L.; Planas, R.; Vargas, V.; Castells, L.; Rodríguez-Martínez, D.; Fernández-Rodríguez, C.; Coll, I.; et al. Comparison of Rifaximin and lactitol in the treatment of acute hepatic encephalopathy: Results of a randomized, double-blind, double-dummy, controlled clinical trial. J. Hepatol. 2003, 38, 51–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, X.Y.; Ding, H.G.; Zheng, J.F.; Fan, C.L.; Li, L. Rifaximin improves survival in cirrhotic patients with refractory ascites: A real-world study. World J. Gastroenterol. 2020, 26, 199–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalambokis, G.N.; Tsianos, E.V. Rifaximin reduces endotoxemia and improves liver function and disease severity in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Hepatology 2012, 55, 655–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, N.M.; Mullen, K.D.; Sanyal, A.; Poordad, F.; Neff, G.; Leevy, C.B.; Sigal, S.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Beavers, K.; Frederick, T.; et al. Rifaximin treatment in hepatic encephalopathy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 362, 1071–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Mullen, K.D.; Sanyal, A.J.; Bass, N.M.; Poordad, F.F.; Sheikh, M.Y.; Frederick, R.T.; Bortey, E.; Forbes, W.P. Rifaximin is safe and well tolerated for long-term maintenance of remission from overt hepatic encephalopathy. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2014, 12, 1390–1397.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Park, J.G.; Tak, W.Y.; Park, S.Y.; Kweon, Y.O.; Chung, W.J.; Jang, B.K.; Bae, S.H.; Lee, H.J.; Jang, J.Y.; Suk, K.T.; et al. Effects of branched-chain amino acid (BCAA) supplementation on the progression of advanced liver disease: A Korean nationwide, multicenter, prospective, observational, cohort study. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Duan, Z.P.; Ha, D.K.; Bengmark, S.; Kurtovic, J.; Riordan, S.M. Synbiotic modulation of gut flora: Effect on minimal hepatic encephalopathy in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 2004, 39, 1441–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tarao, K.; Iwamura, K. Effect of long-term administration of paromomycin sulfate on the level of serum albumin and gamma-globulin in human cirrhosis. Tokai J. Exp. Clin. Med. 1983, 8, 349–357. [Google Scholar]
- Madrid, A.M.; Hurtado, C.; Venegas, M.; Cumsille, F.; Defilippi, C. Longtermtreatment with cisapride and antibiotics in liver cirrhosis: Effect on small intestinal motility, bacterial overgrowth, and liver function. Am. J. Gastroenterol. 2001, 96, 1251–1255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lumsden, A.B.; Henderson, J.M.; Kutner, M.H. Endotoxin levels measured by a chromogenic assay in portal, hepatic and peripheral venous blood in patients with cirrhosis. Hepatology 1988, 8, 232–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- del Pulgar, S.P.; Pizcueta, P.; Engel, P.; Bosch, J. Enhanced monocyte activation and hepatotoxicity in response to endotoxin in portal hypertension. J. Hepatol. 2000, 32, 25–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.S.; Lee, F.Y.; Lee, S.D.; Tsai, Y.T.; Lin, H.C.; Lu, R.H.; Hsu, W.C.; Huang, C.C.; Wang, S.S.; Lo, K.J. Endotoxemia in patients with chronic liver diseases: Relationship to severity of liver diseases, presence of esophageal varices, and hyperdynamic circulation. J. Hepatol. 1995, 22, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, L.; Sharma, B.C.; Sharma, P.; Srivastava, S.; Agrawal, A.; Sarin, S.K. Serum endotoxin and inflammatory mediators in patients with cirrhosis and hepatic encephalopathy. Dig. Liver Dis. 2012, 44, 1027–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaji, K.; Saikawa, S.; Takaya, H.; Fujinaga, Y.; Furukawa, M.; Kitagawa, K.; Ozutsumi, T.; Kaya, D.; Tsuji, Y.; Sawada, Y.; et al. Rifaximin alleviates endotoxemia with decreased serum levels of soluble CD163 and mannose receptor and partial modification of gut microbiota in cirrhotic patients. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Finlin, B.S.; Zhu, B.; Boyechko, T.; Westgate, P.M.; Chia, C.W.; Egan, J.M.; Kern, P.A. Effect of Rifaximin treatment on endotoxemia and insulin sensitivity in humans. J. Endocr. Soc. 2019, 3, 1641–1651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brogna, C.; Cristoni, S.; Brogna, B.; Bisaccia, D.R.; Marino, G.; Viduto, V.; Montano, L.; Piscopo, M. Toxin-like Peptides from the Bacterial Cultures Derived from Gut Microbiome Infected by SARS-CoV-2-New Data for a Possible Role in the Long COVID Pattern. Biomedicines 2022, 11, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Lei, Z.; Ping, J.; Su, J. Effect of rifaximin on gut-lung axis in mice infected with influenza A virus. Comp. Immunol. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2021, 75, 101611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.A.; Tsao, Y.C.; Chen, A.; Lo, G.H.; Lin, C.K.; Yu, H.C.; Cheng, L.C.; Hsu, P.I.; Tsai, W.L. Effect of intravenous albumin on endotoxin removal, cytokines, and nitric oxide production in patients with cirrhosis and spontaneous bacterial peritonitis. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2009, 44, 619–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirchwolf, M.; Ruf, A.E. Role of systemic inflammation in cirrhosis: From pathogenesis to prognosis. World J. Hepatol. 2015, 7, 1974–1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawaratani, H.; Tsujimoto, T.; Douhara, A.; Takaya, H.; Moriya, K.; Namisaki, T.; Noguchi, R.; Yoshiji, H.; Fujimoto, M.; Fukui, H. The effect of inflammatory cytokines in alcoholic liver disease. Mediat. Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 495156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, X.; Shah, Y.M.; Guo, G.L.; Wang, T.; Krausz, K.W.; Idle, J.R.; Gonzalez, F.J. Rifaximin is a gut-specific human pregnane X receptor activator. J. Pharmacol. Exp. Ther. 2007, 322, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Razik, A.; Mousa, N.; Shabana, W.; Refaey, M.; Elzehery, R.; Elhelaly, R.; Zalata, K.; Abdelsalam, M.; Eldeeb, A.A.; Awad, M.; et al. Rifaximin in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: Hit multiple targets with a single shot. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 30, 1237–1246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalambokis, G.N.; Mouzaki, A.; Rodi, M.; Tsianos, E.V. Rifaximin improves thrombocytopenia in patients with alcoholic cirrhosis in association with reduction of endotoxaemia. Liver Int. 2012, 32, 467–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, V.C.; Lee, S.; McPhail, M.J.W.; Da Silva, K.; Guilly, S.; Zamalloa, A.; Witherden, E.; Støy, S.; Manakkat Vijay, G.K.; Pons, N.; et al. Rifaximin-α reduces gut-derived inflammation and mucin degradation in cirrhosis and encephalopathy: RIFSYS randomised controlled trial. J. Hepatol. 2022, 76, 332–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Feng, G.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Feng, L.; Yang, J. Association between lymphocyte-to-monocyte ratio (LMR) and the mortality of HBV-related liver cirrhosis: A retrospective cohort study. BMJ Open 2015, 5, e008033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- State, N. CRP and the prognosis of patients with cirrhosis. Maedica 2021, 16, 353–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walayat, S.; Martin, D.; Patel, J.; Ahmed, U.; Asghar, M.N.; Pai, A.U.; Dhillon, S. Role of albumin in cirrhosis: From a hospitalist’s perspective. J. Community Hosp. Intern. Med. Perspect. 2017, 7, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shen, Y.; Wang, H.; Li, W.; Chen, J. Prognostic significance of the CRP/Alb and neutrophil to lymphocyte ratios in hepatocellular carcinoma patients undergoing TACE and RFA. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2019, 33, e22999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shimizu, T.; Ishizuka, M.; Suzuki, T.; Tanaka, G.; Shiraki, T.; Sakuraoka, Y.; Matsumoto, T.; Kato, M.; Aoki, T.; Kubota, K. The value of the C-reactive protein-to-albumin ratio is useful for predicting survival of patients with Child-Pugh Class A undergoing liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Surg. 2018, 42, 2218–2226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oikonomou, T.; Goulis, I.; Kiapidou, S.; Tagkou, N.; Akriviadis, E.; Papatheodoridis, G.; Cholongitas, E. The significance of C-reactive protein to albumin ratio in patients with decompensated cirrhosis. Ann. Gastroenterol. 2020, 33, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Zhang, X.; Wang, S.; Huo, X.; Wang, J. Small intestinal bacterial overgrowth and evaluation of intestinal barrier function in patients with ulcerative colitis. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 6605–6610. [Google Scholar]

| Variable | Results |
|---|---|
| Age in years | 69 (34–84) |
| Male gender, n (%) | 23 (52) |
| HE grade 1:2:3:4, n (%) | 26:12:4:2 (59:27:9:5) |
| Etiology of liver disease | |
| Alcohol, n (%) | 14 (32) |
| NASH, n (%) | 12 (27) |
| HCV, n (%) | 9 (21) |
| Autoimmune, n (%) | 8 (18) |
| Cryptogenic, n (%) | 1 (2) |
| Liver functional reserve | |
| Child–Pugh score | 8 (6–15) |
| Child–Pugh class A:B:C, n (%) | 9:24:11 (20:55:25) |
| Complication in illnesses | |
| HCC, n (%) | 12 (27) |
| Esophagogastric varices, n (%) | 26 (59) |
| Ascites, n (%) | 18 (41) |
| Concomitant drug * | |
| BCAA, n (%) | 29 (66) |
| Lactulose or Lactitol, n (%) | 15 (34) |
| Zinc preparation, n (%) | 6 (14) |
| Levocarnitine, n (%) | 5 (11) |
| Inflammation-based markers | |
| NLR | 2.73 (1.00–23.00) |
| LMR | 2.75 (0.89–10.00) |
| PLR | 92.83 (26.09–336.84) |
| CRP in mg/dL | 0.41 (0.05–4.55) |
| CAR | 0.15 (0.014–2.68) |
| Variable | Results |
|---|---|
| Age in years | 69 (41–84) |
| Male gender, n (%) | 17 (59) |
| HE grade 1:2:3:4, n (%) | 15:12:1:1 (52:42:3:3) |
| Etiology of liver disease | |
| Alcohol, n (%) | 10 (35) |
| NASH, n (%) | 8 (28) |
| HCV, n (%) | 5 (17) |
| Autoimmune, n (%) | 5 (17) |
| Cryptogenic, n (%) | 1 (3) |
| Liver functional reserve | |
| Child–Pugh score | 8 (6–14) |
| Child–Pugh class A:B:C, n (%) | 4:17:8 (14:59:27) |
| Complication in illnesses | |
| HCC, n (%) | 10 (37) |
| Esophagogastric varices, n (%) | 16 (55) |
| Ascites, n (%) | 10 (37) |
| Concomitant drug * | |
| BCAA, n (%) | 23 (79) |
| Lactulose or Lactitol, n (%) | 9 (31) |
| Zinc preparation, n (%) | 5 (17) |
| Levocarnitine, n (%) | 6 (21) |
| Inflammation-based markers | |
| NLR | 2.52 (1.00–7.4) |
| LMR | 3.14 (1.03–10.00) |
| PLR | 81.93 (26.09–336.84) |
| CRP in mg/dL | 0.38 (0.07–4.55) |
| CAR | 0.13 (0.023–2.68) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kitsugi, K.; Kawata, K.; Noritake, H.; Chida, T.; Ohta, K.; Ito, J.; Takatori, S.; Yamashita, M.; Hanaoka, T.; Umemura, M.; et al. Rifaximin Improves Liver Functional Reserve by Regulating Systemic Inflammation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062210
Kitsugi K, Kawata K, Noritake H, Chida T, Ohta K, Ito J, Takatori S, Yamashita M, Hanaoka T, Umemura M, et al. Rifaximin Improves Liver Functional Reserve by Regulating Systemic Inflammation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(6):2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062210
Chicago/Turabian StyleKitsugi, Kensuke, Kazuhito Kawata, Hidenao Noritake, Takeshi Chida, Kazuyoshi Ohta, Jun Ito, Shingo Takatori, Maho Yamashita, Tomohiko Hanaoka, Masahiro Umemura, and et al. 2023. "Rifaximin Improves Liver Functional Reserve by Regulating Systemic Inflammation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 6: 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062210
APA StyleKitsugi, K., Kawata, K., Noritake, H., Chida, T., Ohta, K., Ito, J., Takatori, S., Yamashita, M., Hanaoka, T., Umemura, M., Matsumoto, M., & Suda, T. (2023). Rifaximin Improves Liver Functional Reserve by Regulating Systemic Inflammation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(6), 2210. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062210





