Adult Body Height Is Associated with the Risk of Type 2 but Not Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study of 783,029 Individuals in Germany
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Database
2.2. Study Population
2.3. Study Outcomes and Variables
2.4. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
3.1. Study Cohort Characteristics
3.2. Incidence of T1D and T2D among Patients of Different Body Height Categories
3.3. Association between the Body Height and the Risk for T1D and T2D
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sun, H.; Saeedi, P.; Karuranga, S.; Pinkepank, M.; Ogurtsova, K.; Duncan, B.B.; Stein, C.; Basit, A.; Chan, J.C.N.; Mbanya, J.C.; et al. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global, regional and country-level diabetes prevalence estimates for 2021 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2022, 183, 109119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beagley, J.; Guariguata, L.; Weil, C.; Motala, A.A. Global estimates of undiagnosed diabetes in adults. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2014, 103, 150–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeedi, P.; Petersohn, I.; Salpea, P.; Malanda, B.; Karuranga, S.; Unwin, N.; Colagiuri, S.; Guariguata, L.; Motala, A.A.; Ogurtsova, K.; et al. Global and regional diabetes prevalence estimates for 2019 and projections for 2030 and 2045: Results from the International Diabetes Federation Diabetes Atlas, 9(th) edition. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2019, 157, 107843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, N.H.; Shaw, J.E.; Karuranga, S.; Huang, Y.; da Rocha Fernandes, J.D.; Ohlrogge, A.W.; Malanda, B. IDF Diabetes Atlas: Global estimates of diabetes prevalence for 2017 and projections for 2045. Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2018, 138, 271–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nørgaard, C.H.; Mosslemi, M.; Lee, C.J.; Torp-Pedersen, C.; Wong, N.D. The Importance and Role of Multiple Risk Factor Control in Type 2 Diabetes. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2019, 21, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schöttker, B.; Raum, E.; Rothenbacher, D.; Müller, H.; Brenner, H. Prognostic value of haemoglobin A1c and fasting plasma glucose for incident diabetes and implications for screening. Eur. J. Epidemiol. 2011, 26, 779–787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, M.B.; Heidemann, C.; Schienkiewitz, A.; Bergmann, M.M.; Hoffmann, K.; Boeing, H. Comparison of anthropometric characteristics in predicting the incidence of type 2 diabetes in the EPIC-Potsdam study. Diabetes Care. 2006, 29, 1921–1923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Njølstad, I.; Arnesen, E.; Lund-Larsen, P.G. Sex differences in risk factors for clinical diabetes mellitus in a general population: A 12-year follow-up of the Finnmark Study. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 147, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenzo, C.; Williams, K.; Stern, M.P.; Haffner, S.M. Height, ethnicity, and the incidence of diabetes: The San Antonio Heart Study. Metabolism. 2009, 58, 1530–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Tan, H.; Jeynes, B. Is femur length the key height component in risk prediction of type 2 diabetes among adults? Diabetes Care. 2009, 32, 739–740. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawlor, D.A.; Ebrahim, S.; Davey Smith, G. The association between components of adult height and Type II diabetes and insulin resistance: British Women’s Heart and Health Study. Diabetologia 2002, 45, 1097–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, M.; Head, J.; Marmot, M. Prospective study of social and other risk factors for incidence of type 2 diabetes in the Whitehall II study. Arch. Intern. Med. 2004, 164, 1873–1880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janghorbani, M.; Amini, M. Effects of gender and height on the oral glucose tolerance test: The isfahan diabetes prevention study. Rev. Diabet. Stud. 2008, 5, 163–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, M.B.; Hoffmann, K.; Boeing, H.; Linseisen, J.; Rohrmann, S.; Möhlig, M.; Pfeiffer, A.F.; Spranger, J.; Thamer, C.; Häring, H.U.; et al. An accurate risk score based on anthropometric, dietary, and lifestyle factors to predict the development of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007, 30, 510–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt, M.I.; Duncan, B.B.; Bang, H.; Pankow, J.S.; Ballantyne, C.M.; Golden, S.H.; Folsom, A.R.; Chambless, L.E. Identifying individuals at high risk for diabetes: The Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities study. Diabetes Care. 2005, 28, 2013–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrestha, S.; Rasmussen, S.H.; Pottegård, A.; Ängquist, L.H.; Jess, T.; Allin, K.H.; Bjerregaard, L.G.; Baker, J.L. Associations between adult height and type 2 diabetes mellitus: A systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. J. Epidemiol. Community Health 2019, 73, 681–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silventoinen, K.; Sammalisto, S.; Perola, M.; Boomsma, D.I.; Cornes, B.K.; Davis, C.; Dunkel, L.; De Lange, M.; Harris, J.R.; Hjelmborg, J.V.; et al. Heritability of adult body height: A comparative study of twin cohorts in eight countries. Twin Res. 2003, 6, 399–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silventoinen, K. Determinants of variation in adult body height. J. Biosoc. Sci. 2003, 35, 263–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khanna, D.; Peltzer, C.; Kahar, P.; Parmar, M.S. Body Mass Index (BMI): A Screening Tool Analysis. Cureus 2022, 14, e22119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emerging Risk Factors Collaboration. Adult height and the risk of cause-specific death and vascular morbidity in 1 million people: Individual participant meta-analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2012, 41, 1419–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perkins, J.M.; Subramanian, S.V.; Davey Smith, G.; Özaltin, E. Adult height, nutrition, and population health. Nutr. Rev. 2016, 74, 149–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nelson, C.P.; Hamby, S.E.; Saleheen, D.; Hopewell, J.C.; Zeng, L.; Assimes, T.L.; Kanoni, S.; Willenborg, C.; Burgess, S.; Amouyel, P.; et al. Genetically determined height and coronary artery disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2015, 372, 1608–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathmann, W.; Bongaerts, B.; Carius, H.J.; Kruppert, S.; Kostev, K. Basic characteristics and representativeness of the German Disease Analyzer database. Int. J. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 2018, 56, 459–466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krieg, S.; Roderburg, C.; Krieg, A.; Luedde, T.; Loosen, S.H.; Kostev, K. The association between body height and cancer: A retrospective analysis of 784,192 outpatients in Germany. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gremke, N.; Griewing, S.; Kalder, M.; Kostev, K. Positive association between body height and breast cancer prevalence: A retrospective study with 135,741 women in Germany. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2022, 196, 349–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rathmann, W.; Kostev, K. Association of glucose-lowering drugs with incident stroke and transient ischaemic attacks in primary care patients with type 2 diabetes: Disease analyzer database. Acta Diabetol. 2022, 59, 1443–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roderburg, C.; Loosen, S.H.; Hoyer, L.; Luedde, T.; Kostev, K. Prevalence of diabetes mellitus among 80,193 gastrointestinal cancer patients in five European and three Asian countries. J. Cancer Res. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 148, 1057–1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eckel, N.; Mühlenbruch, K.; Meidtner, K.; Boeing, H.; Stefan, N.; Schulze, M.B. Characterization of metabolically unhealthy normal-weight individuals: Risk factors and their associations with type 2 diabetes. Metabolism 2015, 64, 862–871. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janghorbani, M.; Momeni, F.; Dehghani, M. Hip circumference, height and risk of type 2 diabetes: Systematic review and meta-analysis. Obes. Rev. 2012, 13, 1172–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wittenbecher, C.; Kuxhaus, O.; Boeing, H.; Stefan, N.; Schulze, M.B. Associations of short stature and components of height with incidence of type 2 diabetes: Mediating effects of cardiometabolic risk factors. Diabetologia 2019, 62, 2211–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conway, B.N.; Shu, X.O.; Zhang, X.; Xiang, Y.B.; Cai, H.; Li, H.; Yang, G.; Gao, Y.T.; Zheng, W. Age at menarche, the leg length to sitting height ratio, and risk of diabetes in middle-aged and elderly Chinese men and women. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e30625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, L.W.; Harris, S.B.; Retnakaran, R.; Gerstein, H.C.; Zinman, B.; Hamilton, J.; Hanley, A.J. Short leg length, a marker of early childhood deprivation, is associated with metabolic disorders underlying type 2 diabetes: The PROMISE cohort study. Diabetes Care. 2013, 36, 3599–3606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vangipurapu, J.; Stancáková, A.; Jauhiainen, R.; Kuusisto, J.; Laakso, M. Short Adult Stature Predicts Impaired β-Cell Function, Insulin Resistance, Glycemia, and Type 2 Diabetes in Finnish Men. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2017, 102, 443–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Häring, H.U.; Hu, F.B.; Schulze, M.B. Divergent associations of height with cardiometabolic disease and cancer: Epidemiology, pathophysiology, and global implications. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2016, 4, 457–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stefan, N.; Cusi, K. A global view of the interplay between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and diabetes. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2022, 10, 284–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumari, S.; Wang, X.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Y.; Huang, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Liu, L.; Meng, G.; Wu, H.; Sun, S.; et al. Height predict incident non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among general adult population in Tianjin, China, independent of body mass index, waist circumference, waist-to-height ratio, and metabolic syndrome. BMC Public Health 2020, 20, 388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeFronzo, R.A. Pathogenesis of type 2 diabetes mellitus. Med. Clin. North Am. 2004, 88, 787–835, ix. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitzle, L.; Ihle, P.; Heidemann, C.; Paprott, R.; Köster, I.; Schmidt, C. Algorithm for the Classification of Type 1 and Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus for the Analysis of Routine Data. Gesundheitswesen 2022. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsarou, A.; Gudbjörnsdottir, S.; Rawshani, A.; Dabelea, D.; Bonifacio, E.; Anderson, B.J.; Jacobsen, L.M.; Schatz, D.A.; Lernmark, Å. Type 1 diabetes mellitus. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2017, 3, 17016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and classification of diabetes mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2009, 32, S62–S67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nüesch, E.; Dale, C.; Palmer, T.M.; White, J.; Keating, B.J.; van Iperen, E.P.; Goel, A.; Padmanabhan, S.; Asselbergs, F.W.; Verschuren, W.M.; et al. Adult height, coronary heart disease and stroke: A multi-locus Mendelian randomization meta-analysis. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 45, 1927–1937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandhu, M.S.; Heald, A.H.; Gibson, J.M.; Cruickshank, J.K.; Dunger, D.B.; Wareham, N.J. Circulating concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-I and development of glucose intolerance: A prospective observational study. Lancet 2002, 359, 1740–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asao, K.; Kao, W.H.; Baptiste-Roberts, K.; Bandeen-Roche, K.; Erlinger, T.P.; Brancati, F.L. Short stature and the risk of adiposity, insulin resistance, and type 2 diabetes in middle age: The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES III), 1988-1994. Diabetes Care. 2006, 29, 1632–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattila, C.; Knekt, P.; Männistö, S.; Rissanen, H.; Laaksonen, M.A.; Montonen, J.; Reunanen, A. Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D concentration and subsequent risk of type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2007, 30, 2569–2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben-Shlomo, Y.; Holly, J.; McCarthy, A.; Savage, P.; Davies, D.; Gunnell, D.; Davey Smith, G. An investigation of fetal, postnatal and childhood growth with insulin-like growth factor I and binding protein 3 in adulthood. Clin. Endocrinol. 2003, 59, 366–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marouli, E.; Graff, M.; Medina-Gomez, C.; Lo, K.S.; Wood, A.R.; Kjaer, T.R.; Fine, R.S.; Lu, Y.; Schurmann, C.; Highland, H.M.; et al. Rare and low-frequency coding variants alter human adult height. Nature 2017, 542, 186–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LeRoith, D.; Yakar, S. Mechanisms of disease: Metabolic effects of growth hormone and insulin-like growth factor 1. Nat. Clin. Pract. Endocrinol. Metab. 2007, 3, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonfig, W.; Kapellen, T.; Dost, A.; Fritsch, M.; Rohrer, T.; Wolf, J.; Holl, R.W. Growth in children and adolescents with type 1 diabetes. J. Pediatr. 2012, 160, 900–903.e902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knerr, I.; Wolf, J.; Reinehr, T.; Stachow, R.; Grabert, M.; Schober, E.; Rascher, W.; Holl, R.W. The ‘accelerator hypothesis’: Relationship between weight, height, body mass index and age at diagnosis in a large cohort of 9,248 German and Austrian children with type 1 diabetes mellitus. Diabetologia. 2005, 48, 2501–2504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, M.; Ahmed, M.L.; Clayton, K.L.; Dunger, D.B. Growth during childhood and final height in type 1 diabetes. Diabet. Med. 1994, 11, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Caju, M.V.; Rooman, R.P.; op de Beeck, L. Longitudinal data on growth and final height in diabetic children. Pediatr. Res. 1995, 38, 607–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danne, T.; Kordonouri, O.; Enders, I.; Weber, B. Factors influencing height and weight development in children with diabetes. Results of the Berlin Retinopathy Study. Diabetes Care. 1997, 20, 281–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mauriac, P. Hepatomegaly, dwarfism, obesity and diabetes in children: Mauriac’s syndrome. Vida Nueva 1951, 67, 57–65. [Google Scholar]
- Traisman, H.S.; Traisman, E.S. Mauriac’s syndrome revisited. Eur. J. Pediatr. 1984, 142, 296–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamborlane, W.V.; Bonfig, W.; Boland, E. Recent advances in treatment of youth with Type 1 diabetes: Better care through technology. Diabet. Med. 2001, 18, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, N. Causes, consequences, and treatment of metabolically unhealthy fat distribution. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol. 2020, 8, 616–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
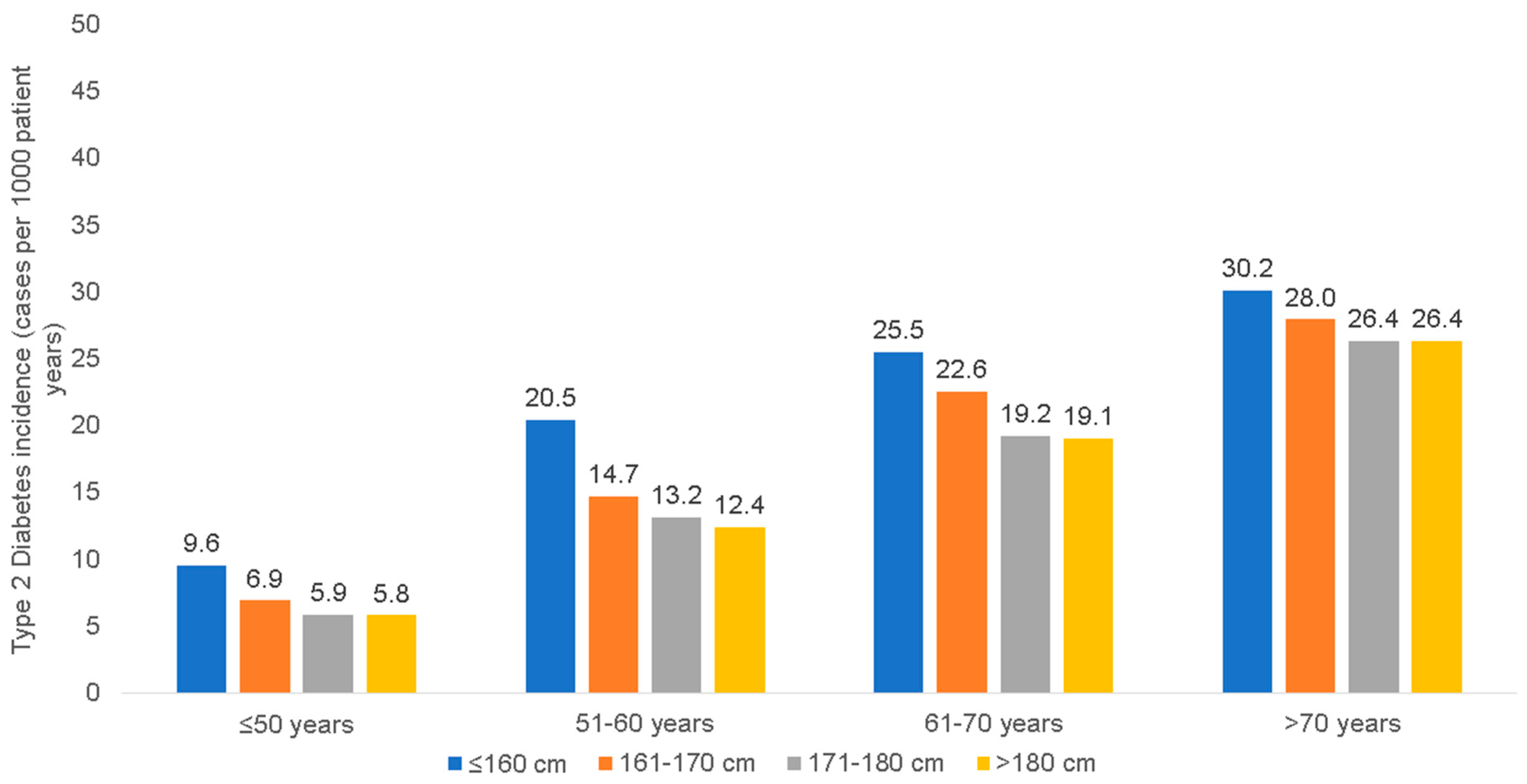
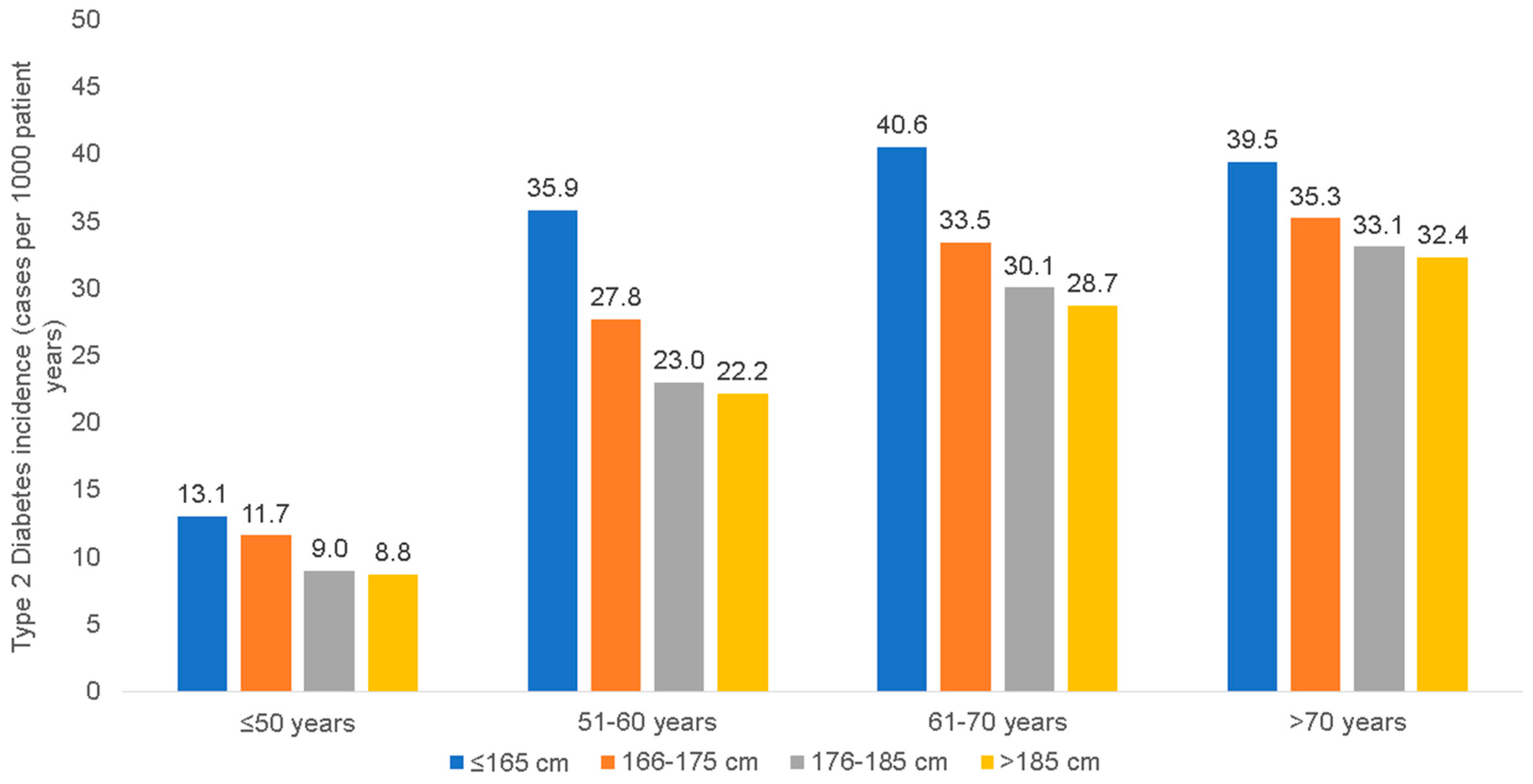
| Variables | Women | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Total | ≤160 cm | 161–170 cm | 171–180 cm | >180 cm | |
| N | 423,203 | 115,621 | 224,741 | 77,995 | 4846 |
| Age at index date (mean, SD) | 50.1 (18.0) | 56.4 (18.8) | 49.3 (17.4) | 43.4 /15.3) | 39.6 (13.2) |
| BMI (mean, SD) | 26.3 (6.7) | 27.1 (6.2) | 26.2 (7.2) | 25.5 (5.9) | 25.5 (5.9) |
| Height (mean, SD) | 165.1 (6.9) | 156.8 (3.3) | 165.8 (2.7) | 174.3 (2.6) | 183.4 (2.9) |
| Weight (mean, SD) | 64.3 | 66.6 | 72.0 | 77.8 | 85.8 |
| Men | |||||
| Total | ≤165 cm | 166–175 cm | 176–185 cm | >185 cm | |
| N | 359,826 | 16,231 | 113,475 | 170,740 | 59,380 |
| Age at index date (mean, SD) | 48.9 (17.3) | 58.8 (19.4) | 53.1 (18.0) | 47.5 (16.4) | 42.4 (14.4) |
| BMI (mean, SD) | 27.3 (5.0) | 27.5 (5.3) | 27.5 (4.9) | 27.3 (5.0) | 27.1 (5.0) |
| Height (mean, SD) | 178.2 (7.5) | 162.3 (3.3) | 171.7 (2.6) | 180.2 (2.8) | 189.6 (3.4) |
| Weight (mean, SD) | |||||
| HbA1c Value (%) | HbA1c Value (mmol/mol) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Body Height Category | Women | Men | Women | Men |
| ≤165 cm | 7.9 | 8.2 | 63 | 66 |
| 166–175 cm | 8.0 | 8.2 | 64 | 66 |
| 176–185 cm | 8.5 | 8.3 | 69 | 67 |
| >185 cm | 7.8 | 8.3 | 62 | 67 |
| Cases per 1000 Patient Years (95% CI) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Body Height Category | Women | Men |
| ≤160 cm | 0.12 (0.10–0.14) | 0.13 (0.11–0.15) |
| 161–170 cm | 0.12 (0.10–0.14) | 0.10 (0.08–0.12) |
| 171–180 cm | 0.19 (0.17–0.21) | 0.13 (0.11–0.15) |
| >180 cm | 0.34 (0.32–0.36) | 0.18 (0.16–0.20) |
| Women | Men | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Risk Increase for Every 10 cm Reduction in Body Height (HR, 95% CI) | p-Value | Risk Increase for Every 10 cm Reduction in Body Height (HR, 95% CI) | p-Value | |
| Type 1 diabetes | 1.03 (0.87–1.23) | 0.711 | 1.06 (0.82–1.22) | 0.779 |
| Type 2 diabetes | 1.15 (1.13–1.17) | <0.001 | 1.10 (1.09–1.12) | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Loosen, S.H.; Krieg, S.; Krieg, A.; Luedde, T.; Kostev, K.; Roderburg, C. Adult Body Height Is Associated with the Risk of Type 2 but Not Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study of 783,029 Individuals in Germany. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062199
Loosen SH, Krieg S, Krieg A, Luedde T, Kostev K, Roderburg C. Adult Body Height Is Associated with the Risk of Type 2 but Not Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study of 783,029 Individuals in Germany. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(6):2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062199
Chicago/Turabian StyleLoosen, Sven H., Sarah Krieg, Andreas Krieg, Tom Luedde, Karel Kostev, and Christoph Roderburg. 2023. "Adult Body Height Is Associated with the Risk of Type 2 but Not Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study of 783,029 Individuals in Germany" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 6: 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062199
APA StyleLoosen, S. H., Krieg, S., Krieg, A., Luedde, T., Kostev, K., & Roderburg, C. (2023). Adult Body Height Is Associated with the Risk of Type 2 but Not Type 1 Diabetes Mellitus: A Retrospective Cohort Study of 783,029 Individuals in Germany. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(6), 2199. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12062199










