The First Pulmonary Hypertension Registry in the United Arab Emirates (UAEPH): Clinical Characteristics, Hemodynamic Parameters with Focus on Treatment and Outcomes for Patients with Group 1-PH
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Humbert, M.; Kovacs, G.; Hoeper, M.M.; Badagliacca, R.; Berger, R.M.F.; Brida, M.; Carlsen, J.; Coats, A.J.S.; Escribano-Subias, P.; Ferrari, P.; et al. 2022 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. 2022, 43, 3618–3731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonneau, G.; Montani, D.; Celermajer, D.; Denton, C.P.; Gatzoulis, M.A.; Krowka, M.; Williams, P.G.; Souza, R. Haemodynamic definitions and updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, N.S.H.; Massam, B.D.; Kulkarni, S.S.; Lang, C.C. Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension: Pathophysiology and Treatment. Diseases 2018, 6, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Badlam, J.B.; Badesch, D.B.; Austin, E.D.; Benza, R.L.; Chung, W.K.; Farber, H.W.; Feldkircher, K.; Frost, A.E.; Poms, A.D.; Lutz, K.A.; et al. United States Pulmonary Hypertension Scientific Registry: Baseline Characteristics. Chest 2020, 159, 311–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badesch, D.B.; Raskob, G.E.; Elliott, C.G.; Krichman, A.M.; Farber, H.W.; Frost, A.E.; Barst, R.J.; Benza, R.L.; Liou, T.G.; Turner, M.; et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension: Baseline characteristics from the REVEAL registry. Chest 2010, 137, 376–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Farber, H.W.; Miller, D.P.; Poms, A.D.; Badesch, D.B.; Frost, A.E.; Rouzic, E.M.-L.; Romero, A.J.; Benton, W.W.; Elliott, C.G.; McGoon, M.D.; et al. Five-Year Outcomes of Patients Enrolled in the REVEAL Registry. Chest 2015, 148, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- D’Alonzo, G.E.; Barst, R.J.; Ayres, S.M.; Bergofsky, E.H.; Brundage, B.H.; Detre, K.M.; Fishman, A.P.; Goldring, R.M.; Groves, B.M.; Kernis, J.T.; et al. Survival in patients with primary pulmonary hypertension: Results from a national prospective registry. Ann. Intern. Med. 1991, 115, 343–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ling, Y.; Johnson, M.K.; Kiely, D.G.; Condliffe, R.; Elliot, C.A.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Howard, L.S.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Sheares, K.K.K.; Corris, P.A.; et al. Changing demographics, epidemiology, and survival of incident pulmonary arterial hypertension: Results from the pulmonary hypertension registry of the United Kingdom and Ireland. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012, 186, 790–796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller-Mottet, S.; Stricker, H.; Domeninghetti, G.; Azzola, A.; Geiser, T.; Schwerzmann, M.; Weilenmann, D.; Schoch, O.; Fellrath, J.-M.; Rochat, T.; et al. Long-Term Data from the Swiss Pulmonary Hypertension Registry. Respiration 2015, 89, 127–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hurdman, J.; Condliffe, R.; Elliot, C.; Davies, C.; Hill, C.; Wild, J.; Capener, D.; Sephton, P.; Hamilton, N.; Armstrong, I.; et al. ASPIRE registry: Assessing the Spectrum of Pulmonary hypertension Identified at a REferral centre. Eur. Respir. J. 2011, 39, 945–955. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Skride, A.; Sablinskis, K.; Lejnieks, A.; Rudzitis, A.; Lang, I. Characteristics and survival data from Latvian pulmonary hypertension registry: Comparison of prospective pulmonary hypertension registries in Europe. Pulm. Circ. 2018, 8, 2045894018780521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Gall, H.; Felix, J.F.; Schneck, F.K.; Milger, K.; Sommer, N.; Voswinckel, R.; Franco, O.H.; Hofman, A.; Schermuly, R.T.; Weissmann, N.; et al. The Giessen Pulmonary Hypertension Registry: Survival in pulmonary hypertension subgroups. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2017, 36, 957–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kozu, K.; Sugimura, K.; Ito, M.; Hirata, K.-I.; Node, K.; Miyamoto, T.; Ueno, S.; Watanabe, H.; Shimokawa, H. Current status of long-term prognosis among all subtypes of pulmonary hypertension in Japan. Int. J. Cardiol. 2020, 300, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Dai, L.-Z.; Xie, W.-P.; Yu, Z.-X.; Wu, B.-X.; Pan, L.; Yuan, P.; Jiang, X.; He, J.; Humbert, M.; et al. Survival of Chinese Patients with Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in the Modern Treatment Era. Chest 2011, 140, 301–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chung, W.-J.; Park, Y.B.; Jeon, C.H.; Jung, J.W.; Ko, K.-P.; Choi, S.J.; Seo, H.S.; Lee, J.S.; Jung, H.O. KORPAH Investigators Baseline Characteristics of the Korean Registry of Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2015, 30, 1429–1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- AlDalaan, A.M.; Saleemi, S.; Weheba, I.; Abdelsayed, A.; Aleid, M.M.; Alzubi, F.; Zaytoun, H.; Alharbi, N. Pulmonary hypertension in Saudi Arabia: First data from the SAUDIPH registry with a focus on pulmonary arterial hypertension. Respirology 2020, 26, 92–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alhamad, E.H.; Cal, J.G.; AlFaleh, H.F.; Alshamiri, M.Q.; AlBoukai, A.A.; Alhomida, S.A. Pulmonary hypertension in Saudi Arabia: A single center experience. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2013, 8, 78–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idrees, M.; Al-Najashi, K.; Khan, A.; Al-Dammas, S.; Al-Awwad, H.; Batubara, E.; Al Otai, A.; Abdulhameed, J.; Fayed, A.; Kashour, T.; et al. Pulmonary arterial hypertension in Saudi Arabia: Patients′ clinical and physiological characteristics and hemodynamic parameters. A single center experience. Ann. Thorac. Med. 2014, 9, 209–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hacıyev, R.; Ünlü, S.; Yalçın, M.R.; Taçoy, G.; Çengel, A. Pulmonary hypertension spectrum: 16 years of experience from a single center. Turk Kardiyol. Dern. Arsivi. 2018, 46, 667–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condon, D.; Nickel, N.P.; Anderson, R.; Mirza, S.; Perez, V.A.D.J. The 6th World Symposium on Pulmonary Hypertension: What’s old is new. F1000Research 2019, 8, 888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frost, A.; Badesch, D.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Gopalan, D.; Khanna, D.; Manes, A.; Oudiz, R.; Satoh, T.; Torres, F.; Torbicki, A. Diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801904. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lau, E.M.; Tamura, Y.; McGoon, M.D.; Sitbon, O. The 2015 ESC/ERS Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension: A practical chronicle of progress. Eur. Respir. J. 2015, 46, 879–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vachiéry, J.-L.; Tedford, R.J.; Rosenkranz, S.; Palazzini, M.; Lang, I.; Guazzi, M.; Coghlan, G.; Chazova, I.; De Marco, T. Pulmonary hypertension due to left heart disease. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Nathan, S.D.; Barbera, J.A.; Gaine, S.P.; Harari, S.; Martinez, F.J.; Olschewski, H.; Olsson, K.M.; Peacock, A.J.; Pepke-Zaba, J.; Provencher, S.; et al. Pulmonary hypertension in chronic lung disease and hypoxia. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 53, 1801914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Kim, N.H.; Delcroix, M.; Jais, X.; Madani, M.M.; Matsubara, H.; Mayer, E.; Ogo, T.; Tapson, V.F.; Ghofrani, H.-A.; Jenkins, D.P. Chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2019, 53, 1801915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boucly, A.; Weatherald, J.; Savale, L.; Jaïs, X.; Cottin, V.; Prevot, G.; Picard, F.; de Groote, P.; Jevnikar, M.; Bergot, E.; et al. Risk assessment, prognosis and guideline implementation in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1700889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Pittrow, D.; Opitz, C.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Rosenkranz, S.; Grünig, E.; Olsson, K.M.; Huscher, D. Risk assessment in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Eur. Respir. J. 2018, 51, 1702606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Pausch, C.; Grünig, E.; Klose, H.; Staehler, G.; Huscher, D.; Pittrow, D.; Olsson, K.M.; Vizza, C.D.; Gall, H.; et al. Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension phenotypes determined by cluster analysis from the COMPERA registry. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2020, 39, 1435–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianzad, A.; van Wezenbeek, J.; Celant, L.R.; Oosterveer, F.P.; Noordegraaf, A.V.; Meijboom, L.J.; de Man, F.S.; Bogaard, H.J.; Handoko, M.L. Idiopathic pulmonary arterial hypertension patients with a high H2FPEF-score: Insights from the Amsterdam UMC PAH-cohort. J. Heart Lung Transplant. 2022, 41, 1075–1085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/sp.poptotl?locations (accessed on 12 September 2022).
- Lau, E.; Giannoulatou, E.; Celermajer, D.; Humbert, M. Epidemiology and treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 603–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humbert, M.; Coghlan, J.G.; Ghofrani, H.-A.; Grimminger, F.; He, J.-G.; Riemekasten, G.; Vizza, C.D.; Boeckenhoff, A.; Meier, C.; Pena, J.D.O.; et al. Riociguat for the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension associated with connective tissue disease: Results from PATENT-1 and PATENT-2. Ann. Rheum. Dis. 2016, 76, 422–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Hoeper, M.M.; Al-Hiti, H.; Benza, R.L.; Chang, S.-A.; Corris, P.A.; Gibbs, J.S.R.; Grünig, E.; Jansa, P.; Klinger, J.R.; Langleben, D.; et al. Switching to riociguat versus maintenance therapy with phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (REPLACE): A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2021, 9, 573–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kjellström, B.; Sandqvist, A.; Hjalmarsson, C.; Nisell, M.; Näsman, P.; Ivarsson, B. Adherence to disease-specific drug treatment among patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension or chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension. ERJ Open Res. 2020, 6, 00299–02020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, K.Y.; Duval, S.; Badesch, D.B.; Bull, T.M.; Chakinala, M.M.; De Marco, T.; Frantz, R.P.; Hemnes, A.; Mathai, S.C.; Rosenzweig, E.B.; et al. Mortality in Pulmonary Arterial Hypertension in the Modern Era: Early Insights from the Pulmonary Hypertension Association Registry. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2022, 11, e024969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Variable | All (n = 159) | Group 1 (n = 83) | Group 2 (n = 19) | Group 3 (n = 23) | Group 4 (n = 34) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year | 47 [35–64] | 41 [32–54] | 70 [59–76] | 59 [53–69] | 42 [33–60] | <0.001 |
| Female, n (%) | 122 (76) | 65 (78) | 16 (80) | 18 (78) | 23 (68) | 0.65 |
| Prevalence, n (%) | 118 (74) | 68 (82) | 15 (75) | 12 (52) | 23 (68) | 0.03 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 27.8 [22.6–31.8] | 27.2 [21.9–20.1] | 29.9 [25.2–36.6] | 27.7 [21.4–33.5] | 28.4 [23.8–34] | 0.19 |
| Follow-up, month | 55.6 [15.2–107.0] | 67.7 [16.2–135.3] | 55.4 [20.2–87.7] | 43.4 [8.2–68.8] | 48.3 [18.2–119.4] | 0.57 |
| Essential hypertension, n (%) | 66 (42) | 25 (30.5) | 18 (90) | 12 (54.6) | 11 (32.4) | <0.001 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 37 (23.4) | 11 (13.4) | 12 (60) | 6 (26.1) | 8 (24.2) | <0.001 |
| Hyperlipidemia, n (%) | (22.7) | (17.1) | (47.1) | (27.3) | (21.2) | 0.068 |
| Coronary artery disease, n (%) | 17 (10.7) | 6 (7.2) | 4 (20) | 4 (17.4) | 3 (9.1) | 0.22 |
| Atrial fibrillation, n (%) | 15 (9.4) | 4 (4.8) | 9 (45) | 2 (8.7) | 0 (0) | <0.001 |
| Pulmonary embolism, n (%) | 32 (20) | 4 (4.8) | 0 (0) | 2 (8.7) | 26 (76.5) | <0.001 |
| Chronic kidney disease, n (%) | 17 (10.6) | 3 (3.6) | 9 (45) | 2(8.7) | 3 (8.8) | <0.001 |
| Hematologic ds | 31 (19.4) | 13 (16.7) | 3 (15) | 3 (13) | 12 (35.3) | 0.098 |
| Baseline 6-MWT, m | 280 [172–393] | 320 [201–407] | 216 [97–306] | 110 [75–384] | 297 [238–366] | 0.03 |
| Baseline NT-proBNP, pg/mL | 484 [146–1726] | 315 [96–1178] | 1164 [392–2808] | 402 [210–2889] | 668 [148–1810] | 0.05 |
| TAPSE, cm | 1.8 [1.5–2.1] | 1.8 [1.6–2.1] | 2 [1.7–2.4] | 1.6 [1.4–2.2] | 1.6 [1.5–2.1] | 0.46 |
| WHO III/IV, n (%) | 103 (65) | 51 (62) | 12 (60) | 17 (77) | 24 (68) | 0.56 |
| mRAP, mmHg | 8 [4–12] | 8 [3–13] | 11 [9–13] | 6 [1–9] | 9 [4–12] | 0.009 |
| mPAP, mmHg | 45 [35–55] | 48 [42–62] | 42 [33–49] | 38 [29–43] | 48 [32–53] | 0.005 |
| PAWP, mmHg | 10 [7–16] | 10 [6–16] | 18 [12–19] | 10 [5–14] | 11 [8–12] | 0.008 |
| CI (Fick method), L/min/m2 | 2.5 [2–3] | 2.7 [2–3.1] | 2.1 [1.9–2.5] | 2.7 [2.3–3.2] | 2.1 [2–2.5] | 0.03 |
| PVR (Fick method), mmHg/L/min | 590 (344–880) | 779 (376–932) | 441 [295.8–628.7] | 452 [333–742] | 660 [225–992] | 0.06 |
| CI (thermodilution method), L/min/m2 | 2.6 [2.0–3.6] | 2.5 [2.0–3.9] | 2.0 [1.9–3.1] | 3.0 [2.3–3.6] | 2.0 [1.8–3.2] | 0.42 |
| PVR (thermodilution method), mmHg/L/min | 640 [350–834] | 702 [334–945] | 622 (338–1003) | 398 [361–611] | 975 (444–6258] | 0.4 |
| SVO2, % | 64 [56–72] | 66 [60–73] | 62 [49–72] | 66 [56–70] | 57 [50–64] | 0.06 |
| LVEF, % | 57 [57–67] | 60 [58–67] | 60 [55–67] | 60 [60–65] | 60 [57–65] | 0.9 |
| RSVP, mmHg | 67 [52–86] | 71 [52–91] | 61 [42–78] | 57 [53–81] | 66 [54–85] | 0.4 |
| FVC, % | 59 [43–75] | 64 [48–77] | 52 [42–76] | 43 [31–58] | 69 [56–81] | 0.006 |
| DLCO, % | 48 [32–63] | 54 [40–65] | 60 [32–82] | 21 [19–36] | 53 [41–72] | 0.006 |
| Variables | Idiopathic (n = 25) | CTD (n = 27) | CHD (n = 26) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age, year | 39 [31–53] | 47 [41–66] | 33 [26–41] | <0.001 |
| Female, n (%) | 19 (79) | 25 (93) | 18 (69) | 0.09 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 28.2 [24.8–31.6] | 28.5 [22–31.5] | 23.4 [18.3–26.5] | 0.03 |
| Prevalence, n (%) | 19 (79) | 25 (93) | 21 (81) | 0.30 |
| WHO III/IV, n (%) | 17 (71) | 17 (65) | 12 (46) | 0.17 |
| Baseline 6-MWT, m | 280 [182.9–378] | 332 [201–218] | 274 [198–374] | 0.77 |
| Baseline NT-proBNP, pg/mL | 1161 [304–2250] | 324 [95–585] | 182 [79–490] | 0.006 |
| mRAP, mmHg | 10 [2–15] | 7 [3–7] | 8 [3–14] | 0.60 |
| mPAP, mmHg | 55 [46–63] | 43 [23–52] | 67 [44–73] | 0.004 |
| PAWP, mmHg | 10 [6–16] | 9 [6–13] | 8 [6–17] | 0.80 |
| CI (Fick method), L/min/m2 | 2.3 [1.9–2.7] | 2.7 [2.0–3.0] | 3.2 [2.3–3.4] | 0.03 |
| PVR (Fick method), mmHg/L/min | 842 [540–1201] | 531 [212–908] | 837 [745–931] | 0.07 |
| CI (thermodilution method), L/min/m2 | 2.3 [1.8–2.9] | 2.4 [2.0–4.3] | 2.8 [2.5–4.1] | 0.15 |
| PVR (thermodilution method), mmHg/L/min | 735 [658–975] | 406 [131–918] | 733 [581–793] | 0.04 |
| SVO2, % | 66 [57–72] | 69 [57–73] | 69 [61–74] | 0.50 |
| TAPSE, cm | 1.8 [1.6–2.0] | 1.7 [1.5–2.5] | 1.8 [1.6–2.0] | 1.00 |
| LVEF, % | 61 [55.5–67] | 60 [59–67] | 60 [56–64] | 0.70 |
| RSVP, mmHg | 81 [56–97] | 54 [41–79] | 86 [70–97] | 0.004 |
| Variables | Idiopathic (n= 25) | CTD (n = 27) | CHD (n = 26) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Baseline | Last Visit | p-Value | Baseline | Last Visit | p-Value | Baseline | Last Visit | p-Value | |
| 6-MWT, m | 280 [183–378] | 389 [171–469] | 0.11 | 332 [201–418] | 358 [229–454] | 0.77 | 274 [198–374] | 392 [255–471] | 0.01 |
| NT-proBNP, pg/mL | 1161 [304–2250] | 341 [109–1783] | 0.57 | 324 [94–585] | 202 [90–2836] | 0.32 | 183 [79–490] | 225 [118–604] | 0.17 |
| WHO III/IV, n (%) | 17 (71) | 14 (58) | 0.55 | 17 (65) | 11 (41) | 0.07 | 12 (46) | 10 (38) | 0.73 |
| RSVP, mmHg | 81 [56–97] | 71 [46–93] | 0.32 | 54 [42–79] | 51 [40–80] | 0.77 | 86 [70–97] | 85 [66–106] | 0.03 |
| Reduced RV function, n (%) | 16 (73) | 14 (67) | 1 | 11 (48) | 7 (39) | 1 | 13 (54) | 11 (61) | 0.69 |
| Enlarged RA, n (%) | 20 (87) | 16 (80) | 0.68 | 10 (42) | 5 (33) | 1 | 14 (70) | 11 (79) | 1 |
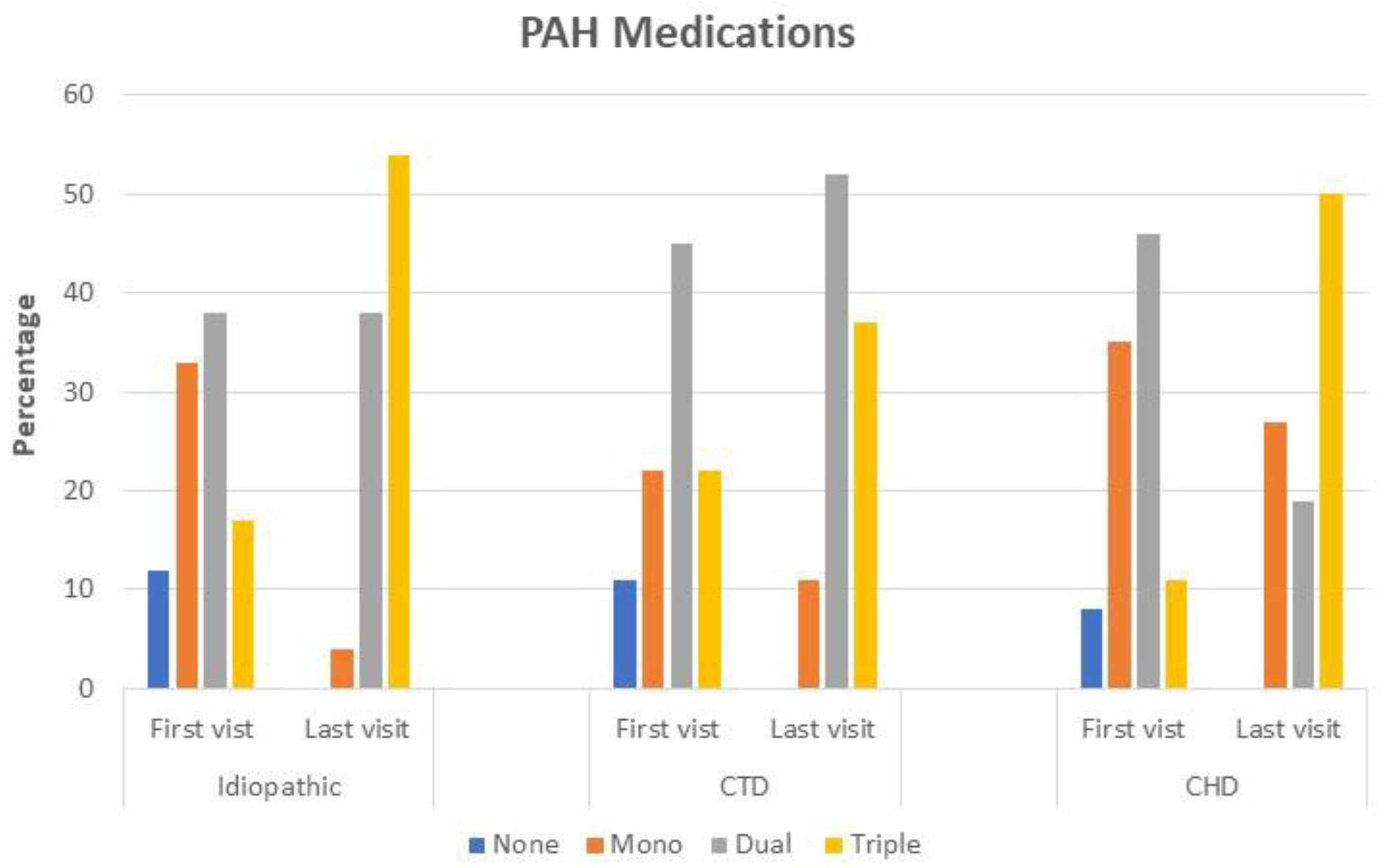
| Medications | |||||||||
| Sildenafil/Tadalafil, n (%) | 14 (58) | 12 (50) | 0.69 | 13 (48) | 8 (30) | 0.12 | 16 (62) | 9 (35) | 0.04 |
| Riociguat, n (%) | 1 (4) | 16 (67) | <0.001 | 6 (22) | 12 (44) | 0.07 | 0 (0) | 14 (54) | <0.001 |
| Endothelin RA, n (%) | 12 (50) | 20 (83) | 0.02 | 19 (70) | 24 (89) | 0.12 | 21 (81) | 24 (92) | 0.37 |
| Iloprost, n (%) | 3 (12) | 2 (8) | 1 | 4 (15) | 4 (15) | 1 | 5 (19) | 5 (19) | 1 |
| Selexipag, n (%) | 0 (0) | 4 (16) | 0.12 | 0 (0) | 5 (18) | 0.06 | 0 (0) | 5 (19) | 0.06 |
| Treprostinil, n (%) | 8 (33) | 9 (41) | 1 | 3 (11) | 7 (26) | 0.25 | 0 (0) | 3 (12) | 0.25 |
| None | 3 (12) | 0 (0) | 0.62 | 3 (11) | 0 (0) | 0.25 | 2 (8) | 0 (0) | 1 |
| Single | 8 (33) | 1 (4) | 0.04 | 6 (22) | 3 (11) | 0.45 | 9 (35) | 7 (27) | 0.62 |
| Dual | 9 (38) | 9 (38) | 1 | 12 (45) | 14 (52) | 0.45 | 12 (46) | 5 (19) | 0.04 |
| Triple | 4 (17) | 13 (54) | 0.02 | 6 (22) | 10 (37) | 0.22 | 3 (11) | 13 (50) | 0.002 |
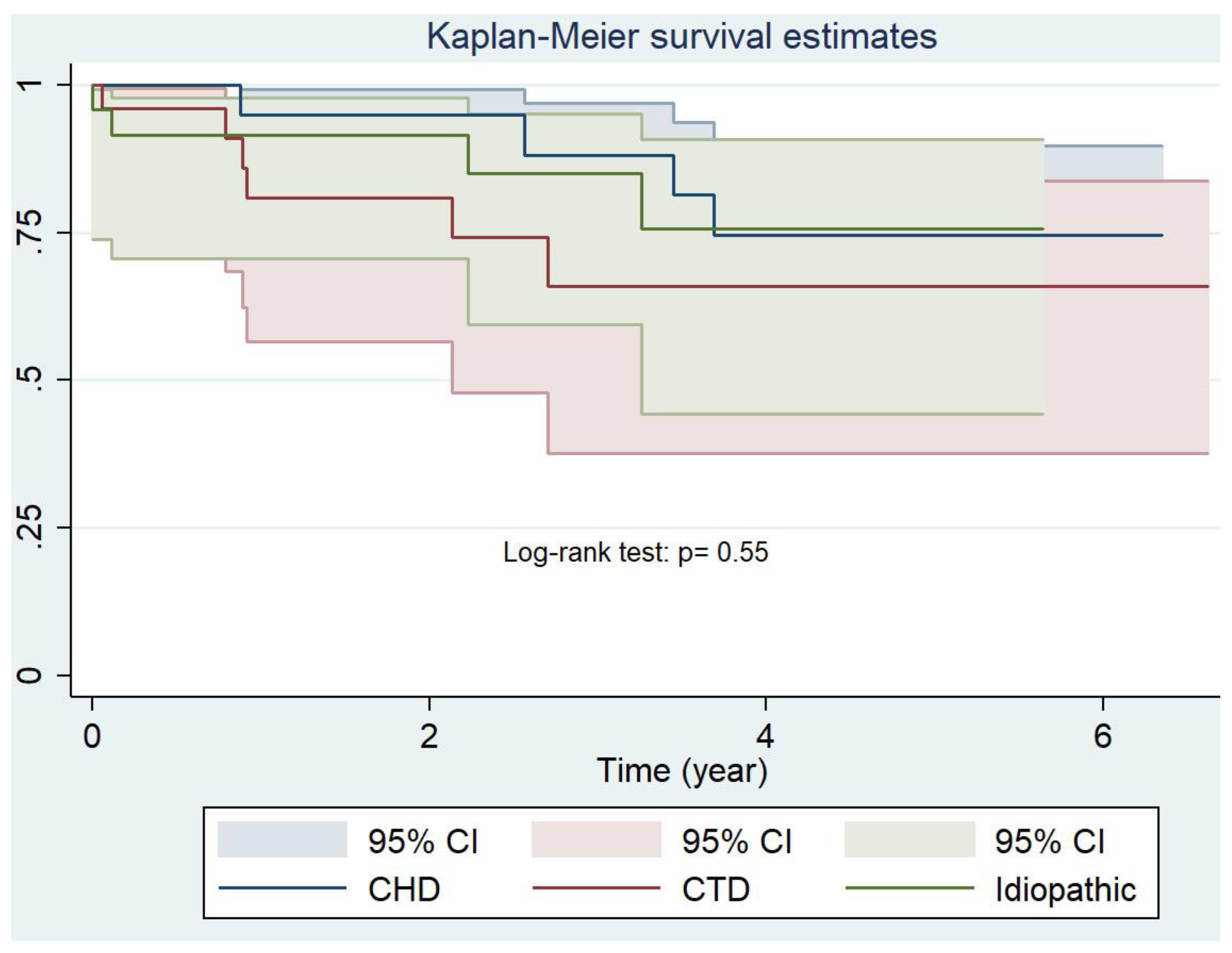
| Probability of Survival | Cumulative Group 1 (n =83) | Idiopathic (n = 25) | CTD (n = 27) | CHD (n = 26) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1st year, % (95% CI) | 86 (75–92) | 90 (66–97) | 82 (60–93) | 95 (71–99) |
| 3rd year, % (95% CI) | 69 (54–80) | 73(41–90) | 66 (38–84) | 75 (45–90) |
| 5th year, % (95% CI) | 69 (54–80) | 73 (41–90) | 66 (38–84) | 75 (45–90) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Saleh, K.; Khan, N.; Dougherty, K.; Bodi, G.; Michalickova, M.; Mohammed, S.; Kerenidi, T.; Sadik, Z.; Mallat, J.; Farha, S.; et al. The First Pulmonary Hypertension Registry in the United Arab Emirates (UAEPH): Clinical Characteristics, Hemodynamic Parameters with Focus on Treatment and Outcomes for Patients with Group 1-PH. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051996
Saleh K, Khan N, Dougherty K, Bodi G, Michalickova M, Mohammed S, Kerenidi T, Sadik Z, Mallat J, Farha S, et al. The First Pulmonary Hypertension Registry in the United Arab Emirates (UAEPH): Clinical Characteristics, Hemodynamic Parameters with Focus on Treatment and Outcomes for Patients with Group 1-PH. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051996
Chicago/Turabian StyleSaleh, Khaled, Naureen Khan, Kelly Dougherty, Govinda Bodi, Miriam Michalickova, Samiuddin Mohammed, Theodora Kerenidi, Ziad Sadik, Jihad Mallat, Samar Farha, and et al. 2023. "The First Pulmonary Hypertension Registry in the United Arab Emirates (UAEPH): Clinical Characteristics, Hemodynamic Parameters with Focus on Treatment and Outcomes for Patients with Group 1-PH" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051996
APA StyleSaleh, K., Khan, N., Dougherty, K., Bodi, G., Michalickova, M., Mohammed, S., Kerenidi, T., Sadik, Z., Mallat, J., Farha, S., & Sabbour, H. (2023). The First Pulmonary Hypertension Registry in the United Arab Emirates (UAEPH): Clinical Characteristics, Hemodynamic Parameters with Focus on Treatment and Outcomes for Patients with Group 1-PH. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1996. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051996







