Assessing the Outcomes of Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection after Therapeutic Plasma Exchange by Number of TPE Sessions
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Ethics
2.2. Selection Criteria and Study Variables
2.3. Definitions and TPE Procedure
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
Patients’ Background Characteristics
4. Discussion
4.1. Literature Findings
4.2. Study Limitations and Future Perspectives
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Necesito, I.V.; Velasco, J.M.S.; Jung, J.; Bae, Y.H.; Lee, J.H.; Kim, S.J.; Kim, H.S. Understanding chaos in COVID-19 and its relationship to stringency index: Applications to large-scale and granular level prediction models. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tarvis, M.; Ziegert, K.; Forsberg, E.; Andersson, J.; Gillsjö, C. From chaos to a new normal—The COVID-19 pandemic as experienced by municipal health and social care providers in Sweden: A qualitative study. Nord. J. Nurs. Res. 2022, 28, 20571585221124379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fericean, R.M.; Oancea, C.; Reddyreddy, A.R.; Rosca, O.; Bratosin, F.; Bloanca, V.; Citu, C.; Alambaram, S.; Vasamsetti, N.G.; Dumitru, C. Outcomes of Elderly Patients Hospitalized with the SARS-CoV-2 Omicron B.1.1.529 Variant: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 2150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Asadi, J.; Rasouli, M.A.; Ghaderi, E.; Roshani, D.; Mohsenpour, B.; Moradi, Y.; Moradi, G. Effectiveness of different treatment regimens on patients with COVID-19, hospitalized in Sanandaj hospitals: A retrospective cohort study. J. Pharm. Policy Pract. 2023, 16, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tirnea, L.; Bratosin, F.; Vidican, I.; Cerbu, B.; Turaiche, M.; Timircan, M.; Margan, M.-M.; Marincu, I. The Efficacy of Convalescent Plasma Use in Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Medicina 2021, 57, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziuzia-Januszewska, L.; Januszewski, M.; Sosnowska-Nowak, J.; Janiszewski, M.; Dobrzyński, P.; Jakimiuk, A.A.; Jakimiuk, A.J. COVID-19 Severity and Mortality in Two Pandemic Waves in Poland and Predictors of Poor Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Hospitalized Young Adults. Viruses 2022, 14, 1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, R.S.Y. Inflammation in COVID-19: From pathogenesis to treatment. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 2021, 14, 831–844. [Google Scholar]
- Niknam, Z.; Jafari, A.; Golchin, A.; Danesh Pouya, F.; Nemati, M.; Rezaei-Tavirani, M.; Rasmi, Y. Potential therapeutic options for COVID-19: An update on current evidence. Eur. J. Med. Res. 2022, 27, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atluri, K.; Aimlin, I.; Arora, S. Current Effective Therapeutics in Management of COVID-19. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Notz, Q.; Schmalzing, M.; Wedekink, F.; Schlesinger, T.; Gernert, M.; Herrmann, J.; Sorger, L.; Weismann, D.; Schmid, B.; Sitter, M.; et al. Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Responses in Severe COVID-19-Induced Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome-An Observational Pilot Study. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 581338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Citu, C.; Gorun, F.; Motoc, A.; Ratiu, A.; Gorun, O.M.; Burlea, B.; Neagoe, O.; Citu, I.M.; Rosca, O.; Bratosin, F.; et al. Evaluation and Comparison of the Predictive Value of 4C Mortality Score, NEWS, and CURB-65 in Poor Outcomes in COVID-19 Patients: A Retrospective Study from a Single Center in Romania. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grigoras, M.L.; Citu, I.M.; Citu, C.; Chiriac, V.D.; Gorun, F.; Levai, M.C.; Manolescu, D.; Rosca, O.; Bratosin, F.; Gurumurthy, S.; et al. Evaluation of FIB-4, NFS, APRI and Liver Function Tests as Predictors for SARS-CoV-2 Infection in the Elderly Population: A Matched Case-Control Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanza, C.; Romenskaya, T.; Manetti, A.C.; Franceschi, F.; La Russa, R.; Bertozzi, G.; Maiese, A.; Savioli, G.; Volonnino, G.; Longhitano, Y. Cytokine Storm in COVID-19: Immunopathogenesis and Therapy. Medicina 2022, 58, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fericean, R.M.; Citu, C.; Manolescu, D.; Rosca, O.; Bratosin, F.; Tudorache, E.; Oancea, C. Characterization and Outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 Infection in Overweight and Obese Patients: A Dynamic Comparison of COVID-19 Pandemic Waves. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Kassim Hassan, M.; Adam Bala, A.; Jatau, A.I. Low rate of COVID-19 vaccination in Africa: A cause for concern. Ther. Adv. Vaccines Immunother. 2022, 10, 25151355221088159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marincu, I.; Citu, C.; Bratosin, F.; Bogdan, I.; Timircan, M.; Gurban, C.V.; Bota, A.V.; Braescu, L.; Grigoras, M.L. Clinical Characteristics and Outcomes of COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients: A Comparison between Complete mRNA Vaccination Profile and Natural Immunity. J. Pers. Med. 2022, 12, 259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, G.; Song, H.; Yip, S.; Zhang, T.; He, D. Impact of low vaccine coverage on the resurgence of COVID-19 in Central and Eastern Europe. One Health 2022, 14, 100402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Citu, C.; Chiriac, V.D.; Citu, I.M.; Gorun, O.M.; Burlea, B.; Bratosin, F.; Popescu, D.-E.; Ratiu, A.; Buca, O.; Gorun, F. Appraisal of COVID-19 Vaccination Acceptance in the Romanian Pregnant Population. Vaccines 2022, 10, 952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Tang, B.; Bai, Y.; Shao, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Tang, S. The resurgence risk of COVID-19 in China in the presence of immunity waning and ADE: A mathematical modelling study. Vaccine 2022, 40, 7141–7150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, M.; Zhang, J.; Gong, J.; Ran, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, L. Epidemic modeling for the resurgence of COVID-19 in Chinese local communities. J. Saf. Sci. Resil. 2022, 3, 229–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alimohamadi, Y.; Tola, H.H.; Abbasi-Ghahramanloo, A.; Janani, M.; Sepandi, M. Case fatality rate of COVID-19: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Prev. Med. Hyg. 2021, 62, E311–E320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manolescu, D.; Timar, B.; Bratosin, F.; Rosca, O.; Citu, C.; Oancea, C. Predictors for COVID-19 Complete Remission with HRCT Pattern Evolution: A Monocentric, Prospective Study. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 1397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, S.; Sahu, A.; Routray, S.S.; Maiti, R.; Mitra, J.K.; Mukherjee, S. Efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange in severe COVID-19 disease: A meta-analysis. Vox. Sang. 2023, 118, 49–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talalaev, M.; Pandav, K.; Mehendale, M.; Gonzalez, L.; Yatzkan, M.C.; Yatzkan, G.D.; Perez-Fernandez, J. Treatment with therapeutic plasma exchange in severe COVID-19 pneumonia: A case report and review of the literature. Respir. Med. Case Rep. 2022, 36, 101587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sergent, S.R.; Ashurst, J.V. Plasmapheresis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022; Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK560566/ (accessed on 7 January 2023).
- Fayed, M.; Patel, N.; Angappan, S.; Nowak, K.; Vasconcelos Torres, F.; Penning, D.H.; Chhina, A.K. Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) Score and Mortality Prediction in Patients With Severe Respiratory Distress Secondary to COVID-19. Cureus 2022, 14, e26911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beigmohammadi, M.T.; Amoozadeh, L.; Rezaei Motlagh, F.; Rahimi, M.; Maghsoudloo, M.; Jafarnejad, B.; Eslami, B.; Salehi, M.R.; Zendehdel, K. Mortality Predictive Value of APACHE II and SOFA Scores in COVID-19 Patients in the Intensive Care Unit. Can. Respir. J. 2022, 2022, 5129314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.H.; Baek, A.R.; Lee, S.I.; Kim, W.Y.; Na, Y.S.; Lee, B.Y.; Seong, G.M.; Baek, M.S. ROX index and SpO2/FiO2 ratio for predicting high-flow nasal cannula failure in hypoxemic COVID-19 patients: A multicenter retrospective study. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0268431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guia, M.F.; Boléo-Tomé, J.P.; Imitazione, P.; Polistina, G.E.; Alves, C.; Ishikawa, O.; Ballenberger, M.; Mina, B.; Fiorentino, G.; Esquinas, A.; et al. Usefulness of the HACOR score in predicting success of CPAP in COVID-19-related hypoxemia. Respir. Med. 2021, 187, 106550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabibi, S.; Tabibi, T.; Conic, R.R.; Banisaeed, N.; Streiff, M.B. Therapeutic Plasma Exchange: A potential Management Strategy for Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. J. Intensive Care Med. 2020, 35, 827–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balagholi, S.; Dabbaghi, R.; Eshghi, P.; Mousavi, S.A.; Heshmati, F.; Mohammadi, S. Potential of therapeutic plasmapheresis in treatment of COVID-19 patients: Immunopathogenesis and coagulopathy. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2020, 59, 102993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, J.; Gratacos-Ginès, J.; Olivas, P.; Costa, M.; Nieto, S.; Mateo, D.; Sánchez, M.B.; Aguilar, F.; Bassegoda, O.; Ruiz, P.; et al. Plasma exchange: An effective rescue therapy in critically ILL patients with coronavirus disease 2019 infection. Crit. Care Med. 2020, 48, e1350–e1355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faqihi, F.; Alharthy, A.; Karakitsos, D. Therapeutic plasma exchange in life-threatening COVID-19 and associated cytokine release syndrome. J. Formos. Med. Assoc. 2020, 119, 1888–1889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khamis, F.; Al-Zakwani, I.; Al Hashmi, S.; Al Dowaiki, S.; Al Bahrani, M.; Pandak, N.; Al Khalili, H.; Memish, Z. Therapeutic plasma exchange in adults with severe COVID-19 infection. Int. J. Infect. Dis. 2020, 99, 214–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dinarello, C.A. Immunological and inflammatory functions of the interleukin-1 family. Annu Rev. Immunol. 2009, 27, 519–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gluck, W.L.; Callahan, S.P.; Brevetta, R.A.; Stenbit, A.E.; Smith, W.M.; Martin, J.C.; Blenda, A.V.; Arce, S.; Edenfield, W.J. Efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange in the treatment of penn class 3 and 4 cytokine release syndrome complicating COVID-19. Respir. Med. 2020, 175, 106188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nusshag, C.; Morath, C.; Speer, C.; Kaelble, F.; Zeier, M.; Boxberger, M.; Schulze-Schleithoff, E.; Fiedler, M.O.; Weigand, M.A.; Merle, U. Plasma Exchange in Patients with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019: A Single-Center Experience. Crit. Care Explor. 2021, 3, e0517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fonseca-González, G.; Alamilla-Sánchez, M.; García-Macas, V.; Herrera-Acevedo, J.; Villalobos-Brito, M.; Tapia-Rangel, E.; Maldonado-Tapia, D.; López-Mendoza, M.; Cano-Cervantes, J.H.; Orozco-Vázquez, J.; et al. Impact of plasmapheresis on severe COVID-19. Sci. Rep. 2023, 13, 163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barac, S.; Onofrei, R.R.; Lazureanu, C.; Barna, R.; Tutelca, A.; Rata, A.L. An In Vivo Observational Histological Study of Peripheral Arterial Damage in Patients with Acute Limb Ischemia in SARS-CoV-2 Infection. Diagnostics 2022, 12, 488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barac, S.; Onofrei, R.R.; Neagoe, P.V.; Popescu, A.I.; Pantea, S.; Rață, A.L. An Observational Study on Patients with Acute Limb Ischemia and SARS-CoV-2 Infection: Early and Late Results in Limb Salvage Rate. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5083. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faqihi, F.; Alharthy, A.; Alodat, M.; Kutsogiannis, D.J.; Brindley, P.G.; Karakitsos, D. Therapeutic plasma exchange in adult critically ill patients with life-treathening SARS-CoV-2 disease: A pilot study. J. Crit. Care 2020, 60, 328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Zhai, H.; Ma, S.; Chen, J.; Gao, Y. Efficacy of therapeutic plasma exchange in severe COVID-19 patients. Br. J. Haematol. 2020, 190, e181–e183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alharthy, A.; Faqihi, F.; Memish, Z.A.; Balhamar, A.; Nasim, N.; Shahzad, A.; Tamim, H.; Alqahtani, S.A.; Brindley, P.G.; Karakitsos, D. Continuous renal replacement therapy with the addition of CytoSorb cartridge in critically ill patients with COVID-19 plus acute kidney injury: A case-series. Artif. Organs 2021, 45, E101–E112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Beraud, M.; Hashami, S.A.; Lozano, M.; Bah, A.; Keith, P. Role of therapeutic plasma exchange in the management of COVID-19-induced cytokine storm syndrome. Transfus. Apher. Sci. 2022, 61, 103433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardi, A.; Meidaninikjeh, S.; Nikfarjam, S.; Majidi Zolbanin, N.; Jafari, R. Interleukin-1 in COVID-19 Infection: Immunopathogenesis and Possible Therapeutic Perspective. Viral. Immunol. 2021, 34, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arthur, T.; Snow, C.; Saleem, N.; Ambler, G.; Nastouli, E. Tocilizumab in COVID-19: A meta-analysis, trial sequential analysis, and meta-regression of randomized-controlled trials. Intensive Care Med. 2021, 47, 641–652. [Google Scholar]
- Ashrafzadeh-Kian, S.; Campbell, M.R.; Jara Aguirre, J.C.; Walsh, J.; Kumanovics, A.; Jenkinson, G. Role of immune mediators in predicting hospitalization of SARS-CoV-2 positive patients. Cytokine 2022, 150, 155790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Variables | 1 TPE (n = 41) | 2 TPE (n = 13) | >2 TPE (n = 11) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BMI (mean ± SD) | 33.7 ± 6.2 | 32.4 ± 5.9 | 33.1 ± 6.0 | 0.793 * |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 54.4 ± 12.5 | 50.8 ± 14.6 | 47.8 ± 9.5 | 0.262 * |
| Age range, years | 28–80 | 21–72 | 37–69 | |
| Gender | 0.775 | |||
| Male | 29 (70.7%) | 10 (76.9%) | 7 (63.6%) | |
| Female | 12 (29.3%) | 3 (23.1%) | 4 (36.4%) | |
| Days from COVID-19 diagnosis and TPE (mean ± SD) | 12.7 ± 8.9 | 13.7 ± 6.0 | 11.6 ± 5.8 | 0.814 * |
| Mechanical ventilation | 0.488 | |||
| Invasive | 24 (58.5%) | 10 (76.9%) | 7 (63.6%) | |
| Non-invasive | 17 (41.5%) | 3 (23.1%) | 3 (36.4%) | |
| Number of comorbidities (n,%) | ||||
| Diabetes mellitus | 6 (14.6%) | 2 (15.4%) | 2 (18.2%) | 0.958 |
| Hypertension | 20 (48.8%) | 7 (53.8%) | 6 (54.5%) | 0.915 |
| Obesity | 17 (41.5%) | 6 (46.2%) | 4 (36.4%) | 0.888 |
| COPD/asthma | 4 (9.8%) | 2 (15.4%) | 0 (0.0%) | 0.423 |
| Variables—Median (IQR) | 1 TPE (n = 41) | 2 TPE (n = 13) | >2 TPE (n = 11) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6, pg/mL | 108.1 (677.5) | 37.0 (187.5) | 305.5 (1462.8) | <0.001 |
| Ferritin, ug/L | 1529.0 (1496.5) | 1224.5 (2426.0) | 1744.0 (2422.3) | 0.094 |
| D-dimers, ug/mL | 3.3 (5.3) | 1.2 (2.9) | 1.7 (3.0) | 0.138 |
| CRP, mg/L | 88.0 (149.6) | 32.5 (124.6) | 111.0 (203.5) | 0.001 |
| LDH, U/L | 575.0 (436.5) | 487.0 (192.8) | 515.5 (311.0) | 0.695 |
| Procalcitonin, ng/mL | 0.3 (1.8) | 0.2 (0.5) | 0.8 (3.3) | 0.059 |
| Fibrinogen, g/L | 4.9 (4.1) | 3.5 (3.4) | 4.7 (3.8) | 0.386 |
| ESR, mm/h | 40.0 (66.0) | 27.5 (45.0) | 45.0 (75.0) | 0.066 |
| Leucocytes, ×103/uL | 12.7 (9.3) | 17.0 (9.5) | 11.9 (7.8) | <0.001 |
| % Lymphocytes | 5.2 (5.6) | 3.7 (2.9) | 7.4 (8.6) | 0.117 |
| Lymphocytes, ×103/uL | 0.6 (0.5) | 0.7 (0.4) | 0.7 (1.0) | 0.639 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 54.0 (38.5) | 71.5 (55.8) | 56.2 (61.1) | 0.036 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.4) | 0.9 (0.6) | 0.7 (1.0) | 0.208 |
| pH | 7.4 (0.2) | 7.4 (0.1) | 7.4 (0.1) | 0.974 |
| Lactate, mmol/L | 2.3 (1.1) | 2.3 (1.2) | 2.2 (1.2) | 0.891 |
| Variables—Median (IQR) | 1 TPE (n = 41) | 2 TPE (n = 13) | >2 TPE (n = 11) | p-Value | p-Value * |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IL-6, pg/mL | 76.0 (371.6) | 17.9 (142.6) | 156.0 (320.5) | <0.001 | <0.001 |
| Ferritin, ug/L | 1141.0 (1469.5) | 722.5 (962.5) | 1307.0 (2105.5) | 0.073 | 0.126 |
| D-dimers, ug/mL | 1.5 (3.8) | 1.5 (3.2) | 1.8 (3.1) | 0.618 | 0.070 |
| CRP, mg/L | 65.0 (86.5) | 20.0 (38.1) | 98.2 (150.5) | <0.001 | 0.119 |
| LDH, U/L | 417.0 (248.0) | 395.5 (227.8) | 424.5 (281.3) | 0.695 | 0.042 |
| Procalcitonin, ng/mL | 0.2 (1.7) | 0.2 (0.4) | 0.8 (3.4) | 0.086 | 0.388 |
| Fibrinogen, g/L | 3.4 (1.8) | 2.4 (2.1) | 3.3 (2.5) | 0.426 | 0.097 |
| ESR, mm/h | 15.0 (22.5) | 11.0 (10.0) | 20.0 (41.3) | 0.044 | <0.001 |
| Leucocytes, ×103/uL | 15.2 (12.5) | 18.5 (11.1) | 14.2 (8.8) | 0.121 | 0.003 |
| % Lymphocytes | 5.6 (8.2) | 4.3 (5.6) | 6.2 (9.5) | 0.204 | 0.088 |
| Lymphocytes, ×103/uL | 0.7 (0.6) | 0.8 (0.7) | 0.8 (1.1) | 0.630 | 0.517 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 51.6 (48.3) | 65.6 (51.6) | 64.0 (54.9) | 0.219 | 0.365 |
| Creatinine, mg/dL | 0.8 (0.6) | 0.8 (0.6) | 0.8 (1.0) | 0.658 | 0.551 |
| pH | 7.4 (0.1) | 7.4 (0.1) | 7.4 (0.1) | 0.906 | 0.925 |
| Lactate, mmol/L | 2.3 (1.1) | 2.3 (1.2) | 2.3 (1.3) | 0.833 | 0.749 |
| Variables | 1 TPE (n = 41) | 2 TPE (n = 13) | >2 TPE (n = 11) | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| MAP before, mmHg (mean ± SD) | 80.3 ± 13.0 | 83.8 ± 14.6 | 79.9 ± 11.8 | 0.768 |
| MAP after, mmHg (mean ± SD) | 75.0 ± 17.0 | 88.7 ± 12.6 | 80.6 ± 11.2 | 0.023 |
| Body temperature before, Celsius (mean ± SD) | 36.5 ± 0.4 | 36.4 ± 0.4 | 36.6 ± 0.7 | 0.573 |
| Body temperature after, Celsius (mean ± SD) | 36.5 ± 0.5 | 36.6 ± 0.4 | 36.7 ± 0.7 | 0.364 |
| SOFA score before TPE | 7.6 ± 3.9 | 7.0 ± 2.7 | 8.2 ± 4.0 | 0.733 |
| SOFA score after TPE | 7.9 ± 3.8 | 6.7 ± 3.0 | 8.3 ± 3.9 | 0.507 |
| APACHE 2 score before TPE | 12.4 ± 4.9 | 11.2 ± 5.0 | 11.5 ± 4.2 | 0.685 |
| APACHE 2 score after TPE | 13.3 ± 5.6 | 11.2 ± 5.4 | 11.7 ± 4.1 | 0.391 |
| Oxygenation index before TPE | 24.1 ± 12.2 | 21.2 ± 5.6 | 20.0 ± 10.1 | 0.456 |
| Oxygenation index after TPE | 22.5 ± 13.1 | 22.8 ± 8.1 | 19.7 ± 10.2 | 0.763 |
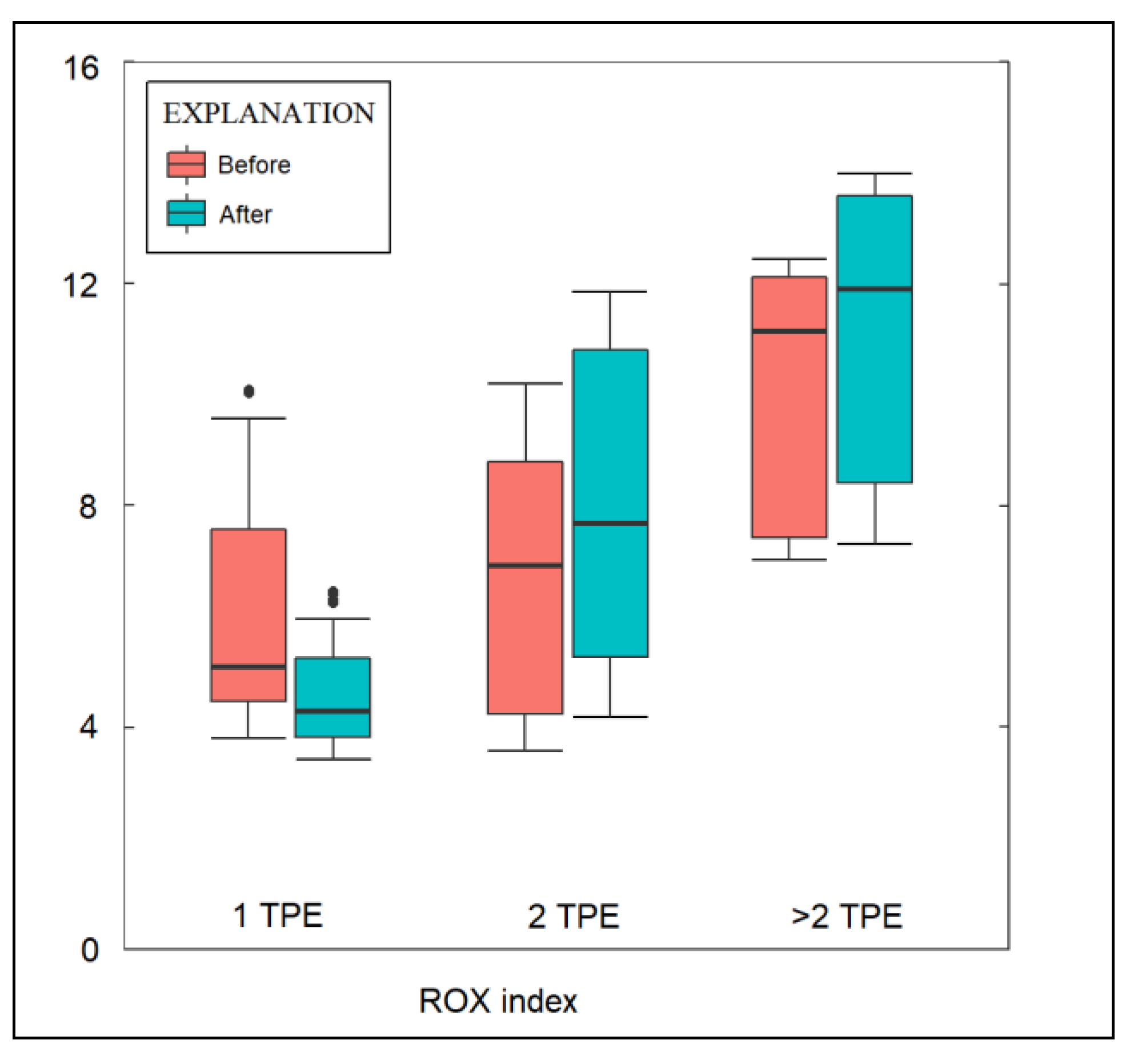
| ROX index before TPE | 6.5 ± 4.6 | 7.4 ± 3.0 | 11.4 ± 4.8 | 0.007 |
| ROX index after TPE | 5.9 ± 5.2 | 8.2 ± 3.2 | 13.1 ± 5.4 | <0.001 |
| HACOR score before TPE | 6.2 ± 0.4 | 6.0 ± 1.1 | 6.0 ± 0.1 | 0.415 |
| HACOR score after TPE | 7.0 ± 2.2 | 5.5 ± 1.1 | 5.8 ± 0.4 | 0.019 |
| PaO2/FiO2 before TPE | 106.6 ± 58.7 | 133.3 ± 65.8 | 144.3 ± 85.9 | 0.161 |
| PaO2/FiO2 after TPE | 109.3 ± 52.9 | 137.4 ± 57.2 | 146.7 ± 83.8 | 0.110 |
| PaO2/FiO2 > 100mmHg before TPE (n,%) | 13 (34.1%) | 8 (61.5%) | 5 (45.5%) | 0.208 |
| PaO2/FiO2 > 100mmHg after TPE (n,%) | 11 (26.8%) | 7 (53.8%) | 3 (27.3%) | 0.178 |
| Intubated, (n,%) | 18 (43.9%) | 5 (38.5%) | 5 (45.5%) | 0.927 |
| 5-day mortality | 20 (48.8%) | 5 (38.5%) | 3 (27.3%) | 0.411 |
| Overall mortality, (n,%) | 32 (78.0%) | 9 (69.2%) | 6 (54.5%) | 0.290 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Porosnicu, T.M.; Sandesc, D.; Jipa, D.; Gindac, C.; Oancea, C.; Bratosin, F.; Fericean, R.M.; Kodimala, S.C.; Pilut, C.N.; Nussbaum, L.A.; et al. Assessing the Outcomes of Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection after Therapeutic Plasma Exchange by Number of TPE Sessions. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051743
Porosnicu TM, Sandesc D, Jipa D, Gindac C, Oancea C, Bratosin F, Fericean RM, Kodimala SC, Pilut CN, Nussbaum LA, et al. Assessing the Outcomes of Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection after Therapeutic Plasma Exchange by Number of TPE Sessions. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(5):1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051743
Chicago/Turabian StylePorosnicu, Tamara Mirela, Dorel Sandesc, Daniel Jipa, Ciprian Gindac, Cristian Oancea, Felix Bratosin, Roxana Manuela Fericean, Shiva Charana Kodimala, Ciprian Nicolae Pilut, Laura Alexandra Nussbaum, and et al. 2023. "Assessing the Outcomes of Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection after Therapeutic Plasma Exchange by Number of TPE Sessions" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 5: 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051743
APA StylePorosnicu, T. M., Sandesc, D., Jipa, D., Gindac, C., Oancea, C., Bratosin, F., Fericean, R. M., Kodimala, S. C., Pilut, C. N., Nussbaum, L. A., & Sirbu, I. O. (2023). Assessing the Outcomes of Patients with Severe SARS-CoV-2 Infection after Therapeutic Plasma Exchange by Number of TPE Sessions. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(5), 1743. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12051743







