Long-Term Results after Autologous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP versus PAP Flaps Based on Quality of Life and Aesthetic Outcome Analysis
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Patients
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
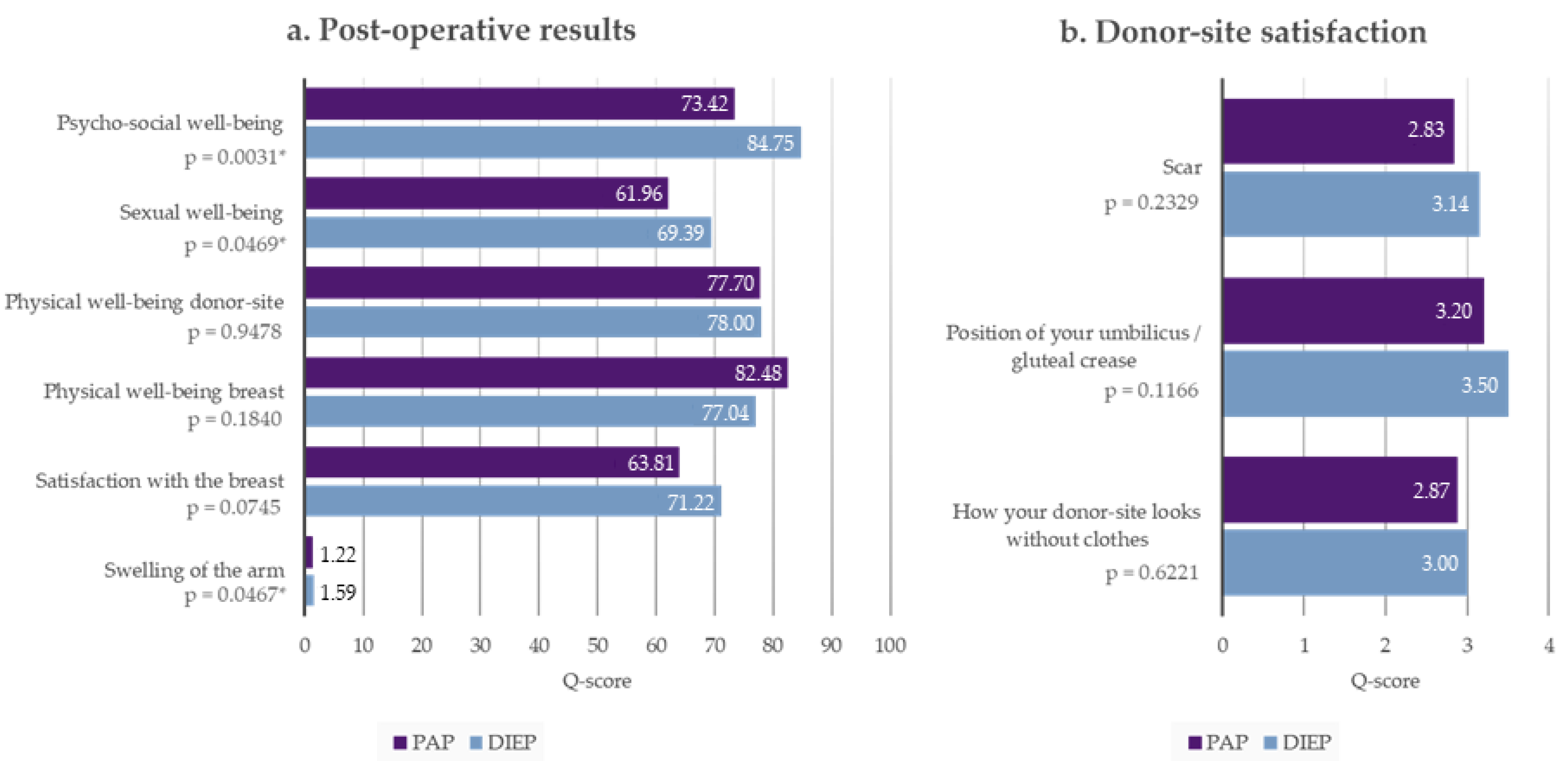
3.2. Breast-Q
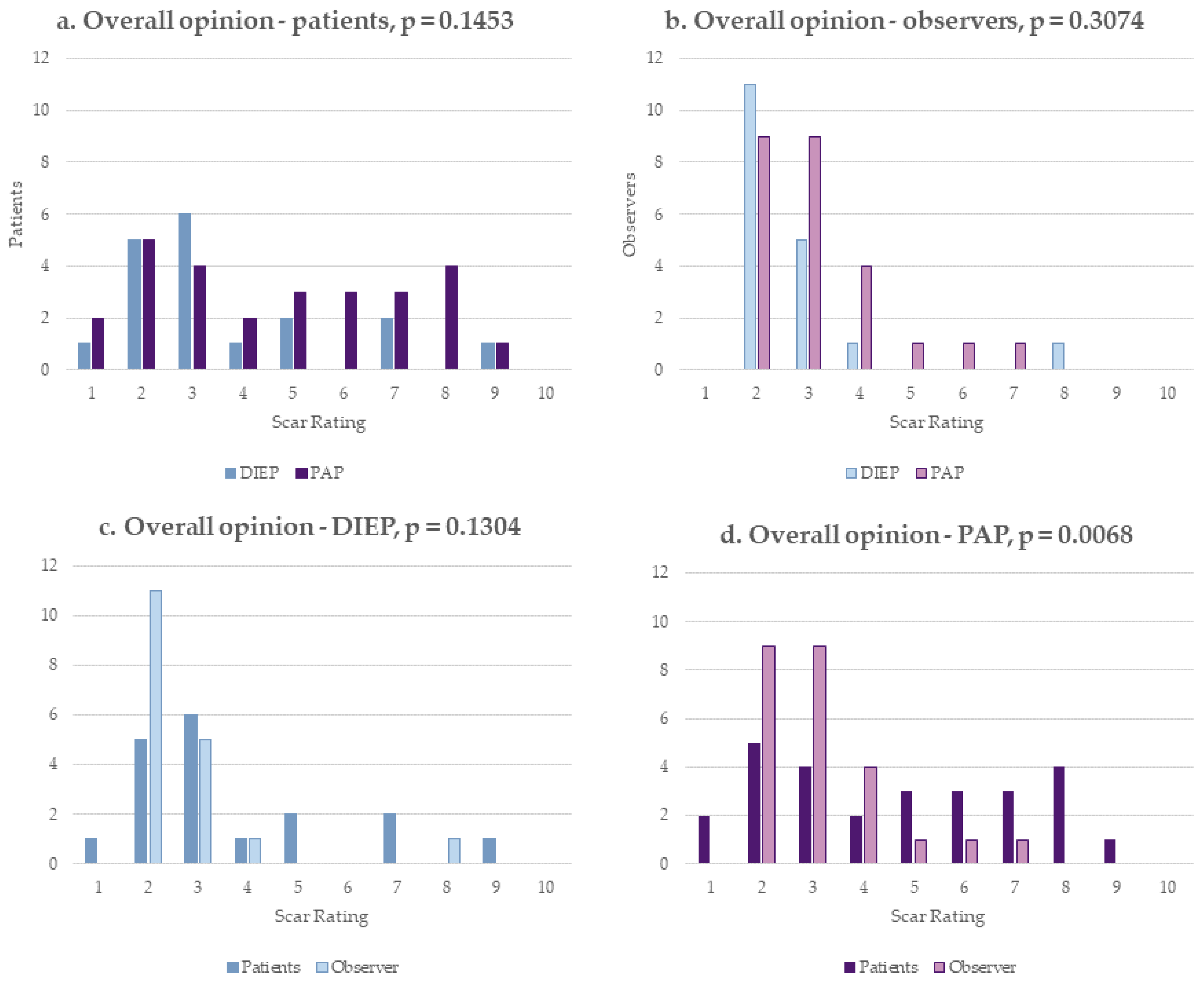
3.3. POSAS
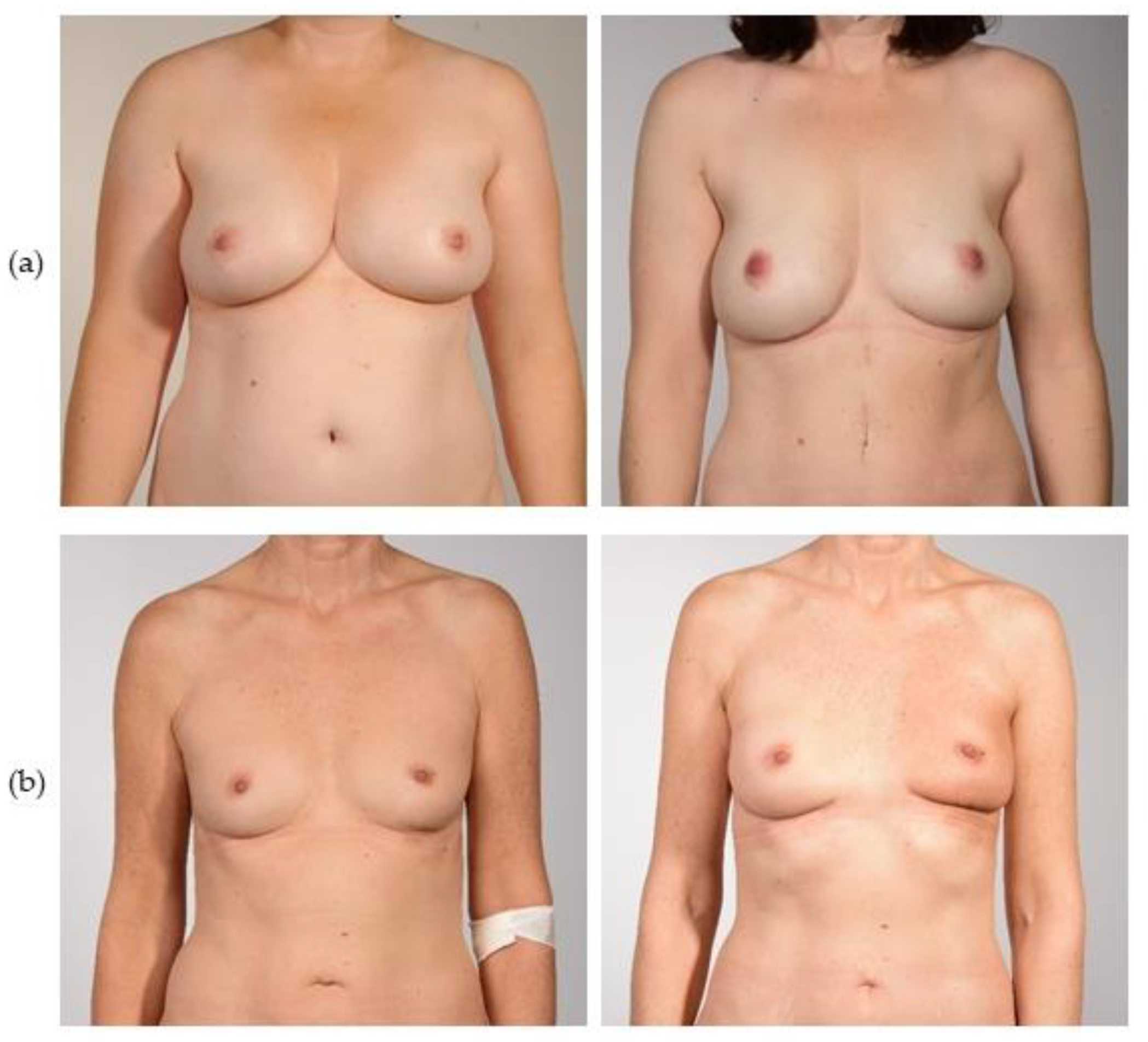
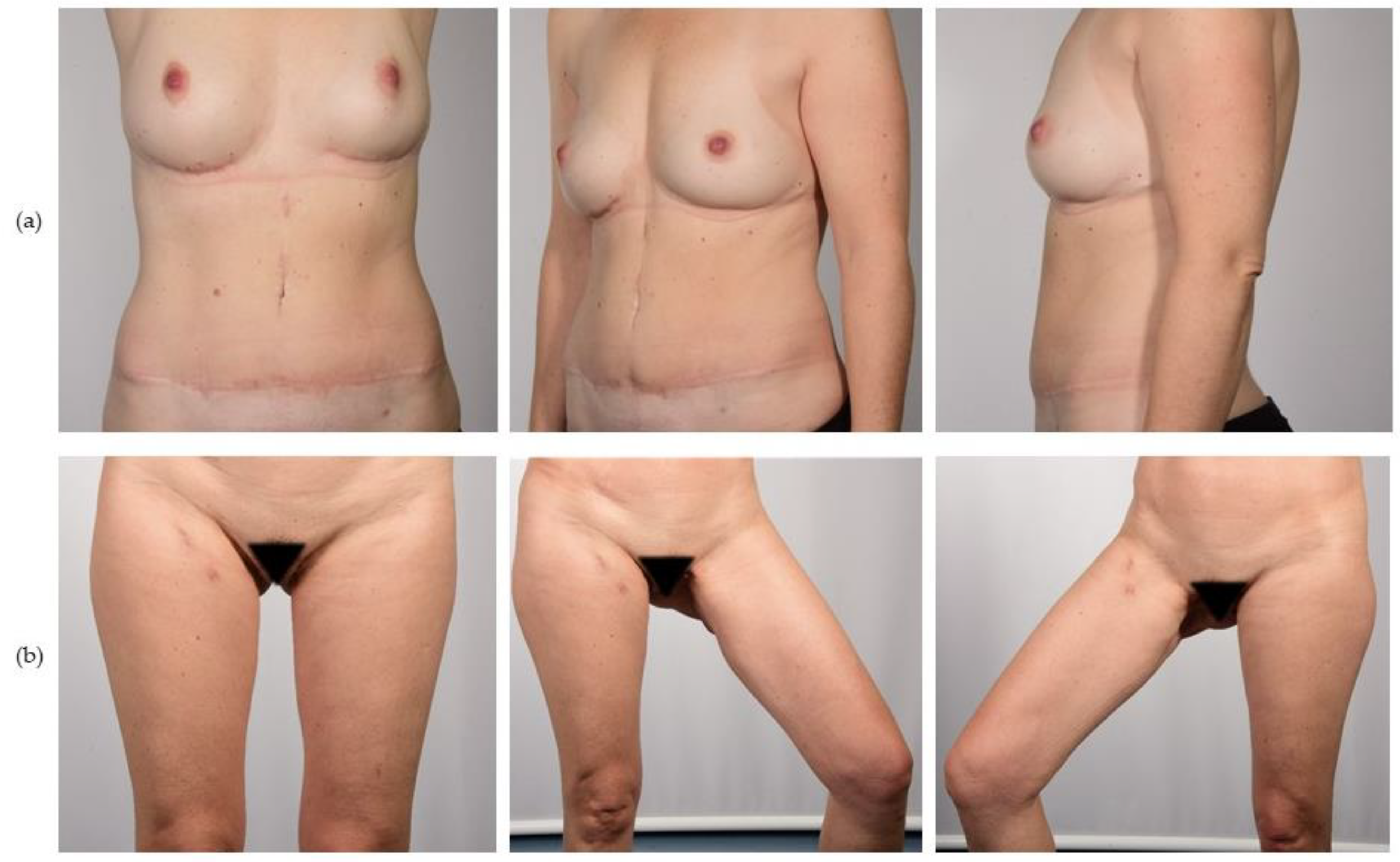
3.4. Cosmetic Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) Program. SEER*Stat Database: Incidence—SEER Research Data, National Cancer Institute. Available online: http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/breast.html (accessed on 28 October 2022).
- Guyomard, V.; Leinster, S.; Wilkinson, M. Systematic review of studies of patients’ satisfaction with breast reconstruction after mastectomy. Breast 2007, 16, 547–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lucas, D.J.; Sabino, J.; Shriver, C.D.; Pawlik, T.M.; Singh, D.P.; Vertrees, A.E. Doing More: Trends in Breast Cancer Surgery, 2005 to 2011. Am. Surg. 2015, 81, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.M.; Freedman, R.A.; Sagara, Y.; Aydogan, F.; Barry, W.T.; Golshan, M. Growing Use of Contralateral Prophylactic Mastectomy Despite no Improvement in Long-term Survival for Invasive Breast Cancer. Ann. Surg. 2017, 265, 581–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, E.S.; Pusic, A.L.; Waljee, J.F.; Kuhn, L.; Hawley, S.T.; Wilkins, E.; Alderman, A.K. Patient-Reported Aesthetic Satisfaction with Breast Reconstruction during the Long-Term Survivorship Perio. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 124, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toyserkani, N.M.; Jørgensen, M.G.; Tabatabaeifar, S.; Damsgaard, T.; Sørensen, J.A. Autologous versus implant-based breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of Breast-Q patient-reported outcomes. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2020, 73, 278–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santosa, K.; Qi, J.; Kim, H.M.; Hamill, J.B.; Wilkins, E.G.; Pusic, A.L. Long-term Patient-Reported Outcomes in Postmastectomy Breast Reconstruction. JAMA Surg. 2018, 153, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miseré, R.M.; van Kuijk, S.M.; Claassens, E.L.; Heuts, E.M.; Piatkowski, A.A.; van der Hulst, R.R. Breast-related and body-related quality of life following autologous breast reconstruction is superior to implant-based breast reconstruction—A long-term follow-up study. Breast 2021, 59, 176–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Treece, P. Deep Inferior Epigastric Perforator Flap for Breast Reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1994, 32, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Granzow, J.W.; Levine, J.L.; Chiu, E.S.; Allen, R.J. Breast reconstruction with the deep inferior epigastric perforator flap: History and an update on current technique. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2006, 59, 571–579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Haddock, N.; Ahn, C.Y.; Sadeghi, A. Breast Reconstruction with the Profunda Artery Perforator Flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2012, 129, 16e–23e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jo, T.; Jeon, D.N.; Han, H.H. The PAP Flap Breast Reconstruction: A Practical Option for Slim Patients. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2021, 38, 027–033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everaars, K.E.; Tjin, E.P.; de Laat, E.H.; Arends, C.R.; Hummelink, S.; Ulrich, D.J. Breast and abdominal scarring after DIEP flap breast reconstruction: An exploration of patient-reported scar quality. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2022, 75, 1805–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, Z.-H.; Chu, C.K.; Asaad, M.; Liu, J.; Selber, J.C.; Butler, C.E.; Largo, R.D. Comparing Donor Site Morbidity for Autologous Breast Reconstruction: Thigh vs. Abdomen. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddock, N.T.; Dickey, R.M.; Perez, K.; Garza, R.; Liu, Y.; Teotia, S.S. BREAST-Q and Donor Site Comparison in Bilateral Stacked Autologous Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murphy, D.C.; Figus, A.; Stocco, C.; Razzano, S. A comparison of patient reported outcome measures in patients who received both DIEP flap and PAP flap breast reconstructions. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2019, 72, 685–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van De Kar, A.L.; Corion, L.U.M.; Smeulders, M.J.C.; Draaijers, L.J.; Van Der Horst, C.M.A.M.; van Zuijlen, P. Reliable and Feasible Evaluation of Linear Scars by the Patient and Observer Scar Assessment Scale. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2005, 116, 514–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duraes, E.F.R.; Durand, P.; Morisada, M.; Scomacao, I.; Duraes, L.C.; de Sousa, J.B.; Abedi, N.; Djohan, R.S.; Bernard, S.; Moreira, A.; et al. A Novel Validated Breast Aesthetic Scale. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2022, 149, 1297–1308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morandi, E.M.; Winkelmann, S.; Pülzl, P.; Augustin, A.; Wachter, T.; Bauer, T.; Egle, D.; Brunner, C.; Wolfram, D. Long-Term Outcome Analysis and Technical Refinements after Autologous Breast Reconstruction with PAP Flap: What We Have Learnt. Breast Care 2022, 17, 450–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavien, P.A.; Barkun, J.; de Oliveira, M.L.; Vauthey, J.N.; Dindo, D.; Schulick, R.D.; de Santibañes, E.; Pekolj, J.; Slankamenac, K.; Bassi, C.; et al. The Clavien-Dindo Classification of Surgical Complications: Five-year experience. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ilonzo, N.; Tsang, A.; Tsantes, S.; Estabrook, A.; Ma, A.M.T. Breast reconstruction after mastectomy: A ten-year analysis of trends and immediate postoperative outcomes. Breast 2017, 32, 7–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Healy, C. The Evolution of Perforator Flap Breast Reconstruction: Twenty Years after the First DIEP Flap. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2013, 30, 121–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haddock, N.T.; Teotia, S.S. Consecutive 265 Profunda Artery Perforator Flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2020, 8, e2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jo, T.; Kim, E.K.; Eom, J.S.; Han, H.H. Comparison of transverse upper gracilis and profunda femoris artery perforator flaps for breast reconstruction: A systematic review. Microsurgery 2020, 40, 916–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augustin, A.; Pülzl, P.; Morandi, E.M.; Winkelmann, S.; Schoberleitner, I.; Brunner, C.; Ritter, M.; Bauer, T.; Wachter, T.; Wolfram, D. Donor-Site Morbidity and Quality of Life after Autologous Breast Reconstruction with PAP versus TMG Flap. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 5682–5697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Espinosa-De-Los-Monteros, A.; Frias-Frias, R.; Alvarez-Tostado-Rivera, A.; Caralampio-Castro, A.; Llanes, S.; Saldivar, A. Postoperative Abdominal Bulge and Hernia Rates in Patients Undergoing Abdominally Based Autologous Breast Reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2020, 86, 476–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, P.B.; Salavati, S.; Feng, L.; Butler, C.E. Abdominal Donor-Site Outcomes for Medial versus Lateral Deep Inferior Epigastric Artery Branch Perforator Harvest. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2011, 127, 2198–2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grünherz, L.; Keijzer, W.; Uyulmaz, S.; Fertsch, S.; Imhof, L.; Käser, S.; Farhadi, J.; Lindenblatt, N. Donor site aesthetics and morbidity after DIEP flap breast reconstruction—A retrospective multicenter study. Breast J. 2020, 26, 1980–1986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, D.P.; Plonczak, A.M.; Reissis, D.; Henry, F.P.; Hunter, J.E.; Wood, S.H.; Jallali, N. Factors that predict deep inferior epigastric perforator flap donor site hernia and bulge. J. Plast. Surg. Hand Surg. 2018, 52, 338–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddock, N.T.; Culver, A.J.; Teotia, S.S. Abdominal weakness, bulge, or hernia after DIEP flaps: An algorithm of management, prevention, and surgical repair with classification. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthetic Surg. 2020, 74, 2194–2201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.C.; Bajaj, A.; Chang, D.W.; Chevray, P. Comparison of Donor-Site Morbidity of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing TRAM Flaps for Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selber, J.C.; Fosnot, J.; Nelson, J.; Goldstein, J.; Bergey, M.; Sonnad, S.; Serletti, J.M. A Prospective Study Comparing the Functional Impact of SIEA, DIEP, and Muscle-Sparing Free TRAM Flaps on the Abdominal Wall: Part II. Bilateral Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 126, 1438–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindenblatt, N.; Gruenherz, L.; Farhadi, J. A systematic review of donor site aesthetic and complications after deep inferior epigastric perforator flap breast reconstruction. Gland. Surg. 2019, 8, 389–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ferreira, L.N.; Pereira, L.N.; Brás, M.D.F.; Ilchuk, K. Quality of life under the COVID-19 quarantine. Qual. Life Res. 2021, 30, 1389–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegwart, L.C.; Sieber, L.; Fischer, S.; Diehm, Y.; Hirche, C.; Kneser, U.; Kotsougiani-Fischer, D. The Use of Semi-Absorbable Mesh and its Impact on Donor-Site Morbidity and Patient-Reported Outcomes in DIEP Flap Breast Reconstruction. Aesthetic Plast. Surg. 2021, 45, 907–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, A.Y.; Momeni, A. Abdominal Flap-based Breast Reconstruction versus Abdominoplasty. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2020, 8, e3112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Characteristic | DIEP | PAP | p-Value | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Mean | (±std) | Mean | (±std) | ||
| Age (years) * | 41.3 | (±6.7) | 43.6 | (±7.4) | 0.3660 |
| Follow-up (months) * | 69.8 | (±34.7) | 34.0 | (±15.8) | 0.0005 |
| BMI (kg/m2) * | 25.3 | (±3.7) | 21.6 | (±2.3) | 0.0010 |
| Flap volume (cc) † | 565.2 | (±207.4) | 327.7 | (±108.2) | <0.0001 |
| Mastectomy volume (cc) † | 519.1 | (±167.3) | 274.8 | (±132.8) | <0.0001 |
| Postoperative hospital stay (days) | 9.6 | (±2.9) | 10.8 | (±4.4) | 0.3675 |
| n | (%) | n | (%) | ||
| Active smoker * | 4 | (22.2) | 1 | (5.6) | 0.3377 |
| Time of reconstruction † | 0.0515 | ||||
| Primary | 28 | (100) | 23 | (85.2) | |
| Secondary | 0 | (0.0) | 4 | (14.8) | |
| Indication for mastectomy † | 0.4182 | ||||
| Breast cancer | 14 | (50.0) | 17 | (63.0) | |
| Nonmalignant | 14 | (50.0) | 10 | (37.0) | |
| Prophylactic | 12 | (42.9) | 9 | (33.3) | |
| Mastitis | 2 | (7.1) | 1 | (3.7) | |
| Positive genetic testing * | 4 | (22.2) | 4 | (22.2) | >0.99 |
| Radiotherapy * | >0.99 | ||||
| Yes | 9 | (50.0) | 10 | (55.6) | |
| Previous radiotherapy | 1 | (5.6) | 3 | (16.7) | |
| Adjuvant | 8 | (44.4) | 7 | (38.9) | |
| No | 9 | (50.0) | 8 | (44.4) | |
| Chemotherapy * | |||||
| Yes | 12 | (66.7) | 11 | (61.1) | >0.99 |
| Previous chemotherapy | 9 | (50.0) | 7 | (38.9) | |
| Adjuvant | 3 | (16.7) | 4 | (22.2) | |
| No | 6 | (33.3) | 7 | (38.9) | |
| Characteristic | DIEP n | (%) * | PAP n | (%) † | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complications breast | 4 | (14.3) | 6 | (22.2) | 0.5027 |
| Complications at donor site | 1 | (5.5) x | 8 | (29.6) | 0.0479 |
| Secondary corrections breast | 5 | (18.5) ≈ | 9 | (34.6) ~ | 0.2238 |
| Secondary corrections donor site | 5 | (27.8) x | 3 | (11.1) | 0.2351 |
| POSAS Score | DIEP | PAP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Patient Scale | Mean | (±std) | Mean | (±std) | p-Value |
| Has the scar been painful for the past few weeks? | 1.33 | (±1.15) | 1.93 | (±1.88) | 0.2498 |
| Has the scar been itching for the past few weeks? | 2.39 | (±1.77) | 1.26 | (±0.84) | 0.0076 |
| Is the scar color different from the color of your normal skin? | 4.00 | (±1.83) | 4.52 | (±2.44) | 0.4556 |
| Is the stiffness of the scar different from your normal skin? | 4.06 | (±2.55) | 4.52 | (±2.56) | 0.5635 |
| Is the thickness of the scar different from your normal skin? | 3.94 | (±2.63) | 4.19 | (±2.40) | 0.7585 |
| Is the scar more irregular than your normal skin? | 4.00 | (±2.67) | 4.37 | (±2.74) | 0.6627 |
| Total score | 19.72 | (±8.50) | 20.78 | (±9.94) | 0.7198 |
| Overall opinion | 3.67 | (±2.08) | 4.72 | (±2.41) | 0.1453 |
| Observer scale | |||||
| Vascularity | 2.39 | (±1.64) | 2.42 | (±1.11) | 0.9495 |
| Pigmentation | 3.11 | (±1.63) | 3.80 | (±1.72) | 0.2032 |
| Thickness | 2.33 | (±1.49) | 3.08 | (±1.09) | 0.0714 |
| Relief | 2.28 | (±1.52) | 3.40 | (±1.41) | 0.0196 |
| Pliability | 3.00 | (±1.70) | 2.36 | (±0.79) | 0.1150 |
| Surface area | 2.89 | (±1.97) | 3.12 | (±1.39) | 0.6623 |
| Total score | 15.16 | (±9.30) | 18.08 | (±6.32) | 0.2329 |
| Overall opinion | 2.72 | (±1.41) | 3.16 | (±1.29) | 0.3074 |
| Questions | DIEP | PAP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Breast | mean | (±std) | Mean | (±std) | p-Value |
| Breast symmetry | 3.22 | (±0.92) | 3.21 | (±1.14) | 0.9733 |
| Breast position | 3.66 | (±0.75) | 3.67 | (±1.01) | 0.9496 |
| Inframammary fold | 3.82 | (±0.8) | 3.68 | (±0.98) | 0.5954 |
| Volume | 3.58 | (±0.75) | 3.51 | (±1.09) | 0.7995 |
| Shape and contour | 3.21 | (±1.03) | 3.11 | (±1.12) | 0.7297 |
| Scar | |||||
| Appearance | 4.22 | (±0.65) | 3.99 | (±0.67) | 0.2183 |
| Nipple-Areola Complex | |||||
| Nipple symmetry | 3.57 | (±0.91) | 3.46 | (±1.06) | 0.7416 |
| Nipple position | 3.57 | (±0.82) | 3.65 | (±0.91) | 0.7484 |
| Overall Appearance | 3.58 | (±0.93) | 3.38 | (±1.02) | 0.4907 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Augustin, A.; Morandi, E.M.; Winkelmann, S.; Schoberleitner, I.; Egle, D.; Ritter, M.; Bauer, T.; Wachter, T.; Wolfram, D. Long-Term Results after Autologous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP versus PAP Flaps Based on Quality of Life and Aesthetic Outcome Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030737
Augustin A, Morandi EM, Winkelmann S, Schoberleitner I, Egle D, Ritter M, Bauer T, Wachter T, Wolfram D. Long-Term Results after Autologous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP versus PAP Flaps Based on Quality of Life and Aesthetic Outcome Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):737. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030737
Chicago/Turabian StyleAugustin, Angela, Evi M. Morandi, Selina Winkelmann, Ines Schoberleitner, Daniel Egle, Magdalena Ritter, Thomas Bauer, Tanja Wachter, and Dolores Wolfram. 2023. "Long-Term Results after Autologous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP versus PAP Flaps Based on Quality of Life and Aesthetic Outcome Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030737
APA StyleAugustin, A., Morandi, E. M., Winkelmann, S., Schoberleitner, I., Egle, D., Ritter, M., Bauer, T., Wachter, T., & Wolfram, D. (2023). Long-Term Results after Autologous Breast Reconstruction with DIEP versus PAP Flaps Based on Quality of Life and Aesthetic Outcome Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 737. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12030737








