Actigraphic Sensors Describe Stroke Severity in the Acute Phase: Implementing Multi-Parametric Monitoring in Stroke Unit
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Actigraphy
2.3. Statistics
3. Results
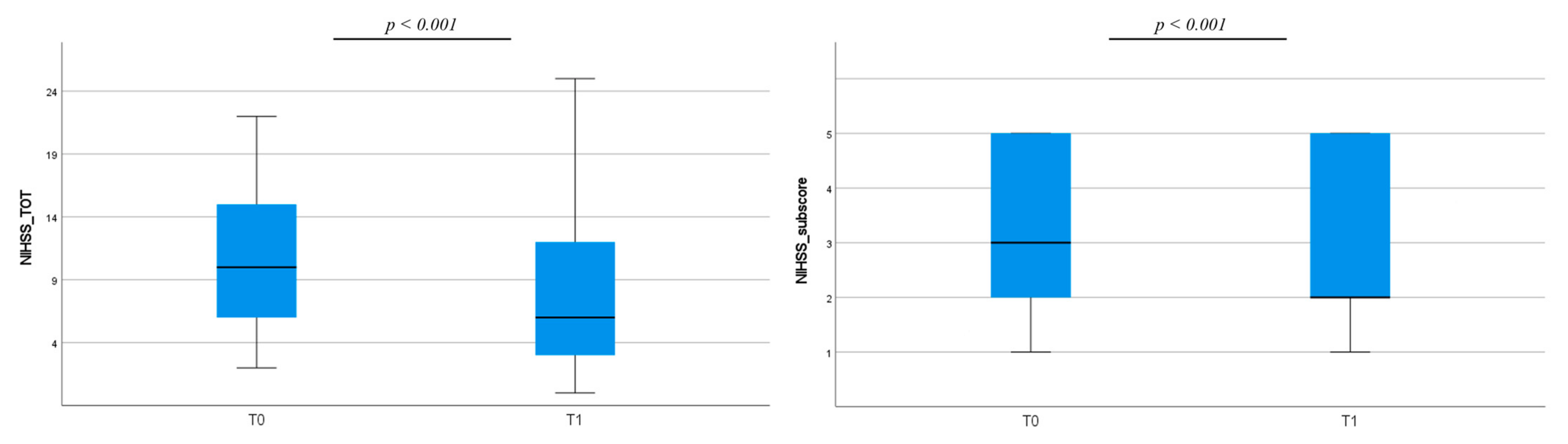
3.1. Clinical Assessment
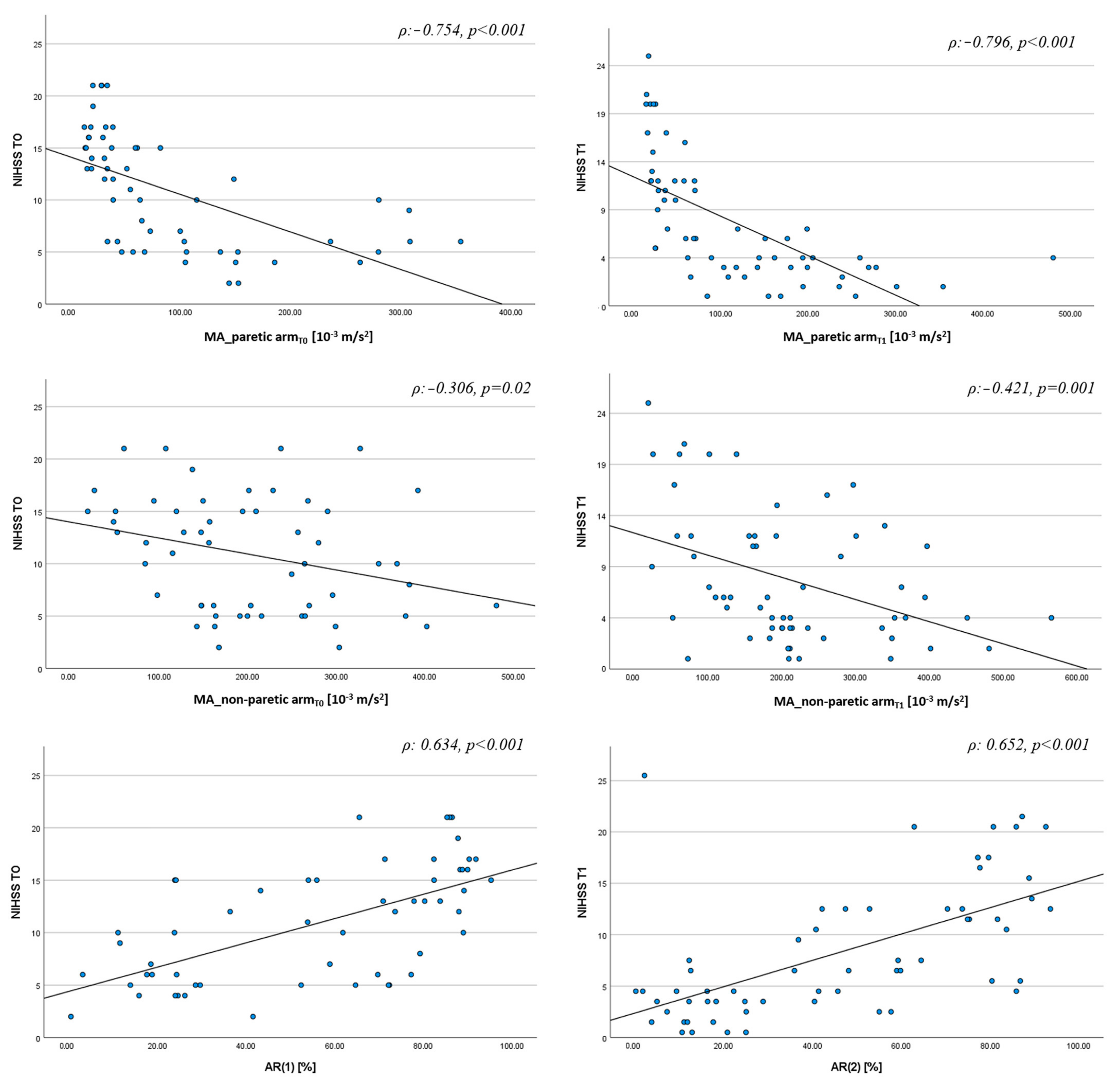
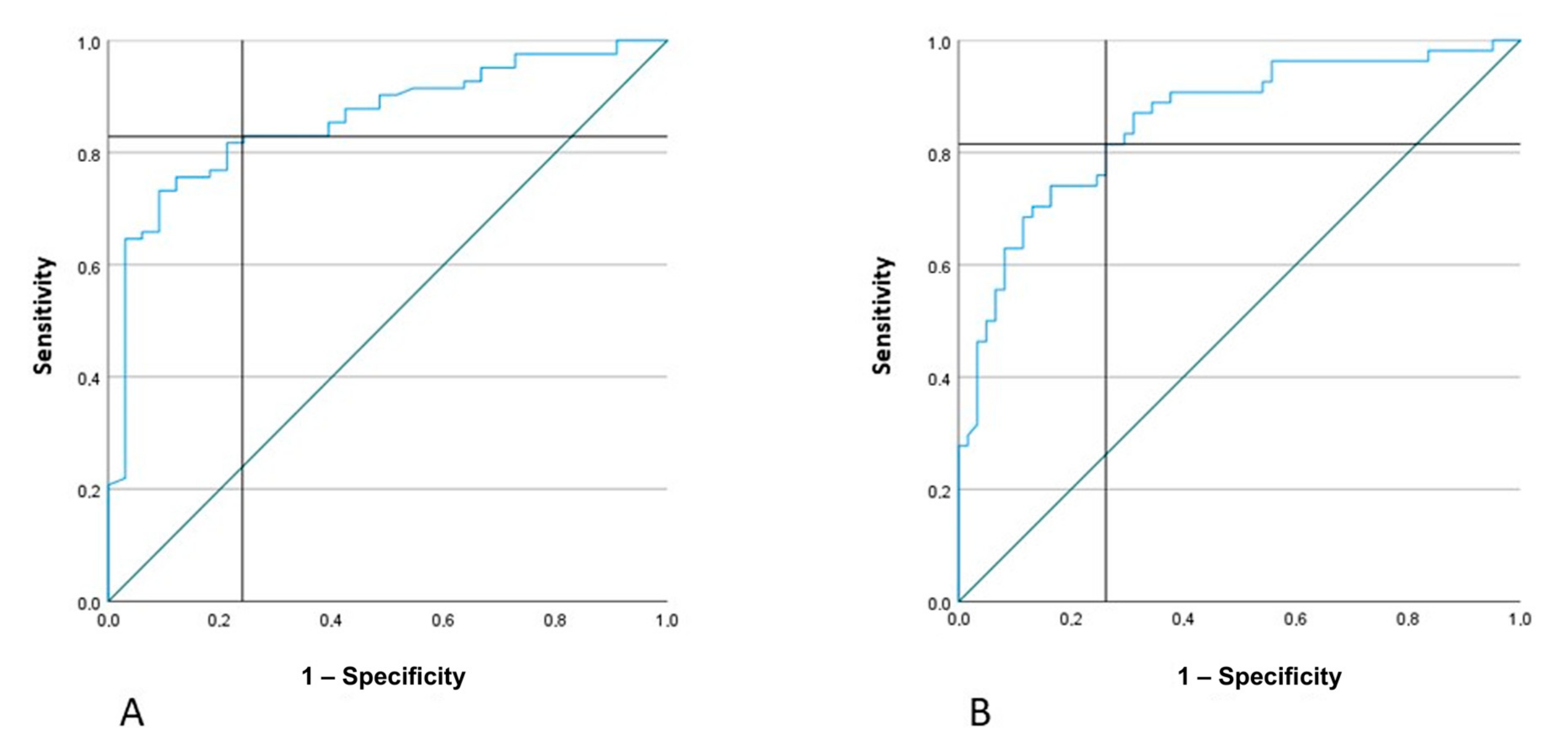
3.2. Actigraphic Assessment
- if AR < 27% and MA of the non-paretic arm <130, the patient has NIHSS ≥ 5
- if AR < 27% and MA of the non-paretic arm >130, the patient has NIHSS < 5
- if AR > 27%, regardless of MA value, the patient has NIHSS ≥ 5
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Katan, M.; Luft, A. Global Burden of Stroke. Semin. Neurol. 2018, 38, 208–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendelson, S.J.; Prabhakaran, S. Diagnosis and Management of Transient Ischemic Attack and Acute Ischemic Stroke: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 1088–1098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dimyan, M.A.; Cohen, L.G. Neuroplasticity in the context of motor rehabilitation after stroke. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2011, 7, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adams, H.P., Jr.; Davis, P.H.; Leira, E.C.; Chang, K.C.; Bendixen, B.H.; Clarke, W.R.; Woolson, R.F.; Hansen, M.D. Baseline NIH Stroke Scale score strongly predicts outcome after stroke: A report of the Trial of Org 10172 in Acute Stroke Treatment (TOAST). Neurology 1999, 53, 126–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamal, J.M.; Grotta, J.C. National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale as an Outcome Measure for Acute Stroke Trials. Stroke 2021, 52, 142–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reale, G.; Giovannini, S.; Iacovelli, C.; Castiglia, S.F.; Picerno, P.; Zauli, A.; Rabuffetti, M.; Ferrarin, M.; Maccauro, G.; Caliandro, P. Actigraphic Measurement of the Upper Limbs for the Prediction of Ischemic Stroke Prognosis: An Observational Study. Sensors 2021, 21, 2479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rabuffetti, M.; Meriggi, P.; Pagliari, C.; Bartolomeo, P.; Ferrarin, M. Differential actigraphy for monitoring asymmetry in upper limb motor activities. Physiol. Meas. 2016, 37, 1798–1812. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iacovelli, C.; Caliandro, P.; Rabuffetti, M.; Padua, L.; Simbolotti, C.; Reale, G.; Ferrarin, M.; Rossini, P.M. Actigraphic measurement of the upper limbs movements in acute stroke patients. J. Neuroeng. Rehabil. 2019, 16, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toba, M.N.; Pagliari, C.; Rabuffetti, M.; Nighoghossian, N.; Rode, G.; Cotton, F.; Spinazzola, L.; Baglio, F.; Migliaccio, R.; Bartolomeo, P. Quantitative Assessment of Motor Neglect. Stroke 2021, 52, 1618–1627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wahlgren, N.; Ahmed, N.; Dávalos, A.; Ford, G.A.; Grond, M.; Hacke, W.; Hennerici, M.G.; Kaste, M.; Kuelkens, S.; Larrue, V.; et al. Thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke in the Safe Implementation of Thrombolysis in Stroke-Monitoring Study (SITS-MOST): An observational study. Lancet 2007, 369, 275–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Emberson, J.; Lees, K.R.; Lyden, P.; Blackwell, L.; Albers, G.; Bluhmki, E.; Brott, T.; Cohen, G.; Davis, S.; Donnan, G.; et al. Effect of treatment delay, age, and stroke severity on the effects of intravenous thrombolysis with alteplase for acute ischaemic stroke: A meta-analysis of individual patient data from randomised trials. Lancet 2014, 384, 1929–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Quirós, M.B.; Douma, E.H.; van den Akker-Scheek, I.; Lamoth, C.J.C.; Maurits, N.M. Quantification of Movement in Stroke Patients under Free Living Conditions Using Wearable Sensors: A Systematic Review. Sensors 2022, 22, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gubbi, J.; Rao, A.S.; Fang, K.; Yan, B.; Palaniswami, M. Motor recovery monitoring using acceleration measurements in post acute stroke patients. Biomed. Eng. Online 2013, 12, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falck, R.S.; Best, J.R.; Li, M.C.R.; Eng, J.J.; Liu-Ambrose, T. Revisiting the MotionWatch8©: Calibrating Cut-Points for Measuring Physical Activity and Sedentary Behavior Among Adults with Stroke. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2019, 11, 203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bochniewicz, E.M.; Emmer, G.; McLeod, A.; Barth, J.; Dromerick, A.W.; Lum, P. Measuring Functional Arm Movement after Stroke Using a Single Wrist-Worn Sensor and Machine Learning. J. Stroke Cerebrovasc. Dis. 2017, 26, 2880–2887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katzan, I.; Schuster, A.; Kinzy, T. Physical Activity Monitoring Using a Fitbit Device in Ischemic Stroke Patients: Prospective Cohort Feasibility Study. JMIR Mhealth Uhealth 2021, 9, e14494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Clinical Data | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Risk factors | |
| Atrial Fibrillation | 21 (32.8%) |
| Arterial Hypertension | 40 (62.5%) |
| Dyslipidemia | 19 (29.7) |
| Smoke | 12 (18.7%) |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 8 (12.5%) |
| Clinical features | |
| Left Hemisphere | 31 (48.4%) |
| NIHSS < 5 at T0 NIHSS 5–9 at T0 NIHSS ≥ 10 at T0 | 6 (9.3%) 21 (32.8%) 37 (57.8%) |
| NIHSS < 5 at T1 NIHSS 5–9 at T1 NIHSS ≥ 10 at T1 | 27 (44%) 12 (20%) 22 (36%) |
| Reperfusion therapies Thrombolysis Mechanical thrombectomy Thrombolysis and Mechanical thrombectomy Ischemic lesion | 10 (16%) 9 (14%) 6 (10%) |
| Superficial | 17 (26.5%) |
| Deep | 20 (31.2%) |
| Superficial and Deep | 27 (42.2%) |
| Etiology (TOAST) | |
| Large artery atherosclerosis | 11 (17.2%) |
| Small vessel disease | 16 (25%) |
| Cardioembolic | 15 (23.4%) |
| Other causes | 4 (6.2%) |
| Undetermined | 18 (28.1%) |
| Variables | NIHSS T0 | NIHSS T1 | NIHSS T0/T1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| AR | 0.616 (<0.001) | 0.312 (0.023) | 0.603 (<0.001) |
| MA_non-paretic arm | −0.285 (0.007) | ---- | −0.314 (<0.001) |
| MA_paretic arm | ---- | −0.431 (0.002) | ---- |
| R2 F | 0.446 22.76 | 0.450 25.10 | 0.482 54.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Reale, G.; Iacovelli, C.; Rabuffetti, M.; Manganotti, P.; Marinelli, L.; Sacco, S.; Furlanis, G.; Ajčević, M.; Zauli, A.; Moci, M.; et al. Actigraphic Sensors Describe Stroke Severity in the Acute Phase: Implementing Multi-Parametric Monitoring in Stroke Unit. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031178
Reale G, Iacovelli C, Rabuffetti M, Manganotti P, Marinelli L, Sacco S, Furlanis G, Ajčević M, Zauli A, Moci M, et al. Actigraphic Sensors Describe Stroke Severity in the Acute Phase: Implementing Multi-Parametric Monitoring in Stroke Unit. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031178
Chicago/Turabian StyleReale, Giuseppe, Chiara Iacovelli, Marco Rabuffetti, Paolo Manganotti, Lucio Marinelli, Simona Sacco, Giovanni Furlanis, Miloš Ajčević, Aurelia Zauli, Marco Moci, and et al. 2023. "Actigraphic Sensors Describe Stroke Severity in the Acute Phase: Implementing Multi-Parametric Monitoring in Stroke Unit" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031178
APA StyleReale, G., Iacovelli, C., Rabuffetti, M., Manganotti, P., Marinelli, L., Sacco, S., Furlanis, G., Ajčević, M., Zauli, A., Moci, M., Giovannini, S., Crosetti, S., Grazzini, M., Castiglia, S. F., Podestà, M., Calabresi, P., Ferrarin, M., & Caliandro, P. (2023). Actigraphic Sensors Describe Stroke Severity in the Acute Phase: Implementing Multi-Parametric Monitoring in Stroke Unit. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 1178. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031178














