Sulodexide Develops Contraction in Human Saphenous Vein via Endothelium-Dependent Nitric Oxide Pathway
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
Calculations and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Carroll, B.J.; Piazza, G.; Goldhaber, S.Z. Sulodexide in Venous Disease. J. Thromb. Haemost. 2019, 17, 31–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afratis, N.; Gialeli, C.; Nikitovic, D.; Tsegenidis, T.; Karousou, E.; Theocharis, A.D.; Pavão, M.S.; Tzanakakis, G.N.; Karamanos, N.K. Glycosaminoglycans: Key Players in Cancer Cell Biology and Treatment. FEBS J. 2012, 279, 1177–1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Masola, V.; Zaza, G.; Onisto, M.; Lupo, A.; Gambaro, G. Glycosaminoglycans, Proteoglycans and Sulodexide and the Endothelium: Biological Roles and Pharmacological Effects. Int. Angiol. 2014, 33, 243–254. [Google Scholar]
- Veraldi, N.; Guerrini, M.; Urso, E.; Risi, G.; Bertini, S.; Bensi, D.; Bisio, A. Fine Structural Characterization of Sulodexide. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2018, 156, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvestro, L.; Lanzarotti, E.; Marchi, E.; Gori, M.; Pescador, R.; Ferro, L.; Milani, M.R.; da Col, R.; Coppini, A. Human Pharmacokinetics of Glycosaminoglycans Using Deuterium-Labeled and Unlabeled Substances: Evidence for Oral Absorption. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1994, 20, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coccheri, S.; Mannello, F. Development and Use of Sulodexide in Vascular Diseases: Implications for Treatment. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2013, 8, 49–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tollefsen, D.M. Vascular Dermatan Sulfate and Heparin Cofactor II. Prog. Mol. Biol. Transl. Sci. 2010, 93, 351–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofosu, F.A. Pharmacological Actions of Sulodexide. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1998, 24, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marchi, E.; Barbanti, M.; Milani, R.; Breccia, A.; Fini, A.; Gattavecchia, E. Organ Glycosaminoglycan Distribution after Intravenous and Oral Administration in Rats. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 1994, 20, 297–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Sun, D.; Song, J.W.; Zullo, J.; Lipphardt, M.; Coneh-Gould, L.; Goligorsky, M.S. Endothelial Cell Dysfunction and Glycocalyx—A Vicious Circle. Matrix Biol. 2018, 71, 421–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, R.D.; Shworak, N.W.; Liu, J.; Schwartz, J.J.; Zhang, L. Heparan Sulfate Proteoglycans of the Cardiovascular System. Specific Structures Emerge but How Is Synthesis Regulated? J. Clin. Investig. 1997, 99, 2062–2070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffetto, J.D.; Calanni, F.; Mattana, P.; Khalil, R.A. Sulodexide Promotes Arterial Relaxation via Endothelium-Dependent Nitric Oxide-Mediated Pathway. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2019, 166, 347–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffetto, J.D.; Yu, W.; Wang, X.; Calanni, F.; Mattana, P.; Khalil, R.A. Sulodexide Improves Contraction and Decreases Matrix Metalloproteinase-2 and -9 in Veins Under Prolonged Stretch. J. Cardiovasc. Pharmacol. 2020, 75, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palareti, G.; Legnani, C.; Antonucci, E.; Zorzi, S.; Bignamini, A.A.; Lodigiani, C.; Tosetto, A.; Bertù, L.; Pengo, V.; Testa, S.; et al. Design and Rationale of a Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Trial on the Efficacy and Safety of Sulodexide for Extended Treatment in Elderly Patients after a First Venous Thromboembolism. Intern. Emerg. Med. 2021, 16, 359–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elleuch, N.; Zidi, H.; Bellamine, Z.; Hamdane, A.; Guerchi, M.; Jellazi, N. Sulodexide in Patients with Chronic Venous Disease of the Lower Limbs: Clinical Efficacy and Impact on Quality of Life. Adv. Ther. 2016, 33, 1536–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, G.M.; Bignamini, A.A.; Davì, G.; Palareti, G.; Matuška, J.; Holý, M.; Pawlaczyk-Gabriel, K.; Džupina, A.; Sokurenko, G.Y.; Didenko, Y.P.; et al. Sulodexide for the Prevention of Recurrent Venous Thromboembolism: The Sulodexide in Secondary Prevention of Recurrent Deep Vein Thrombosis (SURVET) Study: A Multicenter, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial. Circulation 2015, 132, 1891–1897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobiaš, L.; Petrová, M.; Vojtko, R.; Uličná, O.; Vančová, O.; Kristová, V. Effect of Sulodexide on Vascular Responses and Liver Mitochondrial Function in Diabetic Rats. Physiol. Res. 2015, 64, S497–S505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristová, V.; Líšková, S.; Sotníková, R.; Vojtko, R.; Kurtanský, A. Sulodexide Improves Endothelial Dysfunction in Streptozotocin-Induced Diabetes in Rats. Physiol. Res. 2008, 57, 491–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serra, R.; Gallelli, L.; Conti, A.; de Caridi, G.; Massara, M.; Spinelli, F.; Buffone, G.; Caliò, F.G.; Amato, B.; Ceglia, S.; et al. The Effects of Sulodexide on Both Clinical and Molecular Parameters in Patients with Mixed Arterial and Venous Ulcers of Lower Limbs. Drug Des. Dev. Ther. 2014, 8, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Liu, X.; Zhao, Z.; Ni, L.; Liu, C. Sulodexide Recovers Endothelial Function through Reconstructing Glycocalyx in the Balloon-Injury Rat Carotid Artery Model. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91350–91361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikdeli, B.; Chatterjee, S.; Kirtane, A.J.; Parikh, S.A.; Andreozzi, G.M.; Desai, N.R.; Francese, D.P.; Gibson, C.M.; Piazza, G.; Goldhaber, S.Z.; et al. Sulodexide versus Control and the Risk of Thrombotic and Hemorrhagic Events: Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2020, 46, 908–918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sosińska, P.; Baum, E.; Maćkowiak, B.; Maj, M.; Sumińska-Jasińska, K.; Staniszewski, R.; Brȩborowicz, A. Sulodexide Reduces the Proinflammatory Effect of Serum from Patients with Peripheral Artery Disease in Human Arterial Endothelial Cells. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 40, 1005–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianesini, S.; Obi, A.; Onida, S.; Baccellieri, D.; Bissacco, D.; Borsuk, D.; Campisi, C.; Campisi, C.C.; Cavezzi, A.; Chi, Y.; et al. Global Guidelines Trends and Controversies in Lower Limb Venous and Lymphatic Disease. Phlebol. J. Venous Dis. 2019, 34, 4–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tansey, E.A.; Montgomery, L.E.A.; Quinn, J.G.; Roe, S.M.; Johnson, C.D. Understanding Basic Vein Physiology and Venous Blood Pressure through Simple Physical Assessments. Adv. Physiol. Educ. 2019, 43, 423–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ligi, D.; Croce, L.; Mannello, F. Chronic Venous Disorders: The Dangerous, the Good, and the Diverse. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanth, A.M.; Khan, S.U.; Gasparis, A.; Labropoulos, N. The Distribution and Extent of Reflux and Obstruction in Patients with Active Venous Ulceration. Phlebology 2015, 30, 350–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, S.; Fisher, A.B. Mechanotransduction in the Endothelium: Role of Membrane Proteins and Reactive Oxygen Species in Sensing, Transduction, and Transmission of the Signal with Altered Blood Flow. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014, 20, 899–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreozzi, G.M. Role of Sulodexide in the Treatment of CVD. Int. Angiol. 2014, 33, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Raffetto, J.D.; Eberhardt, R.T.; Dean, S.M.; Ligi, D.; Mannello, F. Pharmacologic Treatment to Improve Venous Leg Ulcer Healing. J. Vasc. Surg. Venous Lymphat. Disord. 2016, 4, 371–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cospite, M.; Ferrara, F.; Cospite, V.; Palazzini, E. Sulodexide and the Microcirculatory Component in Microphlebopathies. Curr. Med. Res. Opin. 1992, 13, 56–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borawski, J.; Dubowski, M.; Pawlak, K.; Mysliwiec, M. Sulodexide Induces Hepatocyte Growth Factor Release in Humans. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2007, 558, 167–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luzzi, R.; Belcaro, G.; Dugall, M.; Hu, S.; Arpaia, G.; Ledda, A.; Ippolito, E.; Corsi, M.; Ricci, A.; Cotellese, R.; et al. The Efficacy of Sulodexide in the Prevention of Postthrombotic Syndrome. Clin. Appl. Thromb. Hemost. 2014, 20, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klinger, J.R.; Kadowitz, P.J. The Nitric Oxide Pathway in Pulmonary Vascular Disease. Am. J. Cardiol. 2017, 120, S71–S79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffetto, J.D.; Yu, P.; Reslan, O.M.; Xia, Y.; Khalil, R.A. Endothelium-Dependent Nitric Oxide and Hyperpolarization-Mediated Venous Relaxation Pathways in Rat Inferior Vena Cava. J. Vasc. Surg. 2012, 55, 1716–1725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Raffetto, J.D.; Qiao, X.; Koledova, V.V.; Khalil, R.A. Prolonged Increases in Vein Wall Tension Increase Matrix Metalloproteinases and Decrease Constriction in Rat Vena Cava: Potential Implications in Varicose Veins. J. Vasc. Surg. 2008, 48, 447–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lim, C.S.; Qiao, X.; Reslan, O.M.; Xia, Y.; Raffetto, J.D.; Paleolog, E.; Davies, A.H.; Khalil, R.A. Prolonged Mechanical Stretch Is Associated with Upregulation of Hypoxia-Inducible Factors and Reduced Contraction in Rat Inferior Vena Cava. J. Vasc. Surg. 2011, 53, 764–773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Urbanek, T.; Zbigniew, K.; Begier-Krasińska, B.; Baum, E.; Bręborowicz, A. Sulodexide Suppresses Inflammation in Patients with Chronic Venous Insufficiency. Int. Angiol. 2015, 34, 589–596. [Google Scholar]
- Raffetto, J.D.; Ross, R.L.; Khalil, R.A. Matrix Metalloproteinase 2-Induced Venous Dilation via Hyperpolarization and Activation of K+ Channels: Relevance to Varicose Vein Formation. J. Vasc. Surg. 2007, 45, 373–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raffetto, J.D.; Khalil, R.A. Matrix Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Vascular Remodeling and Vascular Disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2008, 75, 346–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Endothel | Patient | Sex | Age | Comorbidities | Smoke |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intact | Patient-1 | Male | 71 | DM, HT, HL | + |
| Patient-2 | Female | 52 | DM | − | |
| Patient-3 | Male | 68 | HT | − | |
| Patient-4 | Male | 71 | HT | + | |
| Patient-5 | Male | 57 | NONE | + | |
| Patient-6 | Male | 68 | DM, HT | + | |
| Patient-7 | Male | 50 | HT, HL | + | |
| Patient-8 | Male | 62 | DM, HT | + | |
| Denuded | Patient-1 | Male | 70 | DM, HT, HL, BPH | + |
| Patient-2 | Male | 46 | DM, HT | + | |
| Patient-3 | Female | 72 | DM, HT | − | |
| Patient-4 | Male | 62 | DM, HT | + | |
| Patient-5 | Male | 61 | DM, HT, RENAL FAILURE | − | |
| Patient-6 | Male | 56 | DM, HT, HL | + |
| Phenylephrine Stimulated Only | ||||||||
| Groups | Phenylephrine | Sulodexide | ||||||
| 6 × 10−7 | 0.001 mg/mL | 0.005 mg/mL | 0.01 mg/mL | 0.05 mg/mL | 0.1 mg/mL | 0.5 mg/mL | 1.0 mg/mL | |
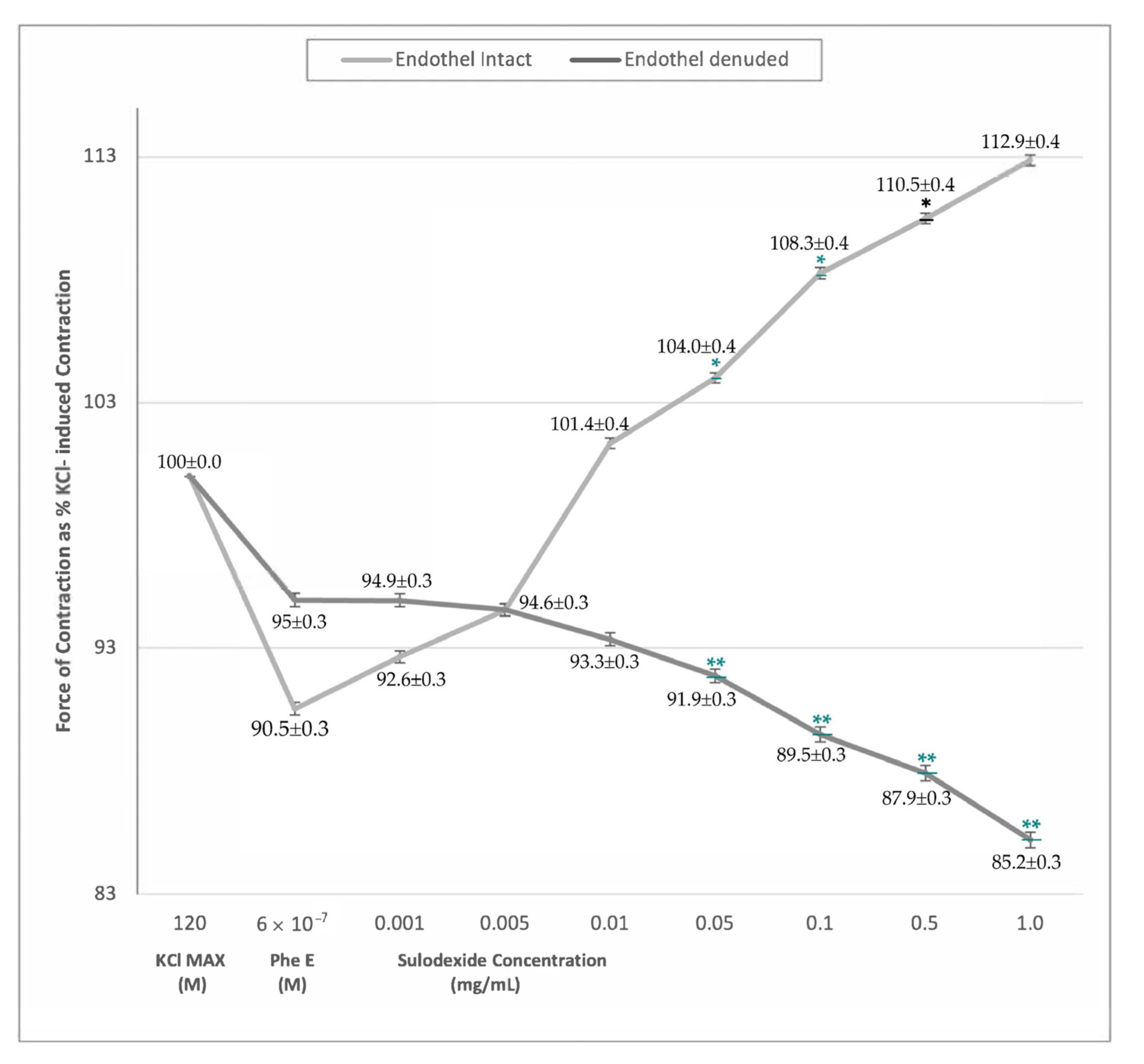
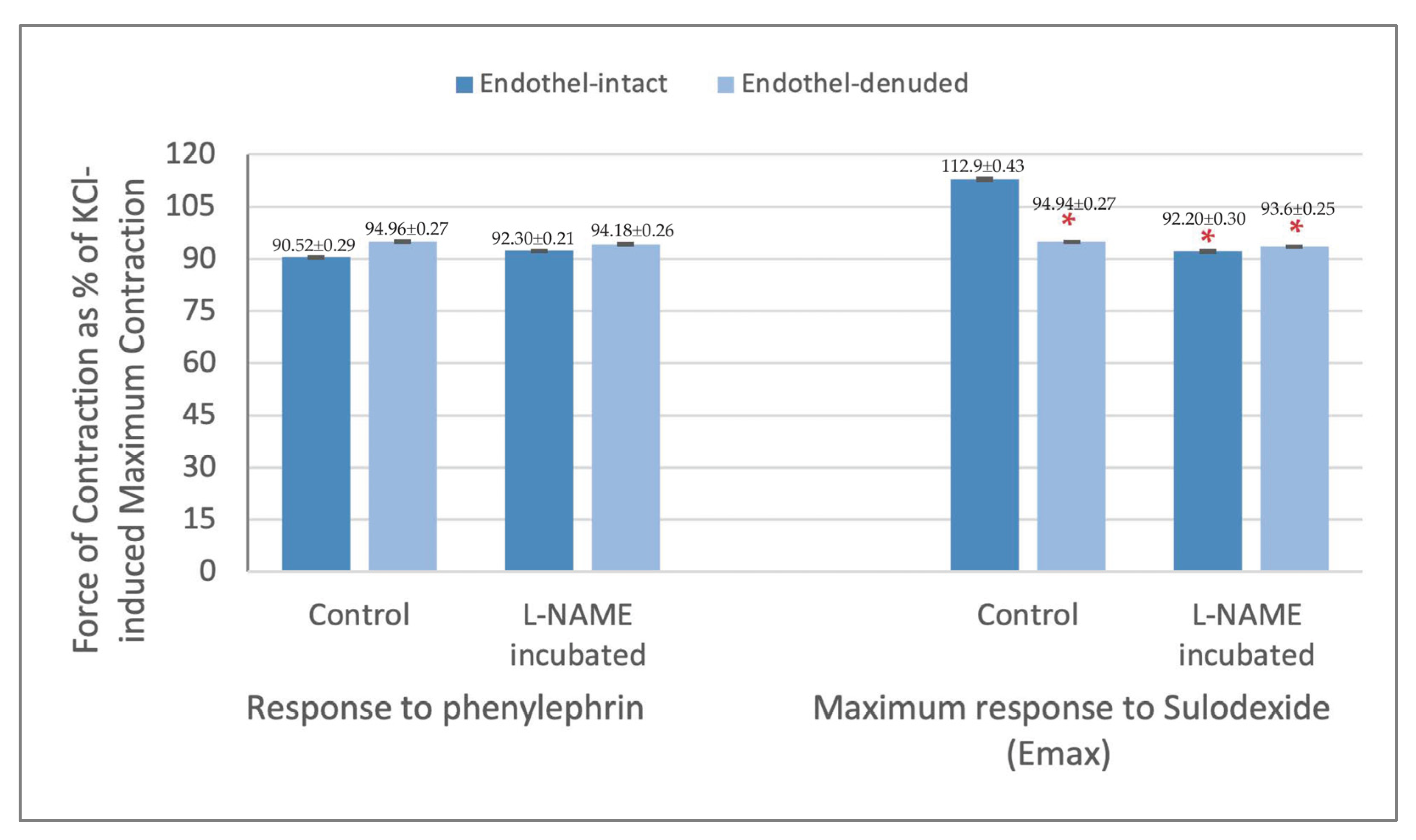
| Endothel-Intact (n = 8) | 90.5% ± 0.3 | 92.6% ± 0.3 | 94.6% ± 0.3 | 101.3% ± 0.4 | 104.0% ± 0.4 * | 108.3% ± 0.4 * | 110.5% ± 0.4 * | 112.9% ± 0.4 * |
| Endothel-Denuded (n = 6) | 95.0% ± 0.3 | 94.9% ± 0.3 | 94.6% ± 0.3 | 93.3% ± 0.3 | 91.9% ± 0.3 ** | 89.5% ± 0.3 ** | 87.9% ± 0.3 ** | 85.2% ± 0.3 ** |
| L-NAME Pre-incubated (10−4 M) | ||||||||
| Groups | Phenylephrine | Sulodexide | ||||||
| 6 × 10−7 | 0.001 mg/mL | 0.005 mg/mL | 0.01 mg/mL | 0.05 mg/mL | 0.1 mg/mL | 0.5 mg/mL | 1.0 mg/mL | |
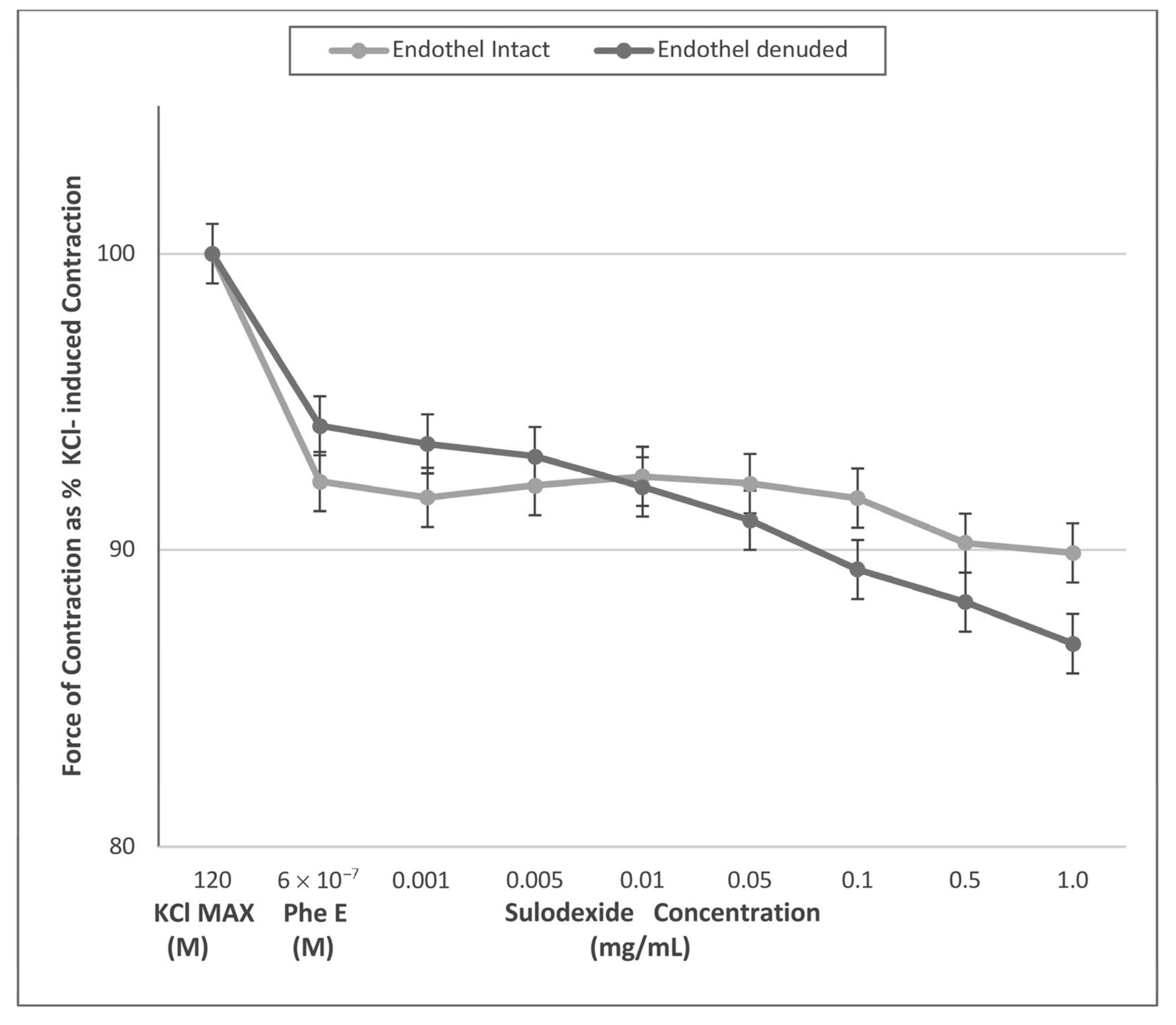
| Endothel-Intact (n = 8) | 92.3% ± 0.2 | 91.8% ± 0.3 | 92.2% ± 0.3 | 92.5% ± 0.3 | 92.2% ± 0.3 | 91.7% ± 0.3 | 90.2% ± 0.4 | 89.9% ± 0.3 |
| Endothel-Denuded (n = 6) | 94.2% ± 0.3 | 93.6% ± 0.3 | 93.1% ± 0.2 | 92.1% ± 0.2 | 91.0% ± 0.2 | 89.3% ± 0.2 | 88.2% ± 0.2 | 86.8% ± 0.2 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Doganci, S.; Ince, M.E.; Demeli, M.; Ors Yildirim, N.; Pehlivanoglu, B.; Yildirim, A.K.; Gianesini, S.; Chi, Y.-W.; Yildirim, V. Sulodexide Develops Contraction in Human Saphenous Vein via Endothelium-Dependent Nitric Oxide Pathway. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031019
Doganci S, Ince ME, Demeli M, Ors Yildirim N, Pehlivanoglu B, Yildirim AK, Gianesini S, Chi Y-W, Yildirim V. Sulodexide Develops Contraction in Human Saphenous Vein via Endothelium-Dependent Nitric Oxide Pathway. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031019
Chicago/Turabian StyleDoganci, Suat, Mehmet Emin Ince, Meric Demeli, Nadide Ors Yildirim, Bilge Pehlivanoglu, Alperen Kutay Yildirim, Sergio Gianesini, Yung-Wei Chi, and Vedat Yildirim. 2023. "Sulodexide Develops Contraction in Human Saphenous Vein via Endothelium-Dependent Nitric Oxide Pathway" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031019
APA StyleDoganci, S., Ince, M. E., Demeli, M., Ors Yildirim, N., Pehlivanoglu, B., Yildirim, A. K., Gianesini, S., Chi, Y.-W., & Yildirim, V. (2023). Sulodexide Develops Contraction in Human Saphenous Vein via Endothelium-Dependent Nitric Oxide Pathway. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 1019. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031019






