Detecting Macular Disease Based on Optical Coherence Tomography Using a Deep Convolutional Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
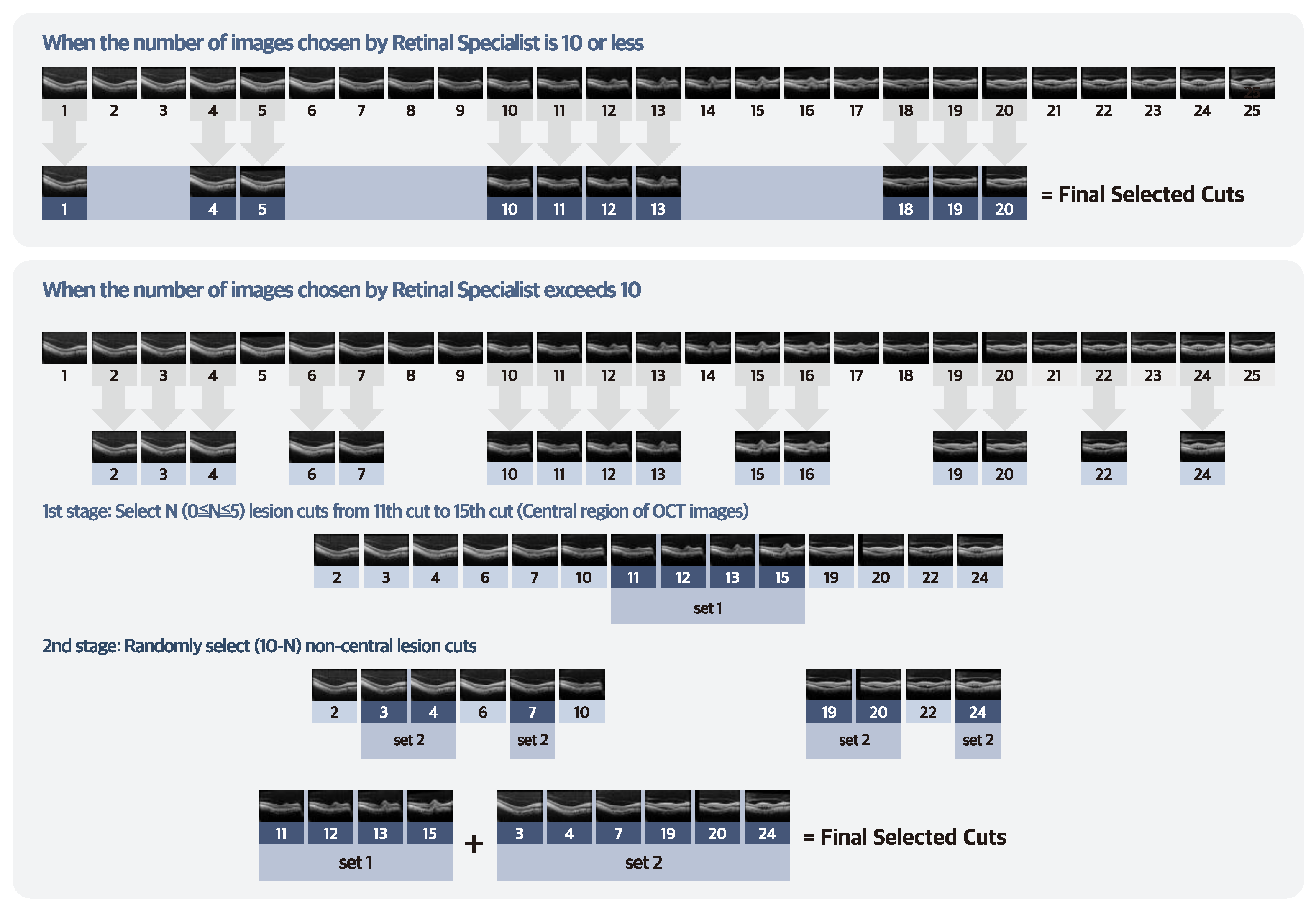
2.1. Data Collection and Labeling
2.2. SD–OCT Dataset Collection
2.3. Experimental Setup
2.4. Data Augmentation
2.5. Model Architecture
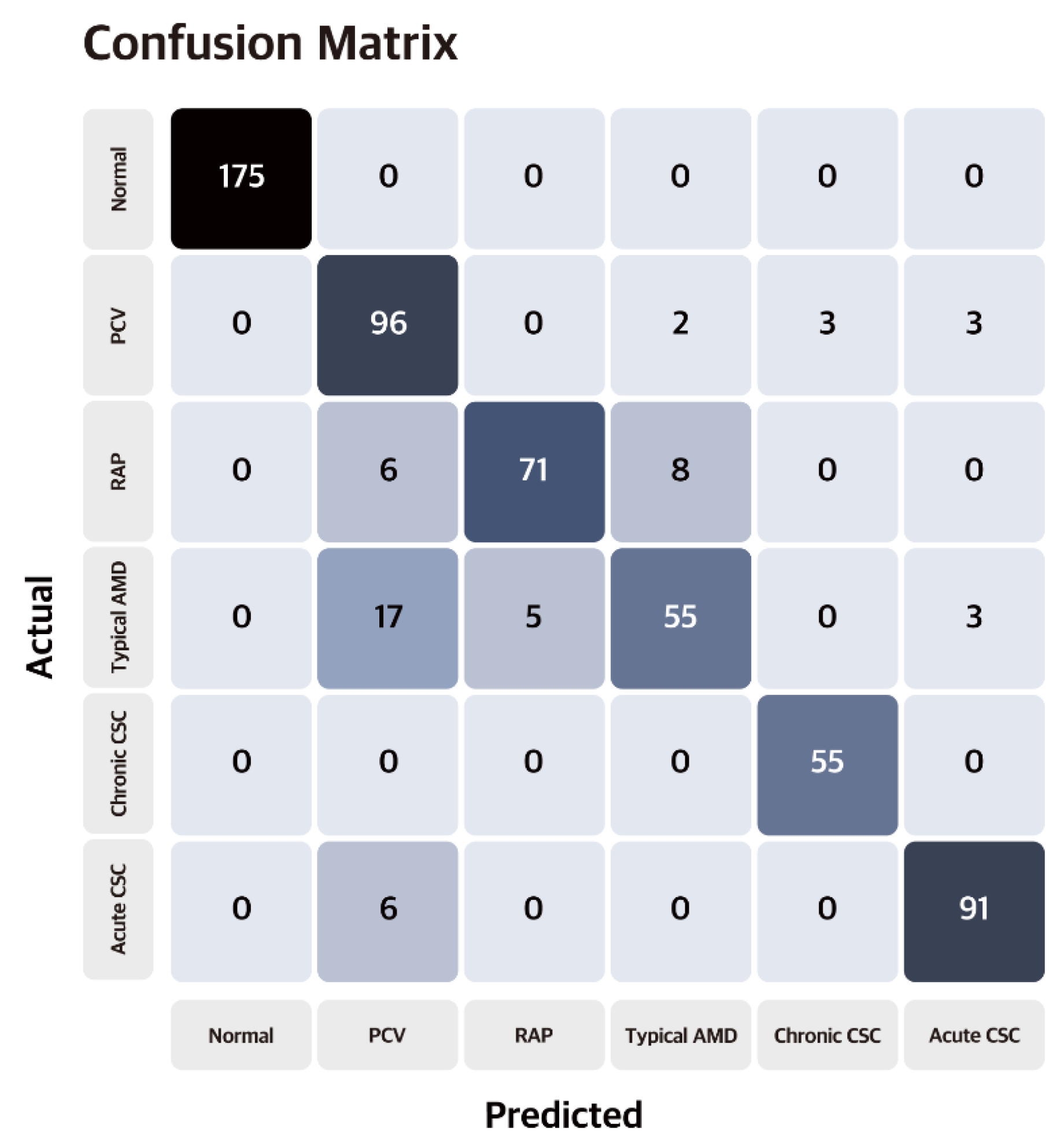
3. Results
3.1. Model Performance
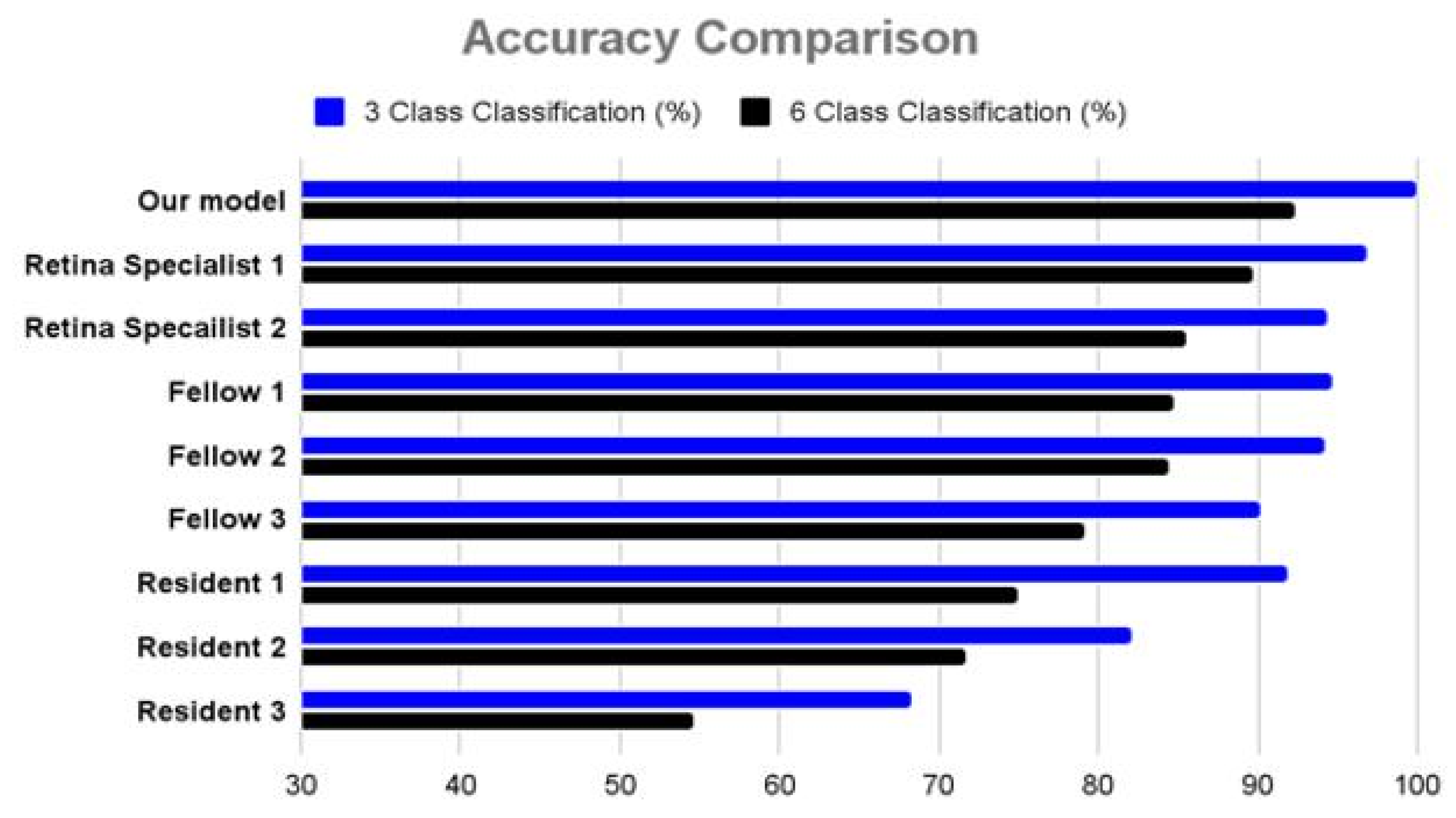
3.2. Comparison with Ophthalmologists
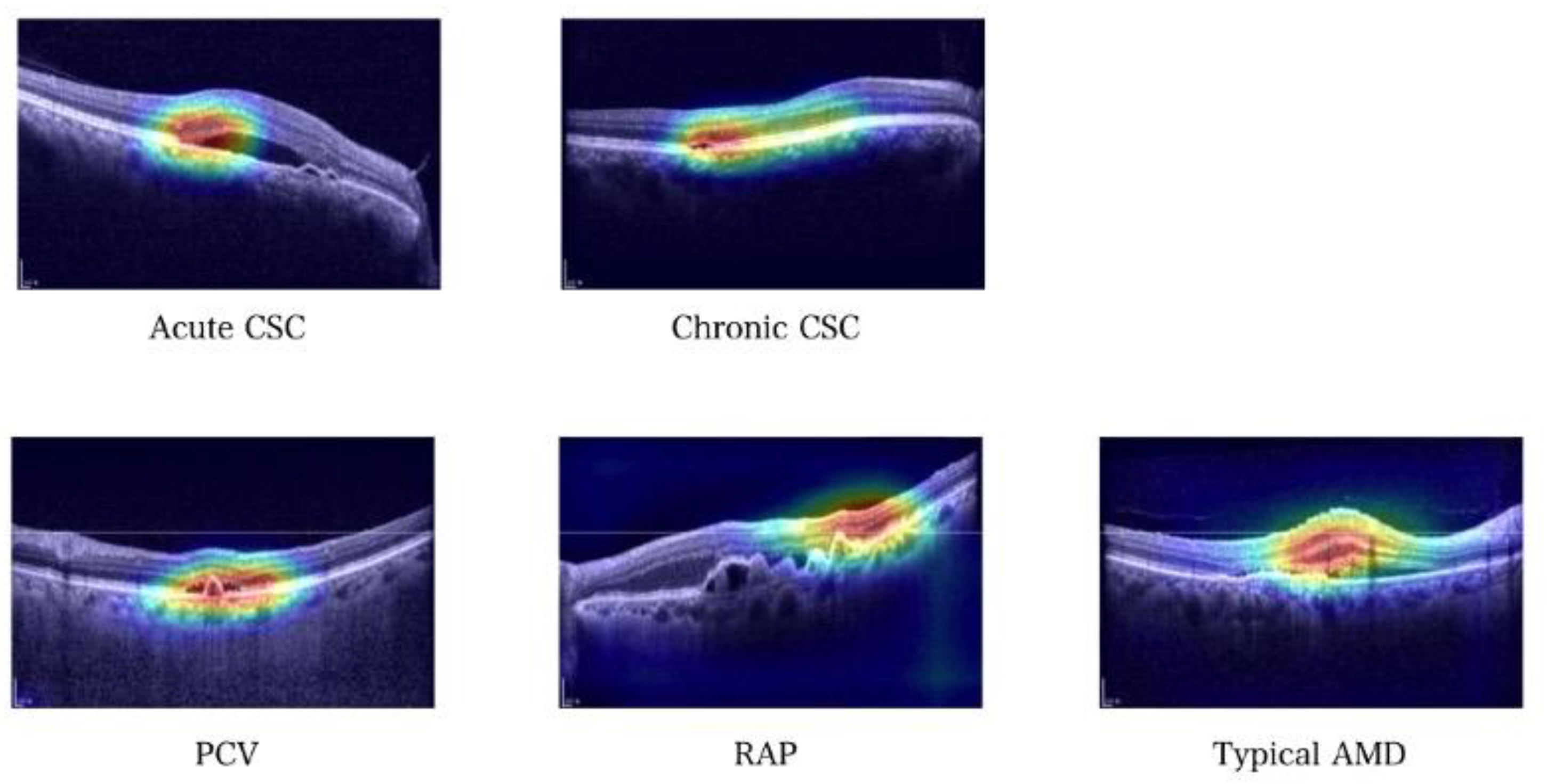
3.3. Gradient-Weighted Class Activation Mapping (Grad–CAM) Images
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wang, M.; Munch, I.C.; Hasler, P.W.; Prunte, C.; Larsen, M. Central serous chorioretinopathy. Acta Ophthalmol. 2008, 86, 126–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Congdon, N.; O’Colmain, B.; Klaver, C.C.; Klein, R.; Munoz, B.; Friedman, D.S.; Kempen, J.; Taylor, H.R.; Mitchell, P.; Eye Diseases Prevalence Research Group. Causes and prevalence of visual impairment among adults in the United States. Arch. Ophthalmol. 2004, 122, 477–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Chang, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Kim, C.G.; Lee, D.W. Age-related differences in the prevalence of subtypes of Neovascular age-related macular degeneration in the first diagnosed eye. Graefes Arch. Clin. Exp. Ophthalmol. 2019, 257, 891–898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manayath, G.J.; Ranjan, R.; Karandikar, S.S.; Shah, V.S.; Saravanan, V.R.; Narendran, V. Central serous chorioretinopathy: Current update on management. Oman J. Ophthalmol. 2018, 11, 200–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tittl, M.K.; Spaide, R.F.; Wong, D.; Pilotto, E.; Yannuzzi, L.A.; Fisher, Y.L.; Freund, B.; Guyer, D.R.; Slakter, J.S.; Sorenson, J.A. Systemic findings associated with central serous chorioretinopathy. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1999, 128, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, D.D.; Choi, S.; Ko, J.; Yoon, J.; Park, J.I.; Hwang, J.S.; Han, J.M.; Lee, H.J.; Sohn, J.; Park, K.H.; et al. Distinguishing retinal angiomatous proliferation from polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy with a deep neural network based on optical coherence tomography. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 9275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoon, J.; Han, J.; Park, J.I.; Hwang, J.S.; Han, J.M.; Sohn, J.; Park, K.H.; Hwang, D.D. Optical coherence tomography-based deep-learning model for detecting central serous chorioretinopathy. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, C.S.; Baughman, D.M.; Lee, A.Y. Deep learning is effective for the classification of OCT images of normal versus Age-related Macular Degeneration. Ophthalmol. Retina 2017, 1, 322–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.H.; Chang, Y.S.; Kim, J.W.; Lee, T.G.; Kim, H.S. Diagnosis of Type 3 Neovascularization Based on Optical Coherence Tomography Images. Retina 2016, 36, 1506–1515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chou, Y.B.; Hsu, C.H.; Chen, W.S.; Chen, S.J.; Hwang, D.K.; Huang, Y.M.; Li, A.F.; Lu, H.H. Deep learning and ensemble stacking technique for differentiating polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy from neovascular age-related macular degeneration. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, W.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J.; Ding, D.; He, F.; Chen, D.; Yang, Z.; Li, X.; Yu, W.; et al. Automated diagnoses of age-related macular degeneration and polypoidal choroidal vasculopathy using bi-modal deep convolutional neural networks. Br. J. Ophthalmol. 2021, 105, 561–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Krizhevsky, A.; Sutskever, I.; Hinton, G.E. Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks. Commun. ACM 2017, 60, 84–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, H.; Cisse, M.; Dauphin, Y.N.; Lopez-Paz, D. mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.09412. [Google Scholar]
- Kingma, D.P.; Ba, J. Adam: A method for stochastic optimization. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.6980. [Google Scholar]
- McHugh, M.L. Interrater reliability: The kappa statistic. Biochem. Med. 2012, 22, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Wang, N.; Chen, T.; Li, M. Empirical evaluation of rectified activations in convolutional network. arXiv 2015, arXiv:1505.00853. [Google Scholar]
- Selvaraju, R.R.; Cogswell, M.; Das, A.; Vedantam, R.; Parikh, D.; Batra, D. Grad-CAM: Visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 618–626. [Google Scholar]
- Han, J.; Choi, S.; Park, J.I.; Hwang, J.S.; Han, J.M.; Lee, H.J.; Ko, J.; Yoon, J.; Hwang, D.D. Classifying neovascular age-related macular degeneration with a deep convolutional neural network based on optical coherence tomography images. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Normal | nAMD | CSC | Total | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PCV | RAP | Typical nAMD | Chronic | Acute | |||
| Image, no | 1975 | 908 | 821 | 754 | 723 | 882 | 6063 |
| Participants, no | 47 | 115 | 101 | 114 | 88 | 103 | 568 |
| Base Model | Custom Layer | 3 Class Classification | 6 Class Classification |
|---|---|---|---|
| VGG–16 | Fully Connected layer | 99.1% | 90.3% |
| Global Average Pooling | 94.1% | 86.9% | |
| VGG–19 | Fully Connected layer | 99.7% | 91.1% |
| Global Average Pooling | 97.6% | 86.1% | |
| Resnet | Fully Connected layer | 98.5% | 87.4% |
| Global Average Pooling | 98.1% | 85.4% |
| Class | Precision | Recall | F1–Score | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Proposed Model | Normal | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 |
| PCV | 0.77 | 0.92 | 0.84 | |
| RAP | 0.93 | 0.84 | 0.88 | |
| Typical nAMD | 0.85 | 0.69 | 0.76 | |
| Chronic CSC | 0.95 | 1.00 | 0.97 | |
| Acute CSC | 0.94 | 0.94 | 0.94 | |
| Retina Specialist 1 | Normal | 0.93 | 0.91 | 0.92 |
| PCV | 0.81 | 0.95 | 0.88 | |
| RAP | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | |
| Typical nAMD | 0.74 | 0.66 | 0.70 | |
| Chronic CSC | 0.92 | 0.86 | 0.89 | |
| Acute CSC | 0.76 | 0.79 | 0.77 | |
| Retina Specialist 2 | Normal | 0.88 | 0.81 | 0.84 |
| PCV | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.84 | |
| RAP | 0.98 | 0.99 | 0.98 | |
| Typical nAMD | 0.63 | 0.72 | 0.67 | |
| Chronic CSC | 0.94 | 0.69 | 0.79 | |
| Acute CSC | 0.64 | 0.71 | 0.67 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Han, J.; Choi, S.; Park, J.I.; Hwang, J.S.; Han, J.M.; Ko, J.; Yoon, J.; Hwang, D.D.-J. Detecting Macular Disease Based on Optical Coherence Tomography Using a Deep Convolutional Network. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031005
Han J, Choi S, Park JI, Hwang JS, Han JM, Ko J, Yoon J, Hwang DD-J. Detecting Macular Disease Based on Optical Coherence Tomography Using a Deep Convolutional Network. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(3):1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031005
Chicago/Turabian StyleHan, Jinyoung, Seong Choi, Ji In Park, Joon Seo Hwang, Jeong Mo Han, Junseo Ko, Jeewoo Yoon, and Daniel Duck-Jin Hwang. 2023. "Detecting Macular Disease Based on Optical Coherence Tomography Using a Deep Convolutional Network" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 3: 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031005
APA StyleHan, J., Choi, S., Park, J. I., Hwang, J. S., Han, J. M., Ko, J., Yoon, J., & Hwang, D. D.-J. (2023). Detecting Macular Disease Based on Optical Coherence Tomography Using a Deep Convolutional Network. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(3), 1005. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12031005






