Selected Exogenous (Occupational and Environmental) Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases in Military and Aviation
Abstract
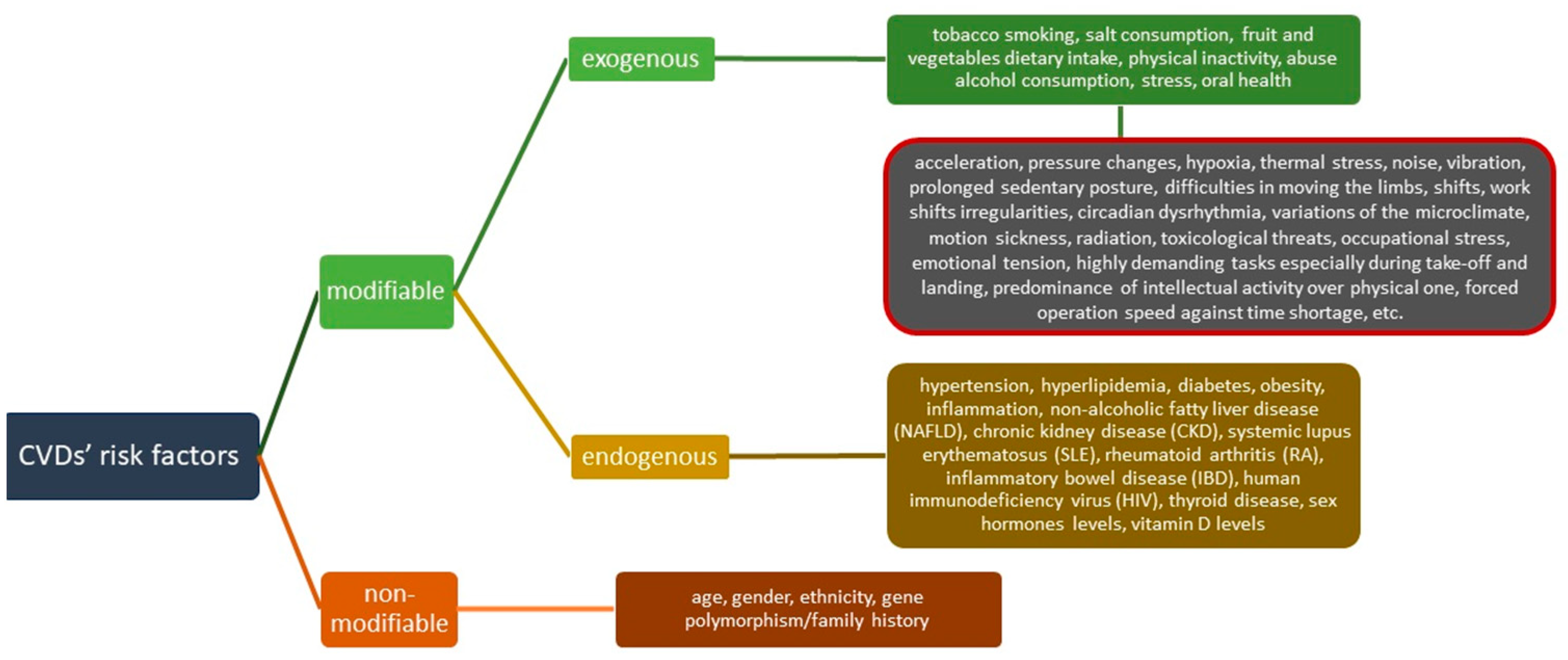
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Noise
3.2. Altitude and Hypoxia
3.3. Acceleration Forces
3.4. Stress
3.5. Tobacco Smoking
3.6. Oral Health
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- WHO. WHO CVDs. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/cardiovascular-diseases-(cvds) (accessed on 2 June 2023).
- Simons, R.; Maire, R. Extending the Age Limit of Commercial Pilots? Eur. Heart J. 2020, 41, 2239–2242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Radjen, S.D.; Jovelic, A.S.; Radjen, G.S.; Hajdukovic, Z.V.; Radakovic, S.S. Metabolic Syndrome and Carotid Artery Intima-Media Thickness in Military Pilots. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2011, 82, 622–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wilson, D.; Driller, M.; Johnston, B.; Gill, N. The Prevalence of Cardiometabolic Health Risk Factors among Airline Pilots: A Systematic Review. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, J.C.; Gerhardt, T.E.; Kwon, E. Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease. In Risk Factors For Coronary Artery Disease; NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health. StatPearls [Internet]; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Parastouei, K.; Sepandi, M.; Eskandari, E. Predicting the 10-Year Risk of Cardiovascular Diseases and Its Relation to Healthy Diet Indicator in Iranian Military Personnel. BMC Cardiovasc. Disord. 2021, 21, 419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, F.L.; Stahlman, S.; Oetting, A.A. Incidence Rates of Diagnoses of Cardiovascular Diseases and Associated Risk Factors, Active Component, US Armed Forces, 2007–2016. MSMR Med. Surveill. Mon. Rep. 2018, 25, 12–18. [Google Scholar]
- Incalcaterra, E.; Accardi, G.; Balistreri, C.R.; Caimi, G.; Candore, G.; Caruso, M.; Caruso, C. Pro-Inflammatory Genetic Markers of Atherosclerosis Topical Collection on Genetics. Curr. Atheroscler. Rep. 2013, 15, 329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maculewicz, E.; Pabin, A.; Kowalczuk, K.; Dziuda, Ł.; Białek, A. Endogenous Risk Factors of Cardiovascular Diseases (CVDs) in Military Professionals with a Special Emphasis on Military Pilots. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, N.; Hamadeh, R. Modifiable Coronary Artery Disease Risk Factors among Airline Pilots. Open Gen. Intern. Med. J. 2008, 2, 3–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaździńska, A.; Jagielski, P.; Turczyńska, M.; Dziuda, Ł.; Gaździński, S. Assessment of Risk Factors for Development of Overweight and Obesity among Soldiers of Polish Armed Forces Participating in the National Health Programme 2016–2020. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 3069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fajfrová, J.; Pavlík, V.; Psutka, J.; Husarová, M.; Krutišová, P.; Fajfr, M. Prevalence of Overweight and Obesity in Professional Soldiers of the Czech Army over an 11-Years Period. Vojn. Pregl. 2016, 73, 422–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngan, W.B.; Belinga, L.E.E.; Nlo’o, A.S.P.E.; Roche, F.; Goethals, L.; Mandengue, S.H.; Bongue, B. Surveillance of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in the Fifth Military Sector Health Center, Ngaoundere, Cameroon: Observational Study. JMIR Form. Res. 2020, 4, e18567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gunlu, S.; Karahan, M.Z. An Evaluation of Cardiovascular Risk Factors among Military Personnel: A Study Conducted in Turkey. Artuklu Int. J. Health Sci. 2022, 2, 31–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGraw, L.K.; Turner, B.S.; Stotts, N.A.; Dracup, K.A. A Review of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in US Military Personnel. J. Cardiovasc. Nurs. 2008, 23, 338–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Florea, M.; Zdrenghea, D. Cardiovascular Disease in the Active Military Population. Acta Medica Transilv. 2010, 2, 187–191. [Google Scholar]
- Baygi, F.; Herttua, K.; Jensen, O.C.; Djalalinia, S.; Mahdavi Ghorabi, A.; Asayesh, H.; Qorbani, M. Global Prevalence of Cardiometabolic Risk Factors in the Military Population: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2020, 20, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mullie, P.; Clarys, P.; Hulens, M.; Vansant, G. Distribution of Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Belgian Army Men. Arch. Environ. Occup. Health 2010, 65, 135–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirzaeipour, F.; Seyedmazhari, M.; Pishgooie, A.H.; Hazaryan, M. Assessment of Risk Factors for Coronary Artery Disease in Military Personnel: A Study from Iran. J. Fam. Med. Prim. Care 2019, 8, 1347–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomei, F.; De Sio, S.; Tomao, E.; Anzelmo, V.; Baccolo, T.P.; Ciarrocca, M.; Cherubini, E.; Valentini, V.; Capozzella, A.; Rosati, M.V. Occupational Exposure to Noise and Hypertension in Pilots. Int. J. Environ. Health Res. 2005, 15, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Petrassi, F.A.; Hodkinson, P.D.; Walters, P.L.; Gaydos, S.J. Hypoxic Hypoxia at Moderate Altitudes: Review of the State of the Science. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2012, 83, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lord, D.; Conlon, H.A. Cardiovascular Risk Factors in Airline Pilots. Workplace Health Saf. 2018, 66, 471–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solovieva, K.B.; Dolbin, I.V.; Koroleva, E.B. Hemodynamic Indicators Varying in Different Flight Phases in Hypertensive Pilots of the Arctic Transport Aviation. Hum. Physiol. 2015, 41, 780–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeeb, H.; Langner, I.; Blettner, M. Cardiovascular Mortality of Cockpit Crew in Germany: Cohort Study. Z. Kardiol. 2003, 92, 483–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molavi, B.; Mehta, J.L. Oxidative Stress in Cardiovascular Disease: Molecular Basis of Its Deleterious Effects, Its Detection, and Therapeutic Considerations. Curr. Opin. Cardiol. 2004, 19, 488–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nayor, M.; Brown, K.J.; Vasan, R.S. The Molecular Basis of Predicting Atherosclerotic Cardiovascular Disease Risk. Circ. Res. 2021, 128, 287–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Z.; He, Y.; Hu, X. Cardio-Oncology: Mechanisms, Drug Combinations, and Reverse Cardio-Oncology. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhamida, E.; Morciano, G.; Perrone, M.; Kahsay, A.E.; Della Sala, M.; Wieckowski, M.R.; Fiorica, F.; Pinton, P.; Giorgi, C.; Patergnani, S. The Interplay of Hypoxia Signaling on Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Inflammation in Cardiovascular Diseases and Cancer: From Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Approaches. Biology 2022, 11, 300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouhamida, E.; Morciano, G.; Pedriali, G.; Ramaccini, D.; Tremoli, E.; Giorgi, C.; Pinton, P.; Patergnani, S. The Complex Relationship between Hypoxia Signaling, Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Inflammation in Calcific Aortic Valve Disease: Insights from the Molecular Mechanisms to Therapeutic Approaches. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 11105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, A.M.O.; Paleologos, E.K.; Howari, F.M. Noise Pollution and Its Impact on Human Health and the Environment. In Pollution Assessment for Sustainable Practices in Applied Sciences and Engineering; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2020; pp. 975–1026. ISBN 9780128095829. [Google Scholar]
- Themann, C.L.; Masterson, E.A. Occupational Noise Exposure: A Review of Its Effects, Epidemiology, and Impact with Recommendations for Reducing Its Burden. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 3879–3905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khoshdel, A.; Mousavi-Asl, B.; Shekarchi, B.; Amini, K.; Mirzaii-Dizgah, I. Arterial Indices and Serum Cystatin C Level in Individuals with Occupational Wide Band Noise Exposure. Noise Health 2016, 18, 362–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stansfeld, S.A.; Matheson, M.P. Noise Pollution: Non-Auditory Effects on Health. Br. Med. Bull. 2003, 68, 243–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alves, J.A.; Paiva, F.N.; Silva, L.T.; Remoaldo, P. Low-Frequency Noise and Its Main Effects on Human Health—A Review of the Literature between 2016 and 2019. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 5205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreia, A.W.; Peters, J.L.; Levy, J.I.; Melly, S.; Dominici, F. Residential Exposure to Aircraft Noise and Hospital Admissions for Cardiovascular Diseases: Multi-Airport Retrospective Study. BMJ 2013, 347, f5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Münzel, T.; Sørensen, M.; Schmidt, F.; Schmidt, E.; Steven, S.; Kröller-Schön, S.; Daiber, A. The Adverse Effects of Environmental Noise Exposure on Oxidative Stress and Cardiovascular Risk. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2018, 28, 873–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jokel, C.; Yankaskas, K.; Robinette, M.B. Noise of Military Weapons, Ground Vehicles, Planes and Ships. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 2019, 146, 3832–3838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheppard, A.; Ralli, M.; Gilardi, A.; Salvi, R. Occupational Noise: Auditory and Non-Auditory Consequences. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 8963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siagian, M.; Basuki, B.; Kusmana, D. High Intensity Interior Aircraft Noise Increases the Risk of High Diastolic Blood Pressure in Indonesian Air Force Pilots. Med. J. Indones. 2009, 18, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Rajguru, R. Military Aircrew and Noise-Induced Hearing Loss: Prevention and Management. Aviat. Space Environ. Med. 2013, 84, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zevitas, C.D.; Spengler, J.D.; Jones, B.; McNeely, E.; Coull, B.; Cao, X.; Loo, S.M.; Hard, A.K.; Allen, J.G. Assessment of Noise in the Airplane Cabin Environment. J. Expo. Sci. Environ. Epidemiol. 2018, 28, 568–578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikolova, R.; Slavtcheva, L.; Zlatev, R.; Vukov, M. Prognozing of the Resistance to Hypoxia in Military Pilots by Cardiovascular and Respiratory Parameters. In Operational Medical Issues in Hypo-and Hyperbaric Conditions; Defense Technical Information Center: Fort Belvoir, VA, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Shaw, D.M.; Cabre, G.; Gant, N. Hypoxic Hypoxia and Brain Function in Military Aviation: Basic Physiology and Applied Perspectives. Front. Physiol. 2021, 12, 665821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, Y.; van den Oord, M.H.A.H.; Frings-Dresen, M.H.W.; Sluiter, J.K. Flight Performance during Exposure to Acute Hypobaric Hypoxia. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2017, 88, 760–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinman, Y.; van den Oord, M.H.A.H.; Frings-Dresen, M.H.W.; Sluiter, J.K. Flight Performance Aspects during Military Helicopter Flights. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2019, 90, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steinman, Y.; Groen, E.; Frings-Dresen, M.H.W. Exposure to Hypoxia Impairs Helicopter Pilots’ Awareness of Environment. Ergonomics 2021, 64, 1481–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pighin, S.; Bonini, N.; Hadjichristidis, C.; Schena, F.; Modena, R.; Savadori, L. Hypoxia and Risk Preferences: Mild Hypoxia Impacts Choices for Low-Probability High-Payoff Bets. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 960773. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bouak, F.; Vartanian, O.; Hofer, K.; Cheung, B. Acute Mild Hypoxic Hypoxia Effects on Cognitive and Simulated Aircraft Pilot Performance. Aerosp. Med. Hum. Perform. 2018, 89, 526–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sucipta, I.J.; Adi, N.P.; Kaunang, D. Relationship of Fatigue, Physical Fitness and Cardiovascular Endurance to the Hypoxic Response of Military Pilots in Indonesia. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 2018, 1073, 042044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulliri, G.; Magnani, S.; Roberto, S.; Ghiani, G.; Sechi, F.; Fanni, M.; Marini, E.; Stagi, S.; Lai, Y.; Rinaldi, A.; et al. Acute Exercise with Moderate Hypoxia Reduces Arterial Oxygen Saturation and Cerebral Oxygenation without Affecting Hemodynamics in Physically Active Males. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 4558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savla, J.J.; Levine, B.D.; Sadek, H.A. The Effect of Hypoxia on Cardiovascular Disease: Friend or Foe? High. Alt. Med. Biol. 2018, 19, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aragón-Vela, J.; Bejder, J.; Huertas, J.R.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Nordsborg, N.B. Does Intermittent Exposure to High Altitude Increase the Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in Workers? A Systematic Narrative Review. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e041532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Upson Muller, T. G·induced Vestibular Dysfunction (‘the Wobblies’) among Aerobatic Pilots: A Case Report and Review. ENT-Ear Nose Throat J. 2002, 81, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linakis, M.W.; Job, K.M.; Liu, X.; Collingwood, S.C.; Pangburn, H.A.; Ott, D.K.; Sherwin, C.M.T. Riding (High) into the Danger Zone: A Review of Potential Differences in Chemical Exposures in Fighter Pilots Resulting from High Altitude and G-Forces. Expert. Opin. Drug Metab. Toxicol. 2017, 13, 925–934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wochyński, Z.; Kowalczuk, K.; Kłossowski, M.; Sobiech, K.A. Effect of Centrifuge Test on Blood Serum Lipids Index of Cadet Pilots. Ann. Agric. Environ. Med. 2016, 23, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cahill, J.; Cullen, P.; Anwer, S.; Gaynor, K.; Wilson, S. The Requirements for New Tools for Use by Pilots and the Aviation Industry to Manage Risks Pertaining to Work-Related Stress (WRS) and Wellbeing, and the Ensuing Impact on Performance and Safety. Technologies 2020, 8, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferres Saint-Aubin, K. Impact of Positive Emotions Enhancement on Physiological Processes and Psychological Functioning in Military Pilots; Wright State University: Bretigny sur Orge, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Dyball, D.; Evans, S.; Boos, C.J.; Stevelink, S.A.M.; Fear, N.T. The Association between PTSD and Cardiovascular Disease and Its Risk Factors in Male Veterans of the Iraq/Afghanistan Conflicts: A Systematic Review. Int. Rev. Psychiatry 2019, 31, 34–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neylon, A.; Canniffe, C.; Anand, S.; Kreatsoulas, C.; Blake, G.J.; Sugrue, D.; McGorrian, C. A Global Perspective on Psychosocial Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2013, 55, 574–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cahill, J.; Cullen, P.; Gaynor, K.; Cahill, J.; Cullen, P.; Gaynor, K. Pilot Wellbeing & Work Related Stress (Wrs). In Proceedings of the 20th International Symposium on Aviation Psychology, Dayton, OH, USA, 7–10 May 2019; pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Urazaliyeva, I.R.; Musaeva, G.I. Risk Factors for Non-Communicable Diseases among Military Personnel. Scholast. J. Nat. Med. Educ. 2023, 2, 117–122. [Google Scholar]
- Hajiyousefi, H.; Asadi, H.; Jafari, A. The Analysis of Occupational Stressors among Pilots; Exercise, as a Strategy to Increase Flight Safety. Int. J. Sport. Stud. 2015, 5, 1263–1274. [Google Scholar]
- Šagud, M.; Jakšić, N.; Vuksan-Ćusa, B.; Lončar, M.; Lončar, I.; Peleš, A.M.; Miličić, D.; Jakovljević, M. Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors in Patients with Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD): A Narrative Review. Psychiatr. Danub. 2017, 29, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibler, J.L. Posttraumatic Stress and Cardiovascular Disease Risk. J. Trauma Dissociation 2009, 10, 135–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hargrave, A.S.; Sumner, J.A.; Ebrahimi, R.; Cohen, B.E. Posttraumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD) as a Risk Factor for Cardiovascular Disease: Implications for Future Research and Clinical Care. Curr. Cardiol. Rep. 2022, 24, 2067–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulmer, C.S.; Bosworth, H.B.; Germain, A.; Lindquist, J.; Olsen, M.; Brancu, M.; The VA Mid-Atlantic Mental Illness Research Education; Beckham, J.C. Associations between Sleep Difficulties and Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Disease in Veterans and Active Duty Military Personnel of the Iraq and Afghanistan Conflicts. J. Behav. Med. 2015, 38, 544–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meško, M.; Karpljuk, D.; Videmšek, M.; Podbregar, I. Personality Profiles and Stress-Coping Strategies of Slovenian Military Pilots. Psihol. Obz./Horiz. Psychol. 2009, 18, 23–38. [Google Scholar]
- Hohmann, M.; Orlick, T. Examining the Psychological Skills Used by Elite Canadian Military Pilots. J. Excell. 2014, 16, 4–19. [Google Scholar]
- Au-Yeung, C.S.; Chao, R.F.; Hsu, L.Y. Why It Is Difficult for Military Personnel to Quit Smoking: From the Perspective of Compensatory Health Beliefs. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18, 12261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dailey, J.I.; Wilson, K.C. Impact of Smoking and Smoking Cessation Medications in Aviators. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2019, 21, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toblin, R.L.; Anderson, J.A.; Riviere, L.A.; McGurk, D.; Sipos, M.L. The Impact of Unit Membership on Smoking among Soldiers. Mil. Med. 2016, 181, 16–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebe Dia, A. Association between Tobacco Smikoing Nad Cadiovascular Disease among Active Duty Soldiers in the United States Army. Ph.D. Thesis, Trident University International, Cypress, CA, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Nieh, C.; Mancuso, J.D.; Powell, T.M.; Welsh, M.M.; Gackstetter, G.D.; Hooper, T.I. Cigarette Smoking Patterns among U.S. Military Service Members before and after Separation from the Military. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0257539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaicaitiene, R.; Cerniauskiene, L.R.; Luksiene, D.I.; Margeviciene, L. Hypercholesterolemia and Smoking Habits of Lithuanian Military Personnel. Mil. Med. 2006, 171, 512–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basaza, R.; Otieno, E.; Musinguzi, A.; Mugyenyi, P.; Haddock, C.K. Factors Influencing Cigarette Smoking among Soldiers and Costs of Soldier Smoking in the Work Place at Kakiri Barracks, Uganda. Tob. Control 2017, 26, 330–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulanday, K.T.; Jeffery, D.D.; Nebeling, L.; Srinivasan, S. Perceived Deterrence of Cigarette Use and Smoking Status among Active Duty Military Personnel. Mil. Med. 2017, 182, e1733–e1741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieh, C.; Powell, T.M.; Gackstetter, G.D.; Hooper, T.I. Smoking Among U.S. Service Members Following Transition From Military to Veteran Status. Health Promot. Pract. 2020, 21, 165S–175S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, A.L.; Severson, H.H.; Andrews, J.A.; Gott, S.P.; Col Jeffrey Cigrang, L.A.; Gordon, J.S.; Hunter, C.M. Smokeless Tobacco Use in Military Personnel. Mil. Med. 2007, 172, 1300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Lin, J.; Zhu, K.; Hoang, P.K.; Soliván-Ortiz, A.M.; Larsen, S.L.; Irwin, S.P.; Schneid, T.R.; Shriver, C.D.; Lee, S. Electronic Cigarette Use and Related Factors among Active Duty Service Members in the U.S. Military. Mil. Med. 2020, 185, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kotamiiki, M. Cigarette Smoking and Autonomic Responses Smoking Induced Differences in Autonomic Responses in Military Pilot Candidates. Clin. Auton. Res. 1995, 5, 31–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thankappan, P.; Kaushik, S.; Gupta, S.; Mandlik, V. Periodontal Diseases in Military Aviation Crew: A Pilot Study in Armed Forces. J. Int. Clin. Dent. Res. Organ. 2015, 7, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell Ngan, W.; Essama Eno Belinga, L.; Essam Nlo’o, S.A.P.; Abeng Mbozo’o, E.; Otsomoti, E.; Mekoulou Ndongo, J.; Bika Lele, E.C.; Hupin, D.; Mandengue, S.H.; Roche, F.; et al. Oral Health Status and Cardiovascular Risk Profile in Cameroonian Military Population. AIMS Public. Health 2021, 8, 100–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Khalifa, K.S. Prevalence of Bruxism and Associated Occupational Stress in Saudi Arabian Fighter Pilots. Oman Med. J. 2022, 37, e351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Risk Factor | Cardiovascular Implications | References |
|---|---|---|
| Noise | Increased susceptibility to cardiovascular events, cardiac disease, hypertension, higher diastolic blood pressure, hypotension, oxidative stress, vascular dysfunction, impaired vasodilation, peripheral vasoconstriction, increased peripheral vascular resistance, arterial wall thickening and stiffness, accelerated progression of atherosclerosis, elevated blood glucose levels, increased heart rate and blood pressure, high resting pulse rate | [20,30,32,33,35,39] |
| Altitude and hypoxia | Lower level of blood or tissue oxygenation, pulmonary barotrauma and cerebral arterial gas embolism, alterations in heart rate and mean blood pressure, enhanced sympathetic tone and pulmonary artery vasoconstriction, reductions in peripheral arterial oxygen saturation and cerebral oxygenation, increased blood pressure and heart rate, acute reduction in cerebral regional oxygen saturation, elevated HDL levels, increased risk of hypertension, changes in the oxygen partial pressure in the arterial blood perfusing the brain, modulation of the sympathetic and parasympathetic cardiac activity, decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen of arterial blood, stimulation of peripheral chemoreceptors in the carotid and aortic arteries, regulation of vascular resistance, arterial pressure, heart rate, cardiac output, and myocardial contractility, increased heart rate and systolic blood pressure, tachycardia, decreases or increases in diastolic blood pressure, significant increase in mean R–R interval values, and a slight indirect downward trend in sympathetic cardiac activity and diastolic pressure values | [42,49,50,51] |
| Acceleration forces | Intravascular contracture, decreased oxygen-carrying capacity, decrease in heart rate, abnormal sympathetic autonomic responses, modulation of membrane fluidity, increased levels of blood serum TAG, increase in HDL levels | [53,54,55] |
| Stress | Effects on blood pressure, effects on cardiac function, influence on endothelial functioning, platelets, and metabolic function, regulation of heart rate variability, low heart rate, non-fatal myocardial infarction, CVD death, increased risk for all types of stroke including fatal stroke, greater general risk of CVD, increased risk of coronary artery disease and related mortality, higher incidence of arterial hypertension, cardiac arrhythmias and myocardial infarction, hypertension, elevated total cholesterol levels, elevated LDL, decreased HDL, elevated TAG levels, elevated homocysteine levels, changes in receptors that regulate blood pressure, allostatic overload, platelet activation, inflammation, arterial hypertension, central obesity, insulin resistance, increased release of inflammatory cytokines involved in platelet activation and endothelial dysfunction, elevated blood pressure | [58,59,63,64,65,66] |
| Tobacco smoking | Increased oxidative stress through generation of ROS, endothelial dysfunction, oxidation of both HDL and LDL, reverse cholesterol transport, elevated plasma fibrinogen levels and inflammatory marker levels (C-reactive protein (CRP) and interleukin-6 (IL-6), increase in the inflammatory process, changes in the thrombosis/fibrinolysis system, hypercholesterolemia, decreased HDL levels, increased blood pressure, increased blood tendency to clotting, increased heart rate, enhanced excretion of thromboxane, which results in increased vasoconstrictive properties of smoking, increased sympathetic activities and plasma catecholamine levels, elevated plasma noradrenaline levels, increased resting heart rate and decreased heart rate variability, higher total cholesterol levels | [9,70,72,74,80] |
| Oral health | Production of inflammatory mediators such as tumor necrosis factor α (TNF-α), interleukins (IL-1, IL-6, IL-8), and CRP, presence of Porphyromonas gingivalis, Aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans, and Streptococcus sanguis in patches of atheroma | [82] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Maculewicz, E.; Pabin, A.; Dziuda, Ł.; Białek, M.; Białek, A. Selected Exogenous (Occupational and Environmental) Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases in Military and Aviation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7492. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237492
Maculewicz E, Pabin A, Dziuda Ł, Białek M, Białek A. Selected Exogenous (Occupational and Environmental) Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases in Military and Aviation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(23):7492. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237492
Chicago/Turabian StyleMaculewicz, Ewelina, Agata Pabin, Łukasz Dziuda, Małgorzata Białek, and Agnieszka Białek. 2023. "Selected Exogenous (Occupational and Environmental) Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases in Military and Aviation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 23: 7492. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237492
APA StyleMaculewicz, E., Pabin, A., Dziuda, Ł., Białek, M., & Białek, A. (2023). Selected Exogenous (Occupational and Environmental) Risk Factors for Cardiovascular Diseases in Military and Aviation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(23), 7492. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12237492









