The Stream Device—A Retrospective Review of 51 Cases
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
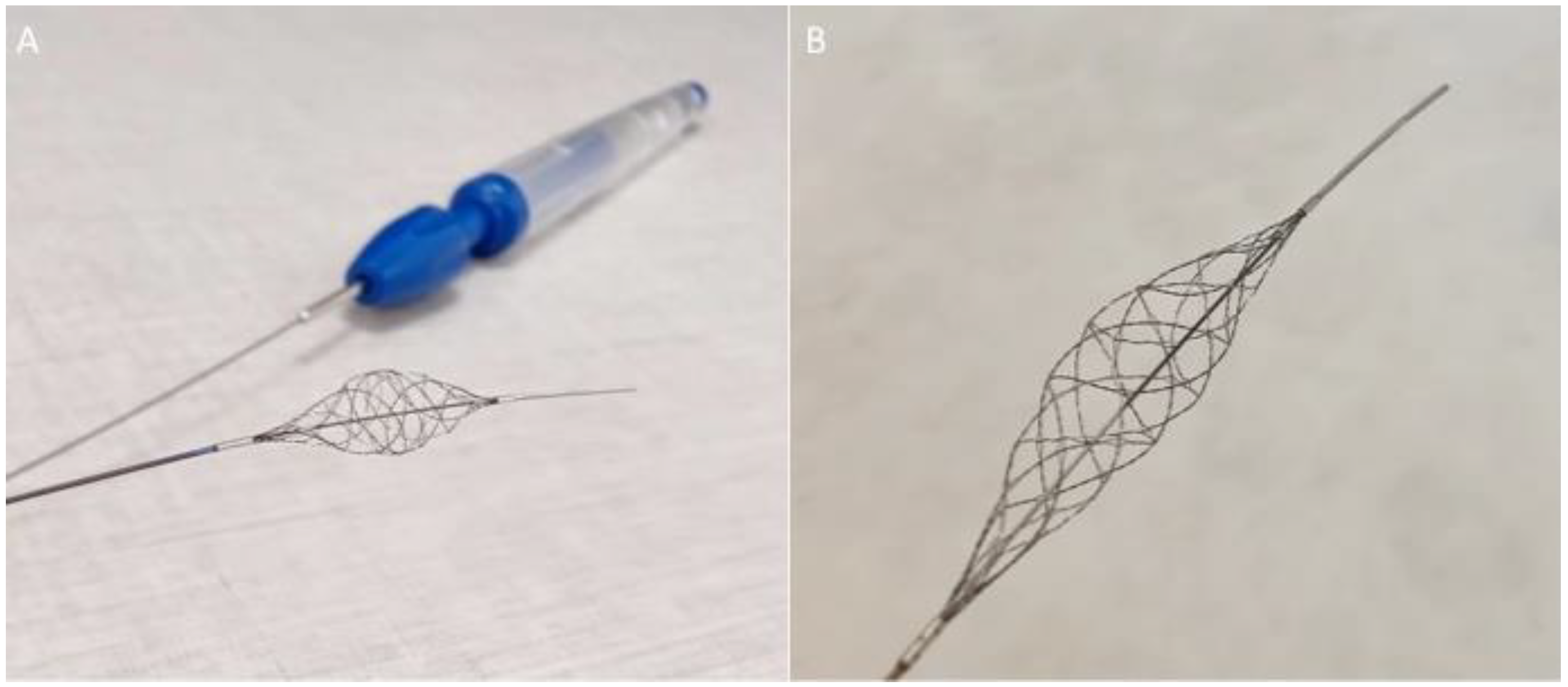
2.1. The Stream Device
- Stream;
- Stream XL;
- Stream 17.
2.2. Patient Selection
2.3. Study Population
- Age ≥ 18;
- National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score of ≥4;
- ASPECT score ≥ 5;
- LVO on CT angiography;
- Pre-morbid mRS of 0–2;
- Life expectancy of >6 month.
2.4. Endovascular Procedure
2.5. Post-Procedure
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Demographics
3.2. Clinical and Angiographic Results
3.3. Procedural Outcomes
3.4. Follow-up Imaging and Clinical Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nogueira, R.G.; Jadhav, A.P.; Haussen, D.C.; Bonafe, A.; Budzik, R.F.; Bhuva, P.; Yavagal, D.R.; Ribo, M.; Cognard, C.; Hanel, R.A.; et al. Thrombectomy 6 to 24 Hours after Stroke with a Mismatch between Deficit and Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 11–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albers, G.W.; Marks, M.P.; Kemp, S.; Christensen, S.; Tsai, J.P.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; McTaggart, R.A.; Torbey, M.T.; Kim-Tenser, M.; Leslie-Mazwi, T.; et al. Thrombectomy for Stroke at 6 to 16 Hours with Selection by Perfusion Imaging. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 708–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sarraj, A.; Hassan, A.E.; Abraham, M.G.; Ortega-Gutierrez, S.; Kasner, S.E.; Hussain, M.S.; Chen, M.; Blackburn, S.; Sitton, C.W.; Churilov, L.; et al. Trial of Endovascular Thrombectomy for Large Ischemic Strokes. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1259–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uchida, K.; Shindo, S.; Yoshimura, S.; Toyoda, K.; Sakai, N.; Yamagami, H.; Matsumaru, Y.; Matsumoto, Y.; Kimura, K.; Ishikura, R.; et al. Association Between Alberta Stroke Program Early Computed Tomography Score and Efficacy and Safety Outcomes With Endovascular Therapy in Patients With Stroke From Large-Vessel Occlusion: A Secondary Analysis of the Recovery by Endovascular Salvage for Cerebral Ultra-Acute Embolism-Japan Large Ischemic Core Trial (RESCUE-Japan LIMIT). JAMA Neurol. 2022, 79, 1260–1266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huo, X.; Ma, G.; Tong, X.; Zhang, X.; Pan, Y.; Nguyen, T.N.; Yuan, G.; Han, H.; Chen, W.; Wei, M.; et al. Trial of Endovascular Therapy for Acute Ischemic Stroke with Large Infarct. N. Engl. J. Med. 2023, 388, 1272–1283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Staessens, S.; Denorme, F.; Francois, O.; Desender, L.; Dewaele, T.; Vanacker, P.; Deckmyn, H.; Vanhoorelbeke, K.; Andersson, T.; De Meyer, S.F. Structural Analysis of Ischemic Stroke Thrombi: Histological Indications for Therapy Resistance. Haematologica 2020, 105, 498–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dumitriu LaGrange, D.; Bernava, G.; Reymond, P.; Wanke, I.; Vargas, M.I.; Machi, P.; Lövblad, K.-O. A High Resolution Scanning Electron Microscopy Analysis of Intracranial Thrombi Embedded along the Stent Retrievers. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 8027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsumoto, T.; Tsurusaki, Y.; Tokunaga, S. Interaction between the Stent Strut and Thrombus Characterized by Contrast-Enhanced High-Resolution Cone Beam CT during Deployment of the Solitaire Stent Retriever. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 843–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Autar, A.S.A.; Hund, H.M.; Ramlal, S.A.; Hansen, D.; Lycklama, À.; Nijeholt, G.J.; Emmer, B.J.; de Maat, M.P.M.; Dippel, D.W.J.; van der Lugt, A.; et al. High-Resolution Imaging of Interaction Between Thrombus and Stent-Retriever in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e008563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Gebrezgiabhier, D.; Reddy, A.S.; Davis, E.; Zheng, Y.; Arturo Larco, J.L.; Shih, A.J.; Pandey, A.S.; Savastano, L.E. Failure Modes and Effects Analysis of Mechanical Thrombectomy for Stroke Discovered in Human Brains. J. Neurosurg. 2021, 136, 197–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brouwer, P.A.; Yeo, L.L.L.; Holmberg, A.; Andersson, T.; Kolloch, J.; KuntzeSöderqvist, Å.; Ohlsson, M.; Holmin, S.; Mpotsaris, A.; Gontu, V.K.; et al. Thrombectomy Using the EmboTrap Device: Core Laboratory-Assessed Results in 201 Consecutive Patients in a Real-World Setting. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2018, 10, 964–968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omrani, O.; Hafezi-Bakhtiari, N.; DeSouza, P.; Nikola, C.; Wong, K.; Lansley, J.; Dhillon, P.; Makalanda, L.; Chan, N.; Harrison, T.; et al. The Initial Experience with the Embotrap III Stent-Retriever in a Real World Setting. Interv. Neuroradiol. J. Peritherapeutic Neuroradiol. Surg. Proced. Relat. Neurosci. 2022, 15910199221142096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Bozorgchami, H.; Ribó, M.; Saver, J.L.; Mattle, H.P.; Chapot, R.; Narata, A.P.; Francois, O.; Jadhav, A.P.; Grossberg, J.A.; et al. Primary Results of the Multicenter ARISE II Study (Analysis of Revascularization in Ischemic Stroke With EmboTrap). Stroke 2018, 49, 1107–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bajrami, A.; Ertugrul, O.; Senadim, S.; Erdem, E.; Baltacioglu, F.; Geyik, S. First Pass Results of Mechanical Thrombectomy with Two-Drop Zone NeVaTM Device. Interv. Neuroradiol. J. Peritherapeutic Neuroradiol. Surg. Proced. Relat. Neurosci. 2022, 15910199221135308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akpinar, C.K.; Ozdemir, A.O.; Gurkas, E.; Bilgic, A.B.; Aykac, O.; Inanc, Y.; Giray, S. Favorable First-Pass Recanalization Rates with NeVaTM Thrombectomy Device in Acute Stroke Patients: Initial Clinical Experience. Interv. Neuroradiol. J. Peritherapeutic Neuroradiol. Surg. Proced. Relat. Neurosci. 2021, 27, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makalanda, L.; Lansley, J.; Wong, K.; Spooner, O.; Bhogal, P. The Q and A-The MIVI Q Catheters for Aspiration Thrombectomy-Initial Experience from London. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 5844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Rueda, M.E.; Ballenilla Marco, F.; Garmendia Lopetegui, E.; Pumar, J.M.; Zamarro, J.; García-Villalba, B.; Díaz-Pérez, J.; Mosqueira, A.; Lüttich, A.; Larrea, J.-A.; et al. Thrombectomy Aspiration Post-Market Study in Acute Stroke with the Q Aspiration Catheter: The TAPAS Study. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2022, 15, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kobeissi, H.; Ghozy, S.; Flood, R.; Mortimer, A.; Crossley, R.; Cox, A.; Minks, D.; Wareham, J. Mechanical Thrombectomy with Q Catheter in Stroke Caused by Primary and Secondary Distal and Medium Vessel Occlusions. Interv. Neuroradiol. J. Peritherapeutic Neuroradiol. Surg. Proced. Relat. Neurosci. 2023, 15910199231167916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sirakov, S.; Sirakov, A.; Minkin, K.; Karakostov, V.; Raychev, R. Early Clinical Experience with Cascade: A Novel Temporary Neck Bridging Device for Embolization of Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2020, 12, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomasello, A.; Hernandez, D.; Gramegna, L.L.; Aixut, S.; Barranco Pons, R.; Jansen, O.; Zawadzki, M.; Lopez-Rueda, A.; Parra-Fariñas, C.; Piñana, C.; et al. Early Experience with a Novel Net Temporary Bridging Device (Cascade) to Assist Endovascular Coil Embolization of Intracranial Aneurysms. J. Neurosurg. 2020, 134, 591–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhogal, P.; Wong, K.; Makalanda, H. The Cascade Device—In Vitro Tests to Assess Coil Protrusion into the Parent Vessel. Interv. Neuroradiol. J. Peritherapeutic Neuroradiol. Surg. Proced. Relat. Neurosci. 2020, 26, 494–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, S.; Weber, A.; Carolus, A.; Drescher, F.; Götz, F.; Weber, W. Coiling of Wide-Necked Carotid Artery Aneurysms Assisted by a Temporary Bridging Device (Comaneci): Preliminary Experience. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 1039–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, R.; Kolodgie, F.D.; Virmani, R.; Eckhouse, R. Comaneci Neck Bridging Device for the Treatment of Cerebral Aneurysms. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2016, 8, 181–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhogal, P.; Simpanen, T.; Wong, K.; Bushi, D.; Sirakov, M.A.; Sirakov, S.; Aggour, M.; Makalanda, L. Use of the Cascade Expandable Net to Treat Cerebral Vasospasm—Initial Clinical Experience from a Single Centre with in Vitro Benchside Tests. CVIR Endovasc. 2021, 4, 82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salem, M.M.; Khalife, J.; Desai, S.; Sharashidze, V.; Badger, C.; Kuhn, A.L.; Monteiro, A.; Salahuddin, H.; Siddiqui, A.H.; Singh, J.; et al. COManeci MechANical Dilation for Vasospasm (COMMAND): Multicenter Experience. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2022, 15, 864–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Castonguay, A.C.; Gupta, R.; Sun, C.-H.J.; Martin, C.; Holloway, W.E.; Mueller-Kronast, N.; English, J.D.; Linfante, I.; Dabus, G.; et al. North American Solitaire Stent Retriever Acute Stroke Registry: Post-Marketing Revascularization and Clinical Outcome Results. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2014, 6, 584–588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dávalos, A.; Pereira, V.M.; Chapot, R.; Bonafé, A.; Andersson, T.; Gralla, J. Solitaire Group Retrospective Multicenter Study of Solitaire FR for Revascularization in the Treatment of Acute Ischemic Stroke. Stroke J. Cereb. Circ. 2012, 43, 2699–2705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Broussalis, E.; Trinka, E.; Hitzl, W.; Wallner, A.; Chroust, V.; Killer-Oberpfalzer, M. Comparison of Stent-Retriever Devices versus the Merci Retriever for Endovascular Treatment of Acute Stroke. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2013, 34, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campbell, B.C.V.; Hill, M.D.; Rubiera, M.; Menon, B.K.; Demchuk, A.; Donnan, G.A.; Roy, D.; Thornton, J.; Dorado, L.; Bonafe, A.; et al. Safety and Efficacy of Solitaire Stent Thrombectomy: Individual Patient Data Meta-Analysis of Randomized Trials. Stroke 2016, 47, 798–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Binning, M.J.; Bartolini, B.; Baxter, B.; Budzik, R.; English, J.; Gupta, R.; Hedayat, H.; Krajina, A.; Liebeskind, D.; Nogueira, R.G.; et al. Trevo 2000: Results of a Large Real-World Registry for Stent Retriever for Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2018, 7, e010867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadhav, A.P.; Desai, S.M.; Budzik, R.F.; Gupta, R.; Baxter, B.; English, J.D.; Bartolini, B.M.; Krajina, A.; Haussen, D.C.; Nogueira, R.G.; et al. First Pass Effect in Patients with Large Vessel Occlusion Strokes Undergoing Neurothrombectomy: Insights from the Trevo Retriever Registry. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2021, 13, 619–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Protto, S.; Pienimäki, J.-P.; Seppänen, J.; Matkaselkä, I.; Ollikainen, J.; Numminen, H.; Sillanpää, N. TREVO and Capture LP Have Equal Technical Success Rates in Mechanical Thrombectomy of Proximal and Distal Anterior Circulation Occlusions. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2017, 9, 644–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Tiberi, R.; Bhogal, P.; Buhk, J.-H.; Behme, D.; Tomasello, A.; Ribo, M. Impact of Stent-Retriever Tip Design on Distal Embolization during Mechanical Thrombectomy: A Randomized in Vitro Evaluation. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belachew, N.F.; Dobrocky, T.; Meinel, T.R.; Hakim, A.; Vynckier, J.; Arnold, M.; Seiffge, D.J.; Wiest, R.; Piechowiak, E.I.; Fischer, U.; et al. Risks of Undersizing Stent Retriever Length Relative to Thrombus Length in Patients with Acute Ischemic Stroke. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2021, 42, 2181–2187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serna Candel, C.; Aguilar Pérez, M.; Bäzner, H.; Henkes, H.; Hellstern, V. First-Pass Reperfusion by Mechanical Thrombectomy in Acute M1 Occlusion: The Size of Retriever Matters. Front. Neurol. 2021, 12, 679402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haussen, D.C.; Al-Bayati, A.R.; Grossberg, J.A.; Bouslama, M.; Barreira, C.; Bianchi, N.; Frankel, M.R.; Nogueira, R.G. Longer Stent Retrievers Enhance Thrombectomy Performance in Acute Stroke. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 6–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zaidat, O.O.; Haussen, D.C.; Hassan, A.E.; Jadhav, A.P.; Mehta, B.P.; Mokin, M.; Mueller-Kronast, N.H.; Froehler, M.T. Impact of Stent Retriever Size on Clinical and Angiographic Outcomes in the STRATIS Stroke Thrombectomy Registry. Stroke 2019, 50, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wenger, K.; Nagl, F.; Wagner, M.; Berkefeld, J. Improvement of Stent Retriever Design and Efficacy of Mechanical Thrombectomy in a Flow Model. Cardiovasc. Intervent. Radiol. 2013, 36, 192–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kara, B.; Selcuk, H.H.; Erbahceci Salik, A.; Zalov, H.; Yildiz, O.; Gul, G.; Balkan, B. Single-Center Experience with the Tigertriever Device for the Recanalization of Large Vessel Occlusions in Acute Ischemic Stroke. J. Neurointerv. Surg. 2019, 11, 455–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Baseline Data | n = 51 |
|---|---|
| Demographics | |
| Age | Median 73 (range 51–89) |
| Female | 51% (n = 26) |
| Co-Morbidities | |
| Smoking | 20 (39.2%) |
| Hypertension | 40 (78.4%) |
| Diabetes Mellitus | 13 (25.5%) |
| Atrial Fibrillation | 26 (51%) |
| Pre-Morbid mRS | |
| 0 | 51 (100%) |
| Stroke Data | |
|---|---|
| NIHSS | Median 17 (range 4–22) |
| IV tPA | 35 (68.6%) |
| Suspected Cause | |
| Cardioembolic | 27 (52.9%) |
| Large-artery Atherosclerosis | 6 (11.8%) |
| Mixed | 5 (9.8%) |
| ESUS (Embolic Stroke of Undetermined Source) | 13 (25.5%) |
| Imaging Findings | |
| Side | |
| R | 29 (56.9%) |
| L | 20 (39.2%) |
| Mid | 2 (3.9%) |
| Tandem Lesion | |
| Y | 8 (15.7%) |
| Clot Location | |
| ICA | 16 (31.4%) |
| M1 | 29 (56.9%) |
| M2 | 4 (7.8%) |
| BA | 2 (3.9%) |
| Hyperdense Clot | 34 (66.7%) |
| Clot Length | 12 ± 6.2 mm (range: 2–26 mm) |
| ASPECT Score | Median 10 (range: 6–10) |
| Procedural Data | |
|---|---|
| Anaesthesia | |
| LA | 49 (96.1%) |
| GA | 2 (3.9%) |
| Distal Aspiration Catheter | 51 (100%) |
| Stream | |
| Stream | 40 (78.4%) |
| Stream XL | 1 (2%) |
| Stream 17 | 10 (19.6%) |
| Angiographic Results | |
| Median No. of passes | 2 (range 1–8) |
| Median No. of passes with Stream | 2 (range 1–4) |
| FPE (eTICI 2c/3) | 13 (25.5%) |
| Modified FPE (eTICI ≥ 2b) | 16 (31.4%) |
| Final eTICI | |
| 0–2a | 5 (9.8%) |
| 2b | 3 (5.9%) |
| 2c | 4 (7.8%) |
| 3 | 39 (76.5%) |
| Distal Embolisation | 3 (5.9%) |
| Embolisation to New territory | 0 |
| Bailout Required | n = 10 |
| Resistant Clot Device Damage | 5 (9.8%) 4 (7.8%) |
| Intracranial Stent Implanted | 1 (1.9%) |
| Carotid Stent Implanted | 2 (3.9%) |
| Follow-up (n = 51) | |
|---|---|
| ASPECT | Median 8 (range 0–10) |
| sICH | 7 (13.7%) |
| SAH | 8 (15.7%) |
| 90-day mRS | |
| 0–2 | 11 (21.6%) |
| 3–5 | 18 (35.3%) |
| 6 | 22 (43.1%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Kupcs, K.; Sproge, P.; Kupca, K.; Bhogal, P. The Stream Device—A Retrospective Review of 51 Cases. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196384
Kupcs K, Sproge P, Kupca K, Bhogal P. The Stream Device—A Retrospective Review of 51 Cases. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196384
Chicago/Turabian StyleKupcs, Karlis, Patricija Sproge, Katrina Kupca, and Pervinder Bhogal. 2023. "The Stream Device—A Retrospective Review of 51 Cases" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196384
APA StyleKupcs, K., Sproge, P., Kupca, K., & Bhogal, P. (2023). The Stream Device—A Retrospective Review of 51 Cases. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6384. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196384






