Effect of Water-Based vs. Land-Based Exercise Intervention (postCOVIDkids) on Exercise Capacity, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Children with Post COVID-19 Condition: A Randomized Controlled Trial
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Design and Setting
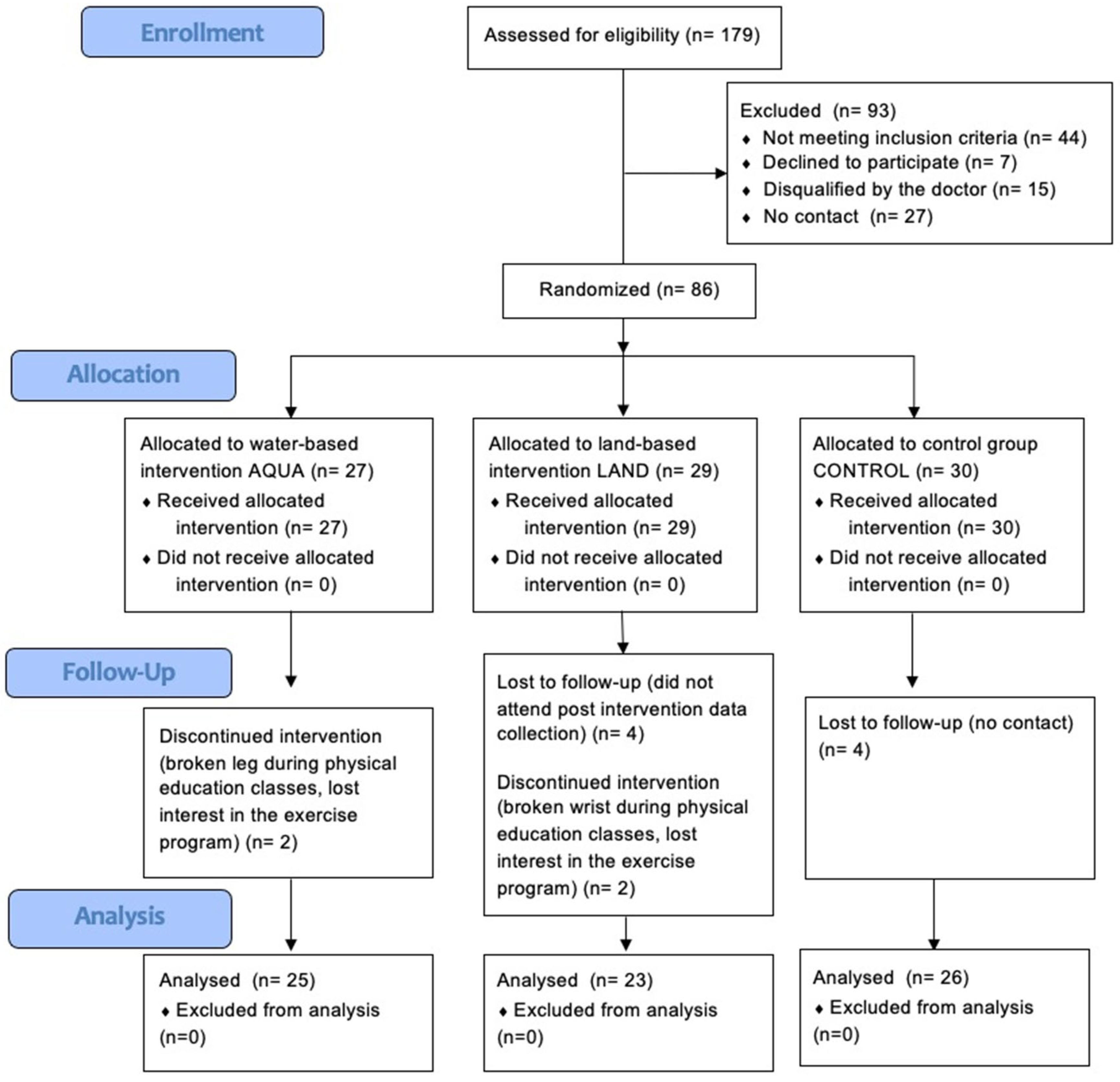
2.2. Participants
2.3. Randomization, Allocation Concealment and Blinding
2.4. Intervention
2.5. Primary Outcomes
2.5.1. Exercise Capacity
2.5.2. Fatigue
2.6. Secondary Outcome
2.7. Procedure
2.8. Statistical Methods
3. Results
3.1. Primary Outcomes
3.2. Secondary Outcome
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization. A clinical case definition for post COVID-19 condition in children and adolescents by expert consensus. In WHO/2019-nCoV/Post_COVID-19_Condition/CA/Clinical_Case_Definition/2023.1; World Health Organization: Geneva, Switzerland, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Buonsenso, D.; Di Gennaro, L.; De Rose, C.; Morello, R.; D’Ilario, F.; Zampino, G.; Piazza, M.; Boner, A.L.; Iraci, C.; O’Connell, S.; et al. Long-term outcomes of pediatric infections: From traditional infectious diseases to long COVID. Future Microbiol. 2022, 17, 551–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baig, A.M. Deleterious Outcomes in Long-Hauler COVID-19: The Effects of SARS-CoV-2 on the CNS in Chronic COVID Syndrome. ACS Chem. Neurosci. 2020, 11, 4017–4020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfefferbaum, B.; North, C.S. Mental Health and the COVID-19 Pandemic. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 510–512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, C.; Prokopich, S.; Loewen, H.; Sanchez-Ramirez, D.C. Long-Term Effect of COVID-19 on Lung Imaging and Function, Cardiorespiratory Symptoms, Fatigue, Exercise Capacity, and Functional Capacity in Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomson, H. Children with long COVID. New Sci. 2021, 249, 10–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izquierdo-Pujol, J.; Moron-Lopez, S.; Dalmau, J.; Gonzalez-Aumatell, A.; Carreras-Abad, C.; Mendez, M.; Rodrigo, C.; Martinez-Picado, J. Post COVID-19 Condition in Children and Adolescents: An Emerging Problem. Front. Pediatr. 2022, 10, 894204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Funk, A.L.; Kuppermann, N.; Florin, T.A.; Tancredi, D.J.; Xie, J.; Kim, K.; Finkelstein, Y.; Neuman, M.I.; Salvadori, M.I.; Yock-Corrales, A.; et al. Post-COVID-19 Conditions Among Children 90 Days After SARS-CoV-2 Infection. JAMA Netw. Open 2022, 5, e2223253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borch, L.; Holm, M.; Knudsen, M.; Ellermann-Eriksen, S.; Hagstroem, S. Long COVID symptoms and duration in SARS-CoV-2 positive children—A nationwide cohort study. Eur. J. Pediatr. 2022, 181, 1597–1607. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Leon, S.; Wegman-Ostrosky, T.; Ayuzo Del Valle, N.C.; Perelman, C.; Sepulveda, R.; Rebolledo, P.A.; Cuapio, A.; Villapol, S. Long-COVID in children and adolescents: A systematic review and meta-analyses. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 9950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiq, M.A.B.; Rathore, F.A.; Clegg, D.; Rasker, J.J. Pulmonary Rehabilitation in COVID-19 patients: A scoping review of current practice and its application during the pandemic. Turk. J. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 2020, 66, 480–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbannaa, R.H.; Mogahed, H.; Zahran, M.; Mohame, E. The effect of photobiomodulation versus placebo on functional capacity and fatigability in post COVID-19 elderly. Adv. Rehab. 2022, 36, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agostini, F.; Mangone, M.; Ruiu, P.; Paolucci, T.; Santilli, V.; Bernetti, A. Rehabilitation setting during and after COVID-19: An overview on recommendations. J. Rehabil. Med. 2021, 53, jrm00141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogonowska-Slodownik, A. The Use of Aquatic Environment for Children with Disabilities. Palaestra 2022, 36, 24–30. [Google Scholar]
- Westergren, T.; Fegran, L.; Nilsen, T.; Haraldstad, K.; Kittang, O.B.; Berntsen, S. Active play exercise intervention in children with asthma: A PILOT STUDY. BMJ Open 2016, 6, e009721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ogonowska-Slodownik, A.; Labecka, M.K.; Kaczmarczyk, K.; McNamara, R.J.; Starczewski, M.; Gajewski, J.; Maciejewska-Skrendo, A.; Morgulec-Adamowicz, N. Water-Based and Land-Based Exercise for Children with Post-COVID-19 Condition (postCOVIDkids)-Protocol for a Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yelling, M.; Lamb, K.L.; Swaine, I.L. Validity of a Pictorial Perceived Exertion Scale for Effort Estimation and Effort Production During Stepping Exercise in Adolescent Children. Eur. Phys. Educ. Rev. 2002, 8, 157–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinov, B.; Kostianev, S.; Turnovska, T. Modified treadmill protocol for evaluation of physical fitness in pediatric age group--comparison with Bruce and Balke protocols. Acta Physiol. Pharmacol. Bulg. 2003, 27, 47–51. [Google Scholar]
- Kulik, A.; Szewczyk, L. Fatigue survey questionnaire. Psychometric properties. In Selected Issues in Clinical and Personality Psychology. Diagnostic Methods in the Study of Children and Adolescents; Oleś, M., Ed.; TN KUL: Lublin, Poland, 2005; pp. 41–61. [Google Scholar]
- Talarska, D.; Michalak, M.; Talarska, P.; Steinborn, B. Children with epilepsy against their healthy peers and those with headaches: Differences-similarities. Neurol. Neurochir. Pol. 2018, 52, 35–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landis, J.R.; Koch, G.G. The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 1977, 33, 159–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varni, J.W.; Burwinkle, T.M.; Seid, M.; Skarr, D. The PedsQL 4.0 as a pediatric population health measure: Feasibility, reliability, and validity. Ambul. Pediatr. 2003, 3, 329–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer, K.C. Pulmonary fibrosis, part I: Epidemiology, pathogenesis, and diagnosis. Expert. Rev. Respir. Med. 2017, 11, 343–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirza, S.; Clay, R.D.; Koslow, M.A.; Scanlon, P.D. COPD Guidelines: A Review of the 2018 GOLD Report. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2018, 93, 1488–1502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buonsenso, D.; Di Giuda, D.; Sigfrid, L.; Pizzuto, D.A.; Di Sante, G.; De Rose, C.; Lazzareschi, I.; Sali, M.; Baldi, F.; Chieffo, D.P.R.; et al. Evidence of lung perfusion defects and ongoing inflammation in an adolescent with post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Lancet Child. Adolesc. Health 2021, 5, 677–680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard-Jones, A.R.; Burgner, D.P.; Crawford, N.W.; Goeman, E.; Gray, P.E.; Hsu, P.; Kuek, S.; McMullan, B.J.; Tosif, S.; Wurzel, D.; et al. COVID-19 in children. II: Pathogenesis, disease spectrum and management. J. Paediatr. Child. Health 2022, 58, 46–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The Lancet. Understanding long COVID: A modern medical challenge. Lancet 2021, 398, 725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vestbo, J.; Hurd, S.S.; Agustí, A.G.; Jones, P.W.; Vogelmeier, C.; Anzueto, A.; Barnes, P.J.; Fabbri, L.M.; Martinez, F.J.; Nishimura, M.; et al. Global strategy for the diagnosis, management, and prevention of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: GOLD executive summary. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2013, 187, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borghi-Silva, A.; Arena, R.; Castello, V.; Simões, R.P.; Martins, L.E.; Catai, A.M.; Costa, D. Aerobic exercise training improves autonomic nervous control in patients with COPD. Respir. Med. 2009, 103, 1503–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, P.; Li, N.; Wang, Z.; Wu, W.; Wang, J. Rehabilitation effects of land and water-based aerobic exercise on lung function, dyspnea, and exercise capacity in patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Medicine 2021, 100, e26976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNamara, R.J.; McKeough, Z.J.; McKenzie, D.K.; Alison, J.A. Water-based exercise training for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 12, Cd008290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wootton, S.L.; Ng, L.W.; McKeough, Z.J.; Jenkins, S.; Hill, K.; Eastwood, P.R.; Hillman, D.R.; Cecins, N.; Spencer, L.M.; Jenkins, C.; et al. Ground-based walking training improves quality of life and exercise capacity in COPD. Eur. Respir. J. 2014, 44, 885–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Pérez-de-Sevilla, G.; Yvert, T.; Blanco, Á.; Sosa Pedreschi, A.I.; Thuissard, I.J.; Pérez-Ruiz, M. Effectiveness of Physical Exercise Interventions on Pulmonary Function and Physical Fitness in Children and Adults with Cystic Fibrosis: A Systematic Review with Meta-Analysis. Healthcare 2022, 10, 2205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Zhang, D.; Huang, Y.; Wu, Z.; Zhang, W. Exercise rehabilitation in pediatric asthma: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Pediatr. Pulmonol. 2022, 57, 2915–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porto, E.F.; Castro, A.A.; Schmidt, V.G.; Rabelo, H.M.; Kümpel, C.; Nascimento, O.A.; Jardim, J.R. Postural control in chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A systematic review. Int. J. Chron. Obs. Pulmon Dis. 2015, 10, 1233–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ringbaek, T.; Brondum, E.; Martinez, G.; Thogersen, J.; Lange, P. Long-term effects of 1-year maintenance training on physical functioning and health status in patients with COPD: A randomized controlled study. J. Cardiopulm. Rehabil. Prev. 2010, 30, 47–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zisi, D.; Chryssanthopoulos, C.; Nanas, S.; Philippou, A. The effectiveness of the active cycle of breathing technique in patients with chronic respiratory diseases: A systematic review. Heart Lung 2022, 53, 89–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shead, D.; Aswegen, H.V. Hydrotherapy in the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease: A qualitative systematic review. Phys. Ther. Rev. 2012, 17, 271–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geytenbeek, J. Evidence of effective hydrotherapy. Physiotherapy 2002, 88, 514–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Andrade, A.D.; Júnior, J.C.; Lins de Barros Melo, T.L.; Rattes Lima, C.S.; Brandão, D.C.; de Melo Barcelar, J. Influence of different levels of immersion in water on the pulmonary function and respiratory muscle pressure in healthy individuals: Observational study. Physiother. Res. Int. 2014, 19, 140–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rae, S.; White, P. Swimming pool-based exercise as pulmonary rehabilitation for COPD patients in primary care: Feasibility and acceptability. Prim. Care Respir. J. 2009, 18, 90–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conijn, J.M.; Smits, N.; Hartman, E.E. Determining at What Age Children Provide Sound Self-Reports: An Illustration of the Validity-Index Approach. Assessment 2020, 27, 1604–1618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cremeens, J.; Eiser, C.; Blades, M. Factors influencing agreement between child self-report and parent proxy-reports on the Pediatric Quality of Life Inventory 4.0 (PedsQL) generic core scales. Health Qual. Life Outcomes 2006, 4, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| AQUA (n = 25) | LAND (n = 23) | CONTROL (n = 26) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Female, n (%) | 15 (60) | 14 (61) | 14 (54) |
| Age (years) | 10.8 (0.8) | 11.0 (0.7) | 10.6 (1.0) |
| Body mass (kg) | 45.2 (14.1) | 43.4 (1.6) | 38.3 (9.5) |
| Height (m) | 1.52 (0.1) | 1.52 (0.1) | 1.46 (0.1) |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 19.3 (4.6) | 18.7 (3.7) | 17.9 (3.6) |
| AQUA | LAND | CONTROL | F2,64 | p | ƞ2 | Between-Group Difference Post-Intervention (95% CI) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AQUA vs. LAND | AQUA vs. CONTROL | LAND vs. CONTROL | ||||||||
| (n = 25) | (n = 23) | (n = 26) | ||||||||
| VO2max (mL/kg/min) | Pre | 40.0 (7.0) | 42.9 (8.3) | 41.6 (6.9) | 4.32 | 0.017 | 0.11 | 2.9 (−1.5 to 7.3) | 1.6 (−2.3 to 5.5.) | 1.3 (−3.1 to 5.7) |
| Post | 42.6 (7.5) a | 45.5 (7.8) | 41.2 (6.8) | 2.9 (−1.5 to 7.4) | 1.4 (−2.6 to 5.4) | 4.3 (0.01. to 8.6) | ||||
| VE (L/min) | Pre | 61.4 (17.4) | 60.7 (9.8) | 54.3 (11.0) | 9.60 | 0.001 | 0.22 | 0.7 (−7.6 to 8.9) | 7.1 (−1.1 to 15.3) | 6.4 (0.4 to 12.5) |
| Post | 69.6 (18.3) a | 68.7 (13.0) b | 53.1 (10.7) c,d | 0.9 (−8.5 to 10.2) | 16.5 (8.0 to 24.9) | 15.6 (8.7 to 22.5) | ||||
| HRmax (beats/min) | Pre | 189 (14) | 195 (6) | 190 (14) | 2.90 | 0.062 | 0.08 | 6.1 (−0.2 to 12.5) | 1.0 (−6.7 to 8.8) | 5.1 (−1.0 to 11.3) |
| Post | 192 (12) | 191 (17) | 187 (13) | 1.8 (−6.9 to 10.6) | 5.4 (−1.6 to 12.6) | 3.6 (−5.5 to 12.8) | ||||
| OUES (L/min) | Pre | 2.14 (0.5) | 2.29 (0.5) | 2.08 (0.5) | 2.95 | 0.059 | 0.08 | 0.1 (−0.1 to 0.5) | 0.1 (−0.2 to −0.3) | 0.2 (−0.1 to 0.5) |
| Post | 2.27 (0.6) | 2.23 (0.5) | 2.05 (0.5) | 0.04 (−0.3 to 0.4) | 0.2 (−0.1 to 0.5) | 0.2 (−0.1 to 0.5) | ||||
| OUES (mL/kg/min) | Pre | 48.6 (7.9) | 55.0 (11.3) | 55.0 (11.6) | 1.97 | 0.147 | 0.06 | 6.3 (0.8 to 11.9) | 6.4 (0.8 to 11.9) | 0.03 (−6.6 to 6.7) |
| Post | 50.1 (7.8) | 52.8 (9.6) | 52.8 (10.6) | 2.7 (−2.3 to 7.8) | 2.7 (−2.5 to 7.9) | 0.04 (−5.9 to 6.0) | ||||
| RER | Pre | 0.98 (0.1) | 0.99 (0.1) | 0.98 (0.1) | 0.48 | 0.623 | 0.01 | 0.006 (−0.03 to 0.04) | 0.004 (−0.03 to 0.04) | 0.01 (−0.01 to 0.03) |
| Post | 1.02 (0.05) | 1.02 (0.03) | 1.00 (0.04) | 0.003 (−0.02 to 0.03) | 0.02 (−0.003 to 0.05) | 0.02 (−0.003 to 0.04) | ||||
| Total fatigue (pts) | Pre | 16.9 (9.8) | 15.3 (8.0) | 15.1 (8.1) | 0.165 | 0.848 | 0.005 | 1.6 (−3.5 to 6.7) | 1.8 (−3.1 to 6.7) | 0.2 (−4.3 to 4.7) |
| Post | 15.1 (8.5) | 13.8 (8.5) | 14.2 (9.4) | 1.2 (−3.6 to 6.1) | 0.8 (−4.1 to 5.8) | 0.4 (−4.6 to 5.4) | ||||
| Total score PedsQL children | Pre | 74.6 (13.1) | 77.3 (11.6) | 76.1 (9.7) | 0.324 | 0.724 | 0.009 | 2.6 (−4.4 to 9.6) | 1.5 (−4.8 to 7.8) | 1.1 (−4.8 to 7.1) |
| Post | 74.3 (13.3) | 78.7 (11.9) | 77.1 (12.2) | 4.3 (−2.8 to 11.5) | 2.7 (−4.3 to 9.7) | 1.6 (−5.2 to 8.4) | ||||
| Total score PedsQL parent | Pre | 66.5 (13.6) | 68.7 (13.5) | 70.6 (17.7) | 2.449 | 0.094 | 0.067 | 2.2 (−5.6 to 9.9) | 4.0 (−4.7 to 12.8) | 1.9 (−7.2 to 10.9) |
| Post | 71.9 (11.9) | 79.2 (9.9) b | 71.8 (17.2) | 7.2 (0.9 to 13.5) | 0.2 (−8.1 to 8.4) | 7.4 (−0.6 to 15.4) | ||||
| Fatigue Level | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (0–14 Points) | Moderate (15–30 Points) | High (31–45 Points) | ||||
| PRE (n/%) | POST (n/%) | PRE (n/%) | POST (n/%) | PRE (n/%) | POST (n/%) | |
| LAND (n = 23) | 8/35 | 12/52 | 14/61 | 10/44 | 1/4 | 1/4 |
| AQUA (n = 25) | 11/44 | 14/56 | 11/44 | 10/40 | 3/12 | 1/4 |
| CONTROL (n = 26) | 15/58 | 17/65 | 9/34 | 6/23 | 2/8 | 3/12 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ogonowska-Slodownik, A.; Labecka, M.K.; Maciejewska-Skrendo, A.; McNamara, R.J.; Kaczmarczyk, K.; Starczewski, M.; Gajewski, J.; Morgulec-Adamowicz, N. Effect of Water-Based vs. Land-Based Exercise Intervention (postCOVIDkids) on Exercise Capacity, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Children with Post COVID-19 Condition: A Randomized Controlled Trial. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 6244. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196244
Ogonowska-Slodownik A, Labecka MK, Maciejewska-Skrendo A, McNamara RJ, Kaczmarczyk K, Starczewski M, Gajewski J, Morgulec-Adamowicz N. Effect of Water-Based vs. Land-Based Exercise Intervention (postCOVIDkids) on Exercise Capacity, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Children with Post COVID-19 Condition: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(19):6244. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196244
Chicago/Turabian StyleOgonowska-Slodownik, Anna, Marta Kinga Labecka, Agnieszka Maciejewska-Skrendo, Renae J. McNamara, Katarzyna Kaczmarczyk, Michał Starczewski, Jan Gajewski, and Natalia Morgulec-Adamowicz. 2023. "Effect of Water-Based vs. Land-Based Exercise Intervention (postCOVIDkids) on Exercise Capacity, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Children with Post COVID-19 Condition: A Randomized Controlled Trial" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 19: 6244. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196244
APA StyleOgonowska-Slodownik, A., Labecka, M. K., Maciejewska-Skrendo, A., McNamara, R. J., Kaczmarczyk, K., Starczewski, M., Gajewski, J., & Morgulec-Adamowicz, N. (2023). Effect of Water-Based vs. Land-Based Exercise Intervention (postCOVIDkids) on Exercise Capacity, Fatigue, and Quality of Life in Children with Post COVID-19 Condition: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(19), 6244. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12196244







