Clinical Performance of the Gore Septal Occluder in Patent Foramen Ovale Closure in Different Septal Anatomies: 1-Year Results from a Single-Center Experience
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population and Imaging
2.2. Procedural Details
2.3. Endpoint and Follow-Up
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Population Characteristics: Clinical and Echocardiography
3.2. Outcomes and Correlates
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- El-Said, H.G.; Moore, J.W. Erosion by the Amplatzer Septal Occluder: Experienced Operator Opinions at Odds with Manufacturer Recommendations? Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2009, 73, 925–930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schoen, S.P.; Boscheri, A.; Lange, S.A.; Braun, M.U.; Fuhrmann, J.; Kappert, U.; Strasser, R.H. Incidence of Aortic Valve Regurgitation and Outcome after Percutaneous Closure of Atrial Septal Defects and Patent Foramen Ovale. Heart 2008, 94, 844–847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahn, E.M.; Wilson, N.; Cutright, W.; Latson, L.A. Development and Testing of the Helex Septal Occluder, a New Expanded Polytetrafluoroethylene Atrial Septal Defect Occlusion System. Circulation 2001, 104, 711–716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pristipino, C.; Sievert, H.; D’Ascenzo, F.; Louis Mas, J.; Meier, B.; Scacciatella, P.; Hildick-Smith, D.; Gaita, F.; Toni, D.; Kyrle, P.; et al. European Position Paper on the Management of Patients with Patent Foramen Ovale. General Approach and Left Circulation Thromboembolism. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3182–3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thaman, R.; Faganello, G.; Gimeno, J.R.; Szantho, G.V.; Nelson, M.; Curtis, S.; Martin, R.P.; Turner, M.S. Efficacy of Percutaneous Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale: Comparison among Three Commonly Used Occluders. Heart 2011, 97, 394–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Bardeleben, R.S.; Richter, C.; Otto, J.; Himmrich, L.; Schnabel, R.; Kampmann, C.; Rupprecht, H.J.; Marx, J.; Hommel, G.; Münzel, T.; et al. Long Term Follow up after Percutaneous Closure of PFO in 357 Patients with Paradoxical Embolism: Difference in Occlusion Systems and Influence of Atrial Septum Aneurysm. Int. J. Cardiol. 2009, 134, 33–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sganzerla, P.; Rondi, M.; Pavone, A.; Aiolfi, E.; Facchinetti, A.; Funaro, A.; Negrini, P. Clinical Performance of the New Gore Septal Occluder in Patent Foramen Ovale Closure: A Single-Center Experience. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2015, 27, 430–434. [Google Scholar]
- Butera, G.; Saracino, A.; Danna, P.; Sganzerla, P.; Chessa, M.; Carminati, M. Transcatheter PFO Closure with GORE® Septal Occluder: Early and Mid-Term Clinical Results. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 82, 944–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Søndergaard, L.; Kasner, S.E.; Rhodes, J.F.; Andersen, G.; Iversen, H.K.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Settergren, M.; Sjöstrand, C.; Roine, R.O.; Hildick-Smith, D.; et al. Patent Foramen Ovale Closure or Antiplatelet Therapy for Cryptogenic Stroke. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 1033–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, B.S.; Shapiro, L.M.; McCarthy, K.P.; Ho, S.Y. Three-Dimensional Imaging of the Atrial Septum and Patent Foramen Ovale Anatomy: Defining the Morphological Phenotypes of Patent Foramen Ovale. Eur. J. Echocardiogr. 2010, 11, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rana, B.S.; Thomas, M.R.; Calvert, P.A.; Monaghan, M.J.; Hildick-Smith, D. Echocardiographic Evaluation of Patent Foramen Ovale Prior to Device Closure. JACC Cardiovasc. Imaging 2010, 3, 749–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pizzino, F.; Khandheria, B.; Carerj, S.; Oreto, G.; Cusmà-Piccione, M.; Todaro, M.C.; Oreto, L.; Vizzari, G.; Di Bella, G.; Zito, C. PFO: Button Me up, but Wait. Comprehensive Evaluation of the Patient. J. Cardiol. 2016, 67, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheli, M.; Canepa, M.; Brunelli, C.; Bezante, G.P.; Favorini, S.; Rollando, D.; Sivori, G.; Viani, E.; Finocchi, C.; Balbi, M. Recurrent and Residual Shunts after Patent Foramen Ovale Closure: Results from a Long-Term Transcranial Doppler Study. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2015, 28, 600–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kavinsky, C.J.; Szerlip, M.; Goldsweig, A.M.; Amin, Z.; Boudoulas, K.D.; Carroll, J.D.; Coylewright, M.; Elmariah, S.; MacDonald, L.A.; Shah, A.P.; et al. SCAI Guidelines for the Management of Patent Foramen Ovale. J. Soc. Cardiovasc. Angiogr. Interv. 2022, 1, 100039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vitarelli, A.; Mangieri, E.; Capotosto, L.; Tanzilli, G.; D’Angeli, I.; Toni, D.; Azzano, A.; Ricci, S.; Placanica, A.; Rinaldi, E.; et al. Echocardiographic Findings in Simple and Complex Patent Foramen Ovale before and after Transcatheter Closure. Eur. Heart J. Cardiovasc. Imaging 2014, 15, 1377–1385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Cheng, G.; Du, Y.; Zhang, Y. Importance of Persistent Right-to-Left Shunt After Patent Foramen Ovale Closure in Cryptogenic Stroke Patients. Tex. Heart Inst. J. 2020, 47, 244–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, A.C.; Lock, J.E. Structural and Compliant Anatomy of the Patent Foramen Ovale in Patients Undergoing Transcatheter Closure. Am. Heart J. 2000, 140, 303–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vizzari, G.; Pizzino, F.; Zwicke, D.; Tajik, A.J.; Carerj, S.; Di Bella, G.; Micari, A.; Khandheria, B.K.; Zito, C. Patent Foramen Ovale: Anatomical Complexity and Long-Tunnel Morphology Related Issues. Am. J. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2021, 11, 316–329. [Google Scholar]
- Lou, Y.; Hua, Y.; Shi, J.; Yang, F.; Wang, Y.; Yang, Y.; Sun, W.; Kong, X.; Zhang, H. Comparison of the Short-Term Efficacy of Different Amplatzer Models and Similar Occluders in the Treatment of Patent Foramen Ovale. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2023, 10, 1092465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvert, P.A.; Rana, B.S.; Kydd, A.C.; Shapiro, L.M. Patent Foramen Ovale: Anatomy, Outcomes, and Closure. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2011, 8, 148–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geis, N.A.; Pleger, S.T.; Katus, H.A.; Hardt, S.E. Using the GORE® Septal Occluder (GSO) in Challenging Patent Foramen Ovale (PFO) Anatomies. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2015, 28, 190–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lockhart, C.J.; Johnston, N.G.; Spence, M.S. Experience Using the New GORE® Septal Occluder at the Margins. Catheter. Cardiovasc. Interv. 2013, 81, 1244–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greutmann, M.; Greutmann-Yantiri, M.; Kretschmar, O.; Senn, O.; Roffi, M.; Jenni, R.; Luescher, T.F.; Eberli, F.R. Percutaneous PFO Closure with Amplatzer PFO Occluder: Predictors of Residual Shunts at 6 Months Follow-Up. Congenit. Heart Dis. 2009, 4, 252–257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giordano, M.; Gaio, G.; Santoro, G.; Palladino, M.T.; Sarubbi, B.; Golino, P.; Russo, M.G. Patent Foramen Ovale with Complex Anatomy: Comparison of Two Different Devices (Amplatzer Septal Occluder Device and Amplatzer PFO Occluder Device 30/35). Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 279, 47–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefebvre, B.; Naidu, S.; Nathan, A.S.; Chen, Z.; Ky, B.; Silvestry, F.E.; Søndergaard, L.; Settergren, M.; Nielsen-Kudsk, J.E.; Rhodes, J.F.; et al. Impact of Echocardiographic Parameters on Recurrent Stroke in the Randomized REDUCE PFO Cryptogenic Stroke Trial. Struct. Heart 2021, 5, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Musto, C.; Cifarelli, A.; Dipasquale, F.; Chin, D.; Nazzaro, M.S.; Stio, R.E.; Pennacchi, M.; De Felice, F. A Comparison Between Gore Cardioform and Amplatzer Septal Occluder for Percutaneous Closure of Patent Foramen Ovale Associated With Atrial Septal Aneurysm: Clinical and Echocardiographic Outcomes. J. Invasive Cardiol. 2021, 33, E857–E862. [Google Scholar]

| Patient Population (n) | 118 |
|---|---|
| Male gender (n) | 60 (50.8%) |
| Age (years) | 55.4 ± 12.7 |
| Current smoker (n, %) | 19 (16.1%) |
| Indication for closure | |
| Stroke (n, %) | 68 (57.6%) |
| Transient Ischemic Attack (n, %) | 50 (42.4%) |
| Head CT or MRI de-novo lesion (n, %) | 101 (85.6%) |
| TEE Doppler study | |
| Small shunt (n, %) | 15 (12.7%) |
| Moderate-to-severe shunt (n, %) | 37 (31.4%) |
| Anatomical setting | |
| PFO only (n, %) | 99 (84%) |
| PFO + ASA (n, %) | 19 (16%) |
| Median procedure time (minutes) | 37 (range 33–45) |
| Median fluoroscopic time (minutes) | 7.3 (range 5.5–10.2) |
| Device used | |
| 20 mm (n, %) | 6 (5.0%) |
| 25 mm (n, %) | 92 (78%) |
| 30 mm (n, %) | 20 (17%) |
| Median contrast administration (mL) | 36 (range 25–54) |
| Complex Anatomy (n. 57) | Simple Anatomy (n. 54) | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 53.9 ± 12.4 | 56.6 ± 13.0 | 0.279 |
| Procedure time (min) | 39.6 ± 12.1 | 41.5 ± 15.2 | 0.502 |
| Fluoroscopy time (min) | 10.1 ± 16.5 | 9.4 ± 5.8 | 0.748 |
| Contrast dye (mL) | 38.2 ± 26.1 | 47.1 ± 26.1 | 0.090 |
| SS thickness (mm) | 5.7 ± 2.3 | 5.7 ± 1.9 | 0.995 |
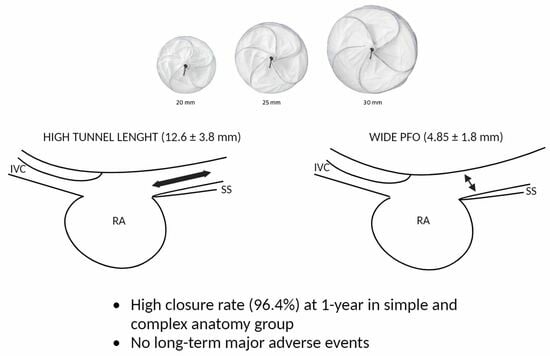
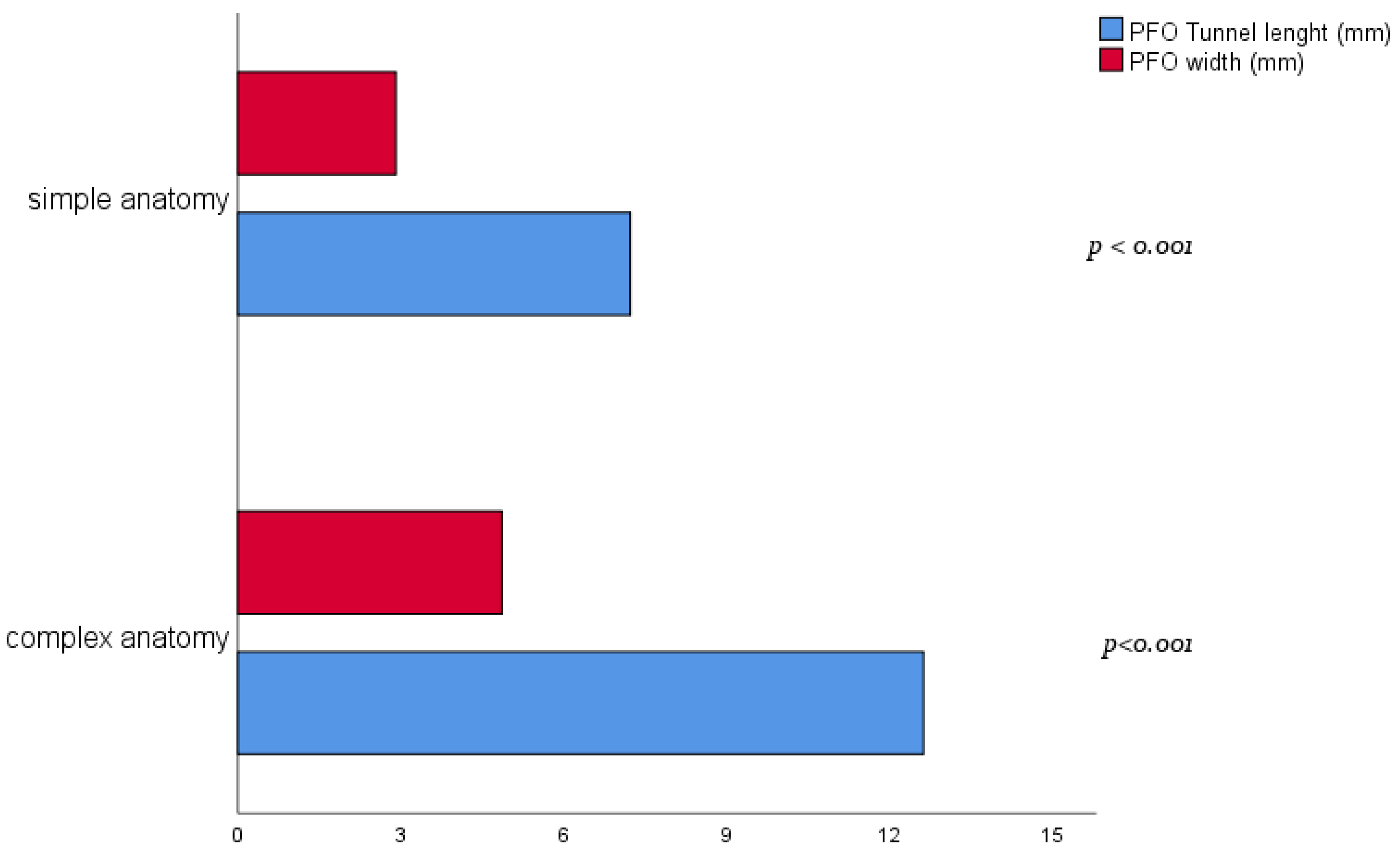
| Tunnel length (mm) | 12.6 ± 3.8 | 7.2 ± 2.0 | <0.001 |
| PFO width (mm) | 4.9 ± 1.8 | 2.9 ± 1.1 | <0.001 |
| Predictor | Anatomical or Functional Closure at 12-m (%) | OR | C.I. 95% | p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Complex vs. simple anatomy * | 107/111 (96.4%) | 0.36 | 0.04–3.6 | 0.39 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Verolino, G.; Calderone, D.; Gavazzoni, M.; Sala, D.; Sganzerla, P. Clinical Performance of the Gore Septal Occluder in Patent Foramen Ovale Closure in Different Septal Anatomies: 1-Year Results from a Single-Center Experience. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5936. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185936
Verolino G, Calderone D, Gavazzoni M, Sala D, Sganzerla P. Clinical Performance of the Gore Septal Occluder in Patent Foramen Ovale Closure in Different Septal Anatomies: 1-Year Results from a Single-Center Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(18):5936. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185936
Chicago/Turabian StyleVerolino, Giuseppe, Dario Calderone, Mara Gavazzoni, Davide Sala, and Paolo Sganzerla. 2023. "Clinical Performance of the Gore Septal Occluder in Patent Foramen Ovale Closure in Different Septal Anatomies: 1-Year Results from a Single-Center Experience" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 18: 5936. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185936
APA StyleVerolino, G., Calderone, D., Gavazzoni, M., Sala, D., & Sganzerla, P. (2023). Clinical Performance of the Gore Septal Occluder in Patent Foramen Ovale Closure in Different Septal Anatomies: 1-Year Results from a Single-Center Experience. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(18), 5936. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185936