Comparing High- and Low-Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Living-Donor Liver Transplantation to Determine Clinical Efficacy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (CHALICE Study)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methods
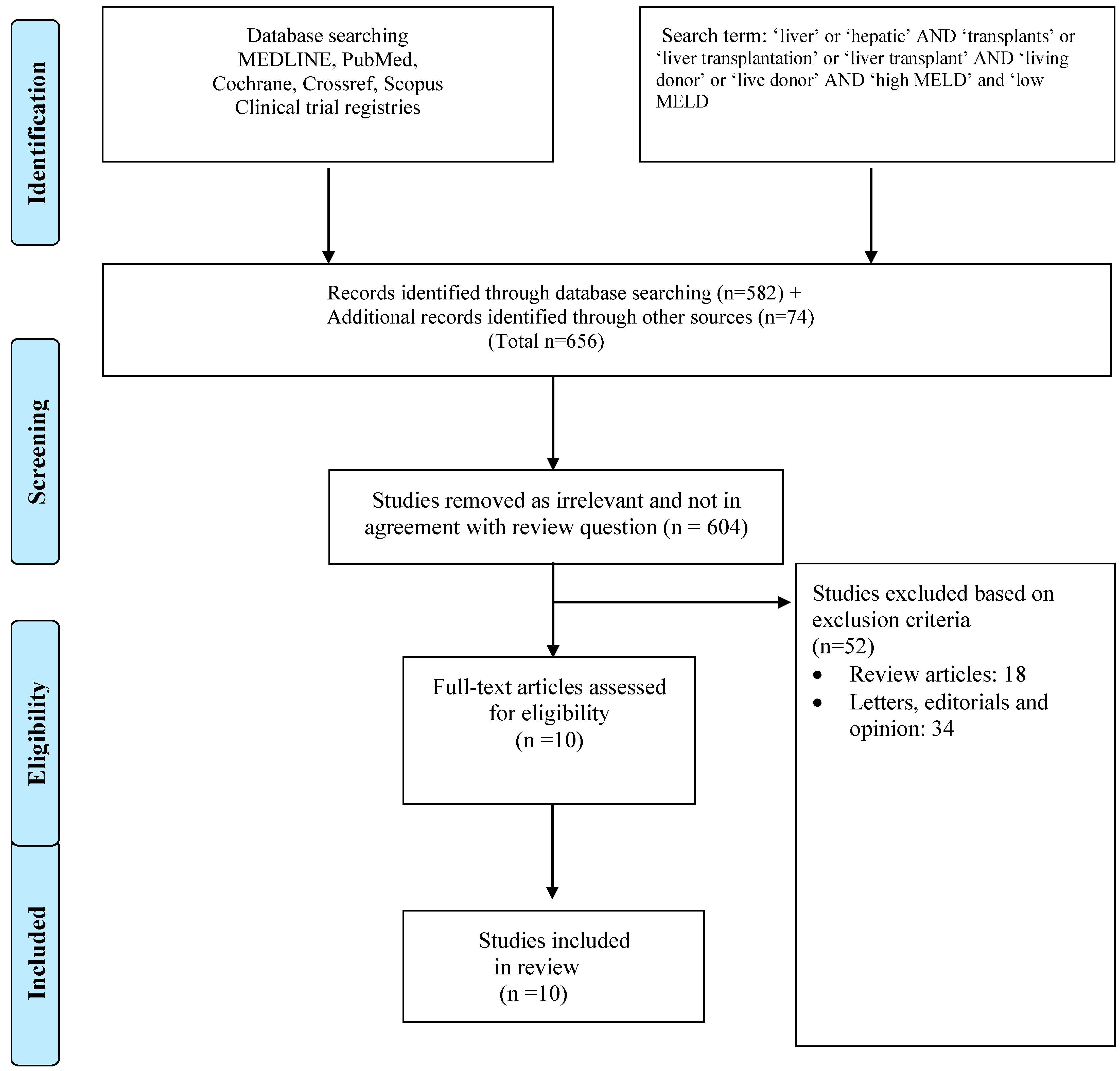
2.1. Literature Search Methodology
2.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria for Study Selection
2.3. Data Extraction and Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Review of the Literature
3.2. Patient Population Characteristics
3.3. Preoperative Characteristics
3.4. Survival Outcomes
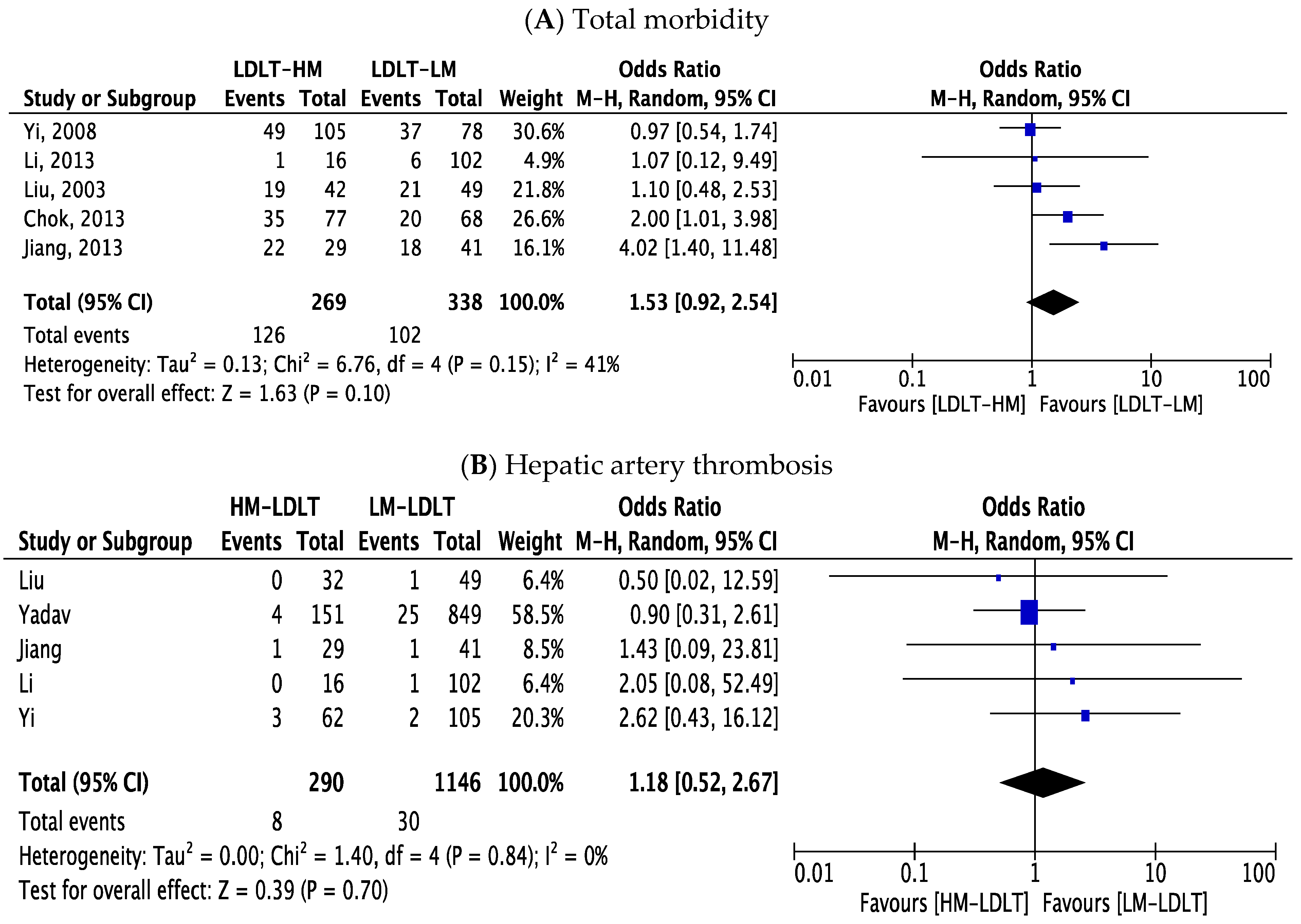
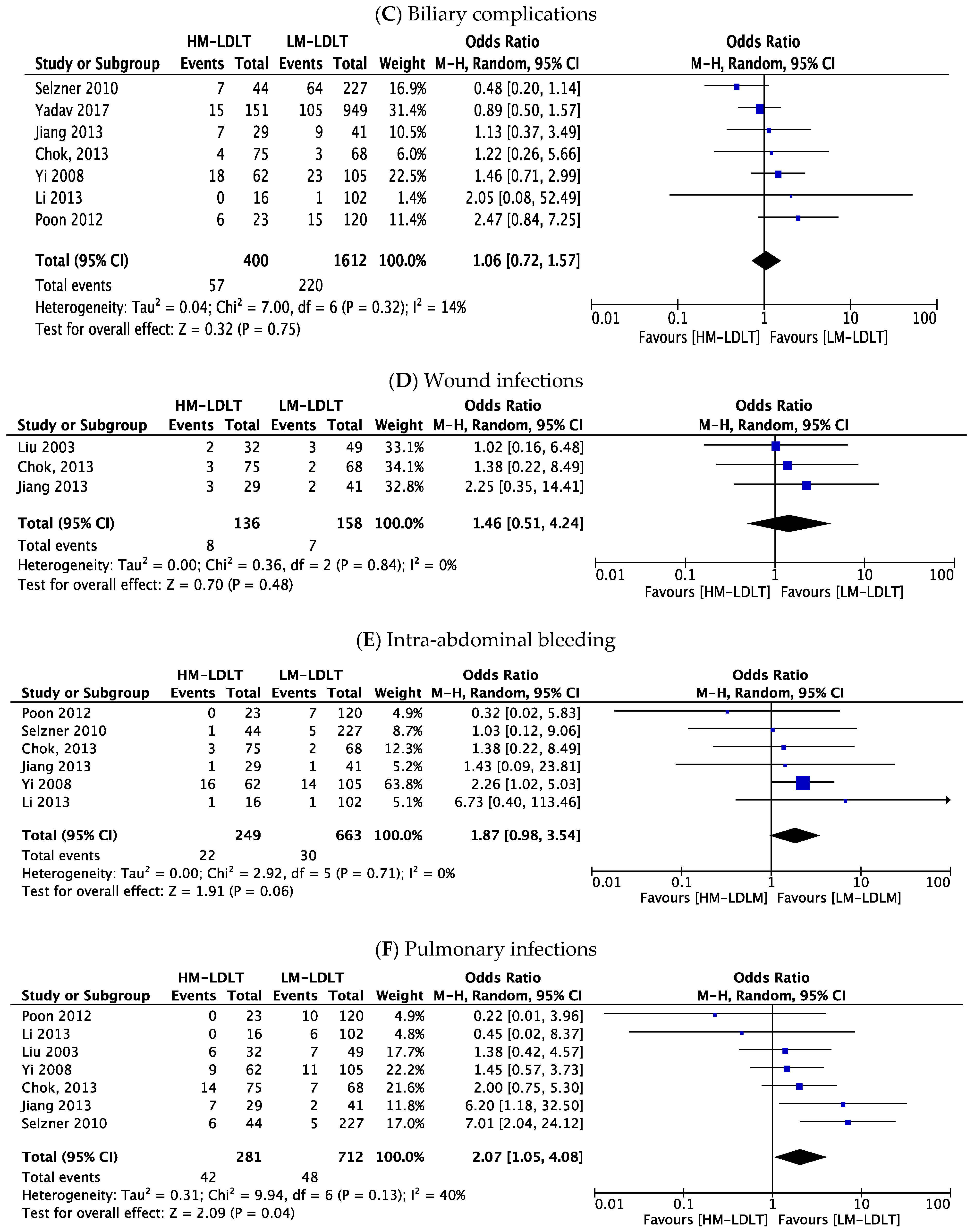
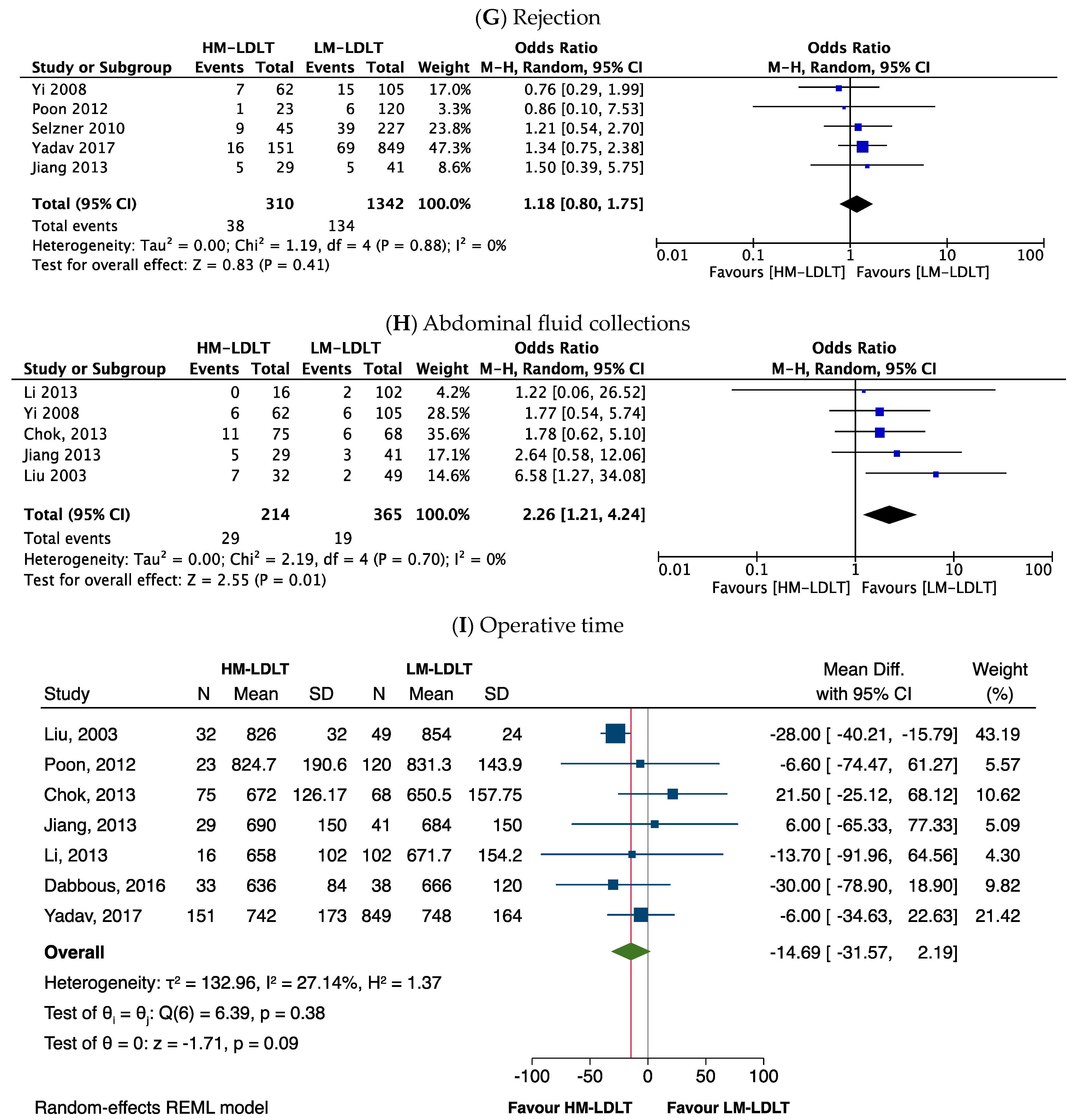
3.5. Perioperative Outcomes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abu-Gazala, S.; Olthoff, K.M. Current Status of Living Donor Liver Transplantation in the United States. Annu. Rev. Med. 2019, 70, 225–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cotter, T.G.; Minhem, M.; Wang, J.; Peeraphatdit, T.; Ayoub, F.; Pillai, A.; Hernandez-Alejandro, R.; di Sabato, D.; Charlton, M. Living Donor Liver Transplantation in the United States: Evolution of Frequency, Outcomes, Center Volumes, and Factors Associated with Outcomes. Liver Transplant. 2021, 27, 1019–1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gruessner, R.W.G.; Gruessner, A.C. Solid-organ Transplants from Living Donors: Cumulative United States Experience on 140,156 Living Donor Transplants Over 28 Years. Transplant. Proc. 2018, 50, 3025–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudow, D.L.; Brown, R.S., Jr. Evaluation of living liver donors. Prog. Transplant. 2003, 13, 110–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernaez, R.; Liu, Y.; Kramer, J.R.; Rana, A.; El-Serag, H.B.; Kanwal, F. Model for end-stage liver disease-sodium underestimates 90-day mortality risk in patients with acute-on-chronic liver failure. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, Q.; Sapisochin, G.; Gorgen, A.; Vitale, A.; Halazun, K.J.; Iesari, S.; Schaefer, B.; Bhangui, P.; Mennini, G.; Wong, T.C.; et al. Evaluation of the Intention-to-Treat Benefit of Living Donation in Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma Awaiting a Liver Transplant. JAMA Surg. 2021, 156, e213112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Humar, A.; Ganesh, S.; Jorgensen, D.; Tevar, A.; Ganoza, A.; Molinari, M.; Hughes, C. Adult Living Donor Versus Deceased Donor Liver Transplant (LDLT Versus DDLT) at a Single Center: Time to Change Our Paradigm for Liver Transplant. Ann. Surg. 2019, 270, 444–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbetta, A.; Aljehani, M.; Kim, M.; Tien, C.; Ahearn, A.; Schilperoort, H.; Sher, L.; Emamaullee, J. Meta-analysis and meta-regression of outcomes for adult living donor liver transplantation versus deceased donor liver transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2021, 21, 2399–2412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.P.; Kwon, H.Y.; Park, J.I.; Yi, N.J.; Suh, K.S.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, M.; Oh, Y.K.; Lim, C.S.; Kim, Y.S. Clinical outcomes of patients with hepatorenal syndrome after living donor liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2012, 18, 1237–1244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shukla, A.; Vadeyar, H.; Rela, M.; Shah, S. Liver Transplantation: East versus West. J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2013, 3, 243–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mueller, M.; D’Addario, M.; Egger, M.; Cevallos, M.; Dekkers, O.; Mugglin, C.; Scott, P. Methods to systematically review and meta-analyse observational studies: A systematic scoping review of recommendations. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2018, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, M.J.; Shamseer, L.; Altman, D.G.; Tetzlaff, J.; Sampson, M.; Tricco, A.C.; Catala-Lopez, F.; Li, L.; Reid, E.K.; Sarkis-Onofre, R.; et al. Epidemiology and Reporting Characteristics of Systematic Reviews of Biomedical Research: A Cross-Sectional Study. PLoS Med. 2016, 13, e1002028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavien, P.A.; Barkun, J.; De Oliveira, M.L.; Vauthey, J.N.; Dindo, D.; Schulick, R.D.; De Santibañes, E.; Pekolj, J.; Slankamenac, K.; Bassi, C.; et al. The Clavien-Dindo classification of surgical complications: Five-year experience. Ann. Surg. 2009, 250, 187–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hozo, S.P.; Djulbegovic, B.; Hozo, I. Estimating the mean and variance from the median, range, and the size of a sample. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2005, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goel, M.K.; Khanna, P.; Kishore, J. Understanding survival analysis: Kaplan-Meier estimate. Int. J. Ayurveda Res. 2010, 1, 274–278. [Google Scholar]
- Austin, P.C.; Wagner, P.; Merlo, J. The median hazard ratio: A useful measure of variance and general contextual effects in multilevel survival analysis. Stat. Med. 2017, 36, 928–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drukker, M.; Weltens, I.; van Hooijdonk, C.F.M.; Vandenberk, E.; Bak, M. Development of a Methodological Quality Criteria List for Observational Studies: The Observational Study Quality Evaluation. Front. Res. Metr. Anal. 2021, 6, 675071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Kwong, J.S.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Sun, F.; Niu, Y.; Du, L. The methodological quality assessment tools for preclinical and clinical studies, systematic review and meta-analysis, and clinical practice guideline: A systematic review. J. Evid. Based Med. 2015, 8, 2–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baker, W.L.; Michael White, C.; Cappelleri, J.C.; Kluger, J.; Coleman, C.I. From the Health Outcomes, Policy, and Economics (HOPE) Collaborative Group. Understanding heterogeneity in meta-analysis: The role of meta-regression. Int. J. Clin. Pract. 2009, 63, 1426–1434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, F.; Sheldon, T.A.; Sutton, A.J.; Abrams, K.R.; Jones, D.R. Methods for exploring heterogeneity in meta-analysis. Eval. Health Prof. 2001, 24, 126–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.L.; Fan, S.T.; Lo, C.M.; Wei, W.I.; Yong, B.H.; Lai, C.L.; Wong, J. Live-donor liver transplantation for acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure. Transplantation 2003, 76, 1174–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshizumi, T.; Taketomi, A.; Soejima, Y.; Uchiyama, H.; Ikegami, T.; Harada, N.; Kayashima, H.; Yamashita, Y.I.; Shimada, M.; Maehara, Y. Impact of donor age and recipient status on left-lobe graft for living donor adult liver transplantation. Transplant. Int. 2008, 21, 81–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yi, N.J.; Suh, K.S.; Lee, H.W.; Shin, W.Y.; Kim, J.; Kim, W.; Kim, Y.J.; Yoon, J.H.; Lee, H.S.; Lee, K.U. Improved outcome of adult recipients with a high model for end-stage liver disease score and a small-for-size graft. Liver Transplant. 2009, 15, 496–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selzner, M.; Kashfi, A.; Cattral, M.S.; Selzner, N.; McGilvray, I.D.; Greig, P.D.; Levy, G.A.; Renner, E.L.; Grant, D.R. Live donor liver transplantation in high MELD score recipients. Ann. Surg. 2010, 251, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Poon, K.S.; Chen, T.H.; Jeng, L.B.; Yang, H.R.; Li, P.C.; Lee, C.C.; Yeh, C.C.; Lai, H.C.; Su, W.P.; Peng, C.Y.; et al. A high model for end-stage liver disease score should not be considered a contraindication to living donor liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2012, 44, 316–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chok, K.S.; Chan, S.C.; Fung, J.Y.; Cheung, T.T.; Chan, A.C.; Fan, S.T.; Lo, C.M. Survival outcomes of right-lobe living donor liver transplantation for patients with high Model for End-stage Liver Disease scores. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 2013, 12, 256–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, L.; Yan, L.; Tan, Y.; Li, B.; Wen, T.; Yang, J.; Zhao, J. Adult-to-adult right-lobe living donor liver transplantation in recipients with hepatitis B virus-related benign liver disease and high model end-stage liver disease scores. Surg. Today 2013, 43, 1039–1048. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Li, B.; Wei, Y.; Yan, L.; Wen, T.; Xu, M.; Wang, W.; Yang, J. Outcome of using small-for-size grafts in living donor liver transplantation recipients with high model for end-stage liver disease scores: A single center experience. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dabbous, H.; Sakr, M.; Abdelhakam, S.; Montasser, I.; Bahaa, M.; Said, H.; El-Meteini, M. Living donor liver transplantation for high model for end-stage liver disease score: What have we learned? World J. Hepatol. 2016, 8, 942–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yadav, S.K.; Saraf, N.; Saigal, S.; Choudhary, N.S.; Goja, S.; Rastogi, A.; Bhangui, P.; Soin, A.S. High MELD score does not adversely affect outcome of living donor liver transplantation: Experience in 1000 recipients. Clin. Transplant. 2017, 31, e13006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthoff, K.M.; Merion, R.M.; Ghobrial, R.M.; Abecassis, M.M.; Fair, J.H.; Fisher, R.A.; Freise, C.E.; Kam, I.; Pruett, T.L.; Everhart, J.E.; et al. Outcomes of 385 adult-to-adult living donor liver transplant recipients: A report from the A2ALL Consortium. Ann. Surg. 2005, 242, 314–323; discussion 23–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olthoff, K.M.; Smith, A.R.; Abecassis, M.; Baker, T.; Emond, J.C.; Berg, C.L.; Beil, C.A.; Burton, J.R., Jr.; Fisher, R.A.; Freise, C.E.; et al. Defining long-term outcomes with living donor liver transplantation in North America. Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 465–475; discussion 73–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tran, L.; Humar, A. Current status of adult liver transplantation: Utilization of living donor versus deceased donor graft. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2021, 26, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, H.J.; Roberts, J.P. Current status of left lobe adult to adult living donor liver transplantation. Curr. Opin. Organ. Transplant. 2021, 26, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Braun, H.J.; Dodge, J.L.; Grab, J.D.; Syed, S.M.; Roll, G.R.; Freise, C.E.; Roberts, J.P.; Ascher, N.L. Living Donor Liver Transplant for Alcoholic Liver Disease: Data from the Adult-to-adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation Study. Transplantation 2020, 104, 285–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imai, D.; Yoshizumi, T.; Sakata, K.; Ikegami, T.; Itoh, S.; Harada, N.; Motomura, T.; Toshima, T.; Mano, Y.; Soejima, Y.; et al. Long-term Outcomes and Risk Factors After Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation. Transplantation 2018, 102, e382–e391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abu-Gazala, S.; Olthoff, K.M. Status of Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation in the United States: Results from the Adult-To-Adult Living Donor Liver Transplantation Cohort Study. Gastroenterol. Clin. N. Am. 2018, 47, 297–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreno Gonzalez, E. Liver transplantation in adult, from living donor. A valid option. Cir. Esp. 2017, 95, 305–306. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.; Wang, X.; Wan, P.; Sha, M.; Zhang, J.; Xia, L.; Tong, Y.; Luo, Y.; Xia, Q. Risk factors and survival outcomes of biliary complications after adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation. United Eur. Gastroenterol. J. 2017, 5, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Azzam, A.Z.; Tanaka, K. Biliary complications after living donor liver transplantation: A retrospective analysis of the Kyoto experience 1999-2004. Indian J. Gastroenterol. 2017, 36, 296–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaprak, O.; Dayangac, M.; Akyildiz, M.; Demirbas, T.; Guler, N.; Bulutcu, F.; Bassullu, N.; Akun, E.; Yuzer, Y.; Tokat, Y. Biliary complications after right lobe living donor liver transplantation: A single-centre experience. HPB 2012, 14, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, D.H.; Ikegami, T.; Balci, D.; Bhangui, P. Biliary reconstruction and complications in living donor liver transplantation. Int. J. Surg. 2020, 82S, 138–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyagi, S.; Kakizaki, Y.; Shimizu, K.; Miyazawa, K.; Nakanishi, W.; Hara, Y.; Tokodai, K.; Nakanishi, C.; Kamei, T.; Ohuchi, N.; et al. Arterial and biliary complications after living donor liver transplantation: A single-center retrospective study and literature review. Surg. Today 2018, 48, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takahashi, Y.; Nishimoto, Y.; Matsuura, T.; Hayashida, M.; Tajiri, T.; Soejima, Y.; Taketomi, A.; Maehara, Y.; Taguchi, T. Surgical complications after living donor liver transplantation in patients with biliary atresia: A relatively high incidence of portal vein complications. Pediatr. Surg. Int. 2009, 25, 745–751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.C.; Chuang, F.R.; Wang, C.C.; Chen, Y.S.; Chen, C.L.; Liu, Y.W.; Cheng, Y.F.; Lee, C.H.; Jawan, B. Early postoperative complications in recipients of living donor liver transplantation. Transplant. Proc. 2004, 36, 2338–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aydin, C.; Otan, E.; Akbulut, S.; Karakas, S.; Kayaalp, C.; Karagul, S.; Colak, C.; Gonultas, F.; Yilmaz, S.E.Z.A.İ. Postoperative Pulmonary Complications After Liver Transplantation: Assessment of Risk Factors for Mortality. Transplant. Proc. 2015, 47, 1488–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kotloff, R.M. Noninfectious pulmonary complications of liver, heart, and kidney transplantation. Clin. Chest. Med. 2005, 26, 623–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghayumi, S.M.; Mehrabi, S.; Zamirian, M.; Haseli, J.; Bagheri Lankarani, K. Pulmonary complications in cirrhotic candidates for liver transplantation. Hepat. Mon. 2010, 10, 105–109. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, Y.H.; Cai, Z.S.; Jiang, Y.; Lu, L.Z.; Zhang, X.J.; Cai, Q.C. Perioperative risk factors for pulmonary complications after liver transplantation. J. Int. Med. Res. 2010, 38, 1845–1855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pei, F.; Shang, K.; Jiang, B.; Wang, H.; Mei, F.; Zhang, Y.; Du, J.; Zhong, H.; You, J. Clinicopathologic study on complications of orthotopic liver transplantation in 54 patients with chronic hepatitis B viral infection. Hepatol. Int. 2013, 7, 468–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mukhtar, A.; Abdelaal, A.; Hussein, M.; Dabous, H.; Fawzy, I.; Obayah, G.; Hasanin, A.; Adel, N.; Ghaith, D.; Bahaa, M.; et al. Infection complications and pattern of bacterial resistance in living-donor liver transplantation: A multicenter epidemiologic study in Egypt. Transplant. Proc. 2014, 46, 1444–1447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.J.; Kim, S.I.; Wie, S.H.; Kim, Y.R.; Hur, J.A.; Choi, J.Y.; Yoon, S.K.; Moon, I.S.; Kim, D.G.; Lee, M.D.; et al. Infectious complications in living-donor liver transplant recipients: A 9-year single-center experience. Transpl. Infect. Dis. 2008, 10, 316–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, W.A.; Sullivan, E.; Bynon, J.S.; Eltzschig, H.; Ju, C. Ischaemia reperfusion injury in liver transplantation: Cellular and molecular mechanisms. Liver Int. 2019, 39, 788–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, R.S., Jr. Pros and cons of living donor liver transplant. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2008, 4, 622–624. [Google Scholar]
- Shaked, A.; Ghobrial, R.M.; Merion, R.M.; Shearon, T.H.; Emond, J.C.; Fair, J.H.; Fisher, R.A.; Kulik, L.M.; Pruett, T.L.; Terrault, N.A. Incidence and Severity of Acute Cellular Rejection in Recipients Undergoing Adult Living Donor or Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2009, 9, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, T.C.L.; Fung, J.Y.Y.; Pang, H.H.; Leung, C.K.L.; Li, H.F.; Sin, S.L.; Ma, K.W.; She, B.W.H.; Dai, J.W.C.; Chan, A.C.Y. Analysis of Survival Benefits of Living Versus Deceased Donor Liver Transplant in High Model for End-Stage Liver Disease and Hepatorenal Syndrome. Hepatology 2021, 73, 2441–2454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, C.L.; Gillespie, B.W.; Merion, R.M.; Brown, R.S., Jr.; Abecassis, M.M.; Trotter, J.F.; Fisher, R.A.; Freise, C.E.; Ghobrial, R.M.; Shaked, A.; et al. Improvement in survival associated with adult-to-adult living donor liver transplantation. Gastroenterology 2007, 133, 1806–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, W.Y.; Suh, K.S.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, J.; Kim, T.; Yi, N.J.; Uk Lee, K. Prognostic factors affecting survival after recurrence in adult living donor liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Liver Transplant. 2010, 16, 678–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gavriilidis, P.; Tobias, A.; Sutcliffe, R.P.; Roberts, K.J. Survival following right lobe split graft, living- and deceased-donor liver transplantation in adult patients: A systematic review and network meta-analysis. Transpl. Int. 2018, 31, 1071–1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, W.; Qiu, J.G.; Cai, Y.; Cheng, L.; Du, C.Y. Increased Surgical Complications but Improved Overall Survival with Adult Living Donor Compared to Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BioMed Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 1320830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.G. A complete treatment of adult living donor liver transplantation: A review of surgical technique and current challenges to expand indication of patients. Am. J. Transplant. 2015, 15, 17–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, S.; Kotsch, K.; Francuski, M.; Reutzel-Selke, A.; Mantouvalou, L.; Klemz, R.; Kuecuek, O.; Jonas, S.; Wesslau, C.; Ulrich, F.; et al. Brain Death Activates Donor Organs and Is Associated with a Worse I/R Injury After Liver Transplantation. Am. J. Transplant. 2007, 7, 1584–1593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danion, J.; Thuillier, R.; Allain, G.; Bruneval, P.; Tomasi, J.; Pinsard, M.; Hauet, T.; Kerforne, T. Evaluation of Liver Quality after Circulatory Death Versus Brain Death: A Comparative Preclinical Pig Model Study. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 9040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]




| Study | Country | High-MELD–Low-MELD Cut-Off | Study Arms (n) | Age, Years (Mean ± SD) | Sex, Male, n (%) | Diagnosis | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HCC | HCV/HBV | ALD | PSC/PBC/AIH/CC | ||||||
| Liu, 2003 [21] | China | 25 | HM-LDLT (32) | 40.6 ± 1.8 | 26 (81.3%) | _ | |||
| LM-LDLT (49) | 48.5 ± 1.1 | 42 (85.7%) | 44 | 5 | |||||
| Yoshizumi, 2007 [22] | Japan | 25 | HM-LDLT (25) | 43.2 ± 12.8 | 11 (44.0%) | ||||
| LM-LDLT (94) | 52.5 ± 11.3 | 53 (56.4%) | |||||||
| Yi, 2008 [23] | Korea | 25 | HM-LDLT (62) | 47.7 ± 8.9 | 46 (74.2%) | ||||
| LM-LDLT (105) | 49.5 ± 7.7 | 75 (71.4%) | 64 | 48 | |||||
| Selzner, 2010 [24] | Canada | 25 | HM-LDLT (44) | 49 ± 10 | 26 (59.1%) | ||||
| LM-LDLT (227) | 51 ± 10 | 129 (56.8%) | 61 | 93 | |||||
| Poon, 2012 [25] | Taiwan | 30 | HM-LDLT (23) | 54.1 ± 7.28 | 15 (65.2%) | ||||
| LM-LDLT (120) | 49.7 ± 8.95 | 94 (78.3%) | 96 | 14 | 10 | ||||
| Chok, 2013 [26] | China | 25 | HM-LDLT (75) | 45.5 ± 8.0 | 27 (36.0%) | ||||
| LM-LDLT (68) | 45.8 ± 12.3 | 21 (30.9) | 50 | 9 | |||||
| Jiang, 2013 [27] | China | 25 | HM-LDLT (29) | 38.5 ± 7.7 | 25 (86.2%) | ||||
| LM-LDLT (41) | 41.5 ± 8.4 | 37 (90.2%) | 41 | ||||||
| Li, 2013 [28] | China | 25 | HM-LDLT (16) | 37.6 ± 7.7 | 8 (50%) | ||||
| LM-LDLT (102) | 44 ± 8.2 | 94 (92.2%) | 68 | 90 | |||||
| Dabbous, 2016 [29] | Egypt | 20 | HM-LDLT (33) | 46.2 ± 7.9 | 32 (97%) | 11 | |||
| LM-LDLT (38) | 47.8 ± 7.8 | 34 (89.5%) | 11 | ||||||
| Yadav, 2017 [30] | India | 25 | HM-LDLT (151) | 43.6 ± 9.74 | 125 (82.8%) | ||||
| LM-LDLT (849) | 50.3 ± 9.81 | 698 (82.2%) | 226 | 376 | 260 | 213 | |||
| Attributes | Number of Studies | MD | CI (95%) | p-Value | I2 (%) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (recipient) | 10 | −3.43 | −6.02, −0.85 | 0.009 ** | 91% | Significantly younger population in HM group |
| Preoperative bilirubin (mg/dL) | 3 | 17.39 | 2.20, 32.59 | 0.02 ** | 99% | Significantly higher bilirubin in HM group |
| GRWR | 4 | −0.02 | −0.05, 0.01 | 0.16 | 0% | No significant difference |
| GW/R ESLW | 3 | −1.41 | −6.79, 3.98 | 0.61 | 92% | No significant difference |
| Attributes | Number of Studies | OR | CI (95%) | p-Value | I2 (%) | Remarks |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Male | 10 | 0.78 | 0.51, 1.19 | 0.26 | 56% | No significant difference |
| Ascites | 3 | 2.72 | 1.57, 4.71 | 0.000 ** | 0% | Significantly higher incidence in HM group |
| Encephalopathy | 3 | 4.35 | 2.41, 7.84 | 0.000 ** | 0% | Significantly higher incidence in HM group |
| A. Outcomes | Odds Ratio | 95% CI | p-Value | I2 (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Major morbidity | 1.53 | 0.92–2.54 | 0.10 | 41% |
| Hepatic artery thrombosis | 1.18 | 0.52–2.67 | 0.70 | 0% |
| Biliary complications | 1.06 | 0.72–1.57 | 0.75 | 14% |
| Wound infections | 1.46 | 0.51–4.24 | 0.48 | 0% |
| Intra-abdominal bleeding | 1.87 | 0.98–3.54 | 0.06 | 0% |
| Pulmonary infections | 2.07 | 1.05–4.08 | 0.04 * | 40% |
| Abdominal fluid collection | 2.26 | 1.21–4.24 | 0.01 * | 0% |
| B. Outcomes | Mean difference | 95% CI | p-Value | I2 (%) |
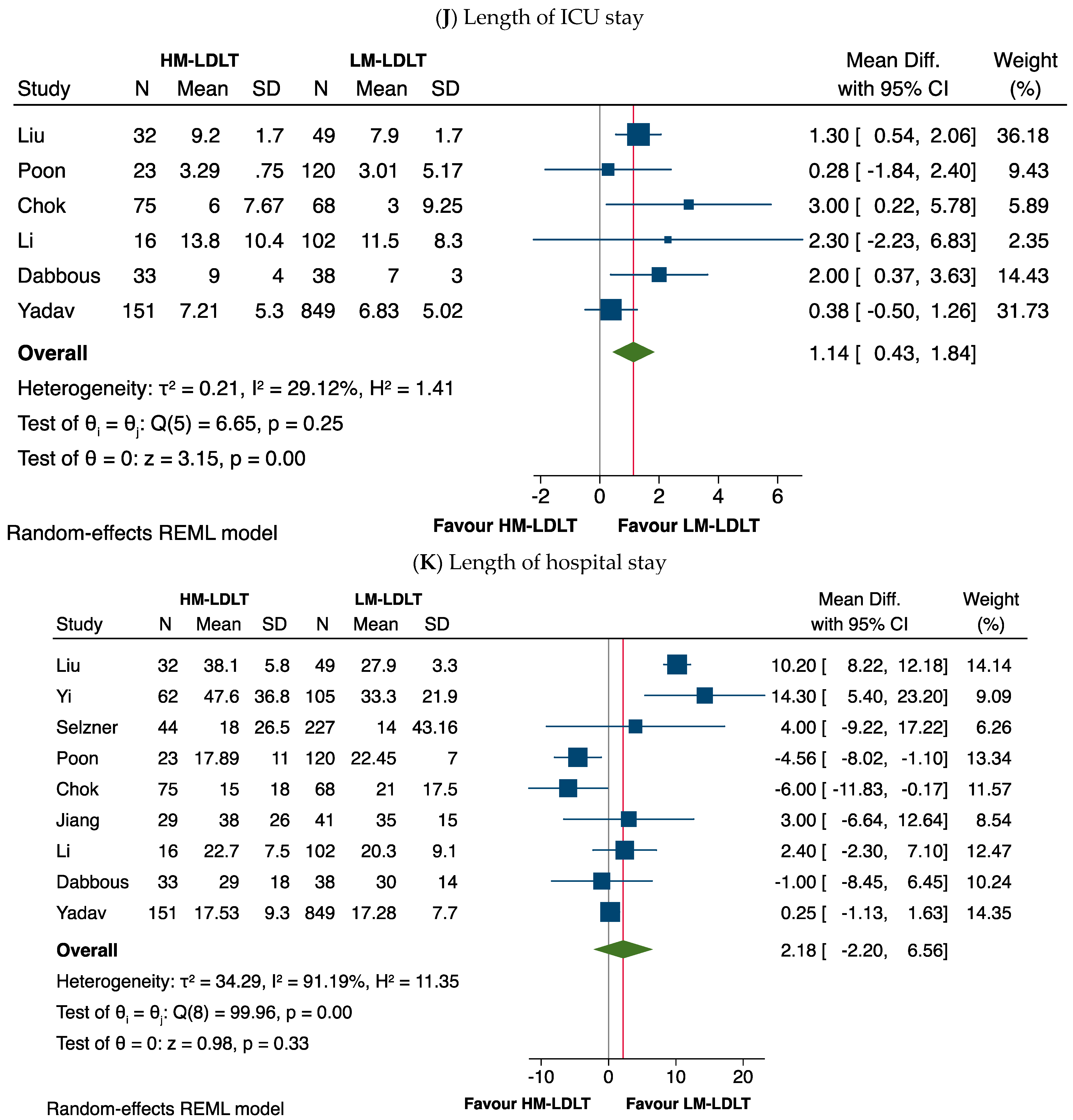
| Length of ICU stay | 1.14 | 0.43–1.84 | 0.00 * | 29% |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jayant, K.; Cotter, T.G.; Reccia, I.; Virdis, F.; Podda, M.; Machairas, N.; Arasaradnam, R.P.; Sabato, D.d.; LaMattina, J.C.; Barth, R.N.; et al. Comparing High- and Low-Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Living-Donor Liver Transplantation to Determine Clinical Efficacy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (CHALICE Study). J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5795. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185795
Jayant K, Cotter TG, Reccia I, Virdis F, Podda M, Machairas N, Arasaradnam RP, Sabato Dd, LaMattina JC, Barth RN, et al. Comparing High- and Low-Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Living-Donor Liver Transplantation to Determine Clinical Efficacy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (CHALICE Study). Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(18):5795. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185795
Chicago/Turabian StyleJayant, Kumar, Thomas G. Cotter, Isabella Reccia, Francesco Virdis, Mauro Podda, Nikolaos Machairas, Ramesh P. Arasaradnam, Diego di Sabato, John C. LaMattina, Rolf N. Barth, and et al. 2023. "Comparing High- and Low-Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Living-Donor Liver Transplantation to Determine Clinical Efficacy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (CHALICE Study)" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 18: 5795. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185795
APA StyleJayant, K., Cotter, T. G., Reccia, I., Virdis, F., Podda, M., Machairas, N., Arasaradnam, R. P., Sabato, D. d., LaMattina, J. C., Barth, R. N., Witkowski, P., & Fung, J. J. (2023). Comparing High- and Low-Model for End-Stage Liver Disease Living-Donor Liver Transplantation to Determine Clinical Efficacy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis (CHALICE Study). Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(18), 5795. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12185795









