The Influence of Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Plasma Level in Patients with Schizophrenia—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
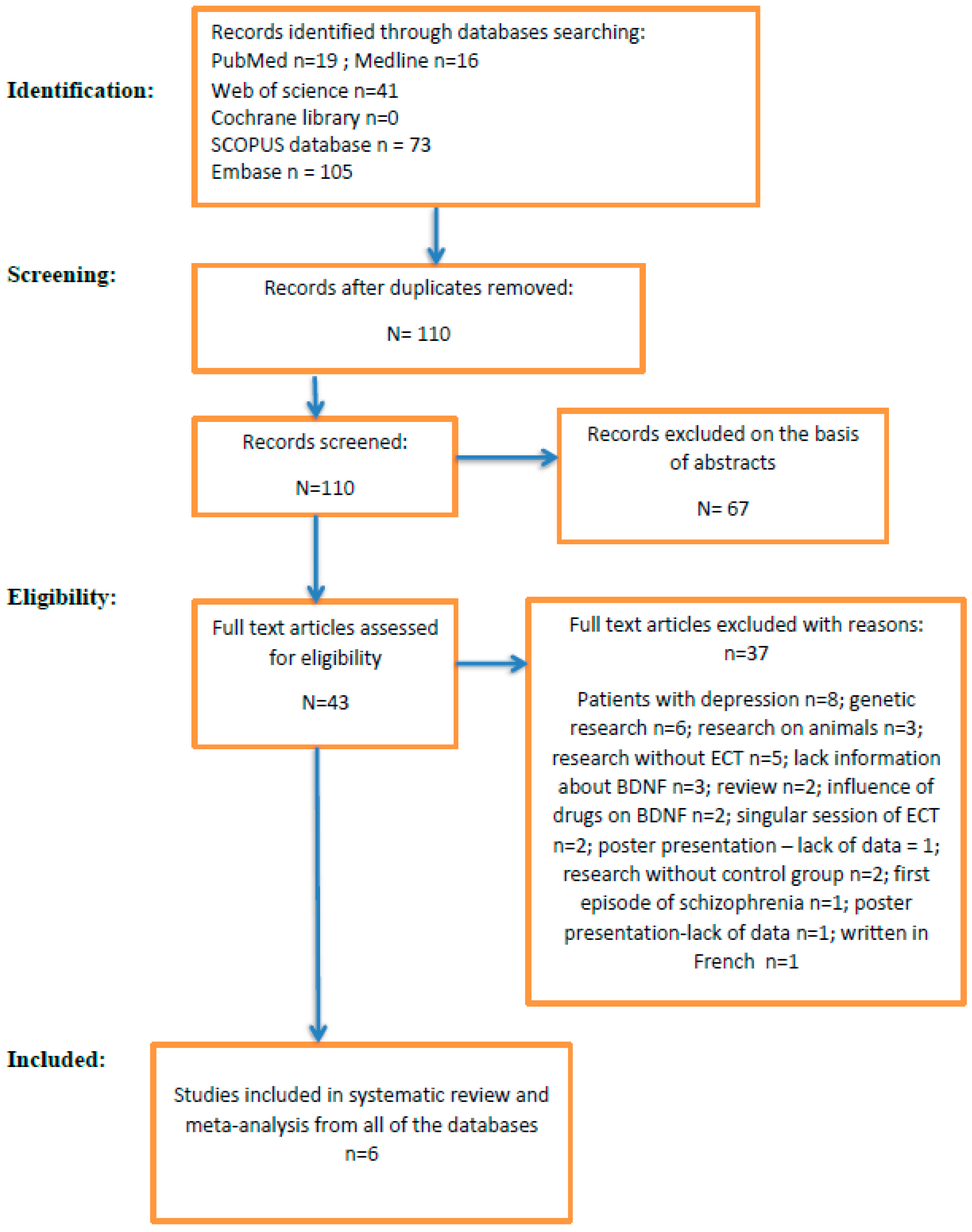
2. Material and Methods
2.1. Data Sources and Search Strategy
2.2. Data Extraction
2.3. Study Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
2.4. Data Collected
2.5. Data Synthesis and Statistical Analysis
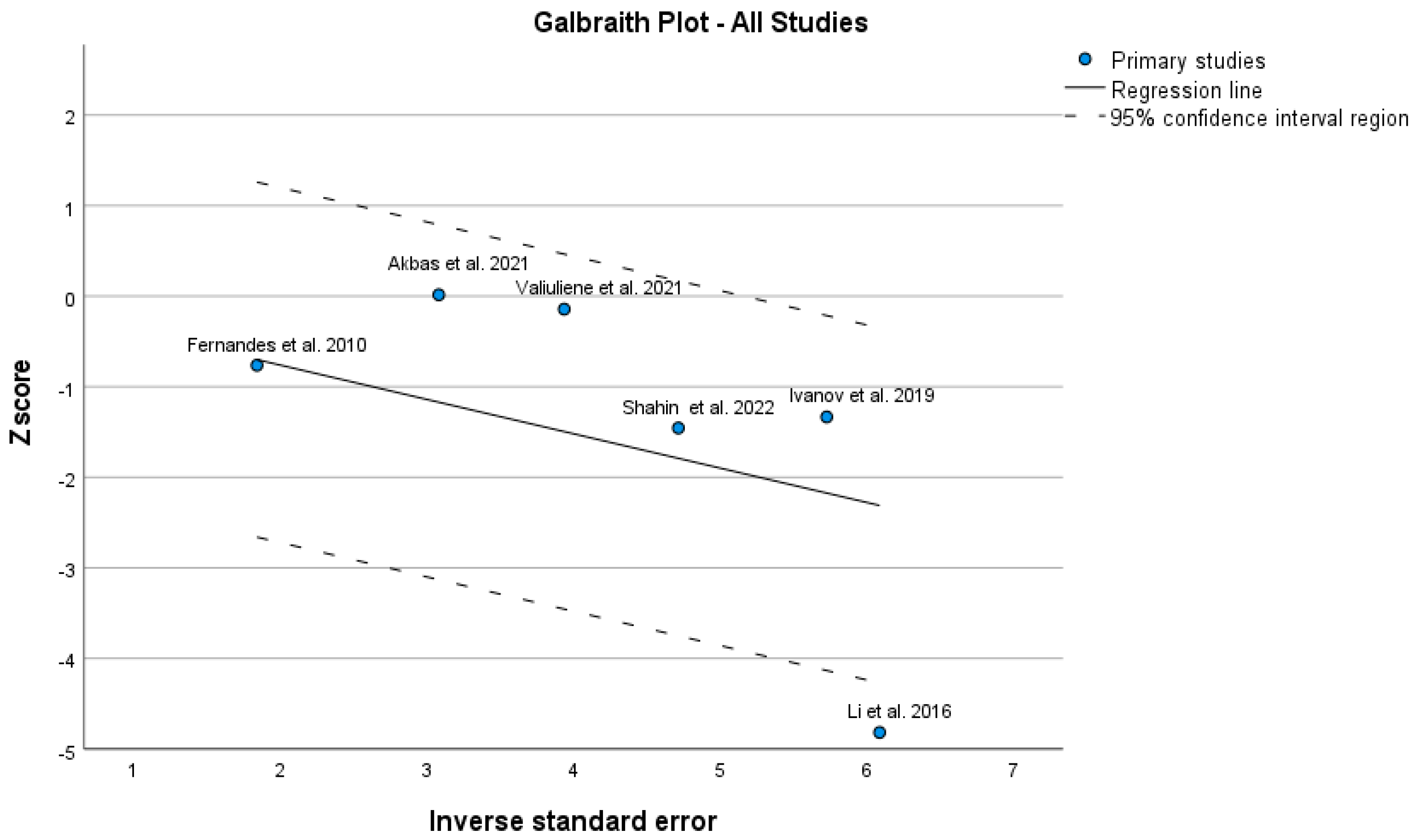
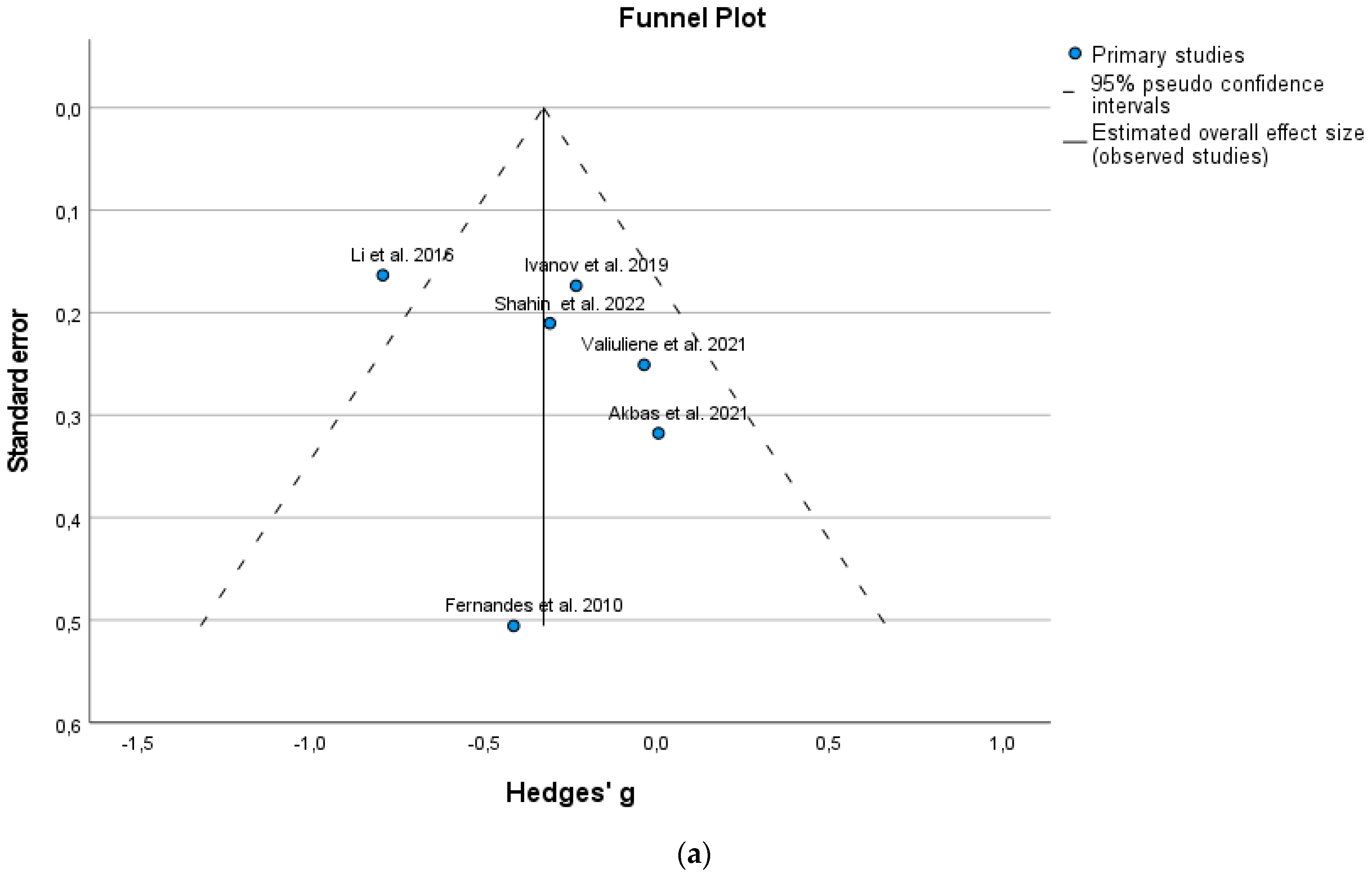
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Limitations
6. Summary
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
References
- Keshri, N.; Nandeesha, H. Dysregulation of Synaptic Plasticity Markers in Schizophrenia. Indian J. Clin. Biochem. 2023, 38, 4–12. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Patlola, S.R.; Donohoe, G.; McKernan, D.P. The relationship between inflammatory biomarkers and cognitive dysfunction in patients with schizophrenia: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 8, 110668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zoupa, E.; Bogiatzidou, O.; Siokas, V.; Liampas, I.; Tzeferakos, G.; Mavreas, V.; Stylianidis, S.; Dardiotis, E. Cognitive Rehabilitation in Schizophrenia-Associated Cognitive Impairment: A Review. Neurol. Int. 2022, 15, 12–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashe, P.C.; Berry, M.D.; Boulton, A.A. Schizophrenia, a neurodegenerative disorder with neurodevelopmental antecedents. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 25, 691–707. [Google Scholar]
- Bathina, S.; Das, U.N. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its clinical implications. Arch. Med. Sci. 2015, 11, 1164–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scalzo, P.; Kümmer, A.; Bretas, T.L.; Cardoso, F.; Teixeira, A.L. Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor correlate with motor impairment in Parkinson’s disease. J. Neurol. 2010, 257, 540–5455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ventriglia, M.; Zanardini, R.; Bonomini, C.; Zanetti, O.; Volpe, D.; Pasqualetti, P.; Gennarelli, M.; Bocchio-Chiavetto, L. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in different neurological diseases. BioMed Res. Int. 2013, 2013, 901082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, F.; Zhou, X.; Moon, C.; Wang, H. Regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression in neurons. Int. J. Physiol. Pathophysiol. Pharmacol. 2012, 4, 188–200. [Google Scholar]
- Green, M.J.; Matheson, S.L.; Shepherd, A.; Weickert, C.S.; Carr, V.J. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels in schizophrenia: A systematic review with meta-analysis. Mol. Psychiatry 2011, 16, 960–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Ye, F.; Xiao, W.; Tang, X.; Sha, W.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J. Increased serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels following electroconvulsive therapy or antipsychotic treatment in patients with schizophrenia. Eur. Psychiatry 2016, 36, 23–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Şimşek, Ş.; Gençoğlan, S.; Yüksel, T.; Kaplan, İ.; Aktaş, H. Lower Brain-Derived Neurotropic Factor Levels in Untreated Adolescents with First-Episode Psychosis. J. Clin. Psychopharmacol. 2015, 35, 596–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weickert, C.S.; Lee, C.H.; Lenroot, R.K.; Bruggemann, J.; Galletly, C.; Liu, D.; Balzan, R.; Pillai, A.; Buckley, P.; Weickert, T.W. Increased plasma Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) levels in females with schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2019, 209, 212–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ray, M.T.; Shannon, T.; Weickert, C.; Webster, M.J. Decreased BDNF and TrkB mRNA expression in multiple cortical areas of patients with schizophrenia and mood disorders. Transl. Psychiatry 2014, 4, e389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, J.; Hyde, T.M.; Cassano, H.L.; Deep-Soboslay, A.; Kleinman, J.E.; Weickert, C.S. Promoter specific alterations of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mRNA in schizophrenia. Neuroscience 2010, 169, 1071–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, B.S.; Steiner, J.; Berk, M.; Molendijk, M.L.; Gonzalez-Pinto, A.; Turck, C.W.; Nardin, P.; Gonçalves, C.A. Peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor in schizophrenia and the role of antipsychotics: Meta-analysis and implications. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 9, 1108–1119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gama, C.S.; Andreazza, A.C.; Kunz, M.; Berk, M.; Belmonte-de-Abreu, P.S.; Kapczinski, F. Serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Neurosci. Lett. 2007, 420, 45–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, H.J.; Nicolato, R.; Barbosa, I.G.; Teixeira do Prado, P.H.; Romano-Silva, M.A.; Teixeira, A.L. Increased serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in chronic institutionalized patients with schizophrenia. Neurosci. Lett. 2008, 439, 157–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedrini, M.; Chendo, I.; Grande, I.; Lobato, M.I.; Belmonte-de-Abreu, P.S.; Lersch, C.; Walz, J.; Kauer-Sant’anna, M.; Kapczinski, F.; Gama, C.S. Serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor and clozapine daily dose in patients with schizophrenia: A positive correlation. Neurosci. Lett. 2011, 491, 207–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leucht, S. Measurements of response, remission, and recovery in schizophrenia and examples for their clinical application. J. Clin. Psychiatry 2014, 75, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbas, I.; Balaban, O.D. Changes in serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor with electroconvulsive therapy and pharmacotherapy and its clinical correlates in male schizophrenia patients. Acta Neuropsychiatr. 2022, 34, 99–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, B.S.; Massuda, R.; Torres, M.; Camargo, D.; Fries, G.R.; Gama, C.S.; Belmonte-de-Abreu, P.S.; Kapczinski, F.; Lobato, M.I. Improvement of schizophrenia with electroconvulsive therapy and serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor levels: Lack of association in a pilot study. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2010, 64, 663–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Page, M.J.; McKenzie, J.E.; Bossuyt, P.M.; Boutron, I.; Hoffmann, T.C.; Mulrow, C.D.; Shamseer, L.; Tetzlaff, J.M.; Akl, E.A.; Brennan, S.E.; et al. The PRISMA 2020 statement: An updated guideline for reporting systematic reviews. BMJ 2021, 372, n71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hedges, L. Distribution Theory for Glass’s Estimator of Effect Size and Related Estimators. J. Edu. Stat. 1981, 6, 107–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hedges, L.V.; Olkin, I. Statistical Methods for Meta-Analysis; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Knapp, G.; Hartung, J. Improved tests for a random effects meta-regression with a single covariate. Stat. Med. 2003, 22, 2693–2710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- IntHout, J.; Ioannidis, J.P.; Borm, G.F. The Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman method for random effects meta-analysis is straightforward and considerably outperforms the standard DerSimonian-Laird method. BMC Med. Res. Methodol. 2014, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röver, C.; Knapp, G.; Friede, T. Hartung-Knapp-Sidik-Jonkman approach and its modification for random-effects meta-analysis with few studies. BMC Med. Res. Meth. 2015, 15, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simes, R.J. Confronting publication bias: A cohort design for meta-analysis. Stat. Med. 1987, 6, 11–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Egger, M.; Davey Smith, G.; Schneider, M.; Minder, C. Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ 1997, 315, 629–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterne, J.A.C.; Egger, M. Regression methods to detect publication and other bias in meta-analysis. In Publication Bias in Meta-Analysis: Prevention, Assessment, and Adjustments; Rothstein, H.R., Sutton, A.J., Borenstein, M., Eds.; Wiley: Chichester, UK, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Duval, S.; Tweedie, R. Trim and fill: A simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 2000, 56, 455–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linyu, S.; Lifeng, L. The trim-and-fill method for publication bias: Practical guidelines and recommendations based on a large database of meta-analyses. Medicine 2019, 98, e15987. [Google Scholar]
- Shahin, O.; Gohar, S.M.; Ibrahim, W.; El-Makawi, S.M.; Fakher, W.; Taher, D.B.; Abdel Samie, M.; Khalil, M.A.; Saleh, A.A. Brain-Derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) plasma level increases in patients with resistant schizophrenia treated with electroconvulsive therapy (ECT). Int. J. Psychiatry Clin. Pract. 2022, 26, 370–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valiuliene, G.; Valiulis, V.; Dapsys, K.; Vitkeviciene, A.; Gerulskis, G.; Navakauskiene, R.; Germanavicius, A. Brain stimulation effects on serum BDNF, VEGF, and TNFα in treatment-resistant psychiatric disorders. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2021, 53, 3791–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanov, M.V.; Zubov, D.S. Electroconvulsive therapy in treatment of resistant schizophrenia: Biological markers of efficacy and safety. Zhurnal Nevrol. I Psikhiatrii Im. S.S. Korsakova 2019, 119, 92–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, B.; Nagappan, G.; Lu, Y. BDNF and synaptic plasticity, cognitive function, and dysfunction. In Handbook of Experimental Pharmacology; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2014; Volume 220, pp. 223–250. [Google Scholar]
- Nagahara, A.H.; Tuszynski, M.H. Potential therapeutic uses of BDNF in neurological and psychiatric disorders. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2011, 10, 209–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akyol, E.S.; Albayrak, Y.; Beyazyüz, M.; Aksoy, N.; Kuloglu, M.; Hashimoto, K. Decreased serum levels of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in schizophrenic patients with deficit syndrome. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2015, 11, 865–872. [Google Scholar]
- Islam, F.; Mulsant, B.H.; Voineskos, A.N.; Rajji, T.K. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor Expression in Individuals with Schizophrenia and Healthy Aging: Testing the Accelerated Aging Hypothesis of Schizophrenia. Curr. Psychiatry Rep. 2017, 19, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koeva, Y.A.; Sivkov, S.T.; Akabaliev, V.H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and its serum levels in schizophrenic patients. Folia Medica 2014, 56, 20–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Li, W.; Lv, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhan, X. BDNF as a biomarker in diagnosis and evaluation of treatment for schizophrenia and depression. Discov. Med. 2018, 26, 127–136. [Google Scholar]
- Zakharyan, R.; Boyajyan, A. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor blood levels are decreased in schizophrenia patients and associate with rs6265 genotypes. Clin. Biochem. 2014, 47, 1052–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, C.Y.W.; Abdin, E.; Seow, E.; Subramaniam, M.; Liu, J.; Peh, C.X.; Tor, P.C. Clinical effectiveness and speed of response of electroconvulsive therapy in treatment-resistant schizophrenia. Psychiatry Clin. Neurosci. 2019, 73, 416–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrides, G.; Malur, C.; Braga, R.J.; Bailine, S.H.; Schooler, N.R.; Malhotra, A.K.; Kane, J.M.; Sanghani, S.; Goldberg, T.E.; John, M.; et al. Electroconvulsive therapy augmentation in clozapine-resistant schizophrenia: A prospective, randomized study. Am. J. Psychiatry 2015, 172, 52–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haghighi, M.; Salehi, I.; Erfani, P.; Jahangard, L.; Bajoghli, H.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E.; Brand, S. Additional ECT increases BDNF-levels in patients suffering from major depressive disorders compared to patients treated with citalopram only. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2013, 47, 908–915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luan, S.; Zhou, B.; Wu, Q.; Wan, H.; Li, H. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor blood levels after electroconvulsive therapy in patients with major depressive disorder: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Asian J. Psychiatry 2020, 51, 101983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brunoni, A.R.; Baeken, C.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Gattaz, W.F.; Vanderhasselt, M.A. BDNF blood levels after electroconvulsive therapy in patients with mood disorders: A systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2014, 15, 411–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pelosof, R.; Santos, L.A.D.; Farhat, L.C.; Gattaz, W.F.; Talib, L.; Brunoni, A.R. BDNF blood levels after electroconvulsive therapy in patients with mood disorders: An updated systematic review and meta-analysis. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2023, 24, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polyakova, M.; Schroeter, M.L.; Elzinga, B.M.; Holiga, S.; Schoenknecht, P.; de Kloet, E.R.; Molendijk, M.L. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and Antidepressive Effect of Electroconvulsive Therapy: Systematic Review and Meta-Analyses of the Preclinical and Clinical Literature. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0141564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salehi, I.; Hosseini, S.M.; Haghighi, M.; Jahangard, L.; Bajoghli, H.; Gerber, M.; Pühse, U.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E.; Brand, S. Electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) and aerobic exercise training (AET) increased plasma BDNF and ameliorated depressive symptoms in patients suffering from major depressive disorder. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2016, 76, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, B.; Molendijk, M.L.; Köhler, C.A.; Soares, J.C.; Leite, C.M.; Machado-Vieira, R.; Ribeiro, T.L.; Silva, J.C.; Sales, P.M.; Quevedo, J.; et al. Peripheral brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) as a biomarker in bipolar disorder: A meta-analysis of 52 studies. BMC Med. 2015, 13, 289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grønli, O.; Stensland, G.Ø.; Wynn, R.; Olstad, R. Neurotrophic factors in serum following ECT: A pilot study. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2009, 10, 295–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okamoto, T.; Yoshimura, R.; Ikenouchi-Sugita, A.; Hori, H.; Umene-Nakano, W.; Inoue, Y.; Ueda, N.; Nakamura, J. Efficacy of electroconvulsive therapy is associated with changing blood levels of homovanillic acid and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in refractory depressed patients: A pilot study. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2008, 32, 1185–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, R.; Azman, K.F.; Yahaya, R.; Shafin, N.; Omar, N.; Ahmad, A.H.; Zakaria, R.; Wijaya, A.; Othman, Z. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in schizophrenia research: A quantitative review and future directions. AIMS Neurosci. 2023, 10, 5–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Atake, K.; Nakamura, T.; Ueda, N.; Hori, H.; Katsuki, A.; Yoshimura, R. The Impact of Aging, Psychotic Symptoms, Medication, and Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor on Cognitive Impairment in Japanese Chronic Schizophrenia Patients. Front. Psychiatry 2018, 9, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, F.; Wang, K.; Du, X.; Deng, H.; Wu, H.E.; Yin, G.; Ning, Y.; Huang, X.; Teixeira, A.L.; de Quevedo, J.; et al. Sex difference in the association of body mass index and BDNF levels in Chinese patients with chronic schizophrenia. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 753–762. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Binford, S.S.; Hubbard, E.M.; Flowers, E.; Miller, B.L.; Leutwyler, H. Serum BDNF Is Positively Associated with Negative Symptoms in Older Adults with Schizophrenia. Biol. Res. Nurs. 2018, 20, 63–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heitz, U.; Papmeyer, M.; Studerus, E.; Egloff, L.; Ittig, S.; Andreou, C.; Vogel, T.; Borgwardt, S.; Graf, M.; Eckert, A.; et al. Plasma and serum brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels and their association with neurocognition in at-risk mental state, first episode psychosis and chronic schizophrenia patients. World J. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 20, 545–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, X.; Zhou, C.; Gao, J.; Duan, W.; Yu, M.; Xiao, W.; Zhang, X.; Dong, H.; Wang, X.; Zhang, X. Serum BDNF and GDNF in Chinese male patients with deficit schizophrenia and their relationships with neurocognitive dysfunction. BMC Psychiatry 2019, 19, 254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Chen, Y.; Wang, Y.; Ren, J.; Zhang, C. Depressive symptoms in schizophrenia patients: A possible relationship between SIRT1 and BDNF. Prog. Neuro-Psychopharmacol. Biol. Psychiatry 2019, 20, 109673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.; Lu, C.; Kang, L.; Li, Q.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Tang, Z.; Lin, Y.; Bai, M.; Xiong, P. Study on correlations of BDNF, PI3K, AKT and CREB levels with depressive emotion and impulsive behaviors in drug-naïve patients with first-episode schizophrenia. BMC Psychiatry 2023, 23, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manchia, M.; Isayeva, U.; Collu, R.; Primavera, D.; Deriu, L.; Caboni, E.; Iaselli, M.N.; Sundas, D.; Tusconi, M.; Pinna, F.; et al. Converging Evidence Points to BDNF as Biomarker of Depressive Symptoms in Schizophrenia-Spectrum Disorders. Brain Sci. 2022, 4, 666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, T.L. Effects of antipsychotics on the BDNF in schizophrenia. Curr. Med. Chem. 2013, 20, 345–350. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, R.Q.; Lin, C.G.; Zhang, W.; Lin, X.D.; Chen, X.S.; Chen, C.; Zhang, L.J.; Huang, Z.Y.; Chen, G.D.; Xu, D.L.; et al. Effects of Risperidone and Paliperidone on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor and N400 in First-Episode Schizophrenia. Chin. Med. J. 2018, 131, 2297–2301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, C.; Sun, Y.; Chen, N.; Chen, S.; Xiu, M.; Zhang, X. Interaction of oxidative stress and BDNF on executive dysfunction in patients with chronic schizophrenia. Psychoneuroendocrinology 2020, 111, 104473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, H.; Zhang, G.; Du, X.; Zhang, Y.; Yin, G.; Dai, J.; He, M.X.; Soares, J.C.; Li, X.; Zhang, X. Suicide attempt, clinical correlates, and BDNF Val66Met polymorphism in chronic patients with schizophrenia. Neuropsychology 2018, 32, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Skibinska, M.; Groszewska, A.; Kapelski, P.; Rajewska-Rager, A.; Pawlak, J.; Dmitrzak-Weglarz, M.; Szczepankiewicz, A.; Twarowska-Hauser, J. Val66Met functional polymorphism and serum protein level of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in acute episode of schizophrenia and depression. Pharmacol. Rep. 2018, 70, 55–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, E.; Hettige, N.C.; Zai, G.; Tomasi, J.; Huang, J.; Zai, C.C.; Pivac, N.; Nikolac Perkovic, M.; Tiwari, A.K.; Kennedy, J.L. BDNF Val66Met polymorphism and clinical response to antipsychotic treatment in schizophrenia and schizoaffective disorder patients: A meta-analysis. Pharmacogenomics J. 2019, 19, 69–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, E.J.; Kim, Y.K. 196G/A of the Brain-derived neurotrophic factor gene polymorphisms predicts suicidal behavior in schizophrenia patients. Psychiatry Investig. 2018, 15, 733–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schweiger, J.I.; Bilek, E.; Schäfer, A.; Braun, U.; Moessnang, C.; Harneit, A.; Post, P.; Otto, K.; Romanczuk-Seiferth, N.; Erk, S.; et al. Effects of BDNF Val66Met genotype and schizophrenia familial risk on a neural functional network for cognitive control in humans. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 590–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitt, K.; Holsboer-Trachsler, E.; Eckert, A. BDNF in sleep, insomnia, and sleep deprivation. Ann. Med. 2016, 48, 42–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wynn, J.K.; Green, M.F.; Hellemann, G.; Karunaratne, K.; Davis, M.C.; Marder, S.R. The effects of curcumin on brain-derived neurotrophic factor and cognition in schizophrenia: A randomized controlled study. Schizophr. Res. 2018, 195, 572–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawełczyk, T.; Grancow-Grabka, M.; Trafalska, E.; Szemraj, J.; Żurner, N.; Pawełczyk, A. An increase in plasma brain derived neurotrophic factor levels is related to n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acid efficacy in first episode schizophrenia: Secondary outcome analysis of the OFFER randomized clinical trial. Psychopharmacology 2019, 236, 2811–2822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökçe, E.; Güneş, E.; Nalçaci, E. Effect of Exercise on Major Depressive Disorder and Schizophrenia: A BDNF Focused Approach. Noro Psikiyatr. Ars. 2019, 56, 302–310. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meshkat, S.; Alnefeesi, Y.; Jawad, M.Y.D.; Di Vincenzo, J.B.; Rodrigues, N.; Ceban, F.; Mw Lui, L.; McIntyre, R.S.; Rosenblat, J.D. Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) as a biomarker of treatment response in patients with Treatment Resistant Depression (TRD): A systematic review & meta-analysis. Psychiatry Res. 2022, 317, 114857. [Google Scholar]
- Faden, J.; Citrome, L. Schizophrenia: One Name, Many Different Manifestations. Med. Clin. N. Am. 2023, 107, 61–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howes, O.D.; Murray, R.M. Schizophrenia: An integrated sociodevelopmental-cognitive model. Lancet 2014, 10, 1677–1687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Yang, F. The interplay of dopamine metabolism abnormalities and mitochondrial defects in the pathogenesis of schizophrenia. Transl. Psychiatry 2022, 12, 464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, R.R.; Carrasco, A.; Corral, S.; Castillo, R.; Gaspar, P.A.; Bustamante, M.L.; Silva, H. BDNF as a Biomarker of Cognition in Schizophrenia/Psychosis: An Updated Review. Front. Psychiatry 2021, 12, 662407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.C.; Du, Y.; Chen, L.; Yuan, Z.Q.; Cheng, Y. MicroRNA schizophrenia: Etiology, biomarkers and therapeutic targets. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 146, 105064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nucifora, F.C., Jr.; Woznica, E.; Lee, B.J.; Cascella, N.; Sawa, A. Treatment resistant schizophrenia: Clinical, biological, and therapeutic perspectives. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019, 131, 104257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenquist, P.B.; Miller, B.; Pillai, A. The antipsychotic effects of ECT: A review of possible mechanisms. J. ECT 2014, 30, 125–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kellner, C.H.; Knapp, R.; Husain, M.M.; Rasmussen, K.; Sampson, S.; Cullum, M.; McClintock, S.M.; Tobias, K.G.; Martino, C.; Mueller, M.; et al. Bifrontal, bitemporal and right unilateral electrode placement in ECT: Randomised trial. Br. J. Psychiatry 2010, 196, 226–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swartz, C.M.; Nelson, A.I. Rational electroconvulsive therapy electrode placement. Psychiatry 2005, 2, 37–43. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]


| Study | Study Design | Control Group | Patients Diagnosed with Schizophrenia That Underwent ECT | Patients Diagnosed with Schizophrenia on Antipsychotic Medication Only | ECT Characteristics | BDNF Mean Level | Symptom Rating Scales before and after Intervention | ||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | %F | Mean Age (years) +/− SD | N | %F | Mean Age (years) +/− SD | Duration of Illness (years) +/− SD | N | %F | Mean Age (years) +/− SD | Duration of Illness (years) +/− SD | Pre ECT | Post ECT | Med. Only Pretreatment | Med. Only Post Treatment | Control Group | ||||
| Fernandes et al. 2010 [21] | Pilot study | 21 | 30 | 35.27 ± 10.34 | 7 | 30 | 35.79 ± 10.85 | Data not available | n/a | Unilateral frontotemporal electrode placement. Charge delivered max 504 mC, current 0.9 A, frequency 30–70 Hz, pulse width 1 ms, duration max 8 s ECT session performed 3 times/week. | 0.14 mg/mL | 0.39 mg/mL | n/a | n/a | 0.39 mg/mL | BPRS, CGI-S | |||
| Li et al. 2016 [10] | Case control study | 77 | 44.2 | 40 ± 12.5 | 80 | 47.5 | 38.1 ± 11.1 | 11.3 ± 8.9 | 80 | 45 | 37.7 ± 12.1 | 11.4 ± 10.0 | Bilateral frontotemporal electrode placement. Maximum charge delivered 504 mC; output current = 0.9 A; frequency between 10–70 Hz; pulse width = 0.5 ms; maximum stimulus duration = 8 s. 8–10 ECT sessions every other day. | 9.7 ng/mL | 11.9 ng/mL | 9.8 ng/mL | 11.7 ng/mL | 12.4 ng/mL | PANSS |
| Ivanov et al. 2019 [35] | Case control study | n/a | 66 | 50 | 33.28 ± 8.7 | 6.6 ± 5.1 | 32 | 50 | 33.28 ± 8.7 | 6.6 ± 5.1 | Bilateral frontotemporal electrode placement. Maximum charge delivered 550 mC; frequency between 27–40 Hz; pulse width = 1–1.5 ms; 3–12 ECT in session | 10.71 ng/mL | 12.30 ng/mL | 9.9 ng/mL | 9.53 ng/mL | n/a | PANSS | ||
| Akbas et al. 2021 [20] | Case control study | 35 | 0 | 40.51 ± 7.16 | 19 | 0 | 32.47 ± 9.53 | 7.00 | 35 | 0 | 35.23 ± 11.64 | 9.00 | Bilateral temporal electrode placement. A maximum of three consecutive attempts were made to achieve adequate (25 s minimum) seizure per session. | 0.320 mg/mL | 0.315 mg/mL | 0.141 mg/mL | 0.468 mg/mL | 1.478 mg/mL | PANSS |
| Valiuliene et al. 2021 [34] | Cohort study | 19 | 78.9 | 45.53 ± 15.02 | 31 | 19 | 34.48 ± 11.35 | Not provided | n/a | Bilateral temporal electrode placement. During the stimulation, 0.5 ms duration biphasic square impulses were applied. Impulse current strength was constant at 0.9 A. Stimulation duration ranged from 0.47 to 4.0 s at 70 Hz frequency. These parameters were adjusted according to each patient and increased gradually in succession. ECT was carried out every 2 days; the number of ECT procedures, depending on clinical progress, ranged from 10 to 20 sessions. | 28.98 ng/mL | 29.3 ng/mL | n/a | n/a | 30.12 ng/mL | PANSS | |||
| Shahin et al. 2022 [33] | Cohort study | n/a | 45 | 28 | 33.49 ± 10.14 | 7.43 ± 5.19 | 15 | 26.7 | 36.40 ± 7.18 | 7.60 ± 4.90 | Bilateral temporal electrode placement. The baseline parameters were pulse width (0.5 milliseconds), frequency (80 Hertz), duration (1 s) and current (800 milli ampere). These parameters were adjusted according to each patient and increased gradually in successive sessions. 4–10 sessions of ECT over 4 weeks. | 8.71 ng/mL | 9.26 ng/mL | 8.26 ng/mL | 8.90 ng/mL | n/a | PANSS | ||
| ID | Study | Effect Size | Std. Error a | t | Sig. (2-Tailed) | 95% Confidence Interval | Weight | Weight (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||||
| 1 | Fernandes et al. 2010 [21] | −0.413 | 0.5424 | −0.762 | 0.446 | −1.477 | 0.650 | 2.832 | 5.7 |
| 2 | Li et al. 2016 [10] | −0.792 | 0.1643 | −4.817 | <0.001 | −1.114 | −0.470 | 11.649 | 23.5 |
| 3 | Ivanov et al. 2019 [35] | −0.233 | 0.1747 | −1.333 | 0.183 | −0.575 | 0.110 | 11.192 | 22.6 |
| 4 | Akbas et al. 2021 [20] | 0.005 | 0.3244 | 0.016 | 0.987 | −0.631 | 0.641 | 6.094 | 12.3 |
| 5 | Valiuliene et al. 2021 [34] | −0.036 | 0.2540 | −0.143 | 0.887 | −0.534 | 0.462 | 8.106 | 16.4 |
| 6 | Shahin et al. 2022 [33] | −0.309 | 0.2121 | −1.455 | 0.146 | −0.724 | 0.107 | 9.631 | 19.5 |
| Effect Size | Std. Error a | t | Sig. (2-Tailed) | 95% Confidence Interval | 95% Prediction Interval b | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | Lower | Upper | |||||
| Overall | −0.328 | 0.1421 | −2.307 | 0.069 | −0.693 | 0.037 | −1.108 | 0.453 |
| Number | Effect Size | Std. Error a | t | Sig. (2-Tailed) | 95% Confidence Interval | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | ||||||
| Observed | 6 | −0.328 | 0.1421 | −2.307 | 0.069 | −0.693 | 0.037 |
| Observed + Imputed b | 7 | −0.375 | 0.1319 | −2.847 | 0.029 | −0.698 | −0.053 |
| Parameter | Coefficient | Std. Error | t | Sig. (2-Tailed) | 95% Confidence Interval | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||
| (Intercept) | −0.596 | 0.3724 | −1.600 | 0.185 | −1.630 | 0.438 |
| SE b | 1.151 | 1.5053 | 0.764 | 0.487 | −3.029 | 5.330 |
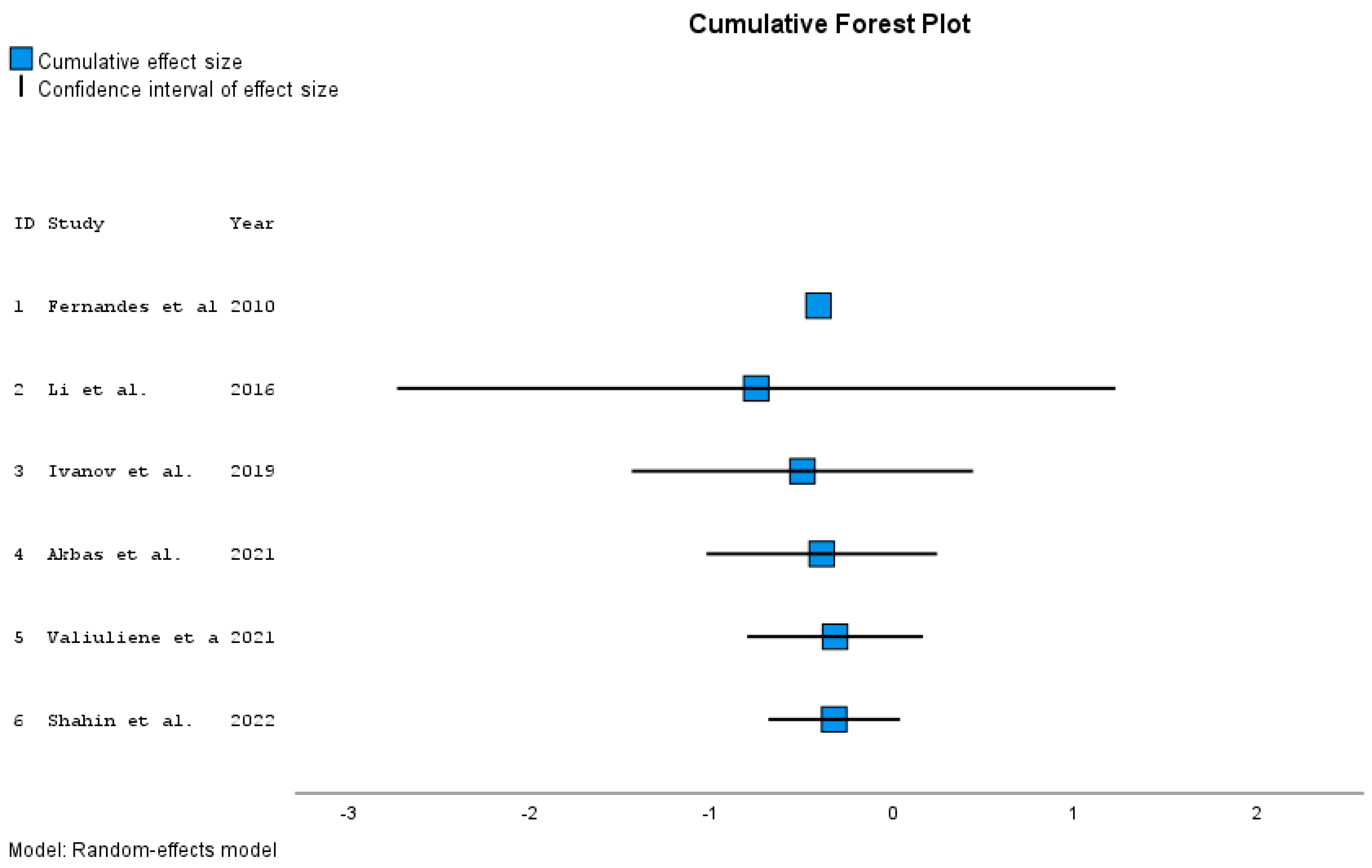
| ID | Study | Effect Size | Std. Error a | t | Sig. (2-Tailed) | 95% Confidence Interval | Year b | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower | Upper | |||||||
| 1 | Fernandes et al. 2010 [21] | −0.413 | 0.5424 | −0.762 | . | . | . | 2010 |
| 2 | Li et al. 2016 [10] | −0.760 | 0.1573 | −4.831 | 0.130 | −2.758 | 1,239 | 2016 |
| 3 | Ivanov et al. 2019 [35] | −0.503 | 0.2219 | −2.267 | 0.152 | −1.458 | 0.452 | 2019 |
| 4 | Akbas et al. 2021 [20] | −0.397 | 0.2019 | −1.965 | 0.144 | −1.039 | 0.246 | 2021 |
| 5 | Valiuliene et al. 2021 [34] | −0.323 | 0.1761 | −1.834 | 0.141 | −0.812 | 0.166 | 2021 |
| 6 | Shahin et al. 2022 [33] | −0.328 | 0.1421 | −2.307 | 0.069 | −0.693 | 0.037 | 2022 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Szota, A.M.; Kowalewska, B.; Ćwiklińska-Jurkowska, M.; Dróżdż, W. The Influence of Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Plasma Level in Patients with Schizophrenia—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175728
Szota AM, Kowalewska B, Ćwiklińska-Jurkowska M, Dróżdż W. The Influence of Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Plasma Level in Patients with Schizophrenia—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(17):5728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175728
Chicago/Turabian StyleSzota, Anna Maria, Beata Kowalewska, Małgorzata Ćwiklińska-Jurkowska, and Wiktor Dróżdż. 2023. "The Influence of Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Plasma Level in Patients with Schizophrenia—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 17: 5728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175728
APA StyleSzota, A. M., Kowalewska, B., Ćwiklińska-Jurkowska, M., & Dróżdż, W. (2023). The Influence of Electroconvulsive Therapy (ECT) on Brain-Derived Neurotrophic Factor (BDNF) Plasma Level in Patients with Schizophrenia—A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5728. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175728