Factors Influencing Postoperative Complications Following Minimally Invasive Ivor Lewis Esophagectomy: A Retrospective Cohort Study
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
3.1. Preoperative Characteristics
3.2. Perioperative Characteristics
3.3. Modeling the Likelihood of an AI and a Multi-Cycle EndoVac Therapy
3.4. Subgroup Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Bray, F.; Ferlay, J.; Soerjomataram, I.; Siegel, R.L.; Torre, L.A.; Jemal, A. Global Cancer Statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2018, 68, 394–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simard, E.P.; Ward, E.M.; Siegel, R.; Jemal, A. Cancers with Increasing Incidence Trends in the United States: 1999 through 2008. CA A Cancer J. Clin. 2012, 62, 118–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, K.C.; Hsu, D.S.; Velotta, J.B. Outcomes of Minimally Invasive and Robot-Assisted Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 3667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoelzen, J.P.; Sander, K.J.; Sesia, M.; Roy, D.; Rijcken, E.; Schnabel, A.; Struecker, B.; Juratli, M.A.; Pascher, A. Robotic-Assisted Esophagectomy Leads to Significant Reduction in Postoperative Acute Pain: A Retrospective Clinical Trial. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2022, 29, 7498–7509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Straatman, J.; van der Wielen, N.; Cuesta, M.A.; Daams, F.; Roig Garcia, J.; Bonavina, L.; Rosman, C.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Gisbertz, S.S.; van der Peet, D.L. Minimally Invasive Versus Open Esophageal Resection: Three-Year Follow-up of the Previously Reported Randomized Controlled Trial: The TIME Trial. Ann. Surg. 2017, 266, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariette, C.; Markar, S.R.; Dabakuyo-Yonli, T.S.; Meunier, B.; Pezet, D.; Collet, D.; D’Journo, X.B.; Brigand, C.; Perniceni, T.; Carrère, N.; et al. Hybrid Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 152–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fabbi, M.; Hagens, E.R.C.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Gisbertz, S.S. Anastomotic Leakage after Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer: Definitions, Diagnostics, and Treatment. Dis. Esophagus 2021, 34, doaa039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steenhagen, E.; van Vulpen, J.K.; van Hillegersberg, R.; May, A.M.; Siersema, P.D. Nutrition in Peri-Operative Esophageal Cancer Management. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 11, 663–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlana, D. Parenteral Nutrition Overview. Nutrients 2022, 14, 4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wobith, M.; Weimann, A. Oral Nutritional Supplements and Enteral Nutrition in Patients with Gastrointestinal Surgery. Nutrients 2021, 13, 2655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhuang, W.; Wu, H.; Liu, H.; Huang, S.; Wu, Y.; Deng, C.; Tian, D.; Zhou, Z.; Shi, R.; Chen, G.; et al. Utility of Feeding Jejunostomy in Patients with Esophageal Cancer Undergoing Esophagectomy with a High Risk of Anastomotic Leakage. J. Gastrointest. Oncol. 2021, 12, 433–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, A.H.; Schoeman, M.N.; Nguyen, N.Q. Long-Term Outcomes of Direct Percutaneous Endoscopic Jejunostomy: A 10-Year Cohort. Endosc. Int. Open 2015, 3, E610–E614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Batran, S.-E.; Hofheinz, R.D.; Pauligk, C.; Kopp, H.-G.; Haag, G.M.; Luley, K.B.; Meiler, J.; Homann, N.; Lorenzen, S.; Schmalenberg, H.; et al. Histopathological Regression after Neoadjuvant Docetaxel, Oxaliplatin, Fluorouracil, and Leucovorin versus Epirubicin, Cisplatin, and Fluorouracil or Capecitabine in Patients with Resectable Gastric or Gastro-Oesophageal Junction Adenocarcinoma (FLOT4-AIO): Results from the Phase 2 Part of a Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised Phase 2/3 Trial. Lancet Oncol. 2016, 17, 1697–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Hagen, P.; Hulshof, M.C.C.M.; van Lanschot, J.J.B.; Steyerberg, E.W.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Wijnhoven, B.P.L.; Richel, D.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.P.; Hospers, G.A.P.; Bonenkamp, J.J.; et al. Preoperative Chemoradiotherapy for Esophageal or Junctional Cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2012, 366, 2074–2084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biere, S.S.A.Y.; van Berge Henegouwen, M.I.; Maas, K.W.; Bonavina, L.; Rosman, C.; Garcia, J.R.; Gisbertz, S.S.; Klinkenbijl, J.H.G.; Hollmann, M.W.; de Lange, E.S.M.; et al. Minimally Invasive versus Open Oesophagectomy for Patients with Oesophageal Cancer: A Multicentre, Open-Label, Randomised Controlled Trial. Lancet 2012, 379, 1887–1892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariette, C.; Markar, S.; Dabakuyo-Yonli, T.S.; Meunier, B.; Pezet, D.; Collet, D.; D’Journo, X.B.; Brigand, C.; Perniceni, T.; Carrere, N.; et al. Health-Related Quality of Life Following Hybrid Minimally Invasive Versus Open Esophagectomy for Patients With Esophageal Cancer, Analysis of a Multicenter, Open-Label, Randomized Phase III Controlled Trial: The MIRO Trial. Ann. Surg. 2020, 271, 1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van der Sluis, P.C.; van der Horst, S.; May, A.M.; Schippers, C.; Brosens, L.A.A.; Joore, H.C.A.; Kroese, C.C.; Haj Mohammad, N.; Mook, S.; Vleggaar, F.P.; et al. Robot-Assisted Minimally Invasive Thoracolaparoscopic Esophagectomy Versus Open Transthoracic Esophagectomy for Resectable Esophageal Cancer: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Ann. Surg. 2019, 269, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Li, B.; Yi, J.; Hua, R.; Chen, H.; Tan, L.; Li, H.; He, Y.; Guo, X.; Sun, Y.; et al. Robot-Assisted Versus Conventional Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy for Resectable Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma: Early Results of a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial: The RAMIE Trial. Ann. Surg. 2022, 275, 646–653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA ICH E6 (R2) Good Clinical Practice–Scientific Guideline. Available online: https://www.ema.europa.eu/en/ich-e6-r2-good-clinical-practice-scientific-guideline (accessed on 23 August 2023).
- World Medical Association. World Medical Association Declaration of Helsinki: Ethical principles for medical research involving human subjects. JAMA 2013, 310, 2191–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathew, G.; Agha, R.; Albrecht, J.; Goel, P.; Mukherjee, I.; Pai, P.; D’Cruz, A.K.; Nixon, I.J.; Roberto, K.; Enam, S.A.; et al. STROCSS 2021: Strengthening the Reporting of Cohort, Cross-Sectional and Case-Control Studies in Surgery. Int. J. Surg. 2021, 96, 106165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Y.W.; Kim, T.; Lee, H.; Min, B.-H.; Kim, H.K.; Choi, Y.S.; Lee, J.H.; Rhee, P.-L.; Kim, J.J.; Zo, J.I.; et al. Endoscopic Vacuum Therapy for Postoperative Esophageal Leak. BMC Surg. 2019, 19, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maier, J.; Kandulski, A.; Donlon, N.E.; Werner, J.M.; Mehrl, A.; Müller, M.; Doenecke, A.; Schlitt, H.J.; Hornung, M.; Weiss, A.R.R. Endoscopic Vacuum Therapy Significantly Improves Clinical Outcomes of Anastomotic Leakages after 2-Stage, 3-Stage, and Transhiatal Esophagectomies. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2023, 408, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Satoskar, S.; Kashyap, S.; Benavides, F.; Jones, R.; Angelico, R.; Singhal, V. Success of Endoscopic Vacuum Therapy for Persistent Anastomotic Leak after Esophagectomy––A Case Report. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2021, 80, 105342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sourani, N.; Miftode, S.; Bockhorn, M. Endoscopic Vacuum Therapy for Anastomotic Leakage after Esophagectomy: A Retrospective Analysis at a Tertiary University Center. Surg. Open Sci. 2022, 11, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gubler, C.; Vetter, D.; Schmidt, H.M.; Müller, P.C.; Morell, B.; Raptis, D.; Gutschow, C.A. Preemptive Endoluminal Vacuum Therapy to Reduce Anastomotic Leakage after Esophagectomy: A Game-Changing Approach? Dis. Esophagus 2019, 32, doy126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P.C.; Morell, B.; Vetter, D.; Raptis, D.A.; Kapp, J.R.; Gubler, C.; Gutschow, C.A. Preemptive Endoluminal Vacuum Therapy to Reduce Morbidity After Minimally Invasive Ivor Lewis Esophagectomy: Including a Novel Grading System for Postoperative Endoscopic Assessment of GI-Anastomoses. Ann. Surg. 2021, 274, 751–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, P.C.; Vetter, D.; Kapp, J.R.; Gubler, C.; Morell, B.; Raptis, D.A.; Gutschow, C.A. Pre-Emptive Endoluminal Negative Pressure Therapy at the Anastomotic Site in Minimally Invasive Transthoracic Esophagectomy (the PreSPONGE Trial): Study Protocol for a Multicenter Randomized Controlled Trial. Int. J. Surg. Protoc. 2021, 25, 7–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Low, D.E.; Alderson, D.; Cecconello, I.; Chang, A.C.; Darling, G.E.; D’Journo, X.B.; Griffin, S.M.; Hölscher, A.H.; Hofstetter, W.L.; Jobe, B.A.; et al. International Consensus on Standardization of Data Collection for Complications Associated With Esophagectomy: Esophagectomy Complications Consensus Group (ECCG). Ann. Surg. 2015, 262, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berkelmans, G.H.; van Workum, F.; Weijs, T.J.; Nieuwenhuijzen, G.A.; Ruurda, J.P.; Kouwenhoven, E.A.; van Det, M.J.; Rosman, C.; van Hillegersberg, R.; Luyer, M.D. The Feeding Route after Esophagectomy: A Review of Literature. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, S785–S791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delany, H.M.; Carnevale, N.J.; Garvey, J.W. Jejunostomy by a Needle Catheter Technique. Surgery 1973, 73, 786–790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wani, M.L.; Ahangar, A.G.; Lone, G.N.; Singh, S.; Dar, A.M.; Bhat, M.A.; Lone, R.A.; Irshad, I. Feeding Jejunostomy: Does the Benefit Overweight the Risk (a Retrospective Study from a Single Centre). Int. J. Surg. 2010, 8, 387–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Seabold, S.; Perktold, J. Statsmodels: Econometric and Statistical Modeling with Python; SCIPY: Austin, TX, USA, 2010; pp. 92–96. [Google Scholar]
- Delacre, M.; Lakens, D.; Leys, C. Why Psychologists Should by Default Use Welch’s t-Test Instead of Student’s t-Test. Int. Rev. Soc. Psychol. 2017, 30, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallat, R. Pingouin: Statistics in Python. J. Open Source Softw. 2018, 3, 1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capovilla, G.; Uzun, E.; Scarton, A.; Moletta, L.; Hadzijusufovic, E.; Provenzano, L.; Salvador, R.; Pierobon, E.S.; Zanchettin, G.; Tagkalos, E.; et al. Minimally Invasive Ivor Lewis Esophagectomy in the Elderly Patient: A Multicenter Retrospective Matched-Cohort Study. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1104109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mann, C.; Berlth, F.; Hadzijusufovic, E.; Lang, H.; Grimminger, P.P. Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy: Clinical Evidence and Surgical Techniques. Langenbecks Arch Surg. 2020, 405, 1061–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berlth, F.; Hadzijusufovic, E.; Mann, C.; Fetzner, U.K.; Grimminger, P. Minimally Invasive Esophagectomy for Esophageal Cancer. Ther. Umsch. 2022, 79, 181–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, M.; Schulze, A.; Bodenstedt, S.; Maier-Hein, L.; Speidel, S.; Nickel, F.; Berlth, F.; Müller-Stich, B.P.; Grimminger, P. Technical innovations and future perspectives. Chirurg 2022, 93, 217–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengardo, V.; Pucetti, F.; Mc Cormack, O.; Chaudry, A.; Allum, W.H. The Impact of Obesity on Esophagectomy: A Meta-Analysis. Dis. Esophagus 2018, 31, dox149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugent, T.S.; Kelly, M.E.; Donlon, N.E.; Fahy, M.R.; Larkin, J.O.; McCormick, P.H.; Mehigan, B.J. Obesity and Anastomotic Leak Rates in Colorectal Cancer: A Meta-Analysis. Int. J. Color. Dis. 2021, 36, 1819–1829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kassis, E.S.; Kosinski, A.S.; Ross, P.; Koppes, K.E.; Donahue, J.M.; Daniel, V.C. Predictors of Anastomotic Leak After Esophagectomy: An Analysis of The Society of Thoracic Surgeons General Thoracic Database. Ann. Thorac. Surg. 2013, 96, 1919–1926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vasiliu, E.C.Z.; Zarnescu, N.O.; Costea, R.; Neagu, S. Review of Risk Factors for Anastomotic Leakage in Colorectal Surgery. Chirurgia 2015, 110, 319–326. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kryzauskas, M.; Bausys, A.; Degutyte, A.E.; Abeciunas, V.; Poskus, E.; Bausys, R.; Dulskas, A.; Strupas, K.; Poskus, T. Risk Factors for Anastomotic Leakage and Its Impact on Long-Term Survival in Left-Sided Colorectal Cancer Surgery. World J. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 18, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liedman, B.; Johnsson, E.; Merke, C.; Ruth, M.; Lundell, L. Preoperative Adjuvant Radiochemotherapy May Increase the Risk in Patients Undergoing Thoracoabdominal Esophageal Resections. Dig. Surg. 2001, 18, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bosset, J.F.; Gignoux, M.; Triboulet, J.P.; Tiret, E.; Mantion, G.; Elias, D.; Lozach, P.; Ollier, J.C.; Pavy, J.J.; Mercier, M.; et al. Chemoradiotherapy Followed by Surgery Compared with Surgery Alone in Squamous-Cell Cancer of the Esophagus. N. Engl. J. Med. 1997, 337, 161–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
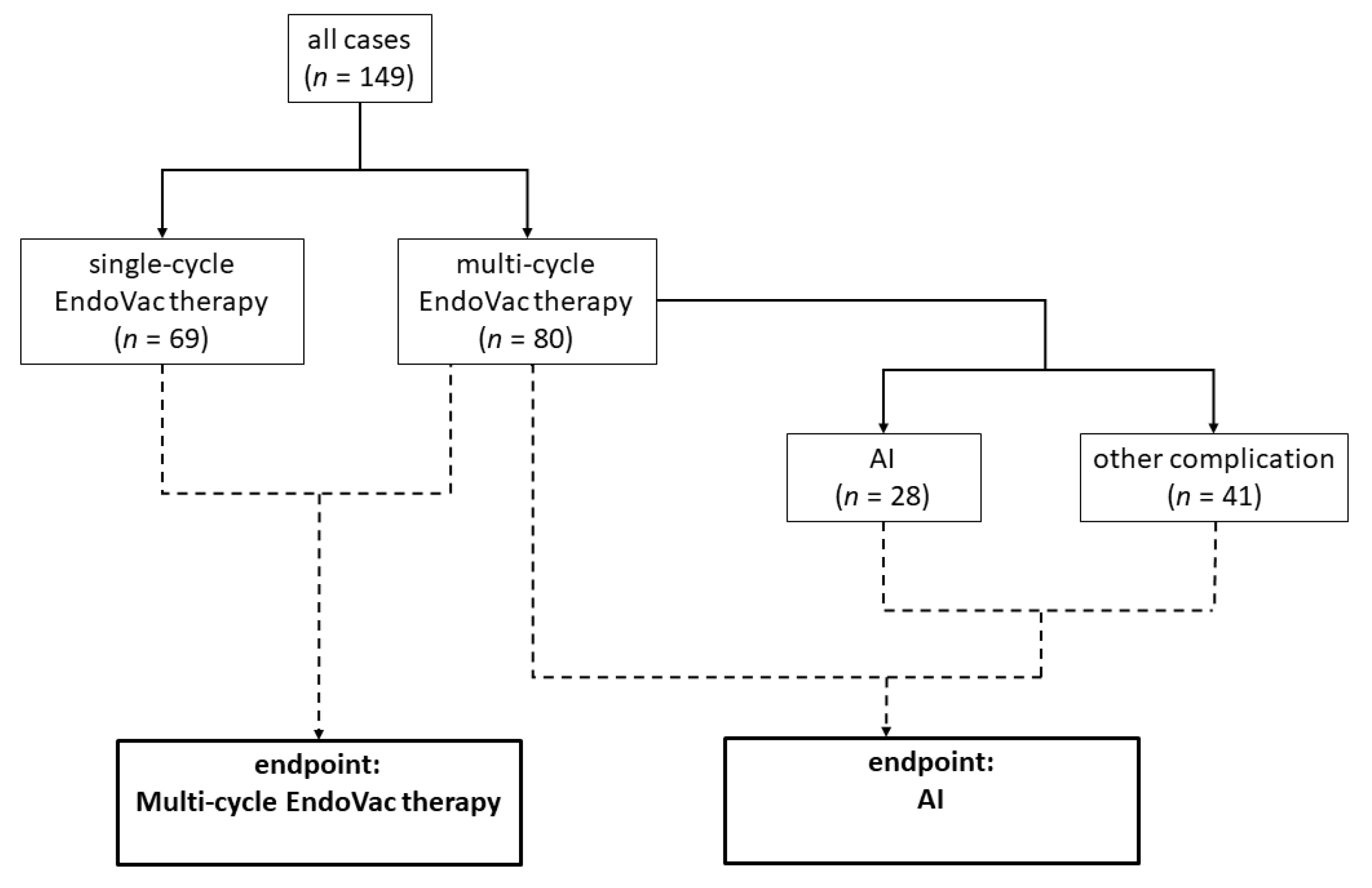
| Endpoint: AI | Endpoint: Multi-Cycle EndoVac Therapy | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Preoperative characteristics | ||||||
| No AI | AI | p-value | Single-cycle | Multi-cycle | p-value | |
| Demographic data | ||||||
| Age in years | 0.842 | 0.882 | ||||
| <65 | 67 | 14 | 36 | 45 | ||
| 65–75 | 33 | 8 | 20 | 21 | ||
| >75 | 21 | 6 | 13 | 14 | ||
| Sex | 0.118 | 0.657 | ||||
| male | 94 | 26 | 54 | 66 | ||
| female | 27 | 2 | 15 | 14 | ||
| BMI in kg/m2 | 0.092 | 0.004 * | ||||
| <25 | 53 | 6 | 37 | 22 | ||
| 25–30 | 41 | 13 | 21 | 33 | ||
| >30 | 27 | 9 | 11 | 25 | ||
| Preoperative diagnostics and therapy | ||||||
| ASA score | 0.744 | 0.094 | ||||
| <2 | 4 | 0 | 4 | 0 | ||
| ≥2 | 117 | 28 | 65 | 80 | ||
| Tumor localization | 0.423 | 0.625 | ||||
| upper or middle third | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | ||
| gastroesophageal junction | 121 | 27 | 79 | 69 | ||
| Neoadjuvant therapy | 0.335 | 0.244 | ||||
| chemotherapy | 47 | 6 | 29 | 24 | ||
| chemoradiotherapy | 65 | 19 | 34 | 50 | ||
| none | 9 | 3 | 6 | 6 | ||
| Charlson comorbidity index | 0.036 | 0.709 | ||||
| <3 | 28 | 1 | 12 | 17 | ||
| ≥3 | 93 | 27 | 57 | 63 | ||
| T-status pretherapy | 0.234 | 0.281 | ||||
| T1 | 8 | 5 | 8 | 5 | ||
| T2 | 25 | 4 | 16 | 13 | ||
| T3 | 86 | 19 | 59 | 46 | ||
| T4 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||
| N-status pretherapy | 0.999 | 0.491 | ||||
| N0 | 27 | 6 | 13 | 20 | ||
| N+ | 94 | 22 | 56 | 60 | ||
| Medication | ||||||
| Blood pressure medication | 0.124 | 0.038 * | ||||
| yes | 69 | 21 | 35 | 55 | ||
| no | 52 | 7 | 34 | 25 | ||
| Cortisone medication | 0.999 | 0.542 | ||||
| yes | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | ||
| no | 119 | 28 | 69 | 78 | ||
| Immunosuppression | 0.162 | 0.298 | ||||
| yes | 1 | 2 | 0 | 3 | ||
| no | 120 | 26 | 69 | 77 | ||
| Anticoagulant | 0.395 | 0.224 | ||||
| yes | 27 | 9 | 13 | 23 | ||
| no | 94 | 19 | 56 | 57 | ||
| Laboratory parameters | ||||||
| Preoperative CRP in mg/dl | 0.999 | 0.999 | ||||
| <0.5 | 33 | 6 | 23 | 16 | ||
| ≥0.5 | 23 | 4 | 16 | 11 | ||
| Preoperative leucocytes | 0.473 | 0.679 | ||||
| <10,000 | 81 | 14 | 64 | 70 | ||
| ≥10,000 | 33 | 9 | 4 | 7 | ||
| Preoperative hemoglobin in mg/dL | 0.763 | 0.999 | ||||
| <12 | 37 | 10 | 22 | 25 | ||
| ≥12 | 84 | 18 | 47 | 55 | ||
| Perioperative characteristics | ||||||
| Treatment group | 0.518 | 0.478 | ||||
| full-robotic | 54 | 10 | 27 | 37 | ||
| hybrid-robotic | 67 | 18 | 42 | 43 | ||
| Surgery duration (complete procedure) in minutes | 0.430 | 0.009 * | ||||
| <360 | 33 | 5 | 25 | 13 | ||
| ≥360 | 88 | 23 | 44 | 67 | ||
| Surgery duration (thoracic part) in minutes | 0.473 | 0.004 * | ||||
| <240 | 81 | 14 | 52 | 43 | ||
| ≥240 | 33 | 9 | 11 | 31 | ||
| Intraoperative blood loss in mL | 0.597 | 0.081 | ||||
| <100 | 37 | 11 | 24 | 24 | ||
| ≥100 | 49 | 10 | 27 | 32 | ||
| R status | 0.999 | 0.999 | ||||
| R0 | 115 | 26 | 65 | 76 | ||
| R1 | 6 | 2 | 4 | 4 | ||
| No AI | AI | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| mean | SD | mean | SD | p-value | |
| Age in years | 64.23 | 9.89 | 66.19 | 9.29 | 0.33 |
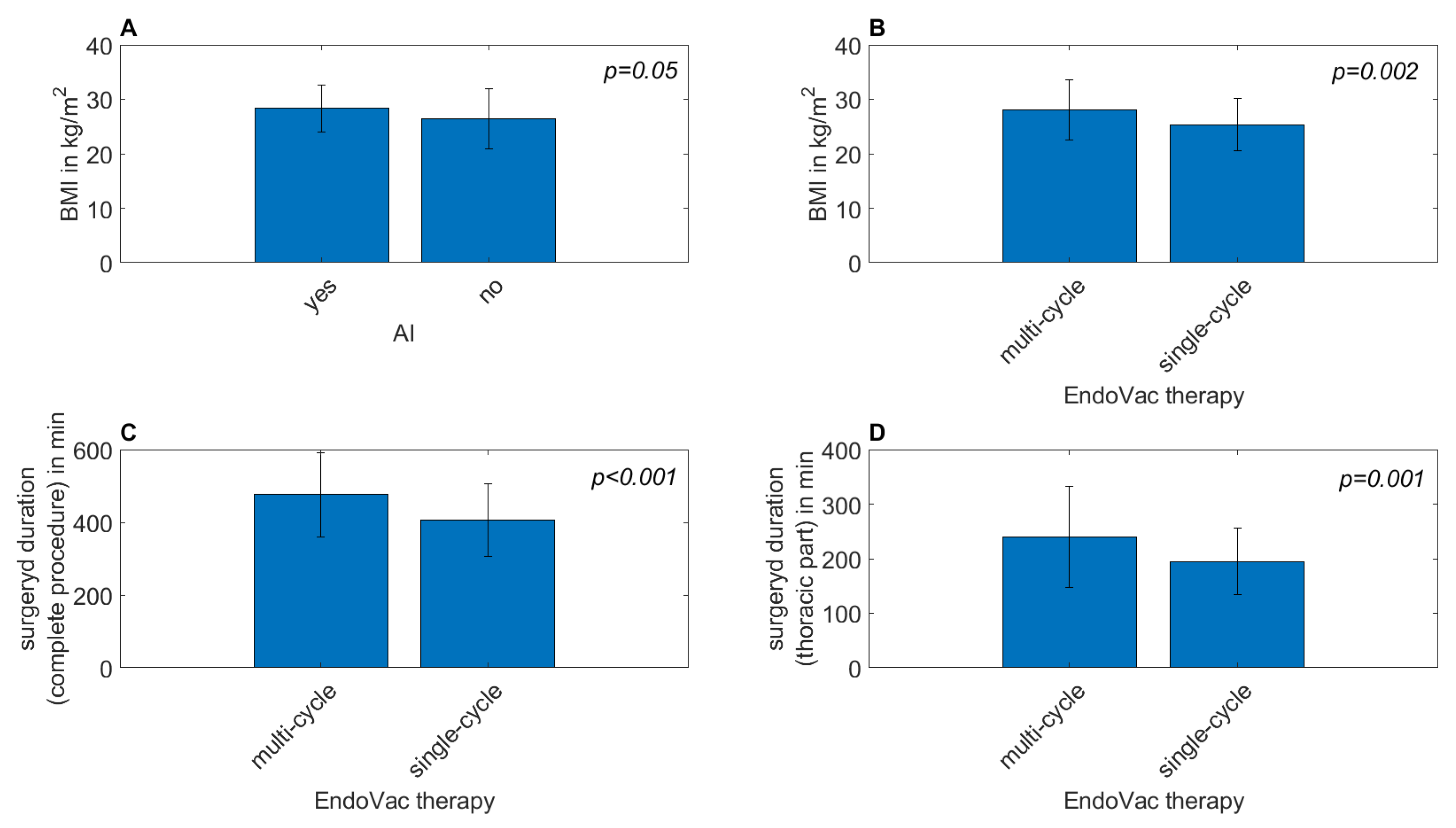
| BMI in kg/m2 | 26.44 | 5.52 | 28.36 | 4.30 | 0.05 * |
| Preoperative CRP in mg/dL | 0.85 | 1.86 | 0.68 | 1.09 | 0.71 |
| Preoperative leucocytes | 6640 | 2120 | 6400 | 1460 | 0.50 |
| Preoperative hemoglobin in mg/dL | 12.56 | 1.45 | 12.77 | 2.20 | 0.64 |
| Surgery duration (complete procedure) in minutes | 436.80 | 107.37 | 473.07 | 137.17 | 0.20 |
| Surgery duration (thoracic part) in minutes | 214.69 | 80.92 | 240.91 | 91.59 | 0.22 |
| Intraoperative blood loss in mL | 246.51 | 358.69 | 304.76 | 470.03 | 0.60 |
| Single-cycle | Multi-cycle | ||||
| mean | SD | mean | SD | p-value | |
| Age in years | 65.17 | 9.32 | 64.10 | 10.19 | 0.508 |
| BMI in kg/m2 | 25.34 | 4.80 | 28.07 | 5.50 | 0.002 * |
| Preoperative CRP in mg/dL | 0.90 | 2.14 | 0.70 | 1.01 | 0.621 |
| Preoperative leucocytes | 6350 | 1960 | 6810 | 2060 | 0.174 |
| Preoperative hemoglobin in mg/dL | 12.49 | 1.49 | 12.70 | 1.72 | 0.417 |
| Surgery duration (complete procedure) in minutes | 405.90 | 100.92 | 476.15 | 115.43 | <0.001 * |
| Surgery duration (thoracic part) in minutes | 195.13 | 61.11 | 239.50 | 93.74 | 0.001 * |
| Intraoperative blood loss in mL | 230.39 | 373.78 | 283.04 | 391.02 | 0.482 |
| Coefficient | Standard Error | p-Value | Odds Ratio | Lower 95% CI | Upper 95% CI | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intercept | −4.381 | 1.143 | <0.001 * | 0.013 | 0.001 | 0.118 |
| BMI in kg/m2 | 0.072 | 0.036 | 0.048 * | 1.074 | 1.001 | 1.15 |
| Blood pressure medication | 0.617 | 0.364 | 0.090 | 1.854 | 0.909 | 3.783 |
| Surgery duration (complete procedure) in minutes | 0.005 | 0.002 | 0.004 * | 1.005 | 1.002 | 1.009 |
| Subgroup Definition | Variable | p-Value |
|---|---|---|
| Endpoint: Multi-cycle EndoVac therapy | ||
| BMI ≥ 25 (n = 90) | ASA score | 0.018 |
| Blood pressure medication | 0.038 | |
| Blood pressure medication (n = 90) | BMI category | 0.003 |
| Hemoglobin preoperative | 0.047 | |
| Surgery duration (thoracic part) | 0.005 | |
| Surgery duration (thoracic part) ≥ 240 min (n = 41) | Neoadjuvant surgery radiochemotherapy vs. chemotherapy or none | 0.035 |
| Surgery duration (full surgery) ≥ 360 min (n = 110) | BMI > 25 | 0.014 |
| ASA score | 0.041 | |
| Charlson comorbidity index ≥ 3 (n = 120) | BMI category | 0.021 |
| Endpoint: AI | ||
| Surgery duration (thoracic part) ≥ 240 min (n = 41) | Neoadjuvant surgery radiochemotherapy vs. chemotherapy or none | 0.024 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Peters, A.K.; Juratli, M.A.; Roy, D.; Merten, J.; Fortmann, L.; Pascher, A.; Hoelzen, J.P. Factors Influencing Postoperative Complications Following Minimally Invasive Ivor Lewis Esophagectomy: A Retrospective Cohort Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175688
Peters AK, Juratli MA, Roy D, Merten J, Fortmann L, Pascher A, Hoelzen JP. Factors Influencing Postoperative Complications Following Minimally Invasive Ivor Lewis Esophagectomy: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(17):5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175688
Chicago/Turabian StylePeters, Antje K., Mazen A. Juratli, Dhruvajyoti Roy, Jennifer Merten, Lukas Fortmann, Andreas Pascher, and Jens Peter Hoelzen. 2023. "Factors Influencing Postoperative Complications Following Minimally Invasive Ivor Lewis Esophagectomy: A Retrospective Cohort Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 17: 5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175688
APA StylePeters, A. K., Juratli, M. A., Roy, D., Merten, J., Fortmann, L., Pascher, A., & Hoelzen, J. P. (2023). Factors Influencing Postoperative Complications Following Minimally Invasive Ivor Lewis Esophagectomy: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5688. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175688





