The Possible Clinical Significance of a Decreased Serum Level of Soluble PD-L1 in Discoid Lupus Erythematosus, but Not in Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus—A Pilot Study
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients and Sample Collection
2.2. Measurement of Autoantibodies
2.3. Measurement of Serum sPD-1 and sPD-L1 Levels
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of the Study Population
3.2. Comparison of Serum sPD-1 Levels in Patient Groups and Healthy Controls
3.3. Comparison of Serum sPD-L1 Levels in Patient Groups and Healthy Controls
3.4. Correlations between Serum sPD-1, sPD-L1 and the Activity of Skin Symptoms
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wenzel, J. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: New insights into pathogenesis and therapeutic strategies. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2019, 15, 519–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, A.; Lehmann, P.; Ruzicka, T. Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2004; pp. 53–58. [Google Scholar]
- Biazar, C.; Sigges, J.; Patsinakidis, N.; Ruland, V.; Amler, S.; Bonsmann, G.; Kuhn, A.; Haust, M.; Nyberg, F.; Bata, Z.; et al. Cutaneous lupus erythematosus: First multicenter database analysis of 1002 patients from the European Society of Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus (EUSCLE). Autoimmun. Rev. 2013, 12, 444–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuhn, A.; Wenzel, J.; Bijl, M. Lupus erythematosus revisited. Semin. Immunopathol. 2016, 38, 97–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elman, S.A.; Joyce, C.; Nyberg, F.; Furukawa, F.; Goodfield, M.; Hasegawa, M.; Marinovic, B.; Szepietowski, J.C.; Dutz, J.; Werth, V.P.; et al. Development of classification criteria for discoid lupus erythematosus: Results of a Delphi exercise. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2017, 77, 261–267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Vos, L.; Guel, T.; Niebel, D.; Bald, S.; ter Steege, A.; Bieber, T.; Wenzel, J. Characterization of B cells in lupus erythematosus skin biopsies in the context of different immune cell infiltration patterns. Front. Med. 2022, 9, 1037408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailly, C.; Thuru, X.; Quesnel, B. Soluble programmed death ligand-1 (Spd-l1): A pool of circulating proteins implicated in health and diseases. Cancers 2021, 13, 3034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Széles, Á.; Fazekas, T.; Váncsa, S.; Váradi, M.; Kovács, P.T.; Krafft, U.; Grünwald, V.; Hadaschik, B.; Csizmarik, A.; Hegyi, P.; et al. Pre-treatment soluble PD-L1 as a predictor of overall survival for immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2023, 72, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khan, M.; Zhao, Z.; Arooj, S.; Fu, Y.; Liao, G. Soluble PD-1: Predictive, Prognostic, and Therapeutic Value for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 587460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharpe, A.H.; Wherry, E.J.; Ahmed, R.; Freeman, G.J. The function of programmed cell death 1 and its ligands in regulating autoimmunity and infection. Nat. Immunol. 2007, 8, 239–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hirahara, S.; Katsumata, Y.; Kawasumi, H.; Kawaguchi, Y.; Harigai, M. Serum levels of soluble programmed cell death protein 1 and soluble programmed cell death protein ligand 2 are increased in systemic lupus erythematosus and associated with the disease activity. Lupus 2020, 29, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Nie, L.; Xu, L.; Wu, X.; Zhang, S.; Xue, J. Serum levels of soluble programmed death-1 (sPD-1) and soluble programmed death ligand 1(sPD-L1) in systemic lupus erythematosus: Association with activity and severity. Scand. J. Immunol. 2020, 92, e12884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wasén, C.; Erlandsson, M.C.; Bossios, A.; Ekerljung, L.; Malmhäll, C.; Töyrä Silfverswärd, S.; Pullerits, R.; Lundbäck, B.; Bokarewa, M.I. Smoking Is Associated With Low Levels of Soluble PD-L1 in Rheumatoid Arthritis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 1677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambichler, T.; Doerler, M.; Scheel, C.H. Onset of subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus after the initiation of immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy of cancer. Lupus 2021, 30, 531–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bui, A.N.; Hirner, J.; Singer, S.; Eberly-Puleo, A.; Larocca, C.; Lian, C.G.; LeBoeuf, N.R. De novo subacute cutaneous lupus erythematosus like eruptions in the setting of PD-1 or PD-L1 inhibitor therapy: Clinical-pathological correlation. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 46, 328–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blakeway, E.A.; Elshimy, N.; Muinonen-Martin, A.; Marples, M.; Mathew, B.; Mitra, A. Cutaneous lupus associated with pembrolizumab therapy for advanced melanoma: A report of three cases. Melanoma Res. 2019, 29, 338–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bolton, C.; Chen, Y.; Hawthorne, R.; Schepel, I.R.M.; Harriss, E.; Hofmann, S.C.; Ellis, S.; Clarke, A.; Wace, H.; Martin, B.; et al. Systematic Review: Monoclonal Antibody-Induced Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Drugs R D 2020, 20, 319–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Király, Z.; Szepesi, Á.; Sebestyén, A.; Kuroli, E.; Rencz, F.; Tóth, B.; Bokor, L.; Szakonyi, J.; Medvecz, M.; Hidvégi, B. Immunohistochemical Study of the PD-1/PD-L1 Pathway in Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus. Pathol. Oncol. Res. 2022, 28, 1610521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albrecht, J.; Taylor, L.; Berlin, J.A.; Dulay, S.; Ang, G.; Fakharzadeh, S.; Kantor, J.; Kim, E.; Militello, G.; Mcginnis, K.; et al. The CLASI (Cutaneous LE Disease Area and Severity Index): An outcome instrument for cutaneous lupus erythematosus. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2005, 125, 889–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gladman, D.D.; Ibanez, D.; Urowitz, M.B. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Disease Activity Index 2000. J. Reumathol. 2002, 29, 288–291. [Google Scholar]
- Vajavaara, H.; Mortensen, J.B.; Leivonen, S.K.; Hansen, I.M.; Ludvigsen, M.; Holte, H.; Jørgensen, J.; Bjerre, M.; D’amore, F.; Leppä, S. Soluble pd-1 but not pd-l1 levels predict poor outcome in patients with high-risk diffuse large b-cell lymphoma. Cancers 2021, 13, 398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frigola, X.; Inman, B.A.; Krco, C.J.; Liu, X.; Harrington, S.M.; Bulur, P.A.; Dietz, A.B.; Dong, H.; Kwon, E.D. Soluble B7-H1: Differences in production between dendritic cells and T cells. Immunol. Lett. 2012, 142, 78–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartosińska, J.; Michalak-Stoma, A.; Kowal, M.; Raczkiewicz, D.; Krasowska, D.; Chodorowska, G.; Giannopoulos, K. Analysis of circulating soluble programmed death 1 (PD-1), neuropilin 1 (NRP-1) and human leukocyte antigen-G (HLA-G) in psoriatic patients. Postepy Dermatol. Alergol. 2019, 36, 167–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Birtas Atesoglu, E.; Tarkun, P.; Demirsoy, E.T.; Geduk, A.; Mehtap, O.; Batman, A.; Kaya, F.; Cekmen, M.B.; Gulbas, Z.; Hacihanefioglu, A. Soluble Programmed Death 1 (PD-1) Is Decreased in Patients with Immune Thrombocytopenia (ITP): Potential Involvement of PD-1 Pathway in ITP Immunopathogenesis. Clin. Appl. Thromb./Hemost. 2016, 22, 248–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yanaba, K.; Hayashi, M.; Yoshihara, Y.; Nakagawa, H. Serum levels of soluble programmed death-1 and programmed death ligand-1 in systemic sclerosis: Association with extent of skin sclerosis. J. Dermatol. 2016, 43, 954–957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
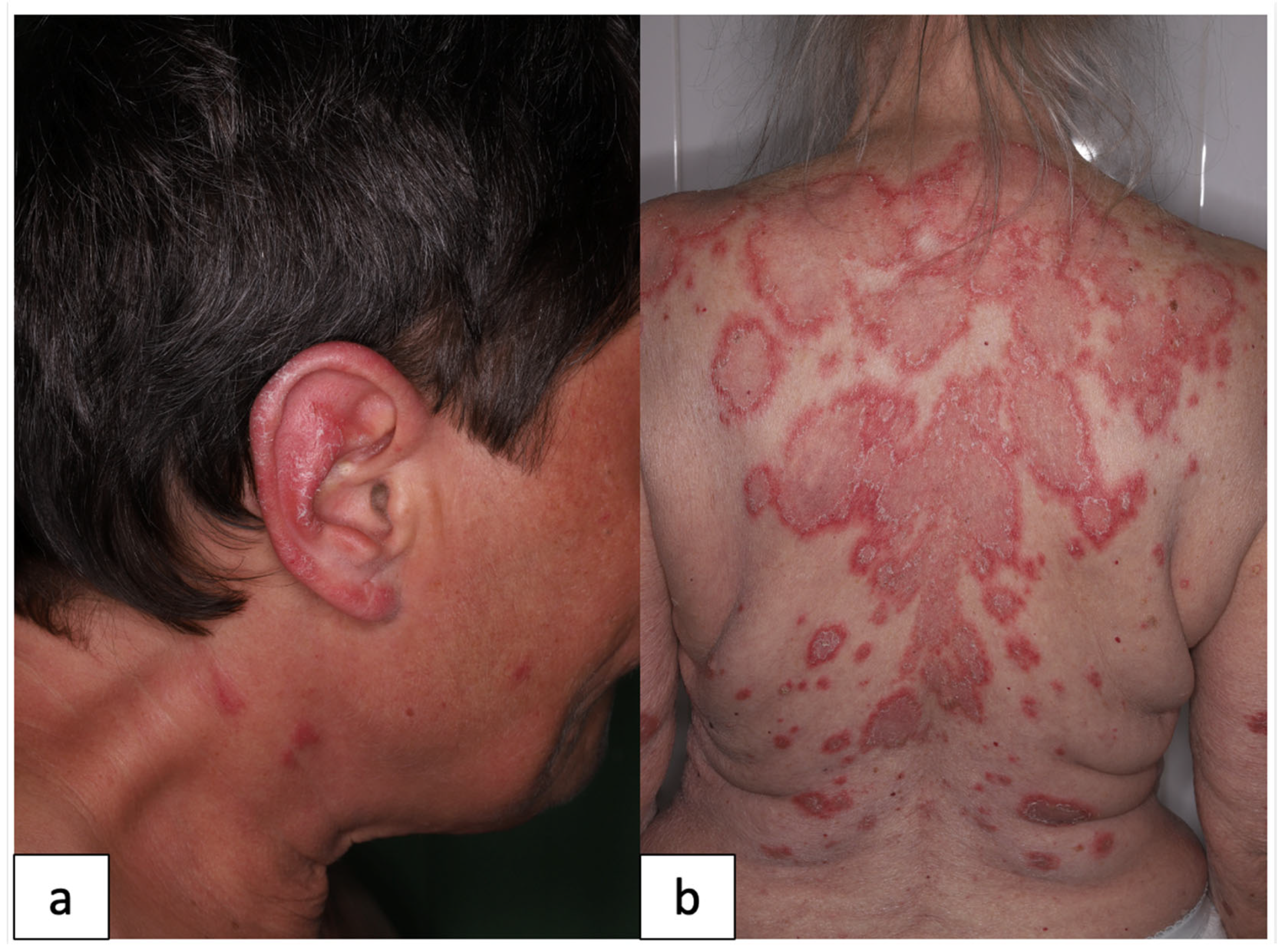

| DLE | SCLE | SLE | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Patient demographics | |||
| Female/male ratio | 19/2 | 13/5 | 9/4 |
| Age (mean ± SD) | 47.6 ± 14.5 | 62.9 ± 15 | 49 ± 17.9 |
| Autoantibody positivity | |||
| ANA | 4/21 | 12/18 | 13/13 |
| anti-SS-A/Ro | 3/21 | 11/18 | 7/13 |
| anti-SS-B/La | 1/21 | 10/18 | 5/13 |
| anti-dsDNA | 0/21 | 0/18 | 9/13 |
| anti-CL | 2/21 | 1/18 | 2/13 |
| anti-β2-GPI | 1/21 | 1/18 | 4/13 |
| Organ manifestations | |||
| Rash | 21/21 | 18/18 | 13/13 |
| Oral ulcer | 0/21 | 0/18 | 2/13 |
| Alopecia | 13/21 | 4/18 | 2/13 |
| Arthritis | 0/21 | 2/18 | 8/13 |
| Proteinuria | 0/21 | 1/18 | 3/13 |
| Leukopenia | 0/21 | 1/18 | 5/13 |
| Thrombocytopenia | 0/21 | 0/18 | 1/13 |
| Hypocomplementemia | 0/21 | 0/18 | 8/13 |
| CLASI-A score (median, min-max) | 6 (1–14) | 6 (1–18) | 6 (3–21) |
| SLEDAI-2K score (median, min-max) | NA | NA | 8 (2–20) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Király, Z.; Nagy, E.; Bokor, L.; Kovács, A.; Marschalkó, M.; Hidvégi, B. The Possible Clinical Significance of a Decreased Serum Level of Soluble PD-L1 in Discoid Lupus Erythematosus, but Not in Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus—A Pilot Study. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5648. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175648
Király Z, Nagy E, Bokor L, Kovács A, Marschalkó M, Hidvégi B. The Possible Clinical Significance of a Decreased Serum Level of Soluble PD-L1 in Discoid Lupus Erythematosus, but Not in Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus—A Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(17):5648. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175648
Chicago/Turabian StyleKirály, Zsófia, Eszter Nagy, Laura Bokor, Anikó Kovács, Márta Marschalkó, and Bernadett Hidvégi. 2023. "The Possible Clinical Significance of a Decreased Serum Level of Soluble PD-L1 in Discoid Lupus Erythematosus, but Not in Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus—A Pilot Study" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 17: 5648. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175648
APA StyleKirály, Z., Nagy, E., Bokor, L., Kovács, A., Marschalkó, M., & Hidvégi, B. (2023). The Possible Clinical Significance of a Decreased Serum Level of Soluble PD-L1 in Discoid Lupus Erythematosus, but Not in Subacute Cutaneous Lupus Erythematosus—A Pilot Study. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(17), 5648. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12175648






