Depression and Anxiety in Association with Polypharmacy in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Data Collection
2.2. Statistics
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Sociodemographic and Clinical Variables Related to Depression and Anxiety
3.3. Polypharmacy and Medication Related to Severity of Depression and Anxiety
3.4. Frequency of Comorbid Diseases in Relation to Depression and Anxiety
3.5. Associations between Switches of Disease-Modifying Therapy and Psychopathological Measures
4. Discussion
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McGinley, M.P.; Goldschmidt, C.H.; Rae-Grant, A.D. Diagnosis and Treatment of Multiple Sclerosis: A Review. JAMA 2021, 325, 765–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dobson, R.; Giovannoni, G. Multiple sclerosis—A review. Eur. J. Neurol. 2019, 26, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Walton, C.; King, R.; Rechtman, L.; Kaye, W.; Leray, E.; Marrie, R.A.; Robertson, N.; La Rocca, N.; Uitdehaag, B.; Van Der Mei, I.; et al. Rising prevalence of multiple sclerosis worldwide: Insights from the Atlas of MS, third edition. Mult. Scler. J. 2020, 26, 1816–1821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- AlSaeed, S.; Aljouee, T.; Alkhawajah, N.M.; Alarieh, R.; AlGarni, H.; Aljarallah, S.; Ayyash, M.; Abu-Shaheen, A. Fatigue, Depression, and Anxiety Among Ambulating Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 844461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamm, C.; Zettl, U.K. Autoimmune disorders affecting both the central and peripheral nervous system. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommer, P.S.; Eichstädt, K.; Ellenberger, D.; Flachenecker, P.; Friede, T.; Haas, J.; Kleinschnitz, C.; Pöhlau, D.; Rienhoff, O.; Stahmann, A.; et al. Symptomatology and symptomatic treatment in multiple sclerosis: Results from a nationwide MS registry. Mult. Scler. J. 2019, 25, 1641–1652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shull, C.M.; Hoyle, B.M.; Iannotta, C.M.; Fletcher, E.M.; Curan, M.M.; Cipollone, V.M. A current understanding of multiple sclerosis. J. Am. Acad. Physician Assist. 2020, 33, 19–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holstiege, J.; Akmatov, M.K.; Klimke, K.; Dammertz, L.; Kohring, C.; Marx, C.; Frahm, N.; Peters, M.; Ellenberger, D.; Zettl, U.K.; et al. Trends in administrative prevalence of multiple sclerosis and utilization patterns of disease modifying drugs in Germany. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2022, 59, 103534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Travers, B.S.; Tsang, B.K.-T.; Barton, J.L. Multiple sclerosis: Diagnosis, disease-modifying therapy and prognosis. Aust. J. Gen. Pract. 2022, 51, 199–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harris, V.K.; Sadiq, S.A. Biomarkers of Therapeutic Response in Multiple Sclerosis: Current Status. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 2014, 18, 605–617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rommer, P.S.; Zettl, U.K. Current Pharmaceutical Trends in Neuroimmunology—Part II: Autoimmunity Beyond the CNS and Other Disorders. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2022, 28, 853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanghì, A.; D’amico, E.; Patti, F. Immunosuppression in relapsing remitting multiple sclerosis: Moving towards personalized treatment. Expert Rev. Neurother. 2020, 20, 771–782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rommer, P.S.; Zettl, U.K. Managing the side effects of multiple sclerosis therapy: Pharmacotherapy options for patients. Expert Opin. Pharmacother. 2018, 19, 483–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Doshi, A.; Chataway, J. Multiple sclerosis, a treatable disease. Clin. Med. 2017, 17, 530–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moore, P.; Hirst, C.; Harding, K.E.; Clarkson, H.; Pickersgill, T.P.; Robertson, N.P. Multiple sclerosis relapses and depression. J. Psychosom. Res. 2012, 73, 272–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zanghì, A.; D’amico, E.; Fermo, S.L.; Patti, F. Exploring polypharmacy phenomenon in newly diagnosed relapsing–remitting multiple sclerosis: A cohort ambispective single-centre study. Ther. Adv. Chronic Dis. 2021, 12, 2040622320983121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lian, G.; Wang, G.; Yin, Q.; Su, Z. A review of possible therapies for multiple sclerosis. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2021, 476, 3261–3270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patejdl, R.; Zettl, U.K. Spasticity in multiple sclerosis: Contribution of inflammation, autoimmune mediated neuronal damage and therapeutic interventions. Autoimmun. Rev. 2017, 16, 925–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patejdl, R.; Zettl, U.K. The pathophysiology of motor fatigue and fatigability in multiple sclerosis. Front. Neurol. 2022, 13, 891415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frahm, N.; Hecker, M.; Zettl, U.K. Polypharmacy in patients with multiple sclerosis: A gender-specific analysis. Biol. Sex Differ. 2019, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masnoon, N.; Shakib, S.; Kalisch-Ellett, L.; Caughey, G.E. What is polypharmacy? A systematic review of definitions. BMC Geriatr. 2017, 17, 230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aparasu, R.R.; Mort, J.R.; Brandt, H. Polypharmacy trends in office visits by the elderly in the United States, 1990 and 2000. Res. Social Adm. Pharm. 2005, 1, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frahm, N.; Hecker, M.; Zettl, U.K. Polypharmacy in Chronic Neurological Diseases: Multiple Sclerosis, Dementia and Parkinson’s Disease. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2021, 27, 4008–4016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chertcoff, A.; Ng, H.S.; Zhu, F.; Zhao, Y.; Tremlett, H. Polypharmacy and multiple sclerosis: A population-based study. Mult. Scler. J. 2023, 29, 107–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bourdette, D.; Herink, M. Polypharmacy in multiple sclerosis: More is not necessarily better. Mult. Scler. J. 2023, 29, 3–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frahm, N.; Hecker, M.; Zettl, U.K. Polypharmacy among patients with multiple sclerosis: A qualitative systematic review. Expert Opin. Drug Saf. 2020, 19, 139–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thelen, J.; Zvonarev, V.; Lam, S.; Burkhardt, C.; Lynch, S.; Bruce, J. Polypharmacy in Multiple Sclerosis: Current Knowledge and Future Directions. Mo. Med. 2021, 118, 239–245. [Google Scholar]
- Thelen, J.M.; Lynch, S.G.; Bruce, A.S.; Hancock, L.M.; Bruce, J.M. Polypharmacy in multiple sclerosis: Relationship with fatigue, perceived cognition, and objective cognitive performance. J. Psychosom. Res. 2014, 76, 400–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachmann, P.; Frahm, N.; Debus, J.L.; Mashhadiakbar, P.; Langhorst, S.E.; Streckenbach, B.; Baldt, J.; Heidler, F.; Hecker, M.; Zettl, U.K. Prevalence and Severity of Potential Drug–Drug Interactions in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis with and without Polypharmacy. Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadovnick, A.D.; Remick, R.A.; Allen, J.; Swartz, E.; Yee, I.M.; Eisen, K.; Farquhar, R.; Hashimoto, S.A.; Hooge, J.; Kastrukoff, L.F.; et al. Depression and multiple sclerosis. Neurology 1996, 46, 628–632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Files, D.K.; Jausurawong, T.; Katrajian, R.; Danoff, R. Multiple sclerosis. Prim. Care 2015, 42, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrie, R.A.; Hanwell, H. General health issues in multiple sclerosis: Comorbidities, secondary conditions, and health behaviors. Continuum. (Minneap. Minn.) 2013, 19, 1046–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giordano, A.; Granella, F.; Lugaresi, A.; Martinelli, V.; Trojano, M.; Confalonieri, P.; Radice, D.; Solari, A. Anxiety and depression in multiple sclerosis patients around diagnosis. J. Neurol. Sci. 2011, 307, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsivgoulis, G.; Triantafyllou, N.; Papageorgiou, C.; Evangelopoulos, M.; Kararizou, E.; Sfagos, C.; Vassilopoulos, D. Associations of the Expanded Disability Status Scale with anxiety and depression in multiple sclerosis outpatients. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2007, 115, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Solaro, C.; Gamberini, G.; Masuccio, F.G. Depression in Multiple Sclerosis: Epidemiology, Aetiology, Diagnosis and Treatment. CNS Drugs 2018, 32, 117–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensari, I.; Pilutti, L.A.; Motl, R.W. Depressive symptomology in multiple sclerosis: Disability, cardiorespiratory fitness and heart rate variability. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2017, 136, 440–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sparaco, M.; Lavorgna, L.; Bonavita, S. Psychiatric disorders in multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2021, 268, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korostil, M.; Feinstein, A. Anxiety disorders and their clinical correlates in multiple sclerosis patients. Mult. Scler. J. 2007, 13, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahl, O.P.; Stordal, E.; Lydersen, S.; Midgard, R. Anxiety and depression in multiple sclerosis. A comparative population-based study in Nord-Trøndelag County, Norway. Mult. Scler. 2009, 15, 1495–1501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Studer, V.; Motta, C.; Polidoro, S.; Perugini, J.; Macchiarulo, G.; Giovannetti, A.M.; Pareja-Gutierrez, L.; Calò, A.; Colonna, I.; et al. Neuroinflammation drives anxiety and depression in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2017, 89, 1338–1347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Egmond, E.; van der Hiele, K.; van Gorp, D.; Jongen, P.J.; van der Klink, J.; Reneman, M.F.; Beenakker, E.A.C.; Eijk, V.; Frequin, S.T.F.M.; Gans, D.; et al. Work difficulties in people with multiple sclerosis: The role of anxiety, depression and coping. Mult. Scler. J. Exp. Transl. Clin. 2022, 8, 20552173221116282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Batista, A.R.; Silva, S.; Lencastre, L.; Guerra, M.P. Biopsychosocial Correlates of Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis Patients. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 14431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Butler, E.; Matcham, F.; Chalder, T. A systematic review of anxiety amongst people with Multiple Sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2016, 10, 145–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thompson, A.J.; Banwell, B.L.; Barkhof, F.; Carroll, W.M.; Coetzee, T.; Comi, G.; Correale, J.; Fazekas, F.; Filippi, M.; Freedman, M.S.; et al. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis: 2017 revisions of the McDonald criteria. Lancet Neurol. 2018, 17, 162–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtzke, J.F. Rating neurologic impairment in multiple sclerosis: An expanded disability status scale (EDSS). Neurology 1983, 33, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Moock, S.; Feng, Y.-S.; Maeurer, M.; Dippel, F.-W.; Kohlmann, T. Systematic literature review and validity evaluation of the Expanded Disability Status Scale (EDSS) and the Multiple Sclerosis Functional Composite (MSFC) in patients with multiple sclerosis. BMC Neurol. 2014, 14, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigmond, A.S.; Snaith, R.P. The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr. Scand. 1983, 67, 361–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bjelland, I.; Dahl, A.A.; Haug, T.T.; Neckelmann, D. The validity of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. An updated literature review. J. Psychosom. Res. 2002, 52, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patten, S.B.; Burton, J.M.; Fiest, K.M.; Wiebe, S.; Bulloch, A.G.; Koch, M.; Dobson, K.S.; Metz, L.M.; Maxwell, C.J.; Jetté, N. Validity of four screening scales for major depression in MS. Mult. Scler. J. 2015, 21, 1064–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrie, R.A.; Zhang, L.; Lix, L.M.; Graff, L.A.; Walker, J.R.; Fisk, J.D.; Patten, S.B.; Hitchon, C.A.; Bolton, J.M.; Sareen, J.; et al. The validity and reliability of screening measures for depression and anxiety disorders in multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2018, 20, 9–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marrie, R.A.; Patel, R.; Bernstein, C.N.; Bolton, J.M.; Graff, A.L.; Marriott, J.J.; Hitchon, A.C.; Figley, C.R.; Kornelsen, J.; Fisk, J.D. Anxiety and depression affect performance on the symbol digit modalities test over time in MS and other immune disorders. Mult. Scler. J. 2021, 27, 1284–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janssens, A.C.J.W.; van Doorn, P.A.; de Boer, J.B.; van der Meché, F.G.A.; Passchier, J.; Hintzen, R.Q. Impact of recently diagnosed multiple sclerosis on quality of life, anxiety, depression and distress of patients and partners. Acta Neurol. Scand. 2003, 108, 389–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Institut für Qualitätssicherung in Prävention und Rehabilitation GmbH. HADS-D, Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale—Deutsche Version. Available online: https://www.assessment-info.de/assessment/seiten/datenbank/vollanzeige/vollanzeige-de.asp?vid=27 (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- Brockmöller, J.; Stingl, J.C.; Gaedigk, A.; Twist, G.P.; Farrow, E.G.; Lowry, A.J.; Soden, E.S.; Miller, A.N.; Koolen, S.L.; Van der Rijt, C.C.; et al. Multimorbidity, polypharmacy and pharmacogenomics in old age. Pharmacogenomics 2017, 18, 515–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology. ATC/DDD Index 2023: WHO Collaborating Centre for Drug Statistics Methodology; 2023. Available online: https://www.whocc.no/atc_ddd_index/ (accessed on 4 August 2023).
- Marrie, R.A.; Miller, A.; Sormani, M.P.; Thompson, A.; Waubant, E.; Trojano, M.; O’Connor, P.; Fiest, K.; Reider, N.; Reingold, S.; et al. Recommendations for observational studies of comorbidity in multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2016, 86, 1446–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ilić, P.; Motl, R.W.; Duffecy, J. Multiple sclerosis and anxiety: Is there an untapped opportunity for exercise? Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2023, 73, 104698. [Google Scholar]
- McIntosh, G.E.; Liu, E.S.; Allan, M.; Grech, L.B. Clinical Practice Guidelines for the Detection and Treatment of Depression in Multiple Sclerosis: A Systematic Review. Neurol. Clin. Pract. 2023, 13, e200154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiest, K.M.; Bernstein, C.N.; Walker, J.R.; Graff, L.A.; Hitchon, C.A.; Peschken, C.A.; Zarychanski, R.; Abou-Setta, A.; Patten, S.B.; Sareen, J.; et al. Systematic review of interventions for depression and anxiety in persons with inflammatory bowel disease. BMC Res. Notes 2016, 9, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustač, F.; Pašić, H.; Medić, F.; Bjedov, B.; Vujević, L.; Alfirević, M.; Vidrih, B.; Tudor, K.I.; Pašić, M.B. Anxiety and Depression as Comorbidities of Multiple Sclerosis. Psychiatr. Danub. 2021, 33, 480–485. [Google Scholar]
- McCabe, M.P. Mood and self-esteem of persons with multiple sclerosis following an exacerbation. J. Psychosom. Res. 2005, 59, 161–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jones, K.H.; Ford, D.V.; Jones, P.A.; John, A.; Middleton, R.M.; Lockhart-Jones, H.; Osborne, L.A.; Noble, J.G. A Large-Scale Study of Anxiety and Depression in People with Multiple Sclerosis: A Survey via the Web Portal of the UK MS Register. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e41910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peres, D.S.; Rodrigues, P.; Viero, F.T.; Frare, J.M.; Kudsi, S.Q.; Meira, G.M.; Trevisan, G. Prevalence of depression and anxiety in the different clinical forms of multiple sclerosis and associations with disability: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Brain, Behav. Immun. Health 2022, 24, 100484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McGuigan, C.; Hutchinson, M. Unrecognised symptoms of depression in a community–based population with multiple sclerosis. J. Neurol. 2006, 253, 219–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marrie, R.A.; Patten, S.B.; Berrigan, L.I.; Tremlett, H.; Wolfson, C.; Warren, S.; Leung, S.; Fiest, K.M.; McKay, K.A.; Fisk, J.D.; et al. Diagnoses of Depression and Anxiety Versus Current Symptoms and Quality of Life in Multiple Sclerosis. Int. J. MS Care 2018, 20, 76–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ploughman, M.; Wallack, E.M.; Chatterjee, T.; Kirkland, M.C.; Curtis, M.E. Under-treated depression negatively impacts lifestyle behaviors, participation and health-related quality of life among older people with multiple sclerosis. Mult. Scler. Relat. Disord. 2020, 40, 101919. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohr, D.C.; Hart, S.L.; Fonareva, I.; Tasch, E.S. Treatment of depression for patients with multiple sclerosis in neurology clinics. Mult. Scler. J. 2006, 12, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cetin, K.; Johnson, K.; Ehde, D.; Kuehn, C.; Amtmann, D.; Kraft, G. Antidepressant use in multiple sclerosis: Epidemiologic study of a large community sample. Mult. Scler. J. 2007, 13, 1046–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feinstein, A. An examination of suicidal intent in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 2002, 59, 674–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feinstein, A. Multiple sclerosis, disease modifying treatments and depression: A critical methodological review. Mult. Scler. 2000, 6, 343–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.; Finlayson, M. Mental Health and Mental Health Service Use Among People Aged 45+ with Multiple Sclerosis. Can. J. Community Ment. Health 2005, 24, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halabchi, F.; Alizadeh, Z.; Sahraian, M.A.; Abolhasani, M. Exercise prescription for patients with multiple sclerosis; potential benefits and practical recommendations. BMC Neurol. 2017, 17, 185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motl, R.W. Exercise and Multiple Sclerosis. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1228, 333–343. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Birjandi, K.C.; Sharafi, J.; Etemadizade, A.; Ghasemi, E. Influence of eight weeks of combined training on adipsin and lipoprotein profile and possible relations with depression, anxiety and stress in women with multiple sclerosis. Horm. Mol. Biol. Clin. Investig. 2022, 44, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

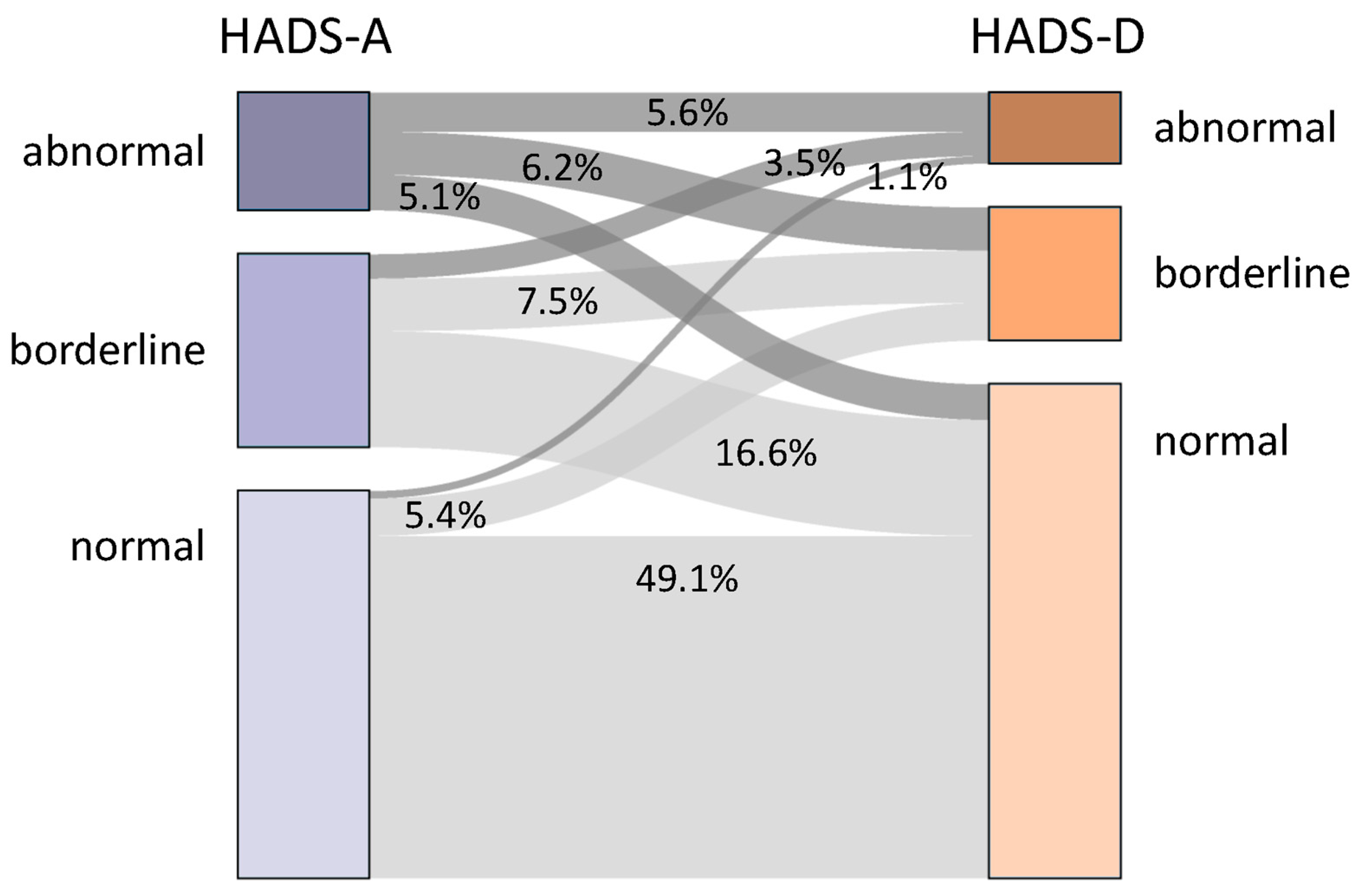
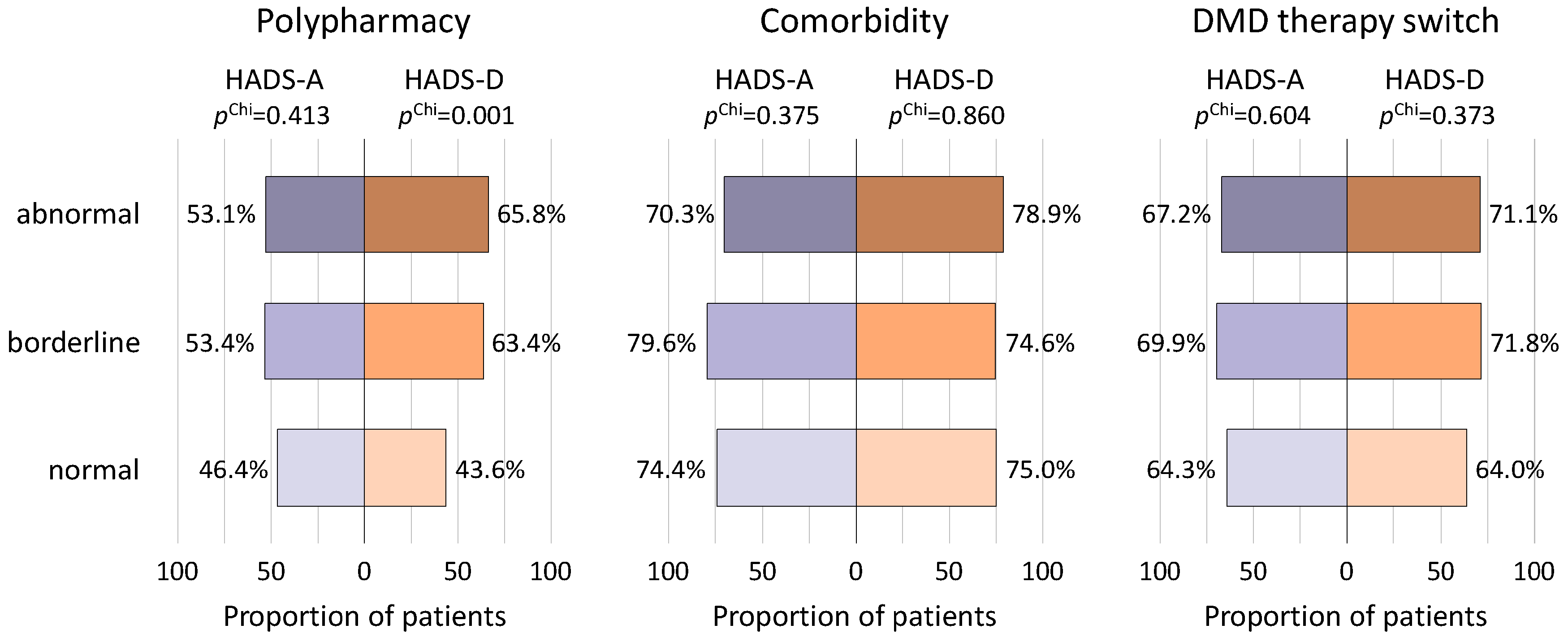

| HADS-A | HADS-D | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HADS score | 0–7 | 8–10 | 11–21 | p | 0–7 | 8–10 | 11–21 | p |
| n (%) | 207 (55.3) | 103 (27.5) | 64 (17.1) | 264 (70.8) | 71 (19.0) | 38 (10.2) | ||
| Sex, n (%) | 0.239 1 | 0.090 1 | ||||||
| Female | 132 (52.8) | 70 (28.0) | 48 (19.2) | 184 (73.9) | 45 (18.1) | 20 (8.0) | ||
| Male | 75 (60.5) | 33 (26.6) | 16 (12.9) | 80 (64.5) | 26 (21.0) | 18 (14.5) | ||
| Age (years), mean ± SD | 49.3 ± 12.2 | 46.7 ± 13.6 | 46.7 ± 13.4 | 0.161 2 | 47.6 ± 12.6 | 50.6 ± 14.1 | 47.3 ± 11.7 | 0.199 2 |
| EDSS score, median | 3.5 | 3.0 | 3.0 | 0.317 3 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 3.25 | 0.002 3* |
| Disease duration (years), mean ± SD | 13.2 ± 8.8 | 12.1 ± 9.4 | 10.9 ± 10.8 | 0.194 2 | 12.7 ± 9.2 | 13.5 ± 10.1 | 9.6 ± 8.4 | 0.097 2 |
| MS course, n (%) | 0.287 1 | 0.128 1 | ||||||
| CIS/RRMS | 134 (51.7) | 76 (29.3) | 49 (18.9) | 189 (73.3) | 40 (15.5) | 29 (11.2) | ||
| SPMS | 56 (65.1) | 19 (22.1) | 11 (12.8) | 56 (65.1) | 23 (26.7) | 7 (8.1) | ||
| PPMS | 17 (58.6) | 8 (27.6) | 4 (13.8) | 19 (65.5) | 8 (27.6) | 2 (6.9) | ||
| HADS-A | HADS-D | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HADS score | 0–7 | 8–10 | 11–21 | p | 0–7 | 8–10 | 11–21 | p |
| n (%) | 207 (55.3) | 103 (27.5) | 64 (17.1) | 264 (70.8) | 71 (19.0) | 38 (10.2) | ||
| Number of drugs taken, mean ± SD | 4.8 ± 2.8 | 5.1 ± 3.0 | 5.1 ± 3.3 | 0.475 | 4.5 ± 2.6 | 6.1 ± 3.6 | 5.5 ± 3.1 | <0.001 *** |
| Prescription drugs, mean ± SD | 3.8 ± 2.6 | 4.0 ± 2.8 | 4.0 ± 3.0 | 0.757 | 3.6 ± 2.4 | 4.9 ± 3.4 | 4.3 ± 3.0 | <0.001 ** |
| Over-the-counter drugs, mean ± SD | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 1.1 ± 1.2 | 1.2 ± 1.1 | 0.430 | 1.0 ± 1.2 | 1.3 ± 1.2 | 1.2 ± 1.3 | 0.157 |
| DMD, mean ± SD | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 0.224 | 0.8 ± 0.4 | 0.7 ± 0.4 | 0.7 ± 0.5 | 0.221 |
| Symptomatic MS drugs, mean ± SD | 1.9 ± 1.9 | 2.0 ± 2.0 | 1.8 ± 1.9 | 0.774 | 1.7 ± 1.8 | 2.4 ± 1.9 | 2.5 ± 2.6 | 0.004 ** |
| Drugs to treat comorbidities and other conditions, mean ± SD | 2.1 ± 2.0 | 2.4 ± 2.2 | 2.6 ± 2.6 | 0.199 | 2.0 ± 1.9 | 3.1 ± 2.8 | 2.1 ± 2.0 | 0.001 ** |
| HADS-A | HADS-D | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HADS score | 0–7 | 8–10 | 11–21 | Total sample | p | 0–7 | 8–10 | 11–21 | Total sample | p |
| n (%) | 207 (55.3) | 103 (27.5) | 64 (17.1) | 374 (100.0) | 264 (70.8) | 71 (19.0) | 38 (10.2) | 373 (100.0) | ||
| A03—Drugs for functional gastrointestinal disorders | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.0) | 1 (1.6) | 2 (0.5) | 0.253 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (2.8) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.5) | 0.014 |
| A10—Drugs used in diabetes | 7 (3.4) | 3 (2.9) | 4 (6.3) | 14 (3.7) | 0.499 | 5 (1.9) | 8 (11.3) | 1 (2.6) | 14 (3.8) | 0.001 * |
| C03—Diuretic drugs | 10 (4.8) | 4 (3.9) | 3 (4.7) | 17 (4.5) | 0.930 | 8 (3.0) | 8 (11.3) | 1 (2.6) | 17 (4.6) | 0.011 |
| C10—Lipid-modifying agents | 22 (10.6) | 12 (11.7) | 5 (7.8) | 39 (10.4) | 0.725 | 24 (9.1) | 14 (19.7) | 1 (2.6) | 39 (10.5) | 0.009 |
| N03—Antiepileptic drugs | 28 (13.5) | 14 (13.6) | 8 (12.5) | 50 (13.2) | 0.975 | 28 (10.6) | 12 (16.9) | 10 (26.3) | 50 (13.4) | 0.018 |
| N04—Antiparkinson drugs | 2 (1.0) | 4 (3.9) | 5 (7.8) | 11 (2.9) | 0.014 | 4 (1.5) | 4 (5.6) | 3 (7.9) | 11 (2.9) | 0.031 |
| N05—Psycholeptic drugs | 3 (1.4) | 3 (2.9) | 7 (10.9) | 13 (3.5) | 0.001 * | 5 (1.9) | 3 (4.2) | 5 (13.2) | 13 (3.5) | 0.002 |
| N06—Psychoanaleptics | 28 (13.5) | 25 (24.3) | 19 (29.7) | 72 (19.5) | 0.005 | 40 (15.2) | 17 (23.9) | 15 (39.5) | 72 (19.3) | <0.001 * |
| V03—All other therapeutic products | 0 (0.0) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (3.1) | 2 (0.5) | 0.008 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (2.8) | 0 (0.0) | 2 (0.5) | 0.014 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Baldt, J.; Frahm, N.; Hecker, M.; Streckenbach, B.; Langhorst, S.E.; Mashhadiakbar, P.; Burian, K.; Meißner, J.; Heidler, F.; Richter, J.; et al. Depression and Anxiety in Association with Polypharmacy in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5379. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165379
Baldt J, Frahm N, Hecker M, Streckenbach B, Langhorst SE, Mashhadiakbar P, Burian K, Meißner J, Heidler F, Richter J, et al. Depression and Anxiety in Association with Polypharmacy in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(16):5379. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165379
Chicago/Turabian StyleBaldt, Julia, Niklas Frahm, Michael Hecker, Barbara Streckenbach, Silvan Elias Langhorst, Pegah Mashhadiakbar, Katja Burian, Janina Meißner, Felicita Heidler, Jörg Richter, and et al. 2023. "Depression and Anxiety in Association with Polypharmacy in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 16: 5379. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165379
APA StyleBaldt, J., Frahm, N., Hecker, M., Streckenbach, B., Langhorst, S. E., Mashhadiakbar, P., Burian, K., Meißner, J., Heidler, F., Richter, J., & Zettl, U. K. (2023). Depression and Anxiety in Association with Polypharmacy in Patients with Multiple Sclerosis. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(16), 5379. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165379







