Understanding the Impact of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis on Smell and Taste: An International Patient Experience Survey
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
2.2. Setting
2.3. Participants
2.4. Data Sources and Variables
2.5. Bias
2.6. Study Size and Statistical Analyses
2.7. Ethical Approval
3. Results
3.1. Demographics
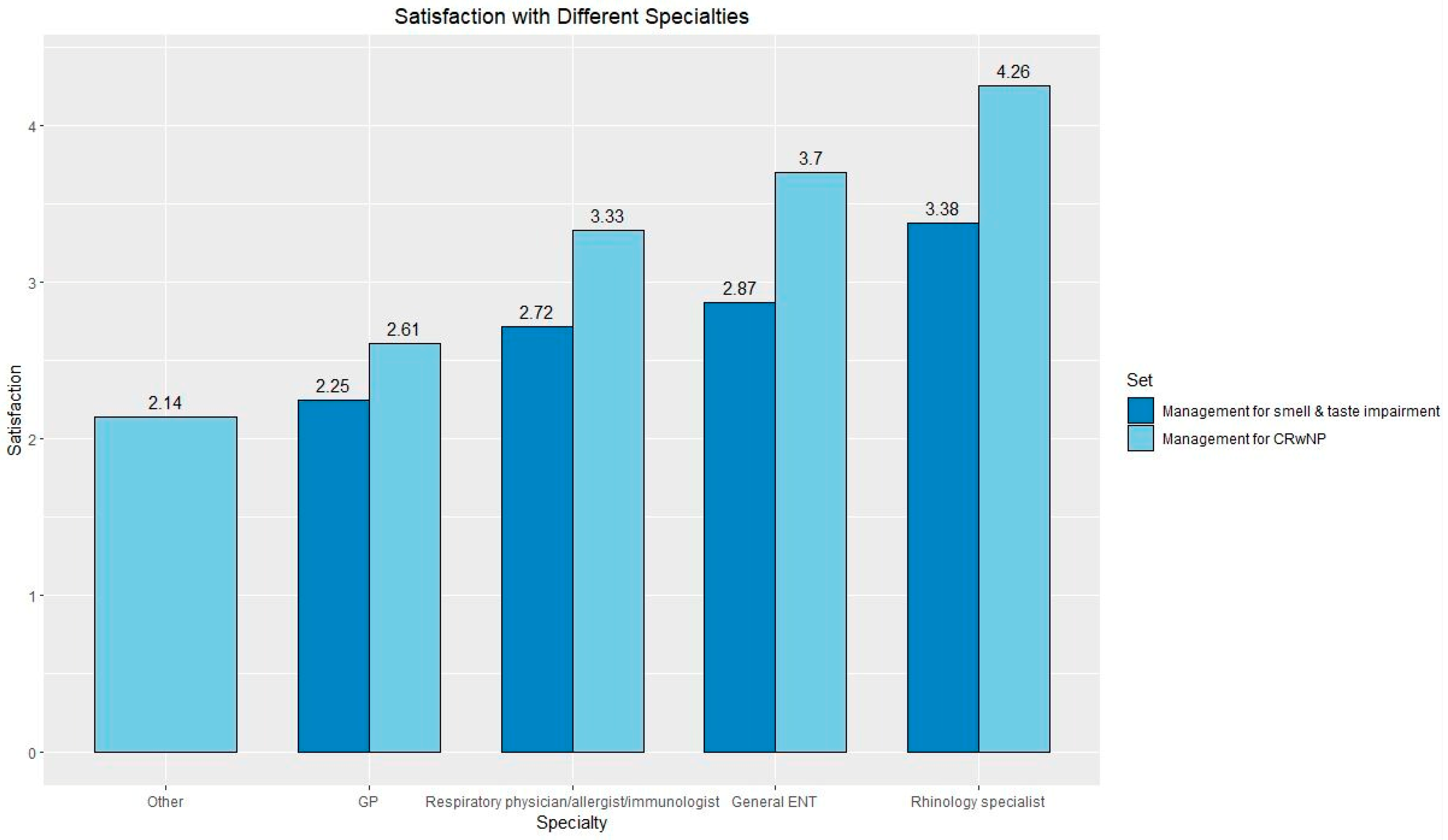
3.2. Patient Experience of Living with CRSwNP
‘Costs for treatments are massive here with sublingual immunotherapy and Budesonide, Flovent, and the potential for Dupixent are all expensive and poorly covered by my insurance.’(Male, 26–40, USA).
‘I find it very frustrating that we can’t get the biologics for such a severe illness. I know my ENT doctor is trying his best, just limited by the medications he can use.’(Female, 56–70, East Midlands, UK).
‘Primary care physicians and allergists require education to manage initial symptoms and referral to competent specialists.’(Female, 56–70, USA).
‘More awareness from the GP of CRSwNP.’(Female, 56–70, South East England).
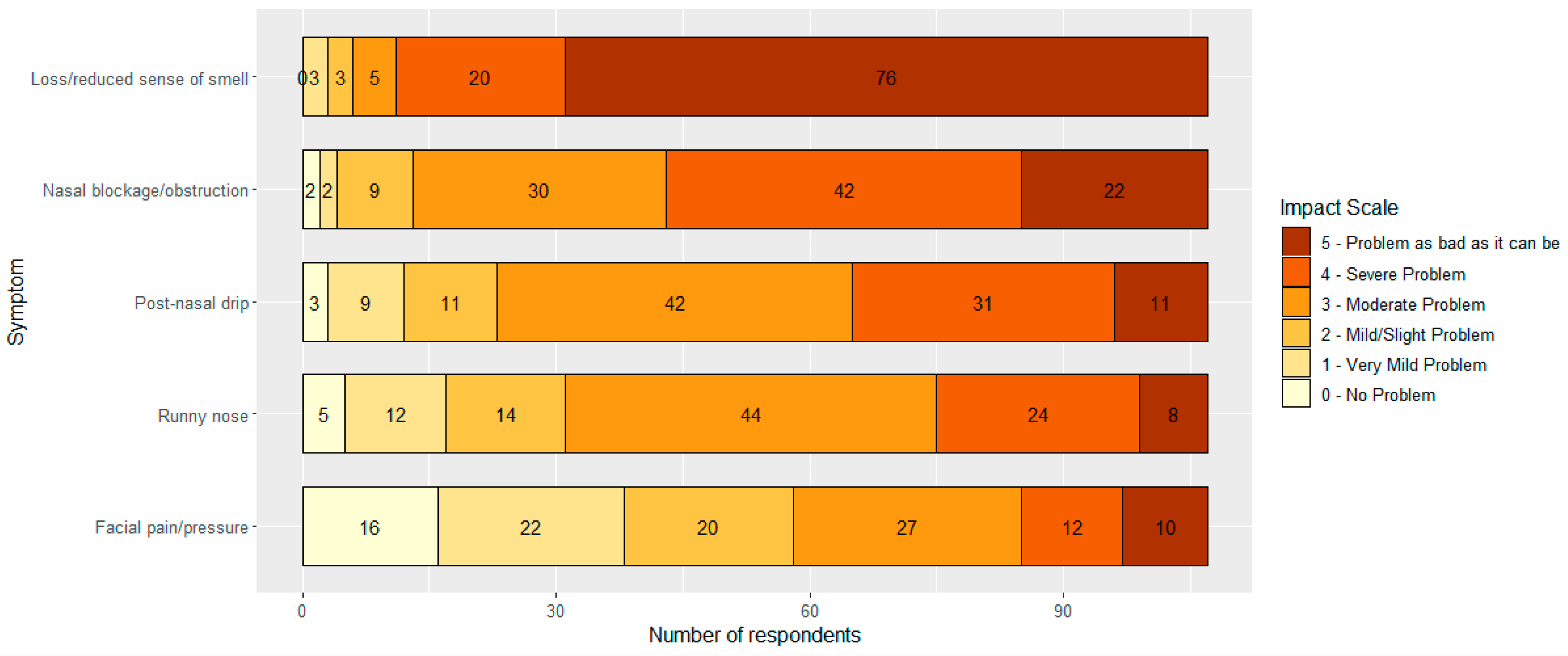
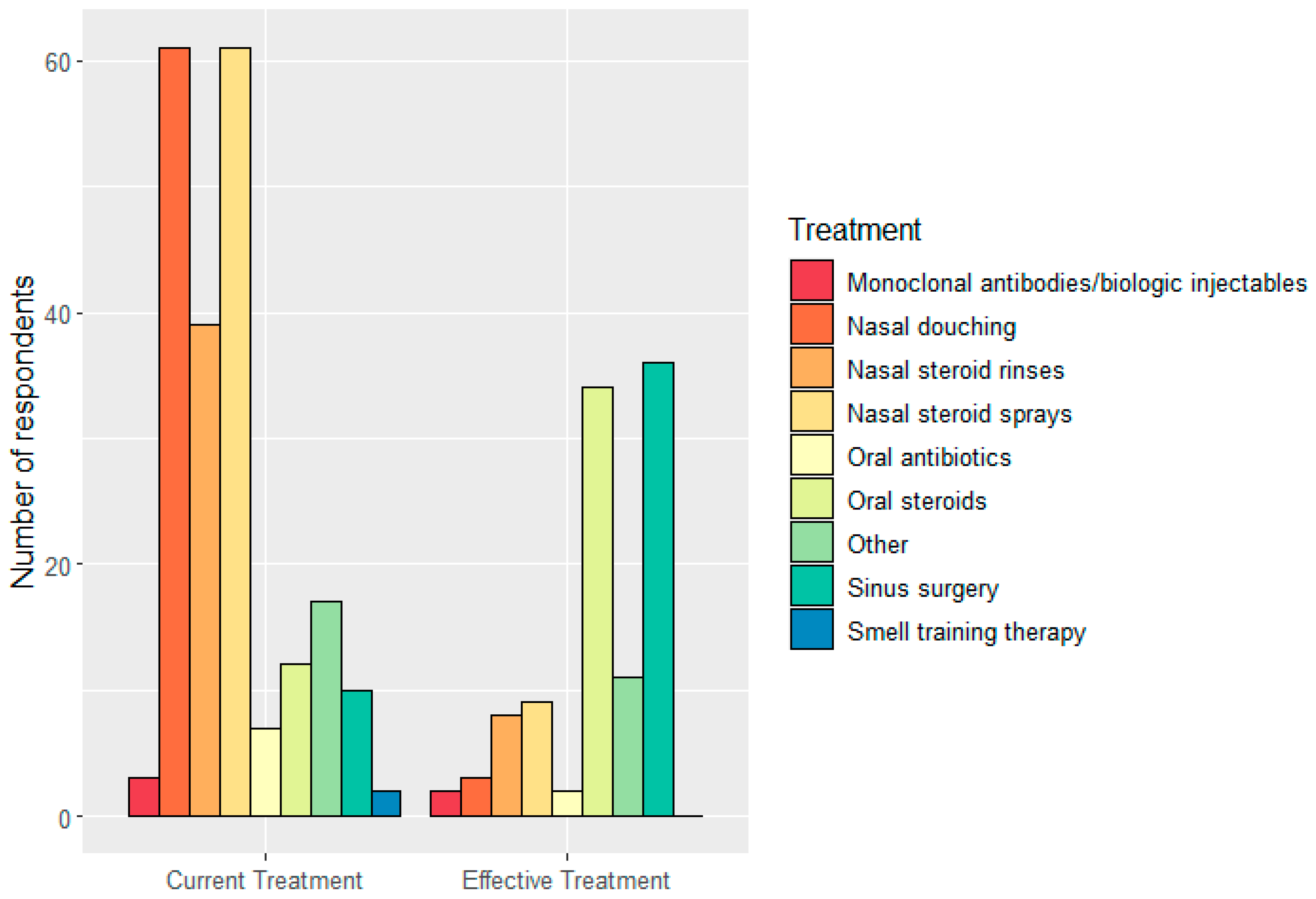
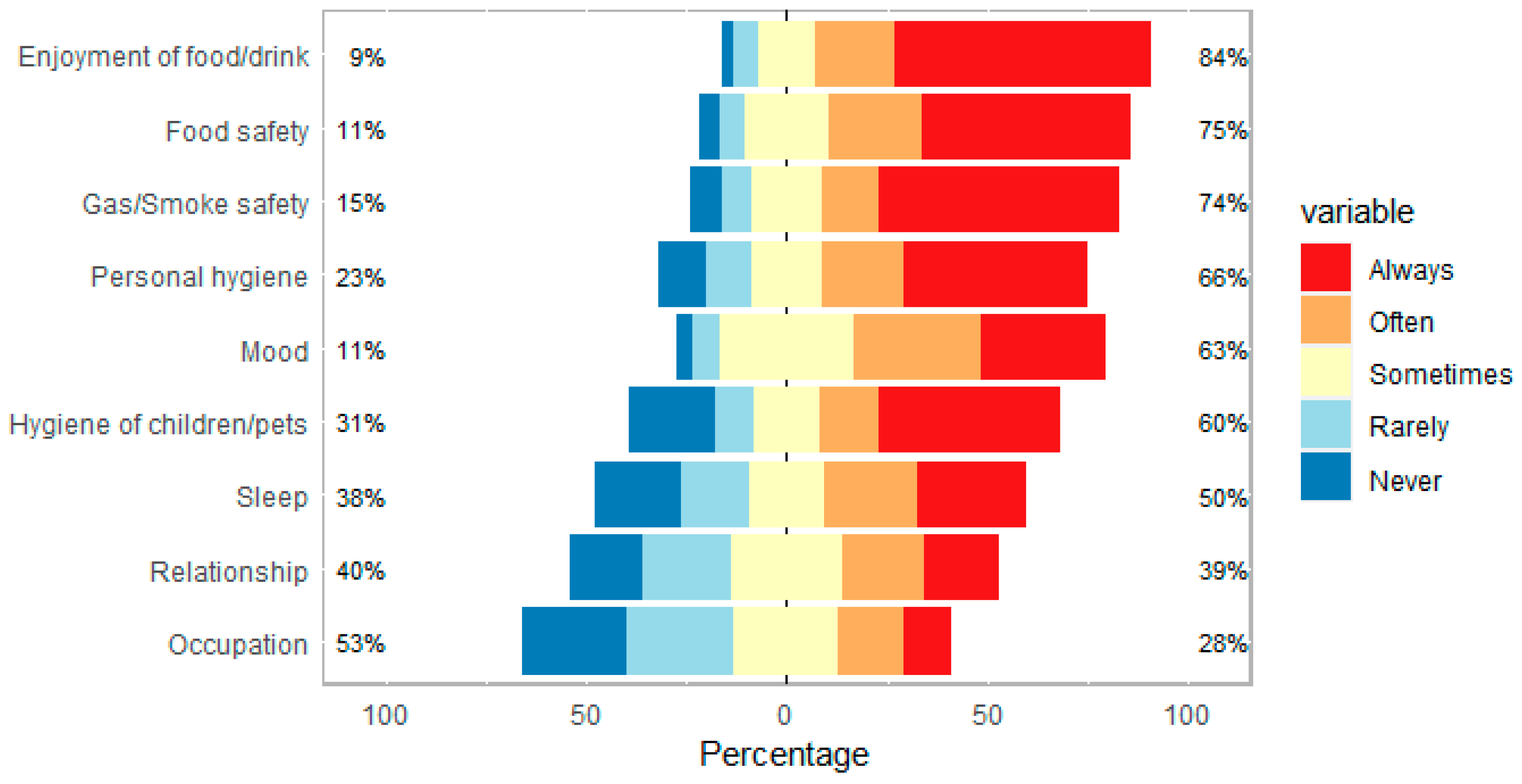
3.3. The Effect of Living with CRSwNP on Smell and/or Taste
4. Discussion
4.1. Key Findings
4.2. Strengths and Limitations
4.3. Comparison with Other Studies
4.4. Implications for Future Research and/or Practice
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Hopkins, C.; Hellings, P.W.; Kern, R.; Reitsma, S.; Toppila-Salmi, S.; Bernal-Sprekelsen, M.; Mullol, J.; Alobid, I.; et al. European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2020. Rhinology 2020, 58, 1–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gliklich, R.E.; Metson, R. The Health Impact of Chronic Sinusitis in Patients Seeking Otolaryngologic Care. Otolaryngol. Head. Neck Surg. 1995, 113, 104–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hastan, D.; Fokkens, W.J.; Bachert, C.; Newson, R.B.; Bislimovska, J.; Bockelbrink, A.; Bousquet, P.J.; Brozek, G.; Bruno, A.; Dahlén, S.E.; et al. Chronic Rhinosinusitis in Europe—An Underestimated Disease. A GA2LEN Study. Allergy 2011, 66, 1216–1223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fokkens, W.J.; Lund, V.J.; Mullol, J.; Bachert, C.; Alobid, I.; Baroody, F.; Cohen, N.; Cervin, A.; Douglas, R.; Gevaert, P.; et al. EPOS 2012: European Position Paper on Rhinosinusitis and Nasal Polyps 2012. A Summary for Otorhinolaryngologists. Rhinology 2012, 50, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stevens, W.W.; Schleimer, R.P.; Kern, R.C. Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2016, 4, 565–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banerji, A.; Piccirillo, J.F.; Thawley, S.E.; Levitt, R.G.; Schechtman, K.B.; Kramper, M.A.; Hamilos, D.L. Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients with Polyps or Polypoid Mucosa Have a Greater Burden of Illness. Am. J. Rhinol. 2007, 21, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Toros, S.Z.; Bölükbasi, S.; Naiboğlu, B.; Er, B.; Akkaynak, C.; Noshari, H.; Egeli, E. Comparative Outcomes of Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients with Chronic Sinusitis and Nasal Polyps. Eur. Arch. Oto-Rhino-Laryngol. 2007, 264, 1003–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erskine, S.; Hopkins, C.; Kumar, N.; Wilson, J.; Clark, A.; Robertson, A.; Kara, N.; Sunkaraneni, V.; Anari, S.; Philpott, C. A Cross Sectional Analysis of a Case-Control Study about Quality of Life in CRS in the UK; a Comparison between CRS Subtypes. Rhinology 2016, 54, 311–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banglawala, S.M.; Oyer, S.L.; Lohia, S.; Psaltis, A.J.; Soler, Z.M.; Schlosser, R.J. Olfactory Outcomes in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis after Medical Treatments: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2014, 4, 986–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philpott, C.M.; Boak, D. The Impact of Olfactory Disorders in the United Kingdom. Chem. Senses 2014, 39, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erskine, S.E.; Philpott, C.M. An Unmet Need: Patients with Smell and Taste Disorders. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2020, 45, 197–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neuland, C.; Bitter, T.; Marschner, H.; Gudziol, H.; Guntinas-Lichius, O. Health-Related and Specific Olfaction-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Chronic Functional Anosmia or Severe Hyposmia. Laryngoscope 2011, 121, 867–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Litvack, J.R.; Fong, K.; Mace, J.; James, K.E.; Smith, T.L. Predictors of Olfactory Dysfunction in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Laryngoscope 2008, 118, 2225–2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mori, E.; Matsuwaki, Y.; Mitsuyama, C.; Okushi, T.; Nakajima, T.; Moriyama, H. Risk Factors for Olfactory Dysfunction in Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Auris Nasus Larynx 2013, 40, 465–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickham, H. Ggplot2: Elegant Graphics for Data Analysis; Use R! Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Chong, L.-Y.; Piromchai, P.; Sharp, S.; Snidvongs, K.; Webster, K.E.; Philpott, C.; Hopkins, C.; Burton, M.J. Biologics for Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2021, 2021, CD013513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meier, E.C.; Schmid-Grendelmeier, P.; Steiner, U.C.; Soyka, M.B. Real-Life Experience of Monoclonal Antibody Treatments in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2021, 182, 736–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erskine, S.E.; Verkerk, M.M.; Notley, C.; Williamson, I.G.; Philpott, C.M. Chronic Rhinosinusitis: Patient Experiences of Primary and Secondary Care—A Qualitative Study. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2016, 41, 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennik, J.; Eyles, C.; Thomas, M.; Hopkins, C.; Little, P.; Blackshaw, H.; Schilder, A.; Savage, I.; Philpott, C.M. Chronic Rhinosinusitis: A Qualitative Study of Patient Views and Experiences of Current Management in Primary and Secondary Care. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e022644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Claeys, N.; Teeling, M.T.; Legrand, P.; Poppe, M.; Verschueren, P.; De Prins, L.; Cools, L.; Cypers, L.; Fokkens, W.J.; Hopkins, C.; et al. Patients Unmet Needs in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps Care: A Patient Advisory Board Statement of EUFOREA. Front. Allergy 2021, 2, 761388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Talat, R.; Speth, M.M.; Gengler, I.; Phillips, K.M.; Caradonna, D.S.; Gray, S.T.; Sedaghat, A.R. Chronic Rhinosinusitis Patients with and without Polyps Experience Different Symptom Perception and Quality of Life Burdens. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2020, 34, 742–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdalla, S.; Alreefy, H.; Hopkins, C. Prevalence of Sinonasal Outcome Test (SNOT-22) Symptoms in Patients Undergoing Surgery for Chronic Rhinosinusitis in the England and Wales National Prospective Audit. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2012, 37, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hopkins, C.; Philpott, C.; Crowe, S.; Regan, S.; Degun, A.; Papachristou, I.; Schilder, A.G.M. Identifying the Most Important Outcomes for Systematic Reviews of Interventions for Rhinosinusitis in Adults: Working with Patients, Public and Practitioners. Rhinology 2016, 54, 20–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Head, K.; Chong, L.Y.; Hopkins, C.; Philpott, C.; Burton, M.J.; Schilder, A.G. Short-course Oral Steroids Alone for Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2016, 2016, CD011991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poetker, D.M.; Jakubowski, L.A.; Lal, D.; Hwang, P.H.; Wright, E.D.; Smith, T.L. Oral Corticosteroids in the Management of Adult Chronic Rhinosinusitis with and without Nasal Polyps: An Evidence-Based Review with Recommendations. Int. Forum Allergy Rhinol. 2013, 3, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasir, M.; Goyal, A.; Sonthalia, S. Corticosteroid Adverse Effects. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Philpott, C. Olfaction in CRS. Available online: https://www.entandaudiologynews.com/features/ent-features/post/olfaction-in-crs (accessed on 12 July 2023).
- Lourijsen, E.S.; Reitsma, S.; Vleming, M.; Hannink, G.; Adriaensen, G.F.J.P.M.; Cornet, M.E.; Hoven, D.R.; Videler, W.J.M.; Bretschneider, J.H.; Reinartz, S.M.; et al. Endoscopic Sinus Surgery with Medical Therapy versus Medical Therapy for Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: A Multicentre, Randomised, Controlled Trial. Lancet Respir. Med. 2022, 10, 337–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calus, L.; Van Bruaene, N.; Bosteels, C.; Dejonckheere, S.; Van Zele, T.; Holtappels, G.; Bachert, C.; Gevaert, P. Twelve-Year Follow-up Study after Endoscopic Sinus Surgery in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis. Clin. Transl. Allergy 2019, 9, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veloso-Teles, R.; Cerejeira, R. Endoscopic Sinus Surgery for Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps: Clinical Outcome and Predictive Factors of Recurrence. Am. J. Rhinol. Allergy 2017, 31, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopkins, C.; Browne, J.; Slack, R.; Lund, V.; Topham, J.; Reeves, B.; Copley, L.; Brown, P.; Van Der Meulen, J. The National Comparative Audit of Surgery for Nasal Polyposis and Chronic Rhinosinusitis. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2006, 31, 390–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ball, S.; Boak, D.; Dixon, J.; Carrie, S.; Philpott, C.M. Barriers to Effective Health Care for Patients Who Have Smell or Taste Disorders. Clin. Otolaryngol. 2021, 46, 1213–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousquet, J.; Brusselle, G.; Buhl, R.; Busse, W.W.; Cruz, A.A.; Djukanovic, R.; Domingo, C.; Hanania, N.A.; Humbert, M.; Gow, A.M.; et al. Care Pathways for the Selection of a Biologic in Severe Asthma. Eur. Respir. J. 2017, 50, 1701782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NHS Health Research Authority ANCHOR-1: Depemokimab in Patients with Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Available online: https://www.hra.nhs.uk/planning-and-improving-research/application-summaries/research-summaries/anchor-1-depemokimab-in-patients-with-chronic-rhinosinusitis-with-nasal-polyps/ (accessed on 2 August 2023).

| Variable | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Gender | |
| Female | 70 (65.4%) |
| Male | 37 (34.6%) |
| Gender neutral | 0 |
| Transgender | 0 |
| Prefer not to say | 0 |
| Age | |
| Under 18 | 0 |
| 18–25 | 3 (2.8%) |
| 26–40 | 20 (18.8%) |
| 41–55 | 36 (33.6%) |
| 56–70 | 36 (33.6%) |
| Over 70 | 12 (11.2%) |
| Region | |
| East of England | 8 (7.5%) |
| East Midlands | 4 (3.7%) |
| West Midlands | 6 (5.6%) |
| Greater London | 6 (5.6%) |
| North West England | 9 (8.4%) |
| North East England | 3 (2.8%) |
| South West England | 13 (12.1%) |
| South East England | 17 (15.9%) |
| Yorkshire and Lincolnshire | 6 (5.6%) |
| Scotland | 4 (3.7%) |
| Wales | 7 (6.5%) |
| Northern Ireland | 0 |
| Abroad | 24 (22.4%) |
| Australia (2) | |
| Canada (4) | |
| Hungary (1) | |
| Iceland (1) | |
| Philippines (1) | |
| Republic of Ireland (1) | |
| South Africa (1) | |
| Sweden (1) | |
| USA (12) | |
| Formally diagnosed with CRSwNP | |
| Yes | 107 (86%) |
| No | 17 (14%) |
| Question | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| How long have you suffered with symptoms of CRSwNP? | |
| Less than a year | 1 (0.9%) |
| 1–2 years | 5 (4.7%) |
| 2–5 years | 12 (11.2%) |
| 5+ years | 87 (81.3%) |
| Not sure | 2 (1.9%) |
| Who diagnosed you with CRSwNP? (Allowed to choose more than one answer) | |
| General Practitioner | 14 (10.8%) |
| General ENT doctor | 56 (43.1%) |
| ENT doctor specializing in rhinology | 48 (36.9%) |
| Respiratory physician/allergist/immunologist | 9 (6.9%) |
| Other | 3 (2.3%) |
| How many times have you been referred to a specialist (e.g., ENT) by your GP for CRSwNP? | |
| 1 | 20 (18.7%) |
| 2–3 | 40 (37.4%) |
| 4–5 | 17 (15.9%) |
| 5+ | 22 (20.6%) |
| Never been referred | 8 (7.48%) |
| How long since you were initially diagnosed with CRSwNP? | |
| Less than a year | 7 (6.5%) |
| 1–2 years | 10 (9.3%) |
| 2–5 years | 15 (14%) |
| 5+ years | 74 (69.2%) |
| Not sure | 1 (0.9%) |
| Are you under any regular follow-up for your CRSwNP? | |
| Yes | 39 (36.4%) |
| No | 66 (61.7%) |
| Not applicable | 2 (1.9%) |
| Who regularly sees you regarding your CRSwNP follow-ups? | |
| General Practitioner | 9 (8.4%) |
| General ENT doctor | 20 (18.7%) |
| ENT doctor specializing in rhinology | 24 (22.4%) |
| Respiratory physician/allergist/immunologist | 3 (2.8%) |
| Not applicable | 51 (47.7%) |
| Which of the following could have been done to improve your care and experience in the management of CRSwNP? (Allowed to choose more than one answer) | |
| The availability of more management options for CRSwNP | 74 (74.7%) |
| Smell testing | 39 (39.4%) |
| More time with the clinician | 29 (29.3%) |
| Mental health support | 24 (24.2%) |
| Other | 14 (14.1%) |
| High Satisfaction Scores | Low Satisfaction Scores | |
|---|---|---|
| Rhinology Specialist | ‘She was thorough in her examinations, concise in explanations and treatment options…I feel they understand my condition.’ (Female, 56–70, USA) ‘Both sinus surgery and follow-up treatment have changed my life for the better…’ (Female, 56–70, East Midlands, UK) ‘A joy to be seen by someone who understood and took a real interest.’ (Female, 56–70, West Midlands) | ‘It’s all very reactionary, not proactive, never given any preventative advice, more just live with it until it gets so bad you need an operation again.’ (Female, 56–70, North West England) ‘You have to wait weeks for a CT scan…weeks to go back for the results…months for an operation. In the mean time you can’t sleep, eat or function properly and are in constant pain.’ (Female, 56–70, North West England) ‘Ability to smell isn’t their focus, it’s the ability to breath.’ (Female, 26–40, USA) ‘The last one said “well you won’t really miss it after that long, will you?” No one would say that if you were blind or deaf.’ (Female, 26–40, South East England) |
| General ENT Clinician | ‘My ENT doctor opened my eyes to the world of sinus health and surgery, showed me how much life I was missing.’ (Male, 26–40, USA) ‘Whilst smell and taste has not returned after surgery, overall wellness has improved. Both before and after surgery all ENT specialists have always been sympathetic and professional when dealing with my anosmia.’ (Male, over 70, North East England) | ‘They give their best support but the treatments in existence simply aren’t great…’ (Female, 26–40, USA) ‘I have moved abroad, best experience in the Netherlands, Germany has been 50:50. UK I felt was very poor.’ (Male, 26–40, Greater London) |
| Respiratory physician/ Allergist/ Immunologist | ‘My healthcare team has been transparent and I’ve finally felt people are taking my symptoms seriously.’ (Male, 26–40, USA) | ‘It is like they don’t really care not realise how exhausting it is.’ (Female, 41–55, Canada) ‘Told to just live with it…nothing he can do.’ (Female, 41–55, South East England) |
| General Practitioner (GP) | ‘GP was sympathetic, nothing he could do and referred me.’ (Male, over 70, North East England) ‘My current GP is the first to take my symptoms seriously. He is an asthmatic and lifetime sufferer of allergies so he related to my condition.’ (Male, 26–40, USA) | ‘Not knowledgeable and doesn’t understand living with the condition.’ (Male, 41–55, South West England) ‘For many years the GP has taken a view that since it cannot be cured, no follow up is necessary. All they do is prescribe Flixonase.’ (Male, over 70, Yorkshire and Lincolnshire) ‘GP doesn’t seem to care that I can’t smell. My physical symptoms have improved so my GP hasn’t been helpful trying to help me get my sense of smell back.’ (Female, 26–40, Republic of Ireland) |
| Other | ‘Without a regular doctor, one gets poor, inconsistent support.’ (Female, over 70, Canada) |
| Question | Frequency (%) |
|---|---|
| Do you have any of the following additional medical conditions that can affect the sense of smell? | |
| Other sinonasal conditions (e.g., Allergies, nasal tumor, olfactory cleft stenosis) | 28 (25.7%) |
| Not applicable | 5 (4.6%) |
| Smell loss after an operation | 6 (5.5%) |
| Smell loss after a viral infection (e.g., Post COVID-19) | 3 (2.8%) |
| Smell loss after a head injury | 1 (1%) |
| Congenital smell loss (smell loss since birth) | 0 |
| Neurodegenerative conditions (Alzheimer’s, Dementia, Parkinson’s Disease) | 0 |
| Other | 0 |
| None of the above | 66 (60.6%) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luke, L.; Lee, L.; Gokani, S.A.; Boak, D.; Boardman, J.; Philpott, C. Understanding the Impact of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis on Smell and Taste: An International Patient Experience Survey. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5367. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165367
Luke L, Lee L, Gokani SA, Boak D, Boardman J, Philpott C. Understanding the Impact of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis on Smell and Taste: An International Patient Experience Survey. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(16):5367. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165367
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuke, Louis, Liam Lee, Shyam Ajay Gokani, Duncan Boak, Jim Boardman, and Carl Philpott. 2023. "Understanding the Impact of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis on Smell and Taste: An International Patient Experience Survey" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 16: 5367. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165367
APA StyleLuke, L., Lee, L., Gokani, S. A., Boak, D., Boardman, J., & Philpott, C. (2023). Understanding the Impact of Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyposis on Smell and Taste: An International Patient Experience Survey. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(16), 5367. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165367







