A History of Innovation: Tracing the Evolution of Imaging Modalities for the Preoperative Planning of Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
3. Early Techniques
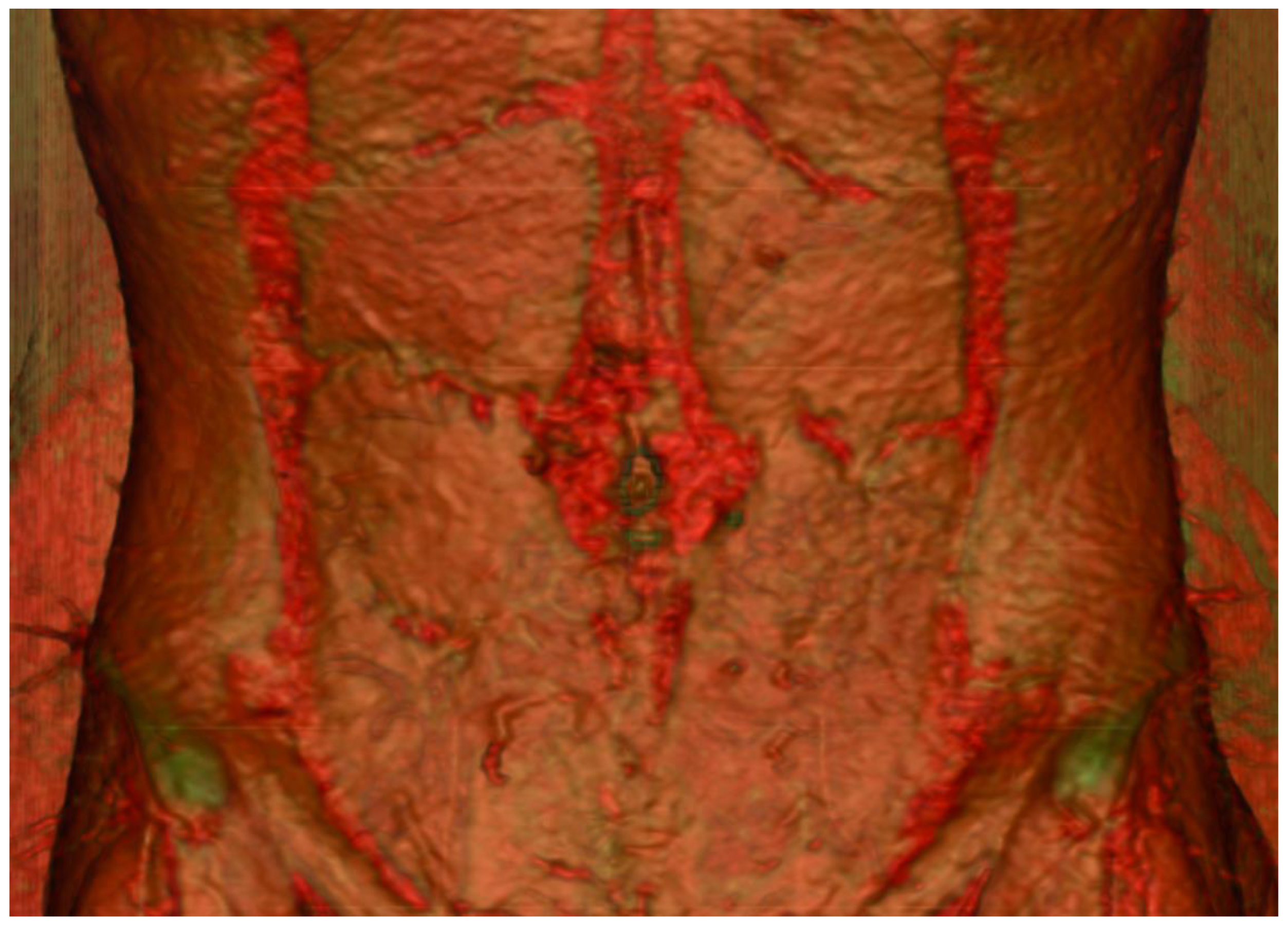
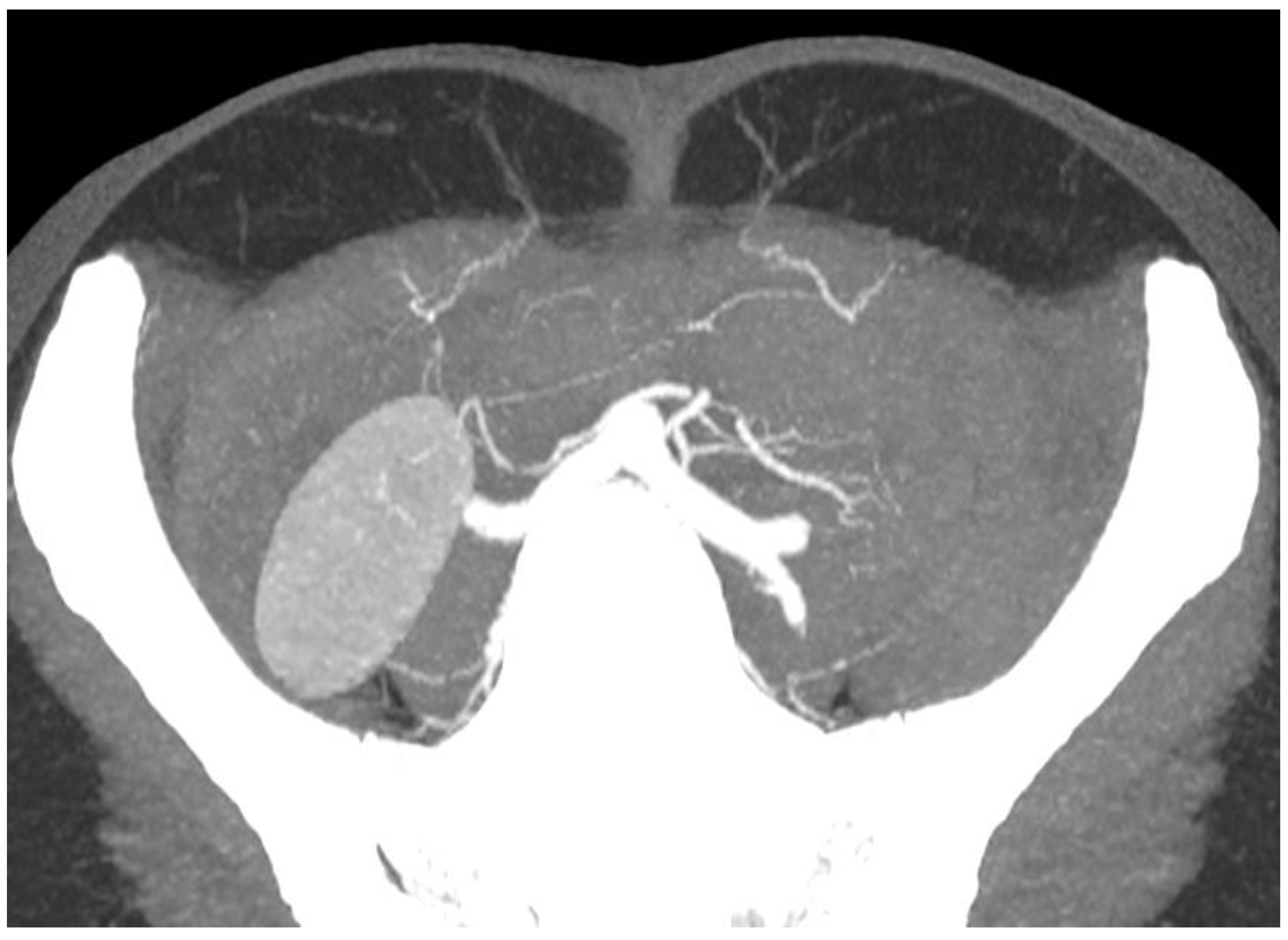
4. Emergence of Advanced Imaging Modalities
5. Development of Imaging Adjuncts
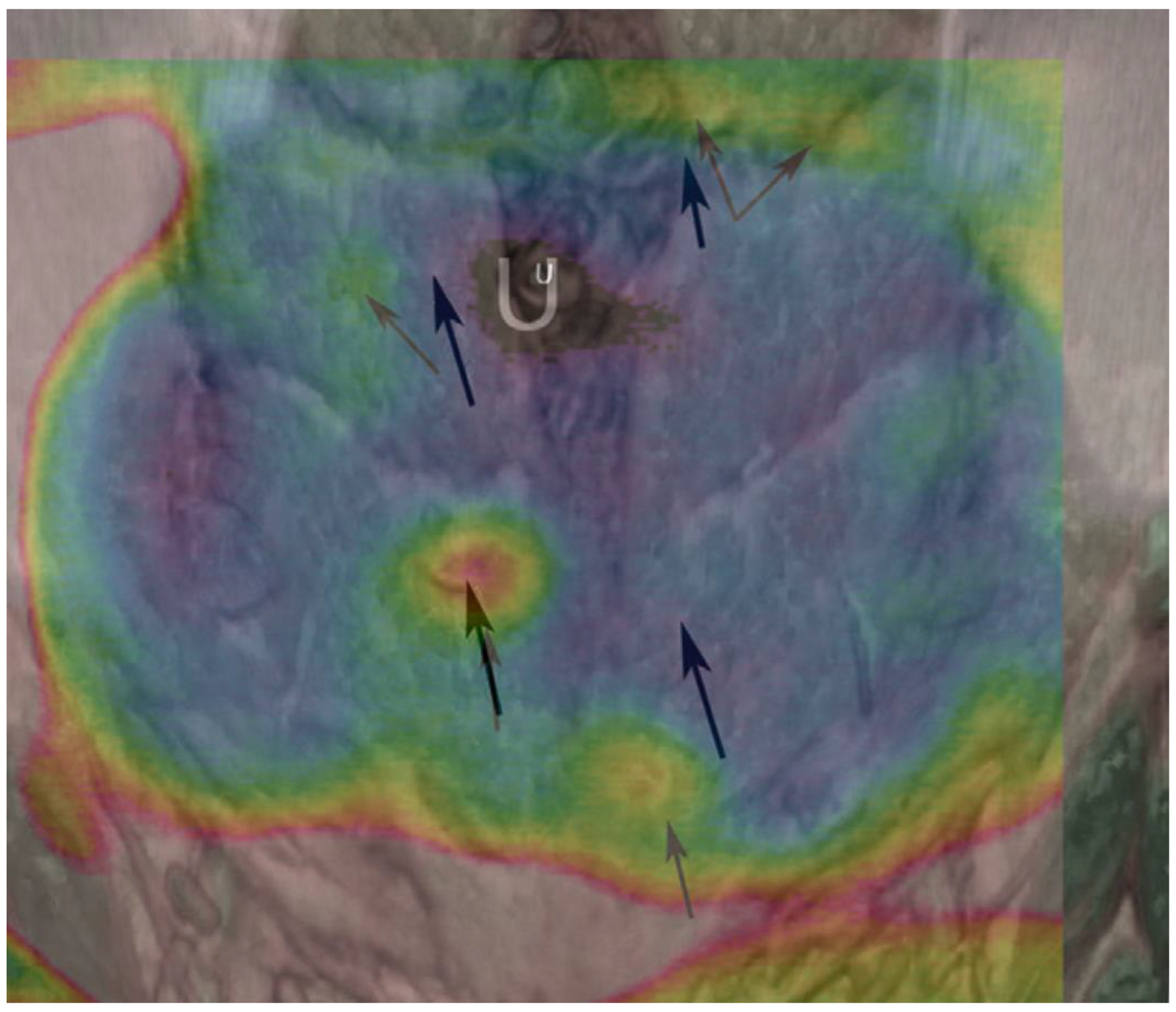
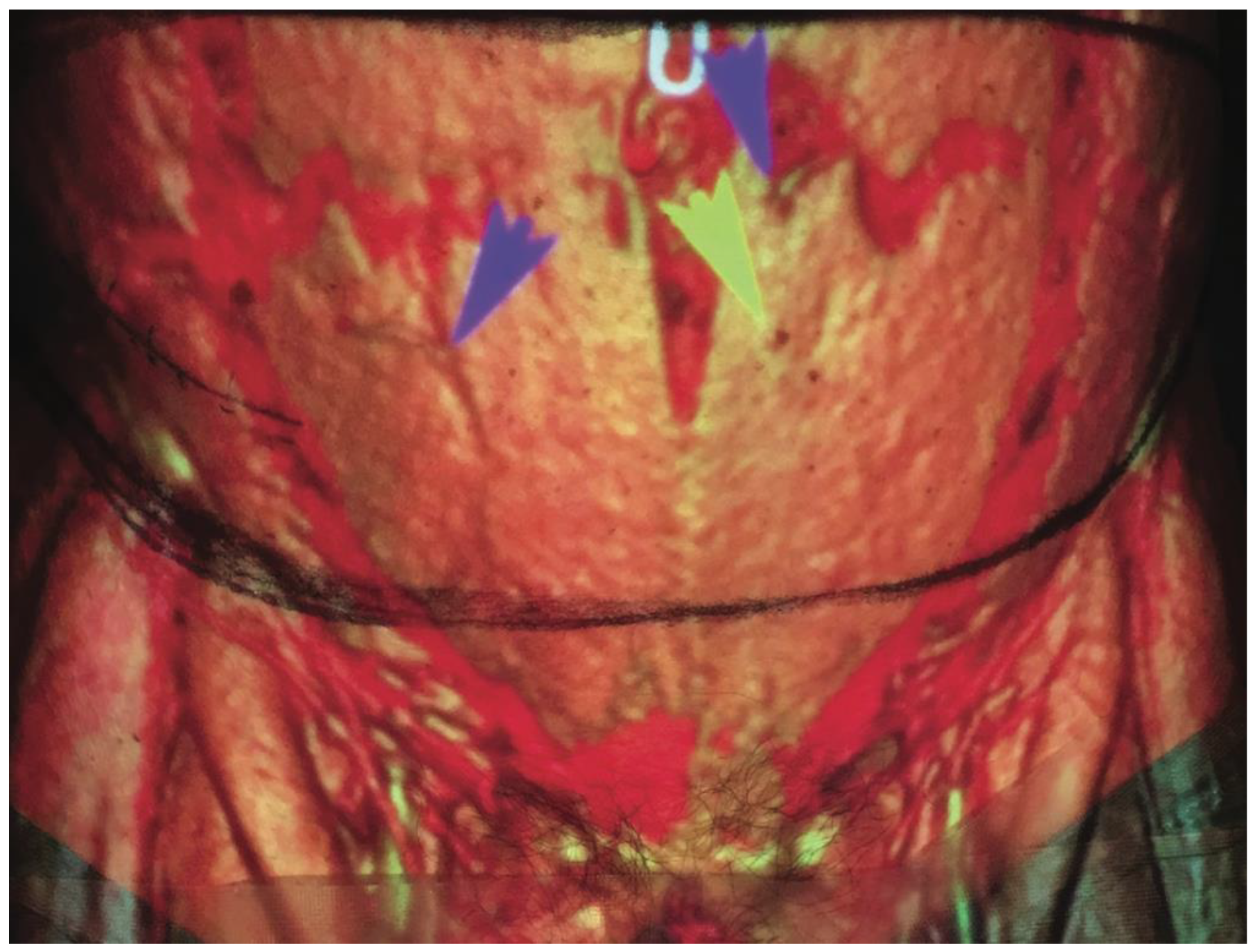
5.1. Direct Infrared Thermography (DIRT)
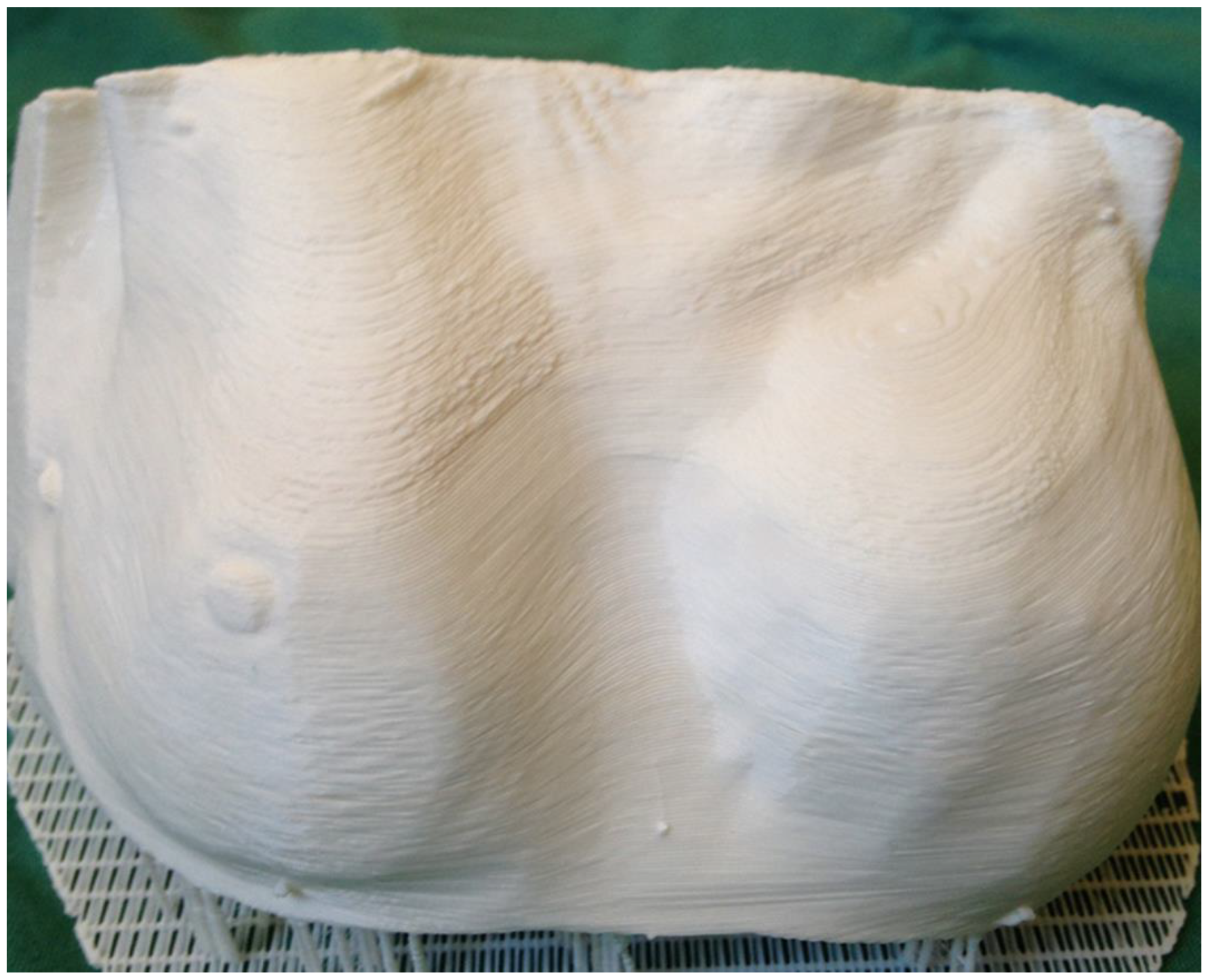
5.2. Three-Dimensional Printing
5.3. Augmented Reality
5.4. Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound
6. Artificial Intelligence in Pre-Operative Planning
7. Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cevik, J.; Hunter-Smith, D.J.; Rozen, W.M. Current Advances in Breast Reconstruction. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seth, I.; Seth, N.; Bulloch, G.; Rozen, W.M.; Hunter-Smith, D.J. Systematic Review of Breast-Q: A Tool to Evaluate Post-Mastectomy Breast Reconstruction. Breast Cancer Targets Ther. 2021, 13, 711–724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Edwards, B.F. Teflon-silicone breast implants. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1963, 32, 519–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gersuny, R. The classic reprint. Concerning a subcutaneous prosthesis: Robert Gersuny. (Uber eine subcutane Prothese. Zeitschrift f. Heilkunde Wien u Leipzig 21:199, 1900). Translated from the German by Miss Rita Euerle. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1980, 65, 525–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cronin, T.D.; Gerow, F.J. Augmentation mammaplasty: A new. “natural feel” prostheses. Excerpta Medica Int. Congr. Ser. 1963, 66, 41–46. [Google Scholar]
- Daniel, R.K.; Taylor, G.I. Distant transfer of an island flap by microvascular anastomoses. A clinical technique. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1973, 52, 111–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taylor, G.I.; Daniel, R.K. The free flap: Composite tissue transfer by vascular anastomosis. Aust. N. Z. J. Surg. 1973, 43, 1–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujino, T.; Harasina, T.; Aoyagi, F. Reconstruction for aplasia of the breast and pectoral region by microvascular transfer of a free flap from the buttock. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1975, 56, 178–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, R.J.; Treece, P. Deep inferior epigastric perforator flap for breast reconstruction. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1994, 32, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, W.M.; Bhullar, H.K.; Hunter-Smith, D. How to assess a CTA of the abdomen to plan an autologous breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2019, 8, S291–S296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boyd, J.B.; Taylor, G.I.; Corlett, R. The vascular territories of the superior epigastric and the deep inferior epigastric systems. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1984, 73, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tansatit, T.; Chokrungvaranont, P.; Sanguansit, P.; Wanidchaphloi, S. Neurovascular anatomy of the deep inferior epigastric perforator flap for breast reconstruction. J. Med. Assoc. Thai. 2006, 89, 1630–1640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Rozen, W.M.; Grinsell, D.; Koshima, I.; Ashton, M.W. Dominance between angiosome and perforator territories: A new anatomical model for the design of perforator flaps. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2010, 26, 539–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, W.M.; Ashton, M.W.; Pan, W.R.; Taylor, G.I. Raising perforator flaps for breast reconstruction: The intramuscular anatomy of the deep inferior epigastric artery. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2007, 120, 1443–1449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satomura, S.; Matsubara, S.; Yoshioka, M. A new method of mechanical vibration measurement and its application. Mem. Inst. Sci. Ind. Res. Osaka Univ. 1956, 13, 125–133. [Google Scholar]
- Satomura, S. Ultrasonic Doppler method for the inspection of cardiac function. J. Acoust. Soc. Am. 1957, 29, 1181–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, T.; Mori, M.; Nimura, Y.; Okimura, M.; Hikita, G. Studies on the examination of the heart with the ultrasonic Doppler method III— Variety Doppler signals IV—Clinical application. Jpn. Circ. J. 1956, 20, 227. [Google Scholar]
- Aoyagi, F.; Fujino, T.; Ohshiro, T. Detection of small vessels for microsurgery by a Doppler flowmeter. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1975, 55, 372–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blondeel, P.N.; Beyens, G.; Verhaeghe, R.; Van Landuyt, K.; Tonnard, P.; Monstrey, S.J.; Matton, G. Doppler flowmetry in the planning of perforator flaps. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1998, 51, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Giunta, R.E.; Geisweid, A.; Feller, A.M. The value of preoperative Doppler sonography for planning free perforator flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2000, 105, 2381–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taylor, G.I.; Doyle, M.; McCarten, G. The Doppler probe for planning flaps: Anatomical study and clinical applications. Br. J. Plast. Surg. 1990, 43, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, M.H.; Chen, H.C.; Santamaria, E.; Chen, H.S.; Kuo, Y.R.; Coessens, B.; Wei, F.C. Preoperative ultrasound Doppler study and clinical correlation of free posterior interosseous flap. Changgeng Yi Xue Za Zhi 1997, 20, 258–264. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, P.; Youssef, A. Efficacy of the handheld Doppler in preoperative identification of the cutaneous perforators in the anterolateral thigh flap. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 928–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stekelenburg, C.M.; Sonneveld, P.M.; Bouman, M.B.; van der Wal, M.B.; Knol, D.L.; de Vet, H.C.; van Zuijlen, P.P. The hand held Doppler device for the detection of perforators in reconstructive surgery: What you hear is not always what you get. Burns 2014, 40, 1702–1706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, U.D.; Miller, J.G. Reliability of handheld Doppler in planning local perforator-based flaps for extremities. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2007, 31, 521–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaw, R.J.; Batstone, M.D.; Blackburn, T.K.; Brown, J.S. Preoperative Doppler assessment of perforator anatomy in the anterolateral thigh flap. Br. J. Oral Maxillofac. Surg. 2010, 48, 419–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, W.M.; Phillips, T.J.; Ashton, M.W.; Stella, D.L.; Gibson, R.N.; Taylor, G.I. Preoperative imaging for DIEA perforator flaps: A comparative study of computed tomographic angiography and Doppler ultrasound. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 121, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wade, R.G.; Watford, J.; Wormald, J.C.R.; Bramhall, R.J.; Figus, A. Perforator mapping reduces the operative time of DIEP flap breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis of preoperative ultrasound, computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2018, 71, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgarello, M.; Visconti, G. Designing Lateral Thoracic Wall Perforator Flaps for Breast Reconstruction Using Ultrasound. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2022, 38, 228–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perez-Iglesias, C.T.; Laikhter, E.; Kang, C.O.; Nassar, A.H.; Maselli, A.M.; Cauley, R.; Lee, B.T. Current Applications of Ultrasound Imaging in the Preoperative Planning of DIEP Flaps. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2022, 38, 221–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curry, G.R.; White, D.N. Color coded ultrasonic differential velocity arterial scanner (Echoflow). Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1978, 4, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eyer, M.K.; Brandestini, M.A.; Phillips, D.J.; Baker, D.W. Color digital echo/Doppler image presentation. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 1981, 7, 21–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brandestini, M. Topoflow—A digital full range Doppler velocity meter. IEEE Trans. Sonics Ultrasonics 1978, 25, 287–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallock, G.G. Evaluation of fasciocutaneous perforators using color duplex imaging. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1994, 94, 644–651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallock, G.G. Doppler sonography and color duplex imaging for planning a perforator flap. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2003, 30, 347–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, B.W.; Luethke, R.; Berg, W.A.; Hamper, U.M.; Manson, P.N. Two-dimensional color Doppler imaging for precision preoperative mapping and size determination of TRAM flap perforators. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1994, 93, 197–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lethaus, B.; Loberg, C.; Kloss-Brandstätter, A.; Bartella, A.K.; Steiner, T.; Modabber, A.; Hölzle, F.; Teichmann, J. Color duplex ultrasonography versus handheld Doppler to plan anterior lateral thigh flaps. Microsurgery 2017, 37, 388–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ensat, F.; Babl, M.; Conz, C.; Rueth, M.J.; Greindl, M.; Fichtl, B.; Herzog, G.; Ussmueller, J.; Spies, M. The efficacy of color duplex sonography in preoperative assessment of anterolateral thigh flap. Microsurgery 2012, 32, 605–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Debelmas, A.; Camuzard, O.; Aguilar, P.; Qassemyar, Q. Reliability of Color Doppler Ultrasound Imaging for the Assessment of Anterolateral Thigh Flap Perforators: A Prospective Study of 30 Perforators. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 762–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogawa, R.; Hyakusoku, H.; Murakami, M. Color Doppler ultrasonography in the planning of microvascular augmented “super-thin” flaps. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2003, 112, 822–828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, W.A.; Chang, B.W.; DeJong, M.R.; Hamper, U.M. Color Doppler flow mapping of abdominal wall perforating arteries for transverse rectus abdominis myocutaneous flap in breast reconstruction: Method and preliminary results. Radiology 1994, 192, 447–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallock, G.G. Acoustic Doppler sonography, color duplex ultrasound, and laser Doppler flowmetry as tools for successful autologous breast reconstruction. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2011, 38, 203–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mijuskovic, B.; Tremp, M.; Heimer, M.M.; Boll, D.; Aschwanden, M.; Zeindler, J.; Kurzeder, C.; Schaefer, D.J.; Haug, M.D.; Kappos, E.A. Color Doppler ultrasound and computed tomographic angiography for perforator mapping in DIEP flap breast reconstruction revisited: A cohort study. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2019, 72, 1632–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napel, S.; Marks, M.P.; Rubin, G.D.; Dake, M.D.; McDonnell, C.H.; Song, S.M.; Enzmann, D.R.; Jeffrey, R.B., Jr. CT angiography with spiral CT and maximum intensity projection. Radiology 1992, 185, 607–610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwartz, R.B.; Jones, K.M.; Chernoff, D.M.; Mukherji, S.K.; Khorasani, R.; Tice, H.M.; Kikinis, R.; Hooton, S.M.; Stieg, P.E.; Polak, J.F. Common carotid artery bifurcation: Evaluation with spiral CT. Work in progress. Radiology 1992, 185, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masia, J.; Clavero, J.A.; Larrañaga, J.R.; Alomar, X.; Pons, G.; Serret, P. Multidetector-row computed tomography in the planning of abdominal perforator flaps. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2006, 59, 594–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, W.M.; Phillips, T.J.; Ashton, M.W.; Stella, D.L.; Taylor, G.I. A new preoperative imaging modality for free flaps in breast reconstruction: Computed tomographic angiography. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 38e–40e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihara, M.; Nakanishi, M.; Nakashima, M.; Narushima, M.; Koshima, I. Utility and anatomical examination of the DIEP flap’s three-dimensional image with multidetector computed tomography. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2008, 122, 40e–41e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alonso-Burgos, A.; García-Tutor, E.; Bastarrika, G.; Cano, D.; Martínez-Cuesta, A.; Pina, L.J. Preoperative planning of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap reconstruction with multislice-CT angiography: Imaging findings and initial experience. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2006, 59, 585–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevik, J.; Rozen, W. A Novel optimization technique of Computed Tomography Angiographic 3D-reconstructions for pre-operative planning of DIEP flaps. JPRAS Open 2023, 35, 38–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald O’Connor, E.; Rozen, W.M.; Chowdhry, M.; Band, B.; Ramakrishnan, V.V.; Griffiths, M. Preoperative computed tomography angiography for planning DIEP flap breast reconstruction reduces operative time and overall complications. Gland Surg. 2016, 5, 93–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, W.M.; Ashton, M.W.; Grinsell, D.; Stella, D.L.; Phillips, T.J.; Taylor, G.I. Establishing the case for CT angiography in the preoperative imaging of abdominal wall perforators. Microsurgery 2008, 28, 306–313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clavero, J.A.; Masia, J.; Larrañaga, J.; Monill, J.M.; Pons, G.; Siurana, S.; Alomar, X. MDCT in the preoperative planning of abdominal perforator surgery for postmastectomy breast reconstruction. AJR Am. J. Roentgenol. 2008, 191, 670–676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scott, J.R.; Liu, D.; Said, H.; Neligan, P.C.; Mathes, D.W. Computed tomographic angiography in planning abdomen-based microsurgical breast reconstruction: A comparison with color duplex ultrasound. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 125, 446–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunis, T.; Heerma van Voss, M.R.; Kon, M.; van Maurik, J.F. CT-angiography prior to DIEP flap breast reconstruction: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microsurgery 2013, 33, 496–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minqiang, X.; Lanhua, M.; Jie, L.; Dali, M.; Jinguo, L. The value of multidetector-row CT angiography for pre-operative planning of breast reconstruction with deep inferior epigastric arterial perforator flaps. Br. J. Radiol. 2010, 83, 40–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smit, J.M.; Dimopoulou, A.; Liss, A.G.; Zeebregts, C.J.; Kildal, M.; Whitaker, I.S.; Magnusson, A.; Acosta, R. Preoperative CT angiography reduces surgery time in perforator flap reconstruction. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2009, 62, 1112–1117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fansa, H.; Schirmer, S.; Frerichs, O.; Gehl, H.B. [Significance of abdominal wall CT-angiography in planning DIEA perforator flaps, TRAM flaps and SIEA flaps]. Handchir. Mikrochir. Plast. Chir. 2011, 43, 81–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Casey, W.J., 3rd; Chew, R.T.; Rebecca, A.M.; Smith, A.A.; Collins, J.M.; Pockaj, B.A. Advantages of preoperative computed tomography in deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2009, 123, 1148–1155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gacto-Sánchez, P.; Sicilia-Castro, D.; Gómez-Cía, T.; Lagares, A.; Collell, T.; Suárez, C.; Parra, C.; Leal, S.; Infante-Cossío, P.; De La Higuera, J.M. Computed tomographic angiography with VirSSPA three-dimensional software for perforator navigation improves perioperative outcomes in DIEP flap breast reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2010, 125, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghattaura, A.; Henton, J.; Jallali, N.; Rajapakse, Y.; Savidge, C.; Allen, S.; Searle, A.E.; Harris, P.A.; James, S.E. One hundred cases of abdominal-based free flaps in breast reconstruction. The impact of preoperative computed tomographic angiography. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2010, 63, 1597–1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rozen, W.M.; Anavekar, N.S.; Ashton, M.W.; Stella, D.L.; Grinsell, D.; Bloom, R.J.; Taylor, G.I. Does the preoperative imaging of perforators with CT angiography improve operative outcomes in breast reconstruction? Microsurgery 2008, 28, 516–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Colakoglu, S.; Tebockhorst, S.; Freedman, J.; Douglass, S.; Siddikoglu, D.; Chong, T.W.; Mathes, D.W. CT angiography prior to DIEP flap breast reconstruction: A randomized controlled trial. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2022, 75, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, W.M.; Ashton, M.W.; Whitaker, I.S.; Wagstaff, M.J.; Acosta, R. The financial implications of computed tomographic angiography in DIEP flap surgery: A cost analysis. Microsurgery 2009, 29, 168–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauterbur, P.C. Image Formation by Induced Local Interactions: Examples Employing Nuclear Magnetic Resonance. Nature 1973, 242, 190–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahn, C.Y.; Narayanan, K.; Shaw, W.W. In vivo anatomic study of cutaneous perforators in free flaps using magnetic resonance imaging. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 1994, 10, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rozen, W.M.; Stella, D.L.; Bowden, J.; Taylor, G.I.; Ashton, M.W. Advances in the pre-operative planning of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flaps: Magnetic resonance angiography. Microsurgery 2009, 29, 119–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chernyak, V.; Rozenblit, A.M.; Greenspun, D.T.; Levine, J.L.; Milikow, D.L.; Chia, F.A.; Erhard, H.A. Breast reconstruction with deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flap: 3.0-T gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging for preoperative localization of abdominal wall perforators. Radiology 2009, 250, 417–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haider, C.R.; Glockner, J.F.; Stanson, A.W.; Riederer, S.J. Peripheral vasculature: High-temporal- and high-spatial-resolution three-dimensional contrast-enhanced MR angiography. Radiology 2009, 253, 831–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Vasile, J.V.; Levine, J.L. Magnetic resonance angiography in perforator flap breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2016, 5, 197–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenspun, D.; Vasile, J.; Levine, J.L.; Erhard, H.; Studinger, R.; Chernyak, V.; Newman, T.; Prince, M.; Allen, R.J. Anatomic imaging of abdominal perforator flaps without ionizing radiation: Seeing is believing with magnetic resonance imaging angiography. J. Reconstr. Microsurg. 2010, 26, 37–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, T.M.; Vasile, J.; Levine, J.L.; Greenspun, D.T.; Allen, R.J.; Chao, M.T.; Winchester, P.A.; Prince, M.R. Perforator flap magnetic resonance angiography for reconstructive breast surgery: A review of 25 deep inferior epigastric and gluteal perforator artery flap patients. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2010, 31, 1176–1184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thimmappa, N.D.; Vasile, J.V.; Ahn, C.Y.; Levine, J.L.; Prince, M.R. MRA of the skin: Mapping for advanced breast reconstructive surgery. Clin. Radiol. 2019, 74, 13–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schaverien, M.V.; Ludman, C.N.; Neil-Dwyer, J.; McCulley, S.J. Contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography for preoperative imaging of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flaps: Advantages and disadvantages compared with computed tomography angiography: A United Kingdom perspective. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2011, 67, 671–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauchot, J.; Aubry, S.; Kastler, A.; Laurent, O.; Kastler, B.; Tropet, Y. Preoperative imaging for deep inferior epigastric perforator flaps: A comparative study of computed tomographic angiography and magnetic resonance angiography. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2012, 35, 795–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cina, A.; Barone-Adesi, L.; Rinaldi, P.; Cipriani, A.; Salgarello, M.; Masetti, R.; Bonomo, L. Planning deep inferior epigastric perforator flaps for breast reconstruction: A comparison between multidetector computed tomography and magnetic resonance angiography. Eur. Radiol. 2013, 23, 2333–2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neil-Dwyer, J.G.; Ludman, C.N.; Schaverien, M.; McCulley, S.J.; Perks, A.G. Magnetic resonance angiography in preoperative planning of deep inferior epigastric artery perforator flaps. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2009, 62, 1661–1665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, M.P.; Hunter-Smith, D.J.; Rozen, W.M. Comparative analysis of fluorescent angiography, computed tomographic angiography and magnetic resonance angiography for planning autologous breast reconstruction. Gland Surg. 2015, 4, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsev, M.; Maclaren, J.; Herbst, M. Motion artifacts in MRI: A complex problem with many partial solutions. J. Magn. Reson. Imaging 2015, 42, 887–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dill, T. Contraindications to magnetic resonance imaging. Heart 2008, 94, 943–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramalho, J.; Semelka, R.C.; Ramalho, M.; Nunes, R.H.; AlObaidy, M.; Castillo, M. Gadolinium-Based Contrast Agent Accumulation and Toxicity: An Update. AJNR Am. J. Neuroradiol. 2016, 37, 1192–1198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ring, E.F. The historical development of thermal imaging in medicine. Rheumatology 2004, 43, 800–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed][Green Version]
- Theuvenet, W.J.; Koeyers, G.F.; Borghouts, M.H. Thermographic assessment of perforating arteries. A preoperative screening method for fasciocutaneous and musculocutaneous flaps. Scand. J. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1986, 20, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salmi, A.M.; Tukiainen, E.; Asko-Seljavaara, S. Thermographic mapping of perforators and skin blood flow in the free transverse rectus abdominis musculocutaneous flap. Ann. Plast. Surg. 1995, 35, 159–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Weerd, L.; Weum, S.; Mercer, J.B. The value of dynamic infrared thermography (DIRT) in perforatorselection and planning of free DIEP flaps. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2009, 63, 274–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whitaker, I.S.; Lie, K.H.; Rozen, W.M.; Chubb, D.; Ashton, M.W. Dynamic infrared thermography for the preoperative planning of microsurgical breast reconstruction: A comparison with CTA. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2012, 65, 130–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weum, S.; Mercer, J.B.; de Weerd, L. Evaluation of dynamic infrared thermography as an alternative to CT angiography for perforator mapping in breast reconstruction: A clinical study. BMC Med. Imaging 2016, 16, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamoto, T.; Todokoro, T.; Koshima, I. Handheld thermography for flap monitoring. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2012, 65, 1747–1748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Weerd, L.; Miland, A.O.; Mercer, J.B. Perfusion dynamics of free DIEP and SIEA flaps during the first postoperative week monitored with dynamic infrared thermography. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2009, 62, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smit, J.M.; Negenborn, V.L.; Jansen, S.M.; Jaspers, M.E.H.; de Vries, R.; Heymans, M.W.; Winters, H.A.H.; van Leeuwen, T.G.; Mullender, M.G.; Krekel, N.M.A. Intraoperative evaluation of perfusion in free flap surgery: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Microsurgery 2018, 38, 804–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Weerd, L.; Mercer, J.B.; Setså, L.B. Intraoperative dynamic infrared thermography and free-flap surgery. Ann. Plast. Surg. 2006, 57, 279–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessy, O.; Potter, S.M. Use of infrared thermography for the assessment of free flap perforators in autologous breast reconstruction: A systematic review. JPRAS Open 2020, 23, 60–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hardwicke, J.T.; Osmani, O.; Skillman, J.M. Detection of Perforators Using Smartphone Thermal Imaging. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2016, 137, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pereira, N.; Valenzuela, D.; Mangelsdorff, G.; Kufeke, M.; Roa, R. Detection of Perforators for Free Flap Planning Using Smartphone Thermal Imaging: A Concordance Study with Computed Tomographic Angiography in 120 Perforators. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2018, 141, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mu, X.; Zhang, J.; Jiang, Y. 3D Printing in Breast Reconstruction: From Bench to Bed. Front. Surg. 2021, 8, 641370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melchels, F.; Wiggenhauser, P.S.; Warne, D.; Barry, M.; Ong, F.R.; Chong, W.S.; Hutmacher, D.W.; Schantz, J.T. CAD/CAM-assisted breast reconstruction. Biofabrication 2011, 3, 034114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diment, L.E.; Thompson, M.S.; Bergmann, J.H.M. Clinical efficacy and effectiveness of 3D printing: A systematic review. BMJ Open 2017, 7, e016891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, M.; Hunter-Smith, D.; Rozen, W. Imaging and printing in plastic and reconstructive surgery part 1: Established techniques. Australas. J. Plast. Surg. 2019, 2, 55–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jablonka, E.M.; Wu, R.T.; Mittermiller, P.A.; Gifford, K.; Momeni, A. 3-DIEPrinting: 3D-printed Models to Assist the Intramuscular Dissection in Abdominally Based Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2019, 7, e2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoon, S.H.; Park, S.; Kang, C.H.; Park, I.K.; Goo, J.M.; Kim, Y.T. Personalized 3D-Printed Model for InforMed. Consent for Stage I Lung Cancer: A Randomized Pilot Trial. Semin. Thorac. Cardiovasc. Surg. 2019, 31, 316–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, P.S.; Choi, C.H.; Han, I.H.; Lee, J.H.; Choi, H.J.; Lee, J.I. Obtaining InforMed. Consent Using Patient Specific 3D Printing Cerebral Aneurysm Model. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2019, 62, 398–404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martelli, N.; Serrano, C.; van den Brink, H.; Pineau, J.; Prognon, P.; Borget, I.; El Batti, S. Advantages and disadvantages of 3-dimensional printing in surgery: A systematic review. Surgery 2016, 159, 1485–1500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, M.P.; Hunter-Smith, D.J.; Spychal, R.T.; Rozen, W.M. 3D volumetric analysis for planning breast reconstructive surgery. Breast Cancer Res. Treat. 2014, 146, 457–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummelink, S.; Verhulst, A.C.; Maal, T.J.J.; Hoogeveen, Y.L.; Schultze Kool, L.J.; Ulrich, D.J.O. An innovative method of planning and displaying flap volume in DIEP flap breast reconstructions. J. Plast. Reconstr. Aesthet. Surg. 2017, 70, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chae, M.P.; Ganhewa, D.; Hunter-Smith, D.J.; Rozen, W.M. Direct augmented reality computed tomographic angiography technique (ARC): An innovation in preoperative imaging. Eur. J. Plast. Surg. 2018, 41, 415–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, O.F.; Nahabedian, M.Y.; Sinkin, J.C. Augmented Reality and Wearable Technology in Image-guided Navigation and Preoperative Planning. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2016, 4, e1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wesselius, T.S.; Meulstee, J.W.; Luijten, G.; Xi, T.; Maal, T.J.J.; Ulrich, D.J.O. Holographic Augmented Reality for DIEP Flap Harvest. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2021, 147, 25e–29e. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratt, P.; Ives, M.; Lawton, G.; Simmons, J.; Radev, N.; Spyropoulou, L.; Amiras, D. Through the HoloLens™ looking glass: Augmented reality for extremity reconstruction surgery using 3D vascular models with perforating vessels. Eur. Radiol. Exp. 2018, 2, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shafarenko, M.S.; Catapano, J.; Hofer, S.O.P.; Murphy, B.D. The Role of Augmented Reality in the Next Phase of Surgical Education. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2022, 10, e4656. [Google Scholar]
- Phan, R.; Chae, M.P.; Hunter-Smith, D.J.; Rozen, W.M. Advances in perforator imaging through holographic CTA and augmented reality: A systematic review. Australas. J. Plast. Surg. 2022, 5, 32–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, W.; Lu, L.; Lazzeri, D.; Zhang, Y.X.; Wang, D.; Innocenti, M.; Qian, Y.; Agostini, T.; Levin, L.S.; Messmer, C. Contrast-enhanced ultrasound combined with three-dimensional reconstruction in preoperative perforator flap planning. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 131, 80–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinser, M.J.; Kröger, N.; Malter, W.; Schulz, T.; Puesken, M.; Mallmann, P.; Zirk, M.; Schröder, K.; Andree, C.; Seidenstuecker, K.; et al. Preoperative Perforator Mapping in DIEP Flaps for Breast Reconstruction. The Impact of New Contrast-Enhanced Ultrasound Techniques. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heneweer, C.; Zirk, M.; Safi, A.; Smeets, R.; Malter, W.; Kröger, N.; Zöller, J.E.; Maintz, D.; Zinser, M. An Innovative Approach for Preoperative Perforator Flap Planning Using Contrast-enhanced B-flow Imaging. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open 2021, 9, e3547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varoquaux, G.; Cheplygina, V. Machine learning for medical imaging: Methodological failures and recommendations for the future. npj Digit. Med. 2022, 5, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aggarwal, R.; Sounderajah, V.; Martin, G.; Ting, D.S.W.; Karthikesalingam, A.; King, D.; Ashrafian, H.; Darzi, A. Diagnostic accuracy of deep learning in medical imaging: A systematic review and meta-analysis. npj Digit. Med. 2021, 4, 65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.; Yun, J.; Cho, Y.; Shin, K.; Jang, R.; Bae, H.J.; Kim, N. Deep Learning in Medical Imaging. Neurospine 2019, 16, 657–668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Neill, A.C.; Yang, D.; Roy, M.; Sebastiampillai, S.; Hofer, S.O.P.; Xu, W. Development and Evaluation of a Machine Learning Prediction Model for Flap Failure in Microvascular Breast Reconstruction. Ann. Surg. Oncol. 2020, 27, 3466–3475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuo, P.J.; Wu, S.C.; Chien, P.C.; Chang, S.S.; Rau, C.S.; Tai, H.L.; Peng, S.H.; Lin, Y.C.; Chen, Y.C.; Hsieh, H.Y.; et al. Artificial neural network approach to predict surgical site infection after free-flap reconstruction in patients receiving surgery for head and neck cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13768–13782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mavioso, C.; Araújo, R.J.; Oliveira, H.P.; Anacleto, J.C.; Vasconcelos, M.A.; Pinto, D.; Gouveia, P.F.; Alves, C.; Cardoso, F.; Cardoso, J.S.; et al. Automatic detection of perforators for microsurgical reconstruction. Breast 2020, 50, 19–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavioso, C.; Correia Anacleto, J.; Vasconcelos, M.A.; Araújo, R.; Oliveira, H.; Pinto, D.; Gouveia, P.; Alves, C.; Cardoso, F.; Cardoso, J.; et al. The development of an automatic tool to improve perforators detection in Angio CT in DIEAP flap breast reconstruction. Eur. J. Cancer 2018, 92, S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, E. Deep Learning for Personalized Preoperative Planning of Microsurgical Free Tissue Transfers. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, Virtual, 22 February–1 March 2022; Volume 36, pp. 13140–13141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Computed Tomographic Angiography | Magnetic Resonance Angiography | |
|---|---|---|
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cevik, J.; Seth, I.; Hunter-Smith, D.J.; Rozen, W.M. A History of Innovation: Tracing the Evolution of Imaging Modalities for the Preoperative Planning of Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165246
Cevik J, Seth I, Hunter-Smith DJ, Rozen WM. A History of Innovation: Tracing the Evolution of Imaging Modalities for the Preoperative Planning of Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(16):5246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165246
Chicago/Turabian StyleCevik, Jevan, Ishith Seth, David J. Hunter-Smith, and Warren M. Rozen. 2023. "A History of Innovation: Tracing the Evolution of Imaging Modalities for the Preoperative Planning of Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 16: 5246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165246
APA StyleCevik, J., Seth, I., Hunter-Smith, D. J., & Rozen, W. M. (2023). A History of Innovation: Tracing the Evolution of Imaging Modalities for the Preoperative Planning of Microsurgical Breast Reconstruction. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(16), 5246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165246






