Genetics of Alzheimer’s Disease in the African American Population
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Identification of AD Risk Genes in EUR Cohorts
3. Association of AD with APOE Genotype in African American Cohorts
4. Candidate Gene Studies in African American Cohorts
| Study Type | Source | African American Cohort Characteristics | Gene | Variant/ Trait | Ref/Alt Allele | RefAF AFR/ EUR * | Effect Size (OR or β) | Uncorrected p-Value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AD Candidate Gene (most significant locus reported) | Erlich et al. 2006 [56] | Family cohort of 243 cases and 224 controls | PON2 | rs987539 | C/T | 29%/50% | NA | ~0.0001 |
| Akomolafe et al. 2006 [61] | Family cohort of 241 cases and 226 controls. | NOS3 | Glu298Asp (rs1799983) | G/T | 93%/66% | NA | 0.002 | |
| Reitz et al. 2011 [63] | Family cohort of 310 cases and 327 controls | SORCS1 | rs1887635 | G/A | 90%/80% | β = 0.30 | 0.053 | |
| Vardarajan et al. 2012 [64] | Family cohort of 513 cases 504 controls | KIAA1033 | rs1196806 | A/G | 7%/15% | OR = 1.5 | 0.03 | |
| Janicki et al. 2013. [65] | Prospective Case/control cohort 185 cases and 389 controls. | CYP19 | rs11070843 | G/A | 23%/15% | OR = 0.6 | 0.027 | |
| McAninch et al. 2018 [66] | Cohort of 3054 participants from multiple studies | DIO2 | Thr92AlaD2 (rs225014) | C/T | 46%/34% | OR = 1.3 # | 0.008 # | |
| AD/Dementia GWAS (excluding APOE region) | Reitz et al. 2013 [67] | 1968 AD cases and 3928 controls | ABCA7 | rs115550680 | G/A | 7%/0% | OR = 1.79 | 2.2 × 10−9 |
| Kunkle et al. 2021 [68] | 2784 AD cases and 5222 controls | IGF1R/ARRDC4 | rs570487962 | C/A | 0.01%/0% | OR= 0.10 | 1.6 × 10−9 | |
| Sherva et al. 2022 [69] | 4012 ADRD cases and 18,435 controls meta-analyzed with 6641 Proxy cases and 45,970 proxy controls | ROBO1 | rs11919682 | C/G | 30%/26% | Dir = − | 1.63 × 10−8 | |
| RP11-340A13.2 | rs148433063 | T/C | 97%/100% | Dir = − | 8.65 × 10−9 | |||
| Above meta-analyzed with Kunkle et al. 2021 [68] cases/controls | TREM2/TREML2 | rs73427293 | A/T | 86%/100% | Dir = − | 2.95 × 10−9 | ||
| RP11-157D6.1 /CD2AP | rs7738720 | T/C | 10%/0% | Dir = − | 1.14 × 10−9 | |||
| ABCA7 | rs73505251 | A/T | 15%/0% | Dir = + | 3.26 × 10−10 | |||
| Mez et al. 2017 [70] | AD liability model for 1825 AD cases and 3784 controls | COBL | rs112404845 | T/A | 1.2%/0% | β = 0.47 | 3.8 × 10−8 | |
| SLC10A2 | rs16961023 | G/C | 2.0%/0% | β = 0.41 | 4.6 × 10−8 | |||
| Candidate gene/Brain MRI Traits | Cuenco et al. 2011 [71] | 158 Discordant sib pairs | TTR | rs3764476/ medial temporal atrophy | A/C | 35%/34% | NA | 0.069 |
| rs3794884/medial temporal atrophy | A/C | 63%/66% | NA | 0.075 | ||||
| Brain MRI Trait GWAS | Melville et al. 2012 [72] | Family cohort including 188 cases and 231 controls | F5/SELP | rs3917854/ hippocampal volume | C/T | 94%/69% | Dir = + | 5.0 × 10−6 |
| PICALM | rs17148741/ hippocampal volume | C/T | 82%/97% | Dir = − | 9.39 × 10−5 | |||
| SYNPR | rs935793/cerebral volume | A/G | 79%/80% | Dir = + | 7.12 × 10−5 | |||
| APOE-region effect modifying SNPs | Choi et al. 2019 [55] | Cohort of 1523 AD cases and 3462 controls | APOE | rs405509 | T/G | 24%/48% | Large effect in EUR but rare in AA; may explain population differences in ε4 effect | |
| Le Guen et al. 2022 [54] | Discovery cohort of 2888 cases and 4957 controls | APOE | R145C (rs769455) | T/C | 2.5%/0% | OR = 3.01 among ε3/ε4 persons | 6.0 × 10−6 | |
| Targeted AD Gene Sequencing | N’Songo et al. 2017 [73] | 131 cases and 107 controls/Replication cohort of 67 cases and 233 controls | PSEN1 | Ser167Phe (rs777923890) | T/C | NA | Alternate allele not present in controls | |
| PSEN2 | Phe111Leu | C/T | NA | |||||
| Cukier et al. 2016 [74] | Variant discovery in 77 cases, Association in 531 cases and 527 controls/Replication cohort of 447 cases and 880 controls | ABCA7 | rs142076058 | 14 bp deletion | 6.7%/0% | OR = 2.13 (Discovery) OR = 1.65 (Replication) | 0.0002 (Discovery) 0.012 (Replication) | |
| Jin et al. 2015 [75] | 906 cases and 2487 controls | TREM2 | rs2234256 | G/A | 15%/0% | OR = 1.27 | 0.01 | |
| rs2234258 | T/C | 5%/0% | OR = 1.35 | 0.08 | ||||
| Logue et al. 2018 [76] | Discovery cohort of 489 cases and 472 controls/Replication cohort of 484 cases and 484 controls | ABCA7 | rs567222111 | 11 bp LOF deletion | 0.99%/0% | OR = 2.42 | 0.022 | |
| Whole exome sequencing | N’Songo et al. 2017 [77] | WES of 131 AD cases and 107 controls/ Combined discovery + Validation cohort of 198 cases and 538 controls | ABCA7 | rs3764647 | G/A | 26%/3.6% | OR = 2.0/ OR = 1.41 | 0.0019/0.017 |
| rs3752239 | C/A | 0.2%/4.1% | OR = ^/ OR = 4.06 | 0.035/0.044 | ||||
| Logue et al. 2014 [78] | Variant discovery WES of 7 cases and association/replication cohorts, including 1459 cases and 2263 controls | AKAP9 | rs144662445 | G/A | 0.5%/0% | OR = 2.75 | 0.014/0.0022 | |
| rs149979685 | T/C | 0.5%/0% | OR = 3.61 | 0.037/0.0022 | ||||
5. Genome-Wide Association Studies for AD Risk
6. AD Biomarker Studies
7. Sequencing Studies in African American Cohorts
8. Linking AKAP9 to AD by Functional Studies
9. Polygenic Risk Scores
10. Leveraging African American Cohorts to Increase Genetic Discovery
11. Importance of Racial/Ethnic Identity and Social Determinants of Health in Genetic Studies of AD
12. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Alzheimer’s Association. 2023 Alzheimer’s disease facts and figures. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 1598–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharp, E.S.; Gatz, M. Relationship between education and dementia: An updated systematic review. Alzheimer Dis. Assoc. Disord. 2011, 25, 289–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, I.E.M.; Martyr, A.; Collins, R.; Brayne, C.; Clare, L. Social isolation and cognitive function in later life: A systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 70, S119–S144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.X.; Cross, P.; Andrews, H.; Jacobs, D.M.; Small, S.; Bell, K.; Merchant, C.; Lantigua, R.; Costa, R.; Stern, Y.; et al. Incidence of AD in African-Americans, Caribbean Hispanics, and Caucasians in northern Manhattan. Neurology 2001, 56, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demirovic, J.; Prineas, R.; Loewenstein, D.; Bean, J.; Duara, R.; Sevush, S.; Szapocznik, J. Prevalence of dementia in three ethnic groups: The South Florida program on aging and health. Ann. Epidemiol. 2003, 13, 472–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayeda, E.R.; Glymour, M.M.; Quesenberry, C.P.; Whitmer, R.A. Inequalities in dementia incidence between six racial and ethnic groups over 14 years. Alzheimers Dement 2016, 12, 216–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnes, L.L. Alzheimer disease in African American individuals: Increased incidence or not enough data? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 56–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gross, A.L.; Mungas, D.M.; Crane, P.K.; Gibbons, L.E.; MacKay-Brandt, A.; Manly, J.J.; Mukherjee, S.; Romero, H.; Sachs, B.; Thomas, M.; et al. Effects of education and race on cognitive decline: An integrative study of generalizability versus study-specific results. Psychol. Aging 2015, 30, 863–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zahodne, L.B.; Manly, J.J.; Azar, M.; Brickman, A.M.; Glymour, M.M. Racial Disparities in Cognitive Performance in Mid- and Late Adulthood: Analyses of Two Cohort Studies. J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 2016, 64, 959–964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, L.R.; Norton, D.; Berman, S.E.; Johnson, S.C.; Bendlin, B.B.; Wieben, O.; Turski, P.; Carlsson, C.; Asthana, S.; Gleason, C.E.; et al. Association of cardiovascular and Alzheimer’s disease risk factors with intracranial arterial blood flow in Whites and African Americans. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2019, 72, 919–929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris, M.I.; Flegal, K.M.; Cowie, C.C.; Eberhardt, M.S.; Goldstein, D.E.; Little, R.R.; Wiedmeyer, H.M.; Byrd-Holt, D.D. Prevalence of diabetes, impaired fasting glucose, and impaired glucose tolerance in U.S. adults. The Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey, 1988–1994. Diabetes Care 1998, 21, 518–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chin, A.L.; Negash, S.; Xie, S.; Arnold, S.E.; Hamilton, R. Quality, and not just quantity, of education accounts for differences in psychometric performance between african americans and white non-hispanics with Alzheimer’s disease. J. Int. Neuropsychol. Soc. 2012, 18, 277–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sisco, S.; Gross, A.L.; Shih, R.A.; Sachs, B.C.; Glymour, M.M.; Bangen, K.J.; Benitez, A.; Skinner, J.; Schneider, B.C.; Manly, J.J. The role of early-life educational quality and literacy in explaining racial disparities in cognition in late life. J. Gerontol. B Psychol. Sci. Soc. Sci. 2015, 70, 557–567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaffe, K.; Falvey, C.; Harris, T.B.; Newman, A.; Satterfield, S.; Koster, A.; Ayonayon, H.; Simonsick, E. Effect of socioeconomic disparities on incidence of dementia among biracial older adults: Prospective study. BMJ 2013, 347, 7051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, D.R. Race and health: Basic questions, emerging directions. Ann. Epidemiol. 1997, 7, 322–333. [Google Scholar]
- Borrell, L.N.; Elhawary, J.R.; Fuentes-Afflick, E.; Witonsky, J.; Bhakta, N.; Wu, A.H.B.; Bibbins-Domingo, K.; Rodriguez-Santana, J.R.; Lenoir, M.A.; Gavin, J.R., 3rd; et al. Race and genetic ancestry in medicine—A time for reckoning with racism. N. Engl. J. Med. 2021, 384, 474–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lewis, A.C.F.; Molina, S.J.; Appelbaum, P.S.; Dauda, B.; Di Rienzo, A.; Fuentes, A.; Fullerton, S.M.; Garrison, N.A.; Ghosh, N.; Hammonds, E.M.; et al. Getting genetic ancestry right for science and society. Science 2022, 376, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babulal, G.M.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Albensi, B.C.; Arenaza-Urquijo, E.; Astell, A.J.; Babiloni, C.; Bahar-Fuchs, A.; Bell, J.; Bowman, G.L.; Brickman, A.M.; et al. Perspectives on ethnic and racial disparities in Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias: Update and areas of immediate need. Alzheimers Dement 2019, 15, 292–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, A.B.; Moser, R.; Chou, W.Y. Race and health profiles in the United States: An examination of the social gradient through the 2009 CHIS adult survey. Public Health 2014, 128, 1076–1086. [Google Scholar]
- Sirugo, G.; Williams, S.M.; Tishkoff, S.A. The missing diversity in human genetic studies. Cell 2019, 177, 1080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, G.R.; Chung, J.; Mez, J.; Barber, R.; Beecham, G.W.; Bennett, D.A.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Byrd, G.S.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Crane, P.K.; et al. Transethnic genome-wide scan identifies novel Alzheimer’s disease loci. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 727–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devi, G.; Ottman, R.; Tang, M.X.; Marder, K.; Stern, Y.; Mayeux, R. Familial aggregation of Alzheimer disease among whites, African Americans, and Caribbean Hispanics in northern Manhattan. Arch. Neurol. 2000, 57, 72–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, R.C.; Cupples, L.A.; Go, R.; Benke, K.S.; Edeki, T.; Griffith, P.A.; Williams, M.; Hipps, Y.; Graff-Radford, N.; Bachman, D.; et al. Risk of dementia among white and African American relatives of patients with Alzheimer disease. JAMA 2002, 287, 329–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachman, D.L.; Green, R.C.; Benke, K.S.; Cupples, L.A.; Farrer, L.A.; MIRAGE Study Group. Comparison of Alzheimer’s disease risk factors in white and African American families. Neurology 2003, 60, 1372–1374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kukull, W.A. The association between smoking and Alzheimer’s disease: Effects of study design and bias. Biol. Psychiatry 2001, 49, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukamal, K.J.; Kuller, L.H.; Fitzpatrick, A.L.; Longstreth, W.T., Jr.; Mittleman, M.A.; Siscovick, D.S. Prospective study of alcohol consumption and risk of dementia in older adults. JAMA 2003, 289, 1405–1413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartz, S.M.; Oehlert, M.; Horton, A.C.; Grucza, R.A.; Fisher, S.L.; Culverhouse, R.C.; Nelson, K.G.; Sumerall, S.W.; Neal, P.C.; Regnier, P.; et al. Daily drinking is associated with increased mortality. Alcohol. Clin. Exp. Res. 2018, 42, 2246–2255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corder, E.H.; Saunders, A.M.; Strittmatter, W.J.; Schmechel, D.E.; Gaskell, P.C.; Small, G.W.; Roses, A.D.; Haines, J.L.; Pericak-Vance, M.A. Gene dose of apolipoprotein E type 4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer’s disease in late onset families. Science 1993, 261, 921–923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrer, L.A.; Cupples, L.A.; Haines, J.L.; Hyman, B.; Kukull, W.A.; Mayeux, R.; Myers, R.H.; Pericak-Vance, M.A.; Risch, N.; van Duijn, C.M. Effects of age, sex, and ethnicity on the association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease. A meta-analysis. APOE and Alzheimer Disease Meta Analysis Consortium. JAMA 1997, 278, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reiman, E.M.; Arboleda-Velasquez, J.F.; Quiroz, Y.T.; Huentelman, M.J.; Beach, T.G.; Caselli, R.J.; Chen, Y.; Su, Y.; Myers, A.J.; Hardy, J.; et al. Exceptionally low likelihood of Alzheimer’s dementia in APOE2 homozygotes from a 5000-person neuropathological study. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, I.E.; Savage, J.E.; Watanabe, K.; Bryois, J.; Williams, D.M.; Steinberg, S.; Sealock, J.; Karlsson, I.K.; Hagg, S.; Athanasiu, L.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies new loci and functional pathways influencing Alzheimer’s disease risk. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 404–413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marioni, R.E.; Harris, S.E.; Zhang, Q.; McRae, A.F.; Hagenaars, S.P.; Hill, W.D.; Davies, G.; Ritchie, C.W.; Gale, C.R.; Starr, J.M.; et al. GWAS on family history of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Psychiatry 2018, 8, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bellenguez, C.; Küçükali, F.; Jansen, I.; Andrade, V.; Moreno-Grau, S.; Amin, N.; Naj, A.C.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Campos-Martin, R.; Holmans, P.A.; et al. New insights on the genetic etiology of Alzheimer’s and related dementia. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 412–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wightman, D.P.; Jansen, I.E.; Savage, J.E.; Shadrin, A.A.; Bahrami, S.; Rongve, A.; Børte, S.; Winsvold, B.S.; Drange, O.K.; Martinsen, A.E.; et al. A genome-wide association study with 1,126,563 individuals identifies new risk loci for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2021, 53, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jonsson, T.; Stefansson, H.; Steinberg, S.; Jonsdottir, I.; Jonsson, P.V.; Snaedal, J.; Bjornsson, S.; Huttenlocher, J.; Levey, A.I.; Lah, J.J.; et al. Variant of TREM2 associated with the risk of Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 107–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guerreiro, R.; Wojtas, A.; Bras, J.; Carrasquillo, M.; Rogaeva, E.; Majounie, E.; Cruchaga, C.; Sassi, C.; Kauwe, J.S.; Younkin, S.; et al. TREM2 variants in Alzheimer’s disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2013, 368, 117–127. [Google Scholar]
- Cruchaga, C.; Karch, C.M.; Jin, S.C.; Benitez, B.A.; Cai, Y.; Guerreiro, R.; Harari, O.; Norton, J.; Budde, J.; Bertelsen, S.; et al. Rare coding variants in the phospholipase D3 gene confer risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Nature 2014, 505, 550–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bis, J.C.; Jian, X.; Kunkle, B.W.; Chen, Y.; Hamilton-Nelson, K.L.; Bush, W.S.; Salerno, W.J.; Lancour, D.; Ma, Y.; Renton, A.E.; et al. Whole exome sequencing study identifies novel rare and common Alzheimer’s-Associated variants involved in immune response and transcriptional regulation. Mol. Psychiatry 2020, 25, 1859–1875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Zhu, C.; Beecham, G.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Ma, Y.; Lancour, D.; Farrell, J.J.; Chung, J.; Alzheimer’s Disease Sequencing Project; Mayeux, R.; et al. A rare missense variant of CASP7 is associated with familial late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 15, 441–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Jun, G.R.; Zhang, X.; Chung, J.; Naj, A.C.; Chen, Y.; Bellenguez, C.; Hamilton-Nelson, K.; Martin, E.R.; Kunkle, B.W.; et al. Analysis of whole-exome sequencing data for Alzheimer disease stratified by APOE genotype. JAMA Neurol. 2019, 76, 1099–1108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Holstege, H.; Hulsman, M.; Charbonnier, C.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Quenez, O.; Grozeva, D.; van Rooij, J.G.J.; Sims, R.; Ahmad, S.; Amin, N.; et al. Exome sequencing identifies rare damaging variants in ATP8B4 and ABCA1 as risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1786–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Howard, B.V.; Gidding, S.S.; Liu, K. Association of apolipoprotein E phenotype with plasma lipoproteins in African-American and white young adults. The CARDIA Study. Coronary Artery Risk Development in Young Adults. Am. J. Epidemiol. 1998, 148, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, M.X.; Stern, Y.; Marder, K.; Bell, K.; Gurland, B.; Lantigua, R.; Andrews, H.; Feng, L.; Tycko, B.; Mayeux, R. The APOE-epsilon4 allele and the risk of Alzheimer disease among African Americans, whites, and Hispanics. JAMA 1998, 279, 751–755. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Graff-Radford, N.R.; Green, R.C.; Go, R.C.; Hutton, M.L.; Edeki, T.; Bachman, D.; Adamson, J.L.; Griffith, P.; Willis, F.B.; Williams, M.; et al. Association between apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease in African American subjects. Arch. Neurol. 2002, 59, 594–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.X.; Maestre, G.; Tsai, W.Y.; Liu, X.H.; Feng, L.; Chung, W.Y.; Chun, M.; Schofield, P.; Stern, Y.; Tycko, B.; et al. Relative risk of Alzheimer disease and age-at-onset distributions, based on APOE genotypes among elderly African Americans, Caucasians, and Hispanics in New York City. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 1996, 58, 574–584. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sahota, A.; Yang, M.; Gao, S.; Hui, S.L.; Baiyewu, O.; Gureje, O.; Oluwole, S.; Ogunniyi, A.; Hall, K.S.; Hendrie, H.C. Apolipoprotein E-associated risk for Alzheimer’s disease in the African-American population is genotype dependent. Ann. Neurol. 1997, 42, 659–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, M.W.; Schu, M.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Buros, J.; Green, R.C.; Go, R.C.; Griffith, P.; Obisesan, T.O.; Shatz, R.; Borenstein, A.; et al. A comprehensive genetic association study of Alzheimer disease in African Americans. Arch. Neurol. 2011, 68, 1569–1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murrell, J.R.; Price, B.; Lane, K.A.; Baiyewu, O.; Gureje, O.; Ogunniyi, A.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Smith-Gamble, V.; Gao, S.; Hendrie, H.C.; et al. Association of apolipoprotein E genotype and Alzheimer disease in African Americans. Arch. Neurol. 2006, 63, 431–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, M.W.; Miller, M.W.; Sherva, R.; ZHang, R.; Harrington, K.M.; Fonda, J.R.; Merritt, V.C.; Panizzon, M.S.; Hauger, R.L.; Wolf, E.J.; et al. Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias among aging veterans: Examining gene-by-environment interactions with posttraumatic stress disorder and traumatic brain injury. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 2549–2559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hendrie, H.C.; Murrell, J.; Baiyewu, O.; Lane, K.A.; Purnell, C.; Ogunniyi, A.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Hall, K.; Callahan, C.M.; Saykin, A.J.; et al. APOE epsilon4 and the risk for Alzheimer disease and cognitive decline in African Americans and Yoruba. Int. Psychogeriatr. 2014, 26, 977–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gureje, O.; Ogunniyi, A.; Baiyewu, O.; Price, B.; Unverzagt, F.W.; Evans, R.M.; Smith-Gamble, V.; Lane, K.A.; Gao, S.; Hall, K.S.; et al. APOE epsilon4 is not associated with Alzheimer’s disease in elderly Nigerians. Ann. Neurol. 2006, 59, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farrer, L.A. Intercontinental epidemiology of Alzheimer disease: A global approach to bad gene hunting. JAMA 2001, 285, 796–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabli, F.; Feliciano, B.E.; Celis, K.; Hamilton-Nelson, K.L.; Whitehead, P.L.; Adams, L.D.; Bussies, P.L.; Manrique, C.P.; Rodriguez, A.; Rodriguez, V.; et al. Ancestral origin of ApoE epsilon4 Alzheimer disease risk in Puerto Rican and African American populations. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le Guen, Y.; Belloy, M.E.; Eger, S.J.; Chen, A.; Kennedy, G.; Thornton, T.A.; Farrer, L.A.; Napolioni, V.; He, Z.; Grecius, M.D. APOE missense variant R145C is associated with increased Alzheimer’s disease risk in African ancestry individuals with the APOE ε3/ε4 genotype. JAMA 2023, 329, 551–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, K.Y.; Lee, J.J.; Gunasekaran, T.I.; Kang, S.; Lee, W.; Jeong, J.; Lim, H.J.; Zhang, X.; Zhu, C.; Won, S.Y.; et al. APOE promoter polymorphism-219T/G is an effect modifier of the influence of APOE ε4 on Alzheimer’s disease risk in a multiracial sample. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8., 1236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erlich, P.M.; Lunetta, K.L.; Cupples, L.A.; Huyck, M.; Green, R.C.; Baldwin, C.T.; Farrer, L.A. MIRAGE Study Group. Polymorphisms in the PON gene cluster are associated with Alzheimer disease. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, 77–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shunmoogam, N.; Naidoo, P.; Chilton, R. Paraoxonase (PON)-1: A brief overview on genetics, structure, polymorphisms and clinical relevance. Vasc. Health Risk Manag. 2018, 14, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Precourt, L.P.; Amre, D.; Denis, M.C.; Lavoie, J.C.; Delvin, E.; Seidman, E.; Levy, E. The three-gene paraoxonase family: Physiologic roles, actions and regulation. Atherosclerosis 2011, 214, 20–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zamora, R.; Vodovotz, Y.; Billiar, T.R. Inducible nitric oxide synthase and inflammatory diseases. Mol. Med. 2000, 6, 347–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krol, M.; Kepinska, M. Human nitric oxide synthase—Its functions, polymorphisms, and inhibitors in the context of inflammation, diabetes and cardiovascular diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 22, 56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akomolafe, A.; Lunetta, K.L.; Erlich, P.M.; Cupples, L.A.; Baldwin, C.T.; Huyck, M.; Green, R.C.; Farrer, L.A. MIRAGE Study Group. Genetic association between endothelial nitric oxide synthase and Alzheimer disease. Clin. Genet. 2006, 70, 49–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rogaeva, E.; Meng, Y.; Lee, J.H.; Gu, Y.; Kawarai, T.; Zou, F.; Katayama, T.; Baldwin, C.T.; Cheng, R.; Hasegawa, H.; et al. The neuronal sortilin-related receptor SORL1 is genetically associated with Alzheimer disease. Nat. Genet. 2007, 39, 168–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reitz, C.; Tokuhiro, S.; Clark, L.N.; Conrad, C.; Vonsattel, J.P.; Hazrati, L.N.; Palotas, A.; Lantigua, R.; Medrano, M.; Jiménez-Velázquez, I.; et al. SORCS1 alters amyloid precursor protein processing and variants may increase Alzheimer’s disease risk. Ann. Neurol. 2011, 69, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardarajan, B.N.; Bruesegem, S.Y.; Harbour, M.E.; Inzelberg, R.; Friedland, R.; St George-Hyslop, P.; Seaman, M.N.; Farrer, L.A. Identification of Alzheimer disease-associated variants in genes that regulate retromer function. Neurobiol. Aging 2012, 33, 2231.e2215–2231.e2230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Janicki, S.C.; Park, N.; Cheng, R.; Schupf, N.; Clark, L.N.; Lee, J.H. Aromatase variants modify risk for Alzheimer’s disease in a multiethnic female cohort. Dement Geriatr. Cogn. Disord. 2013, 35, 340–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McAninch, E.A.; Rajan, K.B.; Evans, D.A.; Jo, S.; Chaker, L.; Peeters, R.P.; Bennett, D.A.; Mash, D.C.; Bianco, A.C. A common DIO2 polymorphism and Alzheimer disease dementia in African and European Americans. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2018, 103, 1818–1826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reitz, C.; Jun, G.; Naj, A.; Rajbhandary, R.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Wang, L.S.; Valladares, O.; Lin, C.F.; Larson, E.B.; Graff-Radford, N.R.; et al. Variants in the ATP-binding cassette transporter (ABCA7), apolipoprotein E 4, and the risk of late-onset Alzheimer disease in African Americans. JAMA 2013, 309, 1483–1492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunkle, B.W.; Schmidt, M.; Klein, H.U.; Naj, A.C.; Hamilton-Nelson, K.L.; Larson, E.B.; Evans, D.A.; De Jager, P.L.; Crane, P.K.; Buxbaum, J.D.; et al. Novel Alzheimer disease risk loci and pathways in African American individuals using the African Genome Resources Panel: A meta-analysis. JAMA Neurol. 2021, 78, 102–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sherva, R.; Zhang, R.; Sahelijo, N.; Jun, G.; Anglin, T.; Chanfreu, C.; Cho, K.; Fonda, J.R.; Gaziano, J.M.; Harrington, K.M.; et al. African ancestry GWAS of dementia in a large military cohort identifies significant risk loci. Mol. Psychiatry 2023, 28, 1293–1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mez, J.; Chung, J.; Jun, G.; Kriegel, J.; Bourlas, A.P.; Sherva, R.; Logue, M.W.; Barnes, L.L.; Bennett, D.A.; Buxbaum, J.D.; et al. Two novel loci, COBL and SLC10A2, for Alzheimer’s disease in African Americans. Alzheimers Dement. 2017, 13, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cuenco, K.T.; Friedland, R.; Baldwin, C.T.; Guo, J.; Vardarajan, B.; Lunetta, K.L.; Cupples, L.A.; Green, R.C.; DeCarli, C.; Farrer, L.A.; et al. Association of TTR polymorphisms with hippocampal atrophy in Alzheimer disease families. Neurobiol. Aging 2011, 32, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Melville, S.A.; Buros, J.; Parrado, A.R.; Vardarajan, B.; Logue, M.W.; Shen, L.; Risacher, S.L.; Kim, S.; Jun, G.; DeCarli, C.; et al. Multiple loci influencing hippocampal degeneration identified by genome scan. Ann. Neurol. 2012, 72, 65–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- N’Songo, A.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Wang, X.; Nguyen, T.; Asmann, Y.; Younkin, S.G.; Allen, M.; Duara, R.; Custo, M.T.; Graff-Radford, N.; et al. Comprehensive screening for disease risk variants in early-onset Alzheimer’s disease genes in African Americans identifies novel PSEN variants. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 56, 1215–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cukier, H.N.; Kunkle, B.W.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Rolati, S.; Hamilton-Nelson, K.L.; Kohli, M.A.; Whitehead, P.L.; Dombroski, B.A.; Van Booven, D.; Lang, R.; et al. ABCA7 frameshift deletion associated with Alzheimer disease in African Americans. Neurol. Genet. 2016, 2, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, S.C.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Benitez, B.A.; Skorupa, T.; Carrell, D.; Patel, D.; Lincoln, S.; Krishnan, S.; Kachadoorian, M.; Reitz, C.; et al. TREM2 is associated with increased risk for Alzheimer’s disease in African Americans. Mol. Neurodegener. 2015, 10, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, M.W.; Lancour, D.; Farrell, J.; Simkina, I.; Fallin, M.D.; Lunetta, K.L.; Farrer, L.A. Targeted Sequencing of Alzheimer Disease Genes in African Americans Implicates Novel Risk Variants. Front. Neurosci. 2018, 12, 592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- N’Songo, A.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Wang, X.; Burgess, J.D.; Nguyen, T.; Asmann, Y.W.; Serie, D.J.; Younkin, S.G.; Allen, M.; Pedraza, O.; et al. African American exome sequencing identifies potential risk variants at Alzheimer disease loci. Neurol. Genet. 2017, 3, e141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Logue, M.W.; Schu, M.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Farrell, J.; Bennett, D.A.; Buxbaum, J.D.; Byrd, G.S.; Ertekin-Taner, N.; Evans, D.; Foroud, T.; et al. Two rare AKAP9 variants are associated with Alzheimer’s disease in African Americans. Alzheimers Dement. 2014, 10, 609–618.e611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dugbartey, A.T. Neurocognitive aspects of hypothyroidism. Arch. Intern. Med. 1998, 158, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamboh, M.I.; Demirci, F.Y.; Wang, X.; Minster, R.L.; Carrasquillo, M.M.; Pankratz, V.S.; Younkin, S.G.; Saykin, A.J.; Jun, G.; Baldwin, C.; et al. Genome-wide association study of Alzheimer’s disease. Transl. Psychiatry 2012, 2, e117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, L.; Chibnik, L.B.; Srivastava, G.P.; Pochet, N.; Yang, J.; Xu, J.; Kozubek, J.; Obholzer, N.; Leurgans, S.E.; Schneider, J.A.; et al. Association of Brain DNA methylation in SORL1, ABCA7, HLA-DRB5, SLC24A4, and BIN1 with pathological diagnosis of Alzheimer disease. JAMA Neurol. 2015, 72, 15–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaziano, J.M.; Concato, J.; Brophy, M.; Fiore, L.; Pyarajan, S.; Breeling, J.; Whitbourne, S.; Deen, J.; Shannon, C.; Humphries, D.; et al. Million Veteran Program: A mega-biobank to study genetic influences on health and disease. J. Clin. Epidemiol. 2016, 70, 214–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter-Zinck, H.; Shi, Y.; Li, M.; Gorman, B.R.; Ji, S.G.; Sun, N.; Webster, T.; Liem, A.; Hsieh, P.; Devineni, P.; et al. Genotyping Array Design and Data Quality Control in the Million Veteran Program. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2020, 106, 535–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bjerke, M.; Engelborghs, S. Cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers for early and differential Alzheimer’s disease diagnosis. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2018, 62, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Thijssen, E.H.; Vermunt, L.; Hansson, O.; Zetterberg, H.; van der Flier, W.M.; Mielke, M.M.; Del Campo, M. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: Towards clinical implementation. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, W.; Xie, F.; Zuo, C.; Guan, Y.; Huang, Y.H. PET Neuroimaging of Alzheimer’s disease: Radiotracers and their utility in clinical research. Front. Aging Neurosci. 2021, 13, 624330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, J.C.; Watts, K.D.; Parker, M.W.; Wu, J.; Kollhoff, A.; Wingo, T.S.; Dorbin, C.D.; Qiu, D.; Hu, W.T. Race modifies the relationship between cognition and Alzheimer’s disease cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2017, 9, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrett, S.L.; McDaniel, D.; Obideen, M.; Trammell, A.R.; Shaw, L.M.; Goldstein, F.C.; Hajjar, I. Racial disparity in cerebrospinal fluid amyloid and tau biomarkers and associated cutoffs for mild cognitive impairment. JAMA Netw. Open 2019, 2, e1917363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, S.; Prokopenko, D.; Dobricic, V.; Kilpert, F.; Bos, I.; Vos, S.J.B.; Tijms, B.M.; Andreasson, U.; Blennow, K.; Vandenberghe, R.; et al. Genome-wide association study of Alzheimer’s disease CSF biomarkers in the EMIF-AD Multimodal Biomarker Discovery dataset. Transl. Psychiatry 2020, 10, 403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansen, I.E.; van der Lee, S.J.; Gomez-Fonseca, D.; de Rojas, I.; Dalmasso, M.C.; Grenier-Boley, B.; Zettergren, A.; Mishra, A.; Ali, M.; Andrade, V.; et al. Genome-wide meta-analysis for Alzheimer’s disease cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers. Acta Neuropathol. 2022, 144, 821–842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, J.; Zhang, X.; Allen, M.; Wang, X.; Ma, Y.; Beecham, G.; Montine, T.J.; Younkin, S.G.; Dickson, D.W.; Golde, T.E.; et al. Genome-wide pleiotropy analysis of neuropathological traits related to Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2018, 10, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, M.; Ang, T.F.A.; Devine, S.A.; Sherva, R.M.; Mukherjee, S.; Trittschuh, E.H.; Gibbons, L.E.; Scollard, P.; Lee, M.; Choi, S.E.; et al. A genome-wide search for pleiotropy in more than 100,000 harmonized longitudinal cognitive domain scores. Mol. Neurodegener. 2023, 18, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramanan, V.K.; Risacher, S.L.; Nho, K.; Kim, S.; Swaminathan, S.; Shen, L.; Foroud, T.M.; Hakonarson, H.; Huentelman, M.J.; Aisen, P.S.; et al. APOE and BCHE as modulators of cerebral amyloid deposition: A florbetapir PET genome-wide association study. Mol. Psychiatry 2014, 19, 351–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohman, T.J.; Koran, M.E.; Thornton-Wells, T.A.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Genetic modification of the relationship between phosphorylated tau and neurodegeneration. Alzheimers Dement 2014, 10, 637–645.e631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanan, V.K.; Nho, K.; Shen, L.; Risacher, S.L.; Kim, S.; McDonald, B.C.; Farlow, M.R.; Foroud, T.M.; Gao, S.; Soininen, H.; et al. FASTKD2 is associated with memory and hippocampal structure in older adults. Mol. Psychiatry 2015, 20, 1197–1204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mormino, E.C.; Betensky, R.A.; Hedden, T.; Schultz, A.P.; Ward, A.; Huijbers, W.; Rentz, D.M.; Johnson, K.A.; Sperling, R.A.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; et al. Amyloid and APOE epsilon4 interact to influence short-term decline in preclinical Alzheimer disease. Neurology 2014, 82, 1760–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hofer, E.; Roshchupkin, G.V.; Adams, H.H.H.; Knol, M.J.; Lin, H.; Li, S.; Zare, H.; Ahmad, S.; Armstrong, N.J.; Satizabal, C.L.; et al. Genetic correlations and genome-wide associations of cortical structure in general population samples of 22,824 adults. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 4796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grasby, K.L.; Jahanshad, N.; Painter, J.N.; Colodro-Conde, L.; Bralten, J.; Hibar, D.P.; Lind, P.A.; Pizzagalli, F.; Ching, C.R.K.; McMahon, M.A.B.; et al. The genetic architecture of the human cerebral cortex. Science 2020, 367, eaay6690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hibar, D.P.; Adams, H.H.H.; Jahanshad, N.; Chauhan, G.; Stein, J.L.; Hofer, E.; Renteria, M.E.; Bis, J.C.; Arias-Vasquez, A.; Ikram, M.K.; et al. Novel genetic loci associated with hippocampal volume. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 13624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, L.T.; Sharp, K.; Alfaro-Almagro, F.; Shi, S.; Miller, K.L.; Douaud, G.; Marchini, J.; Smith, S.M. Genome-wide association studies of brain imaging phenotypes in UK Biobank. Nature 2018, 562, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, M.; Archer, D.B.; Gorijala, P.; Western, D.; Timsina, J.; Fernandez, M.V.; Wang, T.C.; Satizabal, C.L.; Yang, Q.; Beiser, A.S.; et al. Large multi-ethnic genetic analyses of amyloid imaging identify new genes for Alzheimer disease. Acta Neuropathol. Commun. 2023, 11, 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajabli, F.; Tosto, G.; Hamilton-Nelson, K.L.; Kunkle, B.W.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Naj, A.; Whitehead, P.G.; Gardner, O.K.; Bush, W.S.; Sariya, S.; et al. Admixture mapping identifies novel Alzheimer’s disease risk regions in African Americans. Alzheimers Dement. 2023, 19, 2538–2548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ting, S.K.; Benzinger, T.; Kepe, V.; Fagan, A.; Coppola, G.; Porter, V.; Hecimovic, S.; Chakraverty, S.; Alvarez-Retuerto, A.I.; Goate, A.; et al. A novel PSEN1 mutation (I238M) associated with early-onset Alzheimer’s disease in an African-American woman. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2014, 40, 271–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards-Lee, T.; Ringman, J.M.; Chung, J.; Werner, J.; Morgan, A.; St George Hyslop, P.; Thompson, P.; Dutton, R.; Mlikotic, A.; Rogaeva, E.; et al. An African American family with early-onset Alzheimer disease and an APP (T714I) mutation. Neurology 2005, 64, 377–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippon, G.A.; Crook, R.; Baker, M.; Halvorsen, E.; Chin, S.; Hutton, M.; Houlden, H.; Hardy, J.; Lynch, T. Presenilin 1 mutation in an African American family presenting with atypical Alzheimer dementia. Arch. Neurol. 2003, 60, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramirez Aguilar, L.; Acosta-Uribe, J.; Giraldo, M.M.; Moreno, S.; Baena, A.; Alzate, D.; Cuastumal, R.; Aguillon, D.; Madrigal, L.; Saldarriaga, A.; et al. Genetic origin of a large family with a novel PSEN1 mutation (Ile416Thr). Alzheimers Dement. 2019, 15, 709–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruchaga, C.; Haller, G.; Chakraverty, S.; Mayo, K.; Vallania, F.L.; Mitra, R.D.; Faber, K.; Williamson, J.; Bird, T.; Diaz-Arrastia, R.; et al. Rare variants in APP, PSEN1 and PSEN2 increase risk for AD in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease families. PLoS ONE 2012, 7, e31039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassi, C.; Guerreiro, R.; Gibbs, R.; Ding, J.; Lupton, M.K.; Troakes, C.; Al-Sarraj, S.; Niblock, M.; Gallo, J.M.; Adnan, J.; et al. Investigating the role of rare coding variability in Mendelian dementia genes (APP, PSEN1, PSEN2, GRN, MAPT, and PRNP) in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Aging 2014, 35, 2881.e2881–2881.e2886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vardarajan, B.N.; Barral, S.; Jaworski, J.; Beecham, G.W.; Blue, E.; Tosto, G.; Reyes-Dumeyer, D.; Medrano, M.; Lantigua, R.; Naj, A.; et al. Whole genome sequencing of Caribbean Hispanic families with late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Ann. Clin. Transl. Neurol. 2018, 5, 406–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- The 1000 Genomes Project Consortium. A map of human genome variation from population-scale sequencing. Nature 2010, 467, 1061–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.W.; Wyszynski, M.; Madhavan, R.; Sealock, R.; Kim, J.U.; Sheng, M. Yotiao, a novel protein of neuromuscular junction and brain that interacts with specific splice variants of NMDA receptor subunit NR1. J. Neurosci. 1998, 18, 2017–2027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terrin, A.; Monterisi, S.; Stangherlin, A.; Zoccarato, A.; Koschinski, A.; Surdo, N.C.; Mongillo, M.; Sawa, A.; Jordanides, N.E.; Mountford, J.C.; et al. PKA and PDE4D3 anchoring to AKAP9 provides distinct regulation of cAMP signals at the centrosome. J. Cell Biol. 2012, 198, 607–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikezu, T.; Chen, C.; DeLeo, A.M.; Zeldich, E.; Fallin, M.D.; Kanaan, N.M.; Lunetta, K.L.; Abraham, C.R.; Logue, M.W.; Farrer, L.A. Tau phosphorylation is impacted by rare AKAP9 mutations associated with Alzheimer disease in African Americans. J. Neuroimmune Pharmacol. 2018, 13, 254–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- You, Y.; Hersh, S.W.; Aslebagh, R.; Shaffer, S.A.; Ikezu, S.; Mez, J.; Lunetta, K.L.; Logue, M.W.; Farrer, L.A.; Ikezu, T. Alzheimer’s disease associated AKAP9 I2558M mutation alters posttranslational modification and interactome of tau and cellular functions in CRISPR-edited human neuronal cells. Aging Cell 2022, 21, e13617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drummond, E.; Pires, G.; MacMurray, C.; Askenazi, M.; Nayak, S.; Bourdon, M.; Safar, J.; Ueberheide, B.; Wisniewski, T. Phosphorylated tau interactome in the human Alzheimer’s disease brain. Brain 2020, 143, 2803–2817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonnies, E.; Trushina, E. Oxidative Stress, Synaptic Dysfunction, and Alzheimer’s Disease. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2017, 57, 1105–1121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Escott-Price, V.; Sims, R.; Bannister, C.; Harold, D.; Vronskaya, M.; Majounie, E.; Badarinarayan, N.; Gerad/Perades; IGAP consortia; Morgan, K.; et al. Common polygenic variation enhances risk prediction for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2015, 138, 3673–3684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zettergren, A.; Lord, J.; Ashton, N.J.; Benedet, A.L.; Karikari, T.K.; Lantero Rodriguez, J.; Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative; Snellman, A.; Suarez-Calvet, M.; Proitsi, P.; et al. Association between polygenic risk score of Alzheimer’s disease and plasma phosphorylated tau in individuals from the Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupton, M.K.; Strike, L.; Hansell, N.K.; Wen, W.; Mather, K.A.; Armstrong, N.J.; Thalamuthu, A.; McMahon, K.L.; de Zubicaray, G.I.; Assareh, A.A.; et al. The effect of increased genetic risk for Alzheimer’s disease on hippocampal and amygdala volume. Neurobiol. Aging 2016, 40, 68–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabuncu, M.R.; Buckner, R.L.; Smoller, J.W.; Lee, P.H.; Fischl, B.; Sperling, R.A. Alzheimer’s Disease Neuroimaging Initiative The association between a polygenic Alzheimer score and cortical thickness in clinically normal subjects. Cereb. Cortex 2012, 22, 2653–2661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayes, J.P.; Logue, M.W.; Sadeh, N.; Spielberg, J.M.; Verfaellie, M.; Hayes, S.M.; Reagan, A.; Salat, D.H.; Wolf, E.J.; McGlinchey, R.E.; et al. Mild traumatic brain injury is associated with reduced cortical thickness in those at risk for Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 2017, 140, 813–825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Logue, M.W.; Panizzon, M.S.; Elman, J.A.; Gillespie, N.A.; Hatton, S.N.; Gustavson, D.E.; Andreassen, O.A.; Dale, A.M.; Franz, C.E.; Lyons, M.J.; et al. Use of an Alzheimer’s disease polygenic risk score to identify mild cognitive impairment in adults in their 50s. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dudbridge, F. Power and predictive accuracy of polygenic risk scores. PLoS Genet. 2013, 9, e1003348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.R.; Kanai, M.; Kamatani, Y.; Okada, Y.; Neale, B.M.; Daly, M.J. Clinical use of current polygenic risk scores may exacerbate health disparities. Nat. Genet. 2019, 51, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, L.; Shen, H.; Gelaye, B.; Meijsen, J.; Ressler, K.; Feldman, M.; Peterson, R.; Domingue, B. Analysis of polygenic risk score usage and performance in diverse human populations. Nat. Commun. 2019, 10, 3328. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, A.R.; Gignoux, C.R.; Walters, R.K.; Wojcik, G.L.; Neale, B.M.; Gravel, S.; Daly, M.J.; Bustamante, C.D.; Kenny, E.E. Human demographic history impacts genetic risk prediction across diverse populations. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2017, 100, 635–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lake, J.; Warly Solsberg, C.; Kim, J.J.; Acosta-Uribe, J.; Makarious, M.B.; Li, Z.; Levine, K.; Heutink, P.; Alvarado, C.X.; Vitale, D.; et al. Multi-ancestry meta-analysis and fine-mapping in Alzheimer’s disease. Mol. Psychiatry 2023. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wojcik, G.L.; Graff, M.; Nishimura, K.K.; Tao, R.; Haessler, J.; Gignoux, C.R.; Highland, H.M.; Patel, Y.M.; Sorokin, E.P.; Avery, C.L.; et al. Genetic analyses of diverse populations improves discovery for complex traits. Nature 2019, 570, 514–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonham, V.L.; Green, E.D.; Perez-Stable, E.J. Examining how race, ethnicity, and ancestry data are used in biomedical research. JAMA 2018, 320, 1533–1534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Norman, M.A.; Moore, D.J.; Taylor, M.; Franklin, D., Jr.; Cysique, L.; Ake, C.; Lazarretto, D.; Vaida, F.; Heaton, R.K.; Hnrc Group. Demographically corrected norms for African Americans and Caucasians on the Hopkins Verbal Learning Test-Revised, Brief Visuospatial Memory Test-Revised, Stroop Color and Word Test, and Wisconsin Card Sorting Test 64-Card Version. J. Clin. Exp. Neuropsychol. 2011, 33, 793–804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, C.R. The NFL’s Racist ‘Race Norming’ Is an Afterlife of Slavery. Scientific American, 8 July; 2021.
- Belson, K. Black Former N.F.L. Players Say Racial Bias Skews Concussion Payouts. The New York Times, 26 August 2020; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Vyas, D.A.; Eisenstein, L.G.; Jones, D.S. Hidden in plain sight—Reconsidering the use of race correction in clinical algorithms. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine. Using Population Descriptors in Genetics and Genomics Research: A New Framework for an Evolving Field; National Academies of Sciences, Engineering, and Medicine: Washington, DC, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, R.P.; Haywood, C., Jr. Sickle cell trait diagnosis: Clinical and social implications. Hematol. Am. Soc. Hematol. Educ. Program 2015, 2015, 160–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Devaney, S.A.; Malerba, L.; Manson, S.M. The “All of Us” program and indigenous peoples. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1892. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fox, K. The “All of Us” Program and Indigenous Peoples. Reply. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 383, 1982–1983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, M.K.; Fullerton, S.M.; Hammonds, E.M.; Lee, S.S.; Panofsky, A.; Reardon, J. Pangenomics: Prioritize diversity in collaborations. Nature 2023, 619, 698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mena, P.R.; Kunkle, B.W.; Faber, K.; Celis, K.; Adams, L.D.; Foroud, T.M.; Reyes-Dumeyer, D.; Kuzma, A.B.; Naj, A.C.; Martin, E.R.; et al. The Alzheimer’s disease sequencing project–follow up study (ADSP-FUS): Increasing ethnic diversity in Alzheimer’s genetics research with addition of potential new cohorts. Alzheimers Dement. 2020, 16, e046400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feliciano-Astacio, B.E.; Celis, K.; Ramos, J.; Rajabli, F.; Adams, L.D.; Rodriguez, A.; Rodriguez, V.; Bussies, P.L.; Sierra, C.; Manrique, P.; et al. The Puerto Rico Alzheimer Disease Initiative (PRADI): A multisource ascertainment approach. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nafikov, R.A.; Nato, A.Q., Jr.; Sohi, H.; Wang, B.; Brown, L.; Horimoto, A.R.; Vardarajan, B.N.; Barral, S.M.; Tosto, G.; Mayeux, R.P.; et al. Analysis of pedigree data in populations with multiple ancestries: Strategies for dealing with admixture in Caribbean Hispanic families from the ADSP. Genet. Epidemiol. 2018, 42, 500–515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.; Farrell, J.J.; Mez, J.; Martin, E.R.; Bush, W.S.; Ruiz, A.; Boada, M.; de Rojas, I.; Mayeux, R.; Haines, J.L.; et al. Novel loci for Alzheimer’s disease identified by a genome-wide association study in Ashkenazi Jews. Alzheimers Dement. 2023. Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Petrosyan, S.; Khobragade, P.; Banerjee, J.; Chien, S.; Weerman, B.; Gross, A.; Hu, P.; Smith, J.A.; Zhao, W.; et al. Deep phenotyping and genomic data from a nationally representative study on dementia in India. Sci. Data 2023, 10, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lautenbach, D.M.; Christensen, K.D.; Sparks, J.A.; Green, R.C. Communicating genetic risk information for common disorders in the era of genomic medicine. Annu. Rev. Genom. Hum. Genet. 2013, 14, 491–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Visser, L.N.C.; Minguillon, C.; Sanchez-Benavides, G.; Abramowicz, M.; Altomare, D.; Fauria, K.; Frisoni, G.B.; Georges, J.; Ribaldi, F.; Scheltens, P.; et al. Dementia risk communication. A user manual for Brain Health Services-part 3 of 6. Alzheimers Res. Ther. 2021, 13, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
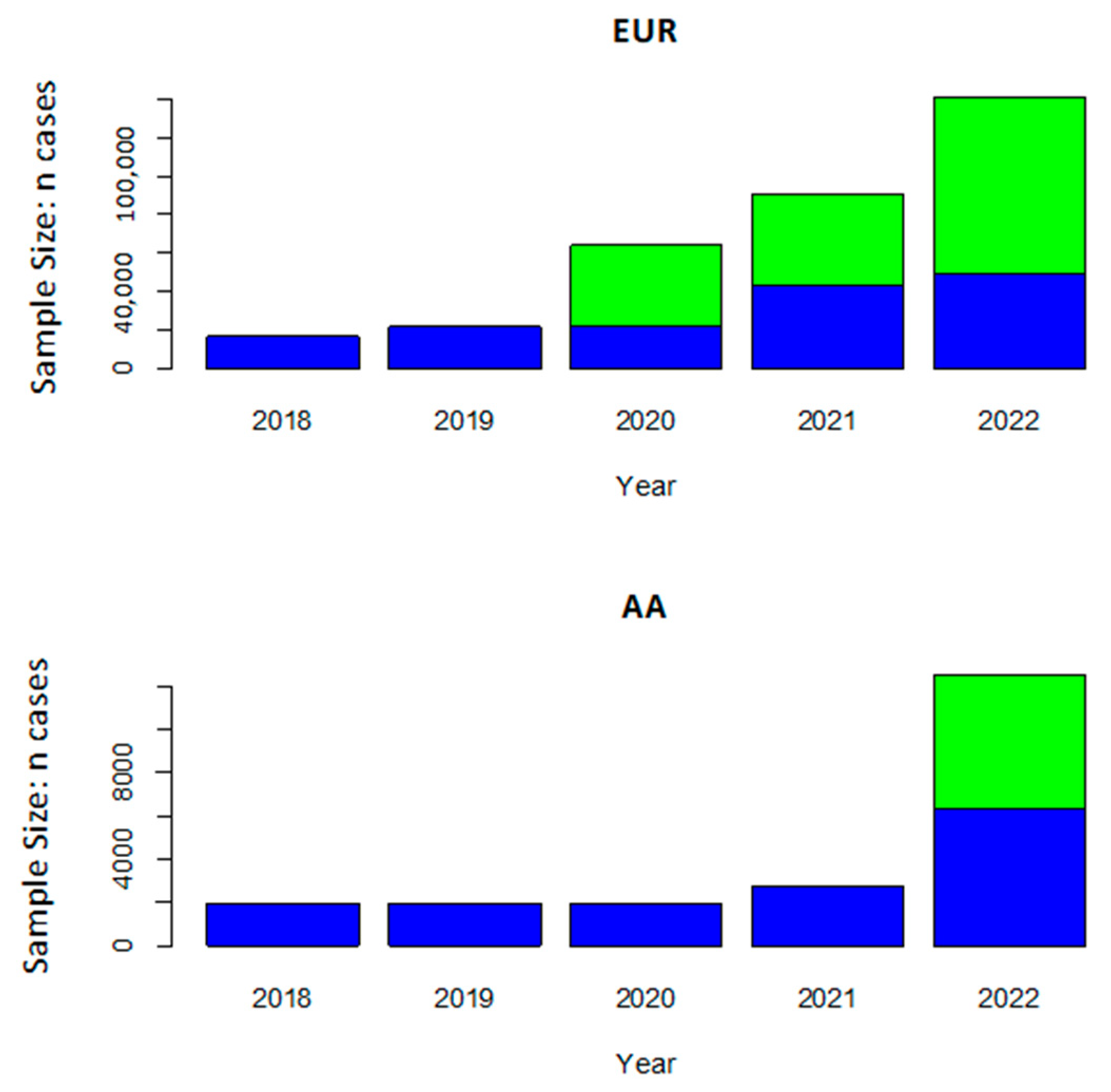
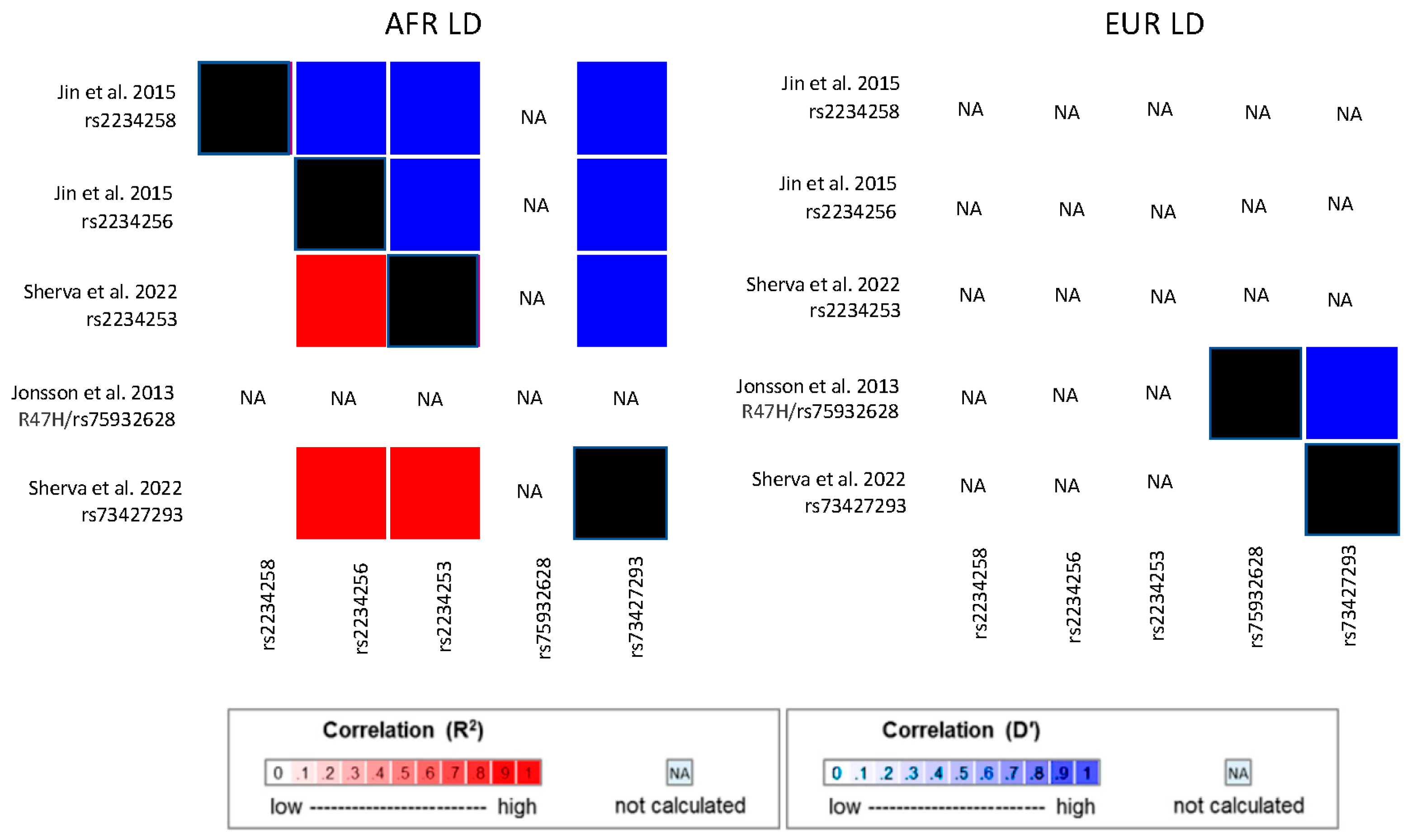
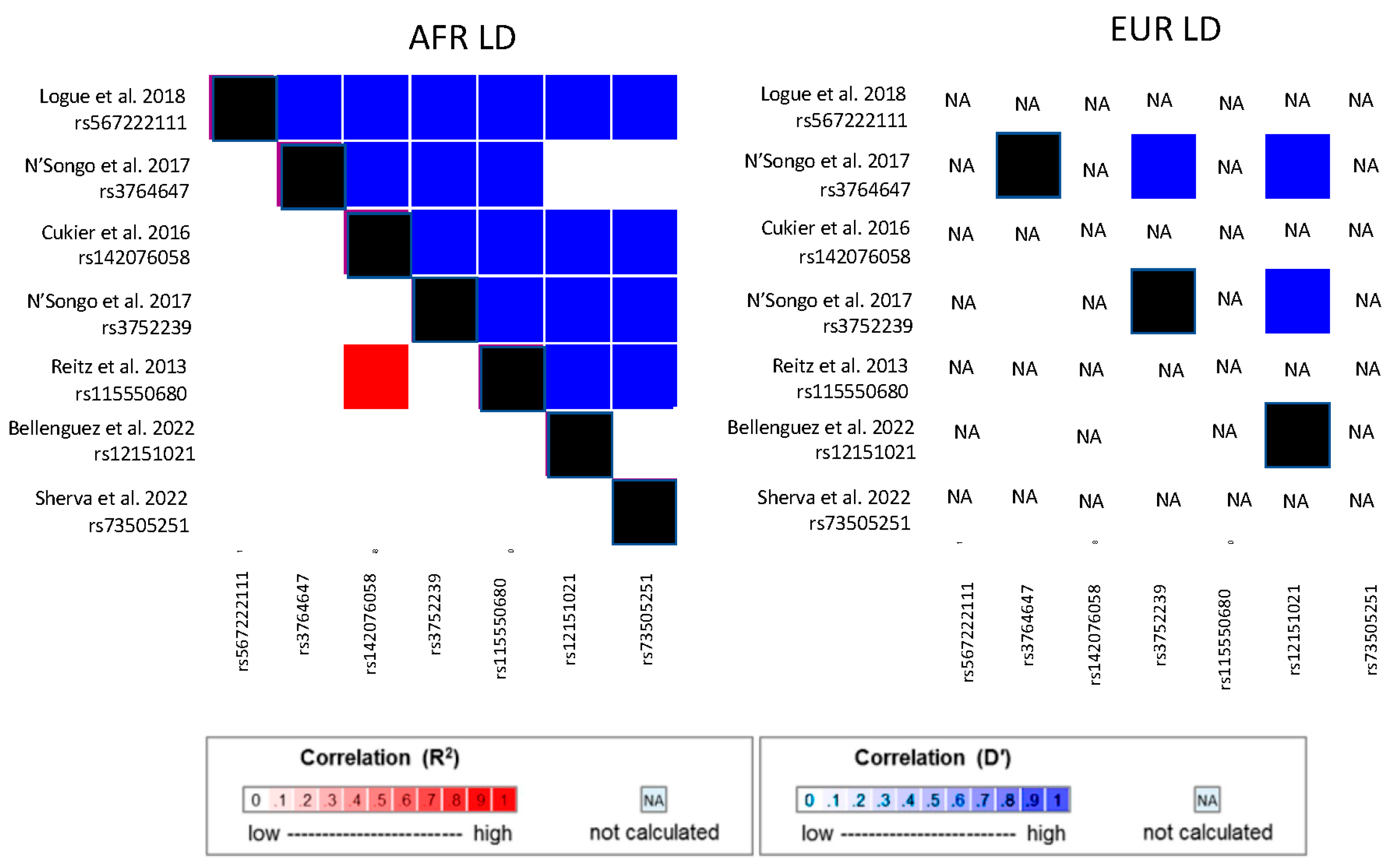
| Study | Cohort Characteristics | APOE Genotype | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ε2/ε2 ε2/ε3 ε2/ε4 | ε2/ε2 ε2/ε3 | ε2/ε2 | ε2/ε3 | ε2/ε4 | ε3/ε4 | ε2/ε4 ε3/ε4 | ε2/ε4 ε3/ε4 ε4ε/4 | ε4/ε4 | ||
| Tang et al. 1996 [45] | New York community-based cohort of 106 AD cases and 154 controls | RR = 1.3 (p > 0.05) | . | . | . | . | . | RR = 0.6 (<0.05) | . | RR = 3.0 (<0.05) |
| Farrer et al. 1997 [29] | Multi-center Cohort of 235 cases and 240 controls | . | . | OR = 2.4 (>0.05) | OR = 0.6 (>0.05) | OR = 1.2 (>0.05) | OR = 2.7 (<0.05) | . | . | OR = 12.5 (<0.05) |
| Sahota et al. 1997 [46] | Indianapolis community-based cohort of 60 AD cases and 228 controls | . | . | . | OR = 0.43 (>0.05) | OR = 0.34 (>0.05) | OR = 1.20 (>0.05) | . | . | OR = 4.83 (<0.05) |
| Tang et al. 1998 [43] | New York community-based cohort of 48 incident cases and 128 controls | . | . | . | . | . | . | . | RR = 1.0 (p > 0.05) | . |
| Graff-Radford et al. 2002 [44] | 338 cases, 301 unrelated controls, and 108 siblings from the MIRAGE Study | . | . | . | OR = 0.41 (p < 0.05) | . | OR = 2.6 (p < 0.05) | . | . | OR = 10.5 (p < 0.05) |
| Murell et al. 2006 [48] | Indianapolis community-based cohort of 162 AD cases and 318 controls | . | OR = 0.42 (0.02) | . | OR = 0.46 (0.047) | OR = 1.34 (0.61) | OR = 2.32 (<0.001) | . | . | OR = 7.19 (<0.001) |
| Logue et al. 2011 [47] | 513 Cases and 496 controls from the MIRAGE and GenerAAtions Studies | . | OR = 0.43 (0.0094) | . | . | . | . | OR = 2.08 (2 × 10−7) | . | OR = 2.62 (3 × 10−14) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Logue, M.W.; Dasgupta, S.; Farrer, L.A. Genetics of Alzheimer’s Disease in the African American Population. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 5189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165189
Logue MW, Dasgupta S, Farrer LA. Genetics of Alzheimer’s Disease in the African American Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(16):5189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165189
Chicago/Turabian StyleLogue, Mark W., Shoumita Dasgupta, and Lindsay A. Farrer. 2023. "Genetics of Alzheimer’s Disease in the African American Population" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 16: 5189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165189
APA StyleLogue, M. W., Dasgupta, S., & Farrer, L. A. (2023). Genetics of Alzheimer’s Disease in the African American Population. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(16), 5189. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12165189






