Short and Long-Term Outcomes of Lesion Index-Guided High-Power Short-Duration Approach for Atrial Fibrillation Ablation
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Population
- Documented paroxysmal or persistent AF (<12 months) with an indication for PVI-only RF ablation;
- Aged 18 years or older;
- Able to sign an informed consent form and willing to compete the required study procedures during follow-up.
- HPSD group: patients who underwent PVI with an LSI-guided HPSD strategy (≥45 W);
- Standard group: patients who underwent PVI with LSI-guided standard PVI (≤40 W).
2.2. Ablation Procedure
2.3. Follow-Up
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Ablation Procedure
3.3. Clinical Follow-Up
4. Discussion
- Significantly enhanced procedural efficiency, resulting in reduced overall procedural and fluoroscopic time;
- Achieved comparable acute and long-term efficacy of PVI;
- Demonstrated a similar level of procedural safety.
5. Conclusions
6. Study Limitations
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benjamin, E.J.; Muntner, P.; Alonso, A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Callaway, C.W.; Carson, A.P.; Chamberlain, A.M.; Chang, A.R.; Cheng, S.; Das, S.R.; et al. Heart Disease and Stroke Statistics-2019 Update: A Report from the American Heart Association. Circulation 2019, 139, e56–e528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrade, J.G.; Champagne, J.; Deyell, M.W.; Essebag, V.; Lauck, S.; Morillo, C.; Sapp, J.; Skanes, A.; Theoret-Patrick, P.; Wells, G.A.; et al. A randomized clinical trial of early invasive intervention for atrial fibrillation (EARLY-AF)—Methods and rationale. Am. Heart J. 2018, 206, 94–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teh, A.W.; Kistler, P.M.; Lee, G.; Medi, C.; Heck, P.M.; Spence, S.J.; Morton, J.B.; Sanders, P.; Kalman, J.M. Long-term effects of catheter ablation for lone atrial fibrillation: Progressive atrial electroanatomic substrate remodeling despite successful ablation. Heart Rhythm 2012, 9, 473–480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aliot, E.; Brandes, A.; Eckardt, L.; Elvan, A.; Gulizia, M.; Heidbuchel, H.; Kautzner, J.; Mont, L.; Morgan, J.; Ng, A.; et al. The EAST study: Redefining the role of rhythmcontrol therapy in atrial fibrillation: EAST, the Early treatment of Atrial fibrillation for Stroke prevention Trial. Eur. Heart J. 2015, 36, 255–256. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Themistoclakis, S.; Calzolari, V.; De Mattia, L.; China, P.; Dello Russo, A.; Fassini, G.; Casella, M.; Caporaso, I.; Indiani, S.; Addis, A.; et al. In vivo Lesion Index (LSI) validation in percutaneous radiofrequency catheter ablation. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2022, 33, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naniwadekar, A.; Dukkipati, S.R. High-power short-duration ablation of atrial fibrillation: A contemporary review. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 44, 528–540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barbhaiya, C.R. High-Power Short-Duration Ablation: In Real Life∗. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 1262–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Winkle, R.A. HPSD ablation for AF high-power short-duration RF ablation for atrial fibrillation: A review. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2021, 32, 2813–2823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Afzal, M.R.; Chatta, J.; Samanta, A.; Waheed, S.; Mahmoudi, M.; Vukas, R.; Gunda, S.; Reddy, M.; Dawn, B.; Lakkireddy, D. Use of contact force sensing technology during radiofrequency ablation reduces recurrence of atrial fibrillation: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Heart Rhythm 2015, 12, 1990–1996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zucchelli, G.; Parollo, M.; Guarracini, F.; Marini, M.; Di Cori, A.; Barletta, V.; De Lucia, R.; Segreti, L.; Bonmassari, R.; Bongiorni, M.G. Standard versus strict stability criteria in radiofrequency paroxysmal atrial fibrillation ablation using ablation index. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2021, 44, 1404–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Gui, C.; Wen, W.; He, Y.; Dai, W.; Zhong, G. Safety and Efficacy of High Power Shorter Duration Ablation Guided by Ablation Index or Lesion Size Index in Atrial Fibrillation Ablation: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Interv. Cardiol. 2021, 2021, 5591590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leo, M.; Pedersen, M.; Rajappan, K.; Ginks, M.R.; Hunter, R.J.; Bowers, R.; Kalla, M.; Bashir, Y.; Betts, T.R. Power, Lesion Size Index and Oesophageal Temperature Alerts During Atrial Fibrillation Ablation. Circ. Arrhythmia Electrophysiol. 2020, 13, e008316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Chun, K.R.J.; Tohoku, S.; Bordignon, S.; Urbanek, L.; Willems, F.; Plank, K.; Hilbert, M.; Konstantinou, A.; Tsianakas, N.; et al. Esophageal Endoscopy After Catheter Ablation of Atrial Fibrillation Using Ablation-Index Guided High-Power. JACC Clin. Electrophysiol. 2020, 6, 1253–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cori, A.; Zucchelli, G.; Faggioni, L.; Segreti, L.; De Lucia, R.; Barletta, V.; Viani, S.; Paperini, L.; Parollo, M.; Soldati, E.; et al. Role of pre-procedural CT imaging on catheter ablation in patients with atrial fibrillation: Procedural outcomes and radiological exposure. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2021, 60, 477–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Cori, A.; Mazzocchetti, L.; Parollo, M.; Giannotti, M.; Canu, A.; Barletta, V.; Volpe, S.D.; De Lucia, R.; Viani, S.; Segreti, L.; et al. Clinical impact of high-density mapping on the acute and long term outcome of atypical atrial flutter ablations. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2022; Online ahead of print. [Google Scholar]
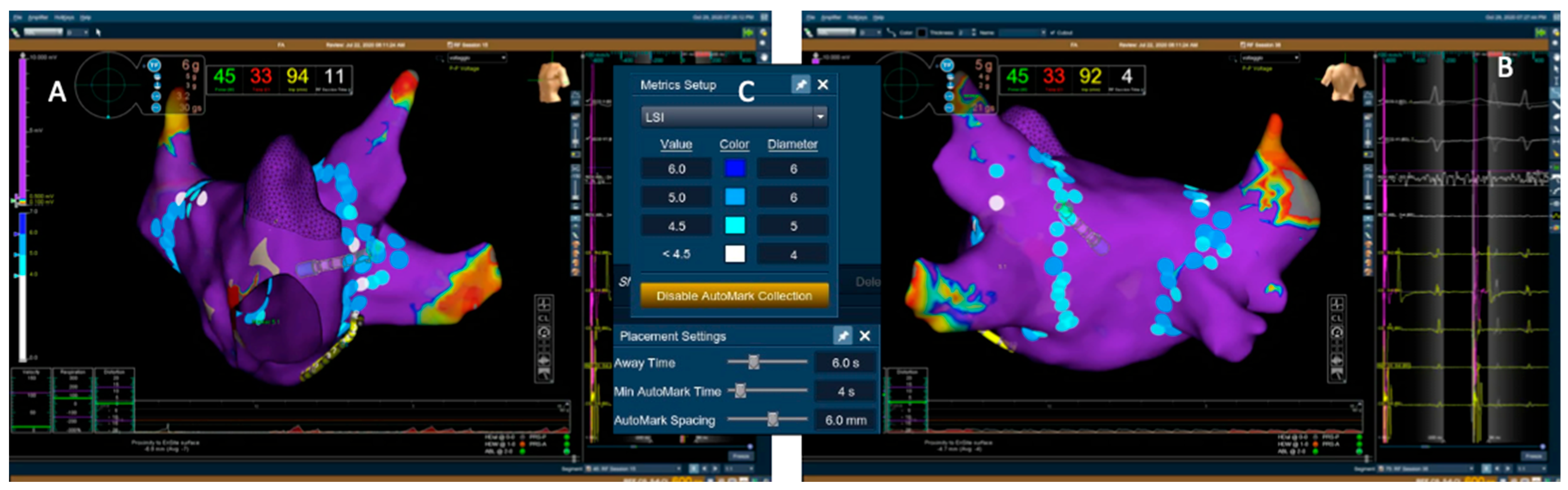
| All Patients (n = 46) | Controls (n = 21) | HPSD (n = 25) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Clinical features | ||||
| Age, years | 65 ± 7 | 65 ± 9 | 64 ± 6 | 0.624 |
| Males, n (%) | 36 (78) | 19 (91) | 17 (68) | 0.084 |
| Hypertension, n (%) | 29 (63) | 14 (67) | 15 (60) | 0.762 |
| History of smoking, n (%) | 20 (44) | 10 (48) | 10 (40) | 0.321 |
| Diabetes, n (%) | 6 (13) | 3 (14) | 3 (12) | 1.000 |
| Dyslipidemia, n (%) | 12 (26) | 7 (33) | 5 (20) | 0.335 |
| OSAS, n (%) | 1 (2) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 0.457 |
| IHD, n (%) | 2 (4) | 1 (5) | 1 (4) | 1.000 |
| History of HF, n (%) | 2 (4) | 0 (0) | 2 (8) | 0.493 |
| CHA2DS2VASc score | 2 (1–3) | 2 (1–2) | 2 (1–3) | 0.576 |
| Symptomatic AF, n (%) | 42 (91) | 20 (95) | 22 (88) | 0.881 |
| Paroxysmal AF, n (%) | 27 (59) | 12 (57) | 15 (60) | 1.000 |
| History of atrial flutter, n (%) | 8 (17) | 6 (29) | 2 (8) | 0.117 |
| History of AVNRT, n (%) | 3 (7) | 0 (0) | 3 (12) | 0.239 |
| Echocardiography | ||||
| LA diameter, mm | 42 ± 6 | 42 ± 5 | 42 ± 6 | 0.757 |
| LA area, cm2 | 24 ± 7 | 23 ± 4 | 25 ± 8 | 0.373 |
| LAVi, ml/m2 | 39 ± 13 | 39 ± 13 | 40 ± 13 | 0.662 |
| LVEF, % | 65 ± 6 | 58 ± 5 | 61 ± 7 | 0.282 |
| Medical therapy | ||||
| Class IC AADs, n (%) | 24 (52) | 13 (62) | 11 (44) | 0.253 |
| Class III AADs, n (%) | 6 (13) | 8 (38) | 14 (56) | 0.253 |
| Oral anticoagulant, n (%) | 43 (94) | 20 (95) | 23 (92) | 1.000 |
| All Patients (n = 46) | Controls (n = 21) | HPSD (n = 25) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Procedural details | ||||
| First pass, n (%) | 21 (46) | 10 (48) | 11 (44) | 1.000 |
| Left carina ablation, n (%) | 13 (28) | 9 (43) | 4 (16) | 0.056 |
| Right carina ablation, n (%) | 11 (24) | 6 (28) | 5 (20) | 0.730 |
| Ablation AF-resolution, n (%) | 4 (9) | 3 (14) | 1 (4) | 0.318 |
| ECV AF-resolution, n (%) | 24 (48) | 11 (53) | 13 (52) | 0.883 |
| Times | ||||
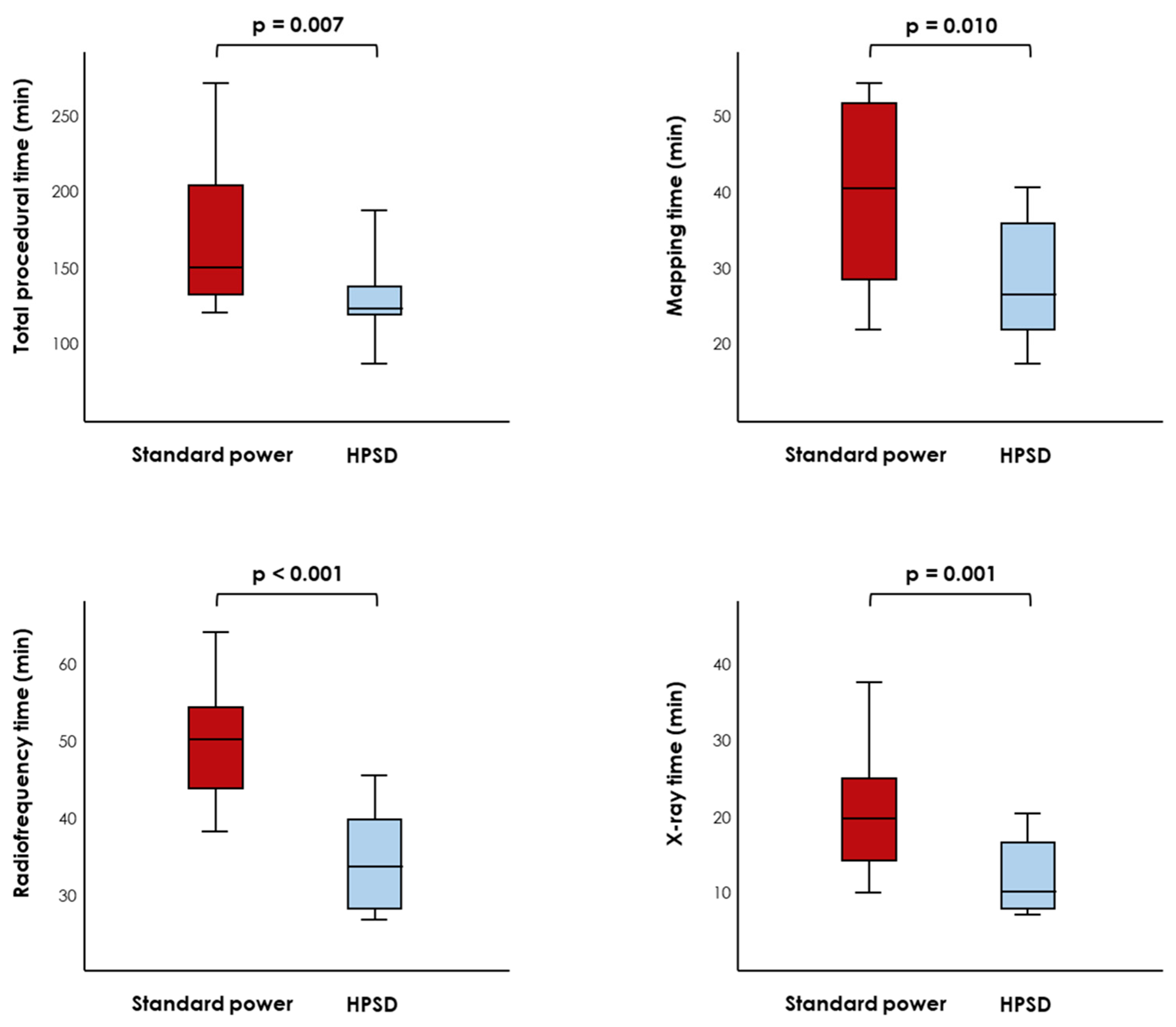
| Procedural time, hours | 2.3 (2.1–3.1) | 2.6 (2.3–3.4) | 2.2 (2.1–2.4) | 0.007 |
| Procedural time, minutes | 140 (128–185) | 155 (139–203) | 131 (126–145) | 0.007 |
| Mapping time, minutes | 37 (28–48) | 40 (27–52) | 25 (20–35) | 0.010 |
| Radiofrequency time, minutes | 37 (28–48) | 49 (41–53) | 29 (23–37) | <0.001 |
| X-ray time, minutes | 17 (11–22) | 21 (16–26) | 12 (10–18) | 0.001 |
| All Patients (n = 46) | Controls (n = 21) | HPSD (n = 25) | p | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Periprocedural complications | ||||
| Vascular complications, n (%) | 1 (2) | 1 (5) | 0 (0) | 0.457 |
| Pericardial effusion, n (%) | 2 (4) | 1 (5) | 1 (4) | 1.000 |
| Cardiac tamponade, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| Stroke/TIA, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| Tracheoesophageal fistula, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| Phrenic nerve lesion, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| PV stenosis, n (%) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 0 (0) | 1.000 |
| Longitudinal data | ||||
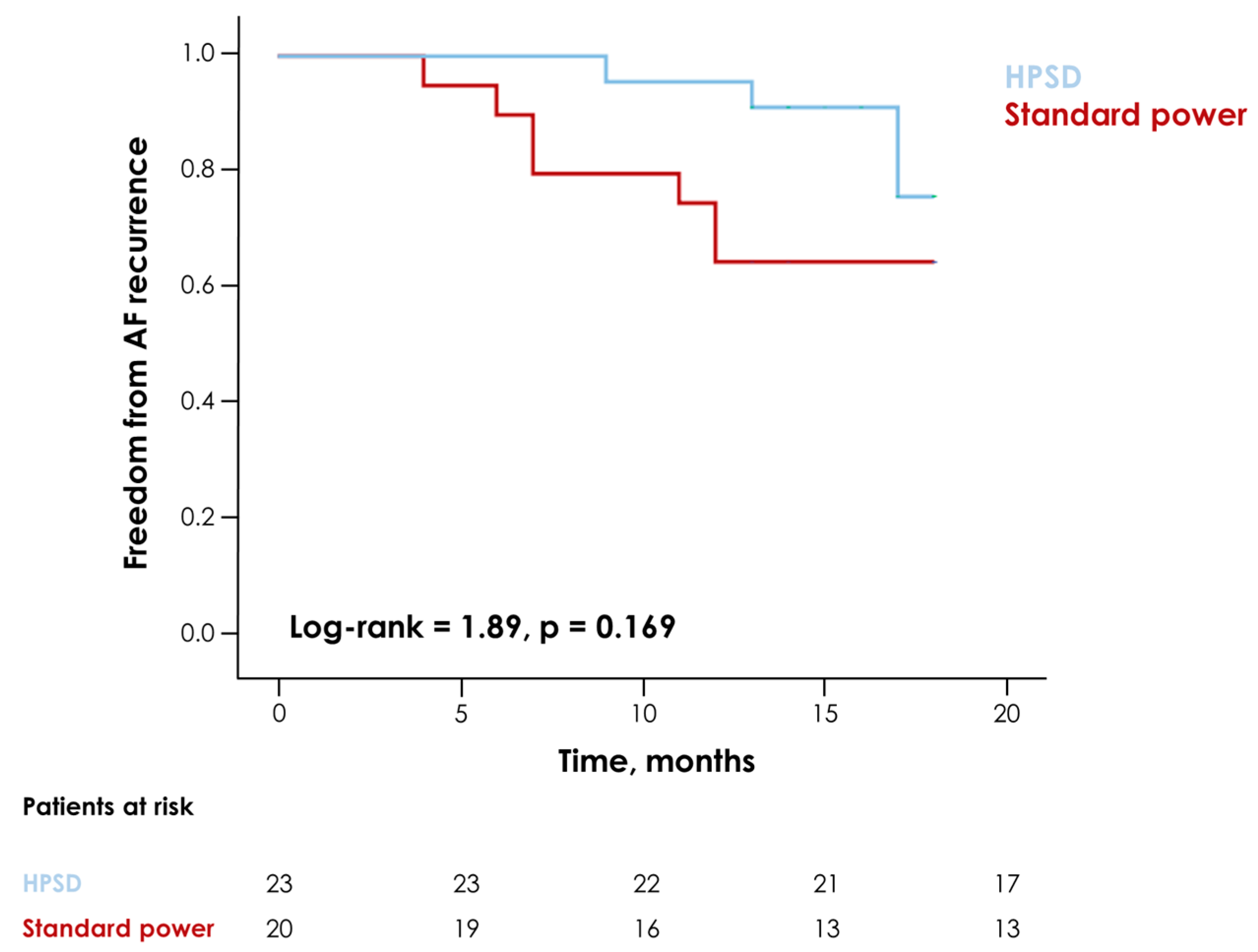
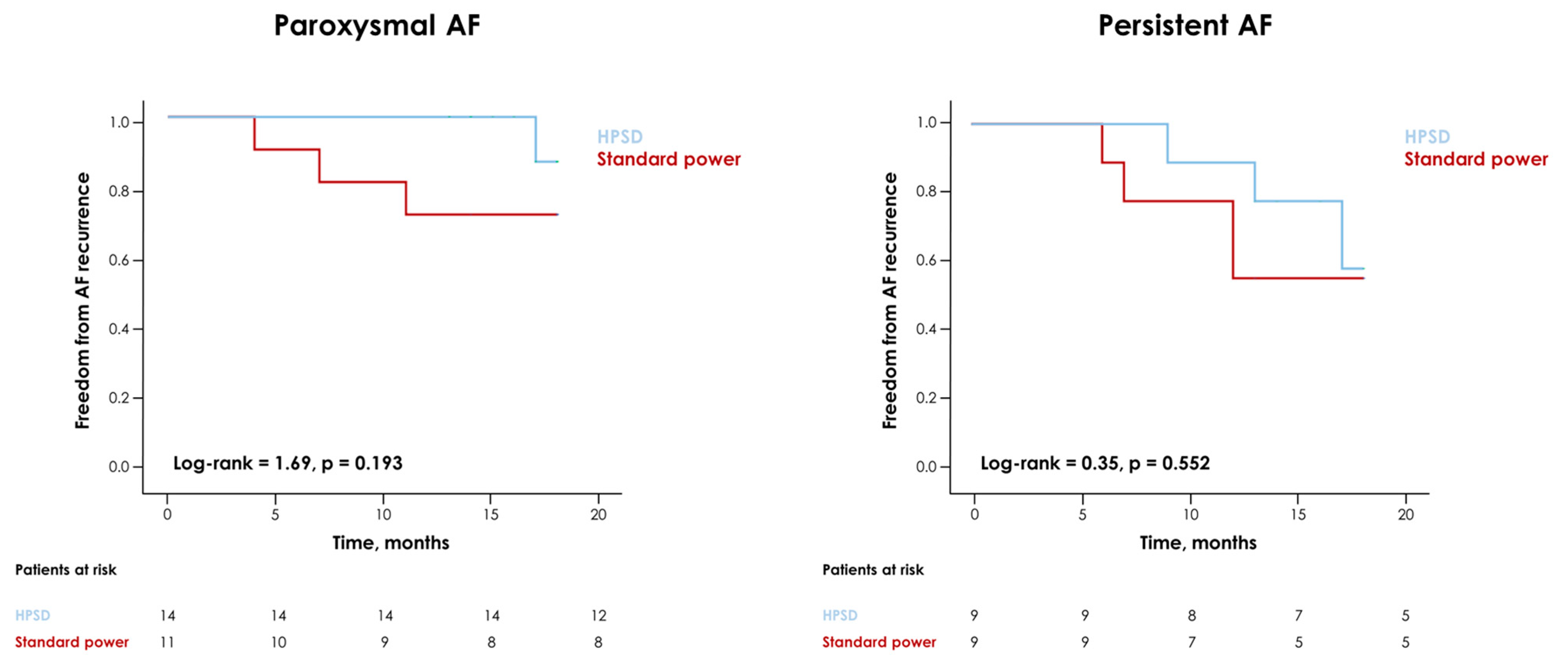
| Recurrence, n (%) | 11 (26) | 7 (35) | 4 (17) | 0.295 |
| Recurrence time, months | 17 (13–18) | 18 (12–18) | 17 (14–18) | 0.990 |
| ECV at follow-up, n (%) | 4 (9) | 2 (10) | 2 (9) | 1.000 |
| Redo at follow-up, n (%) | 2 (5) | 1 (5) | 1 (4) | 1.000 |
| Class IC AADs at follow-up, n (%) | 32 (70) | 15 (71) | 17 (68) | 1.000 |
| Class III AADs at follow-up, n (%) | 12 (26) | 6 (29) | 6 (24) | 0.749 |
| Rate control at follow-up, n (%) | 16 (37) | 9 (45) | 7 (30) | 0.361 |
| Anticoagulants at follow-up, n (%) | 30 (70) | 15 (75) | 15 (65) | 0.526 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Di Cori, A.; Parollo, M.; Gentile, F.; Pistelli, L.; Vitale, C.; Della Volpe, S.; Giannotti Santoro, M.; Mazzocchetti, L.; De Lucia, R.; Canu, A.; et al. Short and Long-Term Outcomes of Lesion Index-Guided High-Power Short-Duration Approach for Atrial Fibrillation Ablation. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4986. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154986
Di Cori A, Parollo M, Gentile F, Pistelli L, Vitale C, Della Volpe S, Giannotti Santoro M, Mazzocchetti L, De Lucia R, Canu A, et al. Short and Long-Term Outcomes of Lesion Index-Guided High-Power Short-Duration Approach for Atrial Fibrillation Ablation. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(15):4986. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154986
Chicago/Turabian StyleDi Cori, Andrea, Matteo Parollo, Francesco Gentile, Lorenzo Pistelli, Carlo Vitale, Salvatore Della Volpe, Mario Giannotti Santoro, Lorenzo Mazzocchetti, Raffaele De Lucia, Antonio Canu, and et al. 2023. "Short and Long-Term Outcomes of Lesion Index-Guided High-Power Short-Duration Approach for Atrial Fibrillation Ablation" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 15: 4986. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154986
APA StyleDi Cori, A., Parollo, M., Gentile, F., Pistelli, L., Vitale, C., Della Volpe, S., Giannotti Santoro, M., Mazzocchetti, L., De Lucia, R., Canu, A., Barletta, V., Grifoni, G., Segreti, L., Bongiorni, M. G., & Zucchelli, G. (2023). Short and Long-Term Outcomes of Lesion Index-Guided High-Power Short-Duration Approach for Atrial Fibrillation Ablation. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(15), 4986. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12154986








