COVID-19 and Fatty Liver Disorders
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Epidemiology
2.1. FLD Epidemiology during COVID-19 Pandemic
2.2. The Incidence of COVID-19 in Subjects with FLD
3. Pathogenesis of Systemic and Liver Damage
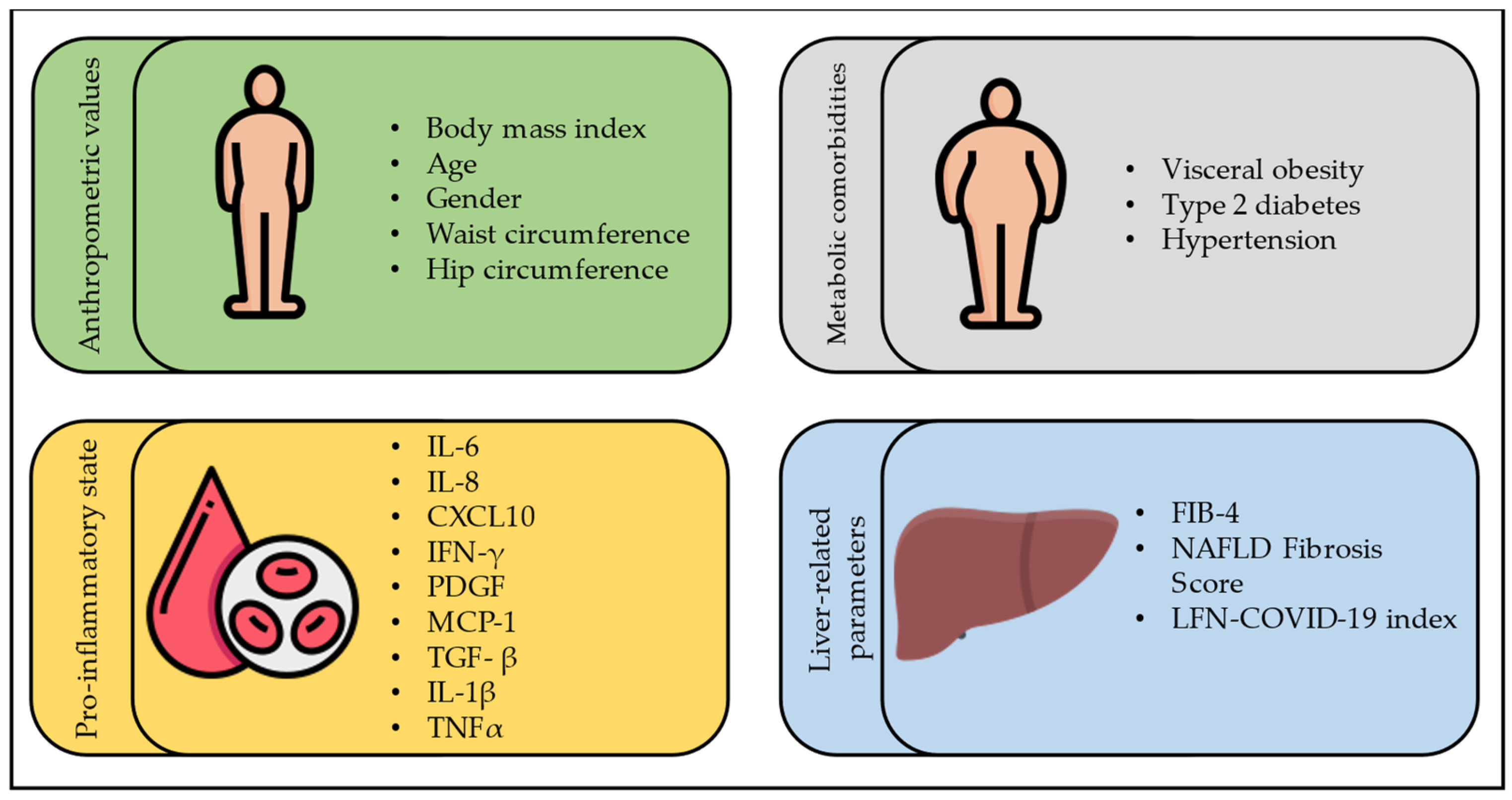
4. Severity of COVID-19 in Subjects with FLD
4.1. COVID-19 and Steatosis
4.2. COVID-19 and Liver Fibrosis
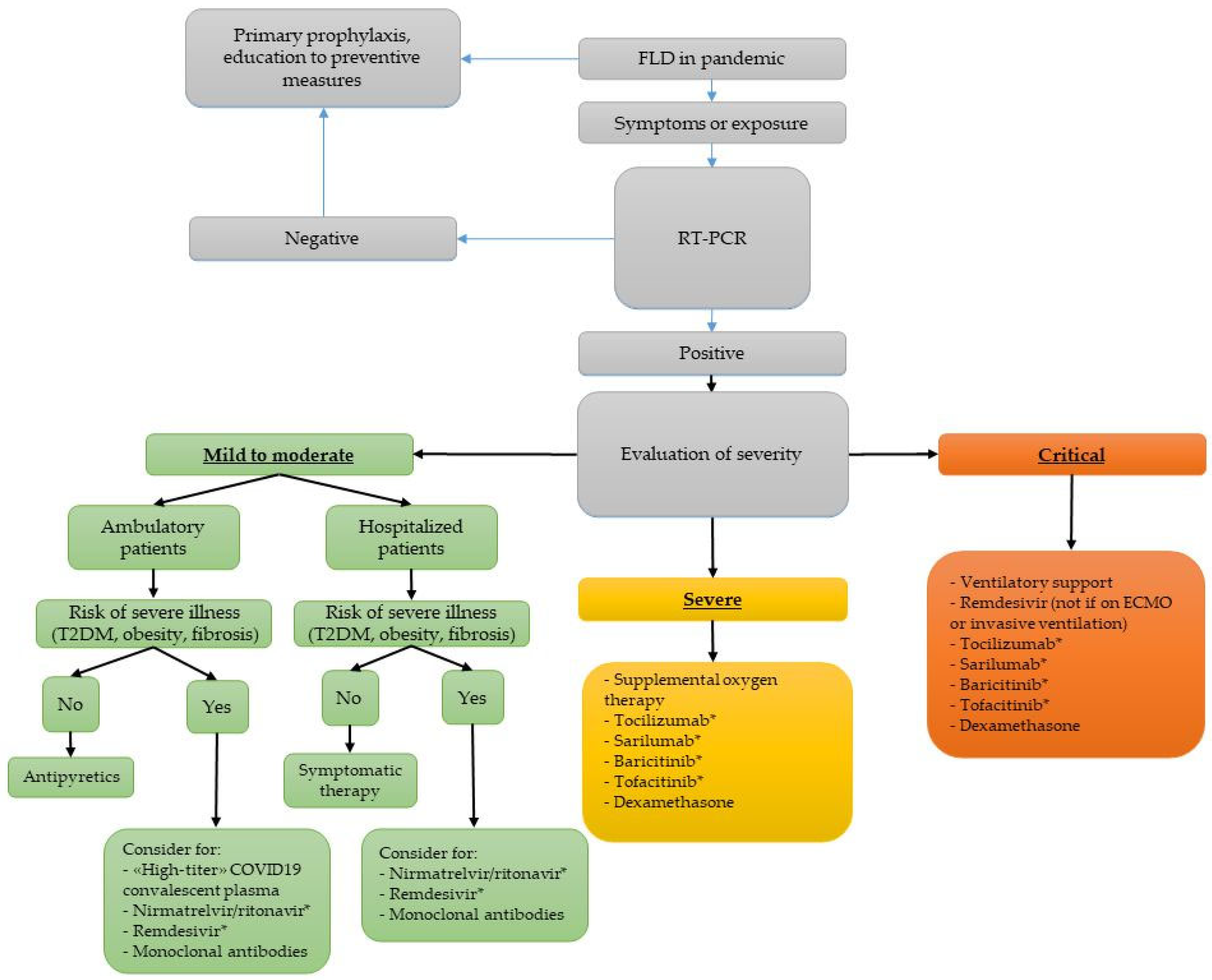
5. Management of COVID-19 in Subjects with FLD
5.1. Clinical Intervention and Treatment
5.2. Telemedicine
5.3. COVID-19 Vaccination
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Guarino, M.; Cossiga, V.; Capasso, M.; Mazzarelli, C.; Pelizzaro, F.; Sacco, R.; Russo, F.P.; Vitale, A.; Trevisani, F.; Cabibbo, G.; et al. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic on the Management of Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guarino, M.; Esposito, I.; Portella, G.; Cossiga, V.; Loperto, I.; Tortora, R.; Cennamo, M.; Capasso, M.; Terracciano, D.; Galeota Lanza, A.; et al. Humoral Response to 2-dose BNT162b2 mRNA COVID-19 Vaccination in Liver Transplant Recipients. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1534–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cossiga, V.; Capasso, M.; Guarino, M.; Loperto, I.; Brusa, S.; Cutolo, F.M.; Attanasio, M.R.; Lieto, R.; Portella, G.; Morisco, F. Safety and Immunogenicity of Anti-SARS-CoV-2 Booster Dose in Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL); European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD); European Association for the Study of Obesity (EASO). EASL-EASD-EASO Clinical Practice Guidelines for the management of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. J. Hepatol. 2016, 64, 1388–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A new definition for metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease: An international expert consensus statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flegal, K.M.; Carroll, M.D.; Kit, B.K.; Ogden, C.L. Prevalence of obesity and trends in the distribution of body mass Index Among US Adults, 1999–2010. JAMA 2012, 307, 491–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Afendy, M.; Fang, Y.; Younossi, Y.; Mir, H.; Srishord, M. Changes in the prevalence of the most common causes of chronic liver diseases in the United States from 1988 to 2008. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2011, 9, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paik, J.M.; Golabi, P.; Younossi, Y.; Mishra, A.; Younossi, Z.M. Changes in the Global Burden of Chronic Liver Diseases from 2012 to 2017: The Growing Impact of NAFLD. Hepatology 2020, 72, 1605–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Stepanova, M.; Negro, F.; Hallaji, S.; Younossi, Y.; Lam, B.; Srishord, M. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in lean individuals in the United States. Medicine 2012, 91, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease—Meta-analytic assessment of prevalence, incidence, and outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fung, J.; Lee, C.K.; Chan, M.; Seto, W.K.; Lai, C.L.; Yuen, M.F.; Hong Kong Liver Health Census Study Group. High prevalence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in the Chinese—Results from the Hong Kong liver health census. Liver Int. 2015, 35, 542–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onyekwere, C.A.; Ogbera, A.O.; Balogun, B.O. Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and the metabolic syndrome in an urban hospital serving an African community. Ann. Hepatol. 2011, 10, 119–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-González, Á.A.; Altisench Jané, B.; Masmiquel Comas, L.; Arroyo Bote, S.; González San Miguel, H.M.; Ramírez Manent, J.I. Impact of COVID-19 Lockdown on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Insulin Resistance in Adults: A before and after Pandemic Lockdown Longitudinal Study. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, H.; Nakamura, N.; Fukumoto, S.; Kimura, T.; Nakano, A.; Nadatani, Y.; Tauchi, Y.; Nishii, Y.; Takashima, S.; Kamada, Y.; et al. Lifestyle changes during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic impact metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease. Liver Int. 2022, 42, 995–1004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slusher, A.L.; Hu, P.; Samuels, S.; Tokoglu, F.; Lat, J.; Li, Z.; Alguard, M.; Strober, J.; Vatner, D.; Shabanova, V.; et al. Rising NAFLD and Metabolic Severity during the SARS-CoV-2 Pandemic among Children with Obesity in the United States. Obesity 2023, 31, 1383–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Montemayor, S.; Mascaró, C.M.; Ugarriza, L.; Casares, M.; Gómez, C.; Martínez, J.A.; Tur, J.A.; Bouzas, C. Intrahepatic Fat Content and COVID-19 Lockdown in Adults with NAFLD and Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2022, 14, 3462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cinque, F.; Cespiati, A.; Lombardi, R.; Costantino, A.; Maffi, G.; Alletto, F.; Colavolpe, L.; Francione, P.; Oberti, G.; Fatta, E.; et al. Interaction between Lifestyle Changes and PNPLA3 Genotype in NAFLD Patients during the COVID-19 Lockdown. Nutrients 2022, 14, 556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shanmugam, H.; Di Ciaula, A.; Di Palo, D.M.; Molina-Molina, E.; Garruti, G.; Faienza, M.F.; van Erpecum, K.; Portincasa, P. Multiplying effects of COVID-19 lockdown on metabolic risk and fatty liver. Eur. J. Clin. Investig. 2021, 51, e13597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rivera-Esteban, J.; Manzano-Nuñez, R.; Broquetas, T.; Serra-Matamala, I.; Bassegoda, O.; Soriano-Varela, A.; Espín, G.; Castillo, J.; Bañares, J.; Carrión, J.A.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the care and outcomes of people with NAFLD-related cirrhosis. JHEP Rep. 2022, 4, 100574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geh, D.; Watson, R.; Sen, G.; French, J.J.; Hammond, J.; Turner, P.; Hoare, T.; Anderson, K.; McNeil, M.; McPherson, S.; et al. COVID-19 and liver cancer: Lost patients and larger tumours. BMJ Open Gastroenterol. 2022, 9, e000794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghoneim, S.; Butt, M.U.; Hamid, O.; Shah, A.; Asaad, I. The incidence of COVID-19 in patients with metabolic syndrome and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis: A population-based study. Metabol. Open. 2020, 8, 100057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wu, S.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, F.; Yu, B.; Zhang, S.; Wu, C.; Wu, G.; Zhong, Y. Association between non-alcoholic fatty liver disease with the susceptibility and outcome of COVID-19: A retrospective study. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 11212–11220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoo, H.W.; Jin, H.Y.; Yon, D.K.; Effenberger, M.; Shin, Y.H.; Kim, S.Y.; Yang, J.M.; Kim, M.S.; Koyanagi, A.; Jacob, L.; et al. Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and COVID-19 Susceptibility and Outcomes: A Korean Nationwide Cohort. J. Korean Med. Sci. 2021, 36, e291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosso, C.; Demelas, C.; Agostini, G.; Abate, M.L.; Vernero, M.; Caviglia, G.P.; D’Amato, D.; Armandi, A.; Tapparo, M.; Guariglia, M.; et al. Expression of SARS-Cov-2 Entry Factors in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis. Viruses 2022, 14, 2397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, M.K.; Mobeen, A.; Chandra, A.; Joshi, S.; Ramachandran, S. A meta-analysis of comorbidities in COVID-19: Which diseases increase the susceptibility of SARS-CoV-2 infection? Comput. Biol. Med. 2021, 130, 104219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Qin, E.; Xu, J.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, G.; Wang, Y.; Lau, G. Non-alcoholic fatty liver diseases in patients with COVID-19: A retrospective study. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calapod, O.P.; Marin, A.M.; Onisai, M.; Tribus, L.C.; Pop, C.S.; Fierbinteanu-Braticevici, C. The Impact of Increased Fib-4 Score in Patients with Type II Diabetes Mellitus on COVID-19 Disease Prognosis. Medicina 2021, 57, 434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mushtaq, K.; Khan, M.U.; Iqbal, F.; Alsoub, D.H.; Chaudhry, H.S.; Ata, F.; Iqbal, P.; Elfert, K.; Balaraju, G.; Almaslamani, M.; et al. NAFLD is a predictor of liver injury in COVID-19 hospitalized patients but not of mortality, disease severity on the presentation or progression—The debate continues. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, R.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Xue, L.; Liu, L.; Yan, X.; Huang, S.; Li, Y.; Yan, X.; Zhang, B.; et al. Clinical Features of Patients with COVID-19 with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1758–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, V.L.; Hawa, F.; Berinstein, J.A.; Reddy, C.A.; Kassab, I.; Platt, K.D.; Hsu, C.Y.; Steiner, C.A.; Louissaint, J.; Gunaratnam, N.T.; et al. Hepatic Steatosis Is Associated with Increased Disease Severity and Liver Injury in Coronavirus Disease-19. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2021, 66, 3192–3198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vrsaljko, N.; Samadan, L.; Viskovic, K.; Mehmedović, A.; Budimir, J.; Vince, A.; Papic, N. Association of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease With COVID-19 Severity and Pulmonary Thrombosis: CovidFAT, a Prospective, Observational Cohort Study. Open Forum Infect. Dis. 2022, 9, ofac073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chai, X.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y.; Han, W.; Lu, Z.; Ke, A.; Zhou, J.; Shi, G.; Fang, N.; Fan, J.; et al. Specific ACE2 Expression in Cholangiocytes May Cause Liver Damage After 2019-nCoV Infection. bioRxiv 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripon, S.; Bilbault, P.; Fabacher, T.; Lefebvre, N.; Lescuyer, S.; Andres, E.; Schmitt, E.; Garnier-KepKA, S.; Borgne, P.L.; Muller, J.; et al. Abnormal liver tests and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease predict disease progression and outcome of patients with COVID-19. Clin. Res. Hepatol. Gastroenterol. 2022, 46, 101894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gjurašin, B.; Jeličić, M.; Kutleša, M.; Papić, N. The Impact of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease on Severe Community-Acquired Pneumonia Outcomes. Life 2022, 13, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halim, C.; Mirza, A.F.; Sari, M.I. The Association between TNF-α, IL-6, and Vitamin D Levels and COVID-19 Severity and Mortality: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Pathogens 2022, 11, 195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papic, N.; Samadan, L.; Vrsaljko, N.; Radmanic, L.; Jelicic, K.; Simicic, P.; Svoboda, P.; Lepej, S.Z.; Vince, A. Distinct Cytokine Profiles in Severe COVID-19 and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Life 2022, 12, 795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yuan, X.; Gao, F.; Zhao, B.; Ding, L.; Huan, M.; Liu, C.; Jiang, L. High Number and Specific Comorbidities Could Impact the Immune Response in COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 899930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zheng, K.I.; Yan, H.D.; Sun, Q.F.; Pan, K.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; George, J.; et al. Association and Interaction between Serum Interleukin-6 Levels and Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in Patients with Severe Coronavirus Disease 2019. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 604100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lv, F.; He, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zu, J.; Henry, L.; Wang, J.; Yeo, Y.H.; Ji, F.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on liver disease-related mortality rates in the United States. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vázquez-Medina, M.U.; Cerda-Reyes, E.; Galeana-Pavón, A.; López-Luna, C.E.; Ramírez-Portillo, P.M.; Ibañez-Cervantes, G.; Torres-Vázquez, J.; Vargas-De-León, C. Interaction of metabolic dysfunction-associated fatty liver disease and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease with advanced fibrosis in the death and intubation of patients hospitalized with coronavirus disease 2019. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 2000–2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.J.; Zheng, K.I.; Wang, X.B.; Sun, Q.F.; Pan, K.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Ma, H.L.; Chen, Y.P.; George, J.; Zheng, M.H. Metabolic-associated fatty liver disease is associated with severity of COVID-19. Liver Int. 2020, 40, 2160–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahamid, M.; Nseir, W.; Khoury, T.; Mahamid, B.; Nubania, A.; Sub-Laban, K.; Schifter, J.; Mari, A.; Sbeit, W.; Goldin, E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with COVID-19 severity independently of metabolic syndrome: A retrospective case-control study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 33, 1578–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tignanelli, C.J.; Bramante, C.T.; Dutta, N.; Tamariz, L.; Usher, M.G.; Ikramuddin, S. Metabolic surgery may protect against admission for COVID-19 in persons with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Surg. Obes. Relat. Dis. 2021, 17, 1780–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forlano, R.; Mullish, B.H.; Mukherjee, S.K.; Nathwani, R.; Harlow, C.; Crook, P.; Judge, R.; Soubieres, A.; Middleton, P.; Daunt, A.; et al. In-hospital mortality is associated with inflammatory response in NAFLD patients admitted for COVID-19. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0240400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nath, P.; Kumar, R.; Mallick, B.; Das, S.; Anand, A.; Panigrahi, S.C.; Duseja, A.; Acharya, S.K.; Chawla, Y.K.; Praharaj, D.L. Effect of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) on COVID-19: A Single-Center Study of 3983 Patients with Review of Literature. Cureus 2022, 14, e26683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Mendez, I.; Aquino-Matus, J.; Gall, S.M.; Prieto-Nava, J.D.; Juarez-Hernandez, E.; Uribe, M.; Castro-Narro, G. Association of liver steatosis and fibrosis with clinical outcomes in patients with SARS-CoV-2 infection (COVID-19). Ann. Hepatol. 2021, 20, 100271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Tian, A.; Zhu, H.; Chen, L.; Wen, J.; Liu, W.; Chen, P. Mendelian Randomization Analysis Reveals No Causal Relationship between Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Severe COVID-19. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 20, 1553–1560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, K.; Kusminski, C.M.; Scherer, P.E. Adipose tissue remodeling and obesity. J. Clin. Invest. 2011, 121, 2094–2101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macías-Rodríguez, R.U.; Solís-Ortega, A.A.; Ornelas-Arroyo, V.J.; Ruiz-Margáin, A.; González-Huezo, M.S.; Urdiales-Morán, N.A.; Román-Calleja, B.M.; Mayorquín-Aguilar, J.M.; González-Regueiro, J.A.; Campos-Murguía, A.; et al. Prognostic performance of an index based on lactic dehydrogenase and transaminases for patients with liver steatosis and COVID-19. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022, 28, 5444–5456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterling, R.K.; Lissen, E.; Clumeck, N.; Sola, R.; Correa, M.C.; Montaner, J.; Sulkowski, M.; Torriani, F.J.; Dieterich, D.T.; Thomas, D.L.; et al. Development of a simple noninvasive index to predict significant fibrosis in patients with HIV/HCV coinfection. Hepatology 2006, 43, 1317–1325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crudele, L.; Novielli, F.; Petruzzelli, S.; Battaglia, S.; Giuliano, A.F.M.; Melodia, R.; Morano, C.M.; Dell’Aquila, P.; Moretti, R.; Castorani, L.; et al. Liver Fibrosis Indices Predict the Severity of SARS-CoV-2 Infection. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 5369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madan, K.; Rastogi, R.; Bhargava, R.; Dagar, V.; Singla, V.; Sahu, A.; Singh, P.; Garg, P.; Aggarwal, B.; Singh, R.K. Is Fatty Liver Associated with Increased Mortality and Morbidity in Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Pneumonia? J. Clin. Exp. Hepatol. 2022, 12, 1320–1327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.W.; Jeon, J.H.; Moon, J.S.; Kim, M.K. High Fibrosis-4 Index Is Related with Worse Clinical Outcome in Patients with Coronavirus Disease 2019 and Diabetes Mellitus: A Multicenter Observational Study. Endocrinol. Metab. 2021, 36, 800–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elfeki, M.A.; Robles, J.; Akhtar, Z.; Ullah, F.; Ganapathiraju, I.; Tran, C.; Inman, C.; Collin, S.M.; Rosa, R. Impact of Fibrosis-4 Index Prior to COVID-19 on Outcomes in Patients at Risk of Non-alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2022, 67, 3333–3339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, R.; Zhu, L.; Wang, J.; Liu, J.; Xue, R.; Xue, L.; Liu, L.; Li, C.; Zhao, H.; Cheng, J.; et al. Risk of severe illness of COVID-19 patients with NAFLD and increased NAFLD fibrosis scores. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2021, 35, e23880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iavarone, M.; D’Ambrosio, R.; Soria, A.; Triolo, M.; Pugliese, N.; Del Poggio, P.; Perricone, G.; Massironi, S.; Spinetti, A.; Buscarini, E.; et al. High rates of 30-day mortality in patients with cirrhosis and COVID-19. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 1063–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OMS. WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard. Available online: https://covid19.who.int/ (accessed on 27 January 2023).
- Bhimraj, A.; Morgan, R.L.; Shumaker, A.H.; Baden, L.; Cheng, V.C.C.; Edwards, K.M.; Gallagher, J.C.; Gandhi, R.T.; Muller, W.J.; Nakamura, M.M.; et al. Infectious Diseases Society of America Guidelines on the Treatment and Management of Patients with COVID-19. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2022, ciac724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Laar, S.A.; de Boer, M.G.J.; Gombert-Handoko, K.B.; Guchelaar, H.J.; Zwaveling, J.; LUMC-COVID-19 Research Group. Liver and kidney function in patients with COVID-19 treated with remdesivir. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 2021, 87, 4450–4454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zampino, R.; Mele, F.; Florio, L.L.; Bertolino, L.; Andini, R.; Galdo, M.; De Rosa, R.; Corcione, A.; Durante-Mangoni, E. Liver injury in remdesivir-treated COVID-19 patients. Hepatol. Int. 2020, 14, 881–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carothers, C.; Birrer, K.; Vo, M. Acetylcysteine for the Treatment of Suspected Remdesivir-Associated Acute Liver Failure in COVID-19: A Case Series. Pharmacotherapy 2020, 40, 1166–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed-Khan, M.A.; Matar, G.; Coombes, K.; Moin, K.; Joseph, B.M.; Funk, C.M. Remdesivir-Associated Acute Liver Failure in a COVID-19 Patient: A Case Report and Literature Review. Cureus 2023, 15, e34221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, K.; Gausman, V.; Poles, M.; Popov, V. Acute Liver Failure Secondary to Remdesivir in the Treatment of COVID-19. ACG Case Rep. J. 2022, 9, e00866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LiverTox: Clinical and Research Information on Drug-Induced Liver Injury. Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases. 2012. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK547852/ (accessed on 10 May 2023).
- Wang, Y.; Lin, Z.; Liu, Z.; Harris, S.; Kelly, R.; Zhang, J.; Ge, W.; Chen, M.; Borlak, J.; Tong, W. A unifying ontology to integrate histological and clinical observations for drug-induced liver injury. Am. J. Pathol. 2013, 182, 1180–1187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Businesswire. Available online: https://www.businesswire.com/news/home/20200420005795/en/University-Hospitals-Expands-Use-of-TempTraq%C2%AE-System-Wide-to-Support-Frontline-Care-Workers-in-the-Fight-Against-COVID-19 (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- Best, J. Apple Watch. Available online: https://www.zdnet.com/article/apple-watch-fitbit-data-can-find-covid-19-infections-days-before-symptoms-show-up/ (accessed on 8 April 2023).
- Serviddio, G.; Villani, R.; Stallone, G.; Scioscia, G.; Foschino-Barbaro, M.P.; Lacedonia, D. Tocilizumab and liver injury in patients with COVID-19. Therap. Adv. Gastroenterol. 2020, 13, 1756284820959183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Kumar, P.; Dungdung, A.; Kumar Gupta, A.; Anurag, A.; Kumar, A. Pattern of liver function and clinical profile in COVID-19: A cross-sectional study of 91 patients. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 1951–1954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, L.; Gualtieri, P.; Pivari, F.; Soldati, L.; Attinà, A.; Cinelli, G.; Leggeri, C.; Caparello, G.; Barrea, L.; Scerbo, F.; et al. Eating habits and lifestyle changes during COVID-19 lockdown: An Italian survey. J. Transl. Med. 2020, 18, 229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deschasaux-Tanguy, M.; Druesne-Pecollo, N.; Esseddik, Y.; de Edelenyi, F.S.; Allès, B.; Andreeva, V.A.; Baudry, J.; Charreire, H.; Deschamps, V.; Egnell, M.; et al. Diet and physical activity during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) lockdown (March–May 2020): Results from the French NutriNet-Santé cohort study. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2021, 113, 924–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, E.; Boyland, E.; Chisholm, A.; Harrold, J.; Maloney, N.G.; Marty, L.; Mead, B.R.; Noonan, R.; Hardman, C.A. Obesity, eating behavior and physical activity during COVID-19 lockdown: A study of UK adults. Appetite 2021, 156, 104853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mascaró, C.M.; Bouzas, C.; Montemayor, S.; García, S.; Mateos, D.; Casares, M.; Gómez, C.; Ugarriza, L.; Borràs, P.A.; Martínez, J.A.; et al. Impact of Physical Activity Differences Due to COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Parameters in Adults with Metabolic Syndrome. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Policarpo, S.; Machado, M.V.; Cortez-Pinto, H. Telemedicine as a tool for dietary intervention in NAFLD-HIV patients during the COVID-19 lockdown: A randomized controlled trial. Clin. Nutr. ESPEN 2021, 43, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motz, V.; Faust, A.; Dahmus, J.; Stern, B.; Soriano, C.; Stine, J.G. Utilization of a Directly Supervised Telehealth-Based Exercise Training Program in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis: Feasibility Study. JMIR Form. Res. 2021, 5, e30239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Hou, Z.; Liu, J.; Gu, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, Z.; Ji, J.; Diao, S.; Qiu, Y.; Zou, S.; et al. Safety and immunogenicity of COVID-19 vaccination in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (CHESS2101): A multicenter study. J. Hepatol. 2021, 75, 439–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, K.S.; Lam, L.K.; Hui, R.W.H.; Mao, X.; Zhang, R.R.; Chan, K.H.; Hung, I.F.; Seto, W.K.; Yuen, M.F. Effect of moderate-to-severe hepatic steatosis on neutralising antibody response among BNT162b2 and CoronaVac recipients. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2022, 28, 553–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Guarino, M.; Cossiga, V.; Cutolo, F.M.; Attanasio, M.R.; Lieto, R.; Morisco, F. COVID-19 and Fatty Liver Disorders. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134316
Guarino M, Cossiga V, Cutolo FM, Attanasio MR, Lieto R, Morisco F. COVID-19 and Fatty Liver Disorders. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(13):4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134316
Chicago/Turabian StyleGuarino, Maria, Valentina Cossiga, Francesco Maria Cutolo, Maria Rosaria Attanasio, Raffaele Lieto, and Filomena Morisco. 2023. "COVID-19 and Fatty Liver Disorders" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 13: 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134316
APA StyleGuarino, M., Cossiga, V., Cutolo, F. M., Attanasio, M. R., Lieto, R., & Morisco, F. (2023). COVID-19 and Fatty Liver Disorders. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(13), 4316. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12134316







