Intrinsic Effects of Exposome in Atopic Dermatitis: Genomics, Epigenomics and Regulatory Layers
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Intrinsic Exposome of AD Overview
3. Genetics of Atopic Dermatitis
4. Epigenetics of Atopic Dermatitis
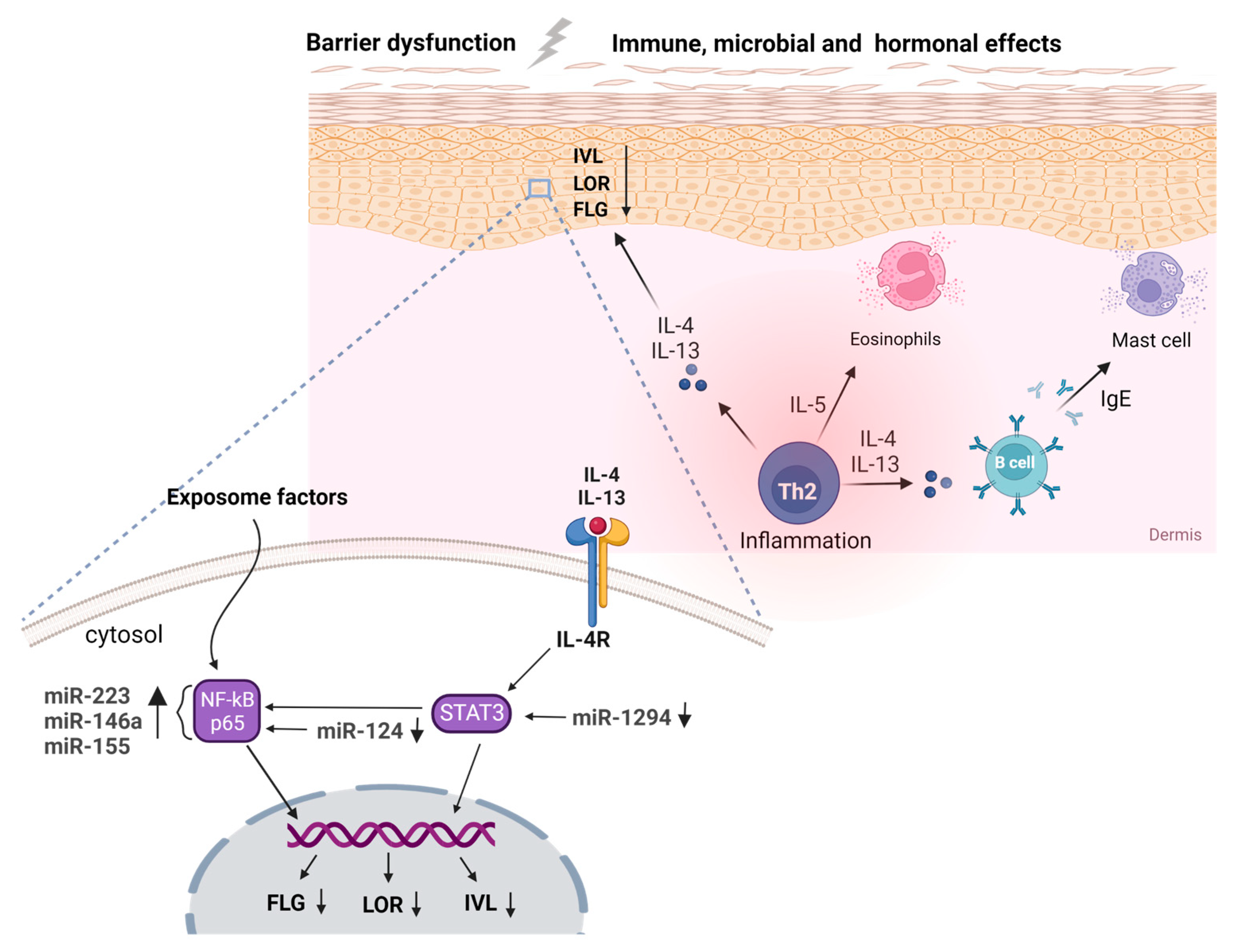
5. Noncoding RNAs in Atopic Dermatitis
6. Regulatory Interactome in Atopic Dermatitis
7. Immune Dysregulation in Atopic Dermatitis
8. Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis
9. Microbial Dysbiosis in Atopic Dermatitis
10. Hormonal Effects and Pregnancy-Maternal Exposome
10.1. Hormonal Effects
10.2. Pregnancy-Maternal Exposome
11. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Nutten, S. Atopic Dermatitis: Global Epidemiology and Risk Factors. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2015, 66, 8–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grafanaki, K.; Bania, A.; Kaliatsi, E.G.; Vryzaki, E.; Vasilopoulos, Y.; Georgiou, S. The Imprint of Exposome on the Development of Atopic Dermatitis across the Lifespan: A Narrative Review. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mastraftsi, S.; Vrioni, G.; Bakakis, M.; Nicolaidou, E.; Rigopoulos, D.; Stratigos, A.J.; Gregoriou, S. Atopic Dermatitis: Striving for Reliable Biomarkers. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facheris, P.; Da Rosa, J.C.; Pagan, A.D.; Angelov, M.; Del Duca, E.; Rabinowitz, G.; Gómez-Arias, P.J.; Rothenberg-Lausell, C.; Estrada, Y.D.; Bose, S.; et al. Age of Onset Defines Two Distinct Profiles of Atopic Dermatitis in Adults. Allergy 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smieszek, S.P.; Welsh, S.; Xiao, C.; Wang, J.; Polymeropoulos, C.; Birznieks, G.; Polymeropoulos, M.H. Correlation of Age-of-Onset of Atopic Dermatitis with Filaggrin Loss-of-Function Variant Status. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ried, J.S.; Li, J.; Zuo, X.B.; Zheng, X.D.; Yin, X.Y.; Sun, L.D.; McAleer, M.A.; O’Regan, G.M.; Fahy, C.M.; Campbell, L.E. Multi-Ancestry Genome-Wide Association Study of 21,000 Cases and 95,000 Controls Identifies New Risk Loci for Atopic Dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2015, 47, 1449–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allis, C.D.; Jenuwein, T. The Molecular Hallmarks of Epigenetic Control. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2016, 17, 487–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Liu, C. Coding or Noncoding, the Converging Concepts of RNAs. Front. Genet. 2019, 10, 496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoshida, T.; Beck, L.A.; De Benedetto, A. Skin Barrier Defects in Atopic Dermatitis: From Old Idea to New Opportunity. Allergol. Int. 2022, 71, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elmose, C.; Thomsen, S.F. Twin Studies of Atopic Dermatitis: Interpretations and Applications in the Filaggrin Era. J. Allergy 2015, 2015, 902359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venter, J.C.; Adams, M.D.; Myers, E.W.; Li, P.W.; Mural, R.J.; Sutton, G.G.; Smith, H.O.; Yandell, M.; Evans, C.A.; Holt, R.A.; et al. The Sequence of the Human Genome. Science 2001, 291, 1304–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huffaker, M.F.; Kanchan, K.; Bahnson, H.T.; Ruczinski, I.; Shankar, G.; Leung, D.Y.M.; Baloh, C.; Du Toit, G.; Lack, G.; Nepom, G.T.; et al. Epidermal Differentiation Complex Genetic Variation in Atopic Dermatitis and Peanut Allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1137–1142.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dębińska, A.; Danielewicz, H.; Sozańska, B. Genetic Variants in Epidermal Differentiation Complex Genes as Predictive Biomarkers for Atopic Eczema, Allergic Sensitization, and Eczema-Associated Asthma in a 6-Year Follow-Up Case–Control Study in Children. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baurecht, H.; Hotze, M.; Brand, S.; Büning, C.; Cormican, P.; Corvin, A.; Ellinghaus, D.; Ellinghaus, E.; Esparza-Gordillo, J.; Fölster-Holst, R.; et al. Genome-Wide Comparative Analysis of Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis Gives Insight into Opposing Genetic Mechanisms. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2015, 96, 104–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, J.-Q.; Chan-Yeung, M.; Becker, A.B.; Dimich-Ward, H.; Ferguson, A.C.; Manfreda, J.; Watson, W.T.A.; Sandford, A.J. Genetic Variants of the IL13 and IL4 Genes and Atopic Diseases in At-Risk Children. Genes Immun. 2003, 4, 385–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.; Kim, J.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kang, M.-J.; Park, Y.M.; Park, M.J.; Rhee, E.-S.; Ahn, K.; Kim, K.W.; Shin, Y.H.; et al. Association of IL13 Genetic Polymorphisms with Atopic Dermatitis. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 125, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hummelshoj, T.; Bodtger, U.; Datta, P.; Malling, H.J.; Oturai, A.; Poulsen, L.K.; Ryder, L.P.; Sorensen, P.S.; Svejgaard, E.; Svejgaard, A. Association between an Interleukin-13 Promoter Polymorphism and Atopy. Eur. J. Immunogenet. 2003, 30, 355–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brandt, E.B. Th2 Cytokines and Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Cell Immunol. 2011, 2, 110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cork, M.J.; Robinson, D.A.; Vasilopoulos, Y.; Ferguson, A.; Moustafa, M.; MacGowan, A.; Duff, G.W.; Ward, S.J.; Tazi-Ahnini, R. New Perspectives on Epidermal Barrier Dysfunction in Atopic Dermatitis: Gene–Environment Interactions. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 3–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McAleer, M.A.; Pohler, E.; Smith, F.J.D.; Wilson, N.J.; Cole, C.; MacGowan, S.; Koetsier, J.L.; Godsel, L.M.; Harmon, R.M.; Gruber, R.; et al. Severe Dermatitis, Multiple Allergies, and Metabolic Wasting Syndrome Caused by a Novel Mutation in the N-Terminal Plakin Domain of Desmoplakin. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2015, 136, 1268–1276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kountikov, E.I.; Poe, J.C.; Maclver, N.J.; Rathmell, J.C.; Tedder, T.F. A Spontaneous Deletion within the Desmoglein 3 Extracellular Domain of Mice Results in Hypomorphic Protein Expression, Immunodeficiency, and a Wasting Disease Phenotype. Am. J. Pathol. 2015, 185, 617–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oji, V.; Eckl, K.-M.; Aufenvenne, K.; Nätebus, M.; Tarinski, T.; Ackermann, K.; Seller, N.; Metze, D.; Nürnberg, G.; Fölster-Holst, R.; et al. Loss of Corneodesmosin Leads to Severe Skin Barrier Defect, Pruritus, and Atopy: Unraveling the Peeling Skin Disease. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2010, 87, 274–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, W.; Guo, X.; Zhou, S.; Zheng, H. Genetic Polymorphisms in Serine Protease Inhibitor Kazal-Type 5 and Risk of Atopic Dermatitis. Medicine 2020, 99, e21256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sliz, E.; Huilaja, L.; Pasanen, A.; Laisk, T.; Reimann, E.; Mägi, R.; Hannula-Jouppi, K.; Peltonen, S.; Salmi, T.; Koulu, L.; et al. Uniting Biobank Resources Reveals Novel Genetic Pathways Modulating Susceptibility for Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 1105–1112.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paternoster, L.; Standl, M.; Chen, C.-M.; Ramasamy, A.; Bønnelykke, K.; Duijts, L.; Ferreira, M.A.; Alves, A.C.; Thyssen, J.P.; Albrecht, E.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Genome-Wide Association Studies Identifies Three New Risk Loci for Atopic Dermatitis. Nat. Genet. 2012, 44, 187–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, N.; Koido, M.; Suzuki, A.; Otomo, N.; Suetsugu, H.; Kochi, Y.; Tomizuka, K.; Momozawa, Y.; Kamatani, Y.; Ikegawa, S.; et al. Eight Novel Susceptibility Loci and Putative Causal Variants in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 1293–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.A.; Vonk, J.M.; Baurecht, H.; Marenholz, I.; Tian, C.; Hoffman, J.D.; Helmer, Q.; Tillander, A.; Ullemar, V.; van Dongen, J.; et al. Shared Genetic Origin of Asthma, Hay Fever and Eczema Elucidates Allergic Disease Biology. Nat. Genet. 2017, 49, 1752–1757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.A.R.; Vonk, J.M.; Baurecht, H.; Marenholz, I.; Tian, C.; Hoffman, J.D.; Helmer, Q.; Tillander, A.; Ullemar, V.; Lu, Y.; et al. Eleven Loci with New Reproducible Genetic Associations with Allergic Disease Risk. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 691–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, J.; Kim, D.; Lee, S.; Jung, J.; Joo, J.W.J.; Jang, W. Integrative Transcriptome-Wide Analysis of Atopic Dermatitis for Drug Repositioning. Commun. Biol. 2022, 5, 615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simard, M.; Madore, A.-M.; Girard, S.; Waserman, S.; Duan, Q.; Subbarao, P.; Sears, M.R.; Moraes, T.J.; Becker, A.B.; Turvey, S.E.; et al. Polygenic Risk Score for Atopic Dermatitis in the Canadian Population. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 147, 406–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.; Jang, H.; Kim, M.; Hong, J.Y.; Kim, Y.H.; Sohn, M.H.; Park, S.-C.; Won, S.; Kim, K.W. Predicting Allergic Diseases in Children Using Genome-Wide Association Study (GWAS) Data and Family History. World Allergy Organ. J. 2021, 14, 100539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arehart, C.H.; Daya, M.; Campbell, M.; Boorgula, M.P.; Rafaels, N.; Chavan, S.; David, G.; Hanifin, J.; Slifka, M.K.; Gallo, R.L.; et al. Polygenic Prediction of Atopic Dermatitis Improves with Atopic Training and Filaggrin Factors. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Duca, E.; Renert-Yuval, Y.; Pavel, A.B.; Mikhaylov, D.; Wu, J.; Lefferdink, R.; Fang, M.; Sheth, A.; Blumstein, A.; Facheris, P.; et al. Proteomic Characterization of Atopic Dermatitis Blood from Infancy to Adulthood. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 2023, 88, 1083–1093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peled, A.; Sarig, O.; Sun, G.; Samuelov, L.; Ma, C.A.; Zhang, Y.; Dimaggio, T.; Nelson, C.G.; Stone, K.D.; Freeman, A.F.; et al. Loss-of-Function Mutations in Caspase Recruitment Domain-Containing Protein 14 (CARD14) Are Associated with a Severe Variant of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 173–181.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heo, W.I.; Park, K.Y.; Lee, M.-K.; Kim, J.H.; Moon, N.J.; Seo, S.J. Association of CDKAL1 Polymorphisms with Early-Onset Atopic Dermatitis in Koreans. Ann. Dermatol. 2018, 30, 276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pigors, M.; Common, J.E.A.; Wong, X.F.C.C.; Malik, S.; Scott, C.A.; Tabarra, N.; Liany, H.; Liu, J.; Limviphuvadh, V.; Maurer-Stroh, S.; et al. Exome Sequencing and Rare Variant Analysis Reveals Multiple Filaggrin Mutations in Bangladeshi Families with Atopic Eczema and Additional Risk Genes. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 2674–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, W.; Xu, W.; Xia, L.; Xie, D.; Wang, L.; Guo, Z.; Cheng, Y.; Liu, Y.; Li, W. Family-Based Whole Exome Sequencing of Atopic Dermatitis Complicated with Cataracts. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 59446–59454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heo, W.I.; Park, K.Y.; Jin, T.; Lee, M.-K.; Kim, M.; Choi, E.H.; Kim, H.-S.; Bae, J.M.; Moon, N.J.; Seo, S.J. Identification of Novel Candidate Variants Including COL6A6 Polymorphisms in Early-Onset Atopic Dermatitis Using Whole-Exome Sequencing. BMC Med. Genet. 2017, 18, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wjst, M. Exome Variants Associated with Asthma and Allergy. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 21028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mikhaylova, A.V.; McHugh, C.P.; Polfus, L.M.; Raffield, L.M.; Boorgula, M.P.; Blackwell, T.W.; Brody, J.A.; Broome, J.; Chami, N.; Chen, M.-H.; et al. Whole-Genome Sequencing in Diverse Subjects Identifies Genetic Correlates of Leukocyte Traits: The NHLBI TOPMed Program. Am. J. Hum. Genet. 2021, 108, 1836–1851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grosche, S.; Marenholz, I.; Esparza-Gordillo, J.; Arnau-Soler, A.; Pairo-Castineira, E.; Rüschendorf, F.; Ahluwalia, T.S.; Almqvist, C.; Arnold, A.; Baurecht, H.; et al. Rare Variant Analysis in Eczema Identifies Exonic Variants in DUSP1, NOTCH4 and SLC9A4. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berna, R.; Mitra, N.; Hoffstad, O.; Wubbenhorst, B.; Nathanson, K.L.; Margolis, D.J. Using a Machine Learning Approach to Identify Low-Frequency and Rare FLG Alleles Associated with Remission of Atopic Dermatitis. JID Innov. 2021, 1, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berna, R.; Mitra, N.; Hoffstad, O.; Wubbenhorst, B.; Nathanson, K.L.; Margolis, D.J. Uncommon Variants in FLG2 and TCHHL1 Are Associated with Remission of Atopic Dermatitis in a Large Longitudinal US Cohort. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2022, 314, 953–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Antonatos, C.; Grafanaki, K.; Asmenoudi, P.; Xiropotamos, P.; Nani, P.; Georgakilas, G.K.; Georgiou, S.; Vasilopoulos, Y. Contribution of the Environment, Epigenetic Mechanisms and Non-Coding RNAs in Psoriasis. Biomedicines 2022, 10, 1934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Jang, A.; Seo, S.J.; Myung, S.C. Epigenetic Regulation of Filaggrin Gene Expression in Human Epidermal Keratinocytes. Ann. Dermatol. 2020, 32, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziyab, A.H.; Karmaus, W.; Holloway, J.W.; Zhang, H.; Ewart, S.; Arshad, S.H. DNA Methylation of the Filaggrin Gene Adds to the Risk of Eczema Associated with Loss-of-Function Variants. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2013, 27, e420–e423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Noh, Y.-H.; Lee, J.; Seo, S.J.; Myung, S.C. Promoter DNA Methylation Contributes to Human β -Defensin-1 Deficiency in Atopic Dermatitis. Anim. Cells Syst. 2018, 22, 172–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thürmann, L.; Grützmann, K.; Klös, M.; Bieg, M.; Winter, M.; Polte, T.; Bauer, T.; Schick, M.; Bewerunge-Hudler, M.; Röder, S.; et al. Early-Onset Childhood Atopic Dermatitis Is Related to NLRP2 Repression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2018, 141, 1482–1485.e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Zhou, B.; Zhao, M.; Tang, J.; Lu, Q. Promoter Demethylation Contributes to TSLP Overexpression in Skin Lesions of Patients with Atopic Dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2014, 39, 48–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, Y.; Yu, B.; Chen, J.; Wu, H.; Xu, Y.; Yang, B.; Lu, Q. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Epigenetically Upregulates Fc Receptor γ Subunit–Related Receptors on Antigen-Presenting Cells and Induces TH2/TH17 Polarization through Dectin-2. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 144, 1025–1035.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barton, S.J.; Ngo, S.; Costello, P.; Garratt, E.; El-Heis, S.; Antoun, E.; Clarke-Harris, R.; Murray, R.; Bhatt, T.; Burdge, G.; et al. DNA Methylation of Th2 Lineage Determination Genes at Birth Is Associated with Allergic Outcomes in Childhood. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 1599–1608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rodríguez, E.; Baurecht, H.; Wahn, A.F.; Kretschmer, A.; Hotze, M.; Zeilinger, S.; Klopp, N.; Illig, T.; Schramm, K.; Prokisch, H.; et al. An Integrated Epigenetic and Transcriptomic Analysis Reveals Distinct Tissue-Specific Patterns of DNA Methylation Associated with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 1873–1883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, J.; Park, S.-G.; Bae, J.-B.; Choi, J.; Lyu, J.-M.; Park, S.H.; Kim, H.S.; Kim, Y.-J.; Kim, S.; Kim, T.-Y. The Characteristics of Genome-Wide DNA Methylation in Naïve CD4+ T Cells of Patients with Psoriasis or Atopic Dermatitis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2012, 422, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boorgula, M.P.; Taub, M.A.; Rafaels, N.; Daya, M.; Campbell, M.; Chavan, S.; Shetty, A.; Cheadle, C.; Barkataki, S.; Fan, J.; et al. Replicated Methylation Changes Associated with Eczema Herpeticum and Allergic Response. Clin. Epigenet. 2019, 11, 122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olisova, O.Y.; Kochergin, N.G.; Kayumova, L.N.; Zavarykina, T.M.; Dmitriev, A.A.; Asanov, A.Y. Skin DNA Methylation Profile in Atopic Dermatitis Patients: A Case–Control Study. Exp. Dermatol. 2020, 29, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acevedo, N.; Benfeitas, R.; Katayama, S.; Bruhn, S.; Andersson, A.; Wikberg, G.; Lundeberg, L.; Lindvall, J.M.; Greco, D.; Kere, J.; et al. Epigenetic Alterations in Skin Homing CD4+CLA+ T Cells of Atopic Dermatitis Patients. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 18020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristensen, L.S.; Andersen, M.S.; Stagsted, L.V.W.; Ebbesen, K.K.; Hansen, T.B.; Kjems, J. The Biogenesis, Biology and Characterization of Circular RNAs. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2019, 20, 675–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moldovan, L.I.; Tsoi, L.C.; Ranjitha, U.; Hager, H.; Weidinger, S.; Gudjonsson, J.E.; Kjems, J.; Kristensen, L.S. Characterization of Circular RNA Transcriptomes in Psoriasis and Atopic Dermatitis Reveals Disease-specific Expression Profiles. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1187–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Fu, J.; Han, X.; Zhang, C.; Xia, L.; Zhu, R.; Huang, S.; Xiao, W.; Yu, H.; Gao, Y.; et al. Hsa_circ_0004287 Inhibits Macrophage-Mediated Inflammation in an N6-Methyladenosine–Dependent Manner in Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 149, 2021–2033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Qi, R.; Xu, J.; Di, Z.; Zheng, H.; Huo, W.; Zhang, L.; Chen, H.; Gao, X. Profiling of Serum and Urinary MicroRNAs in Children with Atopic Dermatitis. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e115448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jia, H.-Z.; Liu, S.-L.; Zou, Y.-F.; Chen, X.-F.; Yu, L.; Wan, J.; Zhang, H.-Y.; Chen, Q.; Xiong, Y.; Yu, B.; et al. MicroRNA-223 Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis by Affecting Histamine-N-Methyltransferase. Cell Mol. Biol. 2018, 64, 103–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasuike, R.; Tamagawa-Mineoka, R.; Nakamura, N.; Masuda, K.; Katoh, N. Plasma MiR223 Is a Possible Biomarker for Diagnosing Patients with Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Allergol. Int. 2021, 70, 153–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taïbi, F.; Metzinger-Le Meuth, V.; Massy, Z.A.; Metzinger, L. MiR-223: An Inflammatory OncomiR Enters the Cardiovascular Field. Biochim. Biophys. Acta-Mol. Basis Dis. 2014, 1842, 1001–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Béres, N.J.; Szabó, D.; Kocsis, D.; Szűcs, D.; Kiss, Z.; Müller, K.E.; Lendvai, G.; Kiss, A.; Arató, A.; Sziksz, E.; et al. Role of Altered Expression of MiR-146a, MiR-155, and MiR-122 in Pediatric Patients with Inflammatory Bowel Disease. Inflamm. Bowel Dis. 2016, 22, 327–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Timis, T.; Orasan, R. Understanding Psoriasis: Role of MiRNAs (Review). Biomed. Rep. 2018, 9, 367–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Xue, H.-B.; Wang, F.; Shu, C.-M.; Zhang, J.-H. MicroRNA-155 May Be Involved in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis by Modulating the Differentiation and Function of T Helper Type 17 (Th17) Cells. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 2015, 181, 142–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, F.; Meng, W.; Ye, S.; Zhang, X.; Mo, X.; Liu, J.; Chen, D.; Lin, Y. MicroRNA-146a as a Potential Regulator Involved in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis. Mol. Med. Rep. 2019, 20, 4645–4653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueta, M.; Nishigaki, H.; Komai, S.; Mizushima, K.; Tamagawa-Mineoka, R.; Naito, Y.; Katoh, N.; Sotozono, C.; Kinoshita, S. Positive Regulation of Innate Immune Response by MiRNA-Let-7a-5p. Front. Genet. 2023, 13, 1025539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nousbeck, J.; McAleer, M.A.; Hurault, G.; Kenny, E.; Harte, K.; Kezic, S.; Tanaka, R.J.; Irvine, A.D. MicroRNA Analysis of Childhood Atopic Dermatitis Reveals a Role for MiR-451a. Br. J. Dermatol. 2021, 184, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.-F.; Zhang, L.-J.; Zhang, J.; Dou, X.; Shao, Y.; Jia, X.-J.; Zhang, W.; Yu, B. MiR-151a Is Involved in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis by Regulating Interleukin-12 Receptor Β2. Exp. Dermatol. 2018, 27, 427–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, B.; Xia, Y.; Lv, J.; Wang, W.; Xuan, Z.; Chen, C.; Jiang, T.; Fang, L.; Wang, L.; Li, Z.; et al. MiR-151a-3p-Rich Small Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Gastric Cancer Accelerate Liver Metastasis via Initiating a Hepatic Stemness-Enhancing Niche. Oncogene 2021, 40, 6180–6194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daugaard, I.; Sanders, K.J.; Idica, A.; Vittayarukskul, K.; Hamdorf, M.; Krog, J.D.; Chow, R.; Jury, D.; Hansen, L.L.; Hager, H.; et al. MiR-151a Induces Partial EMT by Regulating E-Cadherin in NSCLC Cells. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, e366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, S.; Li, J.; Zhang, G.; Wang, Q.; Wu, C.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, H.; Sun, P.; Xiang, R.; Yang, S. Exosomal MiR-451a Functions as a Tumor Suppressor in Hepatocellular Carcinoma by Targeting LPIN1. Cell Physiol. Biochem. 2019, 53, 19–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, H.; Wu, S. MiR-451: A Novel Biomarker and Potential Therapeutic Target for Cancer. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2019, 12, 11069–11082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, L.; Li, M.; Gao, Z.; Ren, H.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Cai, Q.; Jiang, L.; Ren, X.; Yu, Q.; et al. Possible Role of Hsa-MiR-194-5p, via Regulation of HS3ST2, in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis in Children. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2019, 29, 603–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yen, Y.-T.; Yang, J.-C.; Chang, J.-B.; Tsai, S.-C. Down-Regulation of MiR-194-5p for Predicting Metastasis in Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 23, 325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rebane, A.; Runnel, T.; Aab, A.; Maslovskaja, J.; Rückert, B.; Zimmermann, M.; Plaas, M.; Kärner, J.; Treis, A.; Pihlap, M.; et al. MicroRNA-146a Alleviates Chronic Skin Inflammation in Atopic Dermatitis through Suppression of Innate Immune Responses in Keratinocytes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 836–847.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreras-Badosa, G.; Maslovskaja, J.; Vaher, H.; Pajusaar, L.; Annilo, T.; Lättekivi, F.; Hübenthal, M.; Rodriguez, E.; Weidinger, S.; Kingo, K.; et al. MiRNA Expression Profiles of the Perilesional Skin of Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis Patients Are Highly Similar. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 22645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vennegaard, M.T.; Bonefeld, C.M.; Hagedorn, P.H.; Bangsgaard, N.; Løvendorf, M.B.; Ødum, N.; Woetmann, A.; Geisler, C.; Skov, L. Allergic Contact Dermatitis Induces Upregulation of Identical MicroRNAs in Humans and Mice. Contact Dermat. 2012, 67, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, J.; Zhou, B.; Wei, Z.; Luo, Y. IL-32 Promotes the Occurrence of Atopic Dermatitis by Activating the JAK1/MicroRNA-155 Axis. J. Transl. Med. 2022, 20, 207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonkoly, E.; Janson, P.; Majuri, M.-L.; Savinko, T.; Fyhrquist, N.; Eidsmo, L.; Xu, N.; Meisgen, F.; Wei, T.; Bradley, M.; et al. MiR-155 Is Overexpressed in Patients with Atopic Dermatitis and Modulates T-Cell Proliferative Responses by Targeting Cytotoxic T Lymphocyte–Associated Antigen 4. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 581–589.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Y.; Qin, K.; Li, L.; Liu, H.; Xie, Z.; Zeng, K. Identification of Immunological Biomarkers of Atopic Dermatitis by Integrated Analysis to Determine Molecular Targets for Diagnosis and Therapy. Int. J. Gen. Med. 2021, 14, 8193–8209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, S.; Chen, M.; Yin, M.; Feng, H. Identifying the Potential Therapeutic Targets for Atopic Dermatitis Through the Immune Infiltration Analysis and Construction of a CeRNA Network. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 437–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.M.; Xiao, Y.J.; Min, Z.S.; Tan, C. Identification and Interaction Analysis of Key Genes and MicroRNAs in Atopic Dermatitis by Bioinformatics Analysis. Clin. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 44, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Acharjee, A.; Gribaleva, E.; Bano, S.; Gkoutos, G.V. Multi-Omics-Based Identification of Atopic Dermatitis Target Genes and Their Potential Associations with Metabolites and MiRNAs. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2021, 13, 13697–13709. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Zeng, B.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; Huang, P.; Pan, Y. MicroRNA-124 Alleviates Chronic Skin Inflammation in Atopic Eczema via Suppressing Innate Immune Responses in Keratinocytes. Cell Immunol. 2017, 319, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, C.; Jiang, Y.; Yang, C.; Qian, Q.; Mao, J.; Sun, D.; Zhu, T. MiR-1294 Suppresses ROS-Dependent Inflammatory Response in Atopic Dermatitis via Restraining STAT3/NF-ΚB Pathway. Cell Immunol. 2022, 371, 104452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Xiao, X.; Xu, Z. MiR-1294 Inhibits the Progression of Breast Cancer via Regulating ERK Signaling. Bull. Cancer 2022, 109, 999–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, S.-C.; Alalaiwe, A.; Lin, Z.-C.; Lin, Y.-C.; Aljuffali, I.A.; Fang, J.-Y. Anti-Inflammatory MicroRNAs for Treating Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nica, A.C.; Dermitzakis, E.T. Expression Quantitative Trait Loci: Present and Future. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2013, 368, 20120362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sobczyk, M.K.; Richardson, T.G.; Zuber, V.; Min, J.L.; Gaunt, T.R.; Paternoster, L. Triangulating Molecular Evidence to Prioritize Candidate Causal Genes at Established Atopic Dermatitis Loci. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 141, 2620–2629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Puan, K.J.; Andiappan, A.K.; Lee, B.; Westerlaken, G.H.A.; Haase, D.; Melchiotti, R.; Li, Z.; Yusof, N.; Lum, J.; et al. A Functional SNP Associated with Atopic Dermatitis Controls Cell Type-Specific Methylation of the VSTM1 Gene Locus. Genome Med. 2017, 9, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyons, J.J.; Milner, J.D. Primary Atopic Disorders. J. Exp. Med. 2018, 215, 1009–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaseghi-Shanjani, M.; Smith, K.L.; Sara, R.J.; Modi, B.P.; Branch, A.; Sharma, M.; Lu, H.Y.; James, E.L.; Hildebrand, K.J.; Biggs, C.M.; et al. Inborn Errors of Immunity Manifesting as Atopic Disorders. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 148, 1130–1139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turvey, S.E.; Bonilla, F.A.; Junker, A.K. Primary Immunodeficiency Diseases: A Practical Guide for Clinicians. Postgrad. Med. J. 2009, 85, 660–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Bel, K.L.; Ragotte, R.J.; Saferali, A.; Lee, S.; Vercauteren, S.M.; Mostafavi, S.A.; Schreiber, R.A.; Prendiville, J.S.; Phang, M.S.; Halparin, J.; et al. JAK1 Gain-of-Function Causes an Autosomal Dominant Immune Dysregulatory and Hypereosinophilic Syndrome. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2017, 139, 2016–2020.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyoshi, M.K.; Larson, R.P.; Ziegler, S.F.; Geha, R.S. Mechanical Injury Polarizes Skin Dendritic Cells to Elicit a TH2 Response by Inducing Cutaneous Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin Expression. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010, 126, 976–984.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cevikbas, F.; Steinhoff, M. IL-33: A Novel Danger Signal System in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 1326–1329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hvid, M.; Vestergaard, C.; Kemp, K.; Christensen, G.B.; Deleuran, B.; Deleuran, M. IL-25 in Atopic Dermatitis: A Possible Link between Inflammation and Skin Barrier Dysfunction? J. Investig. Dermatol. 2011, 131, 150–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Konishi, H.; Tsutsui, H.; Murakami, T.; Yumikura-Futatsugi, S.; Yamanaka, K.; Tanaka, M.; Iwakura, Y.; Suzuki, N.; Takeda, K.; Akira, S.; et al. IL-18 Contributes to the Spontaneous Development of Atopic Dermatitis-like Inflammatory Skin Lesion Independently of IgE/Stat6 under Specific Pathogen-Free Conditions. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2002, 99, 11340–11345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halling, A.-S.; Rinnov, M.R.; Ruge, I.F.; Gerner, T.; Ravn, N.H.; Knudgaard, M.H.; Trautner, S.; Loft, N.; Skov, L.; Thomsen, S.F.; et al. Skin TARC/CCL17 Increase Precedes the Development of Childhood Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2022, 151, 1550–1557.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulshof, L.; Overbeek, S.A.; Wyllie, A.L.; Chu, M.L.J.N.; Bogaert, D.; de Jager, W.; Knippels, L.M.J.; Sanders, E.A.M.; van Aalderen, W.M.C.; Garssen, J.; et al. Exploring Immune Development in Infants with Moderate to Severe Atopic Dermatitis. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klonowska, J.; Gleń, J.; Nowicki, R.; Trzeciak, M. New Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis—New Therapeutic Targets. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Neis, M.; Peters, B.; Dreuw, A.; Wenzel, J.; Bieber, T.; Mauch, C.; Krieg, T.; Stanzel, S.; Heinrich, P.; Merk, H. Enhanced Expression Levels of IL-31 Correlate with IL-4 and IL-13 in Atopic and Allergic Contact Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006, 118, 930–937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamata, M.; Tada, Y. A Literature Review of Real-World Effectiveness and Safety of Dupilumab for Atopic Dermatitis. JID Innov. 2021, 1, 100042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, L.; Zhang, H.; Chan, L.S. The Involvement of the JAK-STAT Signaling Pathway in Chronic Inflammatory Skin Disease Atopic Dermatitis. JAK-STAT 2013, 2, e24137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsoi, L.C.; Rodriguez, E.; Degenhardt, F.; Baurecht, H.; Wehkamp, U.; Volks, N.; Szymczak, S.; Swindell, W.R.; Sarkar, M.K.; Raja, K.; et al. Atopic Dermatitis Is an IL-13–Dominant Disease with Greater Molecular Heterogeneity Compared to Psoriasis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2019, 139, 1480–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, W.; Yao, L.; Wang, S.; Jia, Z.; Wu, P.; Li, L.; Wei, P.; Wang, X.; et al. MicroRNA-155-5p Is a Key Regulator of Allergic Inflammation, Modulating the Epithelial Barrier by Targeting PKIα. Cell Death Dis. 2019, 10, 884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.-P.; Nguyen, G.H.; Jin, H.-Z. MicroRNA-143 Inhibits IL-13-Induced Dysregulation of the Epidermal Barrier-Related Proteins in Skin Keratinocytes via Targeting to IL-13Rα1. Mol. Cell Biochem. 2016, 416, 63–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Ponandai-Srinivasan, S.; Nandakumar, K.S.; Fabre, S.; Xu Landén, N.; Mavon, A.; Khmaladze, I. Targeting microRNA for Improved Skin Health. Health Sci. Rep. 2021, 4, e374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sääf, A.; Kockum, I.; Wahlgren, C.; Xu, N.; Sonkoly, E.; Ståhle, M.; Nordenskjöld, M.; Bradley, M.; Pivarcsi, A. Are BIC (MiR-155) Polymorphisms Associated with Eczema Susceptibility? Acta Derm. Venereol. 2013, 93, 366–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuji, G.; Ito, T.; Chiba, T.; Mitoma, C.; Nakahara, T.; Uchi, H.; Furue, M. The Role of the OVOL1–OVOL2 Axis in Normal and Diseased Human Skin. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2018, 90, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitamura, Y.; Nunomura, S.; Nanri, Y.; Ogawa, M.; Yoshihara, T.; Masuoka, M.; Tsuji, G.; Nakahara, T.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Conway, S.J.; et al. The IL-13/Periostin/IL-24 Pathway Causes Epidermal Barrier Dysfunction in Allergic Skin Inflammation. Allergy 2018, 73, 1881–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.R. Transgenic Mice Which Overproduce Th2 Cytokines Develop Spontaneous Atopic Dermatitis and Asthma. Int. Immunol. 2004, 16, 1155–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nomura, I.; Goleva, E.; Howell, M.D.; Hamid, Q.A.; Ong, P.Y.; Hall, C.F.; Darst, M.A.; Gao, B.; Boguniewicz, M.; Travers, J.B.; et al. Cytokine Milieu of Atopic Dermatitis, as Compared to Psoriasis, Skin Prevents Induction of Innate Immune Response Genes. J. Immunol. 2003, 171, 3262–3269. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Wilkie, H.; Das, M.; Timilshina, M.; Bainter, W.; Woods, B.; Daya, M.; Boorgula, M.P.; Mathias, R.A.; Lai, P.; et al. The IL-4Rα Q576R Polymorphism Is Associated with Increased Severity of Atopic Dermatitis and Exaggerates Allergic Skin Inflammation in Mice. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2023, 151, 1296–1306.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeBord, D.G.; Carreón, T.; Lentz, T.J.; Middendorf, P.J.; Hoover, M.D.; Schulte, P.A. Use of the “Exposome” in the Practice of Epidemiology: A Primer on -Omic Technologies. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2016, 184, 302–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Conti, P.; Kempuraj, D.; Di Gioacchino, M.; Boucher, W.; Letourneau, R.; Kandere, K.; Barbacane, R.C.; Reale, M.; Felaco, M.; Frydas, S.; et al. Interleukin-6 and Mast Cells. Allergy Asthma Proc. 2002, 23, 331–335. [Google Scholar]
- Niyonsaba, F.; Ushio, H.; Hara, M.; Yokoi, H.; Tominaga, M.; Takamori, K.; Kajiwara, N.; Saito, H.; Nagaoka, I.; Ogawa, H.; et al. Antimicrobial Peptides Human β-Defensins and Cathelicidin LL-37 Induce the Secretion of a Pruritogenic Cytokine IL-31 by Human Mast Cells. J. Immunol. 2010, 184, 3526–3534. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koumaki, D.; Gregoriou, S.; Evangelou, G.; Krasagakis, K. Pruritogenic Mediators and New Antipruritic Drugs in Atopic Dermatitis. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 2091. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novak, N.; Peng, W.M.; Bieber, T.; Akdis, C. FcεRI Stimulation Promotes the Differentiation of Histamine Receptor 1-Expressing Inflammatory Macrophages. Allergy 2013, 68, 454–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miake, S.; Tsuji, G.; Takemura, M.; Hashimoto-Hachiya, A.; Vu, Y.H.; Furue, M.; Nakahara, T. IL-4 Augments IL-31/IL-31 Receptor Alpha Interaction Leading to Enhanced Ccl 17 and Ccl 22 Production in Dendritic Cells: Implications for Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujita, H.; Shemer, A.; Suárez-Fariñas, M.; Johnson-Huang, L.M.; Tintle, S.; Cardinale, I.; Fuentes-Duculan, J.; Novitskaya, I.; Carucci, J.A.; Krueger, J.G.; et al. Lesional Dendritic Cells in Patients with Chronic Atopic Dermatitis and Psoriasis Exhibit Parallel Ability to Activate T-Cell Subsets. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2011, 128, 574–582.e12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candi, E.; Schmidt, R.; Melino, G. The Cornified Envelope: A Model of Cell Death in the Skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2005, 6, 328–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oh, I.Y.; Albea, D.M.; Goodwin, Z.A.; Quiggle, A.M.; Baker, B.P.; Guggisberg, A.M.; Geahlen, J.H.; Kroner, G.M.; de Guzman Strong, C. Regulation of the Dynamic Chromatin Architecture of the Epidermal Differentiation Complex Is Mediated by a C-Jun/AP-1-Modulated Enhancer. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 134, 2371–2380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hitomi, K. Transglutaminases in Skin Epidermis. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2005, 15, 313–319. [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez, E.; Baurecht, H.; Herberich, E.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Brown, S.J.; Cordell, H.J.; Irvine, A.D.; Weidinger, S. Meta-Analysis of Filaggrin Polymorphisms in Eczema and Asthma: Robust Risk Factors in Atopic Disease. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009, 123, 1361–1370.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Margolis, D.J.; Mitra, N.; Berna, R.; Hoffstad, O.; Kim, B.S.; Yan, A.; Zaenglein, A.L.; Fuxench, Z.C.; Quiggle, A.M.; de Guzman Strong, C.; et al. Associating Filaggrin Copy Number Variation and Atopic Dermatitis in African-Americans: Challenges and Opportunities. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2020, 98, 58–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, S.J.; Kroboth, K.; Sandilands, A.; Campbell, L.E.; Pohler, E.; Kezic, S.; Cordell, H.J.; McLean, W.H.I.; Irvine, A.D. Intragenic Copy Number Variation within Filaggrin Contributes to the Risk of Atopic Dermatitis with a Dose-Dependent Effect. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2012, 132, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thyssen, J.P.; Kezic, S. Causes of Epidermal Filaggrin Reduction and Their Role in the Pathogenesis of Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 134, 792–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hachem, J.-P.; Wagberg, F.; Schmuth, M.; Crumrine, D.; Lissens, W.; Jayakumar, A.; Houben, E.; Mauro, T.M.; Leonardsson, G.; Brattsand, M.; et al. Serine Protease Activity and Residual LEKTI Expression Determine Phenotype in Netherton Syndrome. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2006, 126, 1609–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, N.; Saijoh, K.; Jayakumar, A.; Clayman, G.L.; Tohyama, M.; Suga, Y.; Mizuno, Y.; Tsukamoto, K.; Taniuchi, K.; Takehara, K.; et al. Correlation between SPINK5 Gene Mutations and Clinical Manifestations in Netherton Syndrome Patients. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 1148–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komatsu, N.; Saijoh, K.; Kuk, C.; Liu, A.C.; Khan, S.; Shirasaki, F.; Takehara, K.; Diamandis, E.P. Human Tissue Kallikrein Expression in the Stratum Corneum and Serum of Atopic Dermatitis Patients. Exp. Dermatol. 2007, 16, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Voegeli, R.; Rawlings, A.V.; Breternitz, M.; Doppler, S.; Schreier, T.; Fluhr, J.W. Increased Stratum Corneum Serine Protease Activity in Acute Eczematous Atopic Skin. Br. J. Dermatol. 2009, 161, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Has, C. Peeling Skin Disorders: A Paradigm for Skin Desquamation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1689–1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weidinger, S.; Baurecht, H.; Wagenpfeil, S.; Henderson, J.; Novak, N.; Sandilands, A.; Chen, H.; Rodriguez, E.; O’Regan, G.M.; Watson, R.; et al. Analysis of the Individual and Aggregate Genetic Contributions of Previously Identified Serine Peptidase Inhibitor Kazal Type 5 (SPINK5), Kallikrein-Related Peptidase 7 (KLK7), and Filaggrin (FLG) Polymorphisms to Eczema Risk. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008, 122, 560–568.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meyer-Hoffert, U. Reddish, Scaly, and Itchy: How Proteases and Their Inhibitors Contribute to Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Arch. Immunol. Ther. Exp. 2009, 57, 345–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Just, A.C.; Whyatt, R.M.; Perzanowski, M.S.; Calafat, A.M.; Perera, F.P.; Goldstein, I.F.; Chen, Q.; Rundle, A.G.; Miller, R.L. Prenatal Exposure to Butylbenzyl Phthalate and Early Eczema in an Urban Cohort. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1475–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kathuria, P.; Silverberg, J.I. Association of Pollution and Climate with Atopic Eczema in US Children. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2016, 27, 478–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Niwa, Y.; Sumi, H.; Kawahira, K.; Terashima, T.; Nakamura, T.; Akamatsu, H. Protein Oxidative Damage in the Stratum Corneum: Evidence for a Link between Environmental Oxidants and the Changing Prevalence and Nature of Atopic Dermatitis in Japan. Br. J. Dermatol. 2003, 149, 248–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boxberger, M.; Cenizo, V.; Cassir, N.; La Scola, B. Challenges in Exploring and Manipulating the Human Skin Microbiome. Microbiome 2021, 9, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mousa, W.K.; Chehadeh, F.; Husband, S. Microbial Dysbiosis in the Gut Drives Systemic Autoimmune Diseases. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 5936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Meulen, T.; Harmsen, H.; Bootsma, H.; Spijkervet, F.; Kroese, F.; Vissink, A. The Microbiome-Systemic Diseases Connection. Oral Dis. 2016, 22, 719–734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Kim, H. Microbiome of the Skin and Gut in Atopic Dermatitis (AD): Understanding the Pathophysiology and Finding Novel Management Strategies. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alam, M.J.; Xie, L.; Yap, Y.-A.; Marques, F.Z.; Robert, R. Manipulating Microbiota to Treat Atopic Dermatitis: Functions and Therapies. Pathogens 2022, 11, 642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beheshti, R.; Halstead, S.; McKeone, D.; Hicks, S.D. Understanding Immunological Origins of Atopic Dermatitis through Multi-omic Analysis. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. 2022, 33, e13817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Traisaeng, S.; Herr, D.R.; Kao, H.-J.; Chuang, T.-H.; Huang, C.-M. A Derivative of Butyric Acid, the Fermentation Metabolite of Staphylococcus Epidermidis, Inhibits the Growth of a Staphylococcus aureus Strain Isolated from Atopic Dermatitis Patients. Toxins 2019, 11, 311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lamas, A.; Regal, P.; Vázquez, B.; Cepeda, A.; Franco, C.M. Short Chain Fatty Acids Commonly Produced by Gut Microbiota Influence Salmonella enterica Motility, Biofilm Formation, and Gene Expression. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chriett, S.; Dąbek, A.; Wojtala, M.; Vidal, H.; Balcerczyk, A.; Pirola, L. Prominent Action of Butyrate over β-Hydroxybutyrate as Histone Deacetylase Inhibitor, Transcriptional Modulator and Anti-Inflammatory Molecule. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zouboulis, C.C. The Skin as an Endocrine Organ. Dermatoendocrinology 2009, 1, 250–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Passeron, T.; Zouboulis, C.C.; Tan, J.; Andersen, M.L.; Katta, R.; Lyu, X.; Aguilar, L.; Kerob, D.; Morita, A.; Krutmann, J.; et al. Adult Skin Acute Stress Responses to Short-Term Environmental and Internal Aggression from Exposome Factors. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 35, 1963–1975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tai, P.; Wang, J.; Jin, H.; Song, X.; Yan, J.; Kang, Y.; Zhao, L.; An, X.; Du, X.; Chen, X.; et al. Induction of Regulatory T Cells by Physiological Level Estrogen. J. Cell Physiol. 2008, 214, 456–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuramoto, T.; Yokoe, M.; Tanaka, D.; Yuri, A.; Nishitani, A.; Higuchi, Y.; Yoshimi, K.; Tanaka, M.; Kuwamura, M.; Hiai, H.; et al. Atopic Dermatitis-like Skin Lesions with IgE Hyperproduction and Pruritus in KFRS4/Kyo Rats. J. Dermatol. Sci. 2015, 80, 116–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kemmett, D.; Tidman, M.J. The Influence of the Menstrual Cycle and Pregnancy on Atopic Dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 1991, 125, 59–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gratton, R.; Del Vecchio, C.; Zupin, L.; Crovella, S. Unraveling the Role of Sex Hormones on Keratinocyte Functions in Human Inflammatory Skin Diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 3132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farage, M.A.; Neill, S.; MacLean, A.B. Physiological Changes Associated with the Menstrual Cycle. Obstet. Gynecol. Surv. 2009, 64, 58–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanda, N.; Hoashi, T.; Saeki, H. The Roles of Sex Hormones in the Course of Atopic Dermatitis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hannen, R.F.; Michael, A.E.; Jaulim, A.; Bhogal, R.; Burrin, J.M.; Philpott, M.P. Steroid Synthesis by Primary Human Keratinocytes; Implications for Skin Disease. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2011, 404, 62–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chinnappan, M.; Prestwood, C.A.; Edwards, M.; Artami, M.; Thompson, B.M.; Eckert, K.M.; Vale, G.; Zouboulis, C.C.; McDonald, J.G.; et al. Interleukins 4 and 13 Drive Lipid Abnormalities in Skin Cells through Regulation of Sex Steroid Hormone Synthesis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2021, 118, e2100749118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaitsu, M.; Narita, S.-I.; Lambert, K.C.; Grady, J.J.; Estes, D.M.; Curran, E.M.; Brooks, E.G.; Watson, C.S.; Goldblum, R.M.; Midoro-Horiuti, T. Estradiol Activates Mast Cells via a Non-Genomic Estrogen Receptor-α and Calcium Influx. Mol. Immunol. 2007, 44, 1977–1985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narita, S.; Goldblum, R.M.; Watson, C.S.; Brooks, E.G.; Estes, D.M.; Curran, E.M.; Midoro-Horiuti, T. Environmental Estrogens Induce Mast Cell Degranulation and Enhance IgE-Mediated Release of Allergic Mediators. Environ. Health Perspect. 2007, 115, 48–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, V.L.; Gershwin, L.J. Progesterone and Environmental Tobacco Smoke Act Synergistically to Exacerbate the Development of Allergic Asthma in a Mouse Model. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2007, 37, 276–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozma, N.; Halasz, M.; Polgar, B.; Poehlmann, T.G.; Markert, U.R.; Palkovics, T.; Keszei, M.; Par, G.; Kiss, K.; Szeberenyi, J.; et al. Progesterone-Induced Blocking Factor Activates STAT6 via Binding to a Novel IL-4 Receptor. J. Immunol. 2006, 176, 819–826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, T.K.; Heiman, J.R.; Demas, G.E. Sexual Activity Modulates Shifts in TH1/TH2 Cytokine Profile across the Menstrual Cycle: An Observational Study. Fertil. Steril. 2015, 104, 1513–1521.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hughes, G.C. Progesterone and Autoimmune Disease. Autoimmun. Rev. 2012, 11, A502–A514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hall, O.J.; Limjunyawong, N.; Vermillion, M.S.; Robinson, D.P.; Wohlgemuth, N.; Pekosz, A.; Mitzner, W.; Klein, S.L. Progesterone-Based Therapy Protects against Influenza by Promoting Lung Repair and Recovery in Females. PLoS Pathog. 2016, 12, e1005840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Foer, D.; Buchheit, K.M. Presentation and Natural History of Progestogen Hypersensitivity. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2019, 122, 156–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trigunaite, A.; Dimo, J.; Jørgensen, T.N. Suppressive Effects of Androgens on the Immune System. Cell Immunol. 2015, 294, 87–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuseini, H.; Yung, J.A.; Cephus, J.Y.; Zhang, J.; Goleniewska, K.; Polosukhin, V.V.; Peebles, R.S.; Newcomb, D.C. Testosterone Decreases House Dust Mite–Induced Type 2 and IL-17A–Mediated Airway Inflammation. J. Immunol. 2018, 201, 1843–1854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solano, M.E.; Sander, V.A.; Ho, H.; Motta, A.B.; Arck, P.C. Systemic Inflammation, Cellular Influx and up-Regulation of Ovarian VCAM-1 Expression in a Mouse Model of Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS). J. Reprod. Immunol. 2011, 92, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasperska-Zajac, A.; Brzoza, Z.; Rogala, B. Dehydroepiandrosterone and Dehydroepiandrosterone Sulphate in Atopic Allergy and Chronic Urticaria. Inflammation 2008, 31, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opstad, P.K. The Hypothalamo-Pituitary Regulation of Androgen Secretion in Young Men after Prolonged Physical Stress Combined with Energy and Sleep Deprivation. Acta Endocrinol. 1992, 127, 231–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Q.; Ma, J.; Guo, K. MiR-223 Enhances the Neuroprotection of Estradiol against Oxidative Stress Injury by Inhibiting the FOXO3/TXNIP Axis. Neurochem. Res. 2022, 47, 1865–1877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olivieri, F.; Ahtiainen, M.; Lazzarini, R.; Pöllänen, E.; Capri, M.; Lorenzi, M.; Fulgenzi, G.; Albertini, M.C.; Salvioli, S.; Alen, M.J.; et al. Hormone Replacement Therapy Enhances IGF-1 Signaling in Skeletal Muscle by Diminishing MiR-182 and MiR-223 Expressions: A Study on Postmenopausal Monozygotic Twin Pairs. Aging Cell 2014, 13, 850–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinohara, M.; Matsumoto, K. Fetal Tobacco Smoke Exposure in the Third Trimester of Pregnancy Is Associated with Atopic Eczema/Dermatitis Syndrome in Infancy. Pediatr. Allergy Immunol. Pulmonol. 2017, 30, 155–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, I.-J.; Chen, S.-L.; Lu, T.-P.; Chuang, E.Y.; Chen, P.-C. Prenatal Smoke Exposure, DNA Methylation, and Childhood Atopic Dermatitis. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2013, 43, 535–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-I.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Kim, H.-C.; Kim, H.-B.; Kim, J.-H.; Lim, H.; Park, M.J.; Cho, H.-J.; Yoon, J.; et al. Prenatal PM2.5 Exposure and Vitamin D–Associated Early Persistent Atopic Dermatitis via Placental Methylation. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2020, 125, 665–673.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, H.-J.; Sheen, Y.H.; Kang, M.-J.; Lee, S.-H.; Lee, S.-Y.; Yoon, J.; Jung, S.; Lee, S.H.; Kim, Y.-H.; Yang, S.-I.; et al. Prenatal 25-Hydroxyvitamin D Deficiency Affects Development of Atopic Dermatitis via DNA Methylation. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 1215–1218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.B.; Kang, M.J.; Lee, S.Y.; Shin, Y.J.; Hong, S.J. Prenatal Maternal Anxiety Promotes Atopic Dermatitis in Offspring via Placental DNA Methylation Changes. Asian Pacific J. Allergy Immunol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leroux, C.; Chervet, M.L.; German, J.B. Perspective: Milk MicroRNAs as Important Players in Infant Physiology and Development. Adv. Nutr. 2021, 12, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hicks, S.D.; Beheshti, R.; Chandran, D.; Warren, K.; Confair, A. Infant Consumption of MicroRNA MiR-375 in Human Milk Lipids Is Associated with Protection from Atopy. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2022, 116, 1654–1662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dissanayake, E.; Inoue, Y.; Ochiai, S.; Eguchi, A.; Nakano, T.; Yamaide, F.; Hasegawa, S.; Kojima, H.; Suzuki, H.; Mori, C.; et al. Hsa-Mir-144-3p Expression Is Increased in Umbilical Cord Serum of Infants with Atopic Dermatitis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2019, 143, 447–450.e11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herberth, G.; Bauer, M.; Gasch, M.; Hinz, D.; Röder, S.; Olek, S.; Kohajda, T.; Rolle-Kampczyk, U.; von Bergen, M.; Sack, U.; et al. Maternal and Cord Blood MiR-223 Expression Associates with Prenatal Tobacco Smoke Exposure and Low Regulatory T-Cell Numbers. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2014, 133, 543–550.e4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rappaport, S.M.; Li, H.; Grigoryan, H.; Funk, W.E.; Williams, E.R. Adductomics: Characterizing Exposures to Reactive Electrophiles. Toxicol. Lett. 2012, 213, 83–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parker-Lalomio, M.; McCann, K.; Piorkowski, J.; Freels, S.; Persky, V.W. Prenatal Exposure to Polychlorinated Biphenyls and Asthma, Eczema/Hay Fever, and Frequent Ear Infections. J. Asthma 2018, 55, 1105–1115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mogensen, U.B.; Grandjean, P.; Nielsen, F.; Weihe, P.; Budtz-Jørgensen, E. Breastfeeding as an Exposure Pathway for Perfluorinated Alkylates. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 10466–10473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Huang, R.; Hua, L.; Guo, Y.; Huang, L.; Zhao, Y.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J. Prenatal Exposure to Perfluoroalkyl and Polyfluoroalkyl Substances and Childhood Atopic Dermatitis: A Prospective Birth Cohort Study. Environ. Health 2018, 17, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huoman, J.; Martínez-Enguita, D.; Olsson, E.; Ernerudh, J.; Nilsson, L.; Duchén, K.; Gustafsson, M.; Jenmalm, M.C. Combined Prenatal Lactobacillus reuteri and ω-3 Supplementation Synergistically Modulates DNA Methylation in Neonatal T Helper Cells. Clin. Epigenet. 2021, 13, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Dijk, S.J.; Zhou, J.; Peters, T.J.; Buckley, M.; Sutcliffe, B.; Oytam, Y.; Gibson, R.A.; McPhee, A.; Yelland, L.N.; Makrides, M.; et al. Effect of Prenatal DHA Supplementation on the Infant Epigenome: Results from a Randomized Controlled Trial. Clin. Epigenet. 2016, 8, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coppola, S.; Paparo, L.; Chiariotti, L.; Ercolini, D.; Nocerino, R.; de Giovanni di Santa Severina, A.F.; Carucci, L.; De Filippis, F.; Agangi, A.; Napolitano, M.; et al. Effects of the Mediterranean Diet during Pregnancy on the Onset of Allergy in at Risk Children: A Study Protocol of a Multi-Center, Randomized-Controlled, Parallel Groups, Prospective Trial (the PREMEDI Study). Front. Nutr. 2022, 9, 951223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Facheris, P.; Jeffery, J.; Del Duca, E.; Guttman-Yassky, E. The Translational Revolution in Atopic Dermatitis: The Paradigm Shift from Pathogenesis to Treatment. Cell Mol. Immunol. 2023, 20, 448–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Grafanaki, K.; Antonatos, C.; Maniatis, A.; Petropoulou, A.; Vryzaki, E.; Vasilopoulos, Y.; Georgiou, S.; Gregoriou, S. Intrinsic Effects of Exposome in Atopic Dermatitis: Genomics, Epigenomics and Regulatory Layers. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124000
Grafanaki K, Antonatos C, Maniatis A, Petropoulou A, Vryzaki E, Vasilopoulos Y, Georgiou S, Gregoriou S. Intrinsic Effects of Exposome in Atopic Dermatitis: Genomics, Epigenomics and Regulatory Layers. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124000
Chicago/Turabian StyleGrafanaki, Katerina, Charalabos Antonatos, Alexandros Maniatis, Antonia Petropoulou, Eleftheria Vryzaki, Yiannis Vasilopoulos, Sophia Georgiou, and Stamatis Gregoriou. 2023. "Intrinsic Effects of Exposome in Atopic Dermatitis: Genomics, Epigenomics and Regulatory Layers" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124000
APA StyleGrafanaki, K., Antonatos, C., Maniatis, A., Petropoulou, A., Vryzaki, E., Vasilopoulos, Y., Georgiou, S., & Gregoriou, S. (2023). Intrinsic Effects of Exposome in Atopic Dermatitis: Genomics, Epigenomics and Regulatory Layers. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 4000. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12124000







