Prognostic Value of sST2 in Heart Failure
Abstract
:1. Introduction
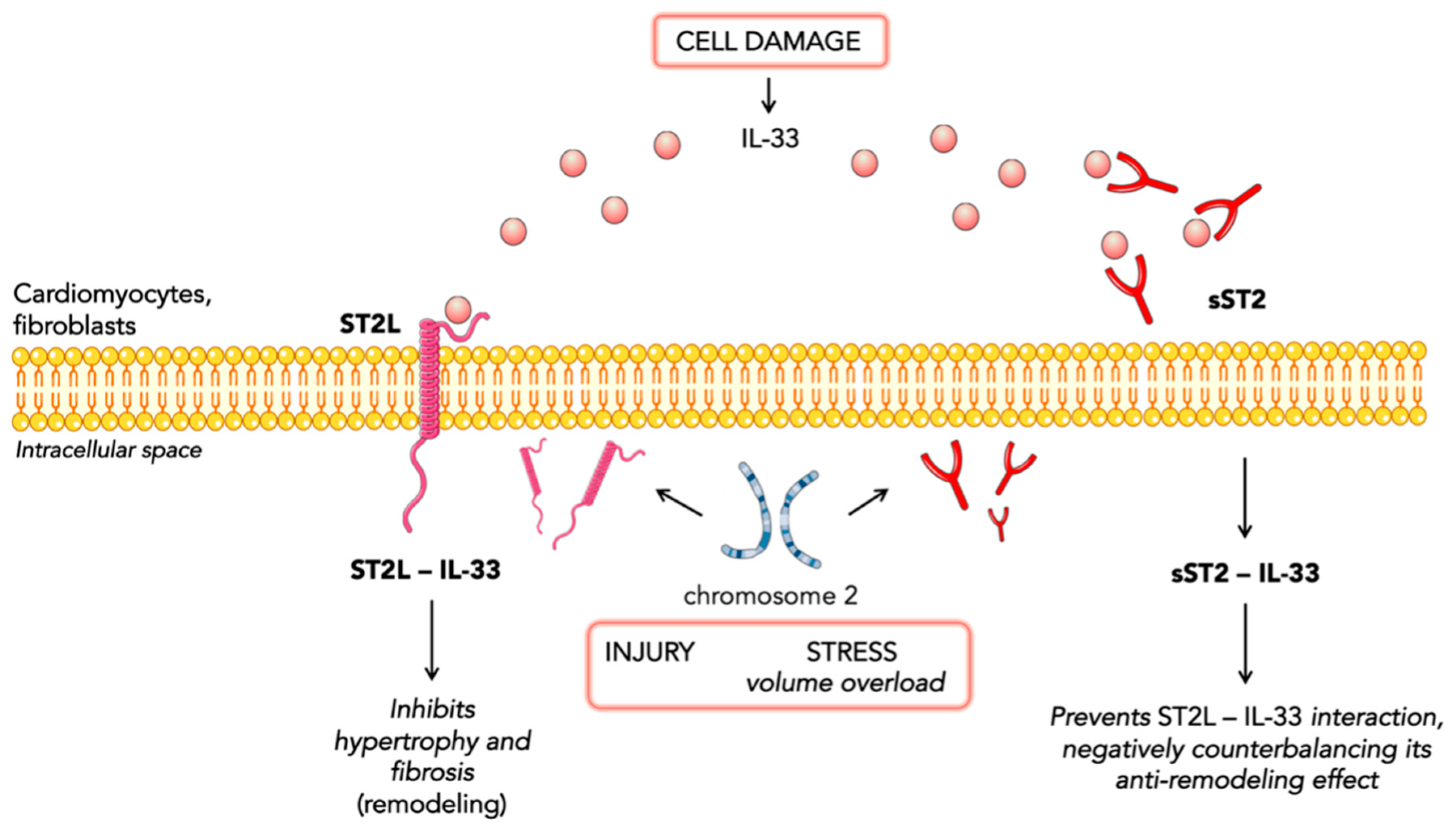
2. ST2 Biology
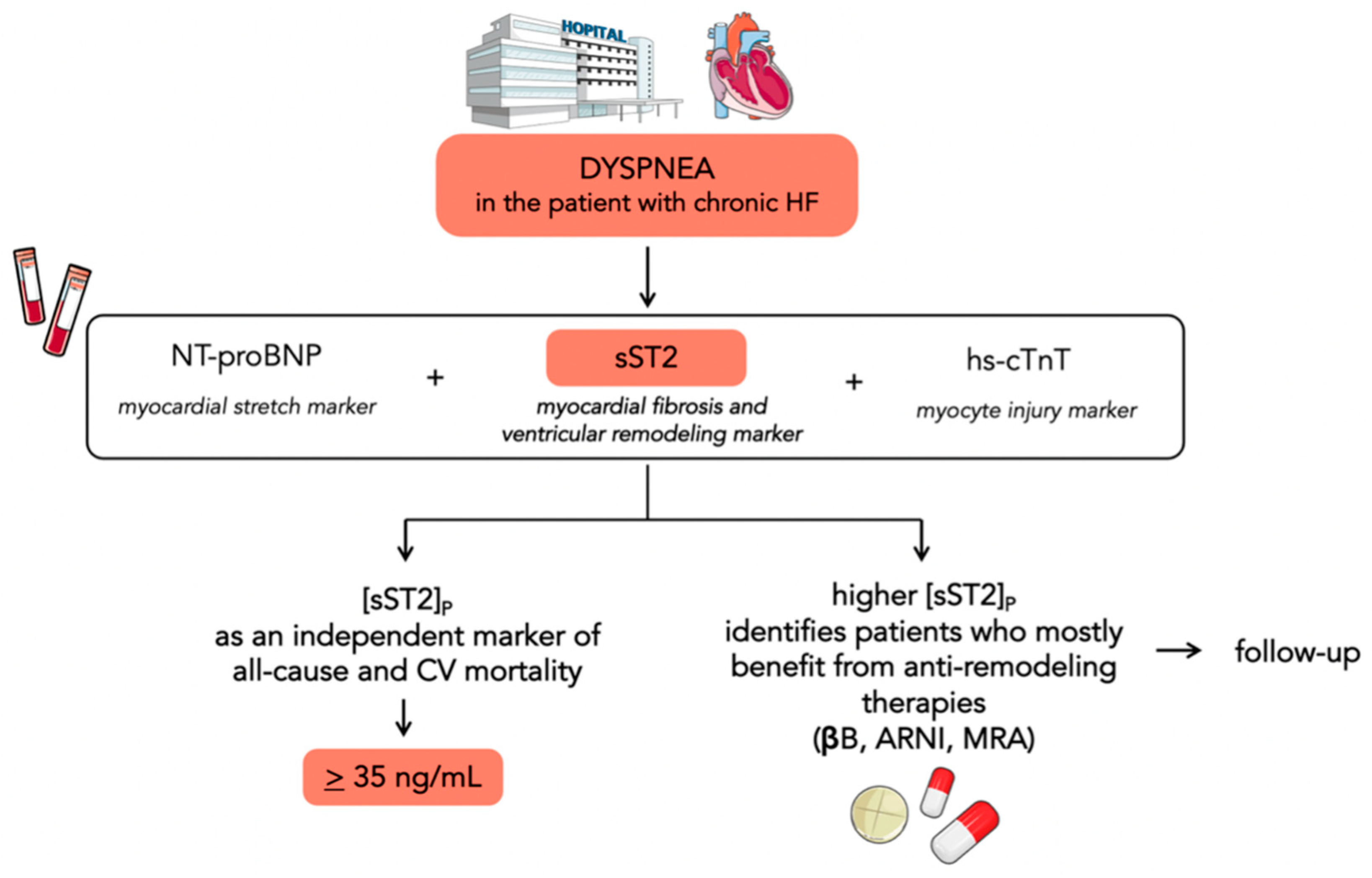
3. Prognostic Value of sST2 in Chronic Heart Failure
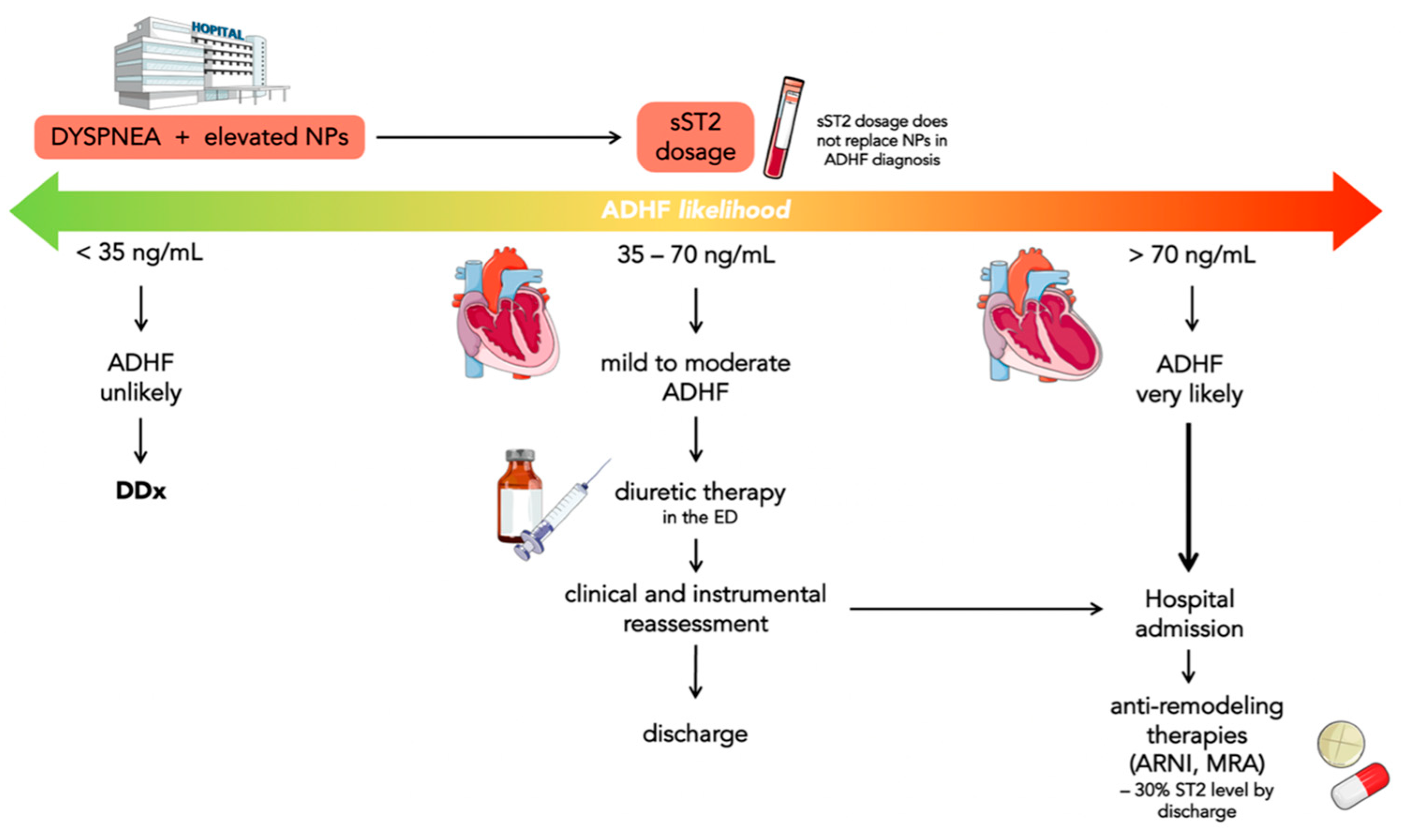
4. Prognostic Value of sST2 in Acute Heart Failure
- sST2 levels <35 ng/mL have been found in less than 10% of ADHF in ED; consequently, ADHF can be reasonably ruled out in these patients;
- sST2 levels between 35 and 70 ng/mL may suggest evaluating the outcome of diuretics efficacy directly in ED and, if there are improvements in symptoms, establish whether patients need hospitalization or not;
- sST2 levels >70 ng/mL indicate patients with a very high risk of ADHF who need hospitalization.
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McDonagh, T.A.; Metra, M.; Adamo, M.; Gardner, R.S.; Baumbach, A.; Böhm, M.; Burri, H.; Butler, J.; Čelutkienė, J.; Chioncel, O.; et al. 2021 ESC Guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur. Heart J. 2021, 42, 3599–3726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schocken, D.D.; Benjamin, E.J.; Fonarow, G.C.; Krumholz, H.M.; Levy, D.; Mensah, G.A.; Narula, J.; Shor, E.S.; Young, J.B.; Hong, Y. American Heart Association Council on Epidemiology and Prevention, American Heart Association Council on Clinical Cardiology, American Heart Association Council on Cardiovascular Nursing, American Heart Association Council on High Blood Pressure Research, Quality of Care and Outcomes Research Interdisciplinary Working Group, & Functional Genomics and Translational Biology Interdisciplinary Working Group. Circulation 2008, 117, 2544–2565. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Chioncel, O.; Lainscak, M.; Seferovic, P.M.; Anker, S.D.; Crespo-Leiro, M.G.; Harjola, V.P.; Ros, E.; Fitó, M.; Estruch, R.; Lapetra, J.; et al. Epidemiology and one-year outcomes in patients with chronic heart failure and preserved, mid-range and reduced ejection fraction: An analysis of the ESC Heart Failure Long-Term Registry. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2017, 19, 1574–1585. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Clerico, A.; Emdin, M. Diagnostic accuracy and prognostic relevance of the measurement of cardiac natriuretic peptides: A review. Clin. Chem. 2004, 50, 33–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Núñez, J.; Núñez, E.; Robles, R.; Bodí, V.; Sanchis, J.; Carratalá, A.; Aparici, M.; Llàcer, A. Prognostic value of brain natriuretic peptide in acute heart failure: Mortality and hospital readmission. Rev. Esp. Cardiol. 2008, 61, 1332–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Mueller, C.; Mirò, O.; Pascual Figal, D.A.; Jacob, J.; Herrero-Puente, P.; Llorens, P.; Wussler, D.; Kozhuharov, N.; et al. Admission high-sensitivity troponin T and NT-proBNP for outcome prediction in acute heart failure. Int. J. Cardiol. 2019, 293, 137–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaggin, H.K.; Szymonifka, J.; Bhardwaj, A.; Belcher, A.; De Berardinis, B.; Motiwala, S.; Wang, T.J.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Head-to-head comparison of serial soluble ST2, growth differentiation factor-15, and highly-sensitive troponin T measurements in patients with chronic heart failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2014, 2, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Felker, G.M.; Anstrom, K.J.; Adams, K.F.; Ezekowitz, J.A.; Fiuzat, M.; Houston-Miller, N.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Mark, D.B.; Piña, I.L.; Passmore, G.; et al. Effect of Natriuretic Peptide-Guided Therapy on Hospitalization or Cardiovascular Mortality in High-Risk Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction: A Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA 2017, 318, 713–720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayes-Genis, A.; Richards, A.M.; Maisel, A.S.; Mueller, C.; Ky, B. Multimarker testing with ST2 in chronic heart failure. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115 (Suppl. S7), 76b–80b. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aimo, A.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Vergaro, G.; Sciarrone, P.; Passino, C.; Emdin, M. Clinical and Prognostic Significance of sST2 in Heart Failure: JACC Review Topic of the Week. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 74, 2193–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mebazaa, A.; Davison, B.; Chioncel, O.; Cohen-Solal, A.; Diaz, R.; Filippatos, G.; Metra, M.; Ponikowski, P.; Sliwa, K.; Voors, A.A.; et al. Safety, tolerability and efficacy of up-titration of guideline-directed medical therapies for acute heart failure (STRONG-HF): A multinational, open-label, randomised, trial. Lancet 2022, 400, 1938–1952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morrow, D.A.; Velazquez, E.J.; DeVore, A.D.; Prescott, M.F.; Duffy, C.I.; Gurmu, Y.; McCague, K.; Rocha, R.; Braunwald, E. Cardiovascular biomarkers in patients with acute decompensated heart failure randomized to sacubitril-valsartan or enalapril in the PIONEER-HF trial. Eur. Heart J. 2019, 40, 3345–3352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bayes-Genis, A.; Aimo, A.; Jhund, P.; Richards, M.; de Boer, R.A.; Arfsten, H.; Fabiani, I.; Lupón, J.; Anker, S.D.; González, A.; et al. Biomarkers in heart failure clinical trials. A review from the Biomarkers Working Group of the Heart Failure Association of the European Society of Cardiology. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2022, 24, 1767–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dale, M.; Nicklin, M.J. Interleukin-1 receptor cluster: Gene organization of IL1R2, IL1R1, IL1RL2 (IL-1Rrp2), IL1RL1 (T1/ST2), and IL18R1 (IL-1Rrp) on human chromosome 2q. Genomics 1999, 57, 177–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergers, G.; Reikerstorfer, A.; Braselmann, S.; Graninger, P.; Busslinger, M. Alternative promoter usage of the Fos-responsive gene Fit-1 generates mRNA isoforms coding for either secreted or membrane-bound proteins related to the IL-1 receptor. EMBO J. 1994, 13, 1176–1188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kakkar, R.; Lee, R.T. The IL-33/ST2 pathway: Therapeutic target and novel biomarker. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2008, 7, 827–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sanada, S.; Hakuno, D.; Higgins, L.J.; Schreiter, E.R.; McKenzie, A.N.; Lee, R.T. IL-33 and ST2 comprise a critical biomechanically induced and cardioprotective signaling system. J. Clin. Investig. 2007, 117, 1538–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Villacorta, H.; Maisel, A.S. Soluble ST2 Testing: A Promising Biomarker in the Management of Heart Failure. Arq. Bras. Cardiol. 2016, 106, 145–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascual-Figal, D.A.; Januzzi, J.L. The biology of ST2: The International ST2 Consensus Panel. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115 (Suppl. S7), 3b–7b. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Y.; Pavey, H.; Wilkinson, I.; Fisk, M. Role of the IL-33/ST2 axis in cardiovascular disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0259026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinberg, E.O.; Shimpo, M.; Hurwitz, S.; Tominaga, S.; Rouleau, J.L.; Lee, R.T. Identification of serum soluble ST2 receptor as a novel heart failure biomarker. Circulation 2003, 107, 721–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ky, B.; French, B.; McCloskey, K.; Rame, J.E.; McIntosh, E.; Shahi, P.; Dries, D.L.; Tang, W.H.; Wu, A.H.; Fang, J.C.; et al. High-sensitivity ST2 for prediction of adverse outcomes in chronic heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2011, 4, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Lupón, J.; de Antonio, M.; Galán, A.; Vila, J.; Zamora, E.; Urrutia, A.; Bayes-Genis, A. Combined use of the novel biomarkers high-sensitivity troponin T and ST2 for heart failure risk stratification vs conventional assessment. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2013, 88, 234–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Emdin, M.; Aimo, A.; Vergaro, G.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Lupón, J.; Latini, R.; Meessen, J.; Anand, I.S.; Cohn, J.N.; Gravning, J.; et al. sST2 Predicts Outcome in Chronic Heart Failure Beyond NT-proBNP and High-Sensitivity Troponin T. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2018, 72, 2309–2320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bayes-Genis, A.; Zamora, E.; de Antonio, M.; Galán, A.; Vila, J.; Urrutia, A.; Díez, C.; Coll, R.; Altimir, S.; Lupón, J. Soluble ST2 serum concentration and renal function in heart failure. J. Card. Fail. 2013, 19, 768–775. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruson, D.; Lepoutre, T.; Ahn, S.A.; Rousseau, M.F. Increased soluble ST2 is a stronger predictor of long-term cardiovascular death than natriuretic peptides in heart failure patients with reduced ejection fraction. Int. J. Cardiol. 2014, 172, e250–e252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergaro, G.; Del Franco, A.; Giannoni, A.; Prontera, C.; Ripoli, A.; Barison, A.; Masci, P.G.; Aquaro, G.D.; Cohen Solal, A.; Padeletti, L.; et al. Galectin-3 and myocardial fibrosis in nonischemic dilated cardiomyopathy. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 184, 96–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayes-Genis, A.; de Antonio, M.; Vila, J.; Peñafiel, J.; Galán, A.; Barallat, J.; Zamora, E.; Urrutia, A.; Lupón, J. Head-to-head comparison of 2 myocardial fibrosis biomarkers for long-term heart failure risk stratification: ST2 versus galectin-3. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2014, 63, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gaggin, H.K.; Motiwala, S.; Bhardwaj, A.; Parks, K.A.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. Soluble concentrations of the interleukin receptor family member ST2 and β-blocker therapy in chronic heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2013, 6, 1206–1213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Maisel, A.; Xue, Y.; van Veldhuisen, D.J.; Voors, A.A.; Jaarsma, T.; Pang, P.S.; Butler, J.; Pitt, B.; Clopton, P.; de Boer, R.A. Effect of spironolactone on 30-day death and heart failure rehospitalization (from the COACH Study). Am. J. Cardiol. 2014, 114, 737–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anand, I.S.; Rector, T.S.; Kuskowski, M.; Snider, J.; Cohn, J.N. Prognostic value of soluble ST2 in the Valsartan Heart Failure Trial. Circ. Heart Fail. 2014, 7, 418–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Zile, M.R.; O’Meara, E.; Claggett, B.; Prescott, M.F.; Solomon, S.D.; Swedberg, K.; Packer, M.; McMurray, J.J.V.; Shi, V.; Lefkowitz, M.; et al. Effects of Sacubitril/Valsartan on Biomarkers of Extracellular Matrix Regulation in Patients With HFrEF. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2019, 73, 795–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, G.; Chen, H.; Zhang, H.; Gu, Y. Long-Term and Short-Term Prognostic Value of Circulating Soluble Suppression of Tumorigenicity-2 Concentration in Chronic Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Cardiology 2021, 146, 433–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vergaro, G.; Gentile, F.; Aimo, A.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr.; Richards, A.M.; Lam, C.S.P.; de Boer, R.A.; Meems, L.M.G.; Latini, R.; Staszewsky, L.; et al. Circulating levels and prognostic cut-offs of sST2, hs-cTnT, and NT-proBNP in women vs. men with chronic heart failure. ESC Heart Fail. 2022, 9, 2084–2095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lupón, J.; Gaggin, H.K.; de Antonio, M.; Domingo, M.; Galán, A.; Zamora, E.; Vila, J.; Peñafiel, J.; Urrutia, A.; Ferrer, E.; et al. Biomarker-assist score for reverse remodeling prediction in heart failure: The ST2-R2 score. Int. J. Cardiol. 2015, 184, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lupón, J.; Sanders-van Wijk, S.; Januzzi, J.L.; de Antonio, M.; Gaggin, H.K.; Pfisterer, M.; Galán, A.; Shah, R.; Brunner-La Rocca, H.P.; Bayes-Genis, A. Prediction of survival and magnitude of reverse remodeling using the ST2-R2 score in heart failure: A multicenter study. Int. J. Cardiol. 2016, 204, 242–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yan, X.; Guo, Y.; Li, L.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z. The sST2 level is an independent influencing factor associated with atrial fibrillation in heart failure patients: A case-control study. J. Thorac. Dis. 2022, 14, 1578–1587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalstad, A.A.; Myhre, P.L.; Laake, K.; Opstad, T.B.; Tveit, A.; Solheim, S.; Arnesen, H.; Seljeflot, I. Biomarkers of ageing and cardiac remodeling are associated with atrial fibrillation. Scand. Cardiovasc. J. 2021, 55, 213–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Li, Y.; Yan, Q.; Wu, W.; Xu, P.; Liu, L.; Luan, C.; Zhang, J.; Zheng, Q.; Xue, J. Higher serum sST2 is associated with increased left atrial low-voltage areas and atrial fibrillation recurrence in patients undergoing radiofrequency ablation. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2022, 64, 733–742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yancy, C.W.; Jessup, M.; Bozkurt, B.; Butler, J.; Casey, D.E., Jr.; Drazner, M.H.; Fonarow, G.C.; Geraci, S.A.; Horwich, T.; Januzzi, J.L.; et al. 2013 ACCF/AHA guideline for the management of heart failure: A report of the American College of Cardiology Foundation/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2013, 62, e147–e239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Heidenreich, P.A.; Bozkurt, B.; Aguilar, D.; Allen, L.A.; Byun, J.J.; Colvin, M.M.; Deswal, A.; Drazner, M.H.; Dunlay, S.M.; Evers, L.R.; et al. 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Joint Committee on Clinical Practice Guidelines. Circulation 2022, 145, e895–e1032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.V.; Januzzi, J.L., Jr. ST2: A novel remodeling biomarker in acute and chronic heart failure. Curr. Heart Fail. Rep. 2010, 7, 9–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aimo, A.; Vergaro, G.; Ripoli, A.; Bayes-Genis, A.; Pascual Figal, D.A.; de Boer, R.A.; Lassus, J.; Mebazaa, A.; Gayat, E.; Breidthardt, T.; et al. Meta-Analysis of Soluble Suppression of Tumorigenicity-2 and Prognosis in Acute Heart Failure. JACC Heart Fail. 2017, 5, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Vark, L.C.; Lesman-Leegte, I.; Baart, S.J.; Postmus, D.; Pinto, Y.M.; Orsel, J.G.; Westenbrink, B.D.; Brunner-la Rocca, H.P.; van Miltenburg, A.J.M.; Boersma, E.; et al. Prognostic Value of Serial ST2 Measurements in Patients With Acute Heart Failure. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2017, 70, 2378–2388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bartunek, J.; Delrue, L.; Van Durme, F.; Muller, O.; Casselman, F.; De Wiest, B.; Croes, R.; Verstreken, S.; Goethals, M.; de Raedt, H.; et al. Nonmyocardial production of ST2 protein in human hypertrophy and failure is related to diastolic load. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2008, 52, 2166–2174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Demyanets, S.; Kaun, C.; Pentz, R.; Krychtiuk, K.A.; Rauscher, S.; Pfaffenberger, S.; Zuckermann, A.; Aliabadi, A.; Gröger, M.; Maurer, G.; et al. Components of the interleukin-33/ST2 system are differentially expressed and regulated in human cardiac cells and in cells of the cardiac vasculature. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2013, 60, 16–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pascual-Figal, D.A.; Pérez-Martínez, M.T.; Asensio-Lopez, M.C.; Sanchez-Más, J.; García-García, M.E.; Martinez, C.M.; Lencina, M.; Jara, R.; Januzzi, J.L.; Lax, A. Pulmonary Production of Soluble ST2 in Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e005488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Filippi, C.; Daniels, L.B.; Bayes-Genis, A. Structural heart disease and ST2: Cross-sectional and longitudinal associations with echocardiography. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115 (Suppl. S7), 59b–63b. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zilinski, J.L.; Shah, R.V.; Gaggin, H.K.; Gantzer, M.L.; Wang, T.J.; Januzzi, J.L. Measurement of multiple biomarkers in advanced stage heart failure patients treated with pulmonary artery catheter guided therapy. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bayés-Genis, A.; González, A.; Lupón, J. ST2 in Heart Failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2018, 11, e005582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espriella, R.; Bayés-Genis, A.; Revuelta-Ló, P.E.; Miñana, G.; Santas, E.; Llàcer, P.; García-Blas, S.; Fernández-Cisnal, A.; Bonanad, C.; Ventura, S.; et al. Soluble ST2 and Diuretic Efficiency in Acute Heart Failure and Concomitant Renal Dysfunction. J. Card. Fail. 2021, 27, 427–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Januzzi, J.L.; Mebazaa, A.; Di Somma, S. ST2 and prognosis in acutely decompensated heart failure: The International ST2 Consensus Panel. Am. J. Cardiol. 2015, 115 (Suppl. S7), 26b–31b. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pascual-Figal, D.A.; Manzano-Fernández, S.; Boronat, M.; Casas, T.; Garrido, I.P.; Bonaque, J.C.; Pastor-Perez, F.; Valdés, M.; Januzzi, J.L. Soluble ST2, high-sensitivity troponin T- and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide: Complementary role for risk stratification in acutely decompensated heart failure. Eur. J. Heart Fail. 2011, 13, 718–725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aleksova, A.; Paldino, A.; Beltrami, A.P.; Padoan, L.; Iacoviello, M.; Sinagra, G.; Emdin, M.; Maisel, A.S. Cardiac Biomarkers in the Emergency Department: The Role of Soluble ST2 (sST2) in Acute Heart Failure and Acute Coronary Syndrome-There is Meat on the Bone. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boisot, S.; Beede, J.; Isakson, S.; Chiu, A.; Clopton, P.; Januzzi, J.; Maisel, A.S.; Fitzgerald, R.L. Serial sampling of ST2 predicts 90-day mortality following destabilized heart failure. J. Card. Fail. 2008, 14, 732–738. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsigkou, V.; Siasos, G.; Bletsa, E.; Panoilia, M.E.; Papastavrou, A.; Kokosias, G.; Oikonomou, E.; Papageorgiou, N.; Zaromitidou, M.; Marinos, G.; et al. The Predictive Role for ST2 in Patients with Acute Coronary Syndromes and Heart Failure. Curr. Med. Chem. 2020, 27, 4479–4493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kercheva, M.; Ryabova, T.; Gusakova, A.; Suslova, T.E.; Ryabov, V.; Karpov, R.S. Serum Soluble ST2 and Adverse Left Ventricular Remodeling in Patients With ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction. Clin. Med. Insights Cardiol. 2019, 13, 1179546819842804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sciatti, E.; Merlo, A.; Scangiuzzi, C.; Limonta, R.; Gori, M.; D’Elia, E.; Aimo, A.; Vergaro, G.; Emdin, M.; Senni, M. Prognostic Value of sST2 in Heart Failure. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3970. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123970
Sciatti E, Merlo A, Scangiuzzi C, Limonta R, Gori M, D’Elia E, Aimo A, Vergaro G, Emdin M, Senni M. Prognostic Value of sST2 in Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):3970. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123970
Chicago/Turabian StyleSciatti, Edoardo, Anna Merlo, Claudio Scangiuzzi, Raul Limonta, Mauro Gori, Emilia D’Elia, Alberto Aimo, Giuseppe Vergaro, Michele Emdin, and Michele Senni. 2023. "Prognostic Value of sST2 in Heart Failure" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 3970. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123970
APA StyleSciatti, E., Merlo, A., Scangiuzzi, C., Limonta, R., Gori, M., D’Elia, E., Aimo, A., Vergaro, G., Emdin, M., & Senni, M. (2023). Prognostic Value of sST2 in Heart Failure. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 3970. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123970





