Challenging the Interpretation of White Blood Cell Counts in Patients with Sepsis Following Packed Cell Transfusion †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Population
2.2. Primary Exposure and Outcome Assessment
2.3. Statistical Analysis
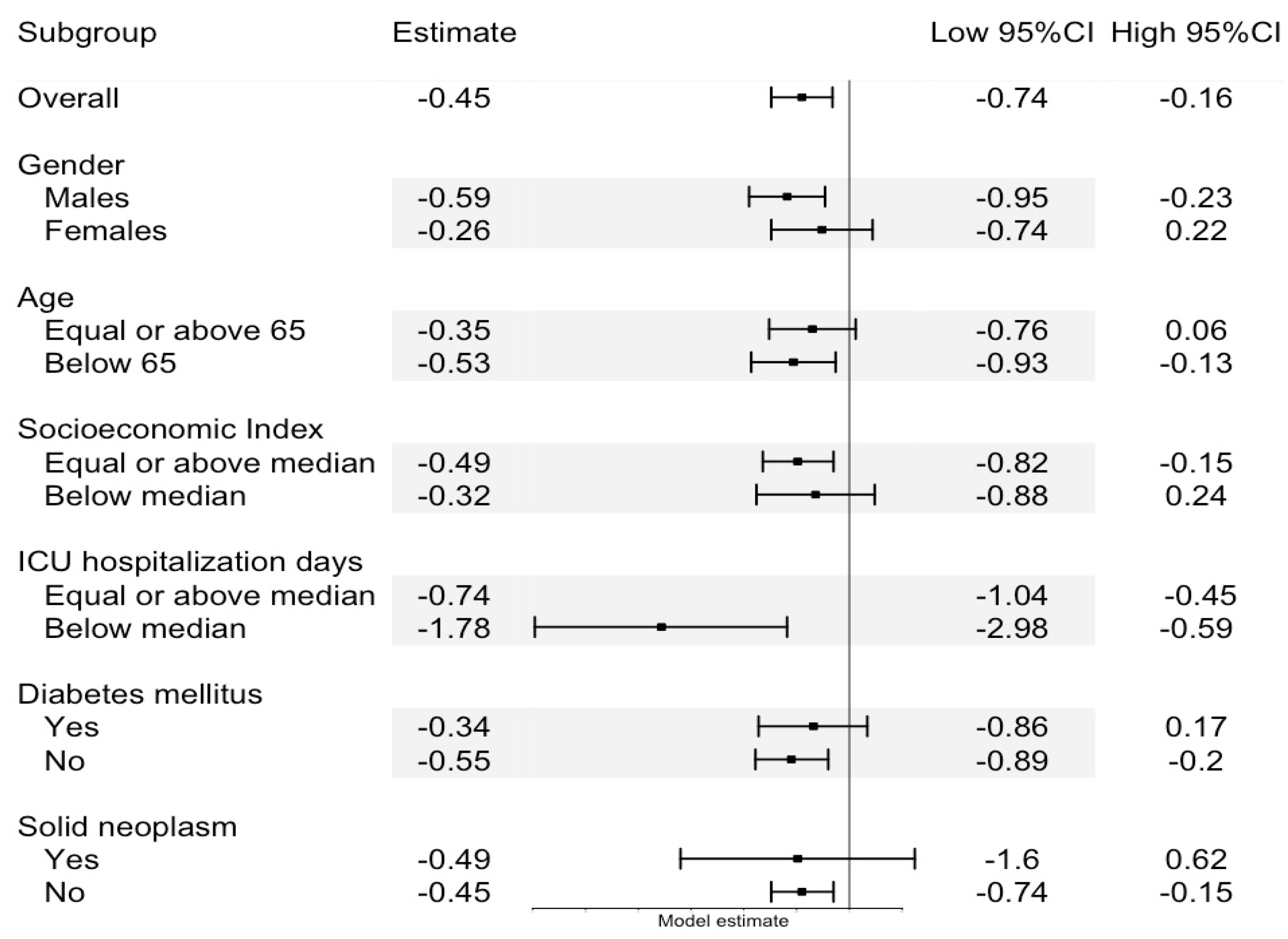
3. Results
3.1. Study Population
3.2. Characteristics of the Hospitalization Course (Table 2)
| Non PCT Group N = 994 | PCT Group N = 962 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| ICU hospitalization days—Median (IQR) | 3 (2, 5) | 8 (3, 20) | <0.001 |
| 30-day post-admission mortality rate | 181 (18%) | 246 (26%) | <0.001 |
| Vasopressor given during ICU stay—n (%) | 256 (26%) | 527 (55%) | <0.001 |
| Mechanical ventilation—n (%) | 994 (100%) | 962 (100%) | 1 |
| ICU hospitalization SOFA score—Median (IQR) | 5.5 (3.5, 7.6) | 7.2 (5.7, 9.3) | <0.001 |
| Initial Mean (SD) WBC count | 13.9 × 109/L (7.0) | 13.9 × 109/L (7.2) | 0.813 |
| Final Mean (SD) WBC count | 12.2 × 109/L (5.9) | 12.8 × 109/L (7.2) | <0.001 |
3.3. Linear Regression Model
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Arpáš, T.; Doubek, M. Differential diagnosis of leukocytosis and leukopenia. Vnitr. Lek. 2022, 68, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lai, Y.-C.; Wang, W.-C. Genetic Analysis Reveals the Important Role of the APC Gene in Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma. Anticancer. Res. 2021, 41, 4295–4304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lyrad, K.; Riley, M.D.; Jedda Rupert, M.D. Evaluation of Patients with Leukocytosis. Am. Fam. Physician 2015, 92, 1004–1011. [Google Scholar]
- Mehari, S.M.; Havill, J.H. Written guidelines for laboratory testing in intensive care—Still effective after 3 years. Crit. Care Resusc. 2001, 3, 158–162. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Philip, E.; Grgurich, J.H. Diagnosis of ventilator-associated pneumonia: Controversies and working toward a gold standard. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 26, 140–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aliberti, S.; Blasi, F.; Zanaboni, A.M.; Peyrani, P.; Tarsia, P.; Gaito, S.; Ramirez, J.A. Duration of antibiotic therapy in hospitalised patients with community-acquired pneumonia. Eur. Respir. J. 2010, 36, 128–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Cerny, J.; Rosmarin, A.G. Why does my patient have leukocytosis? Hematol. Oncol. Clin. N. Am. 2012, 26, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, T.A. Packedred blood cell transfusions in critically ill patients. Crit. Care Nurse 2011, 31, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sadaka, F. Red Blood Cell Transfusion in Sepsis: A Review. J. Blood Disord. Transfus. 2012, S4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Remy, K.E.; Hall, M.W.; Cholette, J.; Juffermans, N.P.; Nicol, K.; Doctor, A.; Blumberg, N.; Spinella, P.C.; Norris, P.J.; Dahmer, M.K.; et al. Mechanisms of red blood cell transfusion-related immunomodulation. Transfusion 2018, 58, 804–815. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Izbicki, G.; Rudensky, B.; Na’amad, M.; Hershko, C.; Huerta, M.; Hersch, M. Transfusion-related leukocytosis in critically ill patients*. Crit. Care Med. 2004, 32, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frenkel, A.; Kachko, E.; Cohen, K.; Novack, V.; Maimon, N. Estimations of a degree of steroid induced leukocytosis in patients with acute infections. Am. J. Emerg. Med. 2018, 36, 749–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murray, C.K.; Hoffmaster, R.M.; Schmit, D.R.; Hospenthal, D.R.; Ward, J.A.; Cancio, L.C.; Wolf, S.E. Evaluation of white blood cell count, neutrophil percentage, and elevated temperature as predictors of bloodstream infection in burn patients. Arch. Surg. 2007, 142, 639–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Rimmer, E.; Garland, A.; Kumar, A.; Doucette, S.; Houston, B.L.; Menard, C.E.; Leeies, M.; Turgeon, A.F.; Mahmud, S.; Houston, D.S.; et al. White blood cell count trajectory and mortality in septic shock: A historical cohort study. Évolution de la numération leucocytaire et mortalité en cas de choc septique: Une étude de cohorte historique. Can. J. Anaesth. 2022, 69, 1230–1239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klein, M.; Hassan, L.; Binyamin, Y.; Frank, D.; Boyko, M.; Zlotnik, A.; Raab, T.; Novack, V.; Frenkel, A. Body temperature variation following packed cell transfusion in adult patients with sepsis—Where will the pendulum stop? Shock 2023, 59, 877–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koenig, S.M.; Truwit, J.D. Ventilator-associated pneumonia: Diagnosis, treatment, and prevention. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2006, 19, 637–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Ahmadinejad, M.; Mohammadzadeh, S.; Pak, H.; Hashemiyazdi, S.; Soltanian, A.; Rahimi, M.; Ahmadinejad, I. Bronchoalveolar lavage of ventilator-associated pneumonia patients for antibiotic resistance and susceptibility test. Health Sci. Rep. 2022, 5, e472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


| Non-PCT Group N = 994 | PCT Group N = 962 | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex—n (%) | 0.986 | ||
| Male | 571 (57%) | 553 (57%) | |
| Age—Mean (SD) | 59 (21) | 59 (21) | 0.938 |
| LMS Social State Score—Median (IQR) | 3.00 (2.00, 5.00) | 3.00 (2.00, 5.00) | 0.208 |
| Hypertension | 517 (52%) | 501 (52%) | 0.976 |
| Myocardial infraction—n (%) | 167 (17%) | 175 (18%) | 0.418 |
| Congestive heart failure—n (%) | 138 (14%) | 148 (15%) | 0.347 |
| COPD—n (%) | 223 (22%) | 209 (22%) | 0.705 |
| Diabetes mellitus—n (%) | 325 (33%) | 305 (32%) | 0.639 |
| Solid neoplasm—n (%) | 61 (6.1%) | 61 (6.3%) | 0.852 |
| Predictors | Estimates | CI | p |
|---|---|---|---|
| PCT given during ICU hospitalization | −0.45 | −0.74–−0.16 | 0.002 |
| WBC count before PCT | −0.19 | −0.21–−0.17 | <0.001 |
| Age | 0.02 | 0.01–0.02 | <0.001 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Klein, M.; Hassan, L.; Katz, R.; Abuhasira, R.; Boyko, M.; Gabay, O.; Frank, D.; Binyamin, Y.; Novack, V.; Frenkel, A. Challenging the Interpretation of White Blood Cell Counts in Patients with Sepsis Following Packed Cell Transfusion. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123912
Klein M, Hassan L, Katz R, Abuhasira R, Boyko M, Gabay O, Frank D, Binyamin Y, Novack V, Frenkel A. Challenging the Interpretation of White Blood Cell Counts in Patients with Sepsis Following Packed Cell Transfusion. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123912
Chicago/Turabian StyleKlein, Moti, Lior Hassan, Rivka Katz, Ran Abuhasira, Matthew Boyko, Ohad Gabay, Dmitry Frank, Yair Binyamin, Victor Novack, and Amit Frenkel. 2023. "Challenging the Interpretation of White Blood Cell Counts in Patients with Sepsis Following Packed Cell Transfusion" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123912
APA StyleKlein, M., Hassan, L., Katz, R., Abuhasira, R., Boyko, M., Gabay, O., Frank, D., Binyamin, Y., Novack, V., & Frenkel, A. (2023). Challenging the Interpretation of White Blood Cell Counts in Patients with Sepsis Following Packed Cell Transfusion. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 3912. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123912






