Analysis of Nephrolithiasis Treatment in Highest Reference Hospital—Occurrence of Acromegaly in the Study Group
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
4. Discussion
Strengths and Weaknesses of the Study
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Thakore, P.; Liang, T.H. Urolithiasis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Vaidyanathan, S.; Selmi, F.; Soni, B.; Hughes, P.; Singh, G.; Pulya, K.; Oo, T. Pyonephrosis and urosepsis in a 41-year old patient with spina bifida: Case report of a preventable death. Patient Saf. Surg. 2012, 6, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efstathiou, S.P.; Pefanis, A.V.; Tsioulos, D.I.; Zacharos, I.D.; Tsiakou, A.G.; Mitromaras, A.G.; Mastorantonakis, S.E.; Kanavaki, S.N.; Mountokalakis, T.D. Acute pyelonephritis in adults: Prediction of mortality and failure of treatment. Arch. Intern. Med. 2003, 163, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hesse, A.; Brändle, E.; Wilbert, D.; Köhrmann, K.U.; Alken, P. Study on the prevalence and incidence of urolithiasis in Germany comparing the years 1979 vs. 2000. Eur. Urol. 2003, 44, 709–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chewcharat, A.; Curhan, G. Trends in the prevalence of kidney stones in the United States from 2007 to 2016. Urolithiasis 2021, 49, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uribarri, J.; Oh, M.S.; Carroll, H.J. The first kidney stone. Ann. Intern. Med. 1989, 111, 1006–1009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Alessandro, C.; Ferraro, P.M.; Cianchi, C.; Barsotti, M.; Gambaro, G.; Cupisti, A. Which Diet for Calcium Stone Patients: A Real-World Approach to Preventive Care. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferraro, P.M.; Bargagli, M.; Trinchieri, A.; Gambaro, G. Risk of Kidney Stones: Influence of Dietary Factors, Dietary Patterns, and Vegetarian–Vegan Diets. Nutrients 2020, 12, 779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siener, R. Nutrition and Kidney Stone Disease. Nutrients 2021, 13, 1917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moftakhar, L.; Jafari, F.; Ghoddusi Johari, M.; Rezaeianzadeh, R.; Hosseini, S.V.; Rezaianzadeh, A. Prevalence and risk factors of kidney stone disease in population aged 40–70 years old in Kharameh cohort study: A cross-sectional population-based study in southern Iran. BMC Urol. 2022, 22, 205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scales, C.D., Jr.; Smith, A.C.; Hanley, J.M.; Saigal, C.S. Urologic Diseases in America Project. Prevalence of kidney stones in the United States. Eur. Urol. 2012, 62, 160–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, J.; Luo, S.; Liu, Y.; Jia, Z.; Chen, P.; Guo, Y.; Zhao, Q.; Ma, X.; et al. A meta-analysis of the efficacy of ureteroscopic lithotripsy and extracorporeal shock wave lithotripsy on ureteral calculi. Acta Cir. Bras. 2014, 29, 346–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, C.H.; Chung, D.Y.; Rha, K.H.; Lee, J.Y.; Lee, S.H. Effectiveness of Percutaneous Nephrolithotomy, Retrograde Intrarenal Surgery, and Extracorporeal Shock Wave Lithotripsy for Treatment of Renal Stones: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Medicina 2020, 57, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, H.; Man, L.; Li, G.; Huang, G.; Liu, N.; Wang, J. Meta-Analysis of Stenting versus Non-Stenting for the Treatment of Ureteral Stones. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0167670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pietropaolo, A.; Hughes, T.; Mani, M.; Somani, B. Outcomes of Ureteroscopy and Laser Stone Fragmentation (URSL) for Kidney Stone Disease (KSD): Comparative Cohort Study Using MOSES Technology 60 W Laser System versus Regular Holmium 20 W Laser. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 2742. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taguchi, K.; Hamamoto, S.; Osaga, S.; Sugino, T.; Unno, R.; Ando, R.; Okada, A.; Yasui, T. Comparison of antegrade and retrograde ureterolithotripsy for proximal ureteral stones: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Transl. Androl. Urol. 2021, 10, 1179–1191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selmi, V.; Sarı, S.; Caniklioğlu, M.; Öztekin, Ü.; Taspinar, M.S.; Işıkay, L. Effect of Endoscopic Ureteral Stone Treatment on Kidney Function. Cureus 2021, 13, e12883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aghamir, S.M.K. Successful retrograde intrarenal surgery (RIRS) for a 2-centimeter stone in a chronic renal failure (CRF) patient. Int. J. Surg. Case Rep. 2021, 87, 106375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thapa, B.B.; Niranjan, V. Mini PCNL over Standard PCNL: What Makes it Better? Surg. J. 2020, 6, e19–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganpule, A.P.; Vijayakumar, M.; Malpani, A.; Desai, M.R. Percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL) a critical review. Int. J. Surg. 2016, 36, 660–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallidonis, P.; Tsaturyan, A.; Lattarulo, M.; Liatsikos, E. Minimally invasive percutaneous nephrolithotomy (PCNL): Techniques and outcomes. Turk. J. Urol. 2020, 46 (Suppl. S1), S58–S63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, T.; Wei, N.; Yu, J.; Lu, Y. Efficacy and safety of laparoscopic pyelolithotomy versus percutaneous nephrolithotomy for treatment of large renal stones: A meta-analysis. J. Int. Med. Res. 2021, 49, 300060520983136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, Y.; Tang, Y.; Deng, L.; Wang, X.; Yang, Y.; Wang, J.; Han, P. Management of large renal stones: Laparoscopic pyelolithotomy versus percutaneous nephrolithotomy. BMC Urol. 2017, 17, 75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danilovic, A.; Ferreira, T.A.C.; Maia, G.V.A.; Torricelli, F.C.M.; Mazzucchi, E.; Nahas, W.C.; Srougi, M. Predictors of surgical complications of nephrectomy for urolithiasis. Int. Braz. J. Urol. 2019, 45, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danilovic, A.; Ferreira, T.A.C.; Vicentini, F.C.; Torricelli, F.C.M.; Marchini, G.S.; Mazzucchi, E.; Nahas, W.C.; Srougi, M. Laparoscopic nephrectomy for urolithiasis: When is better to avoid it. Rev. Col. Bras. Cir. 2019, 46, e20192092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranabir, S.; Baruah, M.P.; Devi, K.R. Nephrolithiasis: Endocrine evaluation. Indian J. Endocrinol. Metab. 2012, 16, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bagale, G.; Pradhan, S.R.; Basnet, A. Recurrent Nephrolithiasis Due to Parathyroid Adenoma. Cureus 2021, 13, e18468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldner, W. Cancer-Related Hypercalcemia. J. Oncol. Pract. 2016, 12, 426–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, O.P. Hypercalcemia in granulomatous disorders: A clinical review. Curr. Opin. Pulm. Med. 2000, 6, 442–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavrentaki, A.; Paluzzi, A.; Wass, J.A.; Karavitaki, N. Epidemiology of acromegaly: Review of population studies. Pituitary 2017, 20, 4–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleem, T.F.; Santhanam, P.; Hamoudeh, E.; Hassan, T.; Faiz, S. Acromegaly caused by growth hormone releasing hormone (GHRH) secreting tumor in multiple endocrine neoplasia (MEN-1). West Va. Med. J. 2012, 108, 26–30. [Google Scholar]
- Zahr, R.; Fleseriu, M. Updates in Diagnosis and Treatment of Acromegaly. Eur. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 57–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bogusławska, A.; Gilis-Januszewska, A.; Godlewska, M.; Nowak, A.; Starzyk, J.; Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A. Sex and age differences among patients with acromegaly. Pol. Arch. Intern. Med. 2022, 12, 16232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akirov, A.; Masri-Iraqi, H.; Dotan, I.; Shimon, I. The Biochemical Diagnosis of Acromegaly. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melmed, S.; Bronstein, M.D.; Chanson, P.; Klibanski, A.; Casanueva, F.F.; Wass, J.A.H.; Strasburger, C.J.; Luger, A.; Clemmons, D.R.; Giustina, A. A Consensus Statement on acromegaly therapeutic outcomes. Nat. Rev. Endocrinol. 2018, 14, 552–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paragliola, R.M.; Salvatori, R. Novel somatostatin receptor ligands therapies for acromegaly. Front. Endocrinol. 2018, 9, 78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ershadinia, N.; Tritos, N.A. Diagnosis and Treatment of Acromegaly: An Update. Mayo Clin. Proc. 2022, 97, 333–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzat, S.; Snyder, P.J.; Young, W.F.; Boyajy, L.D.; Newman, C.; Klibanski, A.; Molitch, M.E.; Boyd, A.E.; Sheeler, L.; Cook, D.M.; et al. Octreotide treatment of acromegaly. A randomized, multicenter study. Ann. Intern. Med. 1992, 117, 711–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Castinetti, F.; Saveanu, A.; Morange, I.; Brue, T. Lanreotide for the treatment of acromegaly. Adv. Ther. 2009, 26, 600–612. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Puig-Domingo, M.; Bernabéu, I.; Picó, A.; Biagetti, B.; Gil, J.; Alvarez-Escolá, C.; Jordà, M.; Marques-Pamies, M.; Soldevila, B.; Gálvez, M.-A.; et al. Pasireotide in the Personalized Treatment of Acromegaly. Front. Endocrinol. 2021, 12, 648411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giustina, A.; Arnaldi, G.; Bogazzi, F.; Cannavò, S.; Colao, A.; De Marinis, L.; De Menis, E.; Degli Uberti, E.; Giorgino, F.; Grottoli, S.; et al. Pegvisomant in acromegaly: An update. J. Endocrinol. Investig. 2017, 40, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo-Castro, M.; Pascual-Corrales, E.; Pian, H.; Ruz-Caracuel, I.; Acitores Cancela, A.; Duque, S.G.; Berrocal, V.R. The Dose of Somatostatin Analogues during Pre-Surgical Treatment Is a Key Factor to Achieve Surgical Remission in Acromegaly. Endocrines 2021, 2, 241–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolanowski, M.; Ruchała, M.; Zgliczyński, W.; Kos-Kudła, B.; Hubalewska-Dydejczyk, A.; Lewiński, A. Diagnostics and treatment of acromegaly-updated recommendations of the Polish Society of Endocrinology. Endokrynol. Pol. 2019, 70, 2–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pines, A.; Olchovsky, D. Urolithiasis in acromegaly. Urology 1985, 26, 240–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Abel, M.; Hoenderop, J.G.; Dardenne, O.; St Arnaud, R.; Van Os, C.H.; Van Leeuwen, H.J.; Bindels, R.J. 1,25-dihydroxyvitamin D(3)-independent stimulatory effect of estrogen on the expression of ECaC1 in the kidney. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2002, 13, 2102–2109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsuchiya, H.; Onishi, T.; Takamoto, S.; Morimoto, S.; Fukuo, K.; Imanaka, S.; Yamamoto, H.; Yukawa, S.; Koh, E.; Sonoda, T.; et al. An acromegalic patient with recurrent urolithiasis. Endocrinol. Jpn. 1985, 32, 851–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, S.; Zhang, L.; Yu, Y.; Wang, C.; Li, J. Acromegaly and non-parathyroid hormone-dependent hypercalcemia: A case report and literature review. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saponaro, F.; Saba, A.; Zucchi, R. An Update on Vitamin D Metabolism. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 6573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zehnder, D.; Bland, R.; Williams, M.C.; McNinch, R.W.; Howie, A.J.; Stewart, P.M.; Hewison, M. Extrarenal Expression of 25-Hydroxyvitamin D3-1α-Hydroxylase. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2001, 86, 888–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, J.S.; Hewison, M. Extrarenal expression of the 25-hydroxyvitamin D-1-hydroxylase. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2012, 523, 95–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gil, Á.; Plaza-Diaz, J.; Mesa, M.D. Vitamin D: Classic and Novel Actions. Ann. Nutr. Metab. 2018, 72, 87–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fleet, J.C.; Schoch, R.D. Molecular mechanisms for regulation of intestinal calcium absorption by vitamin D and other factors. Crit. Rev. Clin. Lab. Sci. 2010, 47, 181–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chihara, K.; Sugimoto, T. The action of GH/IGF-I/IGFBP in osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Horm. Res. 1997, 48 (Suppl. S5), 45–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueland, T. GH/IGF-I and bone resorption in vivo and in vitro. Eur. J. Endocrinol. 2005, 152, 327–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nachtigall, L.B.; Guarda, F.J.; Lines, K.E.; Ghajar, A.; Dichtel, L.; Mumbach, G.; Zhao, W.; Zhang, X.; Tritos, N.A.; Swearingen, B.; et al. Clinical MEN-1 among a Large Cohort of Patients with Acromegaly. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 105, e2271–e2281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thai, J.N.; Tran, T.Y.; Davydov, O.; Gupta, M. Recurrent Kidney Stone Episodes Leading to a Diagnosis of Occult Acromegaly. Urol. Case Rep. 2017, 14, 8–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Valk, E.; Tobe, T.; Stades, A.; Muller, A. Vanishing hypercalciuric kidney stones after treating underlying acromegaly. Endocrinol. Diabetes Metab. Case Rep. 2013, 2013, 130001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brikowski, T.H.; Lotan, Y.; Pearle, M.S. Climate-related increase in the prevalence of urolithiasis in the United States. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2008, 105, 9841–9846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stamatelou, K.; Goldfarb, D.S. Epidemiology of Kidney Stones. Healthcare 2023, 11, 424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brent, R.J. Cost-Benefit Analysis versus Cost-Effectiveness Analysis from a Societal Perspective in Healthcare. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2023, 20, 4637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weinstein, M.C.; Stason, W.B. Foundations of cost-effectiveness analysis for health and medical practices. N. Engl. J. Med. 1977, 296, 716–721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
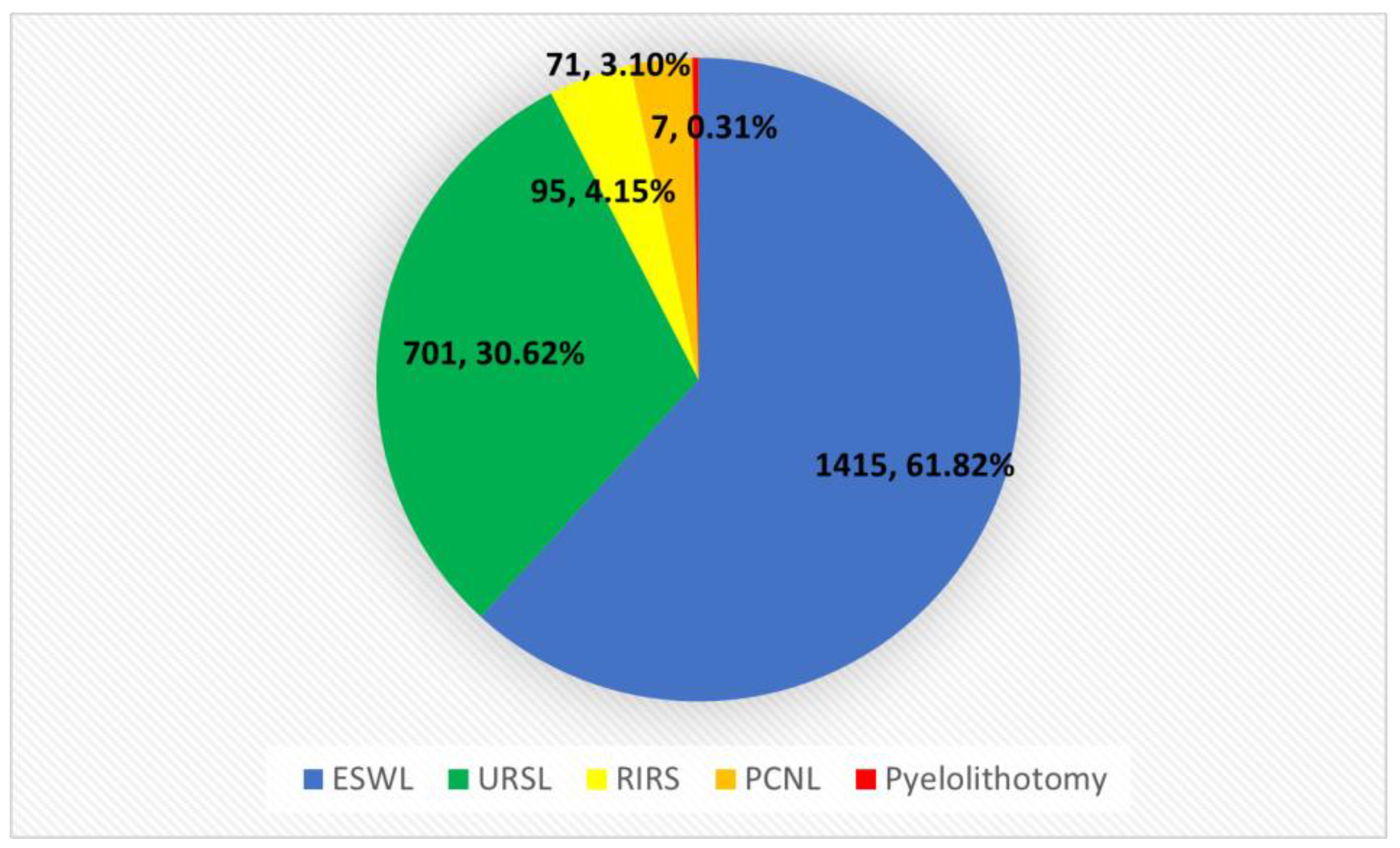
| Year/Method | URSL | RIRS | PCNL | Pyelolithotomy | ESWL | Summary |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 164 | 0 | 12 | 1 | 346 | 523 |
| 2021 | 235 | 27 | 23 | 1 | 495 | 781 |
| 2022 | 302 | 68 | 36 | 5 | 574 | 985 |
| Summary | 701 | 95 | 71 | 7 | 1415 | 2289 |
| Age | Mean | 63.33 |
| SD | 8.06 | |
| Gender | Female | 7 |
| Male | 2 | |
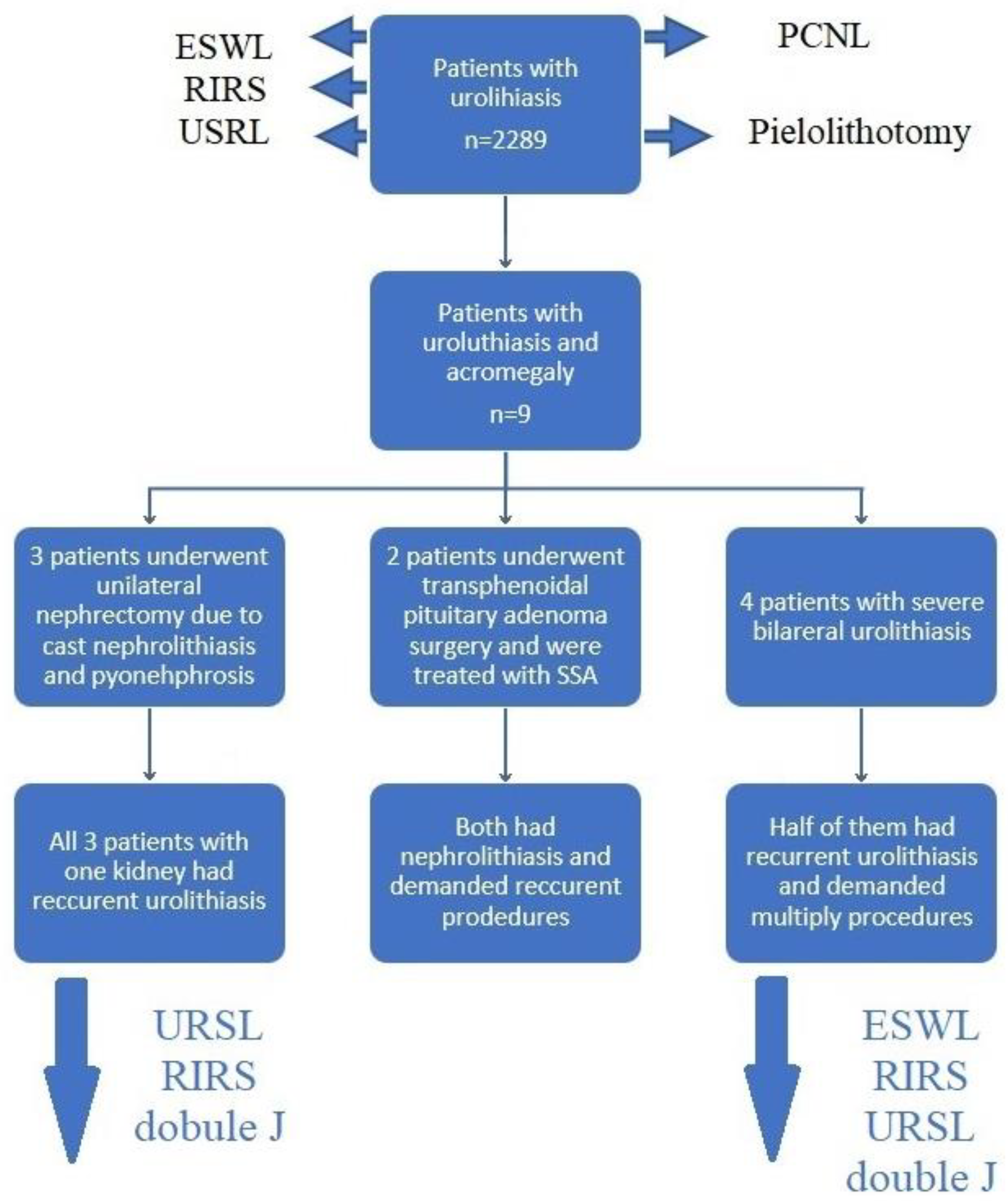
| Acromegaly diagnosis | Before nephrolithiasis | 2 |
| After nephrolithiasis | 7 | |
| Ca [N: 8.6–10.2 mg/dL] | Mean | 9.97 |
| SD | 0.62 | |
| Crea [N: 0.5–0.9 mg/dL] | Mean | 1.06 |
| SD | 0.36 | |
| IGF-1 (Total group n = 9) [ng/mL] * | Mean | 370.89 |
| SD | 101.32 | |
| IGF-1 (de novo group n = 7) [ng/mL] * | Mean | 386.57 |
| SD | 109.54 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ząbkowski, T.; Durma, A.D.; Grabińska, A.; Michalczyk, Ł.; Saracyn, M. Analysis of Nephrolithiasis Treatment in Highest Reference Hospital—Occurrence of Acromegaly in the Study Group. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123879
Ząbkowski T, Durma AD, Grabińska A, Michalczyk Ł, Saracyn M. Analysis of Nephrolithiasis Treatment in Highest Reference Hospital—Occurrence of Acromegaly in the Study Group. Journal of Clinical Medicine. 2023; 12(12):3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123879
Chicago/Turabian StyleZąbkowski, Tomasz, Adam Daniel Durma, Agnieszka Grabińska, Łukasz Michalczyk, and Marek Saracyn. 2023. "Analysis of Nephrolithiasis Treatment in Highest Reference Hospital—Occurrence of Acromegaly in the Study Group" Journal of Clinical Medicine 12, no. 12: 3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123879
APA StyleZąbkowski, T., Durma, A. D., Grabińska, A., Michalczyk, Ł., & Saracyn, M. (2023). Analysis of Nephrolithiasis Treatment in Highest Reference Hospital—Occurrence of Acromegaly in the Study Group. Journal of Clinical Medicine, 12(12), 3879. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12123879





